Spherical wedge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A sphere (from Greek , ) is a surface analogous to the
 As mentioned earlier is the sphere's radius; any line from the center to a point on the sphere is also called a radius. 'Radius' is used in two senses: as a line segment and also as its length.
If a radius is extended through the center to the opposite side of the sphere, it creates a
As mentioned earlier is the sphere's radius; any line from the center to a point on the sphere is also called a radius. 'Radius' is used in two senses: as a line segment and also as its length.
If a radius is extended through the center to the opposite side of the sphere, it creates a
 In three dimensions, the
In three dimensions, the
 In their book ''Geometry and the Imagination'', David Hilbert and Stephan Cohn-Vossen describe eleven properties of the sphere and discuss whether these properties uniquely determine the sphere. Several properties hold for the plane, which can be thought of as a sphere with infinite radius. These properties are:
#''The points on the sphere are all the same distance from a fixed point. Also, the ratio of the distance of its points from two fixed points is constant.''
#: The first part is the usual definition of the sphere and determines it uniquely. The second part can be easily deduced and follows a similar
In their book ''Geometry and the Imagination'', David Hilbert and Stephan Cohn-Vossen describe eleven properties of the sphere and discuss whether these properties uniquely determine the sphere. Several properties hold for the plane, which can be thought of as a sphere with infinite radius. These properties are:
#''The points on the sphere are all the same distance from a fixed point. Also, the ratio of the distance of its points from two fixed points is constant.''
#: The first part is the usual definition of the sphere and determines it uniquely. The second part can be easily deduced and follows a similar
 The basic elements of Euclidean plane geometry are points and lines. On the sphere, points are defined in the usual sense. The analogue of the "line" is the geodesic, which is a great circle; the defining characteristic of a great circle is that the plane containing all its points also passes through the center of the sphere. Measuring by
The basic elements of Euclidean plane geometry are points and lines. On the sphere, points are defined in the usual sense. The analogue of the "line" is the geodesic, which is a great circle; the defining characteristic of a great circle is that the plane containing all its points also passes through the center of the sphere. Measuring by


 In
In
 Another kind of spherical spiral is the Clelia curve, for which the
Another kind of spherical spiral is the Clelia curve, for which the
 If a sphere is intersected by another surface, there may be more complicated spherical curves.
;Example: sphere–cylinder
The intersection of the sphere with equation and the cylinder with equation is not just one or two circles. It is the solution of the non-linear system of equations
:
:
(see implicit curve and the diagram)
If a sphere is intersected by another surface, there may be more complicated spherical curves.
;Example: sphere–cylinder
The intersection of the sphere with equation and the cylinder with equation is not just one or two circles. It is the solution of the non-linear system of equations
:
:
(see implicit curve and the diagram)
File:Einstein gyro gravity probe b.jpg, An image of one of the most accurate human-made spheres, as it refracts the image of Einstein in the background. This sphere was a fused quartz gyroscope for the Gravity Probe B experiment, and differs in shape from a perfect sphere by no more than 40 atoms (less than 10nm) of thickness. It was announced on 1 July 2008 that New Scientist , Technology , Roundest objects in the world created
File:King of spades- spheres.jpg, Deck of playing cards illustrating engineering instruments, England, 1702. King of spades: Spheres
Surface area of sphere proof
{{Authority control Differential geometry Differential topology Elementary geometry Elementary shapes Homogeneous spaces Surfaces Topology
circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
, a curve. In solid geometry
Solid geometry or stereometry is the geometry of Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional Euclidean space (3D space).
A solid figure is the region (mathematics), region of 3D space bounded by a two-dimensional closed surface; for example, a ...
, a sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space
In geometry, a three-dimensional space (3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a mathematical space in which three values ('' coordinates'') are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three- ...
.. That given point is the ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians.
The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubble
A soap bubble (commonly referred to as simply a bubble) is an extremely thin soap film, film of soap or detergent and water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. Soap bubbles usually last for only a few seconds b ...
s take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
, and the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
is an important concept in astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings.
Basic terminology
 As mentioned earlier is the sphere's radius; any line from the center to a point on the sphere is also called a radius. 'Radius' is used in two senses: as a line segment and also as its length.
If a radius is extended through the center to the opposite side of the sphere, it creates a
As mentioned earlier is the sphere's radius; any line from the center to a point on the sphere is also called a radius. 'Radius' is used in two senses: as a line segment and also as its length.
If a radius is extended through the center to the opposite side of the sphere, it creates a diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
. Like the radius, the length of a diameter is also called the diameter, and denoted . Diameters are the longest line segments that can be drawn between two points on the sphere: their length is twice the radius, . Two points on the sphere connected by a diameter are antipodal points of each other.
A unit sphere is a sphere with unit radius (). For convenience, spheres are often taken to have their center at the origin of the coordinate system, and spheres in this article have their center at the origin unless a center is mentioned.
A '' great circle'' on the sphere has the same center and radius as the sphere, and divides it into two equal ''hemispheres''.
Although the figure of Earth is not perfectly spherical, terms borrowed from geography are convenient to apply to the sphere.
A particular line passing through its center defines an '' axis'' (as in Earth's axis of rotation).
The sphere-axis intersection defines two antipodal ''poles'' (''north pole'' and ''south pole''). The great circle equidistant to the poles is called the ''equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
''. Great circles through the poles are called lines of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
or ''meridians''. Small circles on the sphere that are parallel to the equator are circles of latitude (or ''parallels''). In geometry unrelated to astronomical bodies, geocentric terminology should be used only for illustration and noted as such, unless there is no chance of misunderstanding.
Mathematicians consider a sphere to be a two-dimensional closed surface embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are ''Euclidean spaces ...
. They draw a distinction between a ''sphere'' and a '' ball'', which is a solid figure, a three-dimensional manifold with boundary that includes the volume contained by the sphere. An ''open ball'' excludes the sphere itself, while a ''closed ball'' includes the sphere: a closed ball is the union of the open ball and the sphere, and a sphere is the boundary of a (closed or open) ball. The distinction between ''ball'' and ''sphere'' has not always been maintained and especially older mathematical references talk about a sphere as a solid. The distinction between "circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
" and " disk" in the plane is similar.
Small spheres or balls are sometimes called ''spherules'' (e.g., in Martian spherules).
Equations
In analytic geometry, a sphere with center and radius is the locus of all points such that : Since it can be expressed as a quadratic polynomial, a sphere is a quadric surface, a type of algebraic surface. Let be real numbers with and put : Then the equation : has no real points as solutions if and is called the equation of an imaginary sphere. If , the only solution of is the point and the equation is said to be the equation of a point sphere. Finally, in the case , is an equation of a sphere whose center is and whose radius is . If in the above equation is zero then is the equation of a plane. Thus, a plane may be thought of as a sphere of infinite radius whose center is a point at infinity..Parametric
A parametric equation for the sphere with radius and center can be parameterized using trigonometric functions. : The symbols used here are the same as those used in spherical coordinates. is constant, while varies from 0 to and varies from 0 to 2.Properties
Enclosed volume
volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
inside a sphere (that is, the volume of a ball, but classically referred to as the volume of a sphere) is
:
where is the radius and is the diameter of the sphere. Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
first derived this formula ('' On the Sphere and Cylinder'' c. 225 BCE) by showing that the volume inside a sphere is twice the volume between the sphere and the circumscribed cylinder of that sphere (having the height and diameter equal to the diameter of the sphere). This may be proved by inscribing a cone upside down into semi-sphere, noting that the area of a cross section of the cone plus the area of a cross section of the sphere is the same as the area of the cross section of the circumscribing cylinder, and applying Cavalieri's principle. This formula can also be derived using integral calculus (i.e., disk integration) to sum the volumes of an infinite number of circular disks of infinitesimally small thickness stacked side by side and centered along the -axis from to , assuming the sphere of radius is centered at the origin.
At any given , the incremental volume () equals the product of the cross-sectional area of the disk at and its thickness ():
:
The total volume is the summation of all incremental volumes:
:
In the limit as approaches zero, this equation becomes:
:
At any given , a right-angled triangle connects , and to the origin; hence, applying the Pythagorean theorem yields:
:
Using this substitution gives
:
which can be evaluated to give the result
:
An alternative formula is found using spherical coordinates, with volume element
:
so
:
For most practical purposes, the volume inside a sphere inscribed in a cube can be approximated as 52.4% of the volume of the cube, since , where is the diameter of the sphere and also the length of a side of the cube and ≈ 0.5236. For example, a sphere with diameter 1 m has 52.4% the volume of a cube with edge length 1m, or about 0.524 m3.
Surface area
Thesurface area
The surface area (symbol ''A'') of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the d ...
of a sphere of radius is:
:
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
first derived this formula from the fact that the projection to the lateral surface of a circumscribed cylinder is area-preserving. Another approach to obtaining the formula comes from the fact that it equals the derivative
In mathematics, the derivative is a fundamental tool that quantifies the sensitivity to change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is t ...
of the formula for the volume with respect to because the total volume inside a sphere of radius can be thought of as the summation of the surface area of an infinite number of spherical shells of infinitesimal thickness concentrically stacked inside one another from radius 0 to radius . At infinitesimal thickness the discrepancy between the inner and outer surface area of any given shell is infinitesimal, and the elemental volume at radius is simply the product of the surface area at radius and the infinitesimal thickness.
At any given radius , the incremental volume () equals the product of the surface area at radius () and the thickness of a shell ():
:
The total volume is the summation of all shell volumes:
:
In the limit as approaches zero this equation becomes:
:
Substitute :
:
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to yields as a function of :
:
This is generally abbreviated as:
:
where is now considered to be the fixed radius of the sphere.
Alternatively, the area element on the sphere is given in spherical coordinates by . The total area can thus be obtained by integration:
:
The sphere has the smallest surface area of all surfaces that enclose a given volume, and it encloses the largest volume among all closed surfaces with a given surface area. The sphere therefore appears in nature: for example, bubbles and small water drops are roughly spherical because the surface tension locally minimizes surface area.
The surface area relative to the mass of a ball is called the specific surface area
Specific surface area (SSA) is a property of solids defined as the total surface area (SA) of a material per unit mass, (with units of m2/kg or m2/g). Alternatively, it may be defined as SA per solid or bulk volume (units of m2/m3 or m−1).
I ...
and can be expressed from the above stated equations as
:
where is the density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
(the ratio of mass to volume).
Other geometric properties
A sphere can be constructed as the surface formed by rotating acircle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
one half revolution about any of its diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
s; this is very similar to the traditional definition of a sphere as given in Euclid's Elements
The ''Elements'' ( ) is a mathematics, mathematical treatise written 300 BC by the Ancient Greek mathematics, Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid.
''Elements'' is the oldest extant large-scale deductive treatment of mathematics. Drawing on the w ...
. Since a circle is a special type of ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special ty ...
, a sphere is a special type of ellipsoid of revolution. Replacing the circle with an ellipse rotated about its major axis, the shape becomes a prolate spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface (mathematics), surface obtained by Surface of revolution, rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with t ...
; rotated about the minor axis, an oblate spheroid.
A sphere is uniquely determined by four points that are not coplanar. More generally, a sphere is uniquely determined by four conditions such as passing through a point, being tangent to a plane, etc. This property is analogous to the property that three non-collinear points determine a unique circle in a plane.
Consequently, a sphere is uniquely determined by (that is, passes through) a circle and a point not in the plane of that circle.
By examining the common solutions of the equations of two spheres, it can be seen that two spheres intersect in a circle and the plane containing that circle is called the radical plane of the intersecting spheres. Although the radical plane is a real plane, the circle may be imaginary (the spheres have no real point in common) or consist of a single point (the spheres are tangent at that point)..
The angle between two spheres at a real point of intersection is the dihedral angle determined by the tangent planes to the spheres at that point. Two spheres intersect at the same angle at all points of their circle of intersection. They intersect at right angles (are orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic ...
) if and only if the square of the distance between their centers is equal to the sum of the squares of their radii.
Pencil of spheres
If and are the equations of two distinct spheres then : is also the equation of a sphere for arbitrary values of the parameters and . The set of all spheres satisfying this equation is called a pencil of spheres determined by the original two spheres. In this definition a sphere is allowed to be a plane (infinite radius, center at infinity) and if both the original spheres are planes then all the spheres of the pencil are planes, otherwise there is only one plane (the radical plane) in the pencil.Properties of the sphere
 In their book ''Geometry and the Imagination'', David Hilbert and Stephan Cohn-Vossen describe eleven properties of the sphere and discuss whether these properties uniquely determine the sphere. Several properties hold for the plane, which can be thought of as a sphere with infinite radius. These properties are:
#''The points on the sphere are all the same distance from a fixed point. Also, the ratio of the distance of its points from two fixed points is constant.''
#: The first part is the usual definition of the sphere and determines it uniquely. The second part can be easily deduced and follows a similar
In their book ''Geometry and the Imagination'', David Hilbert and Stephan Cohn-Vossen describe eleven properties of the sphere and discuss whether these properties uniquely determine the sphere. Several properties hold for the plane, which can be thought of as a sphere with infinite radius. These properties are:
#''The points on the sphere are all the same distance from a fixed point. Also, the ratio of the distance of its points from two fixed points is constant.''
#: The first part is the usual definition of the sphere and determines it uniquely. The second part can be easily deduced and follows a similar result
A result (also called upshot) is the outcome or consequence of a sequence of actions or events. Possible results include gain, injury, value, and victory. Some types of results include the outcome of an action, the final value of a calculation ...
of Apollonius of Perga for the circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
. This second part also holds for the plane.
#''The contours and plane sections of the sphere are circles.''
#: This property defines the sphere uniquely.
#''The sphere has constant width and constant girth.''
#: The width of a surface is the distance between pairs of parallel tangent planes. Numerous other closed convex surfaces have constant width, for example the Meissner body. The girth of a surface is the circumference
In geometry, the circumference () is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. The circumference is the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to a line segment. More generally, the perimeter is the curve length arou ...
of the boundary of its orthogonal projection on to a plane. Each of these properties implies the other.
#''All points of a sphere are umbilics.''
#: At any point on a surface a normal direction is at right angles to the surface because on the sphere these are the lines radiating out from the center of the sphere. The intersection of a plane that contains the normal with the surface will form a curve that is called a ''normal section,'' and the curvature of this curve is the ''normal curvature''. For most points on most surfaces, different sections will have different curvatures; the maximum and minimum values of these are called the principal curvatures. Any closed surface will have at least four points called '' umbilical points''. At an umbilic all the sectional curvatures are equal; in particular the principal curvatures are equal. Umbilical points can be thought of as the points where the surface is closely approximated by a sphere.
#: For the sphere the curvatures of all normal sections are equal, so every point is an umbilic. The sphere and plane are the only surfaces with this property.
#''The sphere does not have a surface of centers.''
#: For a given normal section exists a circle of curvature that equals the sectional curvature, is tangent to the surface, and the center lines of which lie along on the normal line. For example, the two centers corresponding to the maximum and minimum sectional curvatures are called the ''focal points'', and the set of all such centers forms the focal surface.
#: For most surfaces the focal surface forms two sheets that are each a surface and meet at umbilical points. Several cases are special:
#: * For channel surfaces one sheet forms a curve and the other sheet is a surface
#: * For cones, cylinders, tori and cyclides both sheets form curves.
#: * For the sphere the center of every osculating circle is at the center of the sphere and the focal surface forms a single point. This property is unique to the sphere.
#''All geodesics of the sphere are closed curves.''
#: Geodesics are curves on a surface that give the shortest distance between two points. They are a generalization of the concept of a straight line in the plane. For the sphere the geodesics are great circles. Many other surfaces share this property.
#''Of all the solids having a given volume, the sphere is the one with the smallest surface area; of all solids having a given surface area, the sphere is the one having the greatest volume.''
#: It follows from isoperimetric inequality. These properties define the sphere uniquely and can be seen in soap bubble
A soap bubble (commonly referred to as simply a bubble) is an extremely thin soap film, film of soap or detergent and water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. Soap bubbles usually last for only a few seconds b ...
s: a soap bubble will enclose a fixed volume, and surface tension minimizes its surface area for that volume. A freely floating soap bubble therefore approximates a sphere (though such external forces as gravity will slightly distort the bubble's shape). It can also be seen in planets and stars where gravity minimizes surface area for large celestial bodies.
#''The sphere has the smallest total mean curvature among all convex solids with a given surface area.''
#: The mean curvature is the average of the two principal curvatures, which is constant because the two principal curvatures are constant at all points of the sphere.
#''The sphere has constant mean curvature.''
#: The sphere is the only embedded surface that lacks boundary or singularities with constant positive mean curvature. Other such immersed surfaces as minimal surfaces have constant mean curvature.
#''The sphere has constant positive Gaussian curvature.''
#: Gaussian curvature is the product of the two principal curvatures. It is an intrinsic property that can be determined by measuring length and angles and is independent of how the surface is embedded in space. Hence, bending a surface will not alter the Gaussian curvature, and other surfaces with constant positive Gaussian curvature can be obtained by cutting a small slit in the sphere and bending it. All these other surfaces would have boundaries, and the sphere is the only surface that lacks a boundary with constant, positive Gaussian curvature. The pseudosphere is an example of a surface with constant negative Gaussian curvature.
#''The sphere is transformed into itself by a three-parameter family of rigid motions.''
#: Rotating around any axis a unit sphere at the origin will map the sphere onto itself. Any rotation about a line through the origin can be expressed as a combination of rotations around the three-coordinate axis (see Euler angles). Therefore, a three-parameter family of rotations exists such that each rotation transforms the sphere onto itself; this family is the rotation group SO(3). The plane is the only other surface with a three-parameter family of transformations (translations along the - and -axes and rotations around the origin). Circular cylinders are the only surfaces with two-parameter families of rigid motions and the surfaces of revolution and helicoids are the only surfaces with a one-parameter family.
Treatment by area of mathematics
Spherical geometry
 The basic elements of Euclidean plane geometry are points and lines. On the sphere, points are defined in the usual sense. The analogue of the "line" is the geodesic, which is a great circle; the defining characteristic of a great circle is that the plane containing all its points also passes through the center of the sphere. Measuring by
The basic elements of Euclidean plane geometry are points and lines. On the sphere, points are defined in the usual sense. The analogue of the "line" is the geodesic, which is a great circle; the defining characteristic of a great circle is that the plane containing all its points also passes through the center of the sphere. Measuring by arc length
Arc length is the distance between two points along a section of a curve. Development of a formulation of arc length suitable for applications to mathematics and the sciences is a problem in vector calculus and in differential geometry. In the ...
shows that the shortest path between two points lying on the sphere is the shorter segment of the great circle that includes the points.
Many theorems from classical geometry hold true for spherical geometry as well, but not all do because the sphere fails to satisfy some of classical geometry's postulates, including the parallel postulate. In spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, ge ...
, angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
s are defined between great circles. Spherical trigonometry differs from ordinary trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The fiel ...
in many respects. For example, the sum of the interior angles of a spherical triangle always exceeds 180 degrees. Also, any two similar spherical triangles are congruent.
Any pair of points on a sphere that lie on a straight line through the sphere's center (i.e., the diameter) are called ''antipodal points''on the sphere, the distance between them is exactly half the length of the circumference. Any other (i.e., not antipodal) pair of distinct points on a sphere
*lie on a unique great circle,
*segment it into one minor (i.e., shorter) and one major (i.e., longer) arc, and
*have the minor arc's length be the ''shortest distance'' between them on the sphere.
Spherical geometry is a form of elliptic geometry, which together with hyperbolic geometry makes up non-Euclidean geometry.
Differential geometry
The sphere is a smooth surface with constant Gaussian curvature at each point equal to . As per Gauss's Theorema Egregium, this curvature is independent of the sphere's embedding in 3-dimensional space. Also following from Gauss, a sphere cannot be mapped to a plane while maintaining both areas and angles. Therefore, any map projection introduces some form of distortion. A sphere of radius has area element . This can be found from the volume element in spherical coordinates with held constant. A sphere of any radius centered at zero is an integral surface of the following differential form: : This equation reflects that the position vector and tangent plane at a point are alwaysorthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic ...
to each other. Furthermore, the outward-facing normal vector is equal to the position vector scaled by .
In Riemannian geometry
Riemannian geometry is the branch of differential geometry that studies Riemannian manifolds, defined as manifold, smooth manifolds with a ''Riemannian metric'' (an inner product on the tangent space at each point that varies smooth function, smo ...
, the filling area conjecture states that the hemisphere is the optimal (least area) isometric filling of the Riemannian circle.
Topology
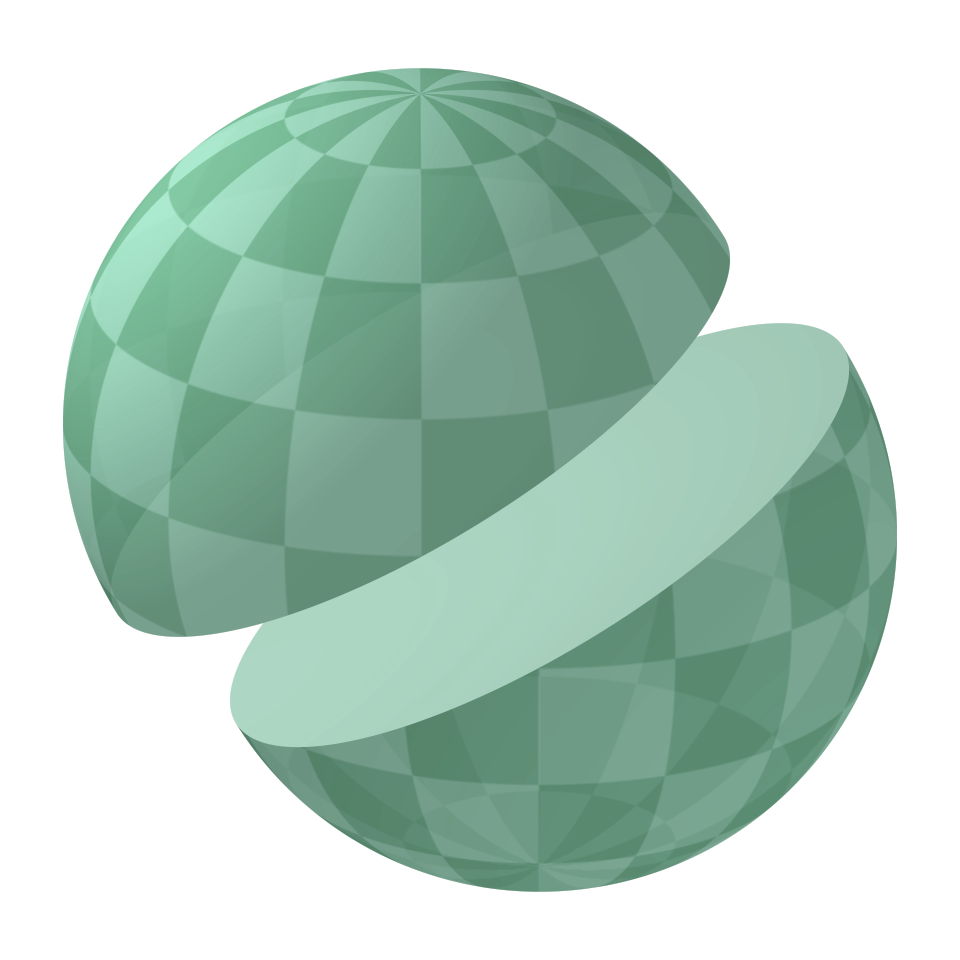
Remarkably, it is possible to turn an ordinary sphere inside out in athree-dimensional space
In geometry, a three-dimensional space (3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a mathematical space in which three values ('' coordinates'') are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three- ...
with possible self-intersections but without creating any creases, in a process called sphere eversion.
The antipodal quotient of the sphere is the surface called the real projective plane, which can also be thought of as the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
with antipodal points of the equator identified.
Curves on a sphere
Circles
Circles on the sphere are, like circles in the plane, made up of all points a certain distance from a fixed point on the sphere. The intersection of a sphere and a plane is a circle, a point, or empty. Great circles are the intersection of the sphere with a plane passing through the center of a sphere: others are called small circles. More complicated surfaces may intersect a sphere in circles, too: the intersection of a sphere with a surface of revolution whose axis contains the center of the sphere (are ''coaxial'') consists of circles and/or points if not empty. For example, the diagram to the right shows the intersection of a sphere and a cylinder, which consists of two circles. If the cylinder radius were that of the sphere, the intersection would be a single circle. If the cylinder radius were larger than that of the sphere, the intersection would be empty.Loxodrome
 In
In navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
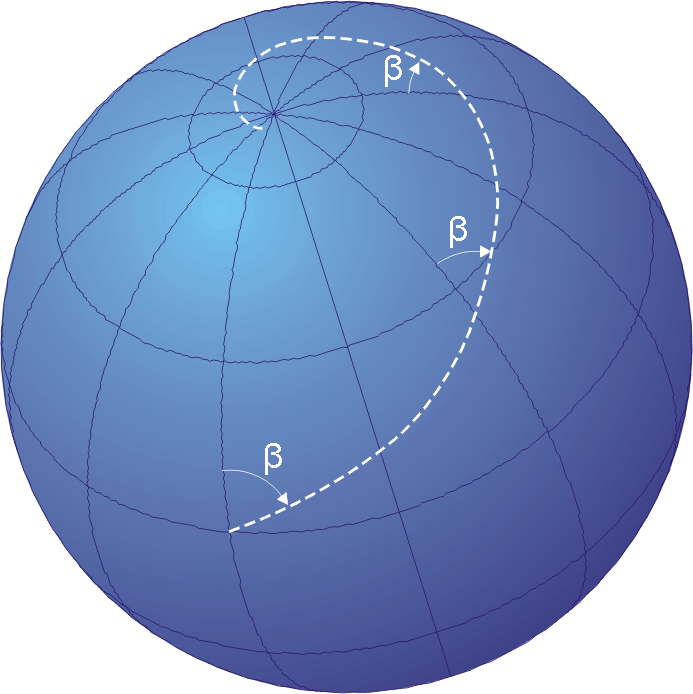
, a ''loxodrome'' or ''rhumb line'' is a path whose bearing, the angle between its tangent and due North, is constant. Loxodromes project to straight lines under the Mercator projection. Two special cases are the meridians which are aligned directly North–South and parallels which are aligned directly East–West. For any other bearing, a loxodrome spirals infinitely around each pole. For the Earth modeled as a sphere, or for a general sphere given a spherical coordinate system, such a loxodrome is a kind of spherical spiral.
Clelia curves
longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
(or azimuth) and the colatitude (or polar angle) are in a linear relationship, . Clelia curves project to straight lines under the equirectangular projection. Viviani's curve () is a special case. Clelia curves approximate the ground track of satellites in polar orbit.
Spherical conics
The analog of a conic section on the sphere is a spherical conic, a quartic curve which can be defined in several equivalent ways. *The intersection of a sphere with a quadratic cone whose vertex is the sphere center *The intersection of a sphere with an elliptic or hyperbolic cylinder whose axis passes through the sphere center *The locus of points whose sum or difference of great-circle distances from a pair of foci is a constant Many theorems relating to planar conic sections also extend to spherical conics.Intersection of a sphere with a more general surface
Generalizations
Ellipsoids
An ellipsoid is a sphere that has been stretched or compressed in one or more directions. More exactly, it is the image of a sphere under anaffine transformation
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, '' affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles.
More general ...
. An ellipsoid bears the same relationship to the sphere that an ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special ty ...
does to a circle.
Dimensionality
Spheres can be generalized to spaces of any number ofdimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coo ...
s. For any natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive in ...
, an ''-sphere,'' often denoted , is the set of points in ()-dimensional Euclidean space that are at a fixed distance from a central point of that space, where is, as before, a positive real number. In particular:
*: a 0-sphere consists of two discrete points, and
*: a 1-sphere is a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
of radius ''r''
*: a 2-sphere is an ordinary sphere
*: a 3-sphere is a sphere in 4-dimensional Euclidean space.
Spheres for are sometimes called hyperspheres.
The -sphere of unit radius centered at the origin is denoted and is often referred to as "the" -sphere. The ordinary sphere is a 2-sphere, because it is a 2-dimensional surface which is embedded in 3-dimensional space.
In topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformat ...
, the -sphere is an example of a compact topological manifold without boundary. A topological sphere need not be smooth; if it is smooth, it need not be diffeomorphic to the Euclidean sphere (an exotic sphere).
The sphere is the inverse image of a one-point set under the continuous function , so it is closed; is also bounded, so it is compact by the Heine–Borel theorem.
Metric spaces
More generally, in ametric space
In mathematics, a metric space is a Set (mathematics), set together with a notion of ''distance'' between its Element (mathematics), elements, usually called point (geometry), points. The distance is measured by a function (mathematics), functi ...
, the sphere of center and radius is the set of points such that .
If the center is a distinguished point that is considered to be the origin of , as in a normed space, it is not mentioned in the definition and notation. The same applies for the radius if it is taken to equal one, as in the case of a unit sphere.
Unlike a ball, even a large sphere may be an empty set. For example, in with Euclidean metric, a sphere of radius is nonempty only if can be written as sum of squares of integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
s.
An octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (: octahedra or octahedrons) is any polyhedron with eight faces. One special case is the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Many types of i ...
is a sphere in taxicab geometry, and a cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It i ...
is a sphere in geometry using the Chebyshev distance.
History
The geometry of the sphere was studied by the Greeks. ''Euclid's Elements
The ''Elements'' ( ) is a mathematics, mathematical treatise written 300 BC by the Ancient Greek mathematics, Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid.
''Elements'' is the oldest extant large-scale deductive treatment of mathematics. Drawing on the w ...
'' defines the sphere in book XI, discusses various properties of the sphere in book XII, and shows how to inscribe the five regular polyhedra within a sphere in book XIII. Euclid does not include the area and volume of a sphere, only a theorem that the volume of a sphere varies as the third power of its diameter, probably due to Eudoxus of Cnidus. The volume and area formulas were first determined in Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
's '' On the Sphere and Cylinder'' by the method of exhaustion. Zenodorus was the first to state that, for a given surface area, the sphere is the solid of maximum volume.
Archimedes wrote about the problem of dividing a sphere into segments whose volumes are in a given ratio, but did not solve it. A solution by means of the parabola and hyperbola was given by Dionysodorus. A similar problemto construct a segment equal in volume to a given segment, and in surface to another segmentwas solved later by al-Quhi.
Gallery
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
n scientists had created even more nearly perfect spheres, accurate to 0.3nm, as part of an international hunt to find a new global standard kilogram.File:King of spades- spheres.jpg, Deck of playing cards illustrating engineering instruments, England, 1702. King of spades: Spheres
Regions
*Hemisphere * Spherical cap * Spherical lune * Spherical polygon * Spherical sector * Spherical segment * Spherical wedge * Spherical zoneSee also
* 3-sphere * Affine sphere * Alexander horned sphere *Celestial spheres
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed star ...
*Curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry that intuitively measure the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line or by which a surface deviates from being a plane. If a curve or su ...
* Directional statistics
* Dyson sphere
* Gauss map
* Hand with Reflecting Sphere, M.C. Escher self-portrait drawing illustrating reflection and the optical properties of a mirror sphere
* Hoberman sphere
* Homology sphere
* Homotopy groups of spheres
* Homotopy sphere
* Lenart Sphere
* Napkin ring problem
* Orb (optics)
* Pseudosphere
* Riemann sphere
* Solid angle
* Sphere packing
* Spherical coordinates
* Spherical cow
*Spherical helix, tangent indicatrix of a curve of constant precession
* Spherical polyhedron
* Sphericity
* Tennis ball theorem
* Volume-equivalent radius
* Zoll sphere
Notes and references
Notes
References
Further reading
*. * *. *. *. *External links
* Mathematica/Uniform Spherical DistributionSurface area of sphere proof
{{Authority control Differential geometry Differential topology Elementary geometry Elementary shapes Homogeneous spaces Surfaces Topology