|
Sicilians
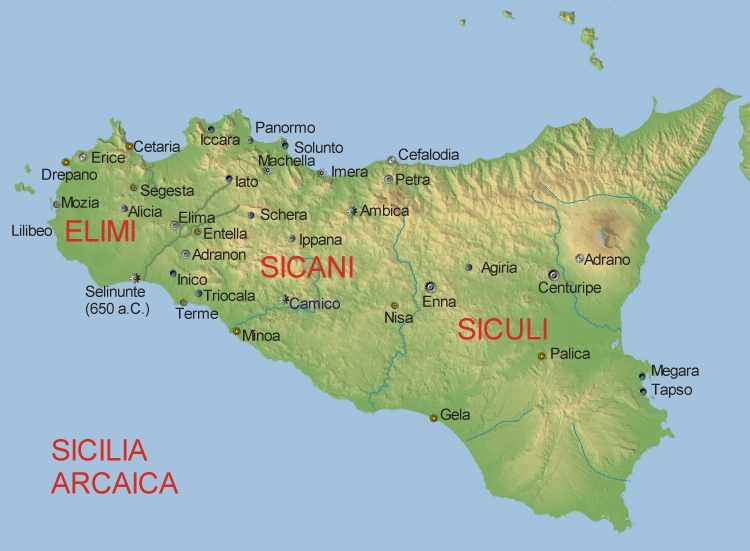
Sicilians or the Sicilian people are a Romance speaking people who are indigenous to the island of Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the largest and most populous of the autonomous regions of Italy. Origin and influences The Sicilian people are indigenous to the island of Sicily, which was first populated beginning in the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods. According to the famous Italian Historian Carlo Denina, the origin of the first inhabitants of Sicily is no less obscure than that of the first Italians, however, there is no doubt that a large part of these early individuals traveled to Sicily from Southern Italy, others from the Islands of Greece, the coasts of West Asia, Iberia and West Europe. Prehistory The aboriginal inhabitants of Sicily, long absorbed into the population, were tribes known to the ancient Greek writers as the Elymians, the Sicanians, and the Sicels, the latter being an Indo-European-speaking people of possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = Ethnicity , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = Sicilian , demographics1_info1 = 98% , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-82 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €89.2 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilian Language
Sicilian ( scn, sicilianu, link=no, ; it, siciliano) is a Romance language that is spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands. A variant, ''Calabro-Sicilian'', is spoken in southern Calabria, where it is called Southern Calabro notably in the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. Dialects of central and southern Calabria, the southern parts of Apulia (Salentino dialect) and southern Salerno in Campania ( Cilentano dialect), on the Italian peninsula, are viewed by some linguists as forming with Sicilian dialects a broader Extreme Southern Italian language group (in Italian ). '' Ethnologue'' (see below for more detail) describes Sicilian as being "distinct enough from Standard Italian to be considered a separate language", and it is recognized as a minority language by UNESCO. It has been referred to as a language by the Sicilian Region. It has the oldest literary tradition of the Italo-Romance languages. A version of the ''UNESCO Courier'' is also availab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italians
, flag = , flag_caption = The national flag of Italy , population = , regions = Italy 55,551,000 , region1 = Brazil , pop1 = 25–33 million , ref1 = , region2 = Argentina , pop2 = 20–25 million , ref2 = , region3 = United States , pop3 = 17-20 million , ref3 = , region4 = France , pop4 = 1-5 million , ref4 = , region5 = Venezuela , pop5 = 1-5 million , ref5 = , region6 = Paraguay , pop6 = 2.5 million , region7 = Colombia , pop7 = 2 million , ref7 = , region8 = Canada , pop8 = 1.5 million , ref8 = , region9 = Australia , pop9 = 1.0 million , ref9 = , region10 = Uruguay , pop10 = 1.0 million , r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half. The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily (officially denominated as one entity ''Regnum Siciliae citra Pharum'' and ''ultra Pharum'', i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which had neither been part of said region nor of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alpine House of Savoy that would eventually annex the Bourbon-led and Southern Italian Kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ''Mezzogiorno'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicels
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, but they rapidly fused into the culture of Magna Graecia. History Archaeological excavation has shown some Mycenean influence on Bronze Age Sicily. The earliest literary mention of Sicels is in the ''Odyssey''. Homer also mentions Sicania, but makes no distinctions: "they were (from) a faraway place and a faraway people and apparently they were one and the same" for Homer, Robin Lane Fox notes. It is possible that the Sicels and the Sicani of the Iron Age had consisted of an Illyrian population who (as with the Messapians) had imposed themselves on a native, Pre-Indo-European ("Mediterranean") population. Thucydides and other classical writers were aware of the traditions according to which the Sicels had once lived in Central Italy, ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic Peoples
The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family. The Italic peoples are descended from the Indo-European speaking peoples who inhabited Italy from at least the second millennium BC onwards. Latins achieved a dominant position among these tribes, establishing ancient Roman civilization. During this development, other Italic tribes adopted Latin language and culture in a process known as Romanization. This process was eventually extended to certain parts of Europe. The ethnic groups which emerged as a result are known as Romance peoples. Classification The Italics were an ethnolinguistic group who are identified by their use of the Italic languages, which form one of the branches of Indo-European languages. Outside of the specialised linguistic literature, the term is also used to describe the ancient peoples of Italy as defined in Roman times, including pre-Roman peoples like the Etruscan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Denina
Carlo Giovanni Maria Denina (1731, Revello – 5 December 1813, Paris) was an Italian historian. The unique contribution of Carlo Denina was to write a history of Italy from a “national” perspective, which significantly differed from other historians who mainly wrote from a “city state” or “localized” perspective during that time. He was born at Revello, Piedmont, in 1731, and was educated at Saluzzo and Turin. In 1753 he was appointed to the chair of humanity at Pinerolo, but he was soon compelled by the influence of the Jesuits to retire from it. In 1756 he graduated as doctor in theology, and began authorship with a theological treatise. Promoted to the professorship of humanity and rhetoric in the college of Turin, he published (1769–1770) his ''Delle revoluzioni d'Italia'', the work on which his reputation is mainly founded. Collegiate honors accompanied the issue of its successive volumes, which, however, at the same time multiplied his foes and stimulated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicanians
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river (Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes. History The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides, claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians. (The name Sicanus has been linked to the modern river known in Spanish as the Júcar.) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse. Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily. A third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymians
The Elymians ( grc-gre, Ἔλυμοι, ''Élymoi''; Latin: ''Elymi'') were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity. Origins According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, the Elymians were a population of Italic origin, who arrived in Sicily after having fought a war with the Oenotrians. Furthermore for the Greek historian, the Elymians would also have contributed to the formation of the Sicels. Today this thesis seems to be the most accredited and is confirmed by linguistic studies. Elymian, a language for which a different affiliation has long been sought in the past, must also be attributed to this linguistic family (Indo-European); however, the ancient tradition according to which the Elymians came from Troy is corroborated by the linguistic data but today the most authoritative opinions see in Elymian an Italic language more or less similar to Latin. Greek historian Philistus refers to the presence of a people of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context. The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean world, the Roman Empire (Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire), and medieval "Christendom" (Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity). Beginning with the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery, roughly from the 15th century, the concept of ''Europe'' as "the West" slowly became distinguished from and eventually replaced the dominant use of "Christendom" as the preferred endonym within the region. By the Age of Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution, the concepts of "Eastern Europe" and "Western Europe" were more regularly used. Historical divisions Classical antiquity and medieval origins Prior to the Roman conquest, a large part of Western Europe had adopted the newly developed La Tène culture. As the Roman domain ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |