Sicilians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sicilians or the Sicilian people are a Romance speaking people who are indigenous to the island of Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the largest and most populous of the autonomous regions of Italy.
Technological and cultural change among the last Hunter-Gatherers of the Maghreb: the Capsian (10,000 B.P. to 6000 B.P.)
''Journal of World Prehistory'' 18(1): 57-105. Another archaeological site, originally identified by Paolo Orsi on the basis of a particular ceramic style, is the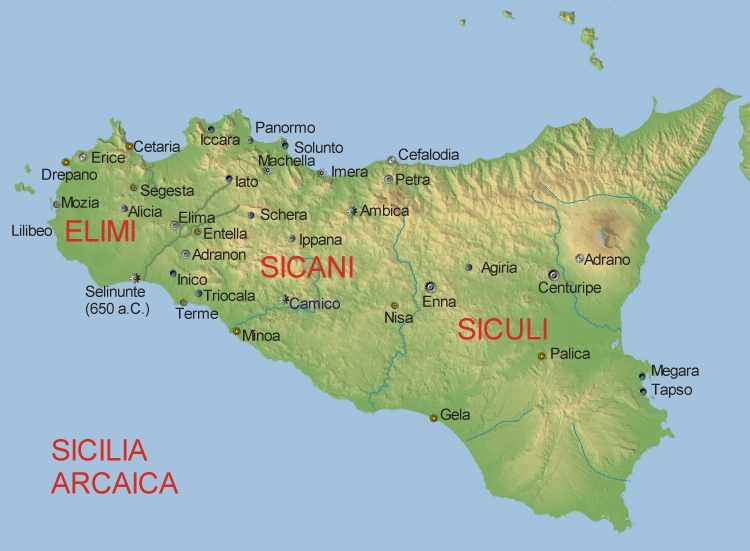
 In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring
In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring
 Sicily has experienced the presence of a number of different cultures and ethnicities in its vast history, including the aboriginal peoples of differing ethnolinguistic origins ( Sicani,
Sicily has experienced the presence of a number of different cultures and ethnicities in its vast history, including the aboriginal peoples of differing ethnolinguistic origins ( Sicani,
 Several studies involving whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from
Several studies involving whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from
 Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian and Sicilian, a distinct and historical
Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian and Sicilian, a distinct and historical
 * The
* The
Origin and influences
The Sicilian people are indigenous to the island of Sicily, which was first populated beginning in thePaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
and Neolithic periods. According to the famous Italian Historian Carlo Denina
Carlo Giovanni Maria Denina (1731, Revello – 5 December 1813, Paris) was an Italian historian. The unique contribution of Carlo Denina was to write a history of Italy from a “national” perspective, which significantly differed from other his ...
, the origin of the first inhabitants of Sicily is no less obscure than that of the first Italians, however, there is no doubt that a large part of these early individuals traveled to Sicily from Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
, others from the Islands of Greece, the coasts of West Asia, Iberia and West Europe.
Prehistory
The aboriginal inhabitants of Sicily, long absorbed into the population, were tribes known to the ancient Greek writers as the Elymians, theSicanians
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, ac ...
, and the Sicels
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, bu ...
, the latter being an Indo-European-speaking people of possible Italic affiliation, who migrated from the Italian mainland (likely from the Amalfi Coast or Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
via the Strait of Messina) during the second millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC.
In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era:
The first half of the mil ...
, after whom the island was named. The Elymian tribes have been speculated to be a Indo-European people who migrated to Sicily from either Central Anatolia, Southern-Coastal Anatolia, Calabria, or one of the Aegean Islands, or perhaps were a collection of native migratory maritime-based tribes from all previously mentioned regions, and formed a common "Elymian" tribal identity/basis after settling down in Sicily. When the Elymians migrated to Sicily is unknown, however scholars of antiquity considered them to be the second oldest inhabitants, while the Sicanians, thought to be the oldest inhabitants of Sicily by scholars of antiquity, were speculated to also be a pre-Indo-European tribe, who migrated via boat from the Xúquer river basin in Castellón, Cuenca, Valencia and Alicante
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in th ...
. Before the Sicanians lived in the easternmost part of the Iberian peninsula. The name 'Sicanus' has been asserted to have a possible link to the modern river known in Valencian as the Xúquer and in Castilian as the Júcar. The Beaker was introduced in Sicily from Sardinia and spread mainly in the north-west and south-west of the island. In the northwest and in the Palermo kept almost intact its cultural and social characteristics, while in the south-west there was a strong integration with local cultures. The only known single bell-shaped glass in eastern Sicily was found in Syracuse.The basic study is Joshua Whatmough in R.S. Conway, J. Whatmough and S.E. Johnson, ''The Prae-Italic Dialects of Italy'' (London 1933) vol. 2:431-500; a more recent study is A. Zamponi, "Il Siculo" in A.L. Prosdocimi, ed., ''Popoli e civiltà dell'Italia antica'', vol. 6 "Lingue e dialetti" (1978949-1012.)
All three tribes lived both a sedentary pastoral
A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music (pastorale) that depicts ...
and orchard farming lifestyle, and a semi-nomadic fishing, transhumance and mixed farming Mixed farming is a type of farming which involves both the growing of crops and the raising of livestock.
Such agriculture occurs across Asia and in countries such as India, Malaysia, Indonesia, Afghanistan, South Africa, China, Central Europe, Can ...
lifestyle. Prior to the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, Paleolithic Sicilians would have lived a hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
lifestyle, just like most human cultures before the Neolithic. The river Salsu was the territorial boundary between the Sicels and Sicanians. They wore basic clothing made of wool, plant fibre
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope.
Fiber crops are characterized by having a large concentration of cellulose, which is what gives them their strength. The fibers may b ...
, papyrus, esparto grass, animal skins
A hide or skin is an animal skin treated for human use.
The word "hide" is related to the German word "Haut" which means skin. The industry defines hides as "skins" of large animals ''e.g''. cow, buffalo; while skins refer to "skins" of smaller an ...
, palm leaves, leather and fur, and created everyday tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ba ...
, as well as weapons, using metal forging, woodworking and pottery. They typically lived in a nuclear family
A nuclear family, elementary family, cereal-packet family or conjugal family is a family group consisting of parents and their children (one or more), typically living in one home residence. It is in contrast to a single-parent family, the larger ...
unit, with some extended family members as well, usually within a drystone hut, a neolithic long house or a simple hut made of mud, stones, wood, palm leaves or grass. Their main methods of transportation were horseback, donkeys and chariots
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 ...
. Evidence of pet wildcats, cirneco dogs and children's toys have been discovered in archaeological digs, especially in cemetery tombs. Their diet was a typical Mediterranean diet, including unique food varieties such as Gaglioppo, Acitana and Diamante citron, while in modern times the Calabrian Salami, which is also produced in Sicily, and sometimes used to make spicy 'Nduja spreadable paste/sauce, is a popular type of salami sold in Brazil and the Anglosphere
The Anglosphere is a group of English-speaking world, English-speaking nations that share historical and cultural ties with England, and which today maintain close political, diplomatic and military co-operation. While the nations included in d ...
. All 3 tribes also specialised in building megalithic single-chambered dolmen tombs, a tradition which dates back to the Neolithic. "An important archaeological site, located in Southeast Sicily, is the Necropolis of Pantalica, a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs. Dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC., recent estimates suggest a figure of just under 4,000 tombs. They extend around the flanks of a large promontory located at the junction of the Anapo river
The Anapo ( Sicilian: ''Ànapu'') is a river in Sicily whose ancient Greek name is similar to the word for "swallowed up" LSJ sv. ἀναπίνω; ἀνάποσις and at many points on its course it runs underground. The Greek myth of Anapos ...
with its tributary, the Calcinara, about 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
. Together with the city of Syracuse, Pantalica was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2005. The site was mainly excavated between 1895 and 1910 by the Italian archeologist, Paolo Orsi, although most of the tombs had already been looted long before his time. Items found within the tombs of Pantalica, some now on display at the Archaeology Museum in Syracuse, were the characteristic red-burnished pottery vessels, and metal objects, including weaponry (small knives and daggers) and clothing, such as bronze fibulae (brooches) and rings, which were placed with the deceased in the tombs. Most of the tombs contained between one to seven individuals of all ages and both sexes. Many tombs were evidently re-opened periodically for more burials. The average human life span at this time was probably around 30 years of age, although the size of the prehistoric population is hard to estimate from the available data, but might have been around 1000 people."
Nuragic
The nuraghe (, ; plural: Logudorese Sardinian , Campidanese Sardinian , Italian ), or also nurhag in English, is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, developed during the Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 B.C. To ...
ceramic remains, (from Sardinia), carbon dated to the 13th century BC, have been found in Lipari. The prehistoric Thapsos culture, associated with the Sicani, shows noticeable influences from Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
.''Pantalica e i suoi monumenti'' di Paolo Orsi The type of burial found in the necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead".
The term usually im ...
of the Thapsos culture, is characterized by large rock-cut chamber tombs, and often of ''tholos-type'' that some scholars believe to be of Mycenaean derivation, while others believe it to be the traditional shape of the hut. The housing are made up of mostly circular huts bounded by stone walls, mainly in small numbers. Some huts have rectangular shape, particularly the roof. The economy was based on farming, herding, hunting and fishing. There are numerous evidences of trading networks, in particular of bronze vessels and weapons of Mycenaean and Nuragic (Sardinian) production. There were close trading relationships/networks established with the ''Milazzo Culture'' of the Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; it, Isole Eolie ; scn, Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after ...
, and with the Apennine culture of mainland southern Italy. In Sicily's earlier prehistory, there is also evidence of trade with the Capsian and Iberomaurusian mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
cultures from Tunisia, with some lithic stone sites attested in certain parts of the island.2005 D. Lubell. Continuité et changement dans l'Epipaléolithique du Maghreb. In, M. Sahnouni (ed.) ''Le Paléolithique en Afrique: l’histoire la plus longue'', pp. 205-226. Paris: Guides de la Préhistoire Mondiale, Éditions Artcom’/Errance.2004 N. RahmaniTechnological and cultural change among the last Hunter-Gatherers of the Maghreb: the Capsian (10,000 B.P. to 6000 B.P.)
''Journal of World Prehistory'' 18(1): 57-105. Another archaeological site, originally identified by Paolo Orsi on the basis of a particular ceramic style, is the
Castelluccio culture
Castelluccio culture is an archaeological feature dating to Ancient Bronze Age (2000 B.C. approximately) of the prehistoric civilization of Sicily, originally identified by Paolo Orsi on the basis of a particular ceramic style, in the homonymous vi ...
which dates back to the Ancient Bronze Age (2000 B.C. approximately), and is seen as sort of a "prehistoric proto-civilization", located between Noto and Siracusa. The discovery of a prehistoric village in Castelluccio di Noto, next to the remains of prehistoric circular huts, led to finds of Ceramic glass decorated with brown lines on a yellow-reddish background, and tri-color with the use of white. The weapons used in the days of Castelluccio culture were green stone and basalt axes and, in the most recent settlements, bronze axes, and frequently carved bones, considered idols similar to those of Malta, and of Troy II and III. Burials were made in rounded tombs carved into the rock, with doors with relief carving of spiral symbols and motifs that evoke the sexual act. The Castelluccio culture is dated to a period between 2200 BC and 1800 BC, although some believe it to be contemporary to the Middle-Late Helladic period (1800/1400 BC)." "Sites related to the Castelluccio culture were present in the villages of south-east Sicily, including Monte Casale
Monte Casale is a mountainous elevation on Sicily in Italy, reaching 910m above sea level, which (with the neighbouring Monte Lauro) formed part of the oldest volcanic formation of the Hyblaean Mountains. Their peaks form the boundary betwe ...
, Cava/Quarry d'Ispica, Pachino, Niscemi, Cava/Quarry Lazzaro, near Noto, of Rosolini, in the rocky Byzantine district of coastal Santa Febronia in Palagonia, in Cuddaru d' Crastu (Tornabé-Mercato d'Arrigo) near Pietraperzia, where there are remains of a fortress partly carved in stone, and - with different ceramic forms - also near Agrigento in Monte Grande. The discovery of a cup of 'Etna type' in the area of Comiso, among local ceramic objects led to the discovery of commercial trades with the Castelluccio sites of Paternò, Adrano and Biancavilla, whose graves differ in making due to the hard basaltic terrain and also for the utilization of the lava caves as chamber tombs. In the area around Ragusa, there have been found evidences of mining among the ancient residents of Castelluccio; tunnels excavated by the use of basalt bats allowed the extraction and production of highly sought flints. Some dolmens, dated back to this same period, with sole funeral function, are found in different parts of Sicily and attributable to a people not belonging to the Castelluccio Culture."
The Sicelian polytheistic worship of the ancient and native chthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
, animistic-cult deities associated with geysers known as the Palici, as well as the worship of the volcano-fire god by the name of Adranos
Adranus or Adranos ( Greek: ) was a fire god worshipped by the Sicels, an ancient population of the island of Sicily. His worship occurred all over the island, but particularly in the town of Adranus, modern Adrano, near Mount Etna. According to ...
, were also worshiped throughout Sicily by the Elymians and Sicanians. Their (Palici) centre of worship was originally based on three small lakes that emitted sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
ous vapors in the Palagonian plains, and as a result these twin brothers were associated with geysers and the underworld. There was also a shrine to the Palici in Palacia, where people could subject themselves or others to tests of reliability through divine judgement; passing meant that an oath could be trusted. The mythological lineage of the Palici is uncertain. According to Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
, the nymph Thalia gave birth to the divine twins while living underneath the Earth. They were most likely either the sons of the native fire god Adranos, or, as Polish historian "Krzysztof Tomasz Witczak" suggests, the Palici may derive from the old Proto-Indo-European mytheme
In structuralism-influenced studies of mythology, a mytheme is a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure (typically involving a relationship between a character, an event, and a theme) from which myths are thought to be constructed—a mi ...
of the divine twins. Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( it, Etna or ; scn, Muncibbeḍḍu or ; la, Aetna; grc, Αἴτνα and ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina a ...
is named after the mythological
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
Sicilian nymph called Aetna, who might have been the possible mother to the Palici twins. Mount Etna was also believed to have been the region where Zeus buried the Serpentine
Serpentine may refer to:
Shapes
* Serpentine shape, a shape resembling a serpent
* Serpentine curve, a mathematical curve
* Serpentine, a type of riding figure
Science and nature
* Serpentine subgroup, a group of minerals
* Serpentinite, a ...
giant Typhon, and the humanoid giant Enceladus in classical mythology. The Cyclopes, giant one eyed humanoid creatures in classical Greco-Roman mythology, known as the maker of Zeus' thunderbolts
A thunderbolt or lightning bolt is a symbolic representation of lightning when accompanied by a loud thunderclap. In Indo-European mythology, the thunderbolt was identified with the 'Sky Father'; this association is also found in later Hell ...
, were traditionally associated with Sicily and the Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; it, Isole Eolie ; scn, Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after ...
. The Cyclopes were said to have been assistants to the Greek blacksmith God Hephaestus, at his forge in Sicily, underneath Mount Etna, or perhaps on one of the nearby Aeolian Islands. The Aeolian Islands, off the coast of Northwestern Sicily, were themselves named after the mythological king and "keeper of the heavy winds" known as Aeolus. In his ''Hymn to Artemis'', Cyrene poet Callimachus states that the Cyclopes on the Aeolian island of Lipari, working "at the anvils of Hephaestus", make the bows and arrows used by Apollo and Artemis. The Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
ic Latin poet Ovid names three Cyclopes "Brontes, Steropes and Acmonides" working as forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to th ...
rs inside Sicilian caves.
Besides Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
(the Greek goddess of agriculture and law), and Persephone (the Greek personified
Personification occurs when a thing or abstraction is represented as a person, in literature or art, as a type of anthropomorphic metaphor. The type of personification discussed here excludes passing literary effects such as "Shadows hold their ...
goddess of vegetation), The Phoenician bull god Moloch (a significant deity also mentioned in the Hebrew Bible), the Phoenician moon goddess of fertility and prosperity
Prosperity is the flourishing, thriving, good fortune and successful social status. Prosperity often produces profuse wealth including other factors which can be profusely wealthy in all degrees, such as happiness and health.
Competing notion ...
Astarte (with her Roman equivalent being Venus), the Punic goddess Tanit, and the weather & war god Baal (which later evolved into the Carthaginian god Baal Hammon
Baal Hammon, properly Baʿal Ḥammon or Baʿal Ḥamon ( Phoenician: ; Punic: ), meaning “Lord Hammon”, was the chief god of Carthage. He was a weather god considered responsible for the fertility of vegetation and esteemed as King of the ...
), as well as the Carthaginian chief god Baal Hammon, also had centres of cultic-worship throughout Sicily. The river Anapo was viewed as the personification of the water god Anapos in Greek-Sicilian mythology. The Elymians inhabited the western parts of Sicily, while the Sicanians inhabited the central parts, and the Sicels inhabited the eastern parts. 
Ancient history
From the 11th century BC, Phoenicians began to settle in western Sicily, having already started colonies on the nearby parts of North Africa and Malta. Sicily was later colonized and heavily settled by Greeks, beginning in the 8th century BC. Initially, this was restricted to the eastern and southern parts of the island. As the Greek and Phoenician communities grew more populous and more powerful, the Sicels and Sicanians were pushed further into the centre of the island. The independent Phoenician colonial settlements were eventually absorbed by Carthage during the 6th Century BC. By the 3rd century BC,Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
was the most populous Greek city state in the world. Sicilian politics was intertwined with politics in Greece itself, leading Athens, for example, to mount the disastrous Sicilian Expedition against Syracuse in 415-413 BC during the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
, which ended up severely affecting a defeated Athens, both politically and economically, in the following years to come. Another battle which Syracuse took part in, this time under the Tyrant Hiero I of Syracuse, was the Battle of Cumae, where the combined navies
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
of Syracuse and Cumae defeated an Etruscan force, resulting in significant territorial loses for the Etruscans. The constant warfare between Ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states eventually opened the door to an emerging third power. In the 3rd century BC, the Messanan Crisis, caused by Mamertine mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
from Campania, when the city-states of Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
( Carthaginian-owned) and Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
( Dorian-owned) were being constantly raided and pillaged by Mamertines, during the period (282-240 BC) when Central, Western and Northeast Sicily were put under Carthaginian rule, motivated the intervention of the Roman Republic into Sicilian affairs, and led to the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
between Rome and Carthage. By the end of the war in 242 BC, and with the death of Hiero II
Hiero II ( el, Ἱέρων Β΄; c. 308 BC – 215 BC) was the Greek tyrant of Syracuse from 275 to 215 BC, and the illegitimate son of a Syracusan noble, Hierocles, who claimed descent from Gelon. He was a former general of Pyrrhus of Epirus a ...
, all of Sicily except Syracuse was in Roman hands, becoming Rome's first province outside of the Italian peninsula. For the next 600 years, Sicily would be a province of the Roman Republic and later Empire. Prior to Roman rule, there were three native Elymian towns by the names of Segesta, Eryx and Entella
Éntella (Greek language, Greek: ), was an ancient city in the interior of Sicily, situated on the left bank of the river Hypsas (modern Belice), and nearly midway between the two seas, being about 40 km from the mouth of the Hypsas, and ...
, as well as several Siculian towns called Agyrion, Kale Akte
Kale (), or leaf cabbage, belongs to a group of cabbage ('' Brassica oleracea'') cultivars grown for their edible leaves, although some are used as ornamentals. Kale plants have green or purple leaves, and the central leaves do not form a he ...
(founded by the Sicel leader Ducetius), Enna and Pantalica, and one Sicanian town known as Thapsos. ( Greek: Θάψος)
Sometime after Carthage conquered most of Sicily except for the Southeast which was still controlled by Syracuse, Pyrrhus of Epirus, the Molossian king of Epirus, was installed as King/Tyrant of Sicily from 278 to 275 BC, even capturing the native Elymian mountain-city of Eryx, which was previously under Carthaginian fortification & protection before he captured it. Pyrrhus even attempted to capture Lilybaeum
Marsala (, local ; la, Lilybaeum) is an Italian town located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth in Sicily.
The town is famous for the docking of Giuse ...
( Siege of Lilybaeum) from the Punics
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, which didn't succeed. A couple years later (275 BC), Envoys from Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
had notified him that of all the Greek cities in Italy, only Tarentum hadn't fallen to the Romans. Upon hearing this, coinciding with the fact that the Sicilian city-states had started becoming hostile towards him, due to him trying to force Sicily into becoming a martial state, Pyrrhus made his decision to depart from the island and dethrone himself, leaving Syracuse and Carthage in charge of the island again. As his ship left the island, he turned and, foreshadowing the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
, said to his companions: "What a wrestling ground we are leaving, my friends, for the Carthaginians and the Romans." While his army was being transported by ship to mainland Italy, Pyrrhus' navy was destroyed by the Carthaginians at the Battle of the Strait of Messina, with 98 warships sunk or disabled out of 110. After Pyrrhus of Epirus landed on Mainland Italy, his Roman opponents had mastered up a large army under Roman consul Manius Curius Dentatus, while he was still Tyrant of Sicily. After Pyrrhus was defeated at the Battle of Beneventum (275 BC) by the Romans, he decided to end his campaigns against Southern Italy, and return to Epirus, resulting in the loss of all his territorial gains in Italy. The city of Tarentum however still remained under Epirote control.
The ancient historian Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
who wrote and recorded the monumental works of manuscripts about universal world/human history called Bibliotheca historica
''Bibliotheca historica'' ( grc, Βιβλιοθήκη Ἱστορική, ) is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, ...
, and the ancient Doric-Greek revolutionary scientist, inventor and mathematician Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
who anticipated modern calculus, and analysis by applying methods of infinitesimal
In mathematics, an infinitesimal number is a quantity that is closer to zero than any standard real number, but that is not zero. The word ''infinitesimal'' comes from a 17th-century Modern Latin coinage ''infinitesimus'', which originally referr ...
s and exhaustion to rigorously derive and prove the range of geometric
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ca ...
theorems, and invented the innovative Archimedean screw
The Archimedes screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest hydraulic machines. Using Archimedes screws as water pumps (Archimedes screw pump (ASP) or screw pump) dates back ...
, compound pulleys, and defensive war machines to protect his native town of Syracuse from invasions, were both born, grew up in, lived and died in Sicily.
Middle ages
As the Roman Empire was falling apart, a Germanic tribe known as the Vandals along with an Iranian tribe known as the Alans took over Sicily for a relatively brief period beginning in 440 AD under the rule of their king Geiseric, forming the Kingdom of the Vandals. The Vandals and Alans gained a monopoly on the Mediterraneangrain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other ...
during their monarchical reign, with all grain taxes being monitored by them. Due to the Western Roman Empire being too preoccupied with war in Gaul, when the Vandals & Alans started invading Sicily in 440, the Romans could not respond. Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II sent a failed expeditionary force to deal with them in 441, which ended in a Vandal-Alan counter-victory. However, they soon lost these newly acquired possessions, except for one toehold in Lilybaeum
Marsala (, local ; la, Lilybaeum) is an Italian town located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth in Sicily.
The town is famous for the docking of Giuse ...
, to Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustul ...
(an Arian Christian Barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by som ...
statesman & general of possible East Germanic & Hunnic descent, and client king under Zeno whose reign over Italy marked the Fall of the Western Roman Empire) in 476 and completely to the Ostrogothic conquest of Sicily by Theodoric the Great which began in 488; although the Goths were Germanic, Theodoric sought to revive Roman culture and government and allowed freedom of religion. In contrast to the prior Carthaginian, Syracusan (Dorian) and Roman Empires which ruled Sicily in the past, Sicily did not serve as a distinct province or administrative region under Germanic control, although it did retain a certain amount of autonomy. The Gothic War Gothic War may refer to:
*Gothic War (248–253), battles and plundering carried out by the Goths and their allies in the Roman Empire.
*Gothic War (367–369), a war of Thervingi against the Eastern Roman Empire in which the Goths retreated to Mont ...
took place between the Ostrogoths and the Byzantine Empire (with its capital-city based at Constantinople, modern Istanbul), and during the reign of Justinian I, Sicily was brought back under Greco-Roman rule under the military expeditions of Byzantine generals Flavius Belisarius and Narses, resulting in Byzantine-Greek language and religion being embraced by the majority of the population. It was Syracuse where the Byzantine Emperor Constans II
Constans II ( grc-gre, Κώνστας, Kōnstas; 7 November 630 – 15 July 668), nicknamed "the Bearded" ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, ὁ Πωγωνᾶτος, ho Pōgōnãtos), was the Eastern Roman emperor from 641 to 668. Constans was the last ...
desired to move his capital in 663 AD, a decision which eventually led to his assassination. Sicily remained under autonomous stable Byzantine rule as the Theme/Province of Sicily ( Theme (Byzantine district)) for several peaceful centuries, until an invasion by Arab Muslims ( Aghlabids from the Banu Tamim Clan) in the 9th century.
Besides Sicily, the Theme or Province of Sicily also included the adjacent region of Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
in Mainland Italy. The capital city of Byzantine Sicily was Syracuse. The province was looked after by the imperial governor known as a Praetor, and was militarily protected under a general by the title of Dux. Sicily itself was divided into many districts known as a Turma. The Byzantine Exarch of Ravennan Italy named Theophylact, between 702 and 709, originally came from Sicily. After he got promoted into the Exarchate, Theophylact marched from Sicily to Rome for unknown reasons, a decision which angered the local Roman soldiers living there, however the newly elected Pope John VI, was able to calm them down. While Theophylact was still Exarch, Byzantine Emperor Justinian II seized all the leading citizens and officials of Ravenna at a local banquet, and dragged them abroad a ship to Constantinople. He sentenced all but one of the Ravennan captives to death, the exception being Archbishop Felix, who was permanently blinded instead. This was due to a recent rebellion which Ravenna took part in, in 695. Justinian II later sacked Ravenna, weakening the Exarchate in charge of it. Theophylact was not a victim of the catastrophe, but was the first Exarch to experience a weakened Ravenna. Theophylact possibly moved back to Sicily after he retired from the Exarchate in 709. Theophylact might have also been the Strategos
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek language, Greek to ...
of Sicily from 700 to 710. The Strategos of Sicily was also able to exercise some control over the autonomous duchies of Naples, Gaeta
Gaeta (; lat, Cāiēta; Southern Laziale: ''Gaieta'') is a city in the province of Latina, in Lazio, Southern Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is from Rome and from Naples.
The town has played a consp ...
and Amalfi, depending on the local political situation or faction at the time.
The Aghlabid invasions were in part caused by the Byzantine-Sicilian military commander Euphemius, who invited the Aghlabids to aid him in his rebellion against the imperial governor of Sicily in 826 AD. A similar situation happened a century prior, when the imperial governor of Sicily (Sergios), had declared a Byzantine official from Constantinople by the name of Basil Onomagoulos Basil Onomagoulos ( el, ) was a Byzantine official who was declared rival emperor in Sicily in 717, taking the regnal name Tiberius.
Basil was from Constantinople, the son of a certain Gregory Onomagoulos. In 717 he was a member of the entourage o ...
( regnal name Tiberius) as rival emperor, when false news reached Sicily that Constantinople had fallen to the Umayyads. When Emperor Leo the Syrian sent an administrative official named Paul to Sicily, the people and army of Syracuse surrendered Basil and his rebels up to him, leading to the beheading of Basil, while the former governor Sergios was able to escape to the parts of Mainland Italy controlled by the Lombards. Another rebellion took place between the years 781–793, when the aristocratic governor of Sicily, Elpidius, was accused of conspiring against Empress Irene
Irene of Athens ( el, Εἰρήνη, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaina (), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler ...
in favour of Nikephoros. After Elpidius's forces were militarily defeated by Empress Irene's large fleet dispatched in Sicily, he, along with his lieutenant, the dux of Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
named Nikephoros, defected to the Abbasid Caliphate, where he was posthumously acknowledged as rival emperor. After losing another military expedition, this time against Asia Minor with the help of the Abbasids, he advised the Abbasid Emir of Mesopotamia, Abd al-Malik ibn Salih, to "throw away his silk and put on his armour", warning him against the aggressive new reign of Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In r ...
. The Muslim conquest was a see-saw affair; the local population resisted fiercely and the Arabs suffered considerable dissension and infighting among themselves during this process. Not until 965 was the island's conquest successfully completed by the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
, with Syracuse in particular resisting almost to the end (Siege of Syracuse (877-878) Siege of Syracuse may refer to:
Sieges
By the Athenians:
* Siege of Syracuse (415–413 BC), during the Sicilian Expedition
By, or in league with, the Carthaginians:
* Siege of Syracuse (397 BC)
* Siege of Syracuse (343 BC)
* Siege of Syracuse (3 ...
). Jawhar the Sicilian, the Fatimid general of Slavic origins that led the conquest of Egypt, under Caliph Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah
Abu Tamim Ma'ad al-Muizz li-Din Allah ( ar, ابو تميم معد المعزّ لدين الله, Abū Tamīm Maʿad al-Muʿizz li-Dīn Allāh, Glorifier of the Religion of God; 26 September 932 – 19 December 975) was the fourth Fatimid calip ...
, was born and grew up in Ragusa, Sicily. Jawhar served as viceroy of Egypt until 973, consolidating Fatimid control over North Africa, and laying the foundations for Cairo.
The first phase of Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
rule began with the conquests of the third Aghlabid Emir Ziyadat Allah I of Ifriqiya, and consolidated with the reign of the ninth Emir Ibrahim II of Ifriqiya after the conquest of Taormina. The first attempt to capture Syracuse was under general Asad ibn al-Furat, although it ended in a Byzantine victory. A strong combination of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
n, Persian and Andalusian troops helped to capture the Island between 830 and 831. After a revolt was suppressed, the Fatimid Caliph Al-Mansur Billah appointed a member of the Kalbid dynasty, Al-Hasan ibn Ali al-Kalbi, as First Emir of Sicily. The Kalbids ruled Sicily from 948 to 1053. Al-Mu'izz ibn Badis, fourth ruler of the Zirid Sanhaja dynasty in North Africa, attempted to annex the island for the Zirids, but his attempts failed. The new Arab rulers initiated revolutionary land reforms, which in turn increased productivity and encouraged the growth of smallholdings, a dent to the dominance of the landed estates. The Arabs further improved irrigation systems through Qanats, introducing oranges, lemons, pistachio, and sugarcane to Sicily. Ibn Hawqal, a Baghdadi merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as indust ...
who visited Sicily in 950, commented that a walled suburb called the Kasr (the palace) was the center of Palermo, with the great Friday mosque on the site of the later Roman Catholic cathedral. The suburb of Al-Khalisa (Kalsa) contained the Sultan's palace, baths, a mosque, government offices, and a private prison. Ibn Hawqual reckoned there were 7,000 individual butchers trading in 150 shops. By 1050, Palermo had a population of 350,000, making it one of the largest cities in Europe, behind Moorish-Spain's capital Córdoba and the Byzantine capital of Constantinople, which had populations over 450–500,000. Palermo's population dropped to 150,000 under Norman rule. By 1330 Palermo's population had declined to 51,000, possibly due to the inhabitants of the region being deported to other regions of Norman Sicily
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
, or to the Norman County of Apulia and Calabria. The local population conquered by the Muslims were Greek-speaking Byzantine Christians, but there were also a significant number of Jews. Christians and Jews were tolerated in Muslim Sicily as dhimmi
' ( ar, ذمي ', , collectively ''/'' "the people of the covenant") or () is a historical term for non-Muslims living in an Islamic state with legal protection. The word literally means "protected person", referring to the state's obligatio ...
s, and had to pay the Jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
poll tax, and Kharaj
Kharāj ( ar, خراج) is a type of individual Islamic tax on agricultural land and its produce, developed under Islamic law.
With the first Muslim conquests in the 7th century, the ''kharaj'' initially denoted a lump-sum duty levied upon the ...
land tax, but were exempt from the Zakat alms-giving tax Muslims had to pay. Many Jews immigrated to Sicily during Muslim rule, but left after the Normans arrived.
 In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring
In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring Norman mercenaries
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
, who were Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
descendants of the Vikings; it was the Normans under Roger I (of the Hauteville dynasty) who conquered Sicily from the Muslims over a period of thirty years until finally controlling the entire island by 1091 as the County of Sicily. In 1130, Roger II founded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
as an independent state with its own Parliament, language, schooling, army and currency, while the Sicilian culture evolved distinct traditions, clothing, linguistic changes, cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
and customs not found in mainland Italy. A great number of families from northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
began settling in Sicily during this time, with some of their descendants forming distinct communities that survive to the present day, such as the Lombards of Sicily. Other migrants arrived from southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
, as well as Normandy southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
, England and other part of North Europe.
The Siculo-Norman rule of the Hauteville dynasty continued until 1198, when Frederick II of Sicily Frederick II of Sicily may refer to:
* Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor (1194–1250), who technically was Frederick I of Sicily but the regnal number II was used of him throughout his various realms
* Frederick III of Sicily
Frederick II (or II ...
, the son of a Siculo-Norman queen and a Swabian-German emperor ascended the throne. In fact, it was during the reign of this Hohenstaufen king Frederick II, that the poetic form known as a sonnet
A sonnet is a poetic form that originated in the poetry composed at the Court of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II in the Sicilian city of Palermo. The 13th-century poet and notary Giacomo da Lentini is credited with the sonnet's invention, ...
was invented by Giacomo da Lentini, the head Poet, Teacher and Notary of the Sicilian School for Poetry. Frederick II was also responsible for the Muslim settlement of Lucera. His descendants governed Sicily until the Papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
invited a French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
prince to take the throne, which led to a decade-and-a-half of French rule under Charles I of Sicily; he was later deposed in the War of the Sicilian Vespers against French rule, which put the daughter of Manfred of Sicily - Constance II and her husband Peter III of Aragon
Peter III of Aragon ( November 1285) was King of Aragon, King of Valencia (as ), and Count of Barcelona (as ) from 1276 to his death. At the invitation of some rebels, he conquered the Kingdom of Sicily and became King of Sicily in 1282, pres ...
, a member of the House of Barcelona, on the throne. Their descendants ruled the Kingdom of Sicily until 1401. Following the Compromise of Caspe in 1412 the Sicilian throne passed to the Iberian monarchs from Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
and Castile.
Modern and contemporary history
In 1735, the Spanish era ended when Charles V from theHouse of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanis ...
was crowned king. For the better part of the next century-and-a-half, Sicily was in personal union with the other Southern Italian Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
, with the official residence located in Naples, under the Bourbon dynasty
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanis ...
. After the Napoleonic Wars, King Ferdinand I Ferdinand I or Fernando I may refer to:
People
* Ferdinand I of León, ''the Great'' (ca. 1000–1065, king from 1037)
* Ferdinand I of Portugal and the Algarve, ''the Handsome'' (1345–1383, king from 1367)
* Ferdinand I of Aragon and Sicily, '' ...
, who had just recently been restored back to the throneship of Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
in 1815, made a decision to administratively and politically merged the two separate Kingdoms of Naples & Sicily, which ended up forming the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
in 1816. In 1861, however, Sicily became part of the Kingdom of Italy as a result of the Risorgimento. Prior to the Risorgimento, the Two Sicilies were conquered by the Kingdom of Sardinia during the Expedition of the Thousand (led by general Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
) in 1860, and subsequently brought under the monarchial realm of Sardinia. After the unification of Italy and the Fascist era, a wave of Sicilian nationalism led to the adoption of the Statute of Sicily The Statute of Sicily establishes the rule of Sicily as the Autonomous Region within the political unity of the Italian State and was issued by King Umberto II of Savoy, on 15 May 1946. Its enactment has thus preceded the birth of the Italian Consti ...
, under which the island has become an autonomous region. Since 1946, the island enjoys the most advanced special status of all the autonomous regions.
Demographics
Siculi
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, wikt:Σικελοί, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic people, Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the na ...
and Elymians), Bruttians, Morgetes, Oenotrians
The Oenotrians (Οἴνωτρες, meaning "tribe led by Oenotrus" or "people from the land of vines - Οἰνωτρία") were an ancient Italic people who inhabited a territory in Southern Italy from Paestum to southern Calabria. By the sixth ce ...
, Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Ancient Greeks (Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these re ...
), Mamertines, Romans and Jews during the ancient and classical periods.
In the early medieval era, Sicily experienced the brief rule of Germanic Vandals and Iranic Alans during the Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans, while under Byzantine, Saracen and Norman rule, there were Byzantine Greeks, Arabs and Normans. From the late medieval period into the modern era, Aragonese, Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex Hist ...
and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
ruled over and left a minor impact on the island, while Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
settled and formed communities which still exist today known as the Arbereshe.
About five million people live in Sicily, making it the fourth most populated region in Italy. However, in the first century after the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of millions of people moving to the Italian mainland and countries like Germany, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, Belgium, the United States, Canada, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Brazil, Argentina, the United Kingdom, France, New Zealand, Singapore and South Africa. Many Sicilian communities, including those formed by the descendants of the Sicilian migrants, are all over the world. It is estimated that the number of people of Sicilian descent in the world is more than six million. The most famous community is represented by the Sicilian Americans
Sicilian Americans ( Sicilian: ''Sìculu-miricani; Italian: Siculoamericani'') are Americans of Italian Sicilian birth or ancestry. They are a large ethnic group in the United States.
The first Sicilians who came to the territory that is now the ...
.
Like the other parts of Southern Italy, immigration to the island is relatively low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
instead, in search of better employment and industrial opportunities. The most recent ISTAT figures show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total of almost 5.1 million population (nearly 3.5% of the population); Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankans
This is a demography of the population of Sri Lanka including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Sri Lanka is an island in the ...
, Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the primary religion is Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
(but with combined Latin & Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
Th ...
s) and the official language is Italian; Sicilian is currently not a recognised language in Italy
Major settlements
In Sicily, there are three ''metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
s'':
# Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
, which has a Larger Urban Zone of 1,044,169 people
# Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
, whose LUZ's populous numbers some 801,280 people
# Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
and its LUZ, with a total of 418,916 people.
Overall, there are fifteen cities and towns with a population above 50,000 people, these are:
# Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
(677,854)
# Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
(315,576)
# Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
(242,121)
# Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
(123,248)
# Marsala
Marsala (, local ; la, Lilybaeum) is an Italian town located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth in Sicily.
The town is famous for the docking of Gius ...
(82,812)
# Gela (77,295)
# Ragusa (73,756)
# Trapani (70,642)
# Vittoria (63,393)
# Caltanissetta (60,221)
# Agrigento (59,190)
# Bagheria
Bagheria (; scn, Baarìa ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Palermo in Sicily, Italy, located approximately 10km to the east of the city centre.
Etymology
According to some sources, the name ''Bagheria'' (by way of old Sicil ...
(56,421)
# Modica (55,294)
# Acireale (53,205)
# Mazara del Vallo (51,413).
Names and surnames
The most common Sicilian names are ''Giuseppe'', ''Maria'' and ''Salvatore''. The most common Sicilian surnames are ''Russo'', ''Messina'' and ''Lombardo''.Diaspora
In 2008, the number of Sicilians abroad was well over 1 million. The countries in which they are most numerous on this date are: United States, Germany, Belgium, Switzerland, Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil, France and Canada The population of the Diaspora without including those in the United States is 629,114 individuals. In the United States, the Sicilian-Americans are a large subset of Americans whose ancestors came from Sicily. This group is perhaps the largest part of the Sicilian diaspora.Genetics
Autosomal studies
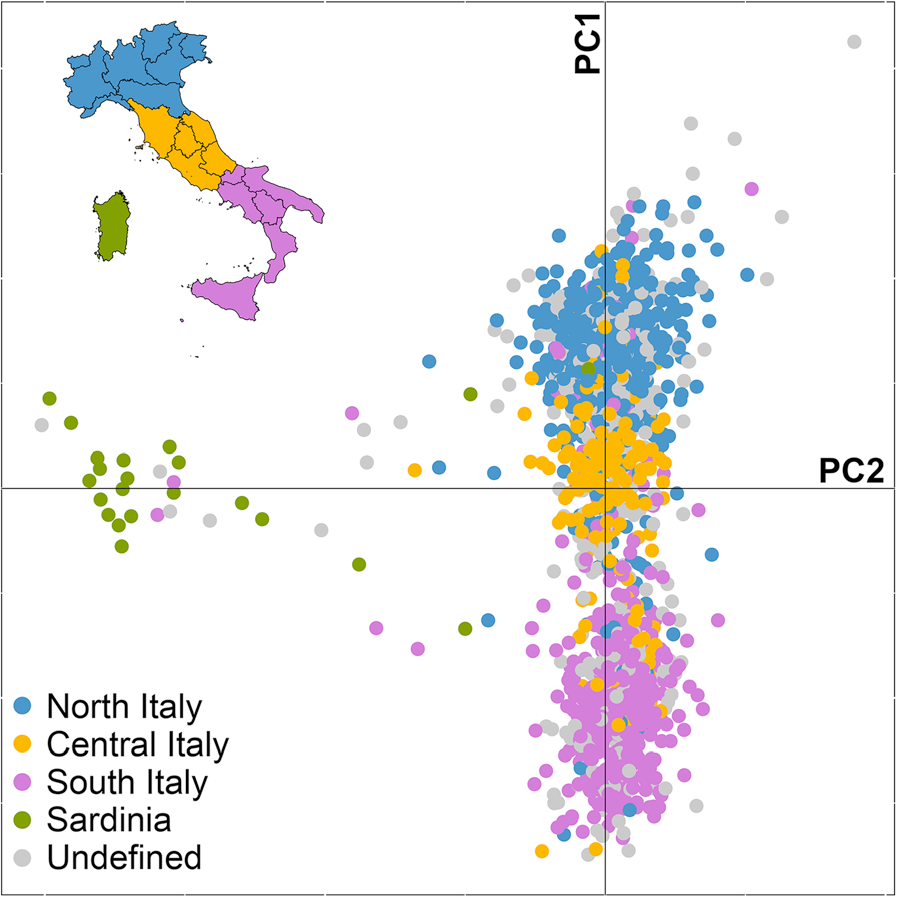
 Several studies involving whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from
Several studies involving whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
, Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
and Sicily belong to their own unique/distinct separate clusters, while a genetic gap is filled by an intermediate Central Italian
Central Italian (Italian: ''dialetti mediani'') refers to Italo-Romance varieties spoken in the so-called ''Area Mediana'', which covers a swathe of the central Italian peninsula. ''Area Mediana'' is also used in a narrower sense to describe the ...
cluster, creating a continuous cline of variation that mirrors geography. Genetically, Sicilians cluster the closest to Southern Italians, and especially to Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
ns. Other studies have also demonstrated that the population of Sicily is genetically very similar to that of Malta, and to Greek speaking groups from the Ionian Islands, the Aegean Islands, Crete and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
, while the rest of mainland Greece appears as slightly differentiated, by clustering with the other Southern Balkan populations of Albania/ Kosovo and the Arbereshe people.
MtDna and Y DNA studies
According to one study,Y-DNA haplogroups
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of ...
were found at the following frequencies in Sicily:
R1 (36.76%), J (29.65%), E1b1b (18.21%), I (7.62%), G (5.93%), T (5.51%), Q (2.54%). R1 and I haplogroups are typical in West European and North European populations while J, T, G, Q and E1b1b (and their various subclades) consist of lineages with differential distribution across West Asia, North Africa and Europe. The five main MtDNA haplogroups present in Sicily are haplogroups H, K, X, W and U, which are also the five most commonly found MtDNA-haplogroups in Europe, the Caucasus and the Middle East.
The Norman Kingdom of Sicily was created in 1130, with Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
as its capital, 70 years after the initial Norman invasion and 40 after the conquest of the last town, Noto in 1091, and would last until 1198. Today, it is in north-west Sicily, around Trapani, Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
and Agrigento where Norman Y-DNA is the most common, with 8% to 20% of the lineages belonging to haplogroup I1. Ancient and medieval Greek genetic paternal legacy is estimated at 37% in Sicily, and Arab-Berber (Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna ( ar, المغرب الأدنى), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia and eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (today's western Libya). It included all of what had previously ...
) between 2% and 6%. Overall the estimated Central Balkan
The Central Balkan National Park ( bg, Национален парк Централен Балкан) lies in the heart of Bulgaria, nestled in the central and higher portions of the Balkan Mountains. Its altitude varies from 550 m. near the town ...
and North Western European paternal contributions in South Italy and Sicily are about 63% and 26% respectively.
Paleogenetics
Fernandes et al. (2019), The Arrival of Steppe and Iranian Related Ancestry in the Islands of the Western Mediterranean, found that in Sicily, Western Steppe Herders ancestry arrived by ∼2200 BCE and likely came at least in part from Spain. 4 of the 5 Early Bronze Age Sicilian males had Steppe-associated Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a2a1a2 (R-P312). Two of these were Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a2a1a2a1 (Z195) which today is largely restricted to Iberia and has been hypothesized to have originated there 2500-2000 BCE.Culture
Languages
 Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian and Sicilian, a distinct and historical
Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian and Sicilian, a distinct and historical Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European languages, I ...
. Many Sicilian words are of Greek origin, while smaller numbers of other loan words are from Norman, Arabic, Catalan, Occitan, Spanish and other languages. Other dialects of Sicilian, or those very closely related to it, are also spoken in southern Calabria, Salento and Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
.
Sicilian was an early influence in the development of standard Italian, although its use remained confined to an intellectual elite. This was a literary language in Sicily created under the auspices of Frederick II and his court of notaries or ''Magna Curia'' which, headed by Giacomo da Lentini, also gave birth to the Sicilian School, widely inspired by troubadour literature. It is in this language that appeared the first sonnet
A sonnet is a poetic form that originated in the poetry composed at the Court of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II in the Sicilian city of Palermo. The 13th-century poet and notary Giacomo da Lentini is credited with the sonnet's invention, ...
, whose invention is attributed to Giacomo da Lentini himself. Sicilian was also the official language of the Kingdom of Sicily from 1300 to 1543. Prior to the 20th century, large numbers of Sicilian people spoke only Sicilian as their mother tongue, with little or no fluent knowledge of Italian. Today, while Sicilian is an unrecognized language being used as part of many people's daily life, Italian is the only official language and predominates in the public arena.
The Siculo-Arabic dialect was a vernacular variety of Arabic once spoken in Sicily and neighbouring Malta between the end of the ninth century to the mid to late thirteenth century. The language became extinct in Sicily, but in Malta it eventually evolved into what is now the Maltese language.
The Siculish
Siculish is the macaronic " Sicilianization" of English language words and phrases by immigrants from Sicily (Italy) to the United States in the early 20th century. The term ''Siculish'' is, however, rather recent, being first recorded in 2005.Lamb ...
dialect is the macaronic "Sicilianization" of English language words and phrases by immigrants from Sicily to the United States in the early 20th century. Forms of Siculish are also to be found in other Sicilian immigrant communities of English-speaking countries, namely Canada and Australia. A surprising similarity can often be found between these forms, through either coincidence, trans-national movements of Sicilian immigrants, or more likely, through the logical adaptation of English using linguistic norms from the Sicilian language.
Ethno-linguistic minorities
There are two main historical ethno-linguistic minorities in Sicily, the Lombards of Sicily and the Arbëreshë: * The Lombards of Sicily are a linguistic minority living in Sicily who speak an isolated variety of Gallo-Italic dialects, the so-called Gallo-Italic of Sicily. The Gallo-Italic of Sicily is a group of Gallo-Italic languages found in about 15 isolated communities of central eastern Sicily. Forming a language island in the Sicilian language, it dates back to migrations fromNorthern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
during the era of Roger I of Sicily and his successors. The Lombards of Sicily, who originally hailed from Northern Italy, settled the central and eastern part of Sicily about 900 years ago, during the Norman conquest of Sicily. Because of linguistic differences among the Gallo-Italic dialects of Sicily, it is supposed that there were different immigration routes. From Piedmont, Liguria, Emilia, and Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
they began to spread south between the 11th and 14th centuries. The most important areas where the Gallo-Italic of Sicily is spoken are Acquedolci, Montalbano Elicona, Novara di Sicilia
Novara di Sicilia (Gallo-Italic of Sicily: Nuè; Sicilian: ''Nuvara'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina in the Italian region of Sicily, located about east of Palermo and some southwest of Messina.
Novara di ...
, Fondachelli-Fantina San Fratello and San Piero Patti ( Province of Messina), Aidone, Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
, Piazza Armerina and Sperlinga
Sperlinga is a comune in the province of Enna, in the central part of the island of Sicily, in southern Italy. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("the prettiest villages in Italy").
Geography
Sperlinga is at about above sea level, o ...
( Province of Enna).
 * The
* The Arbëreshë people
The Arbëreshë (; sq, Arbëreshët e Italisë; it, Albanesi d'Italia), also known as Albanians of Italy or Italo-Albanians, are an Albanian ethnolinguistic group in Southern Italy, mostly concentrated in scattered villages in the region ...
settled in Southern Italy in the 15th to 18th centuries in several waves of migrations. They are the descendants of mostly Tosk Albanian
Tosk ( sq-definite, toskërishtja) is the southern group of dialects of the Albanian language, spoken by the ethnographic group known as Tosks. The line of demarcation between Tosk and Gheg (the northern variety) is the Shkumbin River. Tosk is t ...
refugees of Christian faith who fled to Italy after the Albanian conquest and subsequent Islamisation by the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in the Balkans. They speak their own variant of the Arbëresh language. There are three identified Arbëreshë communities in the province of Palermo, which have maintained unchanged, with different aspects together, the ethnic, linguistic and religious origins. The areas are: Contessa Entellina, Piana degli Albanesi and Santa Cristina Gela; while the varieties of Piana and Santa Cristina Gela are similar enough to be entirely mutually intelligible, the variety of Contessa Entellina is not entirely intelligible. The largest centre is Piana degli Albanesi which, besides being the hub of religious and socio-cultural communities, has guarded and defended their peculiarities intact over time. There are two other communities with a strong historical and linguistic heritage.
* The community of the Greeks of Messina (or Siculo-Greeks) speaks modern Greek with some elements of the ancient Greek language spoken in the island, and Calabrian Greek
The Calabrian dialect of Greek, or
 Historically, Sicily has been home to many religions, including
Historically, Sicily has been home to many religions, including
File:Bruno, Giuseppe (1836-1904) - Ragazzo siciliano - Da Artnet.jpg, Sicilian youth in traditional attire, 1890s
File:Crupi, Giovanni (1849-1925) - n. 0630 - Carretto siciliano - Ackland art museum.jpg, Sicilian cart, 1899
File:Sicilian monk (39322503152).jpg, A Sicilian monk
File:Bruno, Giuseppe (1836-1904) - n. 017 - Vecchio popolano - ebay.jpg, Old man from Sicily, 1890s
Religion
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, Native religion
In religious studies, an ethnic religion is a religion or belief associated with a particular ethnic group. Ethnic religions are often distinguished from universal religions, such as Christianity or Islam, in which gaining converts is a prima ...
s, Judaism, Classical Paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christianity, early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions ot ...
, Carthaginian religions, and Byzantine Orthodoxy, the coexistence of which has been historically seen as an ideal example of religious multiculturalism. Most Sicilians today are baptized as Catholic. Catholicism and Latinization in Sicily originated from the islands Norman occupiers and forced conversion continued under the Spanish invaders, where the majority of Sicily's population were forced to convert from their former religions. Despite the historical push for Catholicism in Sicily, a minority of other religious communities thrive in Sicily.
Sicilian Catholics
For Catholics in Sicily, the Virgin Hodegetria is the patroness of Sicily. The Sicilian people are also known for their deep devotion to some Sicilian female saints: the martyrs Agatha and Lucy, who are the patron saints of Catania and Syracuse respectively, and the hermit Saint Rosalia, patroness of Palermo. Sicilian people have significantly contributed to the history of many religions. There have been four Sicilian Popes ( Agatho, Leo II, Sergius I, and Stephen III) and a Sicilian Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople ( Methodios I). Sicily is also mentioned in the New Testament in the ''Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its messag ...
'', 28:11-13, in which Saint Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
briefly visits Sicily for three days before leaving the Island. It is believed he was the first Christian to ever set foot in Sicily.
Sicilian Muslims
During the period of Muslim rule, many Sicilians converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
. Many Islamic scholars were born on the island, including Al-Maziri, a prominent jurist of the Maliki school of Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
Islamic Law. Under the rule of Frederick II, all Muslims were expelled from the Island following a rebellion of local Saracens who wished to keep their local independence in Western Sicily but were not allowed to due to Pope Gregory IX's demands. Any remaining Muslim was eventually expelled by the Spanish inquisition.
In more recent years, many immigrants from predominantly Muslim countries like Pakistan, Albania, Bangladesh, Morocco, Egypt, and Tunisia have arrived on Sicily. In 1980, Catania, a city on the eastern coast of Sicily, became home to Italy's first modern mosque. Also known as the Omar mosque, it was financed by Libya.
Sicilian Jewish community
There is a legend that the Jews were first brought to Sicily as captive slaves in the 1st century after the Fall of Jerusalem in 70 CE by the Romans. However, it is generally presumed that Sicily's Jewish population was ceded before the destruction of the Temple of Jerusalem. Rabbi Akiva visited the city of Syracuse during one of his trips abroad. Judaism in Sicily was the first monotheistic religion to appear on the Island. The Jewish Sicilian community remained until the Aragonese rulers' Queen Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as List of Aragonese royal consorts, Queen consort ...
and Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from ...
, expelled them in the year 1493 with the Alhambra Decree
The Alhambra Decree (also known as the Edict of Expulsion; Spanish: ''Decreto de la Alhambra'', ''Edicto de Granada'') was an edict issued on 31 March 1492, by the joint Catholic Monarchs of Spain ( Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Arag ...
. On 3 February 1740, the Neapolitan King Charles III - hailed as an Enlightenment King, issued a proclamation containing 37 paragraphs, in which Jews for the first time were formally invited to return to Sicily. However, the effort was generally unsuccessful.
The Sicilian Jewish community still has several active members and has made a limited recovery in recent years. In the year 2005, for the first time since the Expulsion, a Passover Seder was conducted in Sicily (in Palermo), held by a Milanese Rabbi. The Jewish community in Sicily is led in part by Rabbi Stefano Di Mauro, a Sicilian American descendant of Sicilian '' neofiti''. He opened a small synagogue in 2008, but he has not yet set up a full-time Jewish congregation in Sicily. Services are held weekly on Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical storie ...
and the High Holy Days. Also, Shavei Israel has expressed interest in helping to facilitate the return of the Sicilian Bnei Anusim to Judaism.
Art and architecture
Cuisine
Gallery
See also
* List of people from Sicily * Sicilian Wars * Normans of Sicily * Griko people * Maltese people * Kingdom of AfricaReferences
External links
{{Sicily Ethnic groups in Italy Romance peoples