SO(3,1) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Because it is a
Because it is a

 The set of real scalar multiples of this null vector, called a ''null line'' through the origin, represents a ''line of sight'' from an observer at a particular place and time (an arbitrary event we can identify with the origin of Minkowski spacetime) to various distant objects, such as stars. Then the points of the
The set of real scalar multiples of this null vector, called a ''null line'' through the origin, represents a ''line of sight'' from an observer at a particular place and time (an arbitrary event we can identify with the origin of Minkowski spacetime) to various distant objects, such as stars. Then the points of the
 As with any connected Lie group, the coset spaces of the closed subgroups of the restricted Lorentz group, or
As with any connected Lie group, the coset spaces of the closed subgroups of the restricted Lorentz group, or
''Geometric Algebra'', chapter III: Symplectic and Orthogonal Geometry
via
 In
In physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
and mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, the Lorentz group is the group of all Lorentz transformations of Minkowski spacetime
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inert ...
, the classical and quantum
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantizati ...
setting for all (non-gravitational) physical phenomena. The Lorentz group is named for the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. He also derived the Lorentz t ...
.
For example, the following laws, equations, and theories respect Lorentz symmetry:
* The kinematical laws of special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The laws o ...
* Maxwell's field equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
...
in the theory of electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of a ...
* The Dirac equation in the theory of the electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
* The Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying a ...
of particle physics
The Lorentz group expresses the fundamental symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definit ...
of space and time of all known fundamental laws of nature. In small enough regions of spacetime where gravitational variances are negligible, physical laws are Lorentz invariant in the same manner as special relativity.
Basic properties
The Lorentz group is a subgroup of the Poincaré group—the group of all isometries ofMinkowski spacetime
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inert ...
. Lorentz transformations are, precisely, isometries that leave the origin fixed. Thus, the Lorentz group is an isotropy subgroup of the isometry group of Minkowski spacetime. For this reason, the Lorentz group is sometimes called the homogeneous Lorentz group while the Poincaré group is sometimes called the ''inhomogeneous Lorentz group''. Lorentz transformations are examples of linear transformations; general isometries of Minkowski spacetime are affine transformation
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, ''affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles.
More generally, ...
s.
Mathematically, the Lorentz group may be described as the indefinite orthogonal group O(1,3), the matrix Lie group that preserves the quadratic form
In mathematics, a quadratic form is a polynomial with terms all of degree two ("form" is another name for a homogeneous polynomial). For example,
:4x^2 + 2xy - 3y^2
is a quadratic form in the variables and . The coefficients usually belong to a ...
:
on (The vector space equipped with this quadratic form is sometimes written ). This quadratic form is, when put on matrix form (see classical orthogonal group), interpreted in physics as the metric tensor
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, a metric tensor (or simply metric) is an additional structure on a manifold (such as a surface) that allows defining distances and angles, just as the inner product on a Euclidean space allows ...
of Minkowski spacetime.
The Lorentz group is a six-dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), lin ...
al noncompact non-abelian real Lie group
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a group that is also a differentiable manifold. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the additio ...
that is not connected. The four connected components are not simply connected
In topology, a topological space is called simply connected (or 1-connected, or 1-simply connected) if it is path-connected and every path between two points can be continuously transformed (intuitively for embedded spaces, staying within the spac ...
. The identity component (i.e., the component containing the identity element) of the Lorentz group is itself a group, and is often called the restricted Lorentz group, and is denoted SO+(1,3). The restricted Lorentz group consists of those Lorentz transformations that preserve both the orientation
Orientation may refer to:
Positioning in physical space
* Map orientation, the relationship between directions on a map and compass directions
* Orientation (housing), the position of a building with respect to the sun, a concept in building de ...
of space and the direction of time. Its fundamental group
In the mathematical field of algebraic topology, the fundamental group of a topological space is the group of the equivalence classes under homotopy of the loops contained in the space. It records information about the basic shape, or holes, of ...
has order 2, and its universal cover, the indefinite spin group Spin(1,3), is isomorphic to both the special linear group SL(2, C) and to the symplectic group Sp(2, C). These isomorphisms allow the Lorentz group to act on a large number of mathematical structures important to physics, most notably the spinors. Thus, in relativistic quantum mechanics and in quantum field theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and ...
, it is very common to call SL(2, C) the Lorentz group, with the understanding that SO+(1,3) is a specific representation (the vector representation) of it. The biquaternions, popular in geometric algebra
In mathematics, a geometric algebra (also known as a real Clifford algebra) is an extension of elementary algebra to work with geometrical objects such as vectors. Geometric algebra is built out of two fundamental operations, addition and the ge ...
, are also isomorphic to SL(2, C).
The restricted Lorentz group also arises as the point symmetry group
Molecular symmetry in chemistry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain m ...
of a certain ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation whose unknown(s) consists of one (or more) function(s) of one variable and involves the derivatives of those functions. The term ''ordinary'' is used in contrast w ...
.
Connected components
Lie group
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a group that is also a differentiable manifold. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the additio ...
, the Lorentz group O(1,3) is both a group and admits a topological description as a smooth manifold. As a manifold, it has four connected components. Intuitively, this means that it consists of four topologically separated pieces.
The four connected components can be categorized by two transformation properties its elements have:
* Some elements are reversed under time-inverting Lorentz transformations, for example, a future-pointing timelike vector
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inerti ...
would be inverted to a past-pointing vector
* Some elements have orientation reversed by improper Lorentz transformations, for example, certain vierbein
The tetrad formalism is an approach to general relativity that generalizes the choice of basis for the tangent bundle from a coordinate basis to the less restrictive choice of a local basis, i.e. a locally defined set of four linearly independent ...
(tetrads)
Lorentz transformations that preserve the direction of time are called . The subgroup of orthochronous transformations is often denoted O+(1, 3). Those that preserve orientation are called proper, and as linear transformations they have determinant +1. (The improper Lorentz transformations have determinant −1.) The subgroup of proper Lorentz transformations is denoted SO(1, 3).
The subgroup of all Lorentz transformations preserving both orientation and direction of time is called the proper, orthochronous Lorentz group or restricted Lorentz group, and is denoted by SO+(1, 3). (Note that some authors refer to SO(1,3) or even O(1,3) when they actually mean SO+(1, 3).)
The set of the four connected components can be given a group structure as the quotient group
A quotient group or factor group is a mathematical group obtained by aggregating similar elements of a larger group using an equivalence relation that preserves some of the group structure (the rest of the structure is "factored" out). For examp ...
O(1, 3)/SO+(1, 3), which is isomorphic to the Klein four-group
In mathematics, the Klein four-group is a Group (mathematics), group with four elements, in which each element is Involution (mathematics), self-inverse (composing it with itself produces the identity)
and in which composing any two of the three ...
. Every element in O(1,3) can be written as the semidirect product
In mathematics, specifically in group theory, the concept of a semidirect product is a generalization of a direct product. There are two closely related concepts of semidirect product:
* an ''inner'' semidirect product is a particular way in w ...
of a proper, orthochronous transformation and an element of the discrete group
:
where ''P'' and ''T'' are the parity
Parity may refer to:
* Parity (computing)
** Parity bit in computing, sets the parity of data for the purpose of error detection
** Parity flag in computing, indicates if the number of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the r ...
and time reversal operators:
: ''P'' = diag(1, −1, −1, −1)
: ''T'' = diag(−1, 1, 1, 1).
Thus an arbitrary Lorentz transformation can be specified as a proper, orthochronous Lorentz transformation along with a further two
bits of information, which pick out one of the four connected components. This pattern is typical of finite-dimensional Lie groups.
Restricted Lorentz group
The restricted Lorentz group is the identity component of the Lorentz group, which means that it consists of all Lorentz transformations that can be connected to the identity by acontinuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous ...
curve lying in the group. The restricted Lorentz group is a connected normal subgroup
In abstract algebra, a normal subgroup (also known as an invariant subgroup or self-conjugate subgroup) is a subgroup that is invariant under conjugation by members of the group of which it is a part. In other words, a subgroup N of the group G i ...
of the full Lorentz group with the same dimension, in this case with dimension six.
The restricted Lorentz group is generated by ordinary spatial rotations and Lorentz boost
In physics, the Lorentz transformations are a six-parameter family of linear transformations from a coordinate frame in spacetime to another frame that moves at a constant velocity relative to the former. The respective inverse transformation i ...
s (which are rotations in a hyperbolic space that includes a time-like direction). Since every proper, orthochronous Lorentz transformation can be written as a product of a rotation (specified by 3 real parameters) and a boost (also specified by 3 real parameters), it takes 6 real parameters to specify an arbitrary proper orthochronous Lorentz transformation. This is one way to understand why the restricted Lorentz group is six-dimensional. (See also the Lie algebra of the Lorentz group.)
The set of all rotations forms a Lie subgroup
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a group that is also a differentiable manifold. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the add ...
isomorphic to the ordinary rotation group SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition.
By definition, a rotation about the origin is a tr ...
. The set of all boosts, however, does ''not'' form a subgroup, since composing two boosts does not, in general, result in another boost. (Rather, a pair of non-colinear boosts is equivalent to a boost and a rotation, and this relates to Thomas rotation.) A boost in some direction, or a rotation about some axis, generates a one-parameter subgroup
In mathematics, a one-parameter group or one-parameter subgroup usually means a continuous group homomorphism
:\varphi : \mathbb \rightarrow G
from the real line \mathbb (as an additive group) to some other topological group G.
If \varphi is ...
.
Surfaces of transitivity
If a group acts on a space , then a surface is a surface of transitivity if is invariant under (i.e., ) and for any two points there is a such that . By definition of the Lorentz group, it preserves the quadratic form : The surfaces of transitivity of the orthochronous Lorentz group , acting on flatspacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
are the following:
* is the upper branch of a hyperboloid
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by defo ...
of two sheets. Points on this sheet are separated from the origin by a future time-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
vector.
* is the lower branch of this hyperboloid. Points on this sheet are the past time-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
vectors.
* is the upper branch of the light cone, the future light cone.
* is the lower branch of the light cone, the past light cone.
* is a hyperboloid of one sheet. Points on this sheet are space-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
separated from the origin.
*The origin .
These surfaces are , so the images are not faithful, but they are faithful for the corresponding facts about . For the full Lorentz group, the surfaces of transitivity are only four since the transformation takes an upper branch of a hyperboloid (cone) to a lower one and vice versa.
As symmetric spaces
An equivalent way to formulate the above surfaces of transitivity is as a symmetric space in the sense of Lie theory. For example, the upper sheet of the hyperboloid can be written as the quotient space , due to theorbit-stabilizer theorem
In mathematics, a group action on a space is a group homomorphism of a given group into the group of transformations of the space. Similarly, a group action on a mathematical structure is a group homomorphism of a group into the automorphism ...
. Furthermore, this upper sheet also provides a model for three-dimensional hyperbolic space.
Representations of the Lorentz group
These observations constitute a good starting point for finding all infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Lorentz group, in fact, of the Poincaré group, using the method of induced representations. One begins with a "standard vector", one for each surface of transitivity, and then ask which subgroup preserves these vectors. These subgroups are called little groups by physicists. The problem is then essentially reduced to the easier problem of finding representations of the little groups. For example, a standard vector in one of the hyperbolas of two sheets could be suitably chosen as . For each , the vector pierces exactly one sheet. In this case the little group is , therotation group
In mathematics, the orthogonal group in dimension , denoted , is the group of distance-preserving transformations of a Euclidean space of dimension that preserve a fixed point, where the group operation is given by composing transformations. ...
, all of whose representations are known. The precise infinite-dimensional unitary representation under which a particle transforms is part of its classification. Not all representations can correspond to physical particles (as far as is known). Standard vectors on the one-sheeted hyperbolas would correspond to tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. Physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics. If such partic ...
s. Particles on the light cone are photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
s, and more hypothetically, gravitons. The "particle" corresponding to the origin is the vacuum.
Homomorphisms and isomorphisms
Several other groups are either homomorphic or isomorphic to the restricted Lorentz group SO+(1, 3). These homomorphisms play a key role in explaining various phenomena in physics. * The special linear group SL(2, C) is a double covering of the restricted Lorentz group. This relationship is widely used to express theLorentz invariance
In a relativistic theory of physics, a Lorentz scalar is an expression, formed from items of the theory, which evaluates to a scalar, invariant under any Lorentz transformation. A Lorentz scalar may be generated from e.g., the scalar product of ve ...
of the Dirac equation and the covariance of spinors. In other words, the (restricted) Lorentz group is isomorphic to SL(2, C)/
* The symplectic group Sp(2, C) is isomorphic to SL(2, C); it is used to construct Weyl spinor
In physics, particularly in quantum field theory, the Weyl equation is a relativistic wave equation for describing massless spin-1/2 particles called Weyl fermions. The equation is named after Hermann Weyl. The Weyl fermions are one of the three p ...
s, as well as to explain how spinors can have a mass.
* The spin group
In mathematics the spin group Spin(''n'') page 15 is the double cover of the special orthogonal group , such that there exists a short exact sequence of Lie groups (when )
:1 \to \mathrm_2 \to \operatorname(n) \to \operatorname(n) \to 1.
As a L ...
Spin(1, 3) is isomorphic to SL(2, C); it is used to explain spin and spinors in terms of the Clifford algebra
In mathematics, a Clifford algebra is an algebra generated by a vector space with a quadratic form, and is a unital associative algebra. As -algebras, they generalize the real numbers, complex numbers, quaternions and several other hyperc ...
, thus making it clear how to generalize the Lorentz group to general settings in Riemannian geometry, including theories of supergravity and string theory
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these strings propagate through space and interac ...
.
* The restricted Lorentz group is isomorphic
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word is ...
to the projective special linear group
In mathematics, especially in the group theoretic area of algebra, the projective linear group (also known as the projective general linear group or PGL) is the induced action of the general linear group of a vector space ''V'' on the associate ...
PSL(2, C) which is, in turn, isomorphic to the Möbius group
Moebius, Möbius or Mobius may refer to:
People
* August Ferdinand Möbius (1790–1868), German mathematician and astronomer
* Theodor Möbius (1821–1890), German philologist
* Karl Möbius (1825–1908), German zoologist and ecologist
* Paul ...
, the symmetry group
In group theory, the symmetry group of a geometric object is the group of all transformations under which the object is invariant, endowed with the group operation of composition. Such a transformation is an invertible mapping of the ambient ...
of conformal geometry on the Riemann sphere
In mathematics, the Riemann sphere, named after Bernhard Riemann, is a model of the extended complex plane: the complex plane plus one point at infinity. This extended plane represents the extended complex numbers, that is, the complex numbers pl ...
. This relationship is central to the classification of the subgroups of the Lorentz group according to an earlier classification scheme developed for the Möbius group.
The Weyl representation
The Weyl representation or spinor map is a pair ofsurjective
In mathematics, a surjective function (also known as surjection, or onto function) is a function that every element can be mapped from element so that . In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element of i ...
homomorphism
In algebra, a homomorphism is a structure-preserving map between two algebraic structures of the same type (such as two groups, two rings, or two vector spaces). The word ''homomorphism'' comes from the Ancient Greek language: () meaning "same" ...
s from SL(2,C) to SO+(1, 3). They form a matched pair under parity
Parity may refer to:
* Parity (computing)
** Parity bit in computing, sets the parity of data for the purpose of error detection
** Parity flag in computing, indicates if the number of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the r ...
transformations, corresponding to left and right chiral spinors.
One may define an action of SL(2,C) on Minkowski spacetime by writing a point of spacetime as a two-by-two Hermitian matrix in the form
:
in terms of Pauli matrices.
This presentation, the Weyl presentation, satisfies
:
Therefore, one has identified the space of Hermitian matrices (which is four-dimensional, as a ''real'' vector space) with Minkowski spacetime, in such a way that the determinant
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar value that is a function of the entries of a square matrix. It characterizes some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if and ...
of a Hermitian matrix is the squared length of the corresponding vector in Minkowski spacetime. An element acts on the space of Hermitian matrices via
:
where is the Hermitian transpose of . This action preserves the determinant and so SL(2,C) acts on Minkowski spacetime by (linear) isometries. The parity-inverted form of the above is
:
which transforms as
:
That this is the correct transformation follows by noting that
:
remains invariant under the above pair of transformations.
These maps are surjective
In mathematics, a surjective function (also known as surjection, or onto function) is a function that every element can be mapped from element so that . In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element of i ...
, and kernel of either map is the two element subgroup ±''I''. By the first isomorphism theorem, the quotient group PSL(2, C) = SL(2, C) / is isomorphic to SO+(1, 3).
The parity map swaps these two coverings. It corresponds to Hermitian conjugation being an automorphism of These two distinct coverings corresponds to the two distinct chiral actions of the Lorentz group on spinors. The non-overlined form corresponds to right-handed spinors transforming as while the overline form corresponds to left-handed spinors transforming as
It is important to observe that this pair of coverings does ''not'' survive quantization; when quantized, this leads to the peculiar phenomenon of the chiral anomaly
In theoretical physics, a chiral anomaly is the anomalous nonconservation of a chiral current. In everyday terms, it is equivalent to a sealed box that contained equal numbers of left and right-handed bolts, but when opened was found to have more ...
. The classical (i.e., non-quantized) symmetries of the Lorentz group are broken by quantization; this is the content of the Atiyah–Singer index theorem
In differential geometry, the Atiyah–Singer index theorem, proved by Michael Atiyah and Isadore Singer (1963), states that for an elliptic differential operator on a compact manifold, the analytical index (related to the dimension of the space ...
.
Notational conventions
In physics, it is conventional to denote a Lorentz transformation as thus showing the matrix with spacetime indexes A four-vector can be created from the Pauli matrices in two different ways: as and as The two forms are related by aparity transformation
In physics, a parity transformation (also called parity inversion) is the flip in the sign of ''one'' spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it can also refer to the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates (a point refle ...
. Note that
Given a Lorentz transformation the double-covering of the orthochronous Lorentz group by given above can be written as
:
Dropping the this takes the form
:
The parity conjugate form is
:
Proof
That the above is the correct form for indexed notation is not immediately obvious, partly because, when working in indexed notation, it is quite easy to accidentally confuse a Lorentz transform with its inverse, or its transpose. This confusion arises due to the identity being difficult to recognize when written in indexed form. Lorentz transforms are ''not'' tensors under Lorentz transformations! Thus a direct proof of this identity is useful, for establishing its correctness. It can be demonstrated by starting with the identity : where so that the above are just the usual Pauli matrices, and is the matrix transpose, and is complex conjugation. The matrix is : Written as the four-vector, the relationship is : This transforms as : Taking one more transpose, one gets :The symplectic group
The symplectic group Sp(2, C) is isomorphic to SL(2, C). This isomorphism is constructed so as to preserve asymplectic bilinear form In mathematics, a symplectic vector space is a vector space ''V'' over a field ''F'' (for example the real numbers R) equipped with a symplectic bilinear form.
A symplectic bilinear form is a mapping that is
; Bilinear: Linear in each argument ...
on that is, to leave the form invariant under Lorentz transformations. This may be articulated as follows. The symplectic group is defined as
:
where
:
Other common notations are for this element; sometimes is used, but this invites confusion with the idea of almost complex structures, which are not the same, as they transform differently.
Given a pair of Weyl spinors (two-component spinors)
:
the invariant bilinear form is conventionally written as
:
This form is invariant under the Lorentz group, so that for one has
:
This defines a kind of "scalar product" of spinors, and is commonly used to defined a Lorentz-invariant mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
term in Lagrangians. There are several notable properties to be called out that are important to physics. One is that and so
The defining relation can be written as
:
which closely resembles the defining relation for the Lorentz group
:
where is the metric tensor
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, a metric tensor (or simply metric) is an additional structure on a manifold (such as a surface) that allows defining distances and angles, just as the inner product on a Euclidean space allows ...
for Minkowski space and of course, as before.
Covering groups
Since is simply connected, it is theuniversal covering group
In mathematics, a covering group of a topological group ''H'' is a covering space ''G'' of ''H'' such that ''G'' is a topological group and the covering map is a continuous group homomorphism. The map ''p'' is called the covering homomorphism. A ...
of the restricted Lorentz group . By restriction, there is a homomorphism . Here, the special unitary group SU(2), which is isomorphic to the group of unit norm
Naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) and technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive materials (TENORM) consist of materials, usually industrial wastes or by-products enriched with radioactive elements found in the envir ...
quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. Hamilton defined a quatern ...
s, is also simply connected, so it is the covering group of the rotation group SO(3). Each of these covering map A covering of a topological space X is a continuous map \pi : E \rightarrow X with special properties.
Definition
Let X be a topological space. A covering of X is a continuous map
: \pi : E \rightarrow X
such that there exists a discrete sp ...
s are twofold covers in the sense that precisely two elements of the covering group map to each element of the quotient. One often says that the restricted Lorentz group and the rotation group are doubly connected. This means that the fundamental group
In the mathematical field of algebraic topology, the fundamental group of a topological space is the group of the equivalence classes under homotopy of the loops contained in the space. It records information about the basic shape, or holes, of ...
of the each group is isomorphic
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word is ...
to the two-element cyclic group Z2.
Twofold coverings are characteristic of spin group
In mathematics the spin group Spin(''n'') page 15 is the double cover of the special orthogonal group , such that there exists a short exact sequence of Lie groups (when )
:1 \to \mathrm_2 \to \operatorname(n) \to \operatorname(n) \to 1.
As a L ...
s. Indeed, in addition to the double coverings
: Spin+(1, 3) = SL(2, C) → SO+(1, 3)
: Spin(3) = SU(2) → SO(3)
we have the double coverings
: Pin(1, 3) → O(1, 3)
: Spin(1, 3) → SO(1, 3)
: Spin+(1, 2) = SU(1, 1) → SO(1, 2)
These spinorial double coverings are constructed from Clifford algebras
In mathematics, a Clifford algebra is an algebra generated by a vector space with a quadratic form, and is a unital associative algebra. As -algebras, they generalize the real numbers, complex numbers, quaternions and several other hyper ...
.
Topology
The left and right groups in the double covering : SU(2) → SO(3) are deformation retracts of the left and right groups, respectively, in the double covering : SL(2, C) → SO+(1, 3). But the homogeneous space SO+(1, 3)/SO(3) ishomeomorphic
In the mathematical field of topology, a homeomorphism, topological isomorphism, or bicontinuous function is a bijective and continuous function between topological spaces that has a continuous inverse function. Homeomorphisms are the isomorphi ...
to hyperbolic 3-space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to -1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. ...
H3, so we have exhibited the restricted Lorentz group as a principal fiber bundle
In mathematics, a principal bundle is a mathematical object that formalizes some of the essential features of the Cartesian product X \times G of a space X with a group G. In the same way as with the Cartesian product, a principal bundle P is equ ...
with fibers SO(3) and base H3. Since the latter is homeomorphic to R3, while SO(3) is homeomorphic to three-dimensional real projective space RP3, we see that the restricted Lorentz group is ''locally'' homeomorphic to the product of RP3 with R3. Since the base space is contractible, this can be extended to a global homeomorphism.
Conjugacy classes
Because the restricted Lorentz group SO+(1, 3) is isomorphic to the Möbius group PSL(2, C), itsconjugacy classes
In mathematics, especially group theory, two elements a and b of a group are conjugate if there is an element g in the group such that b = gag^. This is an equivalence relation whose equivalence classes are called conjugacy classes. In other wor ...
also fall into five classes:
* Elliptic transformations
* Hyperbolic transformations
* Loxodromic transformations
* Parabolic transformations
* The trivial identity transformation
In the article on Möbius transformation
In geometry and complex analysis, a Möbius transformation of the complex plane is a rational function of the form
f(z) = \frac
of one complex variable ''z''; here the coefficients ''a'', ''b'', ''c'', ''d'' are complex numbers satisfying ''ad'' ...
s, it is explained how this classification arises by considering the fixed points of Möbius transformations in their action on the Riemann sphere, which corresponds here to null eigenspace
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted b ...
s of restricted Lorentz transformations in their action on Minkowski spacetime.
An example of each type is given in the subsections below, along with the effect of the one-parameter subgroup
In mathematics, a one-parameter group or one-parameter subgroup usually means a continuous group homomorphism
:\varphi : \mathbb \rightarrow G
from the real line \mathbb (as an additive group) to some other topological group G.
If \varphi is ...
it generates (e.g., on the appearance of the night sky).
The Möbius transformations are the conformal transformations of the Riemann sphere (or celestial sphere). Then conjugating with an arbitrary element of SL(2,C) obtains the following examples of arbitrary elliptic, hyperbolic, loxodromic, and parabolic (restricted) Lorentz transformations, respectively. The effect on the flow lines of the corresponding one-parameter subgroups is to transform the pattern seen in the examples by some conformal transformation. For example, an elliptic Lorentz transformation can have any two distinct fixed points on the celestial sphere, but points still flow along circular arcs from one fixed point toward the other. The other cases are similar.
Elliptic
An elliptic element of SL(2, C) is : and has fixed points = 0, ∞. Writing the action as and collecting terms, the spinor map converts this to the (restricted) Lorentz transformation : This transformation then represents a rotation about the axis, exp(). The one-parameter subgroup it generates is obtained by taking to be a real variable, the rotation angle, instead of a constant. The corresponding continuous transformations of the celestial sphere (except for the identity) all share the same two fixed points, the North and South poles. The transformations move all other points around latitude circles so that this group yields a continuous counter-clockwise rotation about the axis as increases. The ''angle doubling'' evident in the spinor map is a characteristic feature of ''spinorial double coverings''.Hyperbolic
A hyperbolic element of SL(2,C) is : and has fixed points = 0, ∞. Under stereographic projection from the Riemann sphere to the Euclidean plane, the effect of this Möbius transformation is a dilation from the origin. The spinor map converts this to the Lorentz transformation : This transformation represents a boost along the axis withrapidity
In relativity, rapidity is commonly used as a measure for relativistic velocity. Mathematically, rapidity can be defined as the hyperbolic angle that differentiates two frames of reference in relative motion, each frame being associated with di ...
. The one-parameter subgroup it generates is obtained by taking to be a real variable, instead of a constant. The corresponding continuous transformations of the celestial sphere (except for the identity) all share the same fixed points (the North and South poles), and they move all other points along longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
s away from the South pole and toward the North pole.
Loxodromic
A loxodromic element of SL(2, C) is : and has fixed points = 0, ∞. The spinor map converts this to the Lorentz transformation : The one-parameter subgroup this generates is obtained by replacing ''η'' + i''θ'' with any real multiple of this complex constant. (If ''η'', ''θ'' vary independently, then a ''two-dimensional''abelian subgroup
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is comm ...
is obtained, consisting of simultaneous rotations about the axis and boosts along the -axis; in contrast, the ''one-dimensional'' subgroup discussed here consists of those elements of this two-dimensional subgroup such that the rapidity of the boost and angle of the rotation have a ''fixed ratio''.)
The corresponding continuous transformations of the celestial sphere (excepting the identity) all share the same two fixed points (the North and South poles). They move all other points away from the South pole and toward the North pole (or vice versa), along a family of curves called loxodromes. Each loxodrome spirals infinitely often around each pole.
Parabolic
A parabolic element of SL(2, C) is : and has the single fixed point = ∞ on the Riemann sphere. Under stereographic projection, it appears as an ordinarytranslation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
along the real axis.
The spinor map converts this to the matrix (representing a Lorentz transformation)
:
This generates a two-parameter abelian subgroup, which is obtained by considering a complex variable rather than a constant. The corresponding continuous transformations of the celestial sphere (except for the identity transformation) move points along a family of circles that are all tangent at the North pole to a certain great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geomet ...
. All points other than the North pole itself move along these circles.
Parabolic Lorentz transformations are often called null rotations. Since these are likely to be the least familiar of the four types of nonidentity Lorentz transformations (elliptic, hyperbolic, loxodromic, parabolic), it is illustrated here how to determine the effect of an example of a parabolic Lorentz transformation on Minkowski spacetime.
The matrix given above yields the transformation
:
Now, without loss of generality, pick . Differentiating this transformation with respect to the now real group parameter and evaluating at produces the corresponding vector field (first order linear partial differential operator),
:
Apply this to a function , and demand that it stays invariant; i.e., it is annihilated by this transformation. The solution of the resulting first order linear partial differential equation can be expressed in the form
:
where is an ''arbitrary'' smooth function. The arguments of give three ''rational invariants'' describing how points (events) move under this parabolic transformation, as they themselves do not move,
:
Choosing real values for the constants on the right hand sides yields three conditions, and thus specifies a curve in Minkowski spacetime. This curve is an orbit of the transformation.
The form of the rational invariants shows that these flowlines (orbits) have a simple description: suppressing the inessential coordinate , each orbit is the intersection of a ''null plane'', , with a ''hyperboloid'', . The case 3 = 0 has the hyperboloid degenerate to a light cone with the orbits becoming parabolas lying in corresponding null planes.
A particular null line lying on the light cone is left ''invariant''; this corresponds to the unique (double) fixed point on the Riemann sphere mentioned above. The other null lines through the origin are "swung around the cone" by the transformation. Following the motion of one such null line as increases corresponds to following the motion of a point along one of the circular flow lines on the celestial sphere, as described above.
A choice instead, produces similar orbits, now with the roles of and interchanged.
Parabolic transformations lead to the gauge symmetry of massless particles (like photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
s) with helicity , , ≥ 1. In the above explicit example, a massless particle moving in the direction, so with 4-momentum , is not affected at all by the -boost and -rotation combination defined below, in the "little group" of its motion. This is evident from the explicit transformation law discussed: like any light-like vector, ''P'' itself is now invariant; i.e., all traces or effects of have disappeared. 1 = 2 = 3 = 0, in the special case discussed. (The other similar generator, as well as it and ''z'' comprise altogether the little group of the light-like vector, isomorphic to (2).)
Appearance of the night sky
This isomorphism has the consequence that Möbius transformations of the Riemann sphere represent the way that Lorentz transformations change the appearance of the night sky, as seen by an observer who is maneuvering at relativistic velocities relative to the "fixed stars". Suppose the "fixed stars" live in Minkowski spacetime and are modeled by points on the celestial sphere. Then a given point on the celestial sphere can be associated with , a complex number that corresponds to the point on theRiemann sphere
In mathematics, the Riemann sphere, named after Bernhard Riemann, is a model of the extended complex plane: the complex plane plus one point at infinity. This extended plane represents the extended complex numbers, that is, the complex numbers pl ...
, and can be identified with a null vector (a light-like vector) in Minkowski space
:
or, in the Weyl representation (the spinor map), the Hermitian matrix
:
 The set of real scalar multiples of this null vector, called a ''null line'' through the origin, represents a ''line of sight'' from an observer at a particular place and time (an arbitrary event we can identify with the origin of Minkowski spacetime) to various distant objects, such as stars. Then the points of the
The set of real scalar multiples of this null vector, called a ''null line'' through the origin, represents a ''line of sight'' from an observer at a particular place and time (an arbitrary event we can identify with the origin of Minkowski spacetime) to various distant objects, such as stars. Then the points of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
(equivalently, lines of sight) are identified with certain Hermitian matrices.
Projective geometry and different views of the 2-sphere
This picture emerges cleanly in the language of projective geometry. The (restricted) Lorentz group acts on the projective celestial sphere. This is the space of non-zero null vectors with under the given quotient for projective spaces: if for . This is referred to as the celestial sphere as this allows us to rescale the time coordinate to 1 after acting using a Lorentz transformation, ensuring the space-like part sits on the unit sphere. From the Möbius side, acts on complex projective space , which can be shown to be diffeomorphic to the 2-sphere - this is sometimes referred to as theRiemann sphere
In mathematics, the Riemann sphere, named after Bernhard Riemann, is a model of the extended complex plane: the complex plane plus one point at infinity. This extended plane represents the extended complex numbers, that is, the complex numbers pl ...
. The quotient on projective space leads to a quotient on the group .
Finally, these two can be linked together by using the complex projective vector to construct a null-vector. If is a projective vector, it can be tensored with its Hermitian conjugate to produce a Hermitian matrix. From elsewhere in this article we know this space of matrices can be viewed as 4-vectors. The space of matrices coming from turning each projective vector in the Riemann sphere into a matrix is known as the Bloch sphere.
Lie algebra
As with any Lie group, a useful way to study many aspects of the Lorentz group is via itsLie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an Binary operation, operation called the Lie bracket, an Alternating multilinear map, alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow ...
. Since the Lorentz group is a matrix Lie group, its corresponding Lie algebra is a matrix Lie algebra, which may be computed as
:.
If is the diagonal matrix with diagonal entries , then the Lie algebra consists of matrices such that Proposition 3.25
:.
Explicitly, consists of matrices of the form
:,
where are arbitrary real numbers. This Lie algebra is six dimensional. The subalgebra of consisting of elements in which , , and equal to zero is isomorphic to .
The full Lorentz group , the proper Lorentz group and the proper orthochronous Lorentz group (the component connected to the identity) all have the same Lie algebra, which is typically denoted .
Since the identity component of the Lorentz group is isomorphic to a finite quotient of (see the section above on the connection of the Lorentz group to the Möbius group), the Lie algebra of the Lorentz group is isomorphic to the Lie algebra . As a complex Lie algebra is three dimensional, but is six dimensional when viewed as a real Lie algebra.
Commutation relations of the Lorentz algebra
The standard basis matrices can be indexed as where take values in . These arise from taking only one of to be one, and others zero, in turn. The components can be written as :. The commutation relations are : There are different possible choices of convention in use. In physics, it is common to include a factor of with the basis elements, which gives a factor of in the commutation relations. Then generate boosts and generate rotations. The structure constants for the Lorentz algebra can be read off from the commutation relations. Any set of basis elements which satisfy these relations form a representation of the Lorentz algebra.Generators of boosts and rotations
The Lorentz group can be thought of as a subgroup of thediffeomorphism group
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable.
Definition
Given two ...
of R4 and therefore its Lie algebra can be identified with vector fields on R4. In particular, the vectors that generate isometries on a space are its Killing vector
In mathematics, a Killing vector field (often called a Killing field), named after Wilhelm Killing, is a vector field on a Riemannian manifold (or pseudo-Riemannian manifold) that preserves the metric tensor, metric. Killing fields are the Lie gro ...
s, which provides a convenient alternative to the left-invariant vector field for calculating the Lie algebra. We can write down a set of six generators:
* Vector fields on R4 generating three rotations ''i'' ''J'',
*:
* Vector fields on R4 generating three boosts ''i'' ''K'',
*:
The factor of appears to ensure that the generators of rotations are Hermitian.
It may be helpful to briefly recall here how to obtain a one-parameter group from a vector field, written in the form of a first order linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear r ...
partial differential operator
In mathematics, a differential operator is an operator defined as a function of the differentiation operator. It is helpful, as a matter of notation first, to consider differentiation as an abstract operation that accepts a function and retur ...
such as
:
The corresponding initial value problem (consider a function of a scalar and solve with some initial conditions) is
:
The solution can be written
:
or
:
where we easily recognize the one-parameter matrix group of rotations exp(''i λ Jz'') about the z axis.
Differentiating with respect to the group parameter and setting it ''λ''=0 in that result, we recover the standard matrix,
:
which corresponds to the vector field we started with. This illustrates how to pass between matrix and vector field representations of elements of the Lie algebra. The exponential map plays this special role not only for the Lorentz group but for Lie groups in general.
Reversing the procedure in the previous section, we see that the Möbius transformations that correspond to our six generators arise from exponentiating respectively ''η''/2 (for the three boosts) or ''iθ''/2 (for the three rotations) times the three Pauli matrices
:
Generators of the Möbius group
Another generating set arises via the isomorphism to the Möbius group. The following table lists the six generators, in which * The first column gives a generator of the flow under the Möbius action (after stereographic projection from the Riemann sphere) as a ''real'' vector field on the Euclidean plane. * The second column gives the corresponding one-parameter subgroup of Möbius transformations. * The third column gives the corresponding one-parameter subgroup of Lorentz transformations (the image under our homomorphism of preceding one-parameter subgroup). * The fourth column gives the corresponding generator of the flow under the Lorentz action as a real vector field on Minkowski spacetime. Notice that the generators consist of * Two parabolics (null rotations) * One hyperbolic (boost in the direction) * Three elliptics (rotations about the ''x'', ''y'', ''z'' axes, respectively)Worked example: rotation about the y-axis
Start with : Exponentiate: : This element of represents the one-parameter subgroup of (elliptic) Möbius transformations: : Next, : The corresponding vector field on (thought of as the image of under stereographic projection) is : Writing , this becomes the vector field on : Returning to our element of , writing out the action and collecting terms, we find that the image under the spinor map is the element of : Differentiating with respect to at , yields the corresponding vector field on , : This is evidently the generator of counterclockwise rotation about the -axis.Subgroups of the Lorentz group
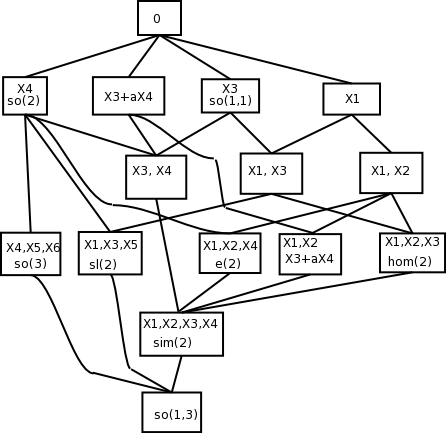
The subalgebras of the Lie algebra of the Lorentz group can be enumerated, up to conjugacy, from which theclosed subgroup
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of Group (mathematics), groups and Topological space, topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the Continuous function, continui ...
s of the restricted Lorentz group can be listed, up to conjugacy. (See the book by Hall cited below for the details.) These can be readily expressed in terms of the generators given in the table above.
The one-dimensional subalgebras of course correspond to the four conjugacy classes of elements of the Lorentz group:
* generates a one-parameter subalgebra of parabolics SO(0, 1),
* generates a one-parameter subalgebra of boosts SO(1, 1),
* generates a one-parameter of rotations SO(2),
* (for any ) generates a one-parameter subalgebra of loxodromic transformations.
(Strictly speaking the last corresponds to infinitely many classes, since distinct give different classes.)
The two-dimensional subalgebras are:
* generate an abelian subalgebra consisting entirely of parabolics,
* generate a nonabelian subalgebra isomorphic to the Lie algebra of the affine group Aff(1),
* generate an abelian subalgebra consisting of boosts, rotations, and loxodromics all sharing the same pair of fixed points.
The three-dimensional subalgebras use the Bianchi classification In mathematics, the Bianchi classification provides a list of all real 3-dimensional Lie algebras (up to isomorphism). The classification contains 11 classes, 9 of which contain a single Lie algebra and two of which contain a continuum-sized family ...
scheme:
* generate a Bianchi V subalgebra, isomorphic to the Lie algebra of Hom(2), the group of ''euclidean homotheties'',
* generate a Bianchi VII subalgebra, isomorphic to the Lie algebra of E(2), the euclidean group
In mathematics, a Euclidean group is the group of (Euclidean) isometries of a Euclidean space \mathbb^n; that is, the transformations of that space that preserve the Euclidean distance between any two points (also called Euclidean transformations). ...
,
* , where , generate a Bianchi VII subalgebra,
* generate a Bianchi VIII subalgebra, isomorphic to the Lie algebra of SL(2, R), the group of isometries of the hyperbolic plane
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai– Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
:For any given line ''R'' and point ''P'' ...
,
* generate a Bianchi IX subalgebra, isomorphic to the Lie algebra of SO(3), the rotation group.
The Bianchi types refer to the classification of three-dimensional Lie algebras by the Italian mathematician Luigi Bianchi
Luigi Bianchi (18 January 1856 – 6 June 1928) was an Italians, Italian mathematician. He was born in Parma, Emilia-Romagna, and died in Pisa. He was a leading member of the vigorous Italian school of algebraic geometry, geometric school which fl ...
.
The four-dimensional subalgebras are all conjugate to
* generate a subalgebra isomorphic to the Lie algebra of Sim(2), the group of Euclidean similitudes.
The subalgebras form a lattice (see the figure), and each subalgebra generates by exponentiation a closed subgroup
In mathematics, topological groups are logically the combination of Group (mathematics), groups and Topological space, topological spaces, i.e. they are groups and topological spaces at the same time, such that the Continuous function, continui ...
of the restricted Lie group. From these, all subgroups of the Lorentz group can be constructed, up to conjugation, by multiplying by one of the elements of the Klein four-group.
 As with any connected Lie group, the coset spaces of the closed subgroups of the restricted Lorentz group, or
As with any connected Lie group, the coset spaces of the closed subgroups of the restricted Lorentz group, or homogeneous spaces
In mathematics, particularly in the theories of Lie groups, algebraic groups and topological groups, a homogeneous space for a group ''G'' is a non-empty manifold or topological space ''X'' on which ''G'' acts transitively. The elements of ''G' ...
, have considerable mathematical interest. A few, brief descriptions:
* The group Sim(2) is the stabilizer of a ''null line''; i.e., of a point on the Riemann sphere—so the homogeneous space SO+(1, 3)/Sim(2) is the Kleinian geometry
In mathematics, a Klein geometry is a type of geometry motivated by Felix Klein in his influential Erlangen program. More specifically, it is a homogeneous space ''X'' together with a transitive action on ''X'' by a Lie group ''G'', which acts a ...
that represents conformal geometry on the sphere ''S''2.
* The (identity component of the) Euclidean group SE(2) is the stabilizer of a null vector, so the homogeneous space SO+(1, 3)/SE(2) is the momentum space of a massless particle; geometrically, this Kleinian geometry represents the ''degenerate'' geometry of the light cone in Minkowski spacetime.
* The rotation group SO(3) is the stabilizer of a timelike vector
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inerti ...
, so the homogeneous space SO+(1, 3)/SO(3) is the momentum space of a massive particle; geometrically, this space is none other than three-dimensional hyperbolic space H3.
Generalization to higher dimensions
The concept of the Lorentz group has a natural generalization to spacetime of any number of dimensions. Mathematically, the Lorentz group of (''n'' + 1)-dimensional Minkowski space is the indefinite orthogonal group O(''n'', 1) of linear transformations of R''n''+1 that preserves the quadratic form : The group O(1, ''n'') preserves the quadratic form : It is isomorphic to O(''n'', 1) but enjoys greater popularity in mathematical physics, primarily because the algebra of the Dirac equation and, more generally, spinor and Clifford algebras, are "more natural" with this signature. A common notation for the vector space , equipped with this choice of quadratic form, is . Many of the properties of the Lorentz group in four dimensions (where ) generalize straightforwardly to arbitrary ''n''. For instance, the Lorentz group O(''n'', 1) has four connected components, and it acts by conformal transformations on the celestial (''n''−1)-sphere in (''n''+1)-dimensional Minkowski space. The identity component SO+(''n'', 1) is an SO(''n'')-bundle over hyperbolic ''n''-space H''n''. The low-dimensional cases and are often useful as "toy models" for the physical case , while higher-dimensional Lorentz groups are used in physical theories such asstring theory
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these strings propagate through space and interac ...
that posit the existence of hidden dimensions. The Lorentz group O(''n'', 1) is also the isometry group of ''n''-dimensional de Sitter space
In mathematical physics, ''n''-dimensional de Sitter space (often abbreviated to dS''n'') is a maximally symmetric Lorentzian manifold with constant positive scalar curvature. It is the Lorentzian analogue of an ''n''-sphere (with its canoni ...
dS''n'', which may be realized as the homogeneous space O(''n'', 1)/O(''n'' − 1, 1). In particular O(4, 1) is the isometry group of the de Sitter universe
A de Sitter universe is a cosmological solution to the Einstein field equations of general relativity, named after Willem de Sitter. It models the universe as spatially flat and neglects ordinary matter, so the dynamics of the universe are dominat ...
dS4, a cosmological model.
See also
Notes
References
Reading List
*Emil Artin
Emil Artin (; March 3, 1898 – December 20, 1962) was an Austrian mathematician of Armenian descent.
Artin was one of the leading mathematicians of the twentieth century. He is best known for his work on algebraic number theory, contributing lar ...
(1957''Geometric Algebra'', chapter III: Symplectic and Orthogonal Geometry
via
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
, covers orthogonal groups O(p,q)
* A canonical reference; ''see chapters 1–6'' for representations of the Lorentz group.
* An excellent resource for Lie theory, fiber bundles, spinorial coverings, and many other topics.
* ''See Lecture 11'' for the irreducible representations of SL(2,C).
*
* .
* ''See Chapter 6'' for the subalgebras of the Lie algebra of the Lorentz group.
* ''See also'' the ''See Section 1.3'' for a beautifully illustrated discussion of covering spaces. ''See Section 3D'' for the topology of rotation groups.
* §41.3
* (Dover reprint edition.) An excellent reference on Minkowski spacetime and the Lorentz group.
* ''See Chapter 3'' for a superbly illustrated discussion of Möbius transformations.
*
*.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lorentz Group
Lie groups
Special relativity
Group theory
Hendrik Lorentz