Shinkansen Series0 R67 JNRcolor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
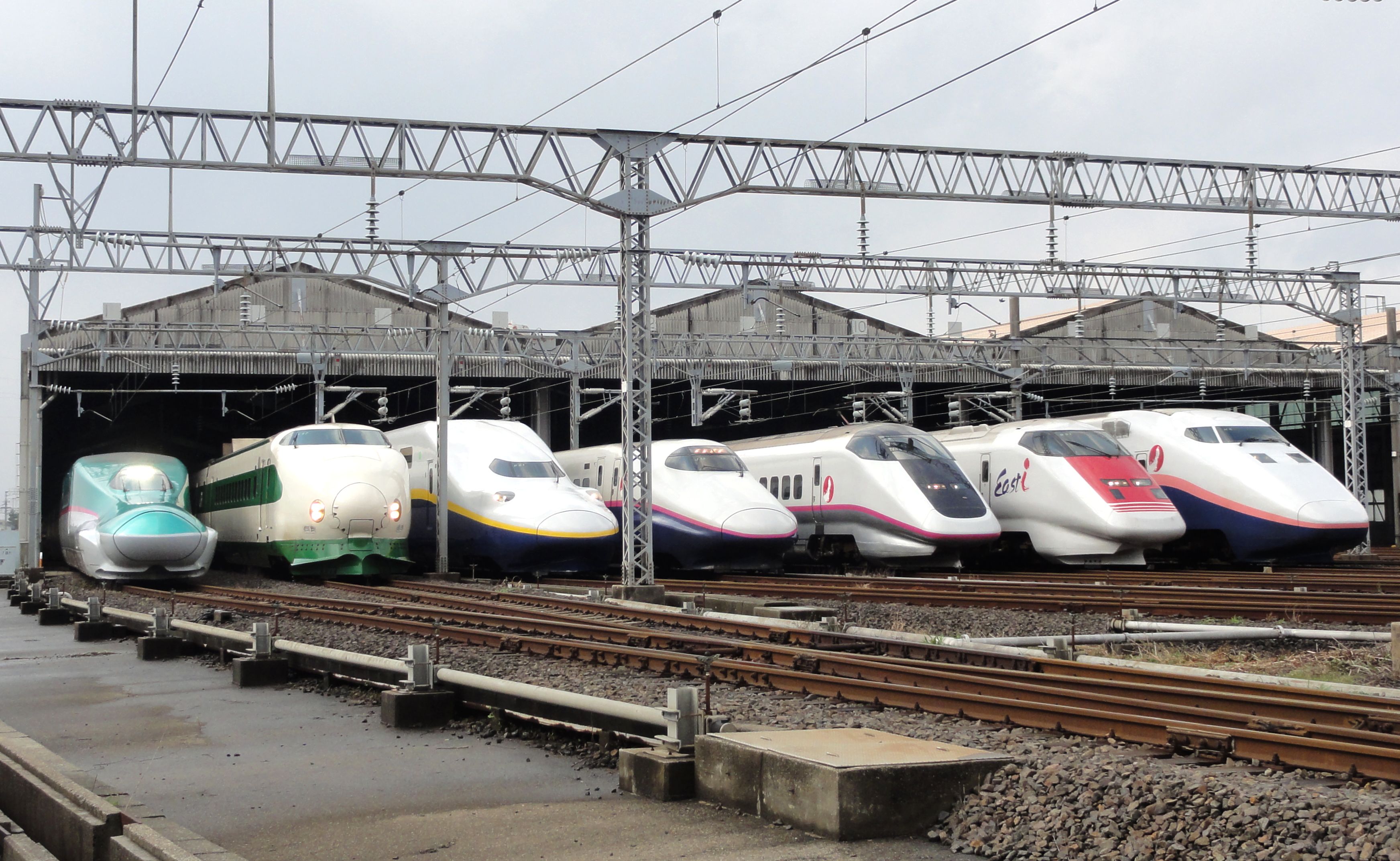


The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
way lines in
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. Initially, it was built to connect distant Japanese regions with
Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond long-distance travel, some sections around the
largest metropolitan areas are used as a commuter rail network.
It is operated by five
Japan Railways Group companies.
Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus-year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there has been not a single passenger fatality or injury on board due to derailments or collisions.
Starting with the
Tokaido Shinkansen () in 1964,
the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of
Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of , and of spur lines with Shinkansen services. The network presently links most major cities on the islands of
Honshu and
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
, and
Hakodate on northern island of
Hokkaido, with an extension to
Sapporo under construction and scheduled to commence in March 2031.
The maximum operating speed is (on a 387.5 km section of the
Tōhoku Shinkansen). Test runs have reached for conventional rail in 1996, and up to a
world record for
SCMaglev trains in April 2015.
The original Tokaido Shinkansen, connecting
Tokyo,
Nagoya and
Osaka, three of Japan's largest cities, is one of the world's busiest high-speed rail lines. In the one-year period preceding March 2017, it carried 159 million passengers, and since its opening more than five decades ago, it has transported more than 6.4 billion total passengers.
At peak times, the line carries up to 16 trains per hour in each direction with 16 cars each (1,323-seat capacity and occasionally additional standing passengers) with a minimum headway of three minutes between trains.
The Shinkansen network of Japan had the highest annual passenger ridership (a maximum of 353 million in 2007) of any
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
network until 2011, when the
Chinese high-speed railway network surpassed it at 370 million passengers annually, reaching over 2.3 billion annual passengers in 2019.
Etymology
in Japanese means 'new trunk line' or 'new main line', but this word is used to describe both the railway lines the trains run on and the trains themselves. In English, the trains are also known as the bullet train. The term originates from 1939, and was the initial name given to the Shinkansen project in its earliest planning stages. Furthermore, the name , used exclusively until 1972 for trains on the
Tōkaidō Shinkansen, is used today in English-language announcements and signage.
History

Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high-speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of
narrow-gauge lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds due to technical limitations of narrow-gauge rail. For example, if a standard-gauge rail has a curve with a maximum speed of , the same curve on narrow-gauge rail will have a maximum allowable speed of . Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high-speed lines than countries where the existing
standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
or
broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
rail system had more upgrade potential.
Among the key people credited with the construction of the first Shinkansen are
Hideo Shima, the Chief Engineer, and
Shinji Sogō, the first President of
Japanese National Railways (JNR) who managed to persuade politicians to back the plan. Other significant people responsible for its technical development were Tadanao Miki, Tadashi Matsudaira, and Hajime Kawanabe based at the
Railway Technical Research Institute (RTRI), part of JNR. They were responsible for much of the technical development of the first line, the
Tōkaidō Shinkansen. All three had worked on aircraft design during
World War II.
Early proposals
The popular English name ''bullet train'' is a literal translation of the Japanese term , a nickname given to the project while it was initially discussed in the 1930s. The name stuck because of the original
0 Series Shinkansen's resemblance to a bullet and its high speed.
The ''Shinkansen'' name was first formally used in 1940 for a proposed standard gauge passenger and freight line between Tokyo and
Shimonoseki that would have used steam and electric locomotives with a top speed of . Over the next three years, the Ministry of Railways drew up more ambitious plans to extend the line to Beijing (through a
tunnel to Korea) and even
Singapore, and build connections to the
Trans-Siberian Railway and other trunk lines in Asia. These plans were abandoned in 1943 as Japan's position in World War II worsened. However, some construction did commence on the line; several tunnels on the present-day Shinkansen date to the war-era project.
Construction
Following the end of World War II, high-speed rail was forgotten for several years while traffic of passengers and freight steadily increased on the conventional
Tōkaidō Main Line along with the reconstruction of Japanese industry and economy. By the mid-1950s the Tōkaidō Line was operating at full capacity, and the Ministry of Railways decided to revisit the Shinkansen project. In 1957,
Odakyu Electric Railway introduced its
3000 series SE Romancecar train, setting a world speed record of for a narrow gauge train. This train gave designers the confidence that they could safely build an even faster standard gauge train. Thus the first Shinkansen, the 0 series, was built on the success of the Romancecar.
In the 1950s, the Japanese national attitude was that railways would soon be outdated and replaced by air travel and highways as in the United States and many countries in Europe. However,
Shinji Sogō, President of
Japanese National Railways, insisted strongly on the possibility of
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
, and the Shinkansen project was implemented.
Government approval came in December 1958, and construction of the first segment of the
Tōkaidō Shinkansen between Tokyo and
Osaka started in April 1959. The cost of constructing the Shinkansen was at first estimated at nearly 200 billion yen, which was raised in the form of a government loan, railway bonds and a low-interest loan of US$80 million from the
World Bank. Initial estimates, however, were deliberately understated and the actual cost was about 400 billion yen. As the budget shortfall became clear in 1963, Sogo resigned to take responsibility.
A test facility for rolling stock, now part of the line, opened in
Odawara in 1962.
Initial success

The Tōkaidō Shinkansen began service on 1 October 1964, in time for the
first Tokyo Olympics. The conventional Limited Express service took six hours and 40 minutes from Tokyo to Osaka, but the Shinkansen made the trip in just four hours, shortened to three hours and ten minutes by 1965. It enabled day trips between Tokyo and Osaka, the two largest metropolises in Japan, significantly changed the style of business and life of the Japanese people, and increased new traffic demand. The service was an immediate success, reaching the 100 million passenger mark in less than three years on 13 July 1967, and one billion passengers in 1976. Sixteen-car trains were introduced for
Expo '70 in Osaka. With an average of 23,000 passengers per hour in each direction in 1992, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen was the world's busiest high-speed rail line. As of 2014, the train's 50th anniversary, daily passenger traffic rose to 391,000 which, spread over its 18-hour schedule, represented an average of just under 22,000 passengers per hour.
The first Shinkansen trains, the
0 series, ran at speeds of up to , later increased to . The last of these trains, with their classic bullet-nosed appearance, were retired on 30 November 2008. A driving car from one of the 0 series trains was donated by JR West to the
National Railway Museum in
York,
United Kingdom in 2001.
Network expansion
The Tōkaidō Shinkansen's rapid success prompted an extension westward to
Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
,
Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
and
Fukuoka (the
San'yō Shinkansen), which was completed in 1975. Prime Minister
Kakuei Tanaka was an ardent supporter of the Shinkansen, and his government proposed an extensive network paralleling most existing trunk lines. Two new lines, the
Tōhoku Shinkansen and
Jōetsu Shinkansen
The is a high-speed shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo and Niigata, Japan, via the Tōhoku Shinkansen, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Despite its name, the line does not pass through the city of Joetsu or the hist ...
, were built following this plan. Many other planned lines were delayed or scrapped entirely as
JNR slid into debt throughout the late 1970s, largely because of the high cost of building the Shinkansen network. By the early 1980s, the company was practically insolvent, leading to its privatization in 1987.
Development of the Shinkansen by the privatised regional JR companies has continued, with new train models developed, each generally with its own distinctive appearance (such as the
500 series introduced by
JR West). Since 2014, Shinkansen trains run regularly at speeds up to on the
Tōhoku Shinkansen, only the
Shanghai maglev train and
China Railway High-speed
China Railway High-speed (CRH) is a high-speed rail service operated by China Railway.
The introduction of CRH series was a major part of the sixth national railway speedup, implemented on April 18, 2007. By the end of 2020, China Railway H ...
networks have commercial services that operate faster.
Since 1970, development has also been underway for the
Chūō Shinkansen, a planned
maglev line from Tokyo to Osaka. On 21 April 2015, a seven-car
L0 series maglev trainset set a
world speed record of .
Technology
To enable high-speed operation, Shinkansen uses a range of advanced technology compared with conventional rail, achieving not only high speed but also a high standard of safety and comfort. Its success has influenced other railways in the world, demonstrating the importance and advantages of
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
.
Routing
Shinkansen routes are completely separate from conventional rail lines (except
Mini-shinkansen which goes through to conventional lines). Consequently, the shinkansen is not affected by slower local or freight trains (except for
Hokkaido Shinkansen while traveling through the
Seikan Tunnel), and has the capacity to operate many high-speed trains punctually. The lines have been built without
road crossings at grade. Tracks are strictly off-limits with penalties against trespassing strictly regulated by law. The routes use tunnels and
viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide v ...
s to go through and over obstacles rather than around them, with a minimum curve radius of 4,000 meters (2,500 meters on the oldest Tōkaidō Shinkansen).
Track

The Shinkansen uses
standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
in contrast to the narrow gauge of older lines.
Continuous welded rail and
swingnose crossing
A swingnose crossing or moveable point frog is a device used at a railway turnout to eliminate the gap at the common crossing (a.k.a. frog) which can cause damage and noise.
Fixed crossing
On a fixed railway crossing, the wheels need only d ...
points are employed, eliminating gaps at turnouts and crossings. Long rails are used, joined by expansion joints to minimize gauge fluctuation due to thermal elongation and shrinkage.
A combination of
ballasted and
slab track is used, with slab track exclusively employed on concrete bed sections such as viaducts and tunnels. Slab track is significantly more cost-effective in tunnel sections, since the lower track height reduces the cross-sectional area of the tunnel, reducing construction costs up to 30%.
However, the smaller diameter of Shinkansen tunnels, compared to some other high-speed lines, has resulted in the issue of
tunnel boom becoming a concern for residents living close to tunnel portals.
The slab track consists of rails, fasteners and track slabs with a cement asphalt mortar. On the roadbed and in tunnels, circular upstands, measuring 400–520 mm in diameter and 200 mm high, are located at 5-metre intervals. The prefabricated upstands are made of either
reinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having hig ...
or pre-stressed reinforced concrete; they prevent the track slab from moving latitudinally or longitudinally. One track slab weighs approximately 5 tons and is 2220–2340 mm wide, 4900–4950 mm long and 160–200 mm thick.
Signal system

The Shinkansen employs an
ATC (Automatic Train Control) system, eliminating the need for trackside signals. It uses a comprehensive system of
Automatic Train Protection
Automatic train protection (ATP) is a type of train protection system which continually checks that the speed of a train is compatible with the permitted speed allowed by signalling, including automatic stop at certain signal aspects. If it is ...
.
manages all train operations, and all tasks relating to train movement, track, station and schedule are networked and computerized.
Electrical systems
Shinkansen uses a
25 kV AC
Railway electrification systems using alternating current (AC) at are used worldwide, especially for high-speed rail. It is usually supplied at the standard utility frequency (typically 50 or 60Hz), which simplifies traction substations. The d ...
overhead power supply (20 kV AC on
Mini-shinkansen lines), to overcome the limitations of the 1,500 V
direct current used on the existing electrified narrow-gauge system. Power is distributed along the train's axles to reduce the heavy axle loads under single power cars.
The AC frequency of the power supply for the Tokaido Shinkansen is 60 Hz.
Trains
Shinkansen trains are
electric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a numbe ...
s, offering fast acceleration, deceleration and reduced damage to the track because of the use of lighter vehicles compared to locomotives or power cars. The coaches are air-sealed to ensure stable air pressure when entering tunnels at high speed.

Traction
The Shinkansen has used the
electric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a numbe ...
configuration from the outset, with the
0 Series Shinkansen having all axles powered. Other railway manufacturers were traditionally reluctant or unable to use distributed traction configurations (
Talgo, the German
ICE 2 and the French (and subsequently South Korean)
TGV (and
KTX-I and
KTX-II) use the
locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
(also known as power car) configuration with the
AVE Class 102 and continues with it for the
Talgo AVRIL because it is not possible to use powered bogies as part of Talgo's bogie design, which uses a modified
Jacobs bogie with a single axle instead of two and allows the wheels to rotate independently of each other, on the ICE 2, TGV and KTX it is because it easily allows for a high ride quality and less electrical equipment.) In Japan, significant engineering desirability exists for the electric multiple unit configuration. A greater proportion of motored axles permits higher acceleration, so the Shinkansen does not lose as much time if stopping frequently. Shinkansen lines have more stops in proportion to their lengths than high-speed lines elsewhere in the world.
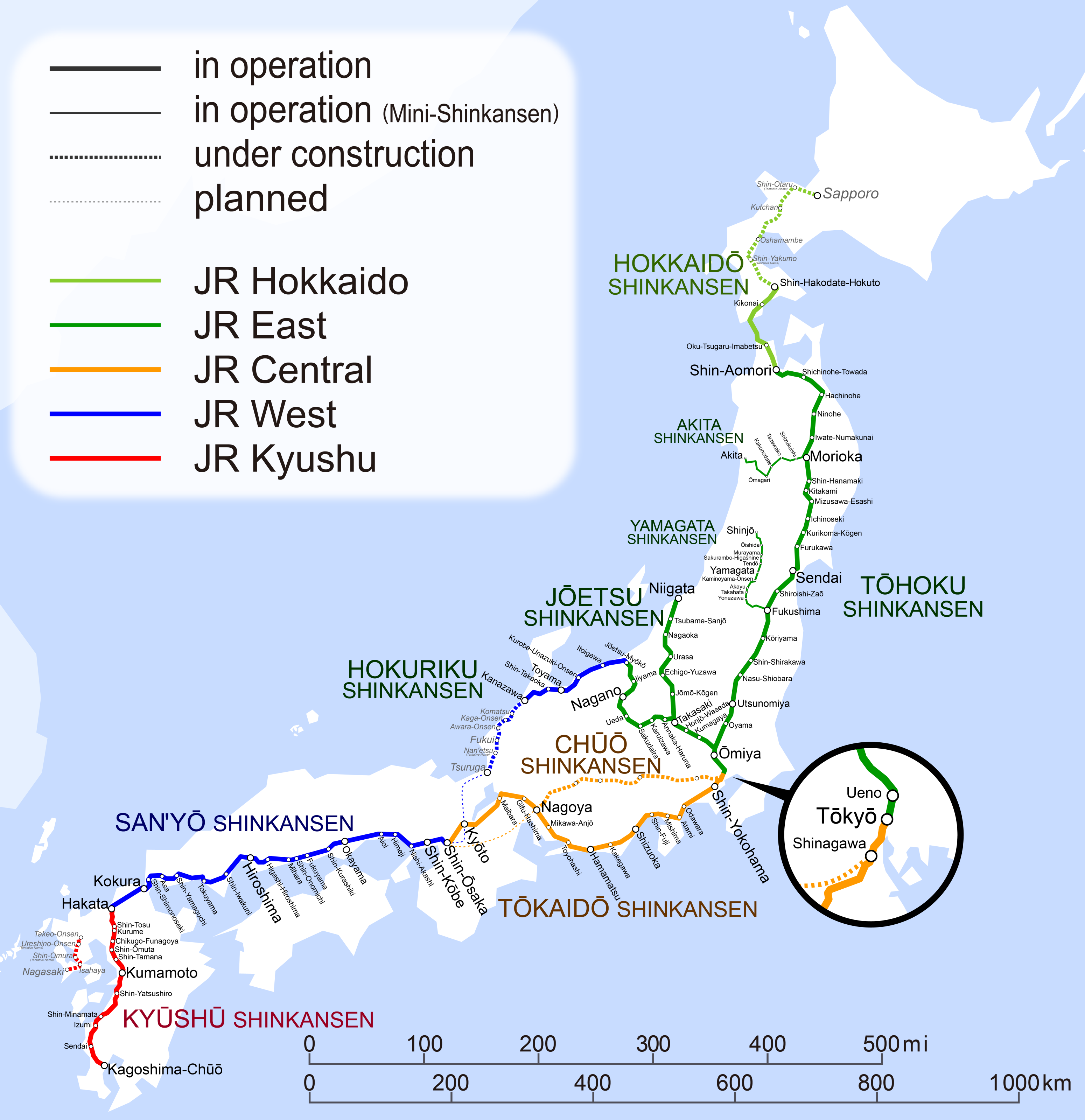
Lines
The main Shinkansen lines are:
In practice, the Tokaido, San'yō, and Kyushu lines form a contiguous west/southbound line from Tokyo, as train services run between the Tokaido and San'yō lines and between the San'yō and Kyushu lines, though the lines are operated by different companies.
The Tokaido Shinkansen tracks are not physically connected to the lines of the Tohoku Shinkansen at Tokyo Station, as they are operated by separate companies and have separate platforms. Therefore, there is no through service between those lines. All northbound services from Tokyo travel along the Tohoku Shinkansen until at least Ōmiya.
Two further lines, known as ''
Mini-shinkansen'', have also been constructed by re-gauging and upgrading existing sections of line:
*
Yamagata Shinkansen (
Fukushima
may refer to:
Japan
* Fukushima Prefecture, Japanese prefecture
**Fukushima, Fukushima, capital city of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan
*** Fukushima University, national university in Japan
*** Fukushima Station (Fukushima) in Fukushima, Fukushim ...
–
Shinjō)
*
Akita Shinkansen (
Morioka –
Akita)
There are two standard-gauge lines not technically classified as Shinkansen lines but run Shinkansen trains as they use tracks leading to Shinkansen storage/maintenance yards:
*
Hakata Minami Line (
Hakata
is a ward of the city of Fukuoka in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan.
Many of Fukuoka Prefecture and Fukuoka City's principal government, commercial, retail and entertainment establishments are located in the district. Hakata-ku is also the locatio ...
–
Hakata-Minami)
*
Gala-Yuzawa Line – technically a branch of the
Jōetsu Line – (
Echigo-Yuzawa –
Gala-Yuzawa)
Lines under construction
The following lines are under construction. These lines except
Chuo Shinkansen, called or ''planned Shinkansen'', are the Shinkansen projects designated in the Basic Plan decided by the government.
*
Hokuriku Shinkansen extension from
Kanazawa to
Tsuruga
is a city located in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 66,123 in 28,604 households and the population density of 260 persons per km2. The total area of the city was .
Geography
Tsuruga is located in central ...
is under construction and is scheduled to open in fiscal 2022. Between Hakusan Depot near Kanazawa and Tsuruga, the Shinkansen station was constructed in conjunction with the rebuilding of the adjoining conventional (narrow gauge) line station in anticipation of construction of the line to Osaka.
*
Hokkaido Shinkansen from to is under construction and scheduled to open by March 2031.
*
Chuo Shinkansen (Tokyo–Nagoya–Osaka) is a planned
maglev line. JR Central has announced a 2027 target date for the line from Tokyo to Nagoya. Construction of the project commenced in 2014.
Planned lines
* The extension of
Hokuriku Shinkansen to
Osaka is proposed, with the route via Obama and Kyoto selected by the government on 20 December 2016.
Construction is proposed to commence in 2030, and take 15 years.
*
Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen has been built to full Shinkansen standards between Takeo Onsen and Nagasaki, with the existing narrow-gauge line from Shin-Tosu to Takeo Onsen to remain as narrow-gauge track, although there is a proposal to build the section between Shin-Tosu and Takeo Onsen to full Shinkansen standards. In 2018, the
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism released
cost-benefit analysis results to compare and contrast full Shinkansen,
mini-Shinkansen, and
Gauge Change Train
The Gauge Change Train (GCT) or is the name given to a Japanese project started in 1994 to develop a high-speed train with variable gauge axles to allow inter-running between the Shinkansen network, and the narrow gauge regional rail network.
T ...
for this section.
* The extension of
Chuo Shinkansen to Osaka is proposed to open in 2037.
Cancelled line
The
Narita Shinkansen project to connect Tokyo to
Narita International Airport
Narita International Airport ( ja, 成田国際空港, Narita Kokusai Kūkō) , also known as Tokyo-Narita, formerly and originally known as , is one of two international airports serving the Greater Tokyo Area, the other one being Haneda Airport ...
, initiated in the 1970s but halted in 1983 after landowner protests, has been officially cancelled and removed from the Basic Plan governing Shinkansen construction. Parts of its planned right-of-way were used by the
Narita Sky Access Line which opened in 2010, and the
Keiyo Line reused space originally set aside for the Narita Shinkansen terminus at
Tokyo Station. Although the Sky Access Line uses standard-gauge track, it was not built to Shinkansen specifications and there are no plans to convert it into a full Shinkansen line.
Proposed lines

Many Shinkansen lines were proposed during the boom of the early 1970s but have yet to be constructed and have subsequently been shelved indefinitely.
* Hokkaido Shinkansen northward extension: Sapporo–Asahikawa
* :
Oshamanbe
is a town located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.
As of 30 October 2016, the town has an estimated population of 5,694. The total land area is 310.75 km2.
Geography
Oshamambe faces Uchiura Bay, which is a bay of the Pacific Ocea ...
–
Muroran–Sapporo
* :
Toyama–Niigata–Aomori
** Toyama–Jōetsu-Myōkō exists as part of the Hokuriku Shinkansen, and Nagaoka–Niigata exists as part of the Jōetsu Shinkansen, with provisions for the Uetsu Shinkansen at Nagaoka.
* : Fukushima–Yamagata–Akita
** Fukushima–Shinjō and Ōmagari–Akita exist as the
Yamagata Shinkansen and
Akita Shinkansen, respectively, but as "Mini-Shinkansen" upgrades of existing track, they do not meet the requirements of the Basic Plan.
* : Nagoya–Tsuruga
* : Osaka–
Oita in 2018 that found the route to be potentially profitable
* : Fukuoka–Ōita–Miyazaki–Kagoshima
* : Ōita–Kumamoto
In addition, the Basic Plan specified that the Jōetsu Shinkansen should start from Shinjuku Station">Shinjuku
is a special ward in Tokyo, Japan. It is a major commercial and administrative centre, housing the northern half of the busiest railway station in the world (Shinjuku Station) and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building, the administration ...
, not
Tokyo Station, which would have required building an additional of track between Shinjuku and Ōmiya. While no construction work was ever started, land along the proposed track, including an underground section leading to Shinjuku Station, remains reserved. If capacity on the current Tokyo–Ōmiya section proves insufficient, at some point, construction of the Shinjuku–Ōmiya link may be reconsidered.
In December 2009, then transport minister Seiji Maehara proposed a bullet train link to
Haneda Airport, using an existing spur that connects the
Tōkaidō Shinkansen to a train depot.
JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
called the plan "unrealistic" due to tight train schedules on the existing line, but reports said that Maehara wished to continue discussions on the idea. The current minister has not indicated whether this proposal remains supported. While the plan may become more feasible after the opening the Chuo Shinkansen (sometimes referred to as a bypass to the Tokaido Shinkansen) frees up capacity, construction is already underway for other rail improvements between Haneda and Tokyo station expected to be completed prior to the opening of the
2020 Tokyo Olympics
The , officially the and also known as , was an international multi-sport event held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some preliminary events that began on 21 July.
Tokyo was selected as the host city during the 1 ...
, so any potential Shinkansen service would likely offer only marginal benefit beyond that.
Service names


Originally intended to carry passenger and freight trains by day and night, the Shinkansen lines carry only passenger trains. The system shuts down between midnight and 06:00 every day for maintenance. The few overnight passenger trains that still run in Japan run on the older narrow gauge network that the Shinkansen parallels.
Tōkaidō, San'yō and Kyushu Shinkansen
* ''
Nozomi'' (express i.e. stops at the least amount of stations, Tokaido and San'yō)
* ''
Hikari'' (semi-express i.e. stops at the most important stations, Tokaido and San'yō)
* ''
Hikari Rail Star'' (semi-express, San'yō)
* ''
Kodama'' (local i.e. stops at all stations along the way, Tokaido and San'yō)
* ''
Sakura
A cherry blossom, also known as Japanese cherry or sakura, is a flower of many trees of Prunus, genus ''Prunus'' or Prunus subg. Cerasus, ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus''. They are common species in East Asia, including China, Korea and especia ...
'' (semi-express, San'yō and Kyushu)
* ''
Mizuho'' (express, San'yō and Kyushu)
* ''
Tsubame'' (local, Kyushu)
Tōhoku, Hokkaido, Yamagata and Akita Shinkansen
* ''
Hayabusa'' (express, Tohoku & Hokkaido, using
E5 series/
H5 series
The and the related are Japanese Shinkansen high-speed train types built by Hitachi Rail and Kawasaki Heavy Industries.
The E5 series is operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East); it was introduced on Tohoku Shinkansen services on 5 ...
trains)
* ''
Hayate'' (local, Tohoku & Hokkaido. The express service was discontinued in 2019)
* ''
Yamabiko
The is a high-speed Shinkansen train service operated on the Tōhoku Shinkansen between and by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) in Japan.
Name
The word ''yamabiko'' is usually translated as 'echo', particularly one which is heard in the ...
'' (semi-express, Tohoku)
* ''
Nasuno'' (local, Tohoku)
* ''
Aoba'' (discontinued)
* ''
Komachi'' (Akita)
* ''
Tsubasa
Tsubasa (written: 翼, 翔, 飛翔 or つばさ in hiragana) is a unisex Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Tsubasa (wrestler), Japanese professional wrestler
*, Japanese footballer
*, Japanese baseball player
*, Japanese ...
'' (Yamagata)
Jōetsu Shinkansen
* ''
Toki / Max Toki'' (semi-express, Jōetsu)
* ''
Tanigawa / Max Tanigawa'' (local, Jōetsu)
* ''
Asahi / Max Asahi'' (discontinued)
Hokuriku Shinkansen
* ''
Kagayaki'' (express, Hokuriku)
* ''
Hakutaka'' (semi-express, Hokuriku)
* ''
Tsurugi'' (local, Hokuriku)
* ''
Asama'' (local, Hokuriku)
Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen
* Kamome
Train types
Trains are up to sixteen cars long. With each car measuring in length, the longest trains are 400 m ( mile) end to end. Stations are similarly long to accommodate these trains. Some of Japan's high-speed maglev trains are considered Shinkansen, while other slower maglev trains (such as the
Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya. While primarily built to serve the Expo 2005 fair site, the line now operates to serve the local community.
Linimo is owned and operated by ...
maglev train line serving local community near the city of
Nagoya in Aichi, Japan) are intended as alternatives to conventional urban
rapid transit systems.
Passenger trains
Tokaido and San'yō Shinkansen
*
0 series: The first Shinkansen trains which entered service in 1964. Maximum operating speed was . More than 3,200 cars were built. Withdrawn in December 2008.
*
100 series: Entered service in 1985, and featured
bilevel cars with restaurant car and compartments. Maximum operating speed was . Later used only on San'yō Shinkansen ''
Kodama'' services. Withdrawn in March 2012.
*
300 series: Entered service in 1992, initially on ''
Nozomi'' services with maximum operating speed of . Withdrawn in March 2012.
*
500 series: Introduced on ''Nozomi'' services in 1997, with an operating speed of . Since 2008, sets have been shortened from 16 to 8 cars for use on San'yō Shinkansen ''Kodama'' services.
*
700 series: Introduced in 1999, with maximum operating speed of . The JR Central owned units were withdrawn in March 2020, with the JR West owned units continuing to operate on the
San'yō Shinkansen line between Shin-Osaka and Hakata.
*
N700 series
The is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed train with tilting capability developed jointly by JR Central and JR West for use on the Tokaido and San'yō Shinkansen lines since 2007, and also operated by JR Kyushu on the Kyushu Shinkansen line.
N ...
: In service since 2007, with a maximum operating speed of .
*
N700A series: An upgraded version of N700 series with improved acceleration & deceleration and quieter traction motors. All N700 series sets are now converted to N700A.
*
N700S series: An evolution of the N700 series. First trainset was rolled out in 2019 with passenger services commencing on 1 July 2020.
File:Shinkansen Series0 R67 JNRcolor.jpg, 0 series
File:Shinkansen100.jpg, 100 series
File:JR Central Shinkansen 300.jpg, 300 series
File:Shinkansen 500 series W2 formation.jpg, 500 series
File:JR Central Shinkansen 700.jpg, 700 series
File:Shinkansen 700 Rail Star (8086223807).jpg, 700 series (Hikari Rail Star)
File:Shinkansen N700 z15.jpg, N700 series
File:Series-N700A-F20.jpg, N700A series
File:Series-N700S-J2.jpg, N700S series
Kyushu Shinkansen
*
800 series: In service since 2004 on ''
Tsubame'' services, with a maximum speed of .
*
N700-7000/8000 series In service since March 2011 on ''
Mizuho'' and ''
Sakura
A cherry blossom, also known as Japanese cherry or sakura, is a flower of many trees of Prunus, genus ''Prunus'' or Prunus subg. Cerasus, ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus''. They are common species in East Asia, including China, Korea and especia ...
'' services with a maximum speed of .
File:JRK-800 U004 2020-10-12.jpg, 800 series
File:Shinkansen N700-7000 S1 (49766090102).jpg, N700 series (Kyushu)
Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen
*
N700S-8000 series: 6-car trains introduced in 2022
on the ''
Kamome'' services with a maximum speed of 260km/h.
File:西九州新幹線かもめ N700S系車両 長崎駅.jpg, N700S 8000 series
Tohoku, Hokkaido, Joetsu, and Hokuriku Shinkansen
*
200 series: The first type introduced on the
Tohoku and
Joetsu Shinkansen in 1982 and withdrawn in April 2013. Maximum speed was . The final configuration was as 10-car sets. 12-car and 16-car sets also operated at earlier times.
*
E1 series:
Bilevel 12-car trains introduced in 1994 and withdrawn in September 2012. Maximum speed was .
*
E2 series: 8/10-car sets in service since 1997 with a maximum speed of .
*
E4 series:
Bilevel 8-car trains introduced in 1997 and withdrawn in October 2021. Maximum speed was .
*
E5 series: 10-car sets in service since March 2011 with a maximum speed of .
*
H5 series
The and the related are Japanese Shinkansen high-speed train types built by Hitachi Rail and Kawasaki Heavy Industries.
The E5 series is operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East); it was introduced on Tohoku Shinkansen services on 5 ...
: The cold weather derivative of the E5 series. 10-car sets entered service from March 2016 on the
Hokkaido Shinkansen with a maximum speed of .
*
E7 series: 12-car trains operated on the
Hokuriku Shinkansen since March 2014, with a maximum speed of .
In 2019, the E7 series began operating on the Joetsu Shinkansen.
*
W7 series: 12-car trains operated on the Hokuriku Shinkansen since March 2015, with a maximum speed of .
Yamagata and Akita Shinkansen
*
400 series: The first
Mini-shinkansen type, introduced in 1992 on
Yamagata Shinkansen ''
Tsubasa
Tsubasa (written: 翼, 翔, 飛翔 or つばさ in hiragana) is a unisex Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Tsubasa (wrestler), Japanese professional wrestler
*, Japanese footballer
*, Japanese baseball player
*, Japanese ...
'' services with a maximum speed of 240 km/h. Withdrawn in April 2010.
*
E3 series: Introduced in 1997 on
Akita Shinkansen ''
Komachi'' and
Yamagata Shinkansen ''
Tsubasa
Tsubasa (written: 翼, 翔, 飛翔 or つばさ in hiragana) is a unisex Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include:
*Tsubasa (wrestler), Japanese professional wrestler
*, Japanese footballer
*, Japanese baseball player
*, Japanese ...
'' services with a maximum speed of 275 km/h. Now operated solely on the Yamagata Shinkansen.
*
E6 series: Introduced in March 2013 on Akita Shinkansen ''Komachi'' services, with a maximum speed of , raised to in March 2014.
*
E8 series: Future replacement of the E3 series for Tsubasa services to be introduced from 2024
File:400 L3 Tsubasa Yamagata 20020824.jpg, 400 series
File:E3-Komachi-R20-131109.JPG, E3 series (Komachi)
File:E3-2000 L67 Akayu Tsubasa 128 20150905.jpg, E3 series (Tsubasa)
File:E6 series Z12 Komachi 20161013.jpg, E6 series
Experimental trains
*
Class 1000 – 1961
*
Class 951 – 1969
*
Class 961 – 1973
*
Class 962 – 1979
*
500-900 series "WIN350" – 1992
*
Class 952/953 "STAR21" – 1992
*
Class 955 "300X" – 1994
*
Gauge Change Train
The Gauge Change Train (GCT) or is the name given to a Japanese project started in 1994 to develop a high-speed train with variable gauge axles to allow inter-running between the Shinkansen network, and the narrow gauge regional rail network.
T ...
– 1998 to present
*
Class E954 "Fastech 360S" – 2004
*
Class E955 "Fastech 360Z" – 2005
*
Class E956 "ALFA-X" – 2019
File:SHINKANSEN 1000A MODEL in KYOTO RAILWAY MUSEUM.JPG, Class 1000
File:951-1 RTRI Kokubunji 199711.jpg, Class 951
File:JNR shinkansen 961 sendai.jpg, Class 961
File:925-10 S2 Takasaki 20020925.jpg, Class 962
File:WIN350 Maibara 19981011.jpg, WIN350
File:STAR21 952-1 Maibara 20060727.JPG, STAR21
File:Shinkansen955-1-2.jpg, 300X
File:Gauge Changing Train 20120912.jpg, Gauge change train (2nd generation)
File:E954 S9 Sendai 20060421.jpg, Fastech 360S
File:E955 Sendai General Shinkansen Depot 20080726.jpg, Fastech 360Z
File:E956S13Sendai.jpg, ALFA-X
Maglev trains
''Note that these trains were and currently are used only for experimental runs, though the L0 series could be a passenger train.''
* LSM200 – 1972
* ML100 – 1972
* ML100A – 1975
* ML-500 – 1977
* ML-500R – 1979
* MLU001 – 1981
* MLU002 – 1987
* MLU002N – 1993
* MLX01 – 1996
*
L0 series – 2012
File:ML100 RTRI 20151010.JPG, ML100
File:ML500 RTRI 20151010.JPG, ML500
File:JR MLX01-1 001.jpg, MLX01
File:Series_L0.JPG, L0 series
Maintenance vehicles
* 911 Type diesel
locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
* 912 Type diesel locomotive
* DD18 Type diesel locomotive
* DD19 Type diesel locomotive
* 941 Type (rescue train)
* 921 Type (track inspection car)
* 922 Type (''
Doctor Yellow
is the nickname for the high-speed test trains that are used on the Japanese Shinkansen ("Bullet Train") dedicated express passenger train routes.
The trains have special equipment on board to monitor the condition of the track and overhead wire ...
'' sets T1, T2, T3)
* 923 Type (''Doctor Yellow'' sets T4, T5)
* 925 Type (''Doctor Yellow'' sets S1, S2)
* E926 Type (''
East i'')
File:Class 922 Doctor Yellow set T2.jpg, Doctor Yellow Type 922
File:Type923-T4.jpg, Doctor Yellow Type 923
File:925-10 S2 Takasaki 20020925.jpg, Doctor Yellow Type 925
File:TypeE926.jpg, Type E926 East-i
File:911 dl.JPG, Type 911 locomotive
File:Tokaido Shinkansen Kyoto station railway track maintenancea line 02.jpg, Track maintenance vehicles stabled along sidings outside Kyoto station
File:Multiple Tie Tamper.jpg, Tamping machine
File:バラスト整理車.jpg, Ballast cleaner
A ballast cleaner (also known as an undercutter, a shoulder ballast cleaning machine) is a machine that specialises in cleaning the railway track ballast (gravel, blue stone or other aggregate) of impurities.
Background and development
Over ti ...
File:延線車.jpg, Overhead line replacement vehicle
File:装柱車.jpg, Loading vehicle
Speed records
Traditional rail

Maglev

Reliability
Punctuality
The Shinkansen is very reliable thanks to several factors, including its near-total separation from slower traffic. In 2016,
JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
reported that the Shinkansen's average delay from schedule per train was 24 seconds. This includes delays due to uncontrollable causes, such as natural disasters. The record in 1997 was 18 seconds.
Safety record
Over the Shinkansen's 50-plus year history, carrying over 10 billion passengers, there have been no passenger fatalities due to train accidents such as derailments or collisions,
despite frequent earthquakes and typhoons. Injuries and a
single fatality have been caused by doors closing on passengers or their belongings; attendants are employed at platforms to prevent such accidents. There have, however, been suicides by passengers jumping both from and in front of moving trains.
On 30 June 2015, a passenger committed suicide on board a Shinkansen train by setting himself on fire, killing another passenger and seriously injuring seven other people.
There have been two derailments of Shinkansen trains in passenger service. The first one occurred during the
Chūetsu earthquake on 23 October 2004. Eight of ten cars of the
''Toki'' No. 325 train on the Jōetsu Shinkansen derailed near
Nagaoka Station in
Nagaoka, Niigata. There were no casualties among the 154 passengers.
Another derailment happened on 2 March 2013 on the
Akita Shinkansen when the ''Komachi'' No. 25 train derailed in blizzard conditions in
Daisen, Akita. No passengers were injured.
In the event of an earthquake, an earthquake detection system can bring the train to a stop very quickly; newer trainsets are lighter and have stronger braking systems, allowing for quicker stopping. A new anti-derailment device was installed after detailed analysis of the Jōetsu derailment.
Several months after the exposure of the
Kobe Steel falsification scandal, which is among the suppliers of
high-strength steel for Shinkansen trainsets, cracks were found upon inspection of a single
bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transp ...
, and removed from service on 11 December 2017.
Impacts
Economics
The Shinkansen has had a significant beneficial effect on Japan's business, economy, society, environment and culture beyond mere construction and operational contributions.
The results in time savings alone from switching from a conventional to a high-speed network have been estimated at 400 million hours, and the system has an economic impact of per year.
That does not include the savings from reduced reliance on imported fuel, which also has
national security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military atta ...
benefits. Shinkansen lines, particularly in the very crowded coastal
Taiheiyō Belt megalopolis, met two primary goals:
* Shinkansen trains reduced the congestion burden on regional transportation by increasing throughput on a minimal land footprint, therefore being economically preferable compared to modes (such as airports or highways) common in less densely populated regions of the world.
* As rail was already the primary urban mode of passenger travel, from that perspective it was akin to a
sunk cost; there was not a significant number of motorists to convince to switch modes. The initial megalopolitan Shinkansen lines were profitable and paid for themselves. Connectivity rejuvenated rural towns such as
Kakegawa that would otherwise be too distant from major cities.
However, upon the introduction of the 1973 Basic Plan the initial prudence in developing Shinkansen lines gave way to political considerations to extend the mode to far less populated regions of the country, partly to spread these benefits beyond the key centres of
Kanto
Kantō (Japanese)
Kanto is a simplified spelling of , a Japanese word, only omitting the diacritics.
In Japan
Kantō may refer to:
*Kantō Plain
*Kantō region
*Kantō-kai, organized crime group
*Kanto (Pokémon), a geographical region in the ' ...
and
Kinki. Although in some cases regional extension was frustrated by protracted land acquisition issues (sometimes influenced by the cancellation of the Narita Shinkansen following fierce protests by locals), over time Shinkansen lines were built to relatively sparsely populated areas with the intent the network would disperse the population away from the capital.
Such expansion had a significant cost. JNR, the national railway company, was already burdened with subsidizing unprofitable rural and regional railways. Additionally it assumed Shinkansen construction debt to the point the government corporation eventually owed some , contributing to it being regionalised and privatized in 1987.
The privatized JRs eventually paid a total of to acquire JNR's Shinkansen network.
Following privatization, the JR group of companies have continued Shinkansen network expansion to less populated areas, but with far more flexibility to
spin-off
Spin-off may refer to:
*Spin-off (media), a media work derived from an existing work
*Corporate spin-off, a type of corporate action that forms a new company or entity
* Government spin-off, civilian goods which are the result of military or gove ...
unprofitable railways or cut costs than in JNR days. Currently, an important factor is the post
bubble zero interest-rate policy
Zero interest-rate policy (ZIRP) is a macroeconomic concept describing conditions with a very low nominal interest rate, such as those in contemporary Japan and in the United States from December 2008 through December 2015. ZIRP is considere ...
that allows JR to borrow huge sums of capital without significant concern regarding
repayment timing.
A
UCLA study found that the presence of a Shinkansen line had helped with housing affordability by making it more realistic for lower-income city workers to live in exurban areas much further away from the city, which tends to have cheaper housing options. That in turn helps the city to "decentralise" and thus reduce the city property prices from what they could have otherwise been.
Environment
Traveling by the Tokaido Shinkansen from Tokyo to Osaka produces only around 16% of the
carbon dioxide of the equivalent journey by car, a saving of 15,000 tons of per year.
Challenges
Noise pollution
Noise pollution concerns have made increasing speed more difficult. In Japan,
population density is high and there have been severe protests against the Shinkansen's noise pollution. Its noise is now limited to less than 70
dB in residential areas.
Improvement and reduction of the
pantograph, weight saving of cars, and construction of
noise barrier
A noise barrier (also called a soundwall, noise wall, sound berm, sound barrier, or acoustical barrier) is an exterior structure designed to protect inhabitants of sensitive land use areas from noise pollution. Noise barriers are the most effecti ...
s and other measures have been implemented. Current research is primarily aimed at reducing operational noise, particularly the
tunnel boom phenomenon caused when trains transit tunnels at high speed.
Earthquake
Because of the risk of earthquakes in Japan, the Urgent Earthquake Detection and Alarm System (UrEDAS) (an
earthquake warning system) was introduced in 1992. It enables automatic braking of Shinkansen trains in the event of large earthquakes.
Heavy snow
The
Tōkaidō Shinkansen often experiences heavy snow in the area around
Maibara Station between December and February, requiring trains to reduce speed thus disrupting the timetable. Snow-dispersing sprinkler systems have been installed, but delays of 10–20 minutes still occur during snowy weather. Snow-related treefalls have also caused service interruptions. Along the
Jōetsu Shinkansen
The is a high-speed shinkansen railway line connecting Tokyo and Niigata, Japan, via the Tōhoku Shinkansen, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Despite its name, the line does not pass through the city of Joetsu or the hist ...
route, snow can be very heavy, with depths of two to three metres; the line is equipped with stronger sprinklers and
slab track to mitigate the snow's effects. Despite having multiple days with delays longer than 30 minutes, the
Tōhoku Shinkansen still presents a slight advantage in reliability compared to air travel on days with significant snowfall.
Ridership
Annual
* The sum of the ridership of individual lines does not equal the ridership of the system because a single rider may be counted multiple times when using multiple lines, to get proper ridership figures for a system, in the above case, is only counted once.
** Only refers to 6 days of operation: 26 March 2016 (opening date) to 31 March 2016 (end of FY2015).
Until 2011, Japan's high-speed rail system had the highest annual patronage of any system worldwide, China's HSR network's patronage reached 1.7 billion and is now the world's highest.
Cumulative comparison
Notes:
* Data in ''italics'' includes extrapolated estimations where data is missing. Turkey and Russia data here is included in "Europe" column, rather than split between Asia and Europe. Only systems with 200 km/h or higher regular service speed are considered.
* "Shinkansen share(%)" refers to percent of Shinkansen ridership (including fully assembled exported trainsets) as a percent of "World" total. Currently this only pertains to Taiwan, but may change if Japan exports Shinkansen to other nations.
* "Shinkansen" column does not include Shinkansen
knock down kits made in Japan exported to
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
for assembly, or any derivative system thereof in China)
* "Asia (other)" column refers to sum of riderships of all HSR systems geographically in Asia that do not use Shinkansen. (this data excludes Russia and Turkey, which geographically have parts in Asia but for sake of convenience included in Europe column)
* For 2013,
Japan's Ministry of Transport has not updated data, nor is summed European data available (even 2012 data is very rough), however Taiwan ridership is 47.49 million and Korea with 54.5 million and China with 672 million in 2013.
Cumulative ridership since October 1964 is over 5 billion passengers for the Tokaido Shinkansen Line alone and 10 billion passengers for Japan's entire shinkansen network.
Nevertheless, China's share is increasing fast, as close to 9.5 billion passengers in that nation have been served by the end of 2018 and is projected to pass Japan's cumulative numbers by as early as 2020.
Future
Speed increases
Tōhoku Shinkansen
E5 series trains, capable of up to , initially limited to 300 km/h, were introduced on the
Tōhoku Shinkansen in March 2011. Operation at the maximum speed of 320 km/h between and on this route commenced on 16 March 2013. It reduced the journey time to around 3 hours for trains from Tokyo to Shin-Aomori, a distance of .
Extensive trials using the
Fastech 360 test trains have shown that operation at is not currently feasible because of problems of
noise pollution (particularly
tunnel boom), overhead wire wear, and braking distances. On 30 October 2012, JR East announced that it was pursuing research and development to increase speeds to 360 km/h on the Tohoku Shinkansen by 2020.
The
ALFA-X is currently undergoing testing.
Hokkaido Shinkansen
Upon commencement of services in 2016, the maximum speed on the approximately 82 km
dual gauge
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to c ...
section of the
Hokkaido Shinkansen (including through the
Seikan Tunnel) was , which was increased to by March 2019.
There are approximately 50 freight trains using the dual gauge section each day, so limiting the travel of such trains to times outside of Shinkansen services is not an option. Because of this and other weather-related factors cited by JR East and JR Hokkaido, the fastest journey time between Tokyo and Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto is currently 3 hours, 57 minutes.
During the 2020-21 New Year Holiday period, certain Shinkansen services were operated at on the dual gauge section and was proposed again for the
Golden Week Holiday period from 3-6 May 2021, due to fewer freight trains operating.
To achieve the full benefit of Shinkansen trains travelling on the dual gauge section at (the maximum speed proposed through the tunnel), alternatives are being considered, such as a system to automatically slow Shinkansen trains to when passing narrow-gauge trains, and/or loading freight trains onto special "
Train on Train" standard-gauge trains (akin to a covered piggyback flatcar train) built to withstand the
shock wave of oncoming Shinkansen trains traveling at full speed. This would enable a travel time from Tokyo to Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto of 3 hours and 45 minutes, a saving of 12 minutes on the current timetable.
Hokuriku extension
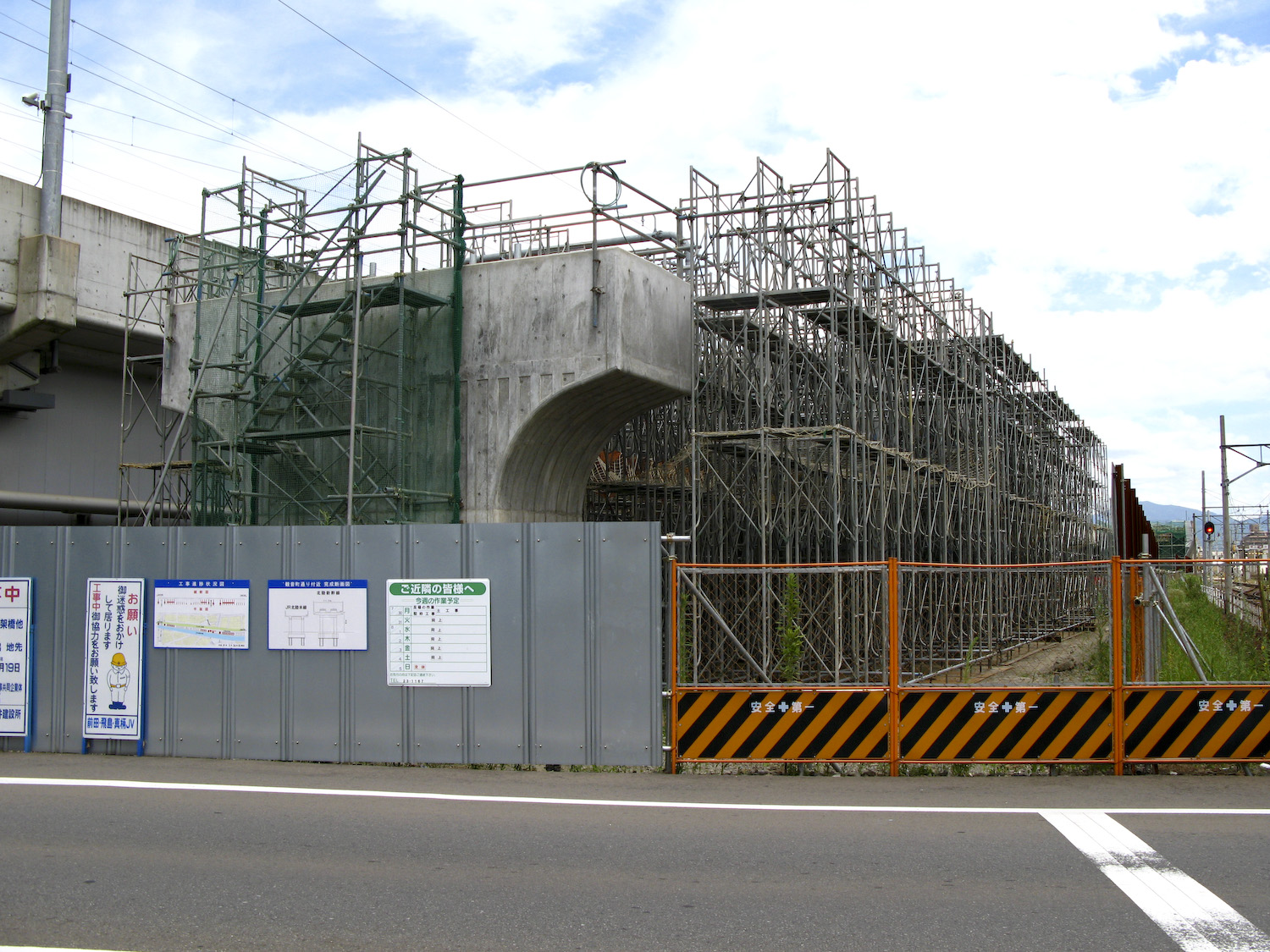

The Hokuriku Shinkansen is being extended from Kanazawa to Tsuruga (proposed for completion by fiscal year 2024) at an estimated cost of 3.04 trillion yen (in 2012 currency).
There are further plans to extend the line from Tsuruga to Osaka, with the Obama-Kyoto route chosen by the government on 20 December 2016,
after a government committee investigated the five nominated routes.
Construction of the extension beyond Tsuruga is not expected to commence before 2030, with a projected 15-year construction period. On 6 March 2017 the government committee announced the chosen route from Kyoto to Shin-Osaka is to be via
Kyotanabe, with a station at
Matsuiyamate on the
Katamachi Line.
Interim plans
To extend the benefits of the Hokuriku Shinkansen to stations west of Tsuruga before the line to Osaka is completed, JR West was working in partnership with Talgo on the development of a
Gauge Change Train
The Gauge Change Train (GCT) or is the name given to a Japanese project started in 1994 to develop a high-speed train with variable gauge axles to allow inter-running between the Shinkansen network, and the narrow gauge regional rail network.
T ...
(CGT) capable of operating under both the 25 kV AC electrification used on the Shinkansen and the 1.5 kV DC system employed on conventional lines. A trial of the proposed bogie was undertaken on a purpose-built gauge-changer at Tsuruga, but it was unsuccessful and the plans were abandoned.
Tohoku extension/Hokkaido Shinkansen
The
Hokkaido Shinkansen forms an extension of the Tohoku Shinkansen north of to
Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto Station
is a railway station on the Hakodate Main Line in Hokuto, Hokkaido, Japan, operated by the Hokkaido Railway Company (JR Hokkaido). The station – rebuilt and very extensively enlarged to serve from March 2016 as the northern terminal of the new ...
(north of the
Hokkaido city of
Hakodate) through the
Seikan Tunnel, which was converted to dual gauge as part of the project, opening in March 2016.
JR Hokkaido is extending the Hokkaido Shinkansen from Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto to to open by March 2031,
with tunnelling work on the 5,265 m Murayama tunnel, situated about 1 km north of Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto Station, commencing in March 2015, and due to be completed by March 2021. The 211.3 km extension will be approximately 76% in tunnels, including major tunnels such as Oshima (~26.5 km), Teine (~18.8 km) and Shiribeshi (~18 km).
Although an extension from Sapporo to
Asahikawa was included in the 1973 list of planned lines, at this time it is unknown whether the Hokkaido Shinkansen will be extended beyond Sapporo.
Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen
JR Kyushu opened the Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen from to (built to full Shinkansen standard) on 23 September 2022, with the existing narrow gauge section between Shin-Tosu and Takeo Onsen proposed to be upgraded as part of this project.
This proposal initially involved introducing
Gauge Change Train
The Gauge Change Train (GCT) or is the name given to a Japanese project started in 1994 to develop a high-speed train with variable gauge axles to allow inter-running between the Shinkansen network, and the narrow gauge regional rail network.
T ...
s (GCT) travelling from Hakata to Shin-Tosu () on the existing Kyushu Shinkansen line, then passing through a specific gauge changing (standard to narrow) section of track linking to the existing
Nagasaki Main Line, along which it would travel to Hizen Yamaguchi (), then onto the
Sasebo Line to Takeo-Onsen (), where another gauge changing section (narrow to standard) would lead onto the final Shinkansen line to Nagasaki (). However, significant technical issues with the axles of the GCT resulted in its cancellation.
On 28 October 2020, JR Kyushu announced it would utilize a 6-car version of the N700S for the isolated Shinkansen section from Nagasaki, with 'cross platform' change to a relay service at Takeo Onsen station to connect to Hakata.
JR Kyushu also announced the service would continue to use the name 'Kamome' for the Hakata-Nagasaki service, which has been in use since 1961.
The Shinkansen line shortens the distance between Hakata and Nagasaki by 6.2% (), and while only 64% of the route is built to full Shinkansen standards, it eliminated the slowest sections of the previous narrow gauge route.
As part of the GCT proposal, the current section of single track between Hizen Yamaguchi and Takeo Onsen was proposed to be duplicated. However, due to the issues with the development of the GCT, the proposal has not advanced.
The initial section between Nagasaki and Takeo Onsen opened on 23 September 2022.
Maglev (''Chuo Shinkansen'')
Maglev trains have been undertaking test runs on the Yamanashi test track since 1997, running at speeds of over . As a result of this extensive testing, maglev technology is almost ready for public usage.
An extension of this test track from to was completed in June 2013, enabling extended high-speed running trials to commence in August 2013. This section will be incorporated into the
Chūō Shinkansen which will eventually link Tokyo to Osaka. Construction of the
Shinagawa to
Nagoya section began in 2014, with 86% of the route to be in tunnels.
The CEO of JR Central originally announced plans to have the
maglev Chūō Shinkansen operating from Tokyo to by 2027,
with a subsequent extension to Osaka by 2037. However, as of 2022,
continuing controversy over routing across the Ōi River has prevented the start of construction in Shizuoka, and there is currently no target date for opening.
Following the shortest route (through the
Japanese Alps
The is a series of mountain ranges in Japan which bisect the main island of Honshu. The peaks that tower over central Honshu have long been the object of veneration and pilgrimage. These mountains had long been exploited by local people for raw m ...
), JR Central estimates that it will take 40 minutes to run from Shinagawa to Nagoya. The planned travel time from Shinagawa to Shin-Osaka is 1 hour 7 minutes. Currently the Tokaido Shinkansen has a minimum connection time of 2 hours 19 minutes.
While the government has granted approval for the shortest route between Tokyo and Nagoya, some prefectural governments, particularly Nagano, lobbied to have the line routed farther north to serve the city of
Chino and either
Ina or . However, that would increase both the travel time (from Tokyo to Nagoya) and the cost of construction. JR Central has confirmed it will construct the line through
Kanagawa Prefecture, and terminate at
Shinagawa Station
is a major railway station in the Takanawa and Konan districts of Minato, Tokyo, Japan, operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), and the private railway operator Keikyu. The Tokaido Shinkan ...
.
The route for the Nagoya to Osaka section is also contested. It is planned to go via
Nara, about 40 km south of
Kyoto. Kyoto is lobbying to have the route moved north and be largely aligned with the existing
Tokaido Shinkansen, which services Kyoto and not Nara.
Mini-Shinkansen
is the name given to the routes where former narrow gauge lines have been converted to standard gauge to allow Shinkansen trains to travel to cities without the expense of constructing full Shinkansen standard lines.
Two mini-shinkansen routes have been constructed: the
Yamagata Shinkansen and
Akita Shinkansen. Shinkansen services to these lines traverse the
Tohoku Shinkansen line from Tokyo before branching off to traditional main lines. On both the Yamagata/Shinjo and Akita lines, the narrow gauge lines were regauged, resulting in the local services being operated by
standard gauge versions of 1,067 mm gauge suburban/interurban rolling stock. On the Akita line between Omagari and Akita, one of the two narrow gauge lines was regauged, and a section of the remaining narrow gauge line is dual gauge, providing the opportunity for Shinkansen services to pass each other without stopping.
The maximum speed on these lines is , however the overall travel time to/from Tokyo is improved due to the elimination of the need for passengers to change trains at
Fukushima
may refer to:
Japan
* Fukushima Prefecture, Japanese prefecture
**Fukushima, Fukushima, capital city of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan
*** Fukushima University, national university in Japan
*** Fukushima Station (Fukushima) in Fukushima, Fukushim ...
and
Morioka respectively.
As the
Loading gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and ke ...
(size of the train that can travel on a line) was not altered when the rail gauge was widened, only Shinkansen trains specially built for these routes can travel on the lines. At present they are the E3 and E6 series trains.
As some of the E3 series on the Yamagata Shinkansen will be retiring soon, they will be replaced by the new
E8 Series Shinkansen
The is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed train type on order for '' Tsubasa'' services announced on 3 March 2020. It is intended to replace the E3 series, raising the top speed of the service from to . It is designed by Ken Okuyama, in cooper ...
trains from Spring 2024 with an increased speed of 300km/h, up from the current 275km/h on the
E3 Series trains.
Whilst no further Mini-shinkansen routes have been proposed to date, it remains an option for providing Shinkansen services to cities on the narrow gauge network.
Proposed Ou Base Tunnel
Construction of a
Base tunnel on the
Yamagata Shinkansen is proposed, with JR East having undertaken a survey of a planned route from Niwasaka to Sekine, just south of Yonezawa station. of the proposed line would be in tunnel, mostly to the north of the existing Fukushima – Yamagata section. To be built on an improved alignment, the tunnel would lower journey times between Fukushima and Yamagata by ~10 min due to a proposed line speed of up to 200 km/h.
The tunnel would avoid the Itaya Toge pass through the Ou mountains west of Fukushima. Gradients range from 3.0% to 3.8% and the line reaches an altitude of . The curvature and steep grades limit train speeds to or less, and the line is vulnerable to heavy rain and snowfall as well as high winds. Between 2011 and 2017 a total of 410 Yamagata mini-Shinkansen services were either suspended or delayed, and 40% of these incidents occurred on the line over the Itaya Toge pass.
If the base tunnel is authorised, detailed design would take five years and construction another 15 years. The cost could increase by if the tunnel were to be built with a cross-section large enough to permit the line to be upgraded to the full Shinkansen loading gauge.
Gauge Change Train
This is the name for the concept of using a single train that is specially designed to travel on both narrow gauge railway lines and the standard gauge used by Shinkansen train services in Japan. The trucks/bogies of the Gauge Change Train (GCT) allow the wheels to be unlocked from the axles, narrowed or widened as necessary, and then relocked. This allows a GCT to traverse both standard gauge and narrow gauge tracks without the expense of regauging lines.
Three test trains have been constructed, with the second set having completed reliability trials on the
Yosan Line east of
Matsuyama (in
Shikoku) in September 2013. The third set was undertaking gauge changing trials at
Shin-Yatsushiro Station (on
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
), commencing in 2014 for a proposed three-year period, however testing was suspended in December 2014 after accumulating approximating 33,000 km, following the discovery of defective thrust bearing oil seals on the bogies.
The train was being trialled between
Kumamoto, travelling on the narrow gauge line to Shin-Yatsushiro, where a gauge changer has been installed, so the GCT could then be trialled on the Shinkansen line to
Kagoshima. It was anticipated the train would travel approximately 600,000 km over the three-year trial.
A new "full standard" Shinkansen line is under construction from Takeo Onsen to , with the Shin-Tosu – Takeo Onsen section of the
Kyushu Shinkansen branch to remain narrow gauge. GCTs were proposed to provide the Shinkansen service from the line's scheduled opening in fiscal 2022, however with the GCT now being cancelled, JR Kyushu has announced it will provide an interim
'relay' service.
Competition with air
Compared with air transport, the Shinkansen has several advantages, including scheduling frequency and flexibility, punctual operation, comfortable seats, and convenient city-centre terminals.
Shinkansen fares are generally competitive with domestic air fares. From a speed and convenience perspective, the Shinkansen's market share has surpassed that of air travel for journeys of less than 750 km, while air and rail remain highly competitive with each other in the 800–900 km range and air has a higher market share for journeys of more than 1,000 km.
During snowy weather, the Shinkansen is known to face fewer delays compared to air travel due to snow. One study done in 2016 concluded that the Tohoku Shinkansen between Tokyo and Aomori had substantially fewer days with delays longer than 30 minutes compared to air travel.
* Tokyo – Nagoya (342 km), Tokyo – Sendai (325 km), Tokyo –
Hanamaki (
Morioka) (496 km), Tokyo – Niigata (300 km): There were air services between these cities, but they were withdrawn after Shinkansen services started. Shinkansen runs between these cities in about two hours or less.
* Tokyo – Osaka (515 km): Shinkansen is dominant because of fast (2 hours 22 minutes) and frequent service (up to every 10 minutes by ''Nozomi''); however, air travel has a certain share (~20–30%).
* Tokyo – Okayama (676 km), Tokyo – Hiroshima (821 km): Shinkansen is reported to have increased its market share from ~40% to ~60% over the last decade.
The Shinkansen takes about three to four hours and there are ''Nozomi'' trains every 30 minutes, but airlines may provide cheaper fares, attracting price-conscious passengers.
* Tokyo – Fukuoka (1,069 km): The Shinkansen takes about five hours on the fastest ''Nozomi'', and discount carriers have made air travel far cheaper, so most people choose air. Additionally, unlike many cities, there is very little convenience advantage for the location of the Shinkansen stations of the two cities as
Fukuoka Airport is located near the central
Tenjin district, and
Fukuoka City Subway Line 1 Line 1 or 1 line may refer to:
Public transport Africa
* Line 1 (Algiers Metro), Algeria
* Cairo Metro Line 1, Egypt
Asia China
* Line 1 (Beijing Subway)
* Line 1 (Changchun Rail Transit)
* Line 1 (Changsha Metro)
* Line 1 (Changzhou Metro)
* L ...
connects the Airport and Tenjin via Hakata Station and
Haneda Airport is similarly conveniently located.
* Osaka – Fukuoka (554 km): One of the most competitive sections. The Shinkansen takes about two and a half hours by ''Nozomi'' or ''Mizuho'', and the JR West ''Hikari Rail Star'' or JR West/JR Kyushu ''Sakura'' trains operate twice an hour, taking about 2 hours and 40 minutes between the two cities. Again the location of the airports involved helps with the popularity of air travel.
* Tokyo – Aomori (675 km): The fastest Shinkansen service between these cities is 3 hours. JAL is reported to have reduced the size of planes servicing this route since the Shinkansen extension opened in 2010.
* Tokyo – Hokuriku (345 km): The fastest Shinkansen service between these cities is 2 hours. ANA is reported to have reduced the number of services from Tokyo to Kanazawa and Toyama from 6 to 4 per day since the Shinkansen extension opened in 2015. The share of passengers travelling this route by air is reported to have dropped from 40% to 10% in the same period.
Shinkansen technology outside Japan
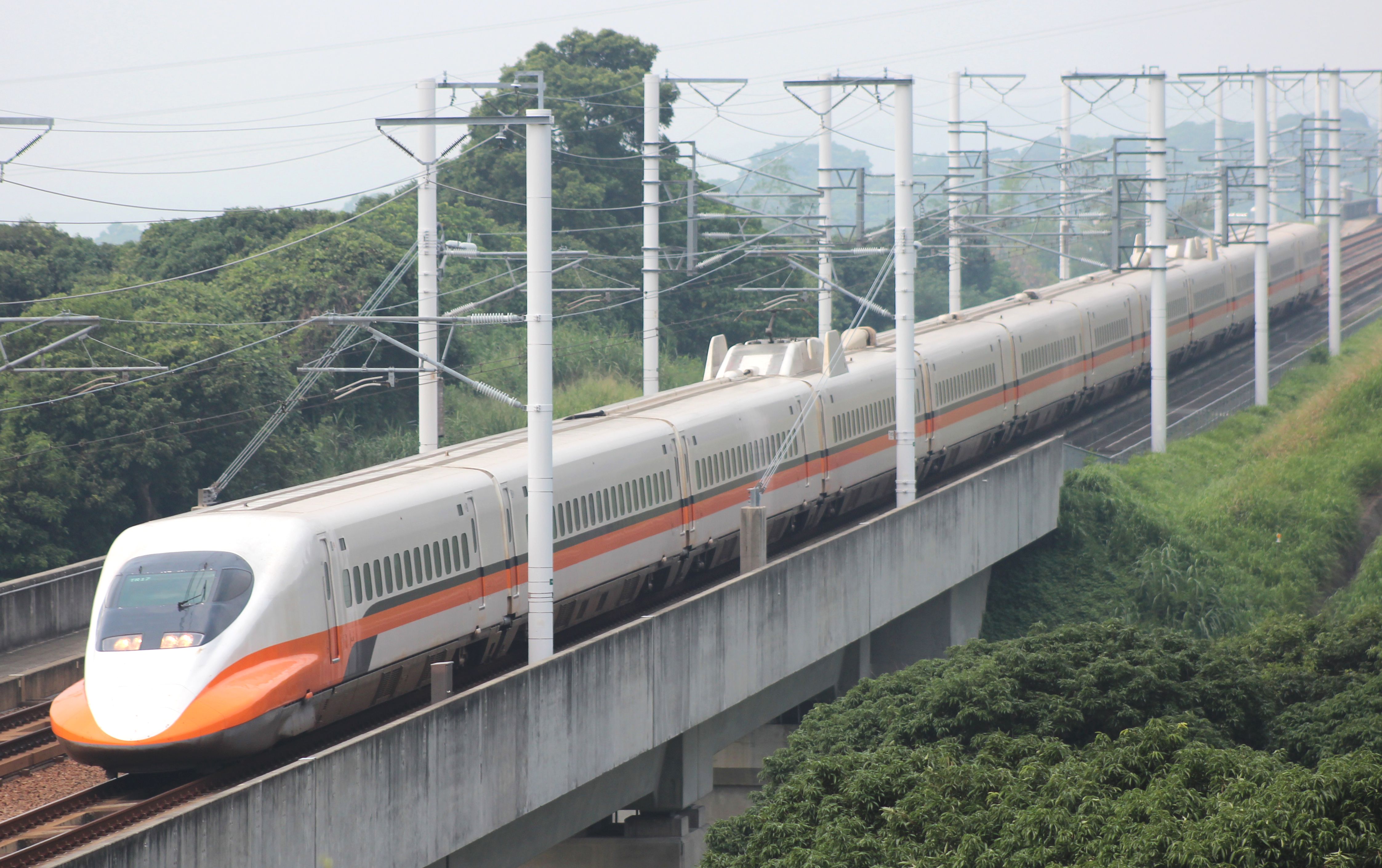
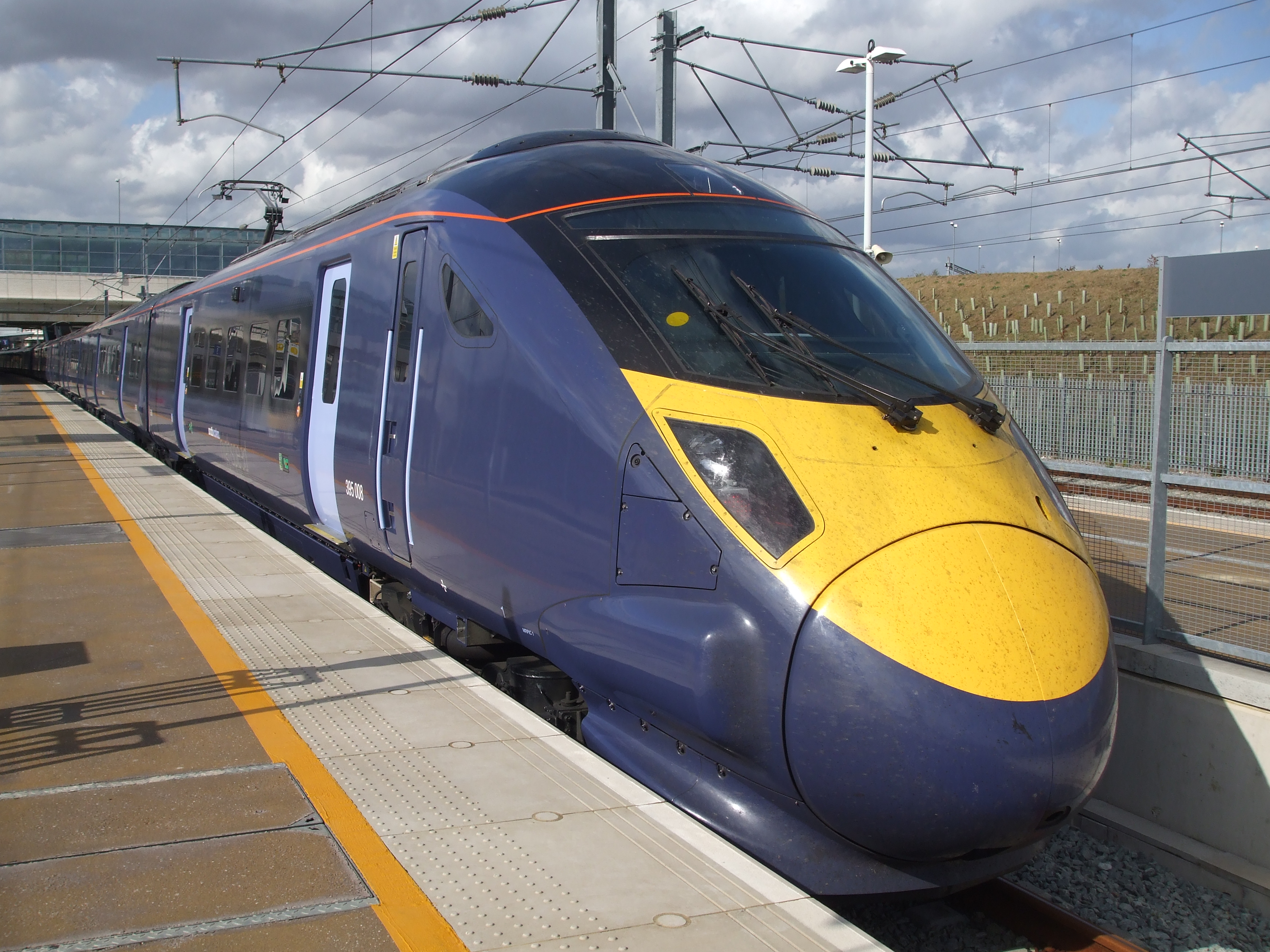



Railways using Shinkansen technology are not limited to those in Japan.
Existing
Taiwan
The first Shinkansen type exported outside Japan.
Taiwan High Speed Rail operates
700T Series sets built by
Kawasaki Heavy Industries. 12-car trains based on
700 series entered service in 2007, with a maximum speed of .
China
The
China Railways CRH2, built by CSR Sifang Loco & Rolling stocks corporation, with the license purchased from a consortium formed of Kawasaki Heavy Industries,
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and
Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
, is based on the
E2-1000 series design.
United Kingdom
Class 395 EMUs were built by Hitachi based on Shinkansen technology for use on high-speed commuter services in Britain on the
High Speed 1
High Speed 1 (HS1), legally the Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL), is a high-speed railway linking London with the Channel Tunnel.
It is part of a line carrying international passenger traffic between the United Kingdom and mainland Europe; ...
line.
Under contract
United States
In 2014, it was announced that
Texas Central Railway would build a ~300-mile (~480 km) long line using the N700 series rolling stock. The trains are proposed to operate at over 320 km/h (200 mph).
India
In December 2015, India and Japan signed an agreement for the construction of India's first high speed rail link
connecting Mumbai to Ahmedabad. Funded primarily through Japanese soft loans, the link is expected to cost up to US$18.6 billion and should be operational in about 6 years.
This followed India and Japan conducting feasibility studies on
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
and
dedicated freight corridors.
The
Indian Ministry of Railways' white-paper Vision 2020
submitted to
Indian Parliament by
Railway Minister Piyush Goyal on 18 December 2009 envisages the implementation of regional high-speed rail projects to provide services at 250–350 km/h.
During Indian Prime Minister
Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh (; born 26 September 1932) is an Indian politician, economist and statesman who served as the 13th prime minister of India from 2004 to 2014. He is also the third longest-serving prime minister after Jawaharlal Nehru and Indir ...
's visit to Tokyo in December 2006, Japan assured cooperation with India in creating a high-speed link between New Delhi and Mumbai. In January 2009, the then Railway Minister
Lalu Prasad
Lalu Prasad Yadav (born 11 June 1948) is an Indian politician and president of the Rashtriya Janata Dal (RJD). He is a former Chief Minister of Bihar (1990-1997), a former Railway Minister of India (2004-2009), and a former Member of Parliam ...
rode a bullet train travelling from Tokyo to Kyoto.
In December 2013 a Japanese consortium was appointed to undertake a feasibility study of a ~500 km high-speed line between
Mumbai and
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per t ...
by July 2015. A total of 7 high-speed lines are in planning stages in India, and Japanese firms have now succeeded in winning contracts to prepare feasibility studies for three of the lines.
The
National High Speed Rail Corporation (NHSRC) was incorporated in 2017 to manage all HSR related activities in India. Under its management, a High Speed Rail Training Institute is being developed with Japanese assistance in
Vadodara,
Gujarat. After the laying of the foundation stone for the
Mumbai and
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per t ...
by the Prime Ministers of India and Japan in September 2017, work began on preparatory surveys along the route. The route consists of approximately elevated viaduct through 11 districts of Gujarat and four districts of
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
, a deep-sea tunnel starting from
BKC in Mumbai, and approximately of at-grade alignment near the other terminus at
Sabarmati, near
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per t ...
. Most of the civil works for the elevated viaduct shall be handled by Indian companies, while the deep-sea tunnel at Mumbai will be handled by a Japanese consortium (along with other technical aspects, such as safety, electricals, communication systems, signaling, and rolling stock).
BHEL of India and
Kawasaki Heavy Industries of Japan have entered into a technology collaboration agreement to build and assemble the rolling stock (of
E5 series) in India. Other potential joint ventures are being explored under the patronage of NHSRC. The line is expected to be operational by 2026.
Proposed subject to funding
Thailand
Japan will provide Shinkansen technology for a high-speed rail link between Bangkok and the northern city of Chiang Mai under an agreement reached with Thailand on 27 May 2015. Total project costs are estimated in excess of 1 trillion yen ($8.1 billion). Several hurdles remain, however, including securing the funding. If the project is realized, it would mark the fifth time Shinkansen technology has been exported.
Potential opportunities
Australia
A private organisation dedicated to aiding the
Australian Government in delivering high speed rail,
Consolidated Land and Rail Australia
Consolidated Land and Rail Australia (trading as CLARA) is a property development consortium proposing a high speed rail network for the Australian east coast that would funded by the development of new smart cities along the route. The company b ...
, has considered purchasing Shinkansen technology or SC Maglev rolling stock for a potential
Melbourne-
Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
-
Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
-
Brisbane line.
A business case has been prepared for the government by
Infrastructure Australia, and was awaiting confirmation of the project within the 2018 federal budget.
Ireland
As part of the Ireland 2040 infrastructural upgrade scheme, a high-speed rail network using Shinkansen technology is being investigated along the
Cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
-
Dublin-
Belfast axis, spanning the island of Ireland from north to south.
United States and Canada
The U.S.
Federal Railroad Administration was in talks with a number of countries concerning high-speed rail, notably Japan, France and Spain. On 16 May 2009, FRA Deputy Chief Karen Rae expressed hope that Japan would offer its technical expertise to
Canada and the
United States. Transportation Secretary
Ray LaHood indicated interest in test riding the Japanese Shinkansen in 2009.
On 1 June 2009,
JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
Chairman, Yoshiyuki Kasai, announced plans to export both the
N700 Series Shinkansen high-speed train system and the
SCMaglev to international export markets, including the United States and Canada.
Brazil
Japan had promoted its Shinkansen technology to the Government of
Brazil for use on the once planned
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
set to link
Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Campinas.
On 14 November 2008, Japanese Deputy Prime Minister
Tarō Asō and Brazilian President
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva talked about this rail project. President Lula asked a consortium of Japanese companies to participate in the bidding process. Prime Minister Aso concurred on the bilateral cooperation to improve rail infrastructure in Brazil, including the Rio–São Paulo–Campinas high-speed rail line.
The Japanese consortium included the
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism,
Mitsui & Co.,
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries,
Kawasaki Heavy Industries and
Toshiba.
Nothing was implemented.
Vietnam
Vietnam Railways
Vietnam Railways (VNR, ) is the state-owned operator of the railway system in Vietnam. The principal route is the single-track North–South Railway line, running between Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. This was built at the metre gau ...
was considering the use of Shinkansen technology for
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
between the capital
Hanoi and the southern commercial hub of
Ho Chi Minh City
, population_density_km2 = 4,292
, population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2
, population_demonym = Saigonese
, blank_name = GRP (Nominal)
, blank_info = 2019
, blank1_name = – Total
, blank1_ ...
, according to the
Nihon Keizai Shimbun
''The Nikkei'', also known as , is the flagship publication of Nikkei, Inc. (based in Tokyo) and the world's largest financial newspaper, with a daily circulation exceeding 1.73 million copies. The Nikkei 225, a stock market index for the Tok ...
, citing an interview with Chief Executive Officer Nguyen Huu Bang. The Vietnamese government had already given basic approval for the Shinkansen system, although it still requires financing and formal consent from the prime minister. Vietnam rejected a funding proposal in 2010, so funding for the $56 billion project is uncertain. Hanoi was exploring additional Japanese funding
Official Development Assistance as well as funds from the
World Bank and
Asian Development Bank. The line would replace the current colonial-era rail line.
Vietnam hoped to launch high-speed trains by 2020 and planned to start by building three sections, including a 90-kilometre stretch between the central coastal cities of
Da Nang
Nang or DanangSee also Danang Dragons ( ; vi, Đà Nẵng, ) is a class-1 municipality and the fifth-largest city in Vietnam by municipal population. It lies on the coast of the East Sea of Vietnam at the mouth of the Hàn River, and is one ...
and
Huế, seen as potentially most profitable. Vietnam Railways had sent engineers to
Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
for technical training.
See also
*
Transport in Japan
*
Rail transport in Japan
*
Shanghai Maglev Train
*
High speed rail in China
*
High speed rail in Europe
High-speed rail (HSR) has developed in Europe as an increasingly popular and efficient means of transport. The first high-speed rail lines on the continent, built in the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s, improved travel times on intra-national corridors ...
*
High speed rail in India
Indian Railways is currently improving their existing conventional lines to handle speeds of up to , and with certain improved corridors seeing speeds of more than . Also, a total of twelve corridors are planned and one of the corridors which ...
*
High speed rail in the United States
Plans for high-speed rail in the United States date back to the High-Speed Ground Transportation Act of 1965. Various state and federal proposals have followed. Despite being one of the world's first countries to get high-speed trains (the Me ...
References
Further reading
*
External links
Shinkansen Data, explanation by International High-speed Rail Association (IHRA)
discussion paper by Christopher Hood in th
''electronic journal of contemporary Japanese studies'' 23 May 2001
a story of how the Shinkansen brought Tokyo and
Osaka closer together.
Bullet on wheels a travel report by Vinod Jacob 19 August 2005
Shinkansen Wheelchair Accessibility review for riders with disabilities.
{{Authority control
High-speed rail in Japan
High-speed trains
Rail transport brands
Railway services introduced in 1964
1964 establishments in Japan


 The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of 
 Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high-speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of narrow-gauge lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds due to technical limitations of narrow-gauge rail. For example, if a standard-gauge rail has a curve with a maximum speed of , the same curve on narrow-gauge rail will have a maximum allowable speed of . Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high-speed lines than countries where the existing
Japan was the first country to build dedicated railway lines for high-speed travel. Because of the mountainous terrain, the existing network consisted of narrow-gauge lines, which generally took indirect routes and could not be adapted to higher speeds due to technical limitations of narrow-gauge rail. For example, if a standard-gauge rail has a curve with a maximum speed of , the same curve on narrow-gauge rail will have a maximum allowable speed of . Consequently, Japan had a greater need for new high-speed lines than countries where the existing  The Tōkaidō Shinkansen began service on 1 October 1964, in time for the first Tokyo Olympics. The conventional Limited Express service took six hours and 40 minutes from Tokyo to Osaka, but the Shinkansen made the trip in just four hours, shortened to three hours and ten minutes by 1965. It enabled day trips between Tokyo and Osaka, the two largest metropolises in Japan, significantly changed the style of business and life of the Japanese people, and increased new traffic demand. The service was an immediate success, reaching the 100 million passenger mark in less than three years on 13 July 1967, and one billion passengers in 1976. Sixteen-car trains were introduced for Expo '70 in Osaka. With an average of 23,000 passengers per hour in each direction in 1992, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen was the world's busiest high-speed rail line. As of 2014, the train's 50th anniversary, daily passenger traffic rose to 391,000 which, spread over its 18-hour schedule, represented an average of just under 22,000 passengers per hour.
The first Shinkansen trains, the 0 series, ran at speeds of up to , later increased to . The last of these trains, with their classic bullet-nosed appearance, were retired on 30 November 2008. A driving car from one of the 0 series trains was donated by JR West to the National Railway Museum in York, United Kingdom in 2001.
The Tōkaidō Shinkansen began service on 1 October 1964, in time for the first Tokyo Olympics. The conventional Limited Express service took six hours and 40 minutes from Tokyo to Osaka, but the Shinkansen made the trip in just four hours, shortened to three hours and ten minutes by 1965. It enabled day trips between Tokyo and Osaka, the two largest metropolises in Japan, significantly changed the style of business and life of the Japanese people, and increased new traffic demand. The service was an immediate success, reaching the 100 million passenger mark in less than three years on 13 July 1967, and one billion passengers in 1976. Sixteen-car trains were introduced for Expo '70 in Osaka. With an average of 23,000 passengers per hour in each direction in 1992, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen was the world's busiest high-speed rail line. As of 2014, the train's 50th anniversary, daily passenger traffic rose to 391,000 which, spread over its 18-hour schedule, represented an average of just under 22,000 passengers per hour.
The first Shinkansen trains, the 0 series, ran at speeds of up to , later increased to . The last of these trains, with their classic bullet-nosed appearance, were retired on 30 November 2008. A driving car from one of the 0 series trains was donated by JR West to the National Railway Museum in York, United Kingdom in 2001.
 The Shinkansen employs an ATC (Automatic Train Control) system, eliminating the need for trackside signals. It uses a comprehensive system of
The Shinkansen employs an ATC (Automatic Train Control) system, eliminating the need for trackside signals. It uses a comprehensive system of 
 Originally intended to carry passenger and freight trains by day and night, the Shinkansen lines carry only passenger trains. The system shuts down between midnight and 06:00 every day for maintenance. The few overnight passenger trains that still run in Japan run on the older narrow gauge network that the Shinkansen parallels.
Originally intended to carry passenger and freight trains by day and night, the Shinkansen lines carry only passenger trains. The system shuts down between midnight and 06:00 every day for maintenance. The few overnight passenger trains that still run in Japan run on the older narrow gauge network that the Shinkansen parallels.


 The Hokuriku Shinkansen is being extended from Kanazawa to Tsuruga (proposed for completion by fiscal year 2024) at an estimated cost of 3.04 trillion yen (in 2012 currency).
There are further plans to extend the line from Tsuruga to Osaka, with the Obama-Kyoto route chosen by the government on 20 December 2016, after a government committee investigated the five nominated routes.
Construction of the extension beyond Tsuruga is not expected to commence before 2030, with a projected 15-year construction period. On 6 March 2017 the government committee announced the chosen route from Kyoto to Shin-Osaka is to be via Kyotanabe, with a station at Matsuiyamate on the Katamachi Line.
The Hokuriku Shinkansen is being extended from Kanazawa to Tsuruga (proposed for completion by fiscal year 2024) at an estimated cost of 3.04 trillion yen (in 2012 currency).
There are further plans to extend the line from Tsuruga to Osaka, with the Obama-Kyoto route chosen by the government on 20 December 2016, after a government committee investigated the five nominated routes.
Construction of the extension beyond Tsuruga is not expected to commence before 2030, with a projected 15-year construction period. On 6 March 2017 the government committee announced the chosen route from Kyoto to Shin-Osaka is to be via Kyotanabe, with a station at Matsuiyamate on the Katamachi Line.

