|
Softwood
file:Pinus sylvestris wood ray section 1 beentree.jpg, Scots Pine, a typical and well-known softwood Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees. The main differences between hardwoods and softwoods is that the structure of hardwoods lack resin canals, whereas softwoods lack pores (though not all softwoods have resin canals). Characteristics Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as pines and spruces. Softwoods are not necessarily softer than hardwoods. In both groups there is an enormous variation in actual wood hardness, the range of density in hardwoods completely including that of softwoods. Some hardwoods (e.g. balsa) are softer than most softwoods, while the hardest hardwoods are much harder than any softwood. The woods of longleaf pine, Douglas fir, and Taxus, yew are much harder in the mechanical sense than several hardwoods. Softwoods are generally most used by the construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or woodchips or fiber. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from angiosperm trees) contrasts with softwood (which is from gymnosperm trees). Characteristics Hardwoods are produced by angiosperm trees that reproduce by flowers, and have broad leaves. Many species are deciduous. Those of temperate regions lose their leaves every autumn as temperatures fall and are dormant in the winter, but those of tropical regions may shed their leaves in response to seasonal or sporadic periods of drought. Hardwood from deciduous species, such as oak, normally shows annual growth rings, but these may be absent in some tropical hardwoods. Hardwoods have a more complex structure than softwoods and are often much slower growing as a result. The dominant feature separating "hardwoods" from softwoods is the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper Pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Hemlock
''Tsuga heterophylla'', the western hemlock or western hemlock-spruce, is a species of hemlock native to the west coast of North America, with its northwestern limit on the Kenai Peninsula, Alaska, and its southeastern limit in northern Sonoma County, California.Farjon, A. (1990). ''Pinaceae. Drawings and Descriptions of the Genera''. Koeltz Scientific Books .Gymnosperm Database''Tsuga heterophylla'' The Latin species name means 'variable leaves'. Description Western hemlock is a large evergreen conifer growing to tall, exceptionally ,Tallest Hemlock, M. D. Vaden, Arborist''Tallest known Hemlock, Tsuga heterophylla''/ref> and with a trunk diameter of up to . It is the largest species of hemlock, with the next largest (mountain hemlock ''Tsuga mertensiana'', known as mountain hemlock, is a species of hemlock native to the west coast of North America, found between Southcentral Alaska and south-central California. Description ''Tsuga mertensiana'' is a large evergreen coni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class (biology), class, Pinopsida. All Neontology, extant conifers are perennial plant, perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include Cedrus, cedars, Pseudotsuga, Douglas-firs, Cupressaceae, cypresses, firs, junipers, Agathis, kauri, larches, pines, Tsuga, hemlocks, Sequoioideae, redwoods, spruces, and Taxaceae, yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecology, ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck (building)
In architecture, a deck is a flat surface capable of supporting weight, similar to a floor, but typically constructed outdoors, often elevated from the ground, and usually connected to a building. The term is a generalization from the deck of a ship. A level architectural deck may be intended for use by people, e.g., what in the UK is usually called a decked patio. "Roof deck" refers to the flat layer of construction materials to which the weather impervious layers are attached to a form a roof. It is known as the "roof deck", and they may be either level (for a "flat" rooftop) or sloped. Functions and materials Wood or timber decking can be used in a number of ways: as part of garden landscaping, to extend the living area of a house, and as an alternative to stone-based features such as patios. Decks are made from treated lumber, composite lumber, composite material, and aluminum. Lumber may be western red cedar, teak, mahogany, ipê, reclaimed and recycled ulin and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parana Pine
''Araucaria angustifolia'', the Paraná pine, Brazilian pine or candelabra tree (, or ), is a critically endangered species in the conifer genus ''Araucaria''. Although the common names in various languages refer to the species as a "pine", it does not belong in the genus ''Pinus''. Origin and taxonomy The genus ''Araucaria'' was part of terrestrial flora since the Triassic and found its apogee in Gondwana. Today, it is restricted to the Southern Hemisphere and has 19 species. Distribution Covering an original area of , it has now lost an estimated 97% of its habitat to logging, agriculture, and silviculture. It is native to southern Brazil (also found in high-altitude areas of southern Minas Gerais, in central Rio de Janeiro and in the east and south of São Paulo, but more typically in the states of Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul). According to a study made by Brazilian researcher Reinhard Maack, the original area of occurrence represented 36.67% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Radiata
''Pinus radiata'' ( syn. ''Pinus insignis''), the Monterey pine, insignis pine or radiata pine, is a species of pine native to the Central Coast of California and Mexico (Guadalupe Island and Cedros island). It is an evergreen conifer in the family Pinaceae. ''P. radiata'' is a versatile, fast-growing, medium-density softwood, suitable for a wide range of uses. Its silviculture reflects a century of research, observation and practice. It is often considered a model for growers of other plantation species. It is the most widely planted pine in the world, valued for rapid growth and desirable lumber and pulp qualities. Although ''P. radiata'' is extensively cultivated as a plantation timber in many temperate parts of the world, it faces serious threats in its natural range, due to the introduction of pine pitch canker (''Fusarium circinatum''). Description ''P. radiata'' is a coniferous evergreen tree growing to tall in the wild, but up to in cultivation in optimum conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Spruce
''Picea abies'', the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. It has branchlets that typically hang downwards, and the largest cones of any spruce, 9–17 cm long. It is very closely related to the Siberian spruce (''Picea obovata''), which replaces it east of the Ural Mountains, and with which it hybridizes freely. The Norway spruce has a wide distribution for it being planted for its wood, and is the species used as the main Christmas tree in several countries around the world. It was the first gymnosperm to have its genome sequenced. The Latin specific epithet ''abies'' means “like ''Abies'', Fir tree” Description Norway spruce is a large, fast-growing evergreen coniferous tree growing tall and with a trunk diameter of 1 to 1.5 m. It can grow fast when young, up to 1 m per year for the first 25 years under good conditions, but becomes slower once over tall. The shoots are orange-brown and glabrous. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
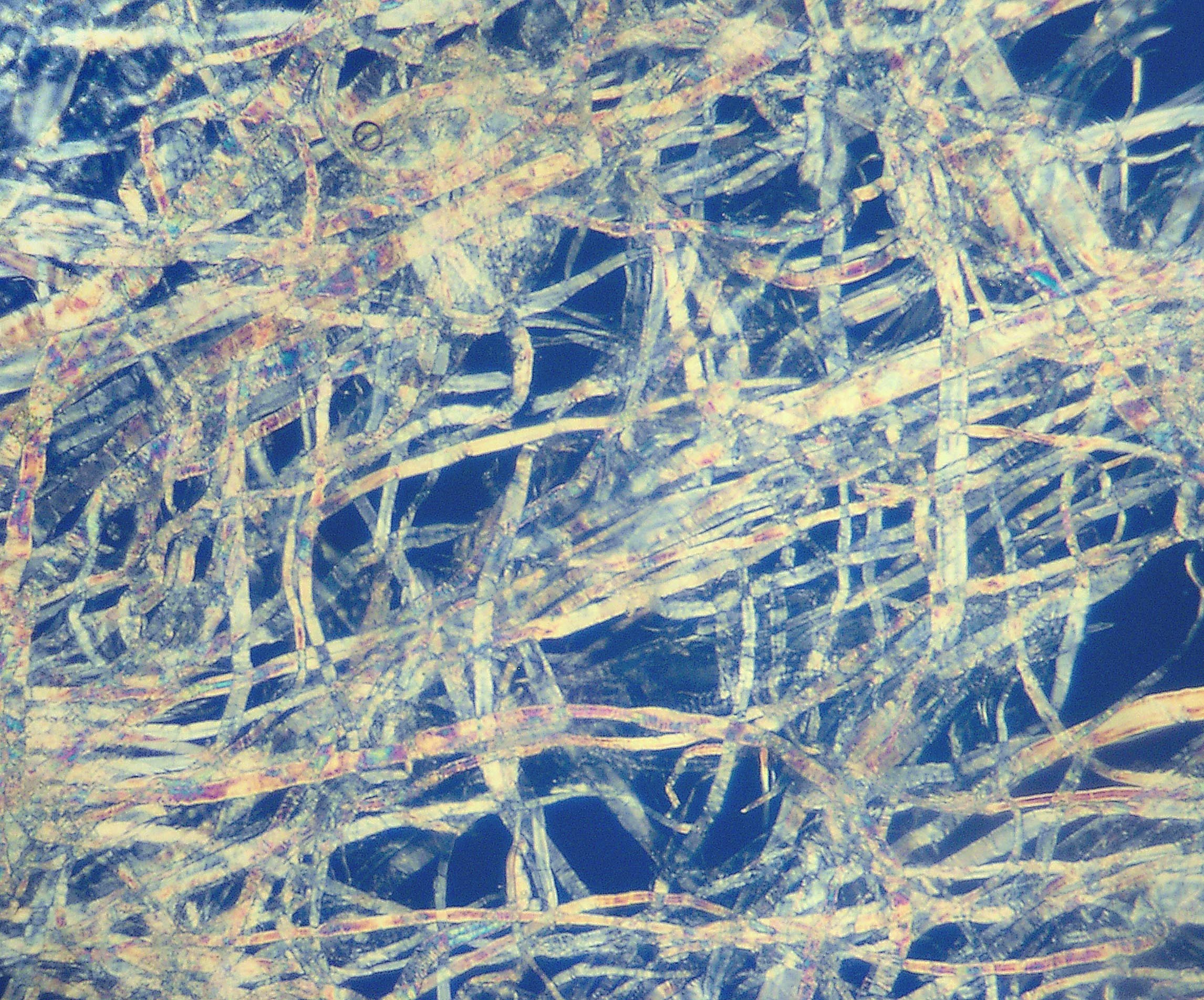
Pinus Sylvestris Wood Ray Section 1 Beentree
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 187 species names of pines as current, together with more synonyms. The American Conifer Society (ACS) and the Royal Horticultural Society accept 121 species. Pines are commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere. ''Pine'' may also refer to the lumber derived from pine trees; it is one of the more extensively used types of lumber. The pine family is the largest conifer family and there are currently 818 named cultivars (or Trinomial nomenclature, trinomials) recognized by the ACS. Description Pine trees are evergreen, coniferous resinous trees (or, rarely, shrubs) growing tall, with the majority of species reaching tall. The smallest are Siberian dwarf pine and Potosi pinyon, and the tallest is an tall ponderosa pine lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''menziesii''), Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca'') and Mexican Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''lindleyana''). Despite its common names, it is not a true fir (genus ''Abies''), spruce (genus '' Picea''), or pine (genus ''Pinus''). It is also not a hemlock; the genus name ''Pseudotsuga'' means "false hemlock". Description Douglas-firs are medium-size to extremely large evergreen trees, tall (although only ''Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii'', common name coast Douglas-firs, reach heights near 100 m) and commonly reach in diameter, although trees with diameters of almost exist. The largest coast Douglas-firs regularly live over 500 years, with the old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |