TATA-box on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The TATA box is a component of the eukaryotic core promoter and generally contains the consensus sequence 5'-TATA(A/T)A(A/T)-3'. In yeast, for example, one study found that various ''
The TATA box is a component of the eukaryotic core promoter and generally contains the consensus sequence 5'-TATA(A/T)A(A/T)-3'. In yeast, for example, one study found that various ''
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, the TATA box (also called the Goldberg–Hogness box) is a sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
of DNA found in the core promoter region of gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in archaea and eukaryotes. The bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
l homolog of the TATA box is called the Pribnow box
The Pribnow box (also known as the Pribnow-Schaller box) is a sequence of ''TATAAT'' of six nucleotides (thymine, adenine, thymine, etc.) that is an essential part of a promoter site on DNA for transcription to occur in bacteria.
It is an idea ...
which has a shorter consensus sequence.
The TATA box is considered a non-coding DNA
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules (e.g. transfer RNA, microRNA, piRNA, ribosomal RNA, and regula ...
sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
(also known as a cis-regulatory element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphoge ...
). It was termed the "TATA box" as it contains a consensus sequence characterized by repeating T and A base pairs. How the term "box" originated is unclear. In the 1980s, while investigating nucleotide sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are usu ...
in mouse genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
loci, the Hogness box sequence was found and "boxed in" at the -31 position. When consensus nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
s and alternative ones were compared, homologous regions were "boxed" by the researchers. The boxing in of sequences sheds light on the origin of the term "box".
The TATA box was first identified in 1978 as a component of eukaryotic promoters. Transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
is initiated at the TATA box in TATA-containing genes. The TATA box is the binding site of the TATA-binding protein
The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds specifically to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene p ...
(TBP) and other transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
s in some eukaryotic genes. Gene transcription by RNA polymerase II depends on the regulation of the core promoter by long-range regulatory elements such as enhancers and silencers. Without proper regulation of transcription, eukaryotic organisms would not be able to properly respond to their environment.
Based on the sequence and mechanism of TATA box initiation, mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s such as insertions, deletions, and point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequence ...
s to this consensus sequence can result in phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
changes. These phenotypic changes can then turn into a disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
phenotype. Some diseases associated with mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s in the TATA box include gastric cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymph ...
, spinocerebellar ataxia
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of s ...
, Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an uns ...
, blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
, β-thalassemia
Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are forms of thalassemia caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia to cli ...
, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
, Gilbert's syndrome
Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a syndrome in which the liver of affected individuals processes bilirubin more slowly than the majority. Many people never have symptoms. Occasionally jaundice (a slight yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes) ...
, and HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey ...
. The TATA-binding protein (TBP) could also be targeted by virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es as a means of viral transcription.
History
Discovery
The TATA box was the first eukaryotic core promoter motif to be identified in 1978 by American biochemist David Hogness while he and his graduate student, Michael Goldberg were on sabbatical at theUniversity of Basel
The University of Basel (Latin: ''Universitas Basiliensis'', German: ''Universität Basel'') is a university in Basel, Switzerland. Founded on 4 April 1460, it is Switzerland's oldest university and among the world's oldest surviving universit ...
in Switzerland. They first discovered the TATA sequence while analyzing 5' DNA promoter sequences in ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
,'' mammalian, and viral genes. The TATA box was found in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
coding gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s transcribed by RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryo ...
.
Evolutionary history
Most research on the TATA box has been conducted on yeast, human, and ''Drosophila'' genomes, however, similar elements have been found in archaea and ancient eukaryotes. In archaea species, the promoter contains an 8 bp AT-rich sequence located ~24 bp upstream of the transcription start site. This sequence was originally called Box A, which is now known to be the sequence that interacts with the homologue of the archaealTATA-binding protein
The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds specifically to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene p ...
(TBP). Also, even though some studies have uncovered several similarities, there are others that have detected notable differences between archaeal and eukaryotic TBP. The archaea protein exhibits a greater symmetry in its primary sequence and in the distribution of electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest ( static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amb ...
charge, which is important because the higher symmetry lowers the protein's ability to bind the TATA box in a polar manner.
Even though the TATA box is present in many eukaryotic promoters, it is not contained in the majority of promoters. One study found less than 30% of 1031 potential promoter regions contain a putative TATA box motif in humans. In ''Drosophila,'' less than 40% of 205 core promoters contain a TATA box. When there is an absence of the TATA box and TBP is not present, the downstream promoter element (DPE) in cooperation with the initiator element
The initiator element (''Inr''), sometimes referred to as initiator motif, is a core promoter that is similar in function to the Pribnow box (in prokaryotes) or the TATA box (in eukaryotes). The ''Inr'' is the simplest functional promoter that is ...
(Inr) bind to the transcription factor II D (TFIID
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters o ...
), initiating transcription in TATA-less promoters. The DPE has been identified in three ''Drosophila'' TATA-less promoters and in the TATA-less human IRF-1 promoter.
Features
Location
Promoter sequences vary betweenbacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, the TATA box is located 25 base pairs upstream
Upstream may refer to:
* Upstream (bioprocess)
* ''Upstream'' (film), a 1927 film by John Ford
* Upstream (networking)
* ''Upstream'' (newspaper), a newspaper covering the oil and gas industry
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream (software ...
of the start site that Rpb4/Rbp7 use to initiate transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
. In metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
, the TATA box is located 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site. While in yeast, ''S. cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have bee ...
'', the TATA box has a variable position which can range from 40 to 100 bp upstream of the start site. The TATA box is also found in 40% of the core promoters of genes that code for the actin cytoskeleton
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other ...
and contractile
Contractility refers to the ability for self-contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue
*Contractile ring in cytokinesis
*Contractile vacuole
*Muscle contraction
**Myocardial contractility
*See contractile cell for ...
apparatus in cells.
The type of core promoter affects the level of transcription and expression of a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. TATA-binding protein (TBP) can be recruited in two ways, by SAGA, a cofactor for RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryo ...
, or by TFIID
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters o ...
. When promoters use the SAGA/TATA box complex to recruit RNA polymerase II, they are more highly regulated and display higher expression levels than promoters using the TFIID/TBP mode of recruitment.
Analogous sequences
In bacteria, promoter regions may contain aPribnow box
The Pribnow box (also known as the Pribnow-Schaller box) is a sequence of ''TATAAT'' of six nucleotides (thymine, adenine, thymine, etc.) that is an essential part of a promoter site on DNA for transcription to occur in bacteria.
It is an idea ...
, which serves an analogous purpose to the eukaryotic TATA box. The Pribnow box has a 6 bp region centered around the -10 position and an 8-12 bp sequence around the -35 region that are both conserved.
A CAAT box (also CAT box) is a region of nucleotides with the following consensus sequence: 5’ GGCCAATCT 3’. The CAAT box is located about 75-80 bases upstream of the transcription initiation site and about 150 bases upstream of the TATA box. It binds transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
s (CAAT TF or CTFs) and thereby stabilizes the nearby preinitiation complex for easier binding of RNA polymerases. CAAT boxes are rarely found in genes that express proteins ubiquitous in all cell types.
Structure
Sequence and prevalence
 The TATA box is a component of the eukaryotic core promoter and generally contains the consensus sequence 5'-TATA(A/T)A(A/T)-3'. In yeast, for example, one study found that various ''
The TATA box is a component of the eukaryotic core promoter and generally contains the consensus sequence 5'-TATA(A/T)A(A/T)-3'. In yeast, for example, one study found that various ''Saccharomyces
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in f ...
'' genomes had the consensus sequence 5'-TATA(A/T)A(A/T)(A/G)-3', yet only about 20% of yeast genes even contained the TATA sequence. Similarly, in humans only 24% of genes have promoter regions containing the TATA box. Genes containing the TATA-box tend to be involved in stress-responses and certain types of metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
and are more highly regulated when compared to TATA-less genes. Generally, TATA-containing genes are not involved in essential cellular functions such as cell growth, DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
, transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
, and translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
because of their highly regulated nature.
The TATA box is usually located 25-35 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site. Genes containing the TATA box usually require additional promoter elements, including an initiator
An initiator can refer to:
* A person who instigates something.
* Modulated neutron initiator, a neutron source used in some nuclear weapons
** Initiator, an Explosive booster
** Initiator, the first Nuclear chain reaction
* Pyrotechnic initiato ...
site located just upstream
Upstream may refer to:
* Upstream (bioprocess)
* ''Upstream'' (film), a 1927 film by John Ford
* Upstream (networking)
* ''Upstream'' (newspaper), a newspaper covering the oil and gas industry
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream (software ...
of the transcription start site and a downstream core element (DCE). These additional promoter regions work in conjunction with the TATA box to regulate initiation of transcription in eukaryotes.
Function
Role in transcription initiation
The TATA-box is the site of preinitiation complex formation, which is the first step in transcription initiation in eukaryotes. Formation of the preinitiation complex begins when the multi-subunit transcription factor II D (TFIID
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters o ...
) binds to the TATA box at its TATA-binding protein (TBP) subunit. TBP binds to the minor groove
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
* Minor chord
** Bar ...
of the TATA box via a region of antiparallel β sheets
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a g ...
in the protein. Three types of molecular interactions contribute to TBP binding to the TATA box:
# Four phenylalanine residues(Phe57, Phe74, Phe148, Phe 165) on TBP bind to DNA and form kinks in the DNA, forcing the DNA minor groove open.
# Four hydrogen bonds form between polar side chains on TBP amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
(Asn27, Asn117, Thr82, Thr173)( and bases in the minor groove
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
* Minor chord
** Bar ...
.
# Numerous hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ...
interactions(~15) form between TBP residues(notably Ile152 and Leu163) and DNA bases, including van der Waals forces.
Additionally, binding of TBP is facilitated by stabilizing interactions with DNA flanking the TATA box, which consists of G-C rich sequences. These secondary interactions induce bending of the DNA and helical unwinding. The degree of DNA bending is species and sequence dependent. For example, one study used the adenovirus TATA promoter sequence (5'-CGCTATAAAAGGGC-3') as a model binding sequence and found that human TBP binding to the TATA box induced a 97° bend toward the major groove
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicator ...
while the yeast TBP protein only induced an 82° bend. X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
studies of TBP/TATA-box complexes generally agree that the DNA goes through an ~80° bend during the process of TBP-binding.
The conformational changes induced by TBP binding to the TATA box allows for additional transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
s and RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryo ...
to bind to the promoter region. TFIID first binds to the TATA box, facilitated by TFIIA
Transcription factor TFIIA is a nuclear protein involved in the RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription of DNA. TFIIA is one of several general (basal) transcription factors ( GTFs) that are required for all transcription events that use RNA ...
binding to the upstream part of the TFIID
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters o ...
complex. TFIIB
Transcription factor II B (TFIIB) is a general transcription factor that is involved in the formation of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex (PIC) and aids in stimulating transcription initiation. TFIIB is localised to the nucleus and pr ...
then binds to the TFIID-TFIIA
Transcription factor TFIIA is a nuclear protein involved in the RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription of DNA. TFIIA is one of several general (basal) transcription factors ( GTFs) that are required for all transcription events that use RNA ...
-DNA complex through interactions both upstream and downstream of the TATA box. RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryo ...
is then recruited to this multi-protein complex with the help of TFIIF
Transcription factor II F (TFIIF) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex.
TFIIF is encoded by the , , and genes.
TFIIF binds to RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II ...
. Additional transcription factors then bind, first TFIIE
Transcription factor II E (TFIIE) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. It is a tetramer of two alpha and two beta chains and interacts with TAF6/TAFII80, ATF7IP, and varicella ...
and then TFIIH
Transcription factor II Human (transcription factor II H; TFIIH) is an important protein complex, having roles in transcription of various protein-coding genes and DNA nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathways. TFIIH first came to light in 1989 ...
. This completes the assembly of the preinitiation complex for eukaryotic transcription. Generally, the TATA box is found at RNA polymerase II promoter regions, although some ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
'' studies have demonstrated that RNA polymerase III
In eukaryote cells, RNA polymerase III (also called Pol III) is a protein that transcribes DNA to synthesize ribosomal 5S rRNA, tRNA and other small RNAs.
The genes transcribed by RNA Pol III fall in the category of "housekeeping" genes whose e ...
can recognize TATA sequences.
This cluster of RNA polymerase II and various transcription factors is known as the basal transcriptional complex (BTC). In this state, it only gives a low level of transcription. Other factors must stimulate the BTC to increase transcription levels. One such example of a BTC stimulating region of DNA is the CAAT box. Additional factors, including the Mediator complex
Mediator is a multiprotein complex that functions as a Transcription (genetics), transcriptional coactivator (genetics), coactivator in all eukaryotes. It was discovered in 1990 in the lab of Roger D. Kornberg, recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in ...
, transcriptional regulatory proteins, and nucleosome-modifying enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s also enhance transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
''.
Interactions
In specific cell types or on specific promoters TBP can be replaced by one of several TBP-related factors (TRF1 inDrosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
, TBPL1/TRF2 in metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
ns, TBPL2/TRF3 in vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s), some of which interact with the TATA box similar to TBP. Interaction of TATA boxes with a variety of activators or repressors can influence the transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
of gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in many ways. Enhancers
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcriptio ...
are long-range regulatory elements that increase promoter activity while silencers repress promoter activity.
Mutations

Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s to the TATA box can range from a deletion or insertion to a point mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequence ...
with varying effects based on the gene that has been mutated. The mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s change the binding of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) for transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
initiation. Thus, there is a resulting change in phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
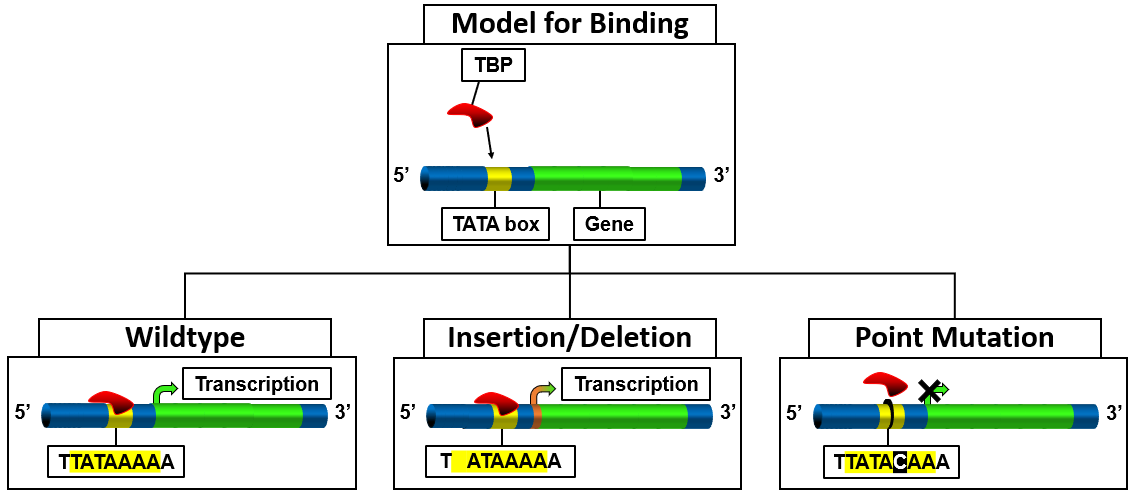
based on the gene that is not being expressed (Figure 3).
Insertions or deletions
One of the first studies of TATA boxmutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s looked at a sequence of DNA from '' Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' for the octopine type cytokinin gene. This specific gene has three TATA boxes. A phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
change was only observed when all three TATA boxes were deleted. An insertion of extra base pairs between the last TATA box and the transcription start site resulted in a shift in the start site; thus, resulting in a phenotypic change. From this original mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
study, a change in transcription can be seen when there is no TATA box to promote transcription, but transcription of a gene will occur when there is an insertion to the sequence. The nature of the resulting phenotype may be affected due to the insertion.
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s in maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
promoters affect the expression of the promoter gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in a plant-organ-specific manner. A duplication
Duplication, duplicate, and duplicator may refer to:
Biology and genetics
* Gene duplication, a process which can result in free mutation
* Chromosomal duplication, which can cause Bloom and Rett syndrome
* Polyploidy, a phenomenon also known ...
of the TATA box leads to a significant decrease in enzymatic activity
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with an ...
in the scutellum and root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s, leaving pollen enzymatic levels unaffected. A deletion of the TATA box leads to a small decrease in enzymatic activity
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with an ...
in the scutellum and root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s, but a large decrease in enzymatic levels in pollen.
Point mutations
Point mutations to the TATA box have similar varyingphenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
changes depending on the gene that is being affected. Studies also show that the placement of the mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
in the TATA box sequence hinders the binding of TBP. For example, a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
from TATAAAA to CATAAAA does completely hinder the binding sufficiently to change transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
, the neighboring sequences can affect if there is a change or not. However, a change can be seen in HeLa
HeLa (; also Hela or hela) is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, named after Henrietta ...
cells with a TATAAAA to TATACAA which leads to a 20 fold decrease in transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
. Some diseases that can be caused due to this insufficiency by specific gene transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
are: Thalassemia, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, chronic hemolytic anemia, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
, hemophilia B Leyden, and thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans ( migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following ...
and myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
.
Savinkova et al. has written a simulation to predict the '' KD'' value for a selected TATA box sequence and TBP. This can be used to directly predict the phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
traits resulting from a selected mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
based on how tightly TBP is binding to the TATA box.
Diseases
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s in the TATA box region affects the binding of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) for transcription initiation, which may cause carriers to have a disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
.
Gastric cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymph ...
is correlated with TATA box polymorphism. The TATA box has a binding site for the transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
of the PG2 gene. This gene produces PG2 serum, which is used as a biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, p ...
for tumours
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
in gastric cancer. Longer TATA box sequences correlates with higher levels of PG2 serum indicating gastric cancer conditions. Carriers with shorter TATA box sequences may produce lower levels of PG2 serum.
Several neurodegenerative disorders
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
are associated TATA box mutations. Two disorders have been highlighted, spinocerebellar ataxia
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of s ...
and Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an uns ...
. In spinocerebellar ataxia, the disease phenotype is caused by expansion of the polyglutamine repeat in the TATA-binding protein (TBP). An accumulation of these polyglutamine-TBP cells will occur, as shown by protein aggregates in brain sections of patients, resulting in a loss of neuronal cells.
Blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
can be caused by excessive cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble ...
formation when the TATA box is targeted by microRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. mi ...
s to increase the level of oxidative stress genes. MicroRNAs can target the 3'-untranslated region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally ...
and bind to the TATA box to activate the transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
of oxidative stress related genes.
SNPs
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
in TATA boxes are associated with B-thalassemia, immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
, and other neurological disorders. SNPs
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
destabilize the TBP/TATA complex which significantly decreases the rate at which TATA-binding proteins (TBP) will bind to the TATA box. This leads to lower levels of transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
affecting the severity of the disease. Results from studies have shown the interaction in vitro so far, but results may be comparable to that in vivo.
Gilbert's syndrome
Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a syndrome in which the liver of affected individuals processes bilirubin more slowly than the majority. Many people never have symptoms. Occasionally jaundice (a slight yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes) ...
is correlated with UTG1A1 TATA box polymorphism. This poses a risk for developing jaundice in newborns.
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. mi ...
s also play a role in replicating virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es such as HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey ...
. Novel HIV-1-encoded microRNA have been found to enhance the production of the virus as well as activating HIV-1 latency by targeting the TATA box region.
Clinical significance
Technology
Many of the studies so far have been performedin vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
, providing only a prediction of what may happen not a real-time representation of what is happening in the cells. Recent studies in 2016 have been done to demonstrate TATA-binding activity in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
. Core promoter-specific mechanisms for transcription initiation by the canonical TBP/TFIID-dependent basal transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
machinery has recently been documented in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
showing the activation by SRF-dependent upstream activating sequence (UAS) of the human ACTB gene involved in TATA-binding.
Cancer therapy
Pharmaceutical companies
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
have been designing cancer therapy
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
drugs to target DNA in traditional methods over the years, and have proven to be successful. However, the toxicity of these drugs have pushed scientists to explore other processes related to DNA that could be targeted instead. In recent years, a collective effort has been made to find cancer-specific molecular targets, such as protein-DNA complexes, which include the TATA binding motif. Compounds that trap the protein-DNA intermediate could result in it being toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
to the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
once they encounter a DNA processing event. Example of drugs that contain such compounds include topotecan
Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form o ...
, SN-38 (topoisomerase I
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
), doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used toge ...
, and mitoxantrone (topoisomerase II
Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. They use the hydrolysis of ATP, unlike Type I topoisomerase. In this process, these enzymes change th ...
). Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, ...
is a compound that binds covalently
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
to adjacent guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
s in the major groove
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicator ...
of DNA, which distorts DNA to allow access of DNA-binding protein
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, becaus ...
s in the minor groove
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
* Minor chord
** Bar ...
. This will destabilize the interaction between the TATA-binding protein (TBP) to the TATA box. The result is to immobilize the TATA-binding protein (TBP) on DNA in order to down-regulate transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
initiation.
Genetic engineering
TATA box modification
Evolutionary changes have pushedplant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclu ...
s to adapt to the changing environmental conditions. In the history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, the development of Earth's aerobic atmosphere resulted in an iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
deficiency in plants. Compared to other members of the same species, ''Malus baccata
''Malus baccata'' is an Asian species of apple known by the common names Siberian crab apple, Siberian crab, Manchurian crab apple and Chinese crab apple. It is native to much of northern Asia, but is also grown elsewhere as an ornamental tree an ...
'' var. ''xiaojinensis'' has a TATA box inserted in the promoter upstream of the iron-regulated transporter 1 (IRT1) promoter. As a result, the promoter activity levels are enhanced, increasing TFIID
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters o ...
activity and subsequently transcription initiation
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called ...
, resulting in a more iron-efficient phenotype.
See also
*Pribnow box
The Pribnow box (also known as the Pribnow-Schaller box) is a sequence of ''TATAAT'' of six nucleotides (thymine, adenine, thymine, etc.) that is an essential part of a promoter site on DNA for transcription to occur in bacteria.
It is an idea ...
* Initiator element
The initiator element (''Inr''), sometimes referred to as initiator motif, is a core promoter that is similar in function to the Pribnow box (in prokaryotes) or the TATA box (in eukaryotes). The ''Inr'' is the simplest functional promoter that is ...
* Kozak consensus sequence
The Kozak consensus sequence (Kozak consensus or Kozak sequence) is a nucleic acid motif that functions as the protein translation initiation site in most eukaryotic mRNA transcripts. Regarded as the optimum sequence for initiating translation in ...
References