|
Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Anatomy Root morphology is divided into four zones: the root cap, the apical meristem, the elongation zone, and the hair. The root cap of new roots helps the root penetrate the soil. These root caps are sloughed off as the root goes deeper creating a slimy surface that provides lubrication. The apical meristem behind the root cap produces new root cells that elongate. Then, root hairs form that absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. The first root in seed producing plants is the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Roots At Riverside
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are some three trillion mature trees in the world. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk typically co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Root
Aerial roots are roots above the ground. They are almost always adventitious. They are found in diverse plant species, including epiphytes such as orchids (''Orchidaceae''), tropical coastal swamp trees such as mangroves, banyan figs ('' Ficus subg. Urostigma''), the warm-temperate rainforest rata (''Metrosideros robusta''), and pohutukawa trees of New Zealand (''Metrosideros excelsa''). Vines such as common ivy (''Hedera helix'') and poison ivy (''Toxicodendron radicans'') also have aerial roots. Types of aerial roots This plant organ that is found in so many diverse plant-families has different specializations that suit the plant-habitat. In general growth-form, they can be technically classed as '' negatively gravitropic'' (grows up and away from the ground) or ''positively gravitropic'' (grows down toward the ground). "Stranglers" (prop-root) Banyan trees are an example of a strangler fig that begins life as an epiphyte in the crown of another tree. Their roots grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM), or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is sometimes mutualistic. In particular species or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules such as sugars by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus, and the fungus supplies to the plant water and mineral nutrients, such as phosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Hair
Root hair, or absorbent hairs, are outgrowths of epidermal cells, specialized cells at the tip of a plant root. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and are only rarely branched. They are found in the region of maturation, of the root. Root hair cells improve plant water absorption by increasing root surface area to volume ratio which allows the root hair cell to take in more water. The large vacuole inside root hair cells makes this intake much more efficient. Root hairs are also important for nutrient uptake as they are main interface between plants and mycorrhizal fungi. Function The function all root hairs is to collect water and mineral nutrients in the soil to be sent throughout the plant. In roots, most water absorption happens through the root hairs. The length of root hairs allows them to penetrate between soil particles and prevents harmful bacterial organisms from entering the plant through the xylem vessels. Increasing the surface area of these hairs makes plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
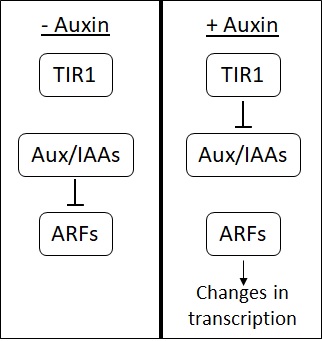
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite. This is in accordance with Justus von Liebig’s law of the minimum. The total essential plant nutrients include seventeen different elements: carbon, oxygen and hydrogen which are absorbed from the air, whereas other nutrients including nitrogen are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants). Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from their growing medium: * the macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H) * the micronutrients (or trace minerals): iron (Fe), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Meristem
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide. Differentiated plant cells generally cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Meristematic cells are undifferentiated or incompletely differentiated. They are totipotent and capable of continued cell division. Division of meristematic cells provides new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and the initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body. The cells are small, with no or small vacuoles and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The plastids ( chloroplasts or chromoplasts), are undifferentiated, but are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Of Water
In higher plants water and minerals are absorbed through root hairs which are in contact with soil water and from the root hairs zone a little the root tips. Active absorption Active absorption refers to the absorption of water by roots with the help of adenosine triphosphate, generated by the root respiration: as the root cells actively take part in the process, it is called active absorption. According to Jenner, active absorption takes place in low transpiring and well-watered plants, and 4% of total water absorption is carried out in this process. The active absorption is carried out by two theories; active osmotic water absorption and Active non-osmotic water absorption. In this process, energy is not required. Active absorption is important for the plants. Active osmotic water absorption The root cells behave as an ideal osmotic pressure system through which water moves up from the soil solution to the root xylem along an increasing gradient of D.P.D. (suction pressure, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Cap
The root cap is a type of tissue at the tip of a plant root. It is also called calyptra. Root caps contain statocytes which are involved in gravity perception in plants. If the cap is carefully removed the root will grow randomly. The root cap protects the growing tip in plants. It secretes mucilage Mucilage is a thick, gluey substance produced by nearly all plants and some microorganisms. These microorganisms include protists which use it for their locomotion. The direction of their movement is always opposite to that of the secretion of m ... to ease the movement of the root through soil, and may also be involved in communication with the soil microbiota. The purpose of the root cap is to enable downward growth of the root, with the root cap covering the sensitive tissue in the root. Also, the root cap enables geoperception or gravitropism. This allows the plant to grow downwards (with gravity) or upwards (against gravity). The root cap is absent in some parasitic plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericycle
The pericycle is a cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis and is the outer most part of the stele of plants. Although it is composed of non-vascular parenchyma cells, it's still considered part of the vascular cylinder because it arises from the procambium as do the vascular tissues it surrounds. In eudicots, it also has the capacity to produce lateral roots. Branch roots arise from this primary meristem tissue. In plants undergoing secondary growth, the pericycle contributes to the vascular cambium often diverging into a cork cambium. In angiosperms certain molecules within the endodermis and the surrounding vasculature are sent to the pericycle which promotes the growth of the root meristems. Location The pericycle is located between the endodermis and phloem in plant roots. In dicot stems, it is situated around the ring of vascular bundles in the stele. Function In dicot roots, the pericycle strengthens the roots and provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


(NRCS_Photo_Gallery).jpg)

