|
Tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels Faster-than-light, faster than light. Physicists posit that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are inconsistent with the known Scientific law#Laws of physics, laws of physics. If such particles did exist they perhaps could be used to send signals faster than light and into the past. According to the theory of relativity this would violate Causality (physics), causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a Quantum field theory, quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyonic Field
In physics, a tachyonic field, or simply tachyon, is a quantum field with an imaginary mass. Although tachyonic particles (particles that move faster than light) are a purely hypothetical concept that violate a number of essential physical principles, at least one field with imaginary mass, the Higgs field, is believed to exist. Under no circumstances do any excitations of tachyonic fields ever propagate faster than light—the presence or absence of a tachyonic (imaginary) mass has no effect on the maximum velocity of signals, and so unlike faster-than-light particles there is no violation of causality. Tachyonic fields play an important role in physics and are discussed in popular books. The term "tachyon" was coined by Gerald Feinberg in a 1967 paper that studied quantum fields with imaginary mass. Feinberg believed such fields permitted faster than light propagation, but it was soon realized that this was not the case. Instead, the imaginary mass creates an instability: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaginary Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh less than it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faster-than-light
Faster-than-light (superluminal or supercausal) travel and communication are the conjectural propagation of matter or information faster than the speed of light in vacuum (). The special theory of relativity implies that only particles with zero rest mass (i.e., photons) may travel ''at'' the speed of light, and that nothing may travel faster. Particles whose speed exceeds that of light ( tachyons) have been hypothesized, but their existence would violate causality and would imply time travel. The scientific consensus is that they do not exist. According to all observations and current scientific theories, matter travels at slower-than-light (subluminal) speed with respect to the locally distorted spacetime region. Speculative faster-than-light concepts include the Alcubierre drive, Krasnikov tubes, traversable wormholes, and quantum tunneling. Some of these proposals find loopholes around general relativity, such as by expanding or contracting space to make the object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Feinberg
Gerald Feinberg (27 May 1933 – 21 April 1992) was a Columbia University physicist, futurist and popular science author. He spent a year as a Member of the Institute for Advanced Study, and two years at the Brookhaven Laboratories. Feinberg went to Bronx High School of Science with Steven Weinberg and Sheldon Glashow and obtained his bachelor's and graduate degrees from Columbia University. His father was Yiddish poet and journalist Leon Feinberg. Among his students were Scott Dodelson, physicist at Carnegie Mellon University. Research He coined the term tachyon for hypothetical faster-than-light particles and analysed their quantum field properties, predicted the existence of the muon neutrino and advocated cryonics as a public service. He was a member of the Foresight Institute's advisory panel. Parapsychology Feinberg wrote a foreword to Edgar Mitchell's book ''Psychic Explorations'' (1974) in which he endorsed psychic phenomena. His concept of a tachyon, a theoretic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
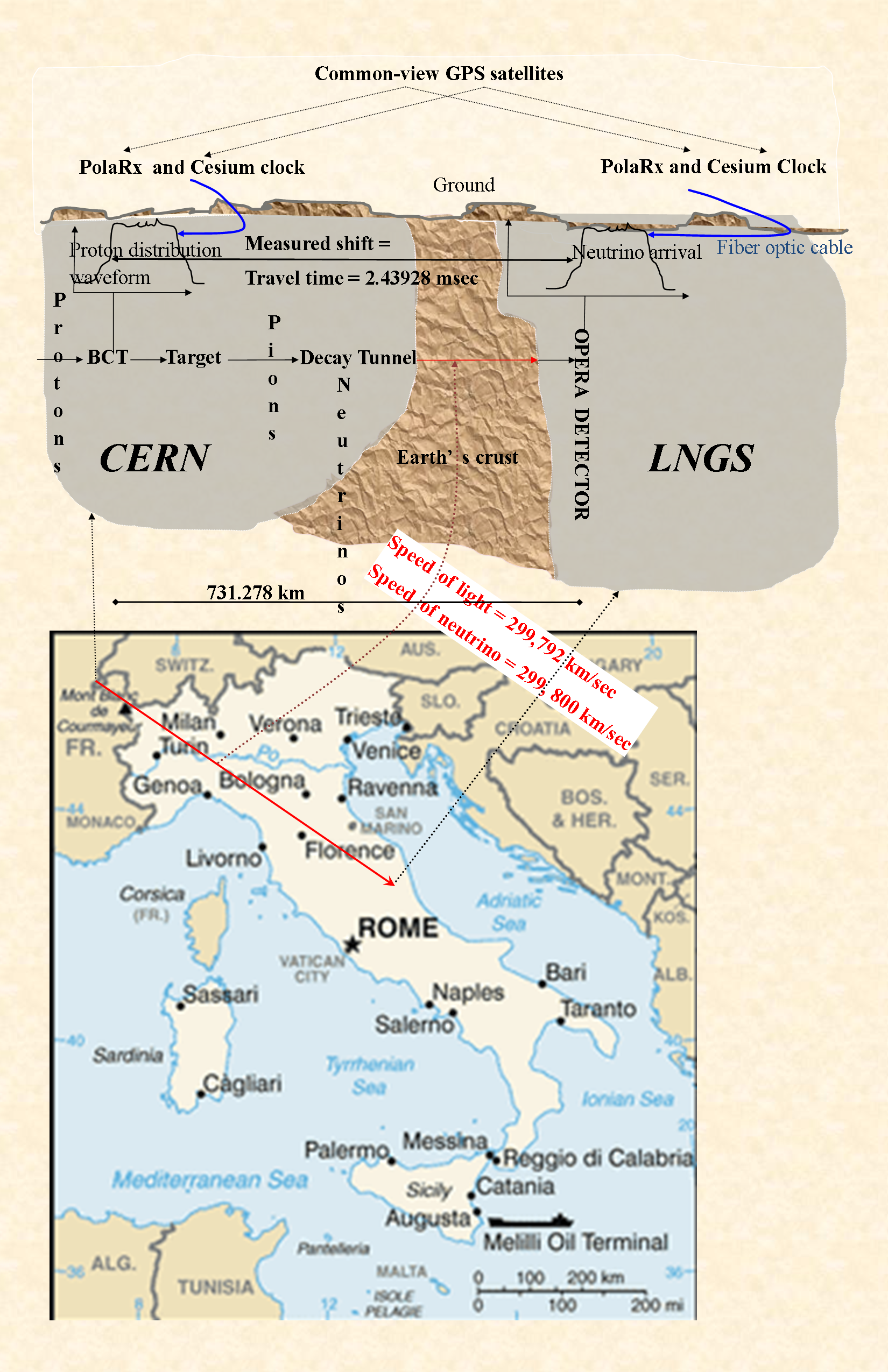
2011 OPERA Faster-than-light Neutrino Anomaly
In 2011, the Oscillation Project with Emulsion-tRacking Apparatus (OPERA experiment, OPERA) experiment mistakenly observed neutrinos appearing to travel faster-than-light, faster than light. Even before the source of the error was discovered, the result was considered anomalous because speeds higher than that of light in vacuum are generally thought to Special relativity#Causality and prohibition of motion faster than light, violate special relativity, a cornerstone of the modern understanding of physics for over a century. On June 8, 2012, after further research and analysis, CERN research director Sergio Bertolucci declared that the speed of neutrinos is consistent with that of light. The press release, made from the 25th International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics in Kyoto, states that the original OPERA results were wrong, due to equipment failures. On July 12, 2012, OPERA updated their paper by including the new sources of errors in their calculations. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradyons
The physics technical term massive particle refers to a massful particle which has real non-zero rest mass (such as baryonic matter), the counter-part to the term massless particle. According to special relativity, the velocity of a massive particle is always less than the speed of light. When highlighting relativistic speeds, the synonyms bradyon (from , ''bradys'', "slow"), tardyon or ittyon are sometimes used to contrast with luxon (which moves at light speed) and hypothetical tachyon (which moves faster than light). See also * Elementary particle In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. The Standard Model presently recognizes seventeen distinct particles—twelve fermions and five bosons. As a c ... References {{particle-stub Particle physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy–momentum Relation
In physics, the energy–momentum relation, or relativistic dispersion relation, is the relativistic equation relating total energy (which is also called relativistic energy) to invariant mass (which is also called rest mass) and momentum. It is the extension of mass–energy equivalence for bodies or systems with non-zero momentum. It can be formulated as: This equation holds for a body or system, such as one or more particles, with total energy , invariant mass , and momentum of magnitude ; the constant is the speed of light. It assumes the special relativity case of flat spacetime and that the particles are free. Total energy is the sum of rest energy E_0 = m_0 c^2 and relativistic kinetic energy: E_K = E - E_0 = \sqrt- m_c^2 Invariant mass is mass measured in a center-of-momentum frame. For bodies or systems with zero momentum, it simplifies to the mass–energy equation E_0 = m_0 c^2, where total energy in this case is equal to rest energy. The Dirac sea mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. The current standard model of particle physics is based on QFT. History Quantum field theory emerged from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of the 20th century. Its development began in the 1920s with the description of interactions between light and electrons, culminating in the first quantum field theory—quantum electrodynamics. A major theoretical obstacle soon followed with the appearance and persistence of various infinities in perturbative calculations, a problem only resolved in the 1950s with the invention of the renormalization procedure. A second major barrier came with QFT's apparent inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Law
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) across all fields of natural science (physics, chemistry, astronomy, geoscience, biology). Laws are developed from data and can be further developed through mathematics; in all cases they are directly or indirectly based on empirical evidence. It is generally understood that they implicitly reflect, though they do not explicitly assert, causal relationships fundamental to reality, and are discovered rather than invented. Scientific laws summarize the results of experiments or observations, usually within a certain range of application. In general, the accuracy of a law does not change when a new theory of the relevant phenomenon is worked out, but rather the scope of the law's application, since the mathematics or statement representin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |