|
Poincaré Group
The Poincaré group, named after Henri Poincaré (1905), was first defined by Hermann Minkowski (1908) as the isometry group of Minkowski spacetime. It is a ten-dimensional non-abelian Lie group that is of importance as a model in our understanding of the most basic fundamentals of physics. Overview The Poincaré group consists of all coordinate transformations of Minkowski space that do not change the spacetime interval between events. For example, if everything were postponed by two hours, including the two events and the path you took to go from one to the other, then the time interval between the events recorded by a stopwatch that you carried with you would be the same. Or if everything were shifted five kilometres to the west, or turned 60 degrees to the right, you would also see no change in the interval. It turns out that the proper length of an object is also unaffected by such a shift. In total, there are ten degrees of freedom for such transformations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
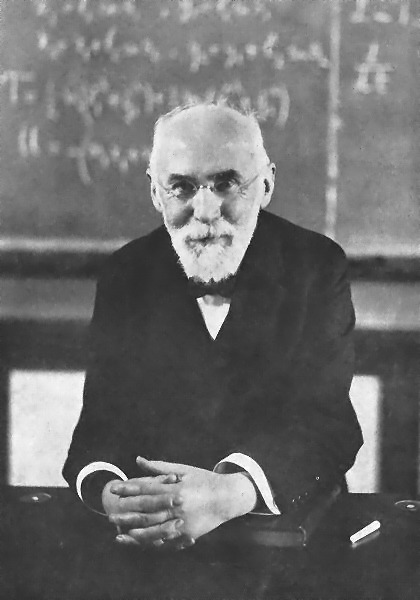
Henri Poincare
Henri is the French form of the masculine given name Henry (given name), Henry, also in Estonian, Finnish, German and Luxembourgish. Bearers of the given name include: People French nobles * Henri I de Montmorency (1534–1614), Marshal and Constable of France * Henri I, Duke of Nemours (1572–1632), the son of Jacques of Savoy and Anna d'Este * Henri II, Duke of Nemours (1625–1659), the seventh Duc de Nemours * Henri, Count of Harcourt (1601–1666), French nobleman * Henri, Dauphin of Viennois (1296–1349), bishop of Metz * Henri de Gondi (other) * Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, Duke of Bouillon (1555–1623), member of the powerful House of La Tour d'Auvergne * Henri Emmanuel Boileau, baron de Castelnau (1857–1923), French mountain climber * Henri, Grand Duke of Luxembourg (born 1955), the head of state of Luxembourg * Henri de Massue, Earl of Galway (1648–1720), French Huguenot soldier and diplomat, one of the principal commanders of Battle of Almansa * Françoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation (mathematics)
Rotation in mathematics is a concept originating in geometry. Any rotation is a motion of a certain space that preserves at least one point. It can describe, for example, the motion of a rigid body around a fixed point. Rotation can have a sign (as in the sign of an angle): a clockwise rotation is a negative magnitude so a counterclockwise turn has a positive magnitude. A rotation is different from other types of motions: translations, which have no fixed points, and (hyperplane) reflections, each of them having an entire -dimensional flat of fixed points in a - dimensional space. Mathematically, a rotation is a map. All rotations about a fixed point form a group under composition called the rotation group (of a particular space). But in mechanics and, more generally, in physics, this concept is frequently understood as a coordinate transformation (importantly, a transformation of an orthonormal basis), because for any motion of a body there is an inverse transformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Invariance
In a relativistic theory of physics, a Lorentz scalar is a scalar expression whose value is invariant under any Lorentz transformation. A Lorentz scalar may be generated from, e.g., the scalar product of vectors, or by contracting tensors. While the components of the contracted quantities may change under Lorentz transformations, the Lorentz scalars remain unchanged. A simple Lorentz scalar in Minkowski spacetime is the ''spacetime distance'' ("length" of their difference) of two fixed events in spacetime. While the "position"-4-vectors of the events change between different inertial frames, their spacetime distance remains invariant under the corresponding Lorentz transformation. Other examples of Lorentz scalars are the "length" of 4-velocities (see below), or the Ricci curvature in a point in spacetime from general relativity, which is a contraction of the Riemann curvature tensor there. Simple scalars in special relativity Length of a position vector In special rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Group
In physics and mathematics, the Lorentz group is the group of all Lorentz transformations of Minkowski spacetime, the classical and quantum setting for all (non-gravitational) physical phenomena. The Lorentz group is named for the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz. For example, the following laws, equations, and theories respect Lorentz symmetry: * The kinematical laws of special relativity * Maxwell's field equations in the theory of electromagnetism * The Dirac equation in the theory of the electron * The Standard Model of particle physics The Lorentz group expresses the fundamental symmetry of space and time of all known fundamental laws of nature. In small enough regions of spacetime where gravitational variances are negligible, physical laws are Lorentz invariant in the same manner as special relativity. Basic properties The Lorentz group is a subgroup of the Poincaré group—the group of all isometries of Minkowski spacetime. Lorentz transformations are, precise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Rotation
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition. By definition, a rotation about the origin is a transformation that preserves the origin, Euclidean distance (so it is an isometry), and orientation (i.e., ''handedness'' of space). Composing two rotations results in another rotation, every rotation has a unique inverse rotation, and the identity map satisfies the definition of a rotation. Owing to the above properties (along composite rotations' associative property), the set of all rotations is a group under composition. Every non-trivial rotation is determined by its axis of rotation (a line through the origin) and its angle of rotation. Rotations are not commutative (for example, rotating ''R'' 90° in the x-y plane followed by ''S'' 90° in the y-z plane is not the same as ''S'' followed by ''R''), making the 3D rotation group a non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a ''center of rotation''. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientation (geometry), orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis, rotation around a axis. The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or ''autorotation''). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal ''spin axis'' can be called a ''pole''; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or ''orbit''), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Lie Group
In geometry, an abelian Lie group is a Lie group that is an abelian group. A connected abelian real Lie group is isomorphic to \mathbb^k \times (S^1)^h. In particular, a connected abelian (real) compact Lie group is a torus; i.e., a Lie group isomorphic to (S^1)^h. A connected complex Lie group that is a compact group is abelian and a connected compact complex Lie group is a complex torus; i.e., a quotient of \mathbb^n by a lattice. Let ''A'' be a compact abelian Lie group with the identity component A_0. If A/A_0 is a cyclic group, then A is topologically cyclic; i.e., has an element that generates a dense subgroup. (In particular, a torus is topologically cyclic.) See also * Cartan subgroup In the theory of algebraic groups, a Cartan subgroup of a connected linear algebraic group G over a (not necessarily algebraically closed) field k is the centralizer of a maximal torus. Cartan subgroups are smooth (equivalently reduced), connec ... Citations Works cited * * Abe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (physics)
In Euclidean geometry, a translation is a geometric transformation that moves every point of a figure, shape or space by the same distance in a given direction. A translation can also be interpreted as the addition of a constant vector to every point, or as shifting the origin of the coordinate system. In a Euclidean space, any translation is an isometry. As a function If \mathbf is a fixed vector, known as the ''translation vector'', and \mathbf is the initial position of some object, then the translation function T_ will work as T_(\mathbf)=\mathbf+\mathbf. If T is a translation, then the image of a subset A under the function T is the translate of A by T . The translate of A by T_ is often written as A+\mathbf . Application in classical physics In classical physics, translational motion is movement that changes the position of an object, as opposed to rotation. For example, according to Whittaker: A translation is the operation changing the positions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force between objects and the Earth. This force is dominated by the combined gravitational interactions of particles but also includes effect of the Earth's rotation. Gravity gives weight to physical objects and is essential to understanding the mechanisms responsible for surface water waves and lunar tides. Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circulation of fluids in multicellular organisms. The gravitational attraction between primordial hydrogen and clumps of dark matter in the early universe caused the hydrogen gas to coalesce, eventually condensing and fusing to form stars. At larger scales this results in galaxies and clust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General theory of relativity, relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time in physics, time, or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ''curvature of spacetime'' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever is present, including matter and radiation. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second-order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity in classical mechanics, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Mapping
In plane geometry, a shear mapping is an affine transformation that displaces each point in a fixed direction by an amount proportional to its signed distance function, signed distance from a given straight line, line parallel (geometry), parallel to that direction. This type of mapping is also called shear transformation, transvection, or just shearing. The transformations can be applied with a shear matrix or transvection, an elementary matrix that represents the Elementary row operations#Row-addition transformations, addition of a multiple of one row or column to another. Such a matrix (mathematics), matrix may be derived by taking the identity matrix and replacing one of the zero elements with a non-zero value. An example is the linear map that takes any point with Cartesian coordinates, coordinates (x,y) to the point (x + 2y,y). In this case, the displacement is horizontal by a factor of 2 where the fixed line is the -axis, and the signed distance is the -coordinate. Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |