Smoke on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Smoke is an
Smoke is an
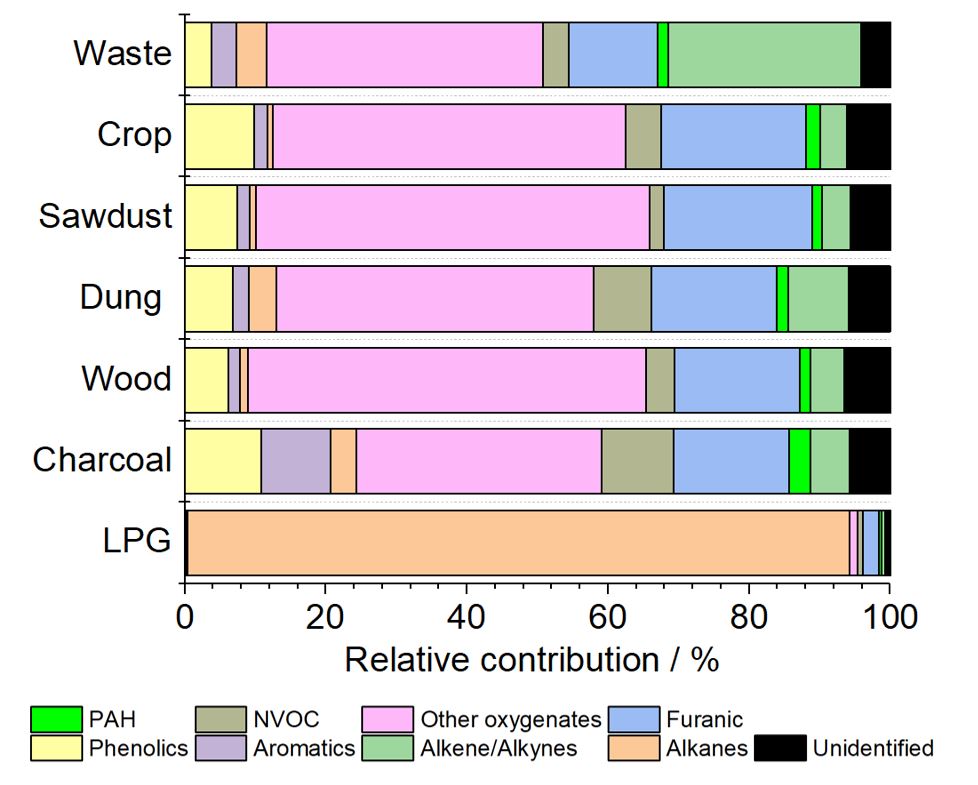 The composition of smoke depends on the nature of the burning fuel and the conditions of combustion. Fires with high availability of oxygen burn at a high temperature and with a small amount of smoke produced; the particles are mostly composed of ash, or with large temperature differences, of condensed aerosol of water. High temperature also leads to production of nitrogen oxides. Sulfur content yields
The composition of smoke depends on the nature of the burning fuel and the conditions of combustion. Fires with high availability of oxygen burn at a high temperature and with a small amount of smoke produced; the particles are mostly composed of ash, or with large temperature differences, of condensed aerosol of water. High temperature also leads to production of nitrogen oxides. Sulfur content yields  Pyrolysis of burning material, especially incomplete combustion or smoldering without adequate oxygen supply, also results in production of a large amount of hydrocarbons, both aliphatic (
Pyrolysis of burning material, especially incomplete combustion or smoldering without adequate oxygen supply, also results in production of a large amount of hydrocarbons, both aliphatic (

 The
The
 Cigarette smoke is a major modifiable risk factor for lung disease,
Cigarette smoke is a major modifiable risk factor for lung disease, 
 Smoke can obscure visibility, impeding occupant exiting from fire areas. In fact, the poor visibility due to the smoke that was in the Worcester Cold Storage Warehouse fire in
Smoke can obscure visibility, impeding occupant exiting from fire areas. In fact, the poor visibility due to the smoke that was in the Worcester Cold Storage Warehouse fire in
 Wood smoke is a major source of air pollution, especially particulate pollution, pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde.
In the United Kingdom domestic combustion, especially for industrial uses, is the largest single source of PM2.5 annually. In some towns and cities in New South Wales, wood smoke may be responsible for 60% of fine particle air pollution in the winter. A year-long sampling campaign in Athens, Greece found a third (31%) of PAH urban air pollution to be caused by wood-burning, roughly as much as that of Diesel locomotive, diesel and Crude oil, oil (33%) and gasoline (29%). It also found that wood-burning is responsible for nearly half (43%) of annual PAH lung cancer-risk compared to the other sources and that wintertime PAH levels were 7 times higher than in other seasons, presumably due to an increased use of fireplaces and heaters. The largest exposure events are periods during the winter with reduced atmospheric dispersion to dilute the accumulated pollution, in particular due to the low wind speeds. Research conducted about biomass burning in 2015, estimated that 38% of European total particulate pollution emissions are composed of domestic wood burning.
Wood smoke (for example from
Wood smoke is a major source of air pollution, especially particulate pollution, pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde.
In the United Kingdom domestic combustion, especially for industrial uses, is the largest single source of PM2.5 annually. In some towns and cities in New South Wales, wood smoke may be responsible for 60% of fine particle air pollution in the winter. A year-long sampling campaign in Athens, Greece found a third (31%) of PAH urban air pollution to be caused by wood-burning, roughly as much as that of Diesel locomotive, diesel and Crude oil, oil (33%) and gasoline (29%). It also found that wood-burning is responsible for nearly half (43%) of annual PAH lung cancer-risk compared to the other sources and that wintertime PAH levels were 7 times higher than in other seasons, presumably due to an increased use of fireplaces and heaters. The largest exposure events are periods during the winter with reduced atmospheric dispersion to dilute the accumulated pollution, in particular due to the low wind speeds. Research conducted about biomass burning in 2015, estimated that 38% of European total particulate pollution emissions are composed of domestic wood burning.
Wood smoke (for example from
'Fire inversions' lock smoke in valleysBurning Issues wood smoke SiteShedding new light on wood smoke
{{Authority control Fire Smoke, Pollution Air pollution
 Smoke is an
Smoke is an aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
(a suspension of airborne particulates and gases) emitted when a material undergoes combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
or pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be cons ...
of fires (including stoves, candle
A candle is an ignitable candle wick, wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a Aroma compound, fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time. ...
s, internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s, oil lamp
An oil lamp is a lamp used to produce light continuously for a period of time using an oil-based fuel source. The use of oil lamps began thousands of years ago and continues to this day, although their use is less common in modern times. The ...
s, and fireplaces), but may also be used for pest control
Pest control is the regulation or management of a species defined as a pest (organism), pest; such as any animal, plant or fungus that impacts adversely on human activities or environment. The human response depends on the importance of the da ...
( fumigation), communication ( smoke signals), defensive and offensive capabilities in the military ( smoke screen), cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from ...
, or smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
(tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, cannabis, etc.). It is used in rituals where incense
Incense is an aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremonial reasons. It ...
, sage, or resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative.
Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death in victims of indoor fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion re ...
s. The smoke kills by a combination of thermal damage, poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
ing and pulmonary irritation caused by carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is ...
and other combustion products.
Smoke is an aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
(or mist) of solid particles and liquid droplets that are close to the ideal range of sizes for Mie scattering of visible light.
Chemical composition
 The composition of smoke depends on the nature of the burning fuel and the conditions of combustion. Fires with high availability of oxygen burn at a high temperature and with a small amount of smoke produced; the particles are mostly composed of ash, or with large temperature differences, of condensed aerosol of water. High temperature also leads to production of nitrogen oxides. Sulfur content yields
The composition of smoke depends on the nature of the burning fuel and the conditions of combustion. Fires with high availability of oxygen burn at a high temperature and with a small amount of smoke produced; the particles are mostly composed of ash, or with large temperature differences, of condensed aerosol of water. High temperature also leads to production of nitrogen oxides. Sulfur content yields sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, or in case of incomplete combustion, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
. Carbon and hydrogen are almost completely oxidized to carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and water. Fires burning with lack of oxygen produce a significantly wider palette of compounds, many of them toxic. Partial oxidation of carbon produces carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, while nitrogen-containing materials can yield hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
, and nitrogen oxides. Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas can be produced instead of water. Contents of halogens
The halogens () are a group (periodic table), group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related chemical element, elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and ten ...
such as chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
(e.g. in polyvinyl chloride or brominated flame retardants) may lead to the production of hydrogen chloride, phosgene, dioxin, and chloromethane, bromomethane and other halocarbons. Hydrogen fluoride can be formed from fluorocarbons, whether fluoropolymers subjected to fire or halocarbon fire suppression agents. Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
and antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
oxides and their reaction products can be formed from some fire retardant additives, increasing smoke toxicity and corrosivity. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), e.g. from burning older transformer oil, and to lower degree also of other chlorine-containing materials, can produce 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, a potent carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruse ...
, and other polychlorinated dibenzodioxins. Pyrolysis of fluoropolymers, e.g. teflon, in presence of oxygen yields carbonyl fluoride (which hydrolyzes readily to HF and CO2); other compounds may be formed as well, e.g. carbon tetrafluoride, hexafluoropropylene, and highly toxic perfluoroisobutene (PFIB).
 Pyrolysis of burning material, especially incomplete combustion or smoldering without adequate oxygen supply, also results in production of a large amount of hydrocarbons, both aliphatic (
Pyrolysis of burning material, especially incomplete combustion or smoldering without adequate oxygen supply, also results in production of a large amount of hydrocarbons, both aliphatic (methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
, ethane, ethylene, acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is u ...
) and aromatic (benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
and its derivates, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons; e.g. benzo yrene, studied as a carcinogen, or retene), terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predomi ...
s. It also results in the emission of a range of smaller oxygenated volatile organic compounds ( methanol, acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
, hydroxy acetone, methyl acetate and ethyl formate) which are formed as combustion by products as well as less volatile oxygenated organic species such as phenolics, furans and furanones. Heterocyclic compounds may be also present. Heavier hydrocarbons may condense as tar; smoke with significant tar content is yellow to brown. Combustion of solid fuels can result in the emission of many hundreds to thousands of lower volatility organic compounds in the aerosol phase. Presence of such smoke, soot, and/or brown oily deposits during a fire indicates a possible hazardous situation, as the atmosphere may be saturated with combustible pyrolysis products with concentration above the upper flammability limit, and sudden inrush of air can cause flashover or backdraft.
Presence of sulfur can lead to formation of gases like hydrogen sulfide, carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the linear formula . It is a colorless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl double bonded to a sulfur atom. Carbonyl sulfide can be considered to ...
, sulfur dioxide, carbon disulfide, and thiols; especially thiols tend to get adsorbed on surfaces and produce a lingering odor even long after the fire. Partial oxidation of the released hydrocarbons yields in a wide palette of other compounds: aldehydes (e.g. formaldehyde, acrolein, and furfural), ketones, alcohols (often aromatic, e.g. phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
, guaiacol, syringol, catechol, and cresols), carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
s ( formic acid, acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
, etc.).
The visible particulate matter in such smokes is most commonly composed of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
( soot). Other particulates may be composed of drops of condensed tar, or solid particles of ash. The presence of metals in the fuel yields particles of metal oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s. Particles of inorganic salts may also be formed, e.g. ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, or sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
. Inorganic salts present on the surface of the soot particles may make them hydrophilic. Many organic compounds, typically the aromatic hydrocarbons, may be also adsorbed on the surface of the solid particles. Metal oxides can be present when metal-containing fuels are burned, e.g. solid rocket fuels containing aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
. Depleted uranium projectiles after impacting the target ignite, producing particles of uranium oxides. Magnetic particles, spherules of magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
-like ferrous ferric oxide, are present in coal smoke; their increase in deposits after 1860 marks the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. (Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles can be also produced in the smoke from meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s burning in the atmosphere.) Magnetic remanence, recorded in the iron oxide particles, indicates the strength of Earth's magnetic field when they were cooled beyond their Curie temperature; this can be used to distinguish magnetic particles of terrestrial and meteoric origin. Fly ash
Coal combustion products (CCPs), also called coal combustion wastes (CCWs) or coal combustion residuals (CCRs), are byproducts of burning coal. They are categorized in four groups, each based on physical and chemical forms derived from coal combust ...
is composed mainly of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
and calcium oxide. Cenospheres are present in smoke from liquid hydrocarbon fuels. Minute metal particles produced by abrasion can be present in engine smokes. Amorphous silica particles are present in smokes from burning silicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber ...
s; small proportion of silicon nitride particles can be formed in fires with insufficient oxygen. The silica particles have about 10 nm size, clumped to 70–100 nm aggregates and further agglomerated to chains. Radioactive particles may be present due to traces of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
, thorium, or other radionuclides in the fuel; hot particles can be present in case of fires during nuclear accidents (e.g. Chernobyl disaster) or nuclear war.
Smoke particulates, like other aerosols, are categorized into three modes based on particle size:
* nuclei mode, with geometric mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a finite collection of positive real numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometri ...
radius between 2.5 and 20 nm, likely forming by condensation of carbon moieties.
* accumulation mode, ranging between 75 and 250 nm and formed by coagulation of nuclei mode particles
* coarse mode, with particles in micrometer range
Most of the smoke material is primarily in coarse particles. Those undergo rapid dry precipitation, and the smoke damage in more distant areas outside of the room where the fire occurs is therefore primarily mediated by the smaller particles.
Aerosol of particles beyond visible size is an early indicator of materials in a preignition stage of a fire.
Burning of hydrogen-rich fuel produces water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
; this results in smoke containing droplets of water. In absence of other color sources (nitrogen oxides, particulates...), such smoke is white and cloud-like.
Smoke emissions may contain characteristic trace elements. Vanadium is present in emissions from oil fired power plants and refineries; oil plants also emit some nickel. Coal combustion produces emissions containing aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, chromium, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, mercury, selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elem ...
, and uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
.
Traces of vanadium in high-temperature combustion products form droplets of molten vanadates. These attack the passivation layers on metals and cause high temperature corrosion, which is a concern especially for internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s. Molten sulfate and lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
particulates also have such effect.
Some components of smoke are characteristic of the combustion source. Guaiacol and its derivatives are products of pyrolysis of lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
and are characteristic of wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
smoke; other markers are syringol and derivates, and other methoxy phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
s. Retene, a product of pyrolysis of conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
trees, is an indicator of forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire ( in Australia), dese ...
s. Levoglucosan is a pyrolysis product of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
. Hardwood
Hardwood is wood from Flowering plant, angiosperm trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostl ...
vs softwood smokes differ in the ratio of guaiacols/syringols. Markers for vehicle exhaust include polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, hopanes, steranes, and specific nitroarenes (e.g. 1-nitropyrene). The ratio of hopanes and steranes to elemental carbon can be used to distinguish between emissions of gasoline and diesel engines.
Many compounds can be associated with particulates; whether by being adsorbed on their surfaces, or by being dissolved in liquid droplets. Hydrogen chloride is well absorbed in the soot particles.
Inert particulate matter can be disturbed and entrained into the smoke. Of particular concern are particles of asbestos.
Deposited hot particles of radioactive fallout and bioaccumulated radioisotopes can be reintroduced into the atmosphere by wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s and forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire ( in Australia), dese ...
s; this is a concern in e.g. the Zone of alienation containing contaminants from the Chernobyl disaster.
Polymers are a significant source of smoke. Aromatic side groups, e.g. in polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It i ...
, enhance generation of smoke. Aromatic groups integrated in the polymer backbone produce less smoke, likely due to significant charring. Aliphatic polymers tend to generate the least smoke, and are non-self-extinguishing. However presence of additives can significantly increase smoke formation. Phosphorus-based and halogen-based flame retardant
Flame retardants are a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an combustion, ignition source and pr ...
s decrease production of smoke. Higher degree of cross-linking between the polymer chains has such effect too.
Visible and invisible particles of combustion

 The
The naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
detects particle sizes greater than 7 μm ( micrometres). Visible particles emitted from a fire are referred to as smoke. Invisible particles are generally referred to as gas or fumes. This is best illustrated when toasting bread in a toaster. As the bread heats up, the products of combustion increase in size. The fumes initially produced are invisible but become visible if the toast is burnt.
An ionization chamber type smoke detector is technically a product of combustion detector, not a smoke detector. Ionization chamber type smoke detectors detect particles of combustion that are invisible to the naked eye. This explains why they may frequently false alarm from the fumes emitted from the red-hot heating elements of a toaster, before the presence of visible smoke, yet they may fail to activate in the early, low-heat smoldering stage of a fire.
Smoke from a typical house fire contains hundreds of different chemicals and fumes. As a result, the damage caused by the smoke can often exceed that caused by the actual heat of the fire. In addition to the physical damage caused by the smoke of a fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion re ...
– which manifests itself in the form of stains – is the often even harder to eliminate problem of a smoky odor. Just as there are contractors that specialize in rebuilding/repairing homes that have been damaged by fire and smoke, fabric restoration companies specialize in restoring fabrics that have been damaged in a fire.
Dangers
Smoke from oxygen-deprived fires contains a significant concentration of compounds that are flammable. A cloud of smoke, in contact with atmospheric oxygen, therefore has the potential of being ignited – either by another open flame in the area, or by its own temperature. This leads to effects like backdraft and flashover. Smoke inhalation is also a danger of smoke that can cause serious injury and death. Many compounds of smoke from fires are highly toxic and/or irritating. The most dangerous iscarbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
leading to carbon monoxide poisoning, sometimes with the additive effects of hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is ...
and phosgene. Smoke inhalation can therefore quickly lead to incapacitation and loss of consciousness. Sulfur oxides, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen fluoride in contact with moisture form sulfuric, hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid, which are corrosive to both lungs and materials.
 Cigarette smoke is a major modifiable risk factor for lung disease,
Cigarette smoke is a major modifiable risk factor for lung disease, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, and many cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s. Smoke can also be a component of ambient air pollution due to the burning of coal in power plants, forest fires or other sources, although the concentration of pollutants in ambient air is typically much less than that in cigarette smoke. One day of exposure to PM2.5 at a concentration of 880 μg/m3, such as occurs in Beijing, China, is the equivalent of smoking one or two cigarettes in terms of particulate inhalation by weight. The analysis is complicated, however, by the fact that the organic compounds present in various ambient particulates may have a higher carcinogenicity than the compounds in cigarette smoke particulates. Secondhand tobacco smoke is the combination of both sidestream and mainstream smoke emissions from a burning tobacco product. These emissions contain more than 50 carcinogenic chemicals. According to the United States Surgeon General's 2006 report on the subject, exposures to secondhand tobacco smoke can activate platelets causing increased clotting and increased risk of thrombus and potentially damage the lining of blood vessels, decrease coronary flow velocity reserves, and reduce heart rate variability, potentially increasing the risk of a heart attack. The chances of these effects occurring increase with increased exposure and time of exposure. The American Cancer Society lists "heart disease, lung infections, increased asthma attacks, middle ear infections, and low birth weight" as ramifications of smoker's emission.
 Smoke can obscure visibility, impeding occupant exiting from fire areas. In fact, the poor visibility due to the smoke that was in the Worcester Cold Storage Warehouse fire in
Smoke can obscure visibility, impeding occupant exiting from fire areas. In fact, the poor visibility due to the smoke that was in the Worcester Cold Storage Warehouse fire in Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the list of United States cities by population, 113th most populous city in the United States. Named after Worcester ...
was the reason why the trapped rescue firefighters could not evacuate the building in time. Because of the striking similarity that each floor shared, the dense smoke caused the firefighters to become disoriented.
Corrosion
Smoke can contain a wide variety of chemicals, many of them aggressive in nature. Examples are hydrochloric acid and hydrobromic acid, produced from halogen-containingplastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
s and fire retardants, hydrofluoric acid released by pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of fluorocarbon fire suppression agents, sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
from burning of sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
-containing materials, nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
from high-temperature fires where nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
gets formed, phosphoric acid and antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
compounds from P and Sb based fire retardants, and many others. Such corrosion is not significant for structural materials, but delicate structures, especially microelectronics, are strongly affected. Corrosion of circuit board traces, penetration of aggressive chemicals through the casings of parts, and other effects can cause an immediate or gradual deterioration of parameters or even premature (and often delayed, as the corrosion can progress over long time) failure of equipment subjected to smoke. Many smoke components are also electrically conductive; deposition of a conductive layer on the circuits can cause crosstalks and other deteriorations of the operating parameters or even cause short circuits and total failures. Electrical contacts can be affected by corrosion of surfaces, and by deposition of soot and other conductive particles or nonconductive layers on or across the contacts. Deposited particles may adversely affect the performance of optoelectronics by absorbing or scattering the light beams.
Corrosivity of smoke produced by materials is characterized by the corrosion index (CI), defined as material loss rate (angstrom/minute) per amount of material gasified products (grams) per volume of air (m3). It is measured by exposing strips of metal to flow of combustion products in a test tunnel. Polymers containing halogen and hydrogen ( polyvinyl chloride, polyolefins with halogenated additives, etc.) have the highest CI as the corrosive acids are formed directly with water produced by the combustion, polymers containing halogen only (e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene) have lower CI as the formation of acid is limited to reactions with airborne humidity, and halogen-free materials (polyolefins, wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
) have the lowest CI. However, some halogen-free materials can also release significant amount of corrosive products.
Smoke damage to electronic equipment can be significantly more extensive than the fire itself. Electrical cable, Cable fires are of special concern; low smoke zero halogen materials are preferable for cable insulation.
When smoke comes into contact with the surface of any substance or structure, the chemicals contained in it are transferred to it. The corrosive properties of the chemicals cause the substance or structure to decompose at a rapid rate. Certain materials or structures absorb these chemicals, which is why clothing, unsealed surfaces, potable water, piping, wood, etc., are replaced in most cases of structural fires.
Health effects of wood smoke
 Wood smoke is a major source of air pollution, especially particulate pollution, pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde.
In the United Kingdom domestic combustion, especially for industrial uses, is the largest single source of PM2.5 annually. In some towns and cities in New South Wales, wood smoke may be responsible for 60% of fine particle air pollution in the winter. A year-long sampling campaign in Athens, Greece found a third (31%) of PAH urban air pollution to be caused by wood-burning, roughly as much as that of Diesel locomotive, diesel and Crude oil, oil (33%) and gasoline (29%). It also found that wood-burning is responsible for nearly half (43%) of annual PAH lung cancer-risk compared to the other sources and that wintertime PAH levels were 7 times higher than in other seasons, presumably due to an increased use of fireplaces and heaters. The largest exposure events are periods during the winter with reduced atmospheric dispersion to dilute the accumulated pollution, in particular due to the low wind speeds. Research conducted about biomass burning in 2015, estimated that 38% of European total particulate pollution emissions are composed of domestic wood burning.
Wood smoke (for example from
Wood smoke is a major source of air pollution, especially particulate pollution, pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde.
In the United Kingdom domestic combustion, especially for industrial uses, is the largest single source of PM2.5 annually. In some towns and cities in New South Wales, wood smoke may be responsible for 60% of fine particle air pollution in the winter. A year-long sampling campaign in Athens, Greece found a third (31%) of PAH urban air pollution to be caused by wood-burning, roughly as much as that of Diesel locomotive, diesel and Crude oil, oil (33%) and gasoline (29%). It also found that wood-burning is responsible for nearly half (43%) of annual PAH lung cancer-risk compared to the other sources and that wintertime PAH levels were 7 times higher than in other seasons, presumably due to an increased use of fireplaces and heaters. The largest exposure events are periods during the winter with reduced atmospheric dispersion to dilute the accumulated pollution, in particular due to the low wind speeds. Research conducted about biomass burning in 2015, estimated that 38% of European total particulate pollution emissions are composed of domestic wood burning.
Wood smoke (for example from wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s or wood ovens) can cause lung damage, artery damage and DNA damage leading to cancer, other respiratory and lung disease and cardiovascular disease. Air pollution, particulate matter and wood smoke may also cause brain damage because of particulates breaching the cardiovascular system and into the brain, which can increase the risk of developmental disorders, neurodegenerative disorders mental disorders, and suicidal behavior, although studies on the link between Depression (clinical), depression and some air pollutants are not consistent. At least one study has identified "the abundant presence in the human brain of magnetite nanoparticles that match precisely the high-temperature magnetite nanospheres, formed by combustion and/or friction-derived heating, which are prolific in urban, airborne particulate matter (PM)." Air pollution has also been linked to a range of other psychosocial problems.
Measurement
As early as the 15th century Leonardo da Vinci commented at length on the difficulty of assessing smoke, and distinguished between black carbon, black smoke (carbonized particles) and white 'smoke' which is not a smoke at all but merely a suspension of harmless water particulates. Smoke from heating appliances is commonly measured in one of the following ways: In-line capture. A smoke sample is simply sucked through a filter which is weighed before and after the test and the mass of smoke found. This is the simplest and probably the most accurate method, but can only be used where the smoke concentration is slight, as the filter can quickly become blocked. The ASTM smoke pump is a simple and widely used method of in-line capture where a measured volume of smoke is pulled through a filter paper and the dark spot so formed is compared with a standard. Filter/dilution tunnel. A smoke sample is drawn through a tube where it is diluted with air, the resulting smoke/air mixture is then pulled through a filter and weighed. This is the internationally recognized method of measuring smoke fromcombustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
.
Electrostatic precipitation. The smoke is passed through an array of metal tubes which contain suspended wires. A (huge) electrical potential is applied across the tubes and wires so that the smoke particles become charged and are attracted to the sides of the tubes. This method can over-read by capturing harmless condensates, or under-read due to the insulating effect of the smoke. However, it is the necessary method for assessing volumes of smoke too great to be forced through a filter, i.e., from bituminous coal.
Ringelmann scale. A measure of smoke color. Invented by Professor Maximilian Ringelmann in Paris in 1888, it is essentially a card with squares of black, white and shades of gray which is held up and the comparative grayness of the smoke judged. Highly dependent on light conditions and the skill of the observer it allocates a grayness number from 0 (white) to 5 (black) which has only a passing relationship to the actual quantity of smoke. Nonetheless, the simplicity of the Ringelmann scale means that it has been adopted as a standard in many countries.
Optical scattering. A light beam is passed through the smoke. A light detector is situated at an angle to the light source, typically at 90°, so that it receives only light reflected from passing particles. A measurement is made of the light received which will be higher as the concentration of smoke particles becomes higher.
Optical obscuration. A light beam is passed through the smoke and a detector opposite measures the light. The more smoke particles are present between the two, the less light will be measured.
Combined optical methods. There are various proprietary optical smoke measurement devices such as the 'nephelometer' or the 'aethalometer' which use several different optical methods, including more than one wavelength of light, inside a single instrument and apply an algorithm to give a good estimate of smoke. It has been claimed that these devices can differentiate types of smoke and so their probable source can be inferred, though this is disputed.
Inference from carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
. Smoke is incompletely burned fuel, carbon monoxide is incompletely burned carbon, therefore it has long been assumed that measurement of CO in flue gas (a cheap, simple and very accurate procedure) will provide a good indication of the levels of smoke. Indeed, several jurisdictions use CO measurement as the basis of smoke control. However it is far from clear how accurate the correspondence is.
Medicinal smoking
Throughout recorded history, humans have used the smoke of medicinal plants to cure illness. A sculpture from Persepolis shows Darius the Great (522–486 BC), the king of Persia, with two censers in front of him for burning Peganum harmala and/or sandalwood Santalum album, which was believed to protect the king from evil and disease. More than 300 plant species in 5 continents are used in smoke form for different diseases. As a method of drug administration, smoking is important as it is a simple, inexpensive, but very effective method of extracting particles containing active agents. More importantly, generating smoke reduces the particle size to a microscopic scale thereby increasing the absorption of its active chemical principles.See also
* Air purifier * Bonfire * Great Smog of London * Health impacts of sawdust * Inversion (meteorology) * Joss paper * Open burning of waste * Smog * Ultrafine particleReferences
Sources
*External links
'Fire inversions' lock smoke in valleys
{{Authority control Fire Smoke, Pollution Air pollution