|
Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar language, Afar, Hadiyya language, Hadiyya, Kambaata language, Kambaata, Saho language, Saho, and Sidama language, Sidama. Official status The Cushitic languages with the greatest number of total speakers are Oromo (37 million), Somali (22 million), Beja (3.2 million), Sidamo language, Sidamo (3 million), and Afar language, Afar (2 million). Oromo serves as one of the official working languages of Ethiopia and is also the working language of several of the states within the Ethiopian federal system including Oromia, Harari Region, Harari and Dire Dawa regional states and of the Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region. Somali is the first of two offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar, Hadiyya, Kambaata, Saho, and Sidama. Official status The Cushitic languages with the greatest number of total speakers are Oromo (37 million), Somali (22 million), Beja (3.2 million), Sidamo (3 million), and Afar (2 million). Oromo serves as one of the official working languages of Ethiopia and is also the working language of several of the states within the Ethiopian federal system including Oromia, Harari and Dire Dawa regional states and of the Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region. Somali is the first of two official languages of Somalia and three official languages of the self declared republic of Somaliland. It also serves as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic subregions of Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara/Sahel. With the exception of its Semitic branch, all branches of the Afroasiatic family are exclusively native to the African continent. Afroasiatic languages have over 500 million native speakers, which is the fourth-largest number of native speakers of any language family (after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo). The phylum has six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic languages, Cushitic, Egyptian language, Egyptian, Semitic languages, Semitic, and Omotic languages, Omotic. The most widely spoken modern Afroasiatic language or dialect continuum by far is Arabic, a ''de facto'' group of Varieties of Arabic, distinct language varieties wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Cushitic Languages
The South Cushitic or Rift languages of Tanzania are a branch of the Cushitic languages. The most numerous is Iraqw, with half a million speakers. These languages are believed to have been originally spoken by Southern Cushitic agro-pastoralists from Ethiopia, who in the third millennium BC began migrating southward into the Great Rift Valley. Urheimat The original homeland of Proto-South Cushitic was in Southwest Ethiopia. South cushitic speakers then migrated south to lake Turkana and further south, entering Tanzania in 2000BC. Classification The Rift languages are named after the Great Rift Valley of Tanzania, where they are found. Hetzron (1980:70ff) suggested that the Rift languages (South Cushitic) are a part of Lowland East Cushitic. Kießling & Mous (2003) have proposed more specifically that they be linked to a Southern Lowland branch, together with Oromo, Somali, and Yaaku–Dullay. It is possible that the great lexical divergence of Rift from East Cushitic is due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beja Language
Beja ( or ) is an Afroasiatic language of the Cushitic branch spoken on the western coast of the Red Sea by the Beja people. Its speakers number around one to two million individuals, and inhabit parts of Egypt, Sudan and Eritrea. Name The name ''Beja'', derived from ar, بجا, bijā, is most common in English-language literature. Native speakers use the term (indefinite) or (definite). Classification Beja is held by most linguists to be part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, constituting the only member of the Northern Cushitic subgroup. As such, Beja contains a number of linguistic innovations that are unique to it, as is also the situation with the other subgroups of Cushitic (e.g. idiosyncratic features in Agaw or Central Cushitic). The characteristics of Beja that differ from those of other Cushitic languages are likewise generally acknowledged as normal branch variation. The relation of the Northern Cushitic branch of Cushitic to the other branches i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland East Cushitic Languages
Lowland East Cushitic is a group of roughly two dozen diverse languages of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic family. Its largest representatives are Somali and Oromo. Classification Lowland East Cushitic classification from Tosco (2020:297):Tosco, Mauro. 2020. East Cushitic. In: Vossen, Rainer and Gerrit J. Dimmendaal (eds.). 2020. ''The Oxford Handbook of African Languages'', 290-299. Oxford: Oxford University Press. *Lowland East Cushitic ** Saho–Afar **Southern ***Nuclear **** Omo–Tana **** Oromoid ***Peripheral (?) **** Dullay **** Yaaku Highland East Cushitic is a coordinate (sister) branch with Lowland East Cushitic in Tosco's (2020) classification. 'Core' East Cushitic classification form Bender (2020 008 91). Saho–Afar is excluded, making it equivalent to Tosco's Southern Lowland East Cushitic, and Yaaku is moved into Western Omo–Tana ('Arboroid'): * 'Core' East Cushitic ** Dullay ** SAOK *** Eastern Omo–Tana ( Somaloid) *** Western Omo–Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
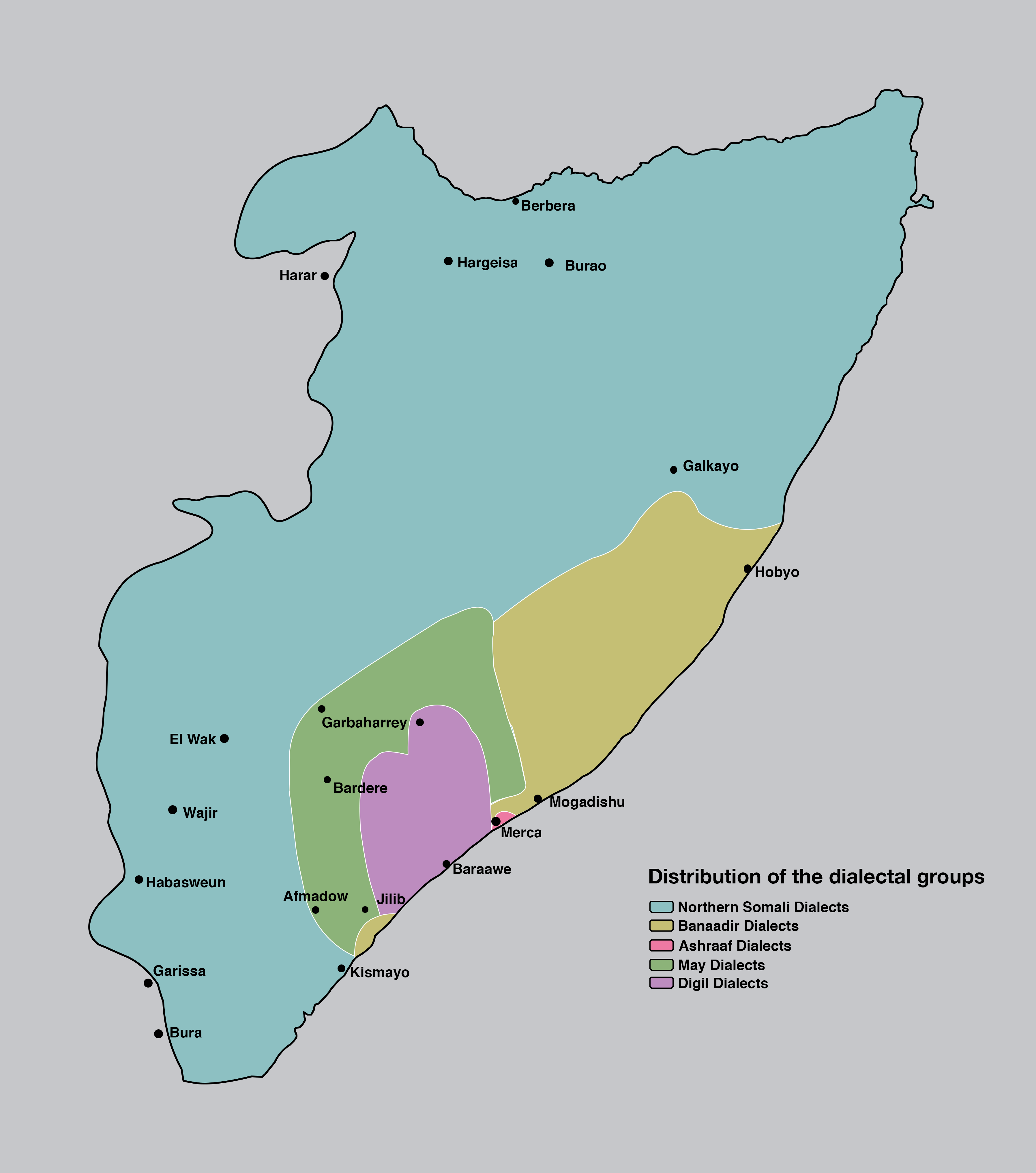
Somali Language
Somali (Latin script: ; Wadaad: ; Osmanya: 𐒖𐒍 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘 ) is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language in Somalia and Ethiopia, and a national language in Djibouti as well as in northeastern Kenya. The Somali language is written officially with the Latin alphabet although the Arabic alphabet and several Somali scripts like Osmanya, Kaddare and the Borama script are informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar and Saho. Somali is the best-documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies of the language dating back to the late 19th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland East Cushitic Languages
Highland East Cushitic, or Sidamic, is a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in south-central Ethiopia. They are often grouped with Lowland East Cushitic, Dullay, and Yaaku as ''East Cushitic'', but that group is not well defined and is considered dubious. The languages are: * Burji (divergent) *Sidamic proper ** Sidama ** Gedeo ** Hadiyya–Libido ** Kambaata– Alaba. Except for Burji, they are closely related. Hadiyya and Libido are especially close, as are Kambaata and Alaba. The most populous language is Sidama, with close to two million speakers. Notes References *Hudson, Grover. 1981. The Highland East Cushitic family vine. ''Sprache und Geschichte in Afrika'' 3.97-124. *Hudson, Grover. 1988. The Highland Cushitic hypothesis. ''Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference of Ethiopian Studies'' (Addis Ababa, 1984), Taddese Beyene, ed., 693-696. Birmingham, England: Elm Press. *Hudson, Grover. 1989. ''Highland East Cushitic Dictionary'' (Kusch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidamo Language
Sidama or Sidaamu Afoo is an Afro-Asiatic language belonging to the Highland East Cushitic branch of the Cushitic family. It is spoken in parts of southern Ethiopia by the Sidama people, particularly in the densely populated Sidama National Regional State (SNRS). Sidaamu Afoo is the ethnic autonym for the language, while Sidaminya is its name in Amharic. Although it is not known to have any specific dialects, it shares over 64% lexical similarity with Alaba-K'abeena, 62% with Kambaata, and 53% with Hadiyya, all of which are other languages spoken in southwestern Ethiopia. The word order is typically SOV. Sidaama has over 100,000 L2 speakers. The literacy rate for L1 speakers is 1%-5%, while for L2 speakers it is 20%. In terms of its writing, Sidaama used an Ethiopic script up until 1993, from which point forward it has used a Latin script. The term ''Sidamo'' has also been used by some authors to refer to larger groupings of East Cushitic and even Omotic languages. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Language
The Afar language ( aa, Qafaraf, links=no; also known as ’Afar Af, Afaraf, Qafar af) is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken by the Afar people inhabiting Djibouti, Eritrea and Ethiopia. Classification Afar is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. It is further categorized in the Lowland East Cushitic sub-group, along with Saho and Somali. Its closest relative is the Saho language. Geographic distribution The Afar language is spoken as a mother tongue by the Afar people in Djibouti, Eritrea, and the Afar Region of Ethiopia. According to '' Ethnologue'', there are 1,379,200 total Afar speakers. Of these, 1,280,000 were recorded in the 2007 Ethiopian census, with 906,000 monolinguals registered in the 1994 census. Official status In Djibouti, Afar is a recognized national language. It is also one of the broadcasting languages of the Radio Television of Djibouti public network. In Eritrea, Afar is recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), p. 26 Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world. It is composed of Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Djibouti; broader definitions also include parts or all of Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, and Uganda. The term Greater Horn Region (GHR) can additionally include Burundi, Rwanda, and Tanzania. It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean and shares a maritime border with the Arabian Peninsula of Western Asia. Names This peninsula has been known by various names. Ancient Greeks and Romans referred to it as Regio Aromatica or Regio Cinnamonifora due to the aromatic plants or as Regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oromo Language
Oromo ( or ; Oromo: ''Afaan Oromoo''), in the linguistic literature of the early 20th century also called Galla (a name with a pejorative meaning and therefore rejected by the Oromo people), is an Afroasiatic language that belongs to the Cushitic branch. It is native to the Ethiopian state of Oromia and Northern Kenya and is spoken predominantly by the Oromo people and neighboring ethnic groups in the Horn of Africa. It is used as a lingua franca particularly in Ethiopia and northeastern Kenya. With more than 36 million speakers making up 33.8% of the total Ethiopian population, Oromo has the largest number of native speakers in Ethiopia, and ranks as the second most widely spoken language in Ethiopia by total number of speakers (including second-language speakers) following Amharic. Forms of Oromo are spoken as a first language by an additional half-million people in parts of northern and eastern Kenya. It is also spoken by smaller numbers of emigrants in other African c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |