Somali People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The
– Ethnologue.com Somali diasporas are also found in parts of the
 The origin of the Somali people which were previously theorized to have been from Southern
The origin of the Somali people which were previously theorized to have been from Southern  In
In
by James Talboys Wheeler, pg 1xvi, 315, 526 The Macrobians were warrior herders and seafarers. According to Herodotus' account, the Persian Emperor Cambyses II, upon his conquest of Egypt (525 BC), sent ambassadors to Macrobia, bringing luxury gifts for the Macrobian king to entice his submission. The Macrobian ruler, who was elected based on his stature and beauty, replied instead with a challenge for his Persian counterpart in the form of an unstrung bow: if the Persians could manage to draw it, they would have the right to invade his country; but until then, they should thank the gods that the Macrobians never decided to invade their empire.John Kitto, James Taylor, ''The popular cyclopædia of Biblical literature: condensed from the larger work'', (Gould and Lincoln: 1856), p.302. The Macrobians were a regional power reputed for their advanced architecture and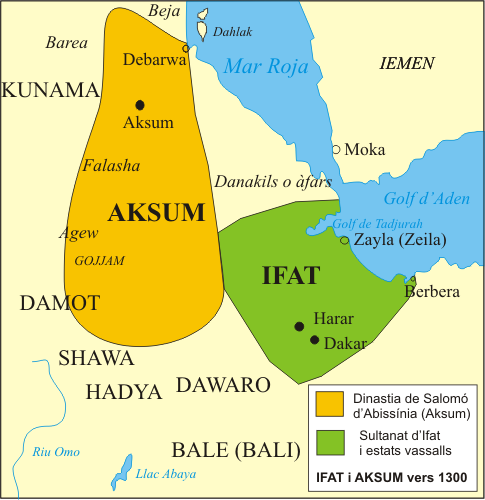 Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of
Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of  According to a trade journal published in 1856,
According to a trade journal published in 1856,  In the late 19th century, after the Berlin Conference had ended, the Scramble for Africa reached the Horn of Africa. Increasing foreign influence in the region culminated in the first darawiish becoming the Ali Gheri clan*
In the late 19th century, after the Berlin Conference had ended, the Scramble for Africa reached the Horn of Africa. Increasing foreign influence in the region culminated in the first darawiish becoming the Ali Gheri clan*
*
* the Drawiish had leaders such as Mohammed Abdullah Hassan, Haji Sudi and Sultan Nur Ahmed Aman, who sought a state in the Nugaal and began one of the longest African conflicts in history. The news of the incident that sparked the 21 year long Dervish rebellion, according to the consul-general James Hayes Sadler, was spread or as he claimed was concocted by Sultan Nur of the Habr Yunis. The incident in question was that of a group of Somali children that were converted to Christianity and adopted by the French Catholic Mission at Berbera in 1899. Whether Sultan Nur experienced the incident first hand or whether he was told of it is not clear but what is known is that he propagated the incident in June 1899, precipitating the religious rebellion of the Dervishes. The Dervish movement successfully stymied British forces four times and forced them to retreat to the coastal region. As a result of its successes against the British, the Dervish movement received support from the Ottomans and Majeerteen Sultanate was founded in the early-18th century. It rose to prominence in the following century, under the reign of the resourceful Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud. Helen Chapin Metz, ed., ''Somalia: a country study'', (The Division: 1993), p.10. His Kingdom controlled Bari Karkaar, Nugaaal, and also central Somalia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The Majeerteen Sultanate maintained a robust trading network, entered into treaties with foreign powers, and exerted strong centralized authority on the domestic front.''Horn of Africa'', Volume 15, Issues 1-4, (Horn of Africa Journal: 1997), p.130.''Transformation towards a regulated economy'', (WSP Transition Programme, Somali Programme: 2000) p.62.
The Majeerteen Sultanate was nearly destroyed in the late-1800s by a power struggle between Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud of the Majeerteen Sultanate and his ambitious cousin, Yusuf Ali Kenadid who founded a separate Kingdom, Sultanate of Hobyo in 1878. Initially Kenadid wanted to seize control of the neighbouring Majeerteen Sultanate, ruled by his cousin Mahamuud. However, he was unsuccessful in this endeavour, and was eventually forced into exile in
Majeerteen Sultanate was founded in the early-18th century. It rose to prominence in the following century, under the reign of the resourceful Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud. Helen Chapin Metz, ed., ''Somalia: a country study'', (The Division: 1993), p.10. His Kingdom controlled Bari Karkaar, Nugaaal, and also central Somalia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The Majeerteen Sultanate maintained a robust trading network, entered into treaties with foreign powers, and exerted strong centralized authority on the domestic front.''Horn of Africa'', Volume 15, Issues 1-4, (Horn of Africa Journal: 1997), p.130.''Transformation towards a regulated economy'', (WSP Transition Programme, Somali Programme: 2000) p.62.
The Majeerteen Sultanate was nearly destroyed in the late-1800s by a power struggle between Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud of the Majeerteen Sultanate and his ambitious cousin, Yusuf Ali Kenadid who founded a separate Kingdom, Sultanate of Hobyo in 1878. Initially Kenadid wanted to seize control of the neighbouring Majeerteen Sultanate, ruled by his cousin Mahamuud. However, he was unsuccessful in this endeavour, and was eventually forced into exile in  In late 1888, Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid entered into a treaty with the Italian government, making his Sultanate of Hobyo an Italian protectorate known as Italian Somalia. His rival Boqor Osman Mahamuud was to sign a similar agreement vis-a-vis his own Majeerteen Sultanate the following year. In signing the agreements, both rulers also hoped to exploit the rival objectives of the European imperial powers so as to more effectively assure the continued independence of their territories. The Italians, for their part, were interested in the territories mainly because of its
In late 1888, Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid entered into a treaty with the Italian government, making his Sultanate of Hobyo an Italian protectorate known as Italian Somalia. His rival Boqor Osman Mahamuud was to sign a similar agreement vis-a-vis his own Majeerteen Sultanate the following year. In signing the agreements, both rulers also hoped to exploit the rival objectives of the European imperial powers so as to more effectively assure the continued independence of their territories. The Italians, for their part, were interested in the territories mainly because of its
countrystudies.us
/ref> Meanwhile, in 1948, under pressure from their World War II allies and to the dismay of the Somalis,Federal Research Division, ''Somalia: A Country Study'', (Kessinger Publishing, LLC: 2004), p.38 the British ceded official control of the Haud (an important Somali grazing area that was brought under British protection via treaties with the Somalis in 1884 and 1886) and the Ogaden to Ethiopia, based on a treaty they signed in 1897 in which the British ceded Somali territory to the Ethiopian Emperor
 Somalis are ethnically of Cushitic ancestry, but have genealogical traditions of descent from various patriarchs associated with the spread of Islam. Being one tribe, they are segmented into various clan groupings, which are important
Somalis are ethnically of Cushitic ancestry, but have genealogical traditions of descent from various patriarchs associated with the spread of Islam. Being one tribe, they are segmented into various clan groupings, which are important
 Within traditional Somali society (as in other ethnic groups of the Horn of Africa and the wider region), there has been social stratification. According to the historian Donald Levine, these comprised high-ranking clans, low-ranking clans, caste groups, and slaves. This rigid hierarchy and concepts of lineal purity contrast with the relative egalitarianism in clan leadership and political control., Quote: "The social organization of Somali society accommodated ideological conceptions of inferiority through investing clan membership with definitions of lineal purity. Somali clans, while fiercely egalitarian with regards to leadership and political control, contain divisions of unequal status".
Nobles constituted the upper tier and were known as ''bilis''. They consist of individuals of ethnic Somali ancestral origin, and have been endogamous.
The lower tier was designated as ''Sab'', and was distinguished by its heterogeneous constitution and agropastoral lifestyle as well as some linguistic and cultural differences. A third Somali caste strata was made up of artisanal groups, which were endogamous and hereditary. Among the caste groups, the '' Midgan'' were traditionally hunters and circumcision performers.Е. de Larajasse (1972), Somali-English and Somali-English Dictionary, Trubner, pages 108, 119, 134, 145
Within traditional Somali society (as in other ethnic groups of the Horn of Africa and the wider region), there has been social stratification. According to the historian Donald Levine, these comprised high-ranking clans, low-ranking clans, caste groups, and slaves. This rigid hierarchy and concepts of lineal purity contrast with the relative egalitarianism in clan leadership and political control., Quote: "The social organization of Somali society accommodated ideological conceptions of inferiority through investing clan membership with definitions of lineal purity. Somali clans, while fiercely egalitarian with regards to leadership and political control, contain divisions of unequal status".
Nobles constituted the upper tier and were known as ''bilis''. They consist of individuals of ethnic Somali ancestral origin, and have been endogamous.
The lower tier was designated as ''Sab'', and was distinguished by its heterogeneous constitution and agropastoral lifestyle as well as some linguistic and cultural differences. A third Somali caste strata was made up of artisanal groups, which were endogamous and hereditary. Among the caste groups, the '' Midgan'' were traditionally hunters and circumcision performers.Е. de Larajasse (1972), Somali-English and Somali-English Dictionary, Trubner, pages 108, 119, 134, 145
178
/ref> The '' Tumal'' (also spelled ''Tomal'') were smiths and leatherworkers, and the Yibir (also spelled ''Yebir'') were the tanners and magicians. According to the anthropologist Virginia Luling, the artisanal caste groups of the north closely resembled their higher caste kinsmen, being generally Caucasoid like other ethnic Somalis. Although ethnically indistinguishable from each other, state Mohamed Eno and Abdi Kusow, upper castes have stigmatized the lower ones. Outside of the Somali caste system were slaves of
 According to data from the Pew Research Center, the creed breakdown of Muslims in the Somali-majority Djibouti is as follows: 77% adhere to Sunnism, 8% are non-denominational Muslim, 2% are
According to data from the Pew Research Center, the creed breakdown of Muslims in the Somali-majority Djibouti is as follows: 77% adhere to Sunnism, 8% are non-denominational Muslim, 2% are
 The Somali language (''Af-Soomaali'') is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. Its nearest relatives are the
The Somali language (''Af-Soomaali'') is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. Its nearest relatives are the  Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern, Benaadir, and Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benaadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast from Adale to south of Merca, including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional
Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern, Benaadir, and Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benaadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast from Adale to south of Merca, including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional
*N.B. ~60% of 774,389 total pop.

 The culture of Somalia is an amalgamation of traditions developed independently and through interaction with neighbouring and far away civilizations, such as other parts of Northeast Africa, the Arabian Peninsula,
The culture of Somalia is an amalgamation of traditions developed independently and through interaction with neighbouring and far away civilizations, such as other parts of Northeast Africa, the Arabian Peninsula,
 * Aar Maanta – UK-based Somali singer, composer, writer and music producer.
* Abdi Sinimo – Prominent Somali artist and inventor of the Balwo musical style.
* Abdullahi Qarshe – Somali musician, poet and playwright known for his innovative styles of music, which included a wide variety of musical instruments such as the guitar, piano and oud.
* Ali Feiruz – Somali musician from Djibouti; part of the Radio Hargeisa generation of Somali artists.
*
* Aar Maanta – UK-based Somali singer, composer, writer and music producer.
* Abdi Sinimo – Prominent Somali artist and inventor of the Balwo musical style.
* Abdullahi Qarshe – Somali musician, poet and playwright known for his innovative styles of music, which included a wide variety of musical instruments such as the guitar, piano and oud.
* Ali Feiruz – Somali musician from Djibouti; part of the Radio Hargeisa generation of Somali artists.
*
 Growing out of the Somali people's rich storytelling tradition, the first few feature-length Somali films and cinematic festivals emerged in the early 1960s, immediately after independence. Following the creation of the Somali Film Agency (SFA) regulatory body in 1975, the local film scene began to expand rapidly. Hassan Sheikh Mumin was considered one of the most prolific and early playwrights and composers in Somali literature. Mumin's most important work is ''Shabeel Naagood'' (1965), a piece that touches on the social position of women, urbanization, changing traditional practices, and the importance of education during the early pre-independence period. Although the issues it describes were later to some degree redressed, the work remains a mainstay of Somali literature. ''Shabeel Naagood'' was translated into English in 1974 under the title ''Leopard Among the Women'' by the Somali Studies pioneer
The Somali filmmaker Ali Said Hassan concurrently served as the SFA's representative in Rome. In the 1970s and early 1980s, popular musicals known as ''riwaayado'' were the main driving force behind the Somali movie industry.
Epic and period films as well as international co-productions followed suit, facilitated by the proliferation of
Growing out of the Somali people's rich storytelling tradition, the first few feature-length Somali films and cinematic festivals emerged in the early 1960s, immediately after independence. Following the creation of the Somali Film Agency (SFA) regulatory body in 1975, the local film scene began to expand rapidly. Hassan Sheikh Mumin was considered one of the most prolific and early playwrights and composers in Somali literature. Mumin's most important work is ''Shabeel Naagood'' (1965), a piece that touches on the social position of women, urbanization, changing traditional practices, and the importance of education during the early pre-independence period. Although the issues it describes were later to some degree redressed, the work remains a mainstay of Somali literature. ''Shabeel Naagood'' was translated into English in 1974 under the title ''Leopard Among the Women'' by the Somali Studies pioneer
The Somali filmmaker Ali Said Hassan concurrently served as the SFA's representative in Rome. In the 1970s and early 1980s, popular musicals known as ''riwaayado'' were the main driving force behind the Somali movie industry.
Epic and period films as well as international co-productions followed suit, facilitated by the proliferation of
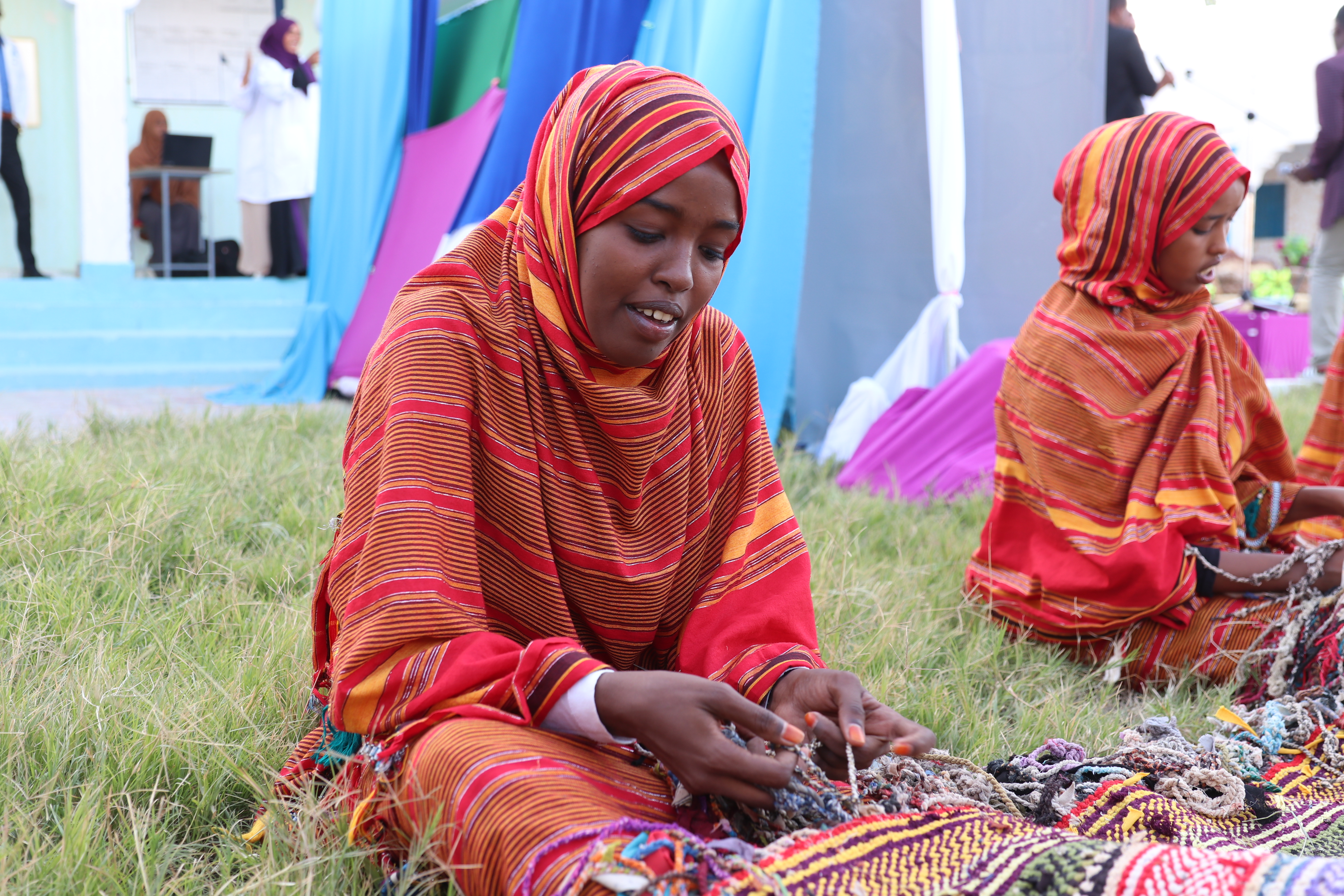
 Somalis have old visual art traditions, which include pottery, jewelry and wood carving. In the medieval period, affluent urbanites commissioned local wood and marble carvers to work on their interiors and houses. Intricate patterns also adorn the mihrabs and pillars of ancient Somali
Somalis have old visual art traditions, which include pottery, jewelry and wood carving. In the medieval period, affluent urbanites commissioned local wood and marble carvers to work on their interiors and houses. Intricate patterns also adorn the mihrabs and pillars of ancient Somali
 Football is the most popular sport amongst Somalis. Important competitions are the Somalia League and
Football is the most popular sport amongst Somalis. Important competitions are the Somalia League and
 The Somali flag is an ethnic flag conceived to represent ethnic Somalis. It was created in 1954 by the Somali scholar Mohammed Awale Liban, after he had been selected by the labour trade union of the Trust Territory of Somalia to come up with a design. Upon
The Somali flag is an ethnic flag conceived to represent ethnic Somalis. It was created in 1954 by the Somali scholar Mohammed Awale Liban, after he had been selected by the labour trade union of the Trust Territory of Somalia to come up with a design. Upon
 The Somalis staple food comes from their livestock, however, the Somali cuisine varies from region to region and consists of a fusion of diverse culinary influences. In the interiors, the cuisine is mainly local with usage of Ethiopian grains and vegetables while in the coast it is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are therefore no pork dishes, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated.
Breakfast (''quraac'') is an important meal for Somalis, some drink tea (''shahie or shaah)'' others
The Somalis staple food comes from their livestock, however, the Somali cuisine varies from region to region and consists of a fusion of diverse culinary influences. In the interiors, the cuisine is mainly local with usage of Ethiopian grains and vegetables while in the coast it is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are therefore no pork dishes, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated.
Breakfast (''quraac'') is an important meal for Somalis, some drink tea (''shahie or shaah)'' others
 Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to
Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to
 Somalis for centuries have practiced a form of customary law, which they call '' xeer''. Xeer is a
Somalis for centuries have practiced a form of customary law, which they call '' xeer''. Xeer is a  Xeer is defined by a few fundamental tenets that are immutable and which closely approximate the principle of '' jus cogens'' in international law: payment of blood money (locally referred to as ''
Xeer is defined by a few fundamental tenets that are immutable and which closely approximate the principle of '' jus cogens'' in international law: payment of blood money (locally referred to as ''
 Somalis constitute the largest ethnic group in Somalia, at approximately 85% of the nation's inhabitants. They also comprise around 60% of the inhabitants in Djibouti.
Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left for the Middle East, Europe and North America. In
Somalis constitute the largest ethnic group in Somalia, at approximately 85% of the nation's inhabitants. They also comprise around 60% of the inhabitants in Djibouti.
Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left for the Middle East, Europe and North America. In  While the distribution of Somalis per country in Europe is hard to measure because the Somali community on the continent has grown so quickly in recent years, the Office for National Statistics estimates that 98,000 people born in Somalia were living in the
While the distribution of Somalis per country in Europe is hard to measure because the Somali community on the continent has grown so quickly in recent years, the Office for National Statistics estimates that 98,000 people born in Somalia were living in the  An estimated 20,000 Somalis emigrated to the U.S. state of
An estimated 20,000 Somalis emigrated to the U.S. state of  There is a sizable Somali community in the United Arab Emirates. Somali-owned businesses line the streets of Deira, the
There is a sizable Somali community in the United Arab Emirates. Somali-owned businesses line the streets of Deira, the
In addition, there is an historical Somali community in the general Sudan area. Primarily concentrated in the north and Khartoum, the expatriate community mainly consists of students as well as some businesspeople.The History of Somali Communities in the Sudan since the First World War
/ref> More recently, Somali entrepreneurs have established themselves in
/ref> In
 *
* * Ahmed Hussen – Somali lawyer. Minister of Immigration of Canada. President of the
* Ahmed Hussen – Somali lawyer. Minister of Immigration of Canada. President of the  *
* *
* *
*
 According to
According to
MtDNA variation in North, East, and Central African populations gives clues to a possible back-migration from the Middle East
, Program of the Seventy-Fourth Annual Meeting of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists (2005) This mitochondrial clade is common among Ethiopians and North Africans, particularly Egyptians and
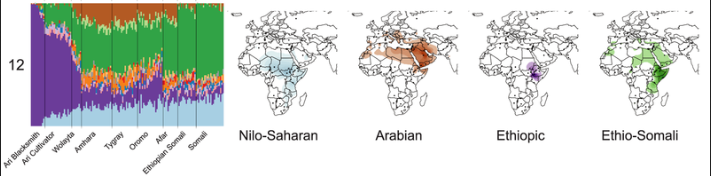

 Research shows that Somalis have a mixture of a type of native African ancestry unique and autochthonous to the Horn of Africa, as well as ancestry originating from a non-African back-migration. According to an
Research shows that Somalis have a mixture of a type of native African ancestry unique and autochthonous to the Horn of Africa, as well as ancestry originating from a non-African back-migration. According to an
 The scholarly term for research concerning Somalis and Greater Somalia is Somali Studies. It consists of several disciplines such as
The scholarly term for research concerning Somalis and Greater Somalia is Somali Studies. It consists of several disciplines such as
Ethnologue population estimates for Somali speakers
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Somali People Cushitic-speaking peoples Indigenous peoples of East Africa Ethnic Somali people, Ethnic groups in Djibouti Ethnic groups in Ethiopia Ethnic groups in Kenya Ethnic groups in Somalia, Ethnic groups in the Arab world Muslim communities in Africa Pastoralists Female genital mutilation Female genital mutilation by country
 The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic
Lowland East Cushitic is a group of roughly two dozen diverse languages of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. Its largest representatives are Somali and Oromo.
Classification
Lowland East Cushitic classification from Tosco (2020:2 ...
Somali language is the shared mother tongue of ethnic Somalis, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family, and are predominantly Sunni Muslim.Mohamed Diriye Abdullahi, ''Culture and Customs of Somalia'', (Greenwood Press: 2001), p.1 They form one of the largest ethnic groups on the African continent, and cover one of the most expansive landmasses by a single ethnic group in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
.
According to most scholars, the ancient Land of Punt and its native inhabitants formed part of the ethnogenesis of the Somali people. An ancient historical kingdom where a great portion of their cultural traditions and ancestry has been said to derive from.Egypt: 3000 Years of Civilization Brought to Life By Christine El MahdyAncient perspectives on Egypt By Roger Matthews, Cornelia Roemer, University College, London.Africa's legacies of urbanization: unfolding saga of a continent By Stefan GoodwinCivilizations: Culture, Ambition, and the Transformation of Nature By Felipe Armesto Fernandez
Somalis share many historical and cultural traits with other Cushitic peoples, especially with Lowland East Cushitic
Lowland East Cushitic is a group of roughly two dozen diverse languages of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. Its largest representatives are Somali and Oromo.
Classification
Lowland East Cushitic classification from Tosco (2020:2 ...
people, specifically the Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
and the Saho.
Ethnic Somalis are principally concentrated in Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
(around 8.8 million), Somaliland (5.7 million), Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er ...
(11.7 million), Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
(2.8 million), and Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Re ...
(534,000).– Ethnologue.com Somali diasporas are also found in parts of the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, North America, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, African Great Lakes region, Southern Africa and Oceania.
Etymology
Samaale, the oldest common ancestor of several Somali clans, is generally regarded as the source of the ethnonym ''Somali''. One other theory is that the name is held to be derived from the words ''soo'' and ''maal'', which together mean "go and milk". This interpretation differs depending on region with northern Somalis imply it refers to go and milk in regards to the camel's milk,Who Cares about Somalia: Hassan's Ordeal ; Reflections on a Nation's Future, By Hassan Ali Jama, page 92 southern Somalis use the transliteration "''sa ''maal''" which refers to cow's milk. This is a reference to the ubiquitouspastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands ( pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The ani ...
of the Somali people. Another plausible etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
proposes that the term ''Somali'' is derived from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
for "wealthy" (''zāwamāl''), again referring to Somali riches in livestock.
Alternatively, the ethnonym ''Somali'' is believed to have been derived from the Automoli (Asmach), a group of warriors from ancient Egypt described by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ...
, who were likely of Meshwesh origin according to Flinders Petrie. ''Asmach'' is thought to have been their Egyptian name, with ''Automoli'' being a Greek derivative of the Hebrew word ''S’mali'' (meaning "on the left hand side").
An ancient Chinese document from the 9th century CE referred to the northern Somalia coast — which was then part of a broader region in Northeast Africa known as Barbara
Barbara may refer to:
People
* Barbara (given name)
* Barbara (painter) (1915–2002), pseudonym of Olga Biglieri, Italian futurist painter
* Barbara (singer) (1930–1997), French singer
* Barbara Popović (born 2000), also known mononymously as ...
, in reference to the area's Berber ( Cushitic) inhabitantsDavid D. Laitin, Said S. Samatar, ''Somalia: Nation in Search of a State'', (Westview Press: 1987), p. 5. — as ''Po-pa-li''.Nagendra Kr Singh, ''International encyclopaedia of Islamic dynasties'', (Anmol Publications PVT. LTD., 2002), p. 524. The first clear written reference of the sobriquet ''Somali'', however, dates back to the 15th century. During the conflict between the Sultanate of Ifat based at Zeila and the Solomonic Dynasty, the Abyssinian emperor had one of his court officials compose a hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn ...
celebrating a military victory over the Sultan of Ifat's eponymous troops. ''Simur'' was also an ancient Harari alias for the Somali people. Somalis overwhelmingly prefer the demonym ''Somali'' over the incorrect ''Somalian'' since the former is an endonym, while the latter is an exonym with double suffixes. The hypernym of the term ''Somali'' from a geopolitical sense is ''Horner
Horner is an English and German surname that derives from the Middle English word for the occupation ''horner'', meaning horn-worker or horn-maker, or even horn-blower.
People
*Alison Horner (born 1966), British businesswoman
*Arthur Horner (disa ...
'' and from an ethnic sense, it is '' Cushite''.
History
 The origin of the Somali people which were previously theorized to have been from Southern
The origin of the Somali people which were previously theorized to have been from Southern Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Er ...
since 1000 BC or from the Arabian peninsula in the eleventh century has now been overturned by newer archeological and linguistic studies which puts the original homeland of the Somali people in Somaliland, which concludes that the Somalis are the indigenous inhabitants of the Horn of Africa for the last 7000 years.
Ancient rock paintings, which date back 5000 years (estimated), have been found in Somaliland. These engravings depict early life in the territory. The most famous of these is the Laas Geel complex. It contains some of the earliest known rock art on the African continent and features many elaborate pastoralist sketches of animal and human figures. In other places, such as the Dhambalin
Dhambalin ("half, vertically cut mountain") is an archaeological site in the central Sahil province of Somaliland. The sandstone rock shelter contains rock art depicting various animals such as horned cattle and goats, as well as giraffes, an ani ...
region, a depiction of a man on a horse is postulated as being one of the earliest known examples of a mounted huntsman.
Inscriptions have been found beneath many of the rock paintings, but archaeologists have so far been unable to decipher this form of ancient writing. During the Stone Age, the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished here with their respective industries
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial secto ...
and factories.
The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to 4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
. The stone implements from the ''Jalelo'' site in Somalia are said to be the most important link in evidence of the universality in palaeolithic times between the East and the West.
 In
In antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, the ancestors of the Somali people were an important link in the Horn of Africa connecting the region's commerce with the rest of the ancient world. Somali sailors and merchants were the main suppliers of frankincense, myrrh and spices, items which were considered valuable luxuries by the Ancient Egyptians, Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
ns, Mycenaeans and Babylonians.
According to most scholars, the ancient Land of Punt and its native inhabitants formed part of the ethnogenesis of the Somali people. The ancient Puntites were a nation of people that had close relations with Pharaonic Egypt during the times of Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
Sahure and Queen Hatshepsut. The pyramidal structures, temples and ancient houses of dressed stone littered around Somalia may date from this period.Man, God and Civilization pg 216
In the classical era, the Macrobians, who may have been ancestral to the Automoli or ancient Somalis, established a powerful tribal kingdom that ruled large parts of modern Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
. They were reputed for their longevity and wealth, and were said to be the "tallest and handsomest of all men".The Geography of Herodotus: Illustrated from Modern Researches and Discoveriesby James Talboys Wheeler, pg 1xvi, 315, 526 The Macrobians were warrior herders and seafarers. According to Herodotus' account, the Persian Emperor Cambyses II, upon his conquest of Egypt (525 BC), sent ambassadors to Macrobia, bringing luxury gifts for the Macrobian king to entice his submission. The Macrobian ruler, who was elected based on his stature and beauty, replied instead with a challenge for his Persian counterpart in the form of an unstrung bow: if the Persians could manage to draw it, they would have the right to invade his country; but until then, they should thank the gods that the Macrobians never decided to invade their empire.John Kitto, James Taylor, ''The popular cyclopædia of Biblical literature: condensed from the larger work'', (Gould and Lincoln: 1856), p.302. The Macrobians were a regional power reputed for their advanced architecture and
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
wealth, which was so plentiful that they shackled their prisoners in golden chains.
After the collapse of Macrobia, several ancient city-states, such as Opone, Essina, Sarapion, Nikon, Malao, Damo and Mosylon near Cape Guardafui, which competed with the Sabaeans, Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Mede ...
ns and Axumites
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
for the wealthy Indo- Greco-Roman trade, also flourished in Somalia.
 Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of
Islam was introduced to the area early on by the first Muslims of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
fleeing prosecution during the first Hejira
The Hijrah or Hijra () was the journey of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina. The year in which the Hijrah took place is also identified as the epoch of the Lunar Hijri and Solar Hijri calendars; its date e ...
with Masjid al-Qiblatayn being built before the Qiblah towards Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
. The town of Zeila's two- mihrab Masjid al-Qiblatayn dates to the 7th century, and is the oldest mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a Place of worship, place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) ...
in Africa.
Consequently the Somalis were some of the earliest non-Arabs that converted to Islam. The peaceful conversion of the Somali population by Somali Muslim scholars in the following centuries, the ancient city-states eventually transformed into Islamic Mogadishu, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
, Zeila, Barawa, Hafun and Merca, which were part of the Berberi civilization. The city of Mogadishu came to be known as the ''City of Islam'', and controlled the East African gold trade for several centuries.
The Sultanate of Ifat, led by the Walashma dynasty with its capital at Zeila, ruled over parts of what is now eastern Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somaliland. The historian al-Umari records that Ifat was situated near the Red Sea coast, and states its size as 15 days travel by 20 days travel. Its army numbered 15,000 horsemen and 20,000 foot soldiers. Al-Umari also credits Ifat with seven "mother cities": Belqulzar, Kuljura, Shimi, Shewa, Adal, Jamme and Laboo.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, several powerful Somali empires dominated the regional trade including the Ajuran Sultanate, which excelled in hydraulic engineering and fortress building, the Adal Sultanate, whose general Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi (Ahmed Gurey) was the first commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain ...
to use cannon warfare on the continent during Adal's conquest of the Ethiopian Empire, and the Sultanate of the Geledi, whose military dominance forced governors of the Omani empire north of the city of Lamu to pay tribute to the Somali Sultan Ahmed Yusuf. The Harla, an early group who inhabited parts of Somalia, Tchertcher and other areas in the Horn, also erected various tumuli. These masons are believed to have been ancestral to the Somalis ("proto-Somali").
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was the most important port in the Horn of Africa between the 18th–19th centuries. For centuries, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
had extensive trade relations with several historic ports in the Arabian Peninsula. Additionally, the Somali and Ethiopian interiors were very dependent on Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
for trade, where most of the goods for export arrived from. During the 1833 trading season, the port town swelled to over 70,000 people, and upwards of 6,000 camels laden with goods arrived from the interior within a single day. Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was the main marketplace in the entire Somali seaboard for various goods procured from the interior, such as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to anima ...
, coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
, frankincense, myrrh, acacia gum, saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma (botany), stigma and stigma (botany)#style, styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly ...
, feathers, ghee, hide (skin), gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
. Historically, the port of Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was controlled indigenously between the mercantile Reer Ahmed Nur and Reer Yunis Nuh sub-clans of the Habar Awal.
 According to a trade journal published in 1856,
According to a trade journal published in 1856, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was described as “the freest port in the world, and the most important trading place on the whole Arabian Gulf.”:
As a tributary of Mocha, which in turn was part of the Ottoman possessions in Western Arabia, the port of Zeila had seen several men placed as governors over the years. The Ottomans based in Yemen held nominal authority of Zeila when Sharmarke Ali Saleh, who was a successful and ambitious Somali merchant, purchased the rights of the town from the Ottoman governor of Mocha and Hodeida.
Allee Shurmalkee li Sharmarkehas since my visit either seized or purchased this town, and hoisted independent colours upon its walls; but as I know little or nothing save the mere fact of its possession by that Soumaulee chief, and as this change occurred whilst I was in Abyssinia, I shall not say anything more upon the subject.However, the previous governor was not eager to relinquish his control of Zeila. Hence in 1841, Sharmarke chartered two dhows (ships) along with fifty Somali Matchlock men and two cannons to target Zeila and depose its Arab Governor, Syed Mohammed Al Barr. Sharmarke initially directed his cannons at the city walls which frightened Al Barr's followers and caused them to abandon their posts and succeeded Al Barr as the ruler of Zeila. Sharmarke's governorship had an instant effect on the city, as he maneuvered to monopolize as much of the regional trade as possible, with his sights set as far as Harar and the Ogaden. In 1845, Sharmarke deployed a few matchlock men to wrest control of neighboring Berbera from that town's then feuding Somali local authorities. Sharmarke's influence was not limited to the Somali coast as he had allies and influence in the interior of the Somali country, the Danakil coast and even further afield in Abyssinia. Among his allies were the Kings of Shewa. When there was tension between the Amir of Harar
Abu Bakr II ibn `Abd al-Munan
Abu or ABU may refer to:
Places
* Abu (volcano), a volcano on the island of Honshū in Japan
* Abu, Yamaguchi, a town in Japan
* Ahmadu Bello University, a university located in Zaria, Nigeria
* Atlantic Baptist University, a Christian university ...
and Sharmarke, as a result of the Amir arresting one of his agents in Harar, Sharmarke persuaded the son of Sahle Selassie, ruler of Shewa, to imprison on his behalf about 300 citizens of Harar then resident in Shewa, for a length of two years.
 In the late 19th century, after the Berlin Conference had ended, the Scramble for Africa reached the Horn of Africa. Increasing foreign influence in the region culminated in the first darawiish becoming the Ali Gheri clan*
In the late 19th century, after the Berlin Conference had ended, the Scramble for Africa reached the Horn of Africa. Increasing foreign influence in the region culminated in the first darawiish becoming the Ali Gheri clan**
* the Drawiish had leaders such as Mohammed Abdullah Hassan, Haji Sudi and Sultan Nur Ahmed Aman, who sought a state in the Nugaal and began one of the longest African conflicts in history. The news of the incident that sparked the 21 year long Dervish rebellion, according to the consul-general James Hayes Sadler, was spread or as he claimed was concocted by Sultan Nur of the Habr Yunis. The incident in question was that of a group of Somali children that were converted to Christianity and adopted by the French Catholic Mission at Berbera in 1899. Whether Sultan Nur experienced the incident first hand or whether he was told of it is not clear but what is known is that he propagated the incident in June 1899, precipitating the religious rebellion of the Dervishes. The Dervish movement successfully stymied British forces four times and forced them to retreat to the coastal region. As a result of its successes against the British, the Dervish movement received support from the Ottomans and
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
. The Ottoman government also named Hassan Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
of the Somali nation, and the German government promised to officially recognise any territories the Dervishes were to acquire. After a quarter of a century of military successes against the British, the Dervishes were finally defeated by Britain in 1920 in part due to the successful deployment of the newly-formed Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
by the British government.
 Majeerteen Sultanate was founded in the early-18th century. It rose to prominence in the following century, under the reign of the resourceful Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud. Helen Chapin Metz, ed., ''Somalia: a country study'', (The Division: 1993), p.10. His Kingdom controlled Bari Karkaar, Nugaaal, and also central Somalia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The Majeerteen Sultanate maintained a robust trading network, entered into treaties with foreign powers, and exerted strong centralized authority on the domestic front.''Horn of Africa'', Volume 15, Issues 1-4, (Horn of Africa Journal: 1997), p.130.''Transformation towards a regulated economy'', (WSP Transition Programme, Somali Programme: 2000) p.62.
The Majeerteen Sultanate was nearly destroyed in the late-1800s by a power struggle between Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud of the Majeerteen Sultanate and his ambitious cousin, Yusuf Ali Kenadid who founded a separate Kingdom, Sultanate of Hobyo in 1878. Initially Kenadid wanted to seize control of the neighbouring Majeerteen Sultanate, ruled by his cousin Mahamuud. However, he was unsuccessful in this endeavour, and was eventually forced into exile in
Majeerteen Sultanate was founded in the early-18th century. It rose to prominence in the following century, under the reign of the resourceful Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud. Helen Chapin Metz, ed., ''Somalia: a country study'', (The Division: 1993), p.10. His Kingdom controlled Bari Karkaar, Nugaaal, and also central Somalia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The Majeerteen Sultanate maintained a robust trading network, entered into treaties with foreign powers, and exerted strong centralized authority on the domestic front.''Horn of Africa'', Volume 15, Issues 1-4, (Horn of Africa Journal: 1997), p.130.''Transformation towards a regulated economy'', (WSP Transition Programme, Somali Programme: 2000) p.62.
The Majeerteen Sultanate was nearly destroyed in the late-1800s by a power struggle between Boqor (King) Osman Mahamuud of the Majeerteen Sultanate and his ambitious cousin, Yusuf Ali Kenadid who founded a separate Kingdom, Sultanate of Hobyo in 1878. Initially Kenadid wanted to seize control of the neighbouring Majeerteen Sultanate, ruled by his cousin Mahamuud. However, he was unsuccessful in this endeavour, and was eventually forced into exile in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
. Both sultanates also maintained written records of their activities, which still exist.
 In late 1888, Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid entered into a treaty with the Italian government, making his Sultanate of Hobyo an Italian protectorate known as Italian Somalia. His rival Boqor Osman Mahamuud was to sign a similar agreement vis-a-vis his own Majeerteen Sultanate the following year. In signing the agreements, both rulers also hoped to exploit the rival objectives of the European imperial powers so as to more effectively assure the continued independence of their territories. The Italians, for their part, were interested in the territories mainly because of its
In late 1888, Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid entered into a treaty with the Italian government, making his Sultanate of Hobyo an Italian protectorate known as Italian Somalia. His rival Boqor Osman Mahamuud was to sign a similar agreement vis-a-vis his own Majeerteen Sultanate the following year. In signing the agreements, both rulers also hoped to exploit the rival objectives of the European imperial powers so as to more effectively assure the continued independence of their territories. The Italians, for their part, were interested in the territories mainly because of its port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as ...
s specifically Port of Bosaso which could grant them access to the strategically important Suez Canal and the Gulf of Aden.Fitzgerald, Nina J. ''Somalia'' (New York: Nova Science, 2002), p 33 The terms of each treaty specified that Italy was to steer clear of any interference in the Sultanates' respective administrations. In return for Italian arms and an annual subsidy, the Sultans conceded to a minimum of oversight and economic concessions. The Italians also agreed to dispatch a few ambassadors to promote both the Sultanates' and their own interests. The new protectorates were thereafter managed by Vincenzo Filonardi through a chartered company
A chartered company is an association with investors or shareholders that is incorporated and granted rights (often exclusive rights) by royal charter (or similar instrument of government) for the purpose of trade, exploration, and/or coloni ...
. An Anglo-Italian border protocol was later signed on 5 May 1894, followed by an agreement in 1906 between Cavalier Pestalozza and General Swaine acknowledging that Baran fell under the Majeerteen Sultanate's administration. With the gradual extension into northern Somalia of Italian colonial rule, both Kingdoms were eventually annexed in the early 20th century.The Majeerteen Sultanates However, unlike the southern territories, the northern sultanates were not subject to direct rule due to the earlier treaties they had signed with the Italians.
Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Britain retained control of both British Somaliland and Italian Somalia as protectorates. In 1945, during the Potsdam Conference, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somalia, but only under close supervision and on the condition — first proposed by the Somali Youth League (SYL) and other nascent Somali political organizations, such as Hizbia Digil Mirifle Somali (HDMS) and the Somali National League (SNL) — that Somalia achieve independence within ten years.Gates, Henry Louis, ''Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience'', (Oxford University Press: 1999), p.1749 British Somalia remained a protectorate of Britain until 1960.Tripodi, Paolo. ''The Colonial Legacy in Somalia'' p. 68 New York, 1999.
To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali Republic state, did not have. Although in the 1950s British colonial officials attempted, through various administrative development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would cause serious difficulties when it came time to integrate the two parts.Helen Chapin Metz, ed. Somalia: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1992countrystudies.us
/ref> Meanwhile, in 1948, under pressure from their World War II allies and to the dismay of the Somalis,Federal Research Division, ''Somalia: A Country Study'', (Kessinger Publishing, LLC: 2004), p.38 the British ceded official control of the Haud (an important Somali grazing area that was brought under British protection via treaties with the Somalis in 1884 and 1886) and the Ogaden to Ethiopia, based on a treaty they signed in 1897 in which the British ceded Somali territory to the Ethiopian Emperor
Menelik Menelek or Menelik may refer to:
* Menelik I, first Emperor of Ethiopia
* Menelik II (1844–1913), Emperor of Ethiopia
*Menelek XIV, fictional Emperor of Abyssinia in the novel ''Beyond Thirty'' by Edgar Rice Burroughs
*Ménélik (born 1970), Fren ...
in exchange for his help against raids by Somali clans.David D. Laitin, ''Politics, Language, and Thought: The Somali Experience'', (University Of Chicago Press: 1977), p.73 Britain included the proviso that the Somali nomads would retain their autonomy, but Ethiopia immediately claimed sovereignty over them.Zolberg, Aristide R., et al., ''Escape from Violence: Conflict and the Refugee Crisis in the Developing World'', (Oxford University Press: 1992), p.106 This prompted an unsuccessful bid by Britain in 1956 to purchase back the Somali lands it had turned over. The British government also granted administration of the almost exclusively Somali-inhabited Northern Frontier District (NFD) to the Kenyan government despite an informal plebiscite demonstrating the overwhelming desire of the region's population to join the newly formed Somali Republic.
A referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
was held in neighboring Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Re ...
(then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p.360. The majority of those who voted no were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.Barrington, Lowell, ''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States'', (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p.115 Djibouti finally gained its independence from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
British Somaliland became independent on 26 June 1960 as the State of Somaliland, and the Trust Territory of Somalia (the former Italian Somalia) followed suit five days later. On 1 July 1960, the two territories united to form the Somali Republic, albeit within boundaries drawn up by Italy and Britain. A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud
Abdullahi Issa Mohamud ( so, Cabdullaahi Ciise Maxamuud, ar, عبد الله عيسى محمد ( 1922 – March 24, 1988) was a Somali politician. He was the Prime Minister of Italian Somalia during the trusteeship period, serving from Februa ...
and Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal other members of the trusteeship and protectorate governments, with Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf as president of the Somali National Assembly, Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as the president of the Somali Republic and Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
(later to become president from 1967 to 1969). On 20 July 1961 and through a popular referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
, the people of Somalia ratified a new constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
, which was first drafted in 1960. The constitution was rejected by the people of Somaliland. In 1967, Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal became Prime Minister, a position to which he was appointed by Shermarke.
On 15 October 1969, while paying a visit to the northern town of Las Anod, Somalia's then President Abdirashid Ali Shermarke was shot dead by one of his own bodyguards. His assassination was quickly followed by a military coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, ...
on 21 October 1969 (the day after his funeral), in which the Somali Army seized power without encountering armed opposition — essentially a bloodless takeover. The putsch was spearheaded by Major General Mohamed Siad Barre, who at the time commanded the army.Moshe Y. Sachs, ''Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations'', Volume 2, (Worldmark Press: 1988), p.290.
Alongside Barre, the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Lieutenant Colonel Salaad Gabeyre Kediye and Chief of Police Jama Korshel. The SRC subsequently renamed the country the Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the Socialism, socialist military government ...
,''The Encyclopedia Americana: complete in thirty volumes. Skin to Sumac'', Volume 25, (Grolier: 1995), p.214. dissolved the parliament and the Supreme Court, and suspended the constitution.Peter John de la Fosse Wiles, ''The New Communist Third World: an essay in political economy'', (Taylor & Francis: 1982), p.279.
The revolutionary army established large-scale public works programs and successfully implemented an urban and rural literacy campaign, which helped dramatically increase the literacy rate. In addition to a nationalization program of industry and land, the new regime's foreign policy placed an emphasis on Somalia's traditional and religious links with the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, eventually joining the Arab League (AL) in 1974.Benjamin Frankel, ''The Cold War, 1945–1991: Leaders and other important figures in the Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, China, and the Third World'', (Gale Research: 1992), p.306. That same year, Barre also served as chairman of the Organization of African Unity (OAU), the predecessor of the African Union (AU).Oihe Yang, ''Africa South of the Sahara 2001'', 30th Ed., (Taylor and Francis: 2000), p.1025.
Demographics
Clans
 Somalis are ethnically of Cushitic ancestry, but have genealogical traditions of descent from various patriarchs associated with the spread of Islam. Being one tribe, they are segmented into various clan groupings, which are important
Somalis are ethnically of Cushitic ancestry, but have genealogical traditions of descent from various patriarchs associated with the spread of Islam. Being one tribe, they are segmented into various clan groupings, which are important kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says th ...
units that play a central part in Somali culture and politics. Clan families are patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritan ...
, and are divided into clans, primary lineages or subclans, and dia-paying kinship groups. The lineage terms ''qabiil'', ''qolo'', ''jilib'' and ''reer'' are often interchangeably used to indicate the different segmentation levels. The clan represents the highest kinship level. It owns territorial properties and is typically led by a clan-head or Sultan. Primary lineages are immediately descended from the clans, and are exogamous political units with no formally installed leader. They comprise the segmentation level that an individual usually indicates he or she belongs to, with their founding patriarch reckoned to between six and ten generations.
The five major clan families are the traditionally nomadic pastoralist Dir, Isaaq, Darod
The Darod ( so, Daarood, ar, دارود) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan was Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as ''Darood''. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripherie ...
, Hawiye and the sedentary agropastoralist Rahanweyn. Minor Somali clans include Benadiri
The Banaadiri people ( so, Reer Benaadir, ar, البنادريون) are a nationality in Somalia. Banaadiris largely inhabit Somalia's southern coastline.
Overview
Although the Benadiri are sometimes described as the founders of Mogadishu (he ...
.
The Dir, Hawiye, Gardere ( Gaalje'el, Degodia, Garre
The Garre (also Gurreh, Karre, "Binukaaf") ( Somali: ''Reer Garre'', Arabic: بنو كاف, romanized: ''Banī kāf'' ) is a major Somali clan whose origins trace back to Samaale who traces the lineage from the Arabian Peninsula through Aqiil A ...
), Hawadle and Ajuran Ajuran may refer to:
* Ajuran Sultanate, a medieval Somali empire
* Ajuran (clan), a Somali clan
* Ajuran currency Ajuran currency was an old coinage system minted in the Ajuran Sultanate. The polity was a Somali people, Somali Muslim kingdom that ...
trace agnatic origins to the patriarch Samaale. Sheikh Darod is asserted to have married a woman from the Dir (while some accounts say Hawiye), thus establishing matrilateral ties with the Samaale family. The Darod have separate paternal traditions of descent through Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti (Sheikh Darod), who is said to have Arabian Banu Hashim origins through Aqiil Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib arriving at a later date from the Arabian peninsula, in the 10th or 11th centuriesI.M. Lewis, ''A Modern History of the Somali'', fourth edition (Oxford: James Currey, 2002), p. 22 and the Isaaq clan traces paternal descent to the Islamic leader Sheikh Isaaq Bin Ahmed Al Hashimi (Sheikh Isaaq), however contemporary genetic studies indicate that none of these clans possess any noticeable Arab ancestry. The Rahanweyn or Sab trace their stirp to the patriarch Sab. Both Samaale and Sab are supposed to have ultimately descended from a common lineage originating in the Arabian peninsula. These traditions of descent from elite Arab forefathers, who settled on the littoral, are debated, although they are based on early Arab documents and northern oral folklore.
A comprehensive genealogy of Somali clans can be found in Abbink (2009), providing detailed family trees and historical background information.
The tombs of the founders of the Darod, Dir and Isaaq major clans, as well as the Abgaal
Abgaal (Somali: Abgaal, Arabic: أبغال) is a subclan of the Hawiye and the even larger Samaale clan. It is one of the major Somali clans and has produced many prominent historical Somali figures including 3 presidents, and the father of t ...
subclan of the Hawiye are all located in northern Somalia. Tradition holds this general area as an ancestral homeland of the Somali people.
Kinship
The traditional political unit among the Somali people has been kinships. Dia-paying groups are groupings of a few small lineages, each consisting of a few hundred to a few thousand members. They trace their foundation to between four and eight generations. Members are socially contracted to support each other in jural and political duties, including paying or receiving dia or blood compensation (''mag'' in Somali). Compensation is obligatory in regards to actions committed by or against a dia-paying group, including blood-compensation in the event of damage, injury or death.Social stratification
 Within traditional Somali society (as in other ethnic groups of the Horn of Africa and the wider region), there has been social stratification. According to the historian Donald Levine, these comprised high-ranking clans, low-ranking clans, caste groups, and slaves. This rigid hierarchy and concepts of lineal purity contrast with the relative egalitarianism in clan leadership and political control., Quote: "The social organization of Somali society accommodated ideological conceptions of inferiority through investing clan membership with definitions of lineal purity. Somali clans, while fiercely egalitarian with regards to leadership and political control, contain divisions of unequal status".
Nobles constituted the upper tier and were known as ''bilis''. They consist of individuals of ethnic Somali ancestral origin, and have been endogamous.
The lower tier was designated as ''Sab'', and was distinguished by its heterogeneous constitution and agropastoral lifestyle as well as some linguistic and cultural differences. A third Somali caste strata was made up of artisanal groups, which were endogamous and hereditary. Among the caste groups, the '' Midgan'' were traditionally hunters and circumcision performers.Е. de Larajasse (1972), Somali-English and Somali-English Dictionary, Trubner, pages 108, 119, 134, 145
Within traditional Somali society (as in other ethnic groups of the Horn of Africa and the wider region), there has been social stratification. According to the historian Donald Levine, these comprised high-ranking clans, low-ranking clans, caste groups, and slaves. This rigid hierarchy and concepts of lineal purity contrast with the relative egalitarianism in clan leadership and political control., Quote: "The social organization of Somali society accommodated ideological conceptions of inferiority through investing clan membership with definitions of lineal purity. Somali clans, while fiercely egalitarian with regards to leadership and political control, contain divisions of unequal status".
Nobles constituted the upper tier and were known as ''bilis''. They consist of individuals of ethnic Somali ancestral origin, and have been endogamous.
The lower tier was designated as ''Sab'', and was distinguished by its heterogeneous constitution and agropastoral lifestyle as well as some linguistic and cultural differences. A third Somali caste strata was made up of artisanal groups, which were endogamous and hereditary. Among the caste groups, the '' Midgan'' were traditionally hunters and circumcision performers.Е. de Larajasse (1972), Somali-English and Somali-English Dictionary, Trubner, pages 108, 119, 134, 145178
/ref> The '' Tumal'' (also spelled ''Tomal'') were smiths and leatherworkers, and the Yibir (also spelled ''Yebir'') were the tanners and magicians. According to the anthropologist Virginia Luling, the artisanal caste groups of the north closely resembled their higher caste kinsmen, being generally Caucasoid like other ethnic Somalis. Although ethnically indistinguishable from each other, state Mohamed Eno and Abdi Kusow, upper castes have stigmatized the lower ones. Outside of the Somali caste system were slaves of
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
*Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for Nationali ...
origin and physiognomy. Their distinct physical features and occupations differentiated them from Somalis and positioned them as inferior within the social hierarchy.
Marriage
Among Somali clans, in order to strengthen alliance ties, marriage is often to another ethnic Somali from a different clan. According to I. M. Lewis, of 89 marriages initiated by men of the Dhulbahante clan, 55 (62%) were therefore with women of Dhulbahante subclans other than those of their husbands; 30 (33.7%) were with women of adjacent clans of other clan families (Isaaq, 28; Hawiye, 3); and 3 (4.3%) were with women of other clans of the Darod clan family (Majerteen 2, Ogaden 1). Such exogamy is always followed by the dia-paying group and usually adhered to by the primary lineage, whereas marriage to lineal kin falls within the prohibited range. These traditional strictures against consanguineous marriage ruled out the patrilateral first cousin marriages that are favored by Arab Bedouins and specially approved by Islam. These marriages were practiced to a limited degree by certain northern Somali subclans. In areas inhabited by diverse clans, such as the southern Mogadishu area, endogamous marriages also served as a means of ensuring clan solidarity in uncertain socio-political circumstances. This inclination was further spurred on by intensified contact with Arab society in the Gulf, wherein first cousin marriage was preferred. Although politically expedient, such endogamous marriage created tension with the traditional principles within Somali culture. In 1975, the most prominent government reforms regardingfamily law
Family law (also called matrimonial law or the law of domestic relations) is an area of the law that deals with family matters and domestic relations.
Overview
Subjects that commonly fall under a nation's body of family law include:
* Marri ...
in a Muslim country were set in motion in the Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the Socialism, socialist military government ...
, which put women and men, including husbands and wives, on complete equal footing. The 1975 Somali Family Law gave men and women equal division of property between the husband and wife upon divorce and the exclusive right to control by each spouse over his or her personal property.
FGM is almost universal in Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
, and many women undergo infibulation, the most extreme form of female genital mutilation. According to a 2005 WHO estimate, about 97.9% of Somalia's women and girls underwent FGM. This was at the time the world's highest prevalence rate of the procedure.
Religion
 According to data from the Pew Research Center, the creed breakdown of Muslims in the Somali-majority Djibouti is as follows: 77% adhere to Sunnism, 8% are non-denominational Muslim, 2% are
According to data from the Pew Research Center, the creed breakdown of Muslims in the Somali-majority Djibouti is as follows: 77% adhere to Sunnism, 8% are non-denominational Muslim, 2% are Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the ...
and 13% declined to answer, and a further report inclusive of Somali Region stipulating 2% adherence to a minority sect (e.g. Ibadism, Quranism etc.). There are some nobles who believe with great pride that they are of Arabian ancestry, and trace their stirp to Muhammad's lineage of Quraysh and those of his companions. Although they do not consider themselves culturally Arabs, except for the shared religion, their presumed noble Arabian origins genealogically unite them. The purpose behind claiming genealogical traditions of descent from the Arabian Peninsula is used to reinforce one's lineage and the various associated patriarchs with the spread of Islam.
Languages
 The Somali language (''Af-Soomaali'') is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. Its nearest relatives are the
The Somali language (''Af-Soomaali'') is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. Its nearest relatives are the Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
and Saho languages. Somali is the best documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies of it dating from before 1900.
The exact number of speakers of Somali is unknown. One source estimates that there are 7.78 million speakers of Somali within Somalia and Somalia themselves and 12.65 million speakers globally. The Somali language is spoken by ethnic Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora.
 Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern, Benaadir, and Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benaadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast from Adale to south of Merca, including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional
Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern, Benaadir, and Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benaadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast from Adale to south of Merca, including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
s which do not exist in Standard Somali. Maay is principally spoken by the Digil and Mirifle ( Rahanweyn) clans in the southwestern areas of Somalia.Andrew Dalby, ''Dictionary of languages: the definitive reference to more than 400 languages'', (Columbia University Press: 1998), p.571.
A number of writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable for ...
s have been used over the years for transcribing the Somali language. Of these, the Somali Latin alphabet is the most widely used, and has been the official writing script in Somalia since the government of former President of Somalia Mohamed Siad Barre formally introduced it in October 1972. The script was developed by the Somali linguist Shire Jama Ahmed specifically for the Somali language. It uses all letters of the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the ...
, except ''p'', ''v'', and ''z''. Besides the Latin script, other orthographies that have been used for centuries for writing Somali include the long-established Arabic script and Wadaad writing. Other writing systems developed in the twentieth century include the Osmanya, Borama and Kaddare scripts, which were invented by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, Abdurahman Sheikh Nuur and Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare, respectively.
In addition to Somali, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
, which is also an Afro-Asiatic tongue, is an official national language in Somalia, Somalia and Djibouti. Many Somalis speak it due to centuries-old ties with the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, the far-reaching influence of the Arabic media, and religious education.Helena Dubnov, ''A grammatical sketch of Somali'', (Kِppe: 2003), pp. 70–71. Somalia and Djibouti are also both members of the Arab League.CIA World Factbook - Djibouti - People and Society*N.B. ~60% of 774,389 total pop.
Culture

 The culture of Somalia is an amalgamation of traditions developed independently and through interaction with neighbouring and far away civilizations, such as other parts of Northeast Africa, the Arabian Peninsula,
The culture of Somalia is an amalgamation of traditions developed independently and through interaction with neighbouring and far away civilizations, such as other parts of Northeast Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
.Mohamed Diriye Abdullahi, ''Culture and Customs of Somalia'', (Greenwood Press: 2001), p.155.
The textile-making communities in Somalia are a continuation of an ancient textile industry, as is the culture of wood carving, pottery and monumental architecture that dominates Somali interiors and landscapes. The cultural diffusion of Somali commercial enterprise can be detected in its cuisine, which contains Southeast Asian influences. Due to the Somali people's passionate love for and facility with poetry, Somalia has often been referred to by scholars as a "Nation of Poets" and a "Nation of Bards" including, among others, the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
novelist Margaret Laurence.
According to Canadian novelist and scholar Margaret Laurence, who originally coined the term "Nation of Poets" to describe the Somali Peninsular, the Eidagale clan were viewed as "the recognized experts in the composition of poetry" by their fellow Somali contemporaries:
Among the tribes, the Eidagalla are the recognized experts in the composition of poetry. One individual poet of the Eidagalla may be no better than a good poet of another tribe, but the Eidagalla appear to have more poets than any other tribe. "if you had a hundred Eidagalla men here," Hersi Jama once told me, "And asked which of them could sing his own gabei ninety-five would be able to sing. The others would still be learning."All of these traditions, including
festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival co ...
s, martial arts, dress, literature, sport and games such as Shax, have immensely contributed to the enrichment of Somali heritage.
Music
Somalis have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somalifolklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, r ...
. Most Somali songs are pentatonic. That is, they only use five pitches per octave in contrast to a heptatonic (seven note) scale, such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (''midho''), songwriters (''laxan'') and singers (''Codka'' or "voice").
Musicians and bands
 * Aar Maanta – UK-based Somali singer, composer, writer and music producer.
* Abdi Sinimo – Prominent Somali artist and inventor of the Balwo musical style.
* Abdullahi Qarshe – Somali musician, poet and playwright known for his innovative styles of music, which included a wide variety of musical instruments such as the guitar, piano and oud.
* Ali Feiruz – Somali musician from Djibouti; part of the Radio Hargeisa generation of Somali artists.
*
* Aar Maanta – UK-based Somali singer, composer, writer and music producer.
* Abdi Sinimo – Prominent Somali artist and inventor of the Balwo musical style.
* Abdullahi Qarshe – Somali musician, poet and playwright known for his innovative styles of music, which included a wide variety of musical instruments such as the guitar, piano and oud.
* Ali Feiruz – Somali musician from Djibouti; part of the Radio Hargeisa generation of Somali artists.
*Dur-Dur
Dur-Dur Band was a musical group from Mogadishu, Somalia. The band was formed in the 1980s and was one of the most well-known acts on the Mogadishu disco scene at the time. The band later performed and recorded based in neighbouring Ethiopia. The ...
– Somali band active during the 1980s and 1990s in Somalia, Djibouti and Ethiopia.
* Hasan Adan Samatar – popular male artist during the 1970s and 80s.
*Hibo Nuura
Hibo Mohamed Nur, more famously known as Hibo Nura ( Somali: Hibo Nuura, Hibo Maxamed Nuur, is one of the most prominent Somali singers born in 1954.
History
Hibo Mohamed Hudon, known as Hibo Nuura was born in Dilla, Somalia in 1954. Nuura beg ...
- popular Somali singer.
* Jonis Bashir – Somali-Italian actor and singer
* Khadija Qalanjo – popular Somali singer in the 1970s and 1980s.
* K'naan – award-winning Somali-Canadian hip hop artist.
* Magool (2 May 1948 – 19 March 2004) – prominent Somali singer considered in Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
as one of the greatest entertainers of all time.
* Maryam Mursal (born 1950) – Somali musician, composer and vocalist whose work has been produced by the record label Real World.
* Mohammed Mooge – Prominent Somali artist from the Radio Hargeisa generation.
* Poly Styrene – Somali-British punk rock singer; best known as being the lead singer of X Ray Spex.
* Saado Ali Warsame – Somali singer-songwriter and modern Qaraami exponent.
* Waaberi – Somalia's foremost musical group that toured through several countries in Northeast Africa and Asia, including Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, Sudan and China.
* Waayaha Cusub – Somali music collective. Organized the international Reconciliation Music Festival in 2013 in Mogadishu.
Cinema and theatre
 Growing out of the Somali people's rich storytelling tradition, the first few feature-length Somali films and cinematic festivals emerged in the early 1960s, immediately after independence. Following the creation of the Somali Film Agency (SFA) regulatory body in 1975, the local film scene began to expand rapidly. Hassan Sheikh Mumin was considered one of the most prolific and early playwrights and composers in Somali literature. Mumin's most important work is ''Shabeel Naagood'' (1965), a piece that touches on the social position of women, urbanization, changing traditional practices, and the importance of education during the early pre-independence period. Although the issues it describes were later to some degree redressed, the work remains a mainstay of Somali literature. ''Shabeel Naagood'' was translated into English in 1974 under the title ''Leopard Among the Women'' by the Somali Studies pioneer
Growing out of the Somali people's rich storytelling tradition, the first few feature-length Somali films and cinematic festivals emerged in the early 1960s, immediately after independence. Following the creation of the Somali Film Agency (SFA) regulatory body in 1975, the local film scene began to expand rapidly. Hassan Sheikh Mumin was considered one of the most prolific and early playwrights and composers in Somali literature. Mumin's most important work is ''Shabeel Naagood'' (1965), a piece that touches on the social position of women, urbanization, changing traditional practices, and the importance of education during the early pre-independence period. Although the issues it describes were later to some degree redressed, the work remains a mainstay of Somali literature. ''Shabeel Naagood'' was translated into English in 1974 under the title ''Leopard Among the Women'' by the Somali Studies pioneer Bogumił W. Andrzejewski
Bogumił Witalis "Goosh" Andrzejewski (1922–1994) was a Polish-born, British-naturalised linguist whose research focused on the Somali language
Somali (Latin script: ; Wadaad writing, Wadaad: ; Osmanya: 𐒖𐒍 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘 ) ...
, who also wrote the introduction. Mumin composed both the play itself and the music used in it. The piece is regularly featured in various school curricula, including Oxford University, which first published the English translation under its press house.
During one decisive passage in the play, the heroine, Shallaayo, laments that she has been tricked into a false marriage by the Leopard in the title:
video
Video is an Electronics, electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving picture, moving image, visual Media (communication), media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, whi ...
technology and national television networks. Said Salah Ahmed during this period directed his first feature film, ''The Somali Darwish'' (''The Somalia Dervishes''), devoted to the Dervish movement. In the 1990s and 2000s, a new wave of more entertainment-oriented movies emerged. Referred to as Somaliwood
Somaliwood is an informal name for the Somali film industry that has developed in Columbus, Ohio, where a large Somali diaspora exists. Following the model of Bollywood, the name is a portmanteau of the words "Somali" and "Cinema of the United Sta ...
, this upstart, youth-based cinematic movement has energized the Somali film industry and in the process introduced innovative storylines, marketing strategies and production techniques. The young directors Abdisalam Aato of Olol Films and Abdi Malik Isak are at the forefront of this quiet revolution.
Art

 Somalis have old visual art traditions, which include pottery, jewelry and wood carving. In the medieval period, affluent urbanites commissioned local wood and marble carvers to work on their interiors and houses. Intricate patterns also adorn the mihrabs and pillars of ancient Somali
Somalis have old visual art traditions, which include pottery, jewelry and wood carving. In the medieval period, affluent urbanites commissioned local wood and marble carvers to work on their interiors and houses. Intricate patterns also adorn the mihrabs and pillars of ancient Somali mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a Place of worship, place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) ...
s. Artistic carving was considered the province of men, whereas the textile industry was mainly that of women. Among the nomads, carving, especially woodwork
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinet making ( cabinetry and furniture), wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first mate ...
, was widespread and could be found on the most basic objects such as spoons, combs and bowls. It also included more complex structures, such as the portable nomadic house, the ''aqal''. In the last several decades, traditional carving of windows, doors and furniture have given way to workshops employing electrical machinery, which deliver the same results in a far shorter time period.
Additionally, henna is an important part of Somali culture. It is worn by Somali women on their hands, arms, feet and neck during wedding ceremonies, Eid
Eid as a name may refer to:
Islamic holidays
An Eid is a Muslim religious festival:
* ''Eid Milad un Nabi'', alternate name for Mawlid (, "Birth of the Prophet"), the date of observance of the birthday of the Islamic prophet Muhammad
* Eid al ...
, Ramadan and other festive occasions. Somali henna designs are similar to those in the Arabian peninsula, often featuring flower motifs and triangular shapes. The palm is also frequently decorated with a dot of henna and the fingertips are dipped in the dye. Henna parties are usually held before the wedding takes place. Somali women have likewise traditionally applied kohl (''kuul'') to their eyes.Katheryne S. Loughran, ''Somalia in word and image'', (Foundation for Cross Cultural Understanding: 1986), p.166. Usage of the eye cosmetic in the Horn region is believed to date to the ancient Land of Punt.''Studies in Ancient Technology'', Volume III, (Brill Archive), p. 18.
Sports
 Football is the most popular sport amongst Somalis. Important competitions are the Somalia League and
Football is the most popular sport amongst Somalis. Important competitions are the Somalia League and Somalia Cup
The Somalia Cup is the top knockout football tournament in Somalia. Horseed
Horseed is a district of Marka, a city in the Shabelle Hoose region in southern Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, ا ...
. The Ocean Stars is Somalia's multi-ethnic national team.
Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
is also played in the country. The FIBA Africa Championship 1981 was hosted in Mogadishu from 15 to 23 December December 1981, during which the national basketball team received the bronze medal. The squad also takes part in the basketball event at the Pan Arab Games. Other team sports include badminton, baseball, table tennis, and volleyball.
In the martial arts, Faisal Jeylani Aweys
Faisal Jeylani Aweys ( so, Faysal Jaylaani Caweeys, ar, فيصل جيلاني عويس) is a Somali taekwondo practitioner.
Personal life
Aweys was born in 1987 in Mogadishu, Somalia. He later moved to Switzerland at the age of 13.
Based in ...
and Mohamed Deq Abdulle also took home a silver medal and fourth place, respectively, at the 2013 Open World Taekwondo
''Taekwondo'', ''Tae Kwon Do'' or ''Taekwon-Do'' (; ko, 태권도/跆拳道 ) is a Korean form of martial arts involving punching and kicking techniques, with emphasis on head-height kicks, spinning jump kicks, and fast kicking techniques. ...
Challenge Cup in Tongeren. The Somali National Olympic committee has devised a special support program to ensure continued success in future tournaments. Additionally, Mohamed Jama has won both world and European titles in K1 and Thai Boxing. Other individuals sports include judo, boxing, athletics, weight lifting, swimming, rowing, fencing and wrestling. Somalis have also produced many world-class distance runners like their neighboring countries with Mo Farah, Abdi Bile and Mohammed Ahmed.
Attire
Traditionally, Somali men typically wear the ''macawis''. It is a sarong that is worn around the waist. On their heads, they often wrap a colorful turban or wear the ''koofiyad'', which is an embroidered fez. Due to Somalia's proximity to and close ties with the Arabian Peninsula, many Somali men also wear the jellabiya (''jellabiyad'' or ''qamiis''). The costume is a long white garment common in theArab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
.Michigan State University. Northeast African Studies Committee, ''Northeast African Studies'', Volume 8, (African Studies Center, Michigan State University: 2001), p.66.
During regular, day-to-day activities, Somali women usually wear the ''guntiino''. It is a long stretch of cloth tied over the shoulder and draped around the waist. The cloth is usually made out of ''alandi'', which is a textile that is common in the Horn region and some parts of North Africa. The garment can be worn in different styles. It can also be made with other fabrics, including white cloth with gold borders. For more formal settings, such as at weddings or religious celebrations like Eid, women wear the ''dirac''. It is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, chiffon, taffeta or saree fabric. The gown is worn over a full-length half-slip and a brassiere. Known as the ''gorgorad'', the underskirt is made out of silk and serves as a key part of the overall outfit. The dirac is usually sparkly and very colorful, the most popular styles being those with gilded borders or threads.
Married women tend to wear headscarves
A headscarf is a scarf covering most or all of the top of a person's, usually women's, hair and head, leaving the face uncovered. A headscarf is formed of a triangular cloth or a square cloth folded into a triangle, with which the head is cov ...
referred to as ''shaash''. They also often cover their upper body with a shawl, which is known as ''garbasaar''. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb, such as the jilbab and abaya, is also commonly worn.
Additionally, Somali women have a long tradition of wearing gold jewelry, particularly bangles. During weddings, the bride is frequently adorned in gold. Many Somali women by tradition also wear gold necklaces and anklets.
Ethnic flag
 The Somali flag is an ethnic flag conceived to represent ethnic Somalis. It was created in 1954 by the Somali scholar Mohammed Awale Liban, after he had been selected by the labour trade union of the Trust Territory of Somalia to come up with a design. Upon
The Somali flag is an ethnic flag conceived to represent ethnic Somalis. It was created in 1954 by the Somali scholar Mohammed Awale Liban, after he had been selected by the labour trade union of the Trust Territory of Somalia to come up with a design. Upon independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the s ...
in 1960, the flag was adopted as the national flag of the nascent Somali Republic. The five-pointed ''Star of Unity'' in the flag's center represents the Somali ethnic group inhabiting the five territories in Greater Somalia.
Cuisine
 The Somalis staple food comes from their livestock, however, the Somali cuisine varies from region to region and consists of a fusion of diverse culinary influences. In the interiors, the cuisine is mainly local with usage of Ethiopian grains and vegetables while in the coast it is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are therefore no pork dishes, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated.
Breakfast (''quraac'') is an important meal for Somalis, some drink tea (''shahie or shaah)'' others
The Somalis staple food comes from their livestock, however, the Somali cuisine varies from region to region and consists of a fusion of diverse culinary influences. In the interiors, the cuisine is mainly local with usage of Ethiopian grains and vegetables while in the coast it is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are therefore no pork dishes, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated.
Breakfast (''quraac'') is an important meal for Somalis, some drink tea (''shahie or shaah)'' others coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
(''qaxwa or bun''). The tea is often in the form of '' haleeb shai'' (Yemeni milk tea) in the north. The main dish is typically a pancake-like bread (''canjeero'' or ''canjeelo'') similar to Ethiopian injera, but smaller and thinner, or ''muufo'' a Somali flat bread traditionally baked on a clay oven. These breads might also be eaten with a stew (''maraqe'') or soup at lunch or dinner. ''Qado'' or lunch is often elaborate, varieties of ''bariis'' ( rice), the most popular being basmati
Basmati, , is a variety of long, slender-grained aromatic rice which is traditionally grown in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the secon ...
are usually served as the main dish alongside goat, lamb or fish. Spices like cumin, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus '' Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, brea ...
, and garden sage
''Salvia officinalis'', the common sage or just sage, is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, thoug ...
are used to aromatize these different rice delicacies. Somalis eat dinner as late as 9 pm. During Ramadan, supper is often served after Tarawih
''Tarawih'' ( ar, تراويح, tarāwīḥ), also rendered in English as ''Taraweeh'', is derived from the Arabic root ر و ح related to rest and relaxation. Tarawih prayers are special Muslim prayers involving reading long portions of the ...
prayers; sometimes as late as 11 pm.
In some regions'', xalwo'' ( halva) is a popular confection eaten during festive occasions such as Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. It is made from sugar, corn starch, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
s are also sometimes added to enhance texture and flavor. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using frankincense (''lubaan'') or incense (''cuunsi''), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a '' dabqaad''.
Literature
 Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to
Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
. With the adoption of the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the ...
in 1972 to transcribe the Somali language, numerous contemporary Somali authors have also released novels, some of which have gone on to receive worldwide acclaim. Most of the early Somali literature is in the Arabic script and ''Wadaad'' writing. This usage was limited to Somali clerics and their associates, as sheikhs preferred to write in the liturgical Arabic language. Various such historical manuscripts in Somali nonetheless exist, which mainly consist of Islamic poems ( qasidas), recitations and chants. Among these texts are the Somali poems by Sheikh Uways and Sheikh Ismaaciil Faarah. The rest of the existing historical literature in Somali principally consists of translations of documents from Arabic.
Authors and poets
* Elmi Boodhari (1908–1940) – Early 20th century poet and pioneer in the genre of Somali love poems. He is popularly known by Somalis as the ''King of romance'' (Boqorki Jacaylka) * Abdillahi Diiriye Guled - Literary scholar and discoverer of the Somali prosodic system * Ali Bu'ul (Cali Bucul) – 19th century poet, military leader and sultan, many of the most well known ''geeraar'' (short styled poems recited on a horse) came from his tongue and are still known today. *Mohamed Ibrahim Warsame 'Hadrawi'
Mohamed Ibrahim Warsame (1943 – 18 August 2022), known by the pseudonym Hadrawi, was a Somali poet, philosopher and songwriter. Having written many notable protest works, Hadrawi has been likened by some to Shakespeare, and his poetry has been ...
– songwriter, philosopher, and Somali Poet Laureate; also dubbed the Somali Shakespeare.
* Hassan Sheikh Mumin – 20th century poet, playwright, broadcaster, actor and composer.
* Nuruddin Farah (born 1943) – Somali writer and winner of the 1998 Neustadt International Prize for Literature.
*Abdillahi Suldaan Mohammed Timacade
Abdillahi Suldaan Mohammed "Timacadde" ( so, Cabdilaahi Suldaan Maxamed, ar, عبد الله سلطان محمد) was a Somali poet. He was among the most prominent bards of his day.
Biography
Timacade was born in 1920 in the small town of Galoo ...
(1920–1973) – prominent Somali poet known for his nationalist poems such as ''Kana siib Kana Saar''.
* Mohamud Siad Togane (born 1943) – Somali-Canadian
Somali Canadians are Canadians of Somali origin or are dual Somali and Canadian nationality.
Overview
Most Somalis arrived in Canada between the late 1980s from Somalia and early 1990s as refugees, with some secondary migration from the United ...
poet, professor, and political activist.
* Maxamed Daahir Afrax – Somali novelist and playwright. Afrax has published several novels and short stories in Somali
Somali may refer to:
Horn of Africa
* Somalis, an inhabitant or ethnicity associated with Greater Somali Region
** Proto-Somali, the ancestors of modern Somalis
** Somali culture
** Somali cuisine
** Somali language, a Cushitic language
** Soma ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
, and has also written two plays, the first being ''Durbaan Been ah'' ("A Deceptive Drum"), which was staged in Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
in 1979. His major contribution in the field of theatre criticism is ''Somali Drama: Historical and Critical Study'' (1987).
* Gaarriye (1949–2012) – Somali poet, most notable for his famous poem ''Hagarlaawe''.
* Nadifa Mohamed – Somali novelist. Winner of the 2010 Betty Trask Prize
The Betty Trask Prize and Awards are for first novels written by authors under the age of 35, who reside in a current or former Commonwealth nation. Each year the awards total £20,000, with one author receiving a larger prize amount, called the ...
.
* Musa Haji Ismail Galal (1917–1980) – was a Somali writer, scholar, linguist, historian and polymath
* Farah Mohamed Jama Awl – Somali author best known for his historical fiction novels.
*Diriye Osman
Diriye Osman ( so, Diriyeh Cismaan, ar, ديري عثمان) (born in 1983) is a Somali-British short story writer, essayist, critic and visual artist. He is the author of the short story collection ''Fairytales For Lost Children'', which won ...
– Somali writer and visual artist. Winner of the 2014 Polari First Book Prize.
*Sofia Samatar
Sofia Samatar (born October 24, 1971) is an American poet, novelist and educator from Indiana.
Early life
Samatar was born in 1971 in northern Indiana, United States. Her father was the Somali scholar, historian and writer Said Sheikh Samatar. ...
– Somali professor and writer. Winner of the 2014 World Fantasy Award.
Law
 Somalis for centuries have practiced a form of customary law, which they call '' xeer''. Xeer is a
Somalis for centuries have practiced a form of customary law, which they call '' xeer''. Xeer is a polycentric
Polycentric is an English adjective, meaning "having more than one center," derived from the Greek words ''polús'' ("many") and ''kentrikós'' ("center"). Polycentricism (or polycentricity) is the abstract noun formed from polycentric. They may r ...
legal system where there is no monopolistic agent that determines what the law should be or how it should be interpreted. It is assumed to have developed exclusively in the Horn of Africa since approximately the 7th century. Given the dearth of loan words from foreign languages within the xeer's nomenclature, the customary law appears to have evolved in situ.
 Xeer is defined by a few fundamental tenets that are immutable and which closely approximate the principle of '' jus cogens'' in international law: payment of blood money (locally referred to as ''
Xeer is defined by a few fundamental tenets that are immutable and which closely approximate the principle of '' jus cogens'' in international law: payment of blood money (locally referred to as ''diya
Diya may refer to:
* ''Diya (film)'', 2018 Tamil- and Telugu-language film
* Diya (Islam), Islamic term for monetary compensation for bodily harm or property damage
* Diya (lamp), ghee- or oil-based candle often used in South Asian religious ceremo ...
'' or ''mag''), assuring good inter- clan relations by treating women justly, negotiating with "peace emissaries" in good faith, and sparing the lives of socially protected groups (e.g. children, women, the pious, poets and guests), family obligations such as the payment of dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
, and sanctions for eloping, rules pertaining to the management of resources such as the use of pasture land, water, and other natural resources, providing financial support to married female relatives and newlyweds, donating livestock and other assets to the poor. The Xeer legal system also requires a certain amount of specialization
Specialization or Specialized may refer to:
Academia
* Academic specialization, may be a course of study or major at an academic institution or may refer to the field in which a specialist practices
* Specialty (medicine), a branch of medical ...
of different functions within the legal framework. Thus, one can find ''odayal'' (judges), ''xeer boggeyaal'' ( jurists), ''guurtiyaal'' (detective
A detective is an investigator, usually a member of a law enforcement agency. They often collect information to solve crimes by talking to witnesses and informants, collecting physical evidence, or searching records in databases. This leads t ...
s), ''garxajiyaal'' (attorney
Attorney may refer to:
* Lawyer
** Attorney at law, in some jurisdictions
* Attorney, one who has power of attorney
* ''The Attorney'', a 2013 South Korean film
See also
* Attorney general, the principal legal officer of (or advisor to) a gove ...
s), ''murkhaatiyal'' ( witnesses) and ''waranle'' (police officer
A police officer (also called a policeman and, less commonly, a policewoman) is a warranted law employee of a police force. In most countries, "police officer" is a generic term not specifying a particular rank. In some, the use of the ...
s) to enforce the law.
Architecture
Somali architecture is a rich and diverse tradition ofengineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
and designing. It involves multiple different construction types, such as stone cities, castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
s, citadels, fortresses, mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a Place of worship, place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) ...
s, mausoleums, towers, tombs, tumuli, cairns, megaliths, menhirs, stelae, dolmens, stone circles, monument
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, hist ...
s, temples, enclosures, cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by ...
s, aqueducts, and lighthouses. Spanning the ancient, medieval and early modern periods in Greater Somalia, it also includes the fusion of Somali architecture with Western designs in contemporary times.
In ancient Somalia, pyramidical structures known in Somali as ''taalo'' were a popular burial style. Hundreds of these dry stone monuments are found around the country today. Houses were built of dressed stone similar to the ones in Ancient Egypt. There are also examples of courtyards and large stone walls enclosing settlements, such as the Wargaade Wall.
The peaceful introduction of Islam in the early medieval era of Somalia's history brought Islamic architectural influences from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
. This had the effect of stimulating a shift in construction from drystone and other related materials to coral stone, sundried bricks, and the widespread use of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
in Somali architecture. Many of the new architectural designs, such as mosques, were built on the ruins of older structures. This practice would continue over and over again throughout the following centuries.
Geographic distribution
 Somalis constitute the largest ethnic group in Somalia, at approximately 85% of the nation's inhabitants. They also comprise around 60% of the inhabitants in Djibouti.
Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left for the Middle East, Europe and North America. In
Somalis constitute the largest ethnic group in Somalia, at approximately 85% of the nation's inhabitants. They also comprise around 60% of the inhabitants in Djibouti.
Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left for the Middle East, Europe and North America. In Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, the cities of Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most pop ...
, Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, maki ...
, Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anc ...
, Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. Th ...
, Winnipeg and Hamilton all harbor Somali populations. Statistics Canada's 2006 census ranks people of Somali descent as the 69th largest ethnic group in Canada.
UN migration estimates of the international migrant stock 2015 suggest that 1,998,764 people from Somalia were living abroad.
 While the distribution of Somalis per country in Europe is hard to measure because the Somali community on the continent has grown so quickly in recent years, the Office for National Statistics estimates that 98,000 people born in Somalia were living in the
While the distribution of Somalis per country in Europe is hard to measure because the Somali community on the continent has grown so quickly in recent years, the Office for National Statistics estimates that 98,000 people born in Somalia were living in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
in 2016. This includes secondary migration of Somalis from mainland European countries. Somalis in Britain are largely concentrated in the cities of London, Sheffield
Sheffield is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is Historic counties o ...
, Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
, Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. It forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of City of Salford, Salford to ...
, Leeds
Leeds () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the thi ...
, and Leicester, with London alone accounting for roughly 78% of Britain's Somali population in 2001. There are also significant Somali communities in continental Europe such as Sweden: 63,853 (2016); Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
: 42,217 (2016); the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
: 39,465 (2016); Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
: 33,900 (2016); Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
: 21,050 (2016); and Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
: 20,007 (2017).
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with list of lakes in Minneapolis, thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. ...
, Saint Paul, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, San Diego, Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
, Washington, D.C., Houston
Houston (; ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas, the Southern United States#Major cities, most populous city in the Southern United States, the List of United States cities by population, fourth-most pop ...
, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,71 ...
, Los Angeles, Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the United ...
, Nashville, Green Bay, Lewiston, Portland, Maine and Cedar Rapids have the largest Somali populations.
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minne ...
some ten years ago and the Twin Cities (Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with list of lakes in Minneapolis, thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. ...
and Saint Paul) now have the highest population of Somalis in North America. The city of Minneapolis hosts hundreds of Somali-owned and operated businesses offering a variety of products, including leather shoes, jewelry and other fashion items, halal meat, and hawala or money transfer services. Community-based video rental stores likewise carry the latest Somali films and music. The number of Somalis has especially surged in the Cedar-Riverside area of Minneapolis.
 There is a sizable Somali community in the United Arab Emirates. Somali-owned businesses line the streets of Deira, the
There is a sizable Somali community in the United Arab Emirates. Somali-owned businesses line the streets of Deira, the Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 emirates of the United Arab Emirates.The Government and Politics ...
city centre, with only Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
ians exporting more products from the city at large. Internet cafés, hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a ref ...
s, coffee shops, restaurants and import-export businesses are all testimony to the Somalis' entrepreneurial spirit. Star African Air is also one of three Somali-owned airline
An airline is a company that provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for codeshare agreements, in which ...
s which are based in Dubai.
Besides their traditional areas of inhabitation in Greater Somalia, a Somali community mainly consisting of entrepreneurs, academics, and students also exists in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
.Somalia: How is the fate of the Somalis in Egypt?In addition, there is an historical Somali community in the general Sudan area. Primarily concentrated in the north and Khartoum, the expatriate community mainly consists of students as well as some businesspeople.The History of Somali Communities in the Sudan since the First World War
/ref> More recently, Somali entrepreneurs have established themselves in
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, investing over $1.5 billion in the Somali enclave of Eastleigh alone.Help Locals Rebuild Their Country By Ensuring World Attention And Peace/ref> In
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
, Somali businesspeople also provide most of the retail trade in informal settlements around the Western Cape province.
Notable individuals of the diaspora
* Abdulrahim Abby Farah Undersecretary General of theUnited Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
1979–1990, Permanent Representative of Somalia to the United Nations 1965–1972.
 *
*Abdusalam H. Omer
Abdisalam Omer Hadliye ( so, Cabdisalaan Cumar Hadliye; ar, عبد السلام عمر), also known as Abdisalan Hadliye Omar, is a Somali economist and politician. He was previously a Chief of Staff at the Executive Office of the Mayor of the ...
– Somali economist and politician. Former Foreign Affairs Minister of Somalia and Governor of the Central Bank of Somalia.
* Abdi Yusuf Hassan – Somali politician, diplomat and journalist. Former director of IRIN and UNHCR Head of External and Media Relations in Southwest and Central Asia.
 * Ahmed Hussen – Somali lawyer. Minister of Immigration of Canada. President of the
* Ahmed Hussen – Somali lawyer. Minister of Immigration of Canada. President of the Canadian Somali Congress
The Canadian Somali Congress (CSC) is a Somali community organization based in Toronto, Ontario.
Overview
Lawyer Ahmed Hussen serves as the CSC's national President.
The body works closely with national and regional authorities to strengthen ci ...
.
* Abdulqawi Yusuf – Prominent Somali international lawyer and current president of the International Court of Justice.
* Abdirahim Hussein Mohamed – Somali politician. Elected Chairman of the Helsinki Centre Youth in 2007 and chairman of the Moniheli cooperation network for multicultural organizations.
* Abdirashid Duale – award-winning Somali entrepreneur, philanthropist, and the CEO of the multinational enterprise Dahabshiil.
* Adan Mohammed – Somali banker, entrepreneur and politician. He previously served as the managing director of Barclays Bank in East and West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mau ...
and is currently the Cabinet Secretary for Industrialization of Kenya.
 *
*Ali Said Faqi
Ali Said Faqi ( so, Cali Saiid Fakhi, ar, علي سعيد فقي) is a Somali people, Somali scientist specializing in toxicology and a diplomat. A leading researcher in his field, he has numerous scientific papers and also authored a book enti ...
– Somali scientist and the leading researcher on the design and interpretation of toxicology studies at the MPI research center in Mattawan, Michigan
Mattawan is a village in Antwerp Township, Van Buren County of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,997 at the 2010 census.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , of which is land ...
.
* Amina Moghe Hersi – Award-winning Somali entrepreneur that has launched several multimillion-dollar projects in Kampala, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The south ...
, such as the Oasis Centre luxury mall and the Laburnam Courts. She also runs Kingstone Enterprises Limited, one of the largest distributors of cement and other hardware materials in Kampala.
* Amina Mohamed – Somali lawyer and politician. Former Chairman of the International Organization for Migration and the World Trade Organisation's General Council, and current Secretary for Foreign Affairs of Kenya.
* ASAP Rocky – rapper.
* Ayaan and Idyl Mohallim – Somali twin fashion designers and owners of the Mataano
Mataano ("Twins" in the Somali language) is a women's fashion line. Founded in 2008, it is owned by Somali- American twin fashion designers Ayaan and Idyl Mohallim.
Founders
Ayaan and Idyl Mohallim were born in Alabama to Somali parents. The ...
brand.
* Ayaan Hirsi Ali – Feminist and atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
activist, writer and politician known for her views critical of Islam and female circumcision.
 *
*Ayub Daud
Ayub Daud ( so, Ayuub Daaud, ar, أيوب داود; born 24 February 1990) is a Somali professional footballer who plays as a forward or attacking midfielder for the Somalia national team.
Club career
The son of Daud Hussein, a former membe ...
– Somali international footballer who plays as a forward/attacking midfielder for FC Crotone on loan from Juventus.
* Faisal Hawar – Somali engineer and entrepreneur. Chairman of the International Somalia Development Foundation and the Maakhir Resource Company.
*Halima Ahmed
Halima Ahmed ( so, Xaliima Axmed) is a Somali political activist.
Personal life
Ahmed was born in Somalia. For her post-secondary education, she earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in International Relations from the Geneva School of Diplomacy in ...
– Somali political activist with the Youth Rehabilitation Center and prospective candidate in the Federal Parliament of Somalia.
* Halima Aden - Somali american model. minnesota first woman to wear a hijab in Miss Minnesota USA pageant
* Hanan Ibrahim – Somali social activist. Received the Queen's Award for Voluntary Service in 2004 and was made an MBE in 2010.
*Hassan Abdillahi
Hassan Abdillahi "Karate" ( so, Xasan Cabdullaahi, ar, حسن عبد الله) is a Somali journalist and social activist. He is the founder and President of Ogaal Radio.
Biography
Abdi hails from the Ogaden Darod clan.
Nicknamed "Karate", he ...
– Somali journalist. President of Ogaal Radio, the largest Somali community station in Canada.
* Hibaaq Osman – Somali political strategist. Founder and Chairperson of the ThinkTank for Arab Women, the Dignity Fund, and Karama.
*Hodan Ahmed
Hodan Ahmed ( so, Hodan Axmed; ar, هودان أحمد) is a Somali political activist. She helped form the Somali Women Parliamentary Association the Transitional Federal Parliament of Somalia, which was succeeded by the Federal Parliament of ...
– Somali political activist and Senior Program Officer at the National Democratic Institute.
* Hodan Nalayeh – Somali media executive and entrepreneur. President of the Cultural Integration Agency and the Vice President of Sales & Programming Development of Cameraworks Productions International.
* Idil Ibrahim – Somali American film director, writer and producer. Founder of Zeila Films.
 *
*Ilhan Omar
Ilhan Abdullahi Omar (born October 4, 1982) is an American politician serving as the U.S. representative for since 2019. She is a member of the Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party. Before her election to Congress, Omar served in the Minnesot ...
– Somali American politician, the first Somali Member of Congress in the United States. Omar currently represents Minnesota's 5th congressional district.
* Iman Mohamed Abdulmajid – international fashion icon, supermodel, actress and entrepreneur; professionally known as ''Iman''.
*Jawahir Ahmed
Jawahir Ahmed ( so, Jawaahir Axmed; ar, جواهر احمد) is a Somalis, Somali-United States, American model.
Personal life
Ahmed was born in 1991 in Logan, Utah to Somali people, Somali parents. Her family had moved to the United States earl ...
– Somali American model. Served as Miss Somalia in 2013 Miss United Nations USA pageant.
*Leila Abukar
Leila Abukar ( so, Leyla Abukar, ar, ليلى أبو بكر) is a Somali-Australian political activist.
Personal life
Abukar was born between 1974 and 1975 in Somalia. She attended a private school in Mogadishu.
When the civil war broke out ...
– Somali-Australian political activist. Recipient of Centenary Medal.
* Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed (Farmajo) – Somali politician and diplomat. Former Prime Minister of Somalia and founder of the Tayo Political Party.
* Mo Farah - Somali-British Olympic gold medalist and world champion long distance runner.
* Musse Olol – Somali American social activist. Recipient of the 2011 Director's Community Leadership Award.
* Mustafa Mohamed – Somali-Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
long-distance runner who mainly competes in the 3,000-meter steeplechase. Won gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
in the 2006 Nordic Cross Country Championships and at the 1st SPAR European Team Championships in Leiria, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
, in 2009. Beat the 31-year-old Swedish record in 2007.
* Nathif Jama Adam – Somali banker and politician. Former senior vice president and the head of the Sharjah Islamic Bank's Investments & International Banking Division, and Governor of Garissa County.
* Shadya Yasin – Somali-Canadian social activist, poet and teacher.
* Omar Abdi Ali – Somali entrepreneur, accountant, financial consultant, philanthropist, and specialist on Islamic finance. Was formerly CEO of Dar al-Maal al-Islami (DMI Trust), which under his management increased its assets from $1.6 billion to $4.0 billion. He is currently the chairman and founder of the multinational real estate corporation Integrated Property Investments Limited and its sister company Quadron investments.
* Rageh Omaar – Somali-British television news presenter and writer. Formerly a BBC news correspondent in 2009, he moved to a new post at Al Jazeera English, where he currently presents the nightly weekday documentary series ''Witness''.
*Sulekha Ali
Sulekha Ali ( so, Suleekha Cali, ar, زليخة علي) is a Somali- Canadian musician. Based in Ottawa, she attended Carleton University, where she graduated with a Bachelor of Arts (BA Hons) degree in Human Rights. Her choice of tertiary studi ...
, a Somali-Canadian musician.
* Waris Dirie – Somali model, author, actress, and social activist. UN Special Ambassador from 1997 to 2003.
*Yasmin Warsame
Yasmin Abshir Warsame ( so, Yasmiin Abshir Warsame, ar, ياسمين ابشير ارسام; born May 5, 1976) is a Somali-Canadian model and activist. In 2004, she was named "The Most Alluring Canadian" in a poll by ''Fashion'' magazine.
Biogr ...
– Somali-Canadian
Somali Canadians are Canadians of Somali origin or are dual Somali and Canadian nationality.
Overview
Most Somalis arrived in Canada between the late 1980s from Somalia and early 1990s as refugees, with some secondary migration from the United ...
model who was named "The Most Alluring Canadian" in a poll by ''Fashion'' magazine.
*Zahra Abdulla
Zahra Abdulla ( so, Sahra Cabdulla, ar, زهراء عبد الله; born 1966) is a Somali-born Finnish politician. She was a member of the Helsinki City Council from 1997 to 2017, representing the Green League.
Biography
Zahra was born in So ...
– Somali politician in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
and member of the Helsinki City Council
The City Council of Helsinki (, ) is the main decision-making organ in the local politics of Helsinki, Finland. The City Council deals with issues such as city planning, schools, health care, and public transport.
The 85-seat Council's membe ...
representing the Green League.
Genetics
Uniparental lineages
According to Y chromosome studies by Sanchez et al. (2005), Cruciani et al. (2004, 2007), the Somalis are paternally closely related to other Afro-Asiatic-speaking groups in Northeast Africa. Besides comprising the majority of the Y-DNA in Somalis, the E1b1b (formerly E3b) haplogroup also makes up a significant proportion of the paternal DNA of Ethiopians, Sudanese, Egyptians, Berbers, North African Arabs, as well as manyMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
populations. Sanchez et al. (2005) observed the E-M78 subclade of E1b1b1a in about 70.6% of their Somali male samples. According to Cruciani et al. (2007), the presence of this subhaplogroup in the Horn region may represent the traces of an ancient migration from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
/Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
. use the term Northeastern Africa to refer to Egypt and Libya, as shown in Table 1 of the study. Prior to , East Africa as a possible place of origin of E-M78, based upon Ethiopian testing. This was because of the high frequency and diversity of E-M78 lineages in the region of Ethiopia. However, were able to study more data, including populations from North Africa who were not represented in the study, and found evidence that the E-M78 lineages which make up a significant proportion of some populations in that region, were relatively young branches (see E-V32 below). They therefore concluded that "Northeast Africa" was the likely place of origin of E-M78 based on "the peripheral geographic distribution of the most derived subhaplogroups with respect to northeastern Africa, as well as the results of quantitative analysis of UEP and microsatellite diversity". So according to E-M35, the parent clade of E-M78, originated in East Africa, subsequently spread to Northeast Africa, and then there was a "back migration" of E-M215 chromosomes that had acquired the E-M78 mutation. therefore note this as evidence for "a corridor for bidirectional migrations" between Northeast Africa (Egypt and Libya in their data) on the one hand and East Africa on the other. The authors believe there were "at least 2 episodes between 23.9–17.3 ky and 18.0–5.9 ky ago".
After haplogroup E1b1b, the second most frequently occurring Y-DNA haplogroup among Somalis is the West Asian haplogroup T (M184). The clade is observed in more than 10% of Somali males generally, with a peak frequency amongst the Somali Dir clan members in Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Re ...
(100%); 25/34 total local samples belonged to haplogroup T (24/24 Dir, 1/1 Hawiye, 0/9 Isaak). and Somalis in Dire Dawa (82.4%), a city with a majority Dir population. Haplogroup T, like haplogroup E1b1b, is also typically found among other populations of Northeast Africa, the Maghreb, the Near East and the Mediterranean.
In Somalis, the Time to Most Recent Common Ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
(TMRCA) was estimated to be 4000–5000 years (2,500 BCE) for the haplogroup E-M78 cluster γ and 2100–2200 years (150 BCE) for Somali T-M184 bearers.
Deep subclade E-Y18629 is commonly found in Somalis and has a formation date of 3,700 YBP (years before present) and a TMRCA of 3,300 YBP.
 According to
According to mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondrion, mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mit ...
studies by Holden (2005) and Richards et al. (2006), a significant proportion of the maternal lineages of Somalis consists of the M1 haplogroup at a rate of over 20%.Hans-Jürgen Bandelt, Vincent Macaulay, Dr. Martin Richards, ''Human mitochondrial DNA and the evolution of Homo sapiens'', Volume 18 of Nucleic acids and molecular biology, (シュプリンガー・ジャパン株式会社: 2006), p.235.AD. Holden (2005)MtDNA variation in North, East, and Central African populations gives clues to a possible back-migration from the Middle East
, Program of the Seventy-Fourth Annual Meeting of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists (2005) This mitochondrial clade is common among Ethiopians and North Africans, particularly Egyptians and
Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, religi ...
ns. M1 is believed to have originated in Asia, where its parent M clade represents the majority of mtDNA lineages. This haplogroup is also thought to possibly correlate with the Afro-Asiatic language family: In addition, Somalis, and other Horn African populations, also carry a significant rate of maternal L lineages associated with sub-Saharan Africa.
"We analysed mtDNA variation in ~250 persons from Libya, Somalia, and Congo/Zambia, as representatives of the three regions of interest. Our initial results indicate a sharp cline in M1 frequencies that generally does not extend into sub-Saharan Africa. While our North and especially East African samples contained frequencies of M1 over 20%, our sub-Saharan samples consisted almost entirely of the L1 or L2 haplogroups only. In addition, there existed a significant amount of homogeneity within the M1 haplogroup. This sharp cline indicates a history of little admixture between these regions. This could imply a more recent ancestry for M1 in Africa, as older lineages are more diverse and widespread by nature, and may be an indication of a back-migration into Africa from the Middle East."
Autosomal ancestry

 Research shows that Somalis have a mixture of a type of native African ancestry unique and autochthonous to the Horn of Africa, as well as ancestry originating from a non-African back-migration. According to an
Research shows that Somalis have a mixture of a type of native African ancestry unique and autochthonous to the Horn of Africa, as well as ancestry originating from a non-African back-migration. According to an autosomal DNA
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
study by Hodgson et al. (2014), the Afro-Asiatic languages were likely spread across Africa and the Near East by an ancestral population(s) carrying a newly identified non-African genetic component, which the researchers dub as the "Ethio-Somali". This component today is most common among Afro-Asiatic-speaking populations in the Horn of Africa. It reaches a frequency peak among ethnic Somalis, representing the majority of their ancestry. The Ethio-Somali component is most closely related to the Maghrebi non-African genetic component, and is believed to have diverged from all other non-African ancestries at least 23,000 years ago. On this basis, the researchers suggest that the original Ethio-Somali carrying population(s) probably arrived in the pre-agricultural period from the Near East, having crossed over into northeastern Africa via the Sinai Peninsula. The population then likely split into two branches, with one group heading westward toward the Maghreb and the other moving south into the Horn. Ancient DNA analysis indicates that this foundational ancestry in the Horn region is akin to that of Neolithic farmers of the southern Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
.
Furthermore, according to Hodgson et al. both the African ancestry (Ethiopic) and the non-African ancestry (Ethio-Somali) in Cushitic speaking populations is significantly differentiated from all neighboring African and non-African ancestries today. The overall genetic ancestry of Cushitic and Semitic speaking populations in the Horn of Africa represents ancestries not found outside of HOA populations. The researchers state:
"The African Ethiopic ancestry is tightly restricted to HOA populations and likely represents an autochthonous HOA population. The non-African ancestry in the HOA, which is primarily attributed to a novel Ethio-Somali inferred ancestry component, is significantly differentiated from all neighboring non-African ancestries in North Africa, the Levant, and Arabia."Moreover, Hodgson et al. (2014) elaborates further:
"We find that most of the non-African ancestry in the HOA can be assigned to a distinct non-African origin Ethio-Somali ancestry component, which is found at its highest frequencies in Cushitic and Semitic speaking HOA populations."Molinaro, Ludovica et al in 2019 characterized the Non-African ancestry in Ethiopian Somalis as being derived from Anatolia Neolithic groups (similar to Tunisian Jews). Ali, A.A., Aalto, M., Jonasson, J. et al. (2020) using principal component analysis showed that approximately 60% of Somali ancestry is East African and 40% Western Eurasian.
Somali studies
 The scholarly term for research concerning Somalis and Greater Somalia is Somali Studies. It consists of several disciplines such as
The scholarly term for research concerning Somalis and Greater Somalia is Somali Studies. It consists of several disciplines such as anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
, sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation and ...
, linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Lingu ...
, historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians hav ...
and archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
. The field draws from old Somali literature, Somali chronicles, records and oral literature, in addition to written accounts and traditions about Somalis from explorers and geographers in the Horn of Africa and the Middle East. Since 1980, prominent ''Somalist'' scholars from around the world have also gathered annually to hold the International Congress of Somali Studies.
See also
*Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
* Somaliland
*Afar people
*Culture of Somalia
*Demographics of Somalia
* Greater Somalia
Notes
References
Bibliography
*Hanley, Gerald, ''Warriors: Life and Death Among the Somalis'', (Eland Publishing Ltd, 2004)External links
Ethnologue population estimates for Somali speakers
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Somali People Cushitic-speaking peoples Indigenous peoples of East Africa Ethnic Somali people, Ethnic groups in Djibouti Ethnic groups in Ethiopia Ethnic groups in Kenya Ethnic groups in Somalia, Ethnic groups in the Arab world Muslim communities in Africa Pastoralists Female genital mutilation Female genital mutilation by country