Sikh Religious Leaders on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late

 During the rule of the Mughal Empire in India, two Sikh gurus were martyred. ( Guru Arjan was martyred on suspicion of helping in betrayal of Mughal Emperor
During the rule of the Mughal Empire in India, two Sikh gurus were martyred. ( Guru Arjan was martyred on suspicion of helping in betrayal of Mughal Emperor 

 After defeating the
After defeating the
 After the annexation of the Sikh kingdom by the British, the British Army began recruiting significant numbers of Sikhs and
After the annexation of the Sikh kingdom by the British, the British Army began recruiting significant numbers of Sikhs and
 The five Ks (''panj kakaar'') are five articles of faith which all baptized (''Amritdhari'') Sikhs are obliged to wear. The symbols represent the ideals of Sikhism: honesty, equality, fidelity, meditating on Waheguru, and never bowing to tyranny.
The five symbols are:
#'' Kesh'': Uncut hair, usually tied and wrapped in a '' turban''.
#'' Kanga'': A wooden comb, usually worn under a ''turban'' to always also keep one's hair clean and well-groomed.
#'' Kachera'': Cotton undergarments, worn by both sexes; the ''kachera'' is a symbol of chastity, and also a symbol of cleanliness. It is also historically appropriate in battle due to increased mobility and comfort when compared to a '' dhoti''.
#'' Kara'': An iron bracelet, a symbol of eternity, strength, and a constant reminder of the strength of will to keep hands away from any kind of unethical practices.
#'' Kirpan'': An iron blade in different sizes. In the UK, Sikhs can wear a small dagger, but in Punjab, they might wear a traditional curved sword from one to three feet in length. ''Kirpan'' is only a weapon of defense and religious protection, used to serve humanity and to be used against oppression.
The five Ks (''panj kakaar'') are five articles of faith which all baptized (''Amritdhari'') Sikhs are obliged to wear. The symbols represent the ideals of Sikhism: honesty, equality, fidelity, meditating on Waheguru, and never bowing to tyranny.
The five symbols are:
#'' Kesh'': Uncut hair, usually tied and wrapped in a '' turban''.
#'' Kanga'': A wooden comb, usually worn under a ''turban'' to always also keep one's hair clean and well-groomed.
#'' Kachera'': Cotton undergarments, worn by both sexes; the ''kachera'' is a symbol of chastity, and also a symbol of cleanliness. It is also historically appropriate in battle due to increased mobility and comfort when compared to a '' dhoti''.
#'' Kara'': An iron bracelet, a symbol of eternity, strength, and a constant reminder of the strength of will to keep hands away from any kind of unethical practices.
#'' Kirpan'': An iron blade in different sizes. In the UK, Sikhs can wear a small dagger, but in Punjab, they might wear a traditional curved sword from one to three feet in length. ''Kirpan'' is only a weapon of defense and religious protection, used to serve humanity and to be used against oppression.
 The Sikhs have a number of musical instruments, including the
The Sikhs have a number of musical instruments, including the
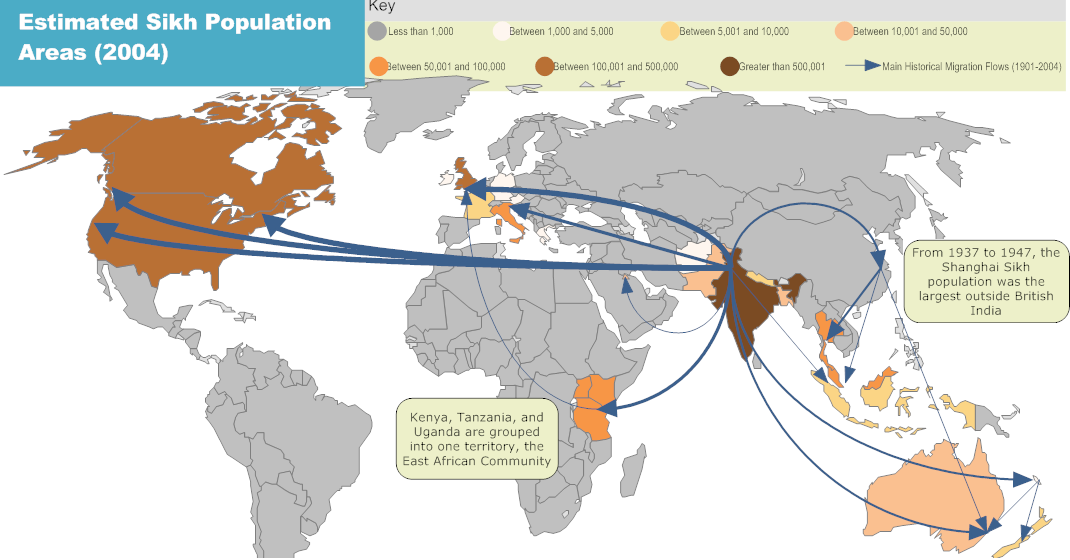 After the
After the
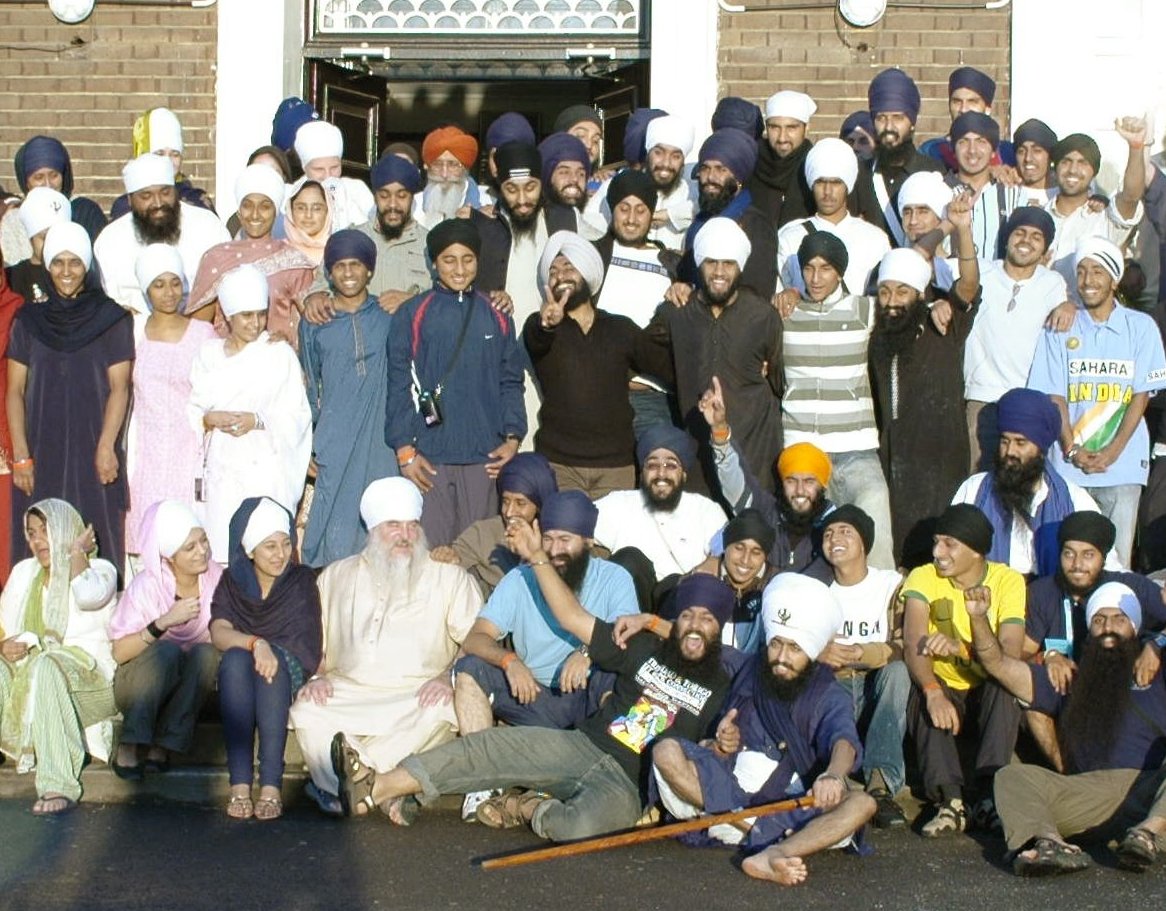 Johnson and Barrett (2004) estimate that the global Sikh population increases annually by 392,633 (1.7% per year, based on 2004 figures); this percentage includes births, deaths, and conversions. Primarily for socio-economic reasons,
Johnson and Barrett (2004) estimate that the global Sikh population increases annually by 392,633 (1.7% per year, based on 2004 figures); this percentage includes births, deaths, and conversions. Primarily for socio-economic reasons,
The Scheduled Castes in the Sikh Community: A Historical Perspective
. ''Economic & Political Weekly'' 38(26):2693–701. . Republished in ''Dalits in Regional Context'' (2004). . In the Shiromani Gurdwara Prabandhak Committee, 20 of the 140 seats are reserved for low-caste Sikhs. Other castes (over 1,000 members) include the Arain,
File:Sikhs in the First World War Q24777.jpg, Sikhs in the First World War, marching with their scripture, Guru Granth Sahib
File:SikhsInFrancePostcard.jpg, alt=Postcard of marching Sikhs with rifles, French postcard depicting the arrival of the 15th Sikh Regiment in France during World War I; the bilingual postcard reads, "Gentlemen of India marching to chasten the German hooligans"
File:Indian sikh soldiers in Italian campaign.jpg, Indian Sikh soldiers in the Italian campaign
File:Sikh soldier with captured Swastika flag.jpg, Sikh soldier with captured
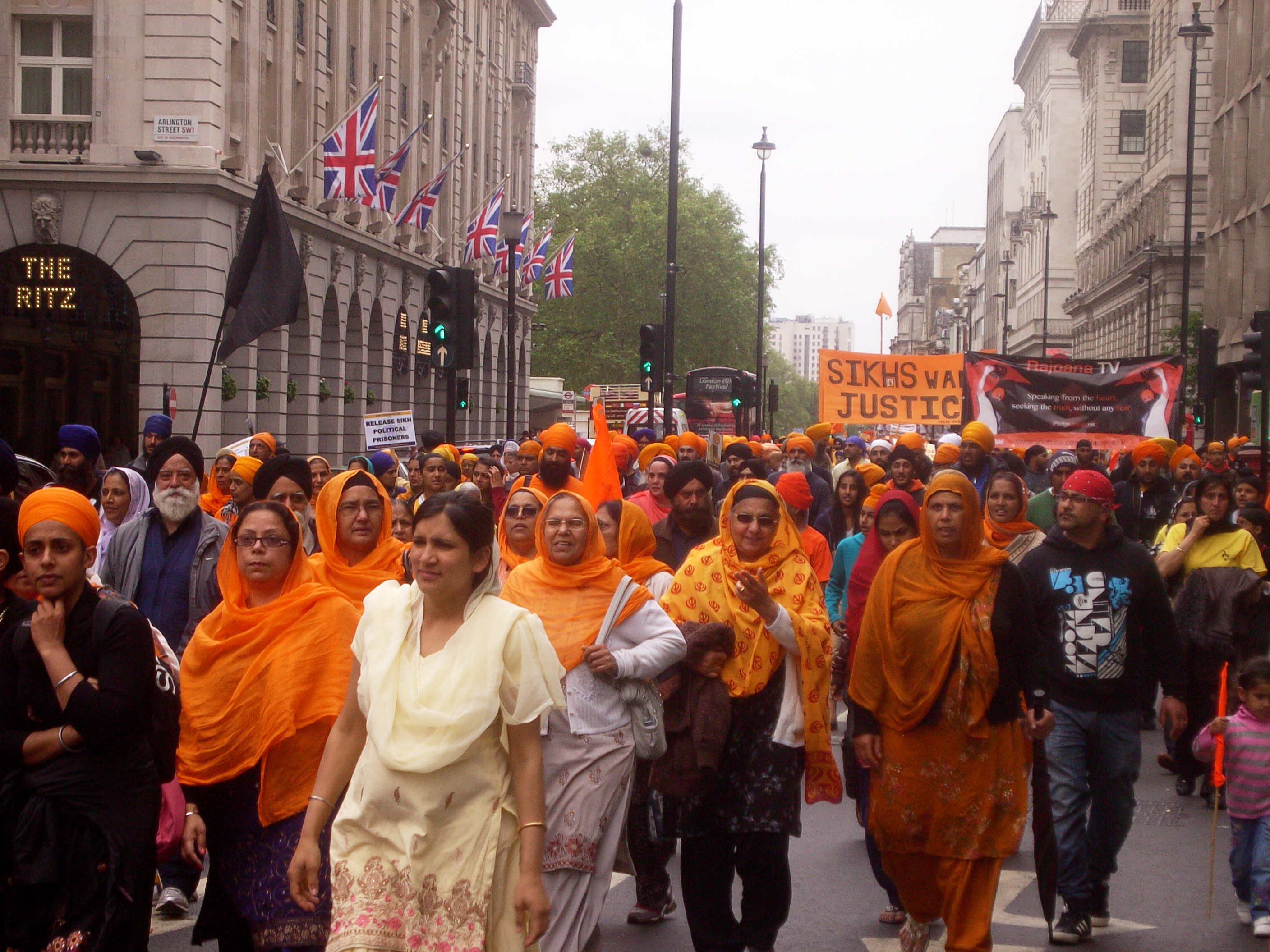 The Khalistan movement is a Sikh separatist movement, which seeks to create a separate country called Khalistān ("The Land of the Khalsa") in the Punjab region of South Asia to serve as a homeland for Sikhs. The territorial definition of the proposed country Khalistan consists of both the Punjab, India, along with Punjab, Pakistan, and includes parts of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh,
The Khalistan movement is a Sikh separatist movement, which seeks to create a separate country called Khalistān ("The Land of the Khalsa") in the Punjab region of South Asia to serve as a homeland for Sikhs. The territorial definition of the proposed country Khalistan consists of both the Punjab, India, along with Punjab, Pakistan, and includes parts of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh,
 Sikh art and culture are nearly synonymous with that of Punjab, and Sikhs are easily recognised by their distinctive turban ( Dastar). Punjab has been called India's melting pot, due to the confluence of invading cultures from the rivers from which the region gets its name. Sikh culture is therefore a synthesis of cultures. Sikhism has forged a unique architecture, which S. S. Bhatti described as "inspired by
Sikh art and culture are nearly synonymous with that of Punjab, and Sikhs are easily recognised by their distinctive turban ( Dastar). Punjab has been called India's melting pot, due to the confluence of invading cultures from the rivers from which the region gets its name. Sikh culture is therefore a synthesis of cultures. Sikhism has forged a unique architecture, which S. S. Bhatti described as "inspired by
The Construction of Religious Boundaries: Culture, Identity, and Diversity in the Sikh Tradition
' - H Oberoi - 1994 University of Chicago Press, . * ''Architectural Heritage of a Sikh State: Faridkot'' by Subhash Parihar, Delhi: Aryan Books International, 2009, . * ''A Study of Religions'' by R. M. Chopra, Anuradha Prakashan, New Delhi, 2015. .
Sikhism
at the BBC {{Sikhism Ethno-cultural designations Ethnoreligious groups Punjabi words and phrases Religious identity
15th century
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD).
In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period.
M ...
in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
region of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated wor ...
. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'.
Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh
Singh (Help:IPA, IPA: ) is a title, middle name or surname that means "lion" in various South Asian and Southeast Asian communities. Traditionally used by the Hindu Kshatriya community, it eventually became a common surname adopted by different ...
'' ('lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
'/'tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus '' Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on u ...
') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur
Kaur ( pa, ਕੌਰ (Gurmukhi), pa, کور (Shahmukhi) en, crown prince) (sometimes spelled as ''Kour''), is a surname or a part of a personal name primarily used by the Sikh and Hindu women of Punjab region. "Kaur" is also sometimes trans ...
'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world.
Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar
Amrit Sanchar (Gurmukhi: ਅੰਮ੍ਰਿਤ ਸੰਸਕਾਰ "nectar ceremony"; also called Amrit Parchar, or Khande di Pahul ਖੰਡੇ ਦੀ ਪਾਹੁਲ) is one of the four Sikh Sanskaars. The Amrit Sanskar is the initiation rite ...
'' ('baptism by Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of their initiation known as Khalsa, and they must at all times have on their bodies five Ks:
# ''kesh'', uncut hair usually kept covered by a dastār, also known as a turban;
# ''kara'', an iron or steel bracelet;
# '' kirpan'', a dagger-like sword tucked into a ''gatra'' strap or a ''kamar kasa'' waistband;
# '' kachera'', a cotton undergarment; and
# ''kanga'', a small wooden comb.
The Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent has been the historic homeland of the Sikhs, having even been ruled by the Sikhs for significant parts of the 18th and 19th centuries. Today, Canada has the largest national Sikh proportion (2.1%) in the world, while Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
state in India has the largest Sikh proportion (58%) amongst all administrative divisions in the world. Many countries, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, recognize Sikhs as a designated religion on their censuses, and, as of 2020, Sikhs are considered as a separate ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
in the United States.
History

Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated wor ...
(1469–1539), the founder of Sikhism, was born in a Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
family to Mehta Kalu and Mata Tripta in the village of Talwandi, present-day Nankana Sahib, near Lahore. Throughout his life, Guru Nanak was a religious leader and social reformer. However, Sikh political history may be said to begin in 1606, with the death of the fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjan Dev. Religious practices were formalised by Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Sing ...
on 30 March 1699, when the Guru initiated five people from a variety of social backgrounds, known as the '' Panj Piare'' ("beloved five"), to form a collective body of initiated Sikhs, known as the '' Khalsa'' ("pure").
The early followers of Guru Nanak were Khatris, but later a large number of Jats joined the faith. Khatris and Brahmins opposed "the demand that the Sikhs set aside the distinctive customs of their castes and families, including the older rituals."
 During the rule of the Mughal Empire in India, two Sikh gurus were martyred. ( Guru Arjan was martyred on suspicion of helping in betrayal of Mughal Emperor
During the rule of the Mughal Empire in India, two Sikh gurus were martyred. ( Guru Arjan was martyred on suspicion of helping in betrayal of Mughal Emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
and Guru Tegh Bahadur was martyred by the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
for opposing their persecution of Kashmiri pandits.) As the Sikh faith grew, the Sikhs subsequently militarized to oppose Mughal rule. Guru Gobind Singh Ji
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind S ...
was assassinated in 1708 by two pathans.


 After defeating the
After defeating the Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry f ...
and Mughals, sovereign states called Misl
The Misls (derived from an Arabic word wikt:مثل#Etymology_3, مِثْل meaning 'equal') were the twelve sovereign states of the Sikh Confederacy, which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian ...
s were formed under Jassa Singh Ahluwalia. The Confederacy of these states was unified and transformed into the Sikh Empire under Maharaja Ranjit Singh. This era was characterised by religious tolerance and pluralism
Pluralism denotes a diversity of views or stands rather than a single approach or method.
Pluralism or pluralist may refer to:
Politics and law
* Pluralism (political philosophy), the acknowledgement of a diversity of political systems
* Plur ...
, including Christians, Muslims, and Hindus in positions of power. Its secular administration implemented military, economic, and governmental reforms. The empire is considered the zenith of political Sikhism, encompassing Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, Ladakh, and Peshawar. Hari Singh Nalwa, the commander-in-chief of the Sikh Khalsa Army in the North-West Frontier, expanded the confederacy to the Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (خیبر درہ) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by traversing pa ...
.
British rule in India
 After the annexation of the Sikh kingdom by the British, the British Army began recruiting significant numbers of Sikhs and
After the annexation of the Sikh kingdom by the British, the British Army began recruiting significant numbers of Sikhs and Punjabis
The Punjabis ( Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. The ...
. During the 1857 Indian mutiny
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the fo ...
, the Sikhs stayed loyal to the British, resulting in heavy recruitment from Punjab to the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
for the next 90 years of the British Raj in colonial India
Colonial India was the part of the Indian subcontinent that was occupied by European colonial powers during the Age of Discovery. European power was exerted both by conquest and trade, especially in spices.
The search for the wealth and prosper ...
. The distinct turban that differentiates a Sikh from other turban wearers is a relic of the rules of the British Indian Army. The British colonial rule saw the emergence of many reform movements in India, including Punjab, such as the formation of the First and Second Singh Sabha in 1873 and 1879 respectively. The Sikh leaders of the Singh Sabha worked to offer a clear definition of Sikh identity and tried to purify Sikh belief and practice.
The later years of British colonial rule saw the emergence of the Akali movement to bring reform in the gurdwaras during the early 1920s. The movement led to the introduction of ''Sikh Gurdwara Bill'' in 1925, which placed all the historical Sikh shrines in India under the control of the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee.
Partition and post-Partition
At the time of the Indian independence movement, the Sikh ruler of theKapurthala State
Kapurthala State, with its capital at Kapurthala, was a former Princely state of Punjab. Ruled by Ahluwalia
Sikh rulers, spread across . According to the 1901 census the state had a population of 314,341 and contained two towns and 167 village ...
fought to oppose the partition of India and advocated for a united, secular country. Sikh organizations, including the Chief Khalsa Dewan and Shiromani Akali Dal led by Master Tara Singh, condemned the Lahore Resolution and the movement to create Pakistan, viewing it as inviting possible persecution. The Sikhs therefore strongly fought against the partition of India. The months leading up to the 1947 partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
were marked by conflict in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
between Sikhs and Muslims. This caused the religious migration of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from West Punjab to the east (modern India), mirroring a simultaneous religious migration of Punjabi Muslims from East Punjab to the west (modern Pakistan).
Following partition, the Government of India had begun to redraw states corresponding to demographic and linguistic boundaries. However, this was not effective in the northern part of the country, as the government reconsidered redrawing states in the north. While states across the country were extensively redrawn on linguistic lines at the behest of linguistic groups, the only languages not considered for statehood were Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, Sindhi and Urdu. Leading to the launch of the Punjabi Suba movement and the presentation for a Punjabi Suba as a policy in April 1948 by Master Tara Singh. Also, on 26 January 1950 Sikh representatives refused to sign the Indian constitution. As Sikhs were recognized as Hindus and Sikhs were not provided with scheduled castes concessions given to Hindu scheduled castes.
The Punjab Suba experienced heavy government crackdown with the Congress Government arresting as many as 21,000 people. Attempted negotiations with Congress-led the agitation to be adjourned twice, though Jawaharlal Nehru continued to reject the demand. On 4 July 1955, government police forces, led by DIG
Digging, also referred to as excavation, is the process of using some implement such as claws, hands, manual tools or heavy equipment, to remove material from a solid surface, usually soil, sand or rock (geology), rock on the surface of Earth. Di ...
Ashwini Kumar, would forced entry into the Golden Temple premises and heavy-handedly arrested protestors and took them into custody, along with the head granthis of the Akal Takht and Golden Temple, volunteer protestors, and even cooks of the temple's langar. The Guru Ram Das Serai and Shiromani Akali Dal offices were also raided, and batons used and tear gas and shells were fired to disperse the protestors gathered on the periphery of the temple, damaging the periphery and Sarovar, or pool, of the temple. The government stopped volunteers on the way to the Golden Temple, and troops were ordered to flag-march through the bazaars and streets surrounding the site. Over 200 protestors were killed, thousands arrested, and thousands, including women and children, were injured.
The Congress government agreed to the Punjab Suba in 1966 after protests and recommendation of the States Reorganisation Commission. The state of East Punjab was later split into the states of Himachal Pradesh, the new state Haryana and current day Punjab. However, there was a growing alienation between Punjabi Sikh and Hindu populations. The latter of which reported Hindi rather than Punjabi as their primary language. The result was that Punjabi-speaking areas were left out of the new state and given to Haryana and Himachal Pradesh resulting in the state of Punjab to be roughly 35,000 square miles smaller than the Punjabi-speaking areas based on pre-1947 census figures. Moreover, the 1966 reorganization left Sikhs highly dissatisfied, with the capital Chandigarh being made into a shared a union territory and the capital of Punjab and Haryana.
In the late 1960s, the Green Revolution in India was first introduced in Punjab as part of a development program issued by international donor agencies and the Government of India. While, Green Revolution in Punjab had several positive impacts, the introduction of the mechanised agricultural techniques led to uneven distribution of wealth. The industrial development was not done at the same pace as agricultural development, the Indian government had been reluctant to set up heavy industries in Punjab due to its status as a high-risk border state with Pakistan. The rapid increase in the higher education opportunities without an adequate rise in the jobs resulted in the increase in the unemployment of educated youth.
In 1973 as a result, of unaddressed grievances and increasing inequality the Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Akali Party'') is a centre-right sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are man ...
put forward the Anandpur Sahib Resolution
The Anandpur Sahib Resolution was a statement with a list of demands made by the Punjabi Sikh political party, the Shiromani Akali Dal, in 1973.
Presentation in 1973
After the tenure of chief minister Gurnam Singh in the Punjab, newly demarcated ...
. The resolution included both religious and political issues. It asked for recognising Sikhism as a religion, it also demanded the devolution of power from the Central to state governments. The Anandpur Resolution was rejected by the government as a secessionist document. Thousands of people joined the movement, feeling that it represented a real solution to demands such as a larger share of water for irrigation and the return of Chandigarh to Punjab.
After unsuccessful negotiations the Dharam Yuddh Morcha ("righteous campaign") was launched on 4 August 1982, by the Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Akali Party'') is a centre-right sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are man ...
in partnership with Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale, with its stated aim being the fulfillment of a set of devolutionary objectives based on the Anandpur Sahib Resolution
The Anandpur Sahib Resolution was a statement with a list of demands made by the Punjabi Sikh political party, the Shiromani Akali Dal, in 1973.
Presentation in 1973
After the tenure of chief minister Gurnam Singh in the Punjab, newly demarcated ...
. Indian police responded to protestors with high-handed police methods creating state repression affecting a very large segment of Punjab's population. Police brutality resulted in retaliatory violence from a section of the Sikh population, widening the scope of the conflict by the use of violence of the state on its own people. A "state of chaos and repressive police methods" combined to create "a mood of overwhelming anger and resentment in the Sikh masses against the authorities". Leading to Sikh leader Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale gaining prominence and demands of independence gain currency, even amongst moderates and Sikh intellectuals. In, 1982 and early 1983 extrajudicial killings by the police of orthodox Sikh youth in rural areas in Punjab provoked reprisals. Over 190 Sikhs had been killed in the first 19 months of the protest movement.
In May 1984, a ''Grain Roko morcha'' was planned and to be initiated on 3June with protestors practising civil disobedience by refusing to pay land revenue, water or electricity bills, and blocking the flow of grain out of Punjab. Indian Prime minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
launched Operation Blue Star on 1June prior to the Grain Roko morcha in order to remove Bhindranwale from the Golden Temple. This subsequently lead to Gandhi's assassination by her Sikh bodyguards. Her assassination was followed by riots against Sikh communities and the killing of thousands of Sikhs throughout India. These events triggered an Insurgency in Punjab which would consume Punjab until the early 1990s.
During the day of Vaisakhi in 1999, Sikhs worldwide celebrated the 300th anniversary of the creation of the Khalsa. Canada Post honoured Sikh Canadians with a commemorative stamp in conjunction with the anniversary. Likewise, on 9 April 1999, Indian president K. R. Narayanan
Kocheril Raman Narayanan (27 October 1921 – 9 November 2005) was an Indian statesman, diplomat, academic, and politician who served as the 9th vice president of India, Vice President of India from 1992 to 1997 and 10th President of India fr ...
issued a stamp commemorating the 300th anniversary of the Khalsa as well.
Culture and religious observations
According to Article I of Chapter 1 of the Sikh ''Rehat Maryada'' ('code of conduct'), the definition of Sikh is:Any human being who faithfully believes in i. One Immortal Being, ii. Ten Gurus, from Guru Nanak Sahib to Guru Gobind Singh Sahib, iii. The Guru Granth Sahib, iv. The utterances and teachings of the ten Gurus and v. the baptism bequeathed by the tenth Guru, and who does not owe allegiance to any other religion, is a Sikh.
Daily routine
From the Guru Granth Sahib: The Sikh Rahit Maryada (Code of Conduct) clearly states thatbaptized
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
Amritdhari Khalsa Sikhs must recite or listen to the recitation of Japji Sahib, Jaap Sahib, the 10 Sawayyas, Sodar Rehraas, and Sohila The collection of hymns called Sohila is repeated at bedtime by Sikhs. It consists of three hymns of Guru Nanak, one of Guru Ram Das, and one of Guru Arjan. The word Sohila is derived from ''sowam wela'' or ''saana-na-wela'' meaning in the Punjabi a ...
. Every Sikh is also supposed take the Hukam (divine order) from the Guru Granth Sahib after awakening in the ambrosial hours of the morning (three hours before the dawn) before eating.
In his 52 Hukams, Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Sing ...
orders his followers to arise during Amritvela (early morning) and to recite the late evening prayer "Sohila The collection of hymns called Sohila is repeated at bedtime by Sikhs. It consists of three hymns of Guru Nanak, one of Guru Ram Das, and one of Guru Arjan. The word Sohila is derived from ''sowam wela'' or ''saana-na-wela'' meaning in the Punjabi a ...
" and the verse "Pavan guru pani pita..." before sleeping.
Five Ks
Music and instruments
 The Sikhs have a number of musical instruments, including the
The Sikhs have a number of musical instruments, including the rebab
The ''rebab'' ( ar, ربابة, ''rabāba'', variously spelled ''rebap'', ''rubob'', ''rebeb'', ''rababa'', ''rabeba'', ''robab'', ''rubab'', ''rebob'', etc) is the name of several related string instruments that independently spread via I ...
, dilruba, taus, jori, and sarinda
Sarinda may refer to:
* ''Sarinda'', a genus of jumping spiders
* Sarinda, an Indian stringed instrument
{{disambig ...
. Playing the sarangi was encouraged by Guru Hargobind. The rebab was played by Bhai Mardana as he accompanied Guru Nanak on his journeys. The jori and sarinda were introduced to Sikh devotional music by Guru Arjan. The ''taus'' (Persian for "peacock") was designed by Guru Hargobind, who supposedly heard a peacock singing and wanted to create an instrument mimicking its sounds. The dilruba was designed by Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Sing ...
at the request of his followers, who wanted a smaller instrument than the taus. After Japji Sahib, all of the shabad in the Guru Granth Sahib were composed as raags. This type of singing is known as Gurmat Sangeet.
When they marched into battle, the Sikhs would play a ''Ranjit nagara'' ("victory drum") to boost morale. Nagaras (usually two to three feet in diameter, although some were up to five feet in diameter) are played with two sticks. The beat of the large drums, and the raising of the Nishan Sahib, meant that the Singhs were on their way.
Demographics
Sikhs number about 25-30 million worldwide, of whom 22–28 million live in India, which thus represents around 90% of the total Sikh population. About 76% of all Indian Sikhs live in the northern Indian State of Punjab, forming a majority of about 58 per cent of the state's population, roughly around 16 million. Karnail Singh Panjoli, member of the Shiromani Gurdwara Prabandhak Committee, says that there are several communities within the term Nanakpanthis too. Apart from Sindhi Hindus, "There are groups like Sikhligarh, Vanjaarey, Nirmaley, Lubaney, Johri, Satnamiye, Udaasiyas, Punjabi Hindus, etc. who call themselves Nanakpanthis despite being Hindus. Substantial communities of Sikhs live in the Indian states or union territories of Haryana, where they number around 1.2 million and form 4.91% of the population, Rajasthan (872k, or 1.27% of the population), Uttar Pradesh (643k, 0.32%), Delhi (570k, 3.4%), Uttarakhand (236k, 2.34%),Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
(234k, 1.87%), Chandigarh (138k, 13.11%) and Himachal Pradesh (86k, 1.16%).
Canada is home to the largest national Sikh proportion (2.1 percent of the total population) in the world. A substantial community of Sikhs exist in the western province of British Columbia, numbering nearly 300,000 persons and forming approximately 5.9 percent of the total population. This represents the third-largest Sikh proportion amongst all global administrative divisions, behind only Punjab and Chandigarh in India. Furthermore, British Columbia, Manitoba, and Yukon hold the distinction of being three of the only four administrative divisions in the world with Sikhism as the second most followed religion among the population.
Migration
Sikh migration from British India began in earnest during the second half of the 19th century, when the British completed their annexation of the Punjab, which led to Sikh migration throughout India and the British Empire. During the Raj, semiskilled Sikh artisans were transported from the Punjab to British East Africa to help build railroads. Sikhs emigrated from India after World War II, most going to the United Kingdom but many also to North America. Some Sikhs who had settled in eastern Africa were expelled by Ugandan dictator Idi Amin in 1972. Economics is a major factor in Sikh migration, and significant communities exist in the United Kingdom, the United States, Malaysia,East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Singapore and Thailand.
 After the
After the Partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
in 1947, many Sikhs from what would become the Punjab of Pakistan
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the ...
migrated to India as well as to Afghanistan due to fear of persecution. Afghanistan was home to hundreds of thousands of Sikhs and Hindus as of the 1970s, but due to the wars in Afghanistan in the 2010s, the vast majority of Afghan Sikhs had migrated to India, Pakistan or the west.
Although the rate of Sikh migration from the Punjab has remained high, traditional patterns of Sikh migration favouring English-speaking countries (particularly the United Kingdom) have changed during the past decade due to stricter immigration laws. Moliner (2006) wrote that as a consequence of Sikh migration to the UK becoming "virtually impossible since the late 1970s," migration patterns evolved to continental Europe. Italy is a rapidly growing destination for Sikh migration, with Reggio Emilia
Reggio nell'Emilia ( egl, Rèz; la, Regium Lepidi), usually referred to as Reggio Emilia, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, and known until 1861 as Reggio di Lombardia, is a city in northern Italy, in the Emilia-Romagna region. It has abou ...
and Vicenza having significant Sikh population clusters. Italian Sikhs are generally involved in agriculture, agricultural processing, the manufacture of machine tools, and horticulture.
Growth
 Johnson and Barrett (2004) estimate that the global Sikh population increases annually by 392,633 (1.7% per year, based on 2004 figures); this percentage includes births, deaths, and conversions. Primarily for socio-economic reasons,
Johnson and Barrett (2004) estimate that the global Sikh population increases annually by 392,633 (1.7% per year, based on 2004 figures); this percentage includes births, deaths, and conversions. Primarily for socio-economic reasons, Indian Sikhs
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
have the lowest adjusted growth rate of any major religious group in India, at 16.9 percent per decade (estimated from 1991 to 2001) and it have further declined to just 8.4 per cent in 2011 census report. Sikhs in the world have the lowest fertility rate of 1.6 children per women as per (2019–20) estimation research. The Sikh population has the lowest gender balance in India, with only 903 women per 1,000 men according to the 2011 Indian census. The estimated world's Sikh population was over 30 million in 2020, and it will reach 42 million by 2050. It is expected to increase up to 62 million by 2100, given that the anticipated growth rate of 1.7% per year and adding at least 400,000 followers annually.
Sikhism is the fastest growing religion in Canada, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and New Zealand.
Castes
Since Sikhism has never actively sought converts, Sikhs have remained a relatively homogeneous ethnic group.Caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
may still be practiced by some Sikhs, despite Guru Nanak's calls for treating everyone equally in Sri Granth Sahib.
Along with Guru Nanak, other Sikh gurus had also denounced the hierarchy of the caste system, however, they all belonged to the same caste, the Khatris. Most Sikhs belong to the Jat (Jatt), traditionally agrarian in occupation. Despite being very small in numbers, the Khatri and Arora
Arora is a community of Punjab, comprising both Hindus and Sikhs. The name is derived from their native place Aror.
Historically, the Arora section of the Khatri community had been principally found in West Punjab, in the districts to the sou ...
(Moneylenders) castes also wield considerable influence within the Sikh community. Other common Sikh castes include Ahluwalias (brewers), ''Kambojs'' or ''Kambos'' (rural caste), ''Ramgarhias'' (artisans), Brahman (Priestly class), Rajputs (kshatriyas), ''Sainis'' ( agrarian), ''Rai'' Sikh (rural caste), ''Labanas'' (merchants), ''Kumhars'', ''Mazhabi
Mazhabi Sikh (also known as Mazbhabi, Mazbhi, Majhabhi or Majabhi) is a community from Northern India, especially Punjab region, who follow Sikhism. The word ''Mazhabi'' is derived from the Arabic term ''mazhab'' (Mazhab means religion or sect ...
'' and the Ramdasia/ ''Ravidasias''(Chamar).
Some Sikhs, especially those belonging to the landowning dominant castes, have not shed all their prejudices against the Dalits. While Dalits were allowed entry into the village gurdwaras, in some gurdwaras, they were not be permitted to cook or serve ''langar'' (communal meal). Therefore, wherever they could mobilize resources, the Sikh Dalits of Punjab have tried to construct their own gurdwara and other local level institutions in order to attain a certain degree of cultural autonomy. In 1953, Sikh leader and activist Master Tara Singh succeeded in persuading the Indian government to include Sikh castes of the converted untouchables in the list of scheduled castes.Puri, Harish K. (2003).The Scheduled Castes in the Sikh Community: A Historical Perspective
. ''Economic & Political Weekly'' 38(26):2693–701. . Republished in ''Dalits in Regional Context'' (2004). . In the Shiromani Gurdwara Prabandhak Committee, 20 of the 140 seats are reserved for low-caste Sikhs. Other castes (over 1,000 members) include the Arain,
Bhatra
The Bhatra Sikhs (also known as Bhat Sikhs) are a sub-group within the Sikhs who originated from the bards of the time of Guru Nanak. In the 20th century publication A Glossary of the Tribes and Castes of the Punjab and North-West Frontier Pr ...
, Bairagi, Bania, Basith, Bawaria, Bazigar
Bazigar (from fa, بازیگر bazi + gar), or Goaars, are an ethnic group of north-western India. They are primarily found in Punjab and in Pakistan's Punjab, but there are also communities in Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Chandigarh, Himachal ...
, Bhabra, Chamar, Chhimba (cotton farmers), Darzi, Dhobi, Gujar, Jhinwar, Kahar, Kalal
The Kalwar, Kalal or Kalar are an Indian caste historically found in Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Jammu & Kashmir and other parts of north and central India. The caste is traditionally associated with the distillation and selling ...
, Kumhar, Lohar, Mahtam
The Mahtam are a clan found among the Punjabis of India and Pakistan. They practice Hindu, Sikh and Muslim religions.
During British rule in India, they were stigmatised under the Criminal Tribes Act 1871.Megh Megh may refer to
* Megh (raga), a classical Indian raga
* Meghwal, a people of northwest India and Pakistan
* Cyclone Megh, a cyclone in the Arabian sea that struck the island of Socotra in 2015
*Rain. another name for rain in Gujarati
Gujarati ma ...
, Mirasi, Mochi, Nai
Nai or NAI may refer to:
Music
* ''Nai'' (album), an album by singer Anna Vissi
* Nai (pan flute), a wind instrument, also known as a pan flute (Romania and Moldova)
* "Nai" (song), a 2007 CD single by Irini Merkouri
Organizations
* National A ...
, Ramgharia
The Ramgarhia is a caste from the Punjab region of northwestern India, encompassing members of the Lohar and Tarkhan subgroups.
Etymology
Originally called Thoka, meaning ''carpenter'', the Ramgarhia are named after Jassa Singh Ramgarhia, whos ...
, Sansi, Sudh, Tarkhan and Kashyap
3HO
The 3HO(Healthy, Happy, Holy) organization or Sikh Dharma International claims to have inspired a moderate growth in non-Indian adherents of Sikhism. They are mainly centered around Española, New Mexico, and Los Angeles, California, United States of America.Diaspora
As Sikhs wear turbans and keep beards, Sikh men in Western countries have been mistaken forMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Arabic, and/or Afghan since the September 11 attacks and the Iraq War. Several days after the 9/11 attacks, Sikh-American gas station owner Balbir Singh Sodhi was murdered in Arizona by a man who took Sodhi to be a member of al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
, marking the first recorded hate-crime in America motivated by 9/11. CNN would go on to suggest an increase in hate crimes against Sikh men in the US and the UK after the 9/11 attacks.
In an attempt to foster Sikh leaders in the Western world, youth initiatives by a number of organisations exist. The Sikh Youth Alliance of North America sponsors an annual Sikh Youth Symposium
The Sikh Youth Symposium is an annual public speaking and debate competition held for the Sikh youth across the United States of America and Canada, encouraging them to reconnect with their cultural foundations and religious roots. Organized by ...
.
The Sikh diaspora has been most successful in the UK, and UK Sikhs have the highest percentage of home ownership (82%) of any religious community. UK Sikhs are the second-wealthiest religious group in the UK (after the Jewish community), with a median total household wealth of .
In May 2019, the UK government exempted " Kirpan" from the list of banned knives. The U.K. government passed an amendment by which Sikhs in the country would be allowed to carry kirpans and use them during religious and cultural functions. The bill was amended to ensure that it would not impact the right of the British Sikh community to possess and supply kirpans, or religious swords. Similarly, the Sikh American Legal Defense and Education Fund overturned a 1925 Oregon law banning the wearing of turbans by teachers and government officials in 2010.
Agriculture
Historically, most Indians have been farmers and 66 per cent of the Indian population are engaged in agriculture. Indian Sikhs are employed in agriculture to a lesser extent; India's 2001 census found 39 per cent of the working population of the Punjab employed in this sector. According to the Swedish political scientist Ishtiaq Ahmad, a factor in the success of the Indian green revolution was the "Sikh cultivator, often the Jat and Kamboj or Kamboh, whose courage, perseverance, spirit of enterprise and muscle prowess proved crucial." However, Indian physicist Vandana Shiva wrote that the green revolution made the "negative and destructive impacts of science (i.e. the green revolution) on nature and society" invisible, and was a catalyst for Punjabi Sikh and Hindu tensions despite a growth in material wealth.Sikhs in modern history
Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh (; born 26 September 1932) is an Indian politician, economist and statesman who served as the 13th prime minister of India from 2004 to 2014. He is also the third longest-serving prime minister after Jawaharlal Nehru and Indir ...
is an Indian economist, academic, and politician who served as the 13th Prime Minister of India from 2004 to 2014. The first and only Sikh and non-Hindu in office, Singh was also the first prime minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to be re-elected after completing a full five-year term.
Notable Sikhs in science include nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
scientist Piara Singh Gill
Piara Singh Gill (28October 1911 – 23March 2002) was an Indian nuclear physicist and a pioneer in cosmic ray nuclear physics.''Up Against Odds: Autobiography of an Indian Scientist''. (South Asia Books, 1993. ) He was the first Director of ...
, fibre-optics pioneer Narinder Singh Kapany
Narinder Singh Kapany FREng (31 October 1926 – 4 December 2020) was an Indian-American physicist best known for his work on fiber optics.
; and physicist, science writer and broadcaster Simon Singh.
In business, the UK-based clothing retailers New Look and the Thai-based JASPAL were founded by Sikhs. India's largest pharmaceutical company, Ranbaxy Laboratories, is headed by Sikhs. Apollo Tyres
Apollo Tyres Limited is an Indian Multinational tyre manufacturing company headquartered in Gurugram, Haryana. It was incorporated in 1972, and its first plant was commissioned in Perambra in Chalakudy, Kerala (India). The company now has fiv ...
is headed by Onkar Singh Kanwar. In Singapore, Kartar Singh Thakral expanded his family's trading business, Thakral Holdings, into assets totalling almost and is Singapore's 25th-richest person. Sikh Bob Singh Dhillon is the first Indo-Canadian billionaire. Mastercard CEO
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especially ...
was a Sikh named Ajaypal Singh Banga
Ajaypal Singh Banga (born November 10, 1959) is an Indian-American business executive. He is currently Vice Chairman at General Atlantic. He was executive chairman of Mastercard, after having previously served as president and chief executive off ...
.
In sports, Sikhs include England cricketer Monty Panesar; former 400-metre runner Milkha Singh
Milkha Singh (20 November 1929 18 June 2021), also known as The Flying Sikh, was an Indian track and field sprinter who was introduced to the sport while serving in the Indian Army. He is the only athlete to win gold at 400 metres at the As ...
; his son, professional golfer Jeev Milkha Singh; Indian wrestler and actor Dara Singh
Dara Singh Randhawa (born Deedar Singh Randhawa; 19 November 1928 – 12 July 2012) was an Indian professional wrestler, actor, director and politician. He started acting in 1952 and was the first sportsman to be nominated to the Rajya Sab ...
; former Indian hockey team captains Sandeep Singh, Ajitpal Singh and Balbir Singh Sr.; former Indian cricket captain Bishen Singh Bedi; Harbhajan Singh, India's most successful off spin cricket bowler; Yuvraj Singh, World Cup winning allrounder; Maninder Singh, World Cup winning off spinner; and Navjot Singh Sidhu, former Indian cricketer-turned-politician.
Sikhs in Bollywood, in the arts in general, include poet and lyricist Rajkavi Inderjeet Singh Tulsi; Gulzar; Jagjit Singh; Dharmendra; Sunny Deol
Ajay Singh Deol (born 19 October 1956), better known by his stage name Sunny Deol, is an Indian actor, film director, producer, politician and current Member of Parliament from Gurdaspur (Lok Sabha constituency) of Punjab, India. As an actor, ...
; writer Khushwant Singh; actresses Neetu Singh, Simran Judge, Poonam Dhillon, Mahi Gill, Esha Deol, Parminder Nagra
Parminder Kaur Nagra (born 5 October 1975) is a British actress of Indian Punjabi descent and Sikh heritage. She is known for portraying Jess Bhamra in the film ''Bend It Like Beckham'' (2002) and Dr. Neela Rasgotra in the NBC medical drama s ...
, Gul Panag
Gul Panag (born Gulkirat Kaur Panag, 3 January 1979; Chandigarh, India) is an Indian actress, voice actress, model, and former beauty queen who competed in the Miss Universe pageant. Panag began her career in Bollywood with the 2003 film ''Dhoo ...
, Mona Singh, Namrata Singh Gujral; and directors Gurinder Chadha and Parminder Gill.
Sikhs in Punjabi Music industry include Sidhu Moosewala, Diljit Dosanjh, Babu Singh Maan, Surjit Bindrakhia
Surjit Bindrakhia (born Surjit Bains; 15 April 1962 – 17 November 2003) was a singer from Punjab, India. He was known for his unique voice and hekh, in which he sings a note continuously in one breath. His biggest hits include ''Meri Nath Dig ...
, Ammy Virk, Karan Aujla, Jazzy B, Miss Pooja.
In the Indian and British armies
According to a 1994 estimate, Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus comprised 10 to 15% of all ranks in the Indian Army. The Indian government does not release religious or ethnic origins of a military personnel, but a 1991 report by Tim McGirk estimated that 20% of Indian Army officers were Sikhs. Together with the Gurkhas recruited from Nepal, the Maratha Light Infantry from Maharashtra and the Jat Regiment, the Sikhs are one of the few communities to have exclusive regiments in the Indian Army. The Sikh Regiment is one of the most-decorated regiments in the army, with 73 Battle Honours, 14 Victoria Crosses, 21 first-class Indian Orders of Merit (equivalent to the Victoria Cross), 15 Theatre Honours, 5 COAS Unit Citations, two Param Vir Chakras, 14 Maha Vir Chakras, 5 Kirti Chakras, 67 Vir Chakras, and 1,596 other awards. The highest-ranking general in the history of the Indian Air Force is a Punjabi Sikh, Marshal of the Air Force Arjan Singh. Plans by the United Kingdom Ministry of Defence for a Sikh infantry regiment were scrapped in June 2007. Sikhs supported the British during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. By the beginning of World War I, Sikhs in theBritish Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
totaled over 100,000 (20 per cent of the force). Until 1945, fourteen Victoria Crosses (VC) were awarded to Sikhs, a per-capita regimental record. In 2002, the names of all Sikh VC and George Cross
The George Cross (GC) is the highest award bestowed by the British government for non-operational gallantry or gallantry not in the presence of an enemy. In the British honours system, the George Cross, since its introduction in 1940, has been ...
recipients were inscribed on the monument of the Memorial Gates on Constitution Hill Constitution Hill may refer to:
*Constitution Hill, New South Wales, Australia
*Constitution Hill, Aberystwyth
* Constitution Hill, Birmingham
* Constitution Hill, London, a road in the City of Westminster in London
* Constitution Hill, Swansea
*Con ...
, next to Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
. Chanan Singh Dhillon was instrumental in campaigning for the memorial.
During World War I, Sikh battalions fought in Egypt, Palestine, Mesopotamia, Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles ...
and France. Six battalions of the Sikh Regiment were raised during World War II, serving in the Second Battle of El Alamein, the Burma and Italian campaigns and in Iraq, receiving 27 battle honours. Around the world, Sikhs are commemorated in Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
cemeteries.
Swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍) is an ancient religious and cultural symbol, predominantly in various Eurasian, as well as some African and American cultures, now also widely recognized for its appropriation by the Nazi Party and by neo-Nazis. It ...
flag of Nazi Germany
File:Japanese shooting blindfolded Sikh prisoners.jpg, alt=See caption, Japanese soldiers shooting blindfolded Sikh prisoners in World War II
Khalistan movement
Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, and Rajasthan.''Amritsar to Lahore: A Journey Across the India-Pakistan Border'' - Stephen Alter "''Ever since the separatist movement gathered force in the 1980s, Pakistan has sided with the Sikhs, the territorial ambitions of Khalistan have at times included Chandigarh, sections of the Indian Punjab, including whole North India and some parts of western states of India.''"
Khalistan movement began as an expatriate venture. In 1971, the first explicit call for Khalistan was made in an advertisement published in the ''New York Times'' by an expat ( Jagjit Singh Chohan). By proclaiming the formation of Khalistan, he was able to collect millions of dollars from the Sikh diaspora. On 12 April 1980, he declared the formation of the "National Council of Khalistan", at Anandpur Sahib. He declared himself as the President of the council, and named Balbir Singh Sandhu as its Secretary General. In May 1980, Chohan traveled to London and announced the formation of Khalistan. A similar announcement was made by Balbir Singh Sandhu in Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
, where he began releasing stamps and currency of Khalistan. The inaction of the authorities in Amritsar and elsewhere was decried as a political stunt by the Congress(I)
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Em ...
party of Indira Gandhi by the Akali Dal, headed by the Sikh leader Harchand Singh Longowal.
The movement flourished in the Indian state of Punjab following Operation Blue Star. As proponents were able to generate funding from a grieving diaspora. In June 1985, Air India Flight 182 was bombed by Babbar Khalsa, a pro-Khalistani terrorist organization. In January 1986, the Golden Temple was occupied by militants belonging to All India Sikh Students Federation
The All India Sikh Students Federation (AISSF), is a Sikh student organisation and political organisation in India. AISSF was formed in 1943. as the youth wing of the Akali Dal, which is a Sikh political party in the Indian Punjab.
Origin
Befor ...
and Damdami Taksal. On 26 January 1986, a gathering known as the Sarbat Khalsa (a de facto parliament) passed a resolution (''gurmattā'') favouring the creation of Khalistan. Subsequently, a number of rebel militant groups in favour of Khalistan waged a major insurgency against the government of India. Indian security forces suppressed the insurgency in the early 1990s, but Sikh political groups such as the Khalsa Raj Party
Jagjit Singh Chohan was the founder of the Khalistan movement that sought to create an independent Sikh state in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
Politics
Jagjit Singh grew up in Tanda in Punjab's Hoshiarpur district, about 180 km ...
and SAD (A) continued to pursue an independent Khalistan through non-violent means. Pro-Khalistan organisations such as Dal Khalsa (International)
Dal Khalsa is a Sikh organisation, based in the city of Amritsar. The organisation was formed in 1978 and came to prominence under the inspiration and time of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale in 1981. The primary aim of Dal Khalsa is to achieve the i ...
are also active outside India, supported by a section of the Sikh diaspora.
In the 1990s, the insurgency abated, and the movement failed to reach its objective due to multiple reasons including a heavy police crackdown on separatists, divisions among the Sikhs and loss of support from the Sikh population. However, various pro-Khalistan groups, both political and militant, remain committed to the separatist movement. There are claims of funding from Sikhs outside India to attract young people into militant groups.
Art and culture
 Sikh art and culture are nearly synonymous with that of Punjab, and Sikhs are easily recognised by their distinctive turban ( Dastar). Punjab has been called India's melting pot, due to the confluence of invading cultures from the rivers from which the region gets its name. Sikh culture is therefore a synthesis of cultures. Sikhism has forged a unique architecture, which S. S. Bhatti described as "inspired by
Sikh art and culture are nearly synonymous with that of Punjab, and Sikhs are easily recognised by their distinctive turban ( Dastar). Punjab has been called India's melting pot, due to the confluence of invading cultures from the rivers from which the region gets its name. Sikh culture is therefore a synthesis of cultures. Sikhism has forged a unique architecture, which S. S. Bhatti described as "inspired by Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated wor ...
's creative mysticism" and "is a mute harbinger of holistic humanism based on pragmatic spirituality". The American non-profit organization United Sikhs has fought to have Sikh included on the U.S. census as well, arguing that Sikhs "self-identify as an ethnic minority" and believe "that they are more than just a religion".
During the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
and Afghan persecution of the Sikhs during the 17th and 18th centuries, the latter were concerned with preserving their religion and gave little thought to art and culture. With the rise of Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839), popularly known as Sher-e-Punjab or "Lion of Punjab", was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire, which ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He s ...
and the Sikh Raj
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore ...
in Lahore and Delhi, there was a change in the landscape of art and culture in Punjab; Hindus and Sikhs could build decorated shrines without the fear of destruction or looting.
The Sikh Confederacy was the catalyst for a uniquely Sikh form of expression, with Ranjit Singh commissioning forts, palaces, bungas (residential places), and colleges in a Sikh style. Sikh architecture is characterised by gilded fluted domes, cupolas, kiosks, stone lanterns, ornate baluster
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its cons ...
s, and square roofs. A pinnacle of Sikh style is Harmandir Sahib (also known as the Golden Temple) in Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
.
Sikh culture is influenced by militaristic motifs (with the Khanda the most obvious), and most Sikh artifacts—except for the relics of the Gurus—have a military theme. This theme is evident in the Sikh festivals of Hola Mohalla and Vaisakhi, which feature marching and displays of valor.
Although the art and culture of the Sikh diaspora have merged with that of other Indo-immigrant groups into categories like "British Asian", "Indo-Canadian" and "Desi-Culture", a minor cultural phenomenon that can be described as "political Sikh" has arisen. The art of diaspora Sikhs like Amarjeet Kaur Nandhra, and Amrit and Rabindra Kaur Singh (The Singh Twins
The Singh Twins (twin sisters Amrit Singh MBE and Rabindra Kaur Singh MBE) are British artists who work together on their artworks. Their work draws on both traditional Indian (in particular, Sikh) tradition, Western medieval illuminated manuscript ...
) is influenced by their Sikhism and current affairs in Punjab.
Bhangra and Giddha
Giddha ( pa, گدها, ਗਿੱਧਾ, ) is a popular folk dance of women in the Punjab region. The dance is often considered derived from the ancient dance known as the ring dance and is just as energetic as bhangra; at the same time it ma ...
are two forms of Punjabi folk dancing which have been adapted and pioneered by Sikhs. Punjabi Sikhs have championed these forms of expression worldwide, resulting in Sikh culture becoming linked to Bhangra (although "Bhangra is not a Sikh institution but a Punjabi one").
Painting
Sikh painting is a direct offshoot of the Kangra school of painting. In 1810, Ranjeet Singh (1780–1839) occupied Kangra Fort and appointed Sardar Desa Singh Majithia his governor of the Punjab hills. In 1813, the Sikh army occupied Guler State, and Raja Bhup Singh became a vassal of the Sikhs. With the Sikh kingdom of Lahore becoming the paramount power, some of the Pahari painters from Guler migrated to Lahore for the patronage of Maharaja Ranjeet Singh and his Sardars. The Sikh school adapted Kangra painting to Sikh needs and ideals. Its main subjects are the ten Sikh gurus and stories from Guru Nanak'sJanamsakhi
The Janamsakhis ( pa, ਜਨਮਸਾਖੀ, IAST: ''Janam-sākhī'', ''lit.'' ''birth stories''), are legendary biographies of Guru Nanak – the founder of Sikhism. Popular in the Sikh history, these texts are considered by scholars as imagina ...
s. The tenth Guru, Gobind Singh, left a deep impression on the followers of the new faith because of his courage and sacrifices. Hunting scenes and portraits are also common in Sikh painting.
From 2007 to present renowned Sikh painter Kanwar Singh has been creating exceptional paintings exclusively devoted to the Sikh religion and history for over ten years. His work is continually exhibited world-wide in prominent heritage sites such as the Virasat-e-Khalsa museum at Anandpur Sahib. A travelling art exhibition has been launched called, Journey of the Mind commencing its UK tour in the city of Birmingham before moving onto Bristol, Nottingham, Glasgow and London throughout 2022 and 2023.
Shrines
There is an old Sikh shrine called 'Prachin Guru Nanak Math', which lies at a small hill, just next to Bishnumati bridge at Balaju. Guru Nanak is said to have visited Nepal during his third Udasi while returning from Mount Kailash in Tibet. Nanak is said to have stayed at Balaju and Thapathali in Kathmandu. The Nanal Math shrine at Balaju is managed by the Guru-Ji and the Udasin Akardha, a sect developed by Guru Nanak's son, Sri Chandra.See also
* History of Punjab * Ganga Sagar (urn) * Jat Sikh * List of British Sikhs * Mazhabi Sikh * Sikhism by country * Sikhism in India * Turban training centreExplanatory notes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
* *Further reading
* ''The Sikhs in History: A Millennium Study'' by Sangat Singh, Noel Quinton King. New York, 1995. . * ''A History of the Sikhs: Volume 1: 1469–1838'' by Khushwant Singh. Oxford India Paperbacks (13 January 2005). . * ''The Sikhs'' by Patwant Singh. Image (17 July 2001). * ''The Sikhs of the Punjab'' by J. S. Grewal. Published by Cambridge University Press (28 October 1998). . * ''The Sikhs: History, Religion, and Society'' by W. H. McLeod. Published by Columbia University Press (15 April 1989). * ''The Sikh Diaspora: Tradition and Change in an Immigrant Community (Asian Americans — Reconceptualising Culture, History, Politics)'' by Michael Angelo. Published by Routledge (1 September 1997). . * ''Glory of Sikhism'' by R. M. Chopra, Sanbun Publishers, 2001, , . * ''The Philosophical and Religious Thought of Sikhism'' by R. M. Chopra, 2014, Sparrow Publication, Kolkata, . *The Construction of Religious Boundaries: Culture, Identity, and Diversity in the Sikh Tradition
' - H Oberoi - 1994 University of Chicago Press, . * ''Architectural Heritage of a Sikh State: Faridkot'' by Subhash Parihar, Delhi: Aryan Books International, 2009, . * ''A Study of Religions'' by R. M. Chopra, Anuradha Prakashan, New Delhi, 2015. .
External links
Sikhism
at the BBC {{Sikhism Ethno-cultural designations Ethnoreligious groups Punjabi words and phrases Religious identity