S-Bahn Stuttgart In Plochingen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The S-Bahn is the name of hybrid urban-
The S-Bahn is the name of hybrid urban-


 The "S" stood for "station". Just before the opening of the first line in the Copenhagen S-train network, the newspaper '' Politiken'' on 17 February 1934 held a competition about the name, which in Danish became known as ''Den elektriske enquete'' or "The electrical survey" (as the Copenhagen S-trains would become the first electrical railways in Denmark). But since an "S" already was put up at all the stations, weeks before the survey, the result became ''S-tog'' which means "S-train".John Poulsen: S-bane 1934-2009 side 47 This was also just a few years after the S-trains had opened in Berlin and Hamburg. Today the Copenhagen S-trains uses six lines and serves 86 stations, 32 of them are located inside the (quite tiny) municipality borders. Each line uses 6 t.p.h (trains per hour) in each direction, with exception of the (yellow) F-line. The F-line has departures in each direction every five minutes, or 12 t.p.h. service .
The "S" stood for "station". Just before the opening of the first line in the Copenhagen S-train network, the newspaper '' Politiken'' on 17 February 1934 held a competition about the name, which in Danish became known as ''Den elektriske enquete'' or "The electrical survey" (as the Copenhagen S-trains would become the first electrical railways in Denmark). But since an "S" already was put up at all the stations, weeks before the survey, the result became ''S-tog'' which means "S-train".John Poulsen: S-bane 1934-2009 side 47 This was also just a few years after the S-trains had opened in Berlin and Hamburg. Today the Copenhagen S-trains uses six lines and serves 86 stations, 32 of them are located inside the (quite tiny) municipality borders. Each line uses 6 t.p.h (trains per hour) in each direction, with exception of the (yellow) F-line. The F-line has departures in each direction every five minutes, or 12 t.p.h. service .
 The beginning of the 20th century saw the first electric trains, which in Germany operated at 15,000 V on
The beginning of the 20th century saw the first electric trains, which in Germany operated at 15,000 V on







 The oldest and largest S-Bahn system in Austria is the Vienna S-Bahn, which predominantly uses non exclusive rails tracks outside of Vienna. It was established in 1962, although it was usually referred to as ''Schnellbahn'' until 2005. The white "S" on a blue circle used as the logo is said to reflect the layout of the central railway line in Vienna. However, it has now been changed for a more stylized version that is used all through Austria, except Salzburg. The rolling stock was blue for a long time, reflecting the logo colour, but red is used uniformly for nearly all local traffic today.
The oldest and largest S-Bahn system in Austria is the Vienna S-Bahn, which predominantly uses non exclusive rails tracks outside of Vienna. It was established in 1962, although it was usually referred to as ''Schnellbahn'' until 2005. The white "S" on a blue circle used as the logo is said to reflect the layout of the central railway line in Vienna. However, it has now been changed for a more stylized version that is used all through Austria, except Salzburg. The rolling stock was blue for a long time, reflecting the logo colour, but red is used uniformly for nearly all local traffic today.
 In 2004, the Salzburg S-Bahn went into service as the first
In 2004, the Salzburg S-Bahn went into service as the first
 The suburban railways of Brussels are being integrated into the Brussels Regional Express Network (French: ''Réseau Express Régional Bruxellois'', ''RER''; Dutch: ''Gewestelijk ExpresNet'', GEN), which is identified by the letter ''S'' across both languages. In 2018, the S-train was also introduced in
The suburban railways of Brussels are being integrated into the Brussels Regional Express Network (French: ''Réseau Express Régional Bruxellois'', ''RER''; Dutch: ''Gewestelijk ExpresNet'', GEN), which is identified by the letter ''S'' across both languages. In 2018, the S-train was also introduced in
 In the Czech Republic, integrated commuter rail systems exist in Prague and Moravian-Silesian Region. Both systems are called ''Esko'', which is how ''S'' letter is usually called in Czech. Esko Prague has been operating since 9 December 2007 as a part of the Prague Integrated Transport system.
In the Czech Republic, integrated commuter rail systems exist in Prague and Moravian-Silesian Region. Both systems are called ''Esko'', which is how ''S'' letter is usually called in Czech. Esko Prague has been operating since 9 December 2007 as a part of the Prague Integrated Transport system.
 Copenhagen S-train connects the city centre, other inner and outer boroughs and suburbs with each other. The average distance between stations is 2.0 km, shorter in the city core and inner boroughs, longer at the end of lines that serve suburbs. Of the 86 stations, 32 are located within the central parts of the city. Some stations are located around 40 km from Copenhagen city centre. For this reason the fares vary depending on distances. One-day-passes which tourist buy are valid only in the most central parts of the S-train system. Weekdays each line have departures every 10th minute with exception for the F-line, which departures every fifth minute. Where several lines use the same branches, up to around 30 trains per hour (in each direction) service exists. On Sundays the seven lines are reduced to four lines, but all stations are served at least every 10th minute. The three railway stations at
Copenhagen S-train connects the city centre, other inner and outer boroughs and suburbs with each other. The average distance between stations is 2.0 km, shorter in the city core and inner boroughs, longer at the end of lines that serve suburbs. Of the 86 stations, 32 are located within the central parts of the city. Some stations are located around 40 km from Copenhagen city centre. For this reason the fares vary depending on distances. One-day-passes which tourist buy are valid only in the most central parts of the S-train system. Weekdays each line have departures every 10th minute with exception for the F-line, which departures every fifth minute. Where several lines use the same branches, up to around 30 trains per hour (in each direction) service exists. On Sundays the seven lines are reduced to four lines, but all stations are served at least every 10th minute. The three railway stations at
 The trains of the Berlin and Hamburg S-Bahn systems ran on separate tracks from the beginning. When other cities started implementing their systems in the 1960s, they mostly had to use the existing intercity rail tracks, and they still more or less use such tracks.
The central intercity stations of Frankfurt, Leipzig, Munich and
The trains of the Berlin and Hamburg S-Bahn systems ran on separate tracks from the beginning. When other cities started implementing their systems in the 1960s, they mostly had to use the existing intercity rail tracks, and they still more or less use such tracks.
The central intercity stations of Frankfurt, Leipzig, Munich and



 The oldest network in Switzerland is the Bern S-Bahn, which was established in stages from 1974 onward and has adopted the term S-Bahn since 1995. It is also the only one in Switzerland to use a coloured "S" logo. In 1990, the Zürich S-Bahn, went into service. As of 2022, this network comprises 32 services, covering a large area in Switzerland (and parts of southern Germany). Further S-Bahn services were set up in the course of the '' Bahn 2000'' initiative in Central Switzerland (a collaborative network of ''
The oldest network in Switzerland is the Bern S-Bahn, which was established in stages from 1974 onward and has adopted the term S-Bahn since 1995. It is also the only one in Switzerland to use a coloured "S" logo. In 1990, the Zürich S-Bahn, went into service. As of 2022, this network comprises 32 services, covering a large area in Switzerland (and parts of southern Germany). Further S-Bahn services were set up in the course of the '' Bahn 2000'' initiative in Central Switzerland (a collaborative network of ''
suburban rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are con ...
systems serving a metropolitan region in German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit systems, while smaller ones often resemble commuter or even regional rail
Regional rail, also known as local trains and stopping trains, are passenger rail services that operate between towns and cities. These trains operate with more stops over shorter distances than inter-city rail, but fewer stops and faster serv ...
. The term derives from ''Schnellbahn'', ''Stadtbahn'' or ''Stadtschnellbahn''.
Similar systems in Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
are known as S-Bahn as well. In Belgium it is known as S-Trein (Flemish) or Train S (French). In Belgium there are S-Trains in the five largest cities: Brussels, Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
, Ghent and Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
. In Denmark, they are known as S-tog , in the Czech Republic as Esko or S-lines.
Characteristics
There is no complete definition of an S-Bahn system. S-Bahn are, where they exist, the most local type of railway stopping at all existing stations inside and around a city, while other mainline trains only call at major stations. They are slower than mainline railways but usually serve as fast crosstown services within the city. The Copenhagen S-tog for example goes up to , faster than most urban heavy rail and mass transit. S-Bahn trains generally serve the hinterland of a certain city, rather than connecting different cities, although in high population density areas a few exceptions from this exist. A good example of such an exception is the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn, which interconnects the cities, towns and suburbs of theRuhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
, a large urban agglomeration, not unlike the large network of regional trains which also serve the area. Most S-Bahn systems are entirely built on older local railways, or in some cases parallel to an existing dual track railway. Most use existing local mainline railway trackage, but a few branches and lines can be purpose-built S-Bahn lines. S-Bahn trains typically use overhead lines or a third rail for traction power. In Hamburg both methods are used, depending on which line is powered.
In smaller S-Bahn systems and suburban sections of larger ones, trains typically share tracks with other rail traffic, with the Berlin S-Bahn, Hamburg S-Bahn
The Hamburg S-Bahn is a suburban commuter railway network in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Together, the S-Bahn, the Hamburg U-Bahn, the AKN railway and the regional railway form the backbone of railway public transport in the city and the s ...
and Copenhagen S-train being notable exceptions. Busy S-Bahn corridors sometimes have sections of exclusive trackage of their own but parallel to mainline railways. Many of the larger S-Bahn systems will also have central corridors of exclusive trackage that individual suburban branches feed into, creating a high frequency trunk corridor. In many cases, the central corridor is a dedicated underground line in the city centre with close stop spacing and a high frequency, similar to metro systems, created from the combined interlining of the multiple branches. A good example of this is the Berliner Stadtbahn in the Berlin's S-Bahn, which is regarded as a tourist attraction. However, in more lightly used sections outside the city centre, S-Bahn services commonly share tracks with other trains.
Further out from the central parts of a city the individual services branch off into lines where the distances between stations can exceed 5 km, similar to commuter rail. This allows the S-Bahn to serve a dual transport purpose: local transport within a city centre and suburban transport between central boroughs of larger cities, and to suburbs. Frequencies vary wildly between systems with short headways in the core sections of large networks to headways of over 20 minutes in remote sections of the network, late at night and/or on Sundays and in smaller systems. The rolling stock typically used for S-Bahn systems reflects its hybrid purpose. The interior is designed for short journeys with provision for standing passengers but may have more space allocated to larger and more numerous seats. Integration with other local transport for ticketing, connectivity and easy interchange between lines or other system like metros is typical for the S-Bahn. Where both S-Bahn and metro exist, the number of interchange stations between the two systems is substantial with metro tickets being valid on S-Bahn services, and vice versa. The S-Bahn Mitteldeutschland constitutes the main local railway system for Leipzig but also connects to Halle Halle may refer to:
Places Germany
* Halle (Saale), also called Halle an der Saale, a city in Saxony-Anhalt
** Halle (region), a former administrative region in Saxony-Anhalt
** Bezirk Halle, a former administrative division of East Germany
** Hall ...
, where a few stations are located. The Rostock S-Bahn is an example of a smaller S-Bahn system.
Etymology
Germany, Austria and Switzerland
The name ''S-Bahn'' is an abbreviation for the German "Stadtschnellbahn" (meaning "city rapid railway") and was introduced in December 1930 in Berlin. The name was introduced at the time of the reconstruction of the suburban commuter train tracks— the first section to be electrified was a section of the Berlin–Stettin railway from Berlin Nordbahnhof to Bernau bei Berlin station in 1924, leading to the formation of the Berlin S-Bahn. The main line Berliner Stadtbahn (English: ''City railway of Berlin'') was electrified with a 750 volt third rail in 1928 (some steam trains ran until 1929) and the circle line Berliner Ringbahn was electrified in 1929. The electrification continued on the radial suburban railway tracks along with changing the timetable of the train system into a rapid transit model with no more than 20 minutes headway per line where a number of lines overlapped on the main line. The system peaked during the1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (German: ''Olympische Sommerspiele 1936''), officially known as the Games of the XI Olympiad (German: ''Spiele der XI. Olympiade'') and commonly known as Berlin 1936 or the Nazi Olympics, were an international multi-sp ...
in Berlin to a train schedule below 2 minutes.
The idea of heavy rail rapid transit was not unique to Berlin. Hamburg had an electric railway between the central station ("Hauptbahnhof") and Altona which opened in 1906 and in 1934 the system adopted the S-Bahn label from Berlin. The same year in Denmark, Copenhagen's S-tog opened its first line. In Austria, Vienna had its ''Stadtbahn'' main line electrified in 1908 and also introduced the term ''Schnellbahn'' ("rapid railway") in 1954 for its planned commuter railway network (which started operations in 1962). The S-Bahn label was sometimes used as well, but the name was only switched to S-Bahn Wien
The Vienna S-Bahn is a suburban commuter rail network in Vienna, Austria. As opposed to the city-run urban metro network, the Vienna U-Bahn, it extends beyond the borders of the city, is operated by the ÖBB (Austrian Federal Railways), and cons ...
in 2005. As for Munich, a first breaking ground for an S-Bahn-like rapid transport system, executed by the Nazi government of Adolf Hitler, took place in 1938 in Lindwurmstrasse near what is now Goetheplatz underground station (line U6). Said system was supposed to run through tunnels in downtown areas. The planning process mainly consisted of the bundling and interconnecting of existing suburban and local railways, plus the construction of a few new lines. Plans and construction work - including the building shell of Goetheplatz station - came to a very early halt during World War II and were not pursued in its aftermath. Very extensive nowadays, Munich's existing S-Bahn-System, together with the first two U-Bahn lines, began to operate prior to the 1972 Summer Olympics
The 1972 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XX Olympiad () and commonly known as Munich 1972 (german: München 1972), was an international multi-sport event held in Munich, West Germany, from 26 August to 11 September 1972. ...
only.
The term ''S-Bahn'' was until 14 March 2012 a registered wordmark of Deutsche Bahn
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the se ...
, where at the request of a transportation association the Federal Patent Court of Germany ordered the wordmark to be removed from the records of the German Patent and Trade Mark Office. Prior to the said event Deutsche Bahn collected a royalty of 0.4 cents per train kilometer for the usage of the said term.
Denmark


 The "S" stood for "station". Just before the opening of the first line in the Copenhagen S-train network, the newspaper '' Politiken'' on 17 February 1934 held a competition about the name, which in Danish became known as ''Den elektriske enquete'' or "The electrical survey" (as the Copenhagen S-trains would become the first electrical railways in Denmark). But since an "S" already was put up at all the stations, weeks before the survey, the result became ''S-tog'' which means "S-train".John Poulsen: S-bane 1934-2009 side 47 This was also just a few years after the S-trains had opened in Berlin and Hamburg. Today the Copenhagen S-trains uses six lines and serves 86 stations, 32 of them are located inside the (quite tiny) municipality borders. Each line uses 6 t.p.h (trains per hour) in each direction, with exception of the (yellow) F-line. The F-line has departures in each direction every five minutes, or 12 t.p.h. service .
The "S" stood for "station". Just before the opening of the first line in the Copenhagen S-train network, the newspaper '' Politiken'' on 17 February 1934 held a competition about the name, which in Danish became known as ''Den elektriske enquete'' or "The electrical survey" (as the Copenhagen S-trains would become the first electrical railways in Denmark). But since an "S" already was put up at all the stations, weeks before the survey, the result became ''S-tog'' which means "S-train".John Poulsen: S-bane 1934-2009 side 47 This was also just a few years after the S-trains had opened in Berlin and Hamburg. Today the Copenhagen S-trains uses six lines and serves 86 stations, 32 of them are located inside the (quite tiny) municipality borders. Each line uses 6 t.p.h (trains per hour) in each direction, with exception of the (yellow) F-line. The F-line has departures in each direction every five minutes, or 12 t.p.h. service .
History
Germany
Early steam services
In 1882, the growing number of steam-powered trains around Berlin prompted the Prussian State Railway to construct separate rail tracks for suburban traffic. The ''Berliner Stadtbahn'' connected Berlin's eight intercity rail stations which were spread throughout the city (all but the ''Stettiner Bahnhof'' which today is a pure S-Bahn station known as Berlin Nordbahnhof; as the city ''Stettin'' today is Polish citySzczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
). A lower rate for the newly founded ''Berliner Stadt-, Ring- und Vorortbahn'' (Berlin City, Circular and Suburban Rail) was introduced on 1 October 1891. This rate and the growing succession of trains made the short-distance service stand out from other railways.
The second suburban railway was the '' Hamburg-Altonaer Stadt- und Vorortbahn'' connecting Hamburg with Altona and Blankenese. The Altona office of the Prussian State Railway established the electric powered railway in 1906.See picture of Berliner Stadtbahn by Hackescher Markt S-Bahn station, the third rail is clearly seen between the two S-Bahn tracks. Original name of that station was "Börse", or "the Stock Market" (which now is located in Frankfurt am Main)
Electricity
 The beginning of the 20th century saw the first electric trains, which in Germany operated at 15,000 V on
The beginning of the 20th century saw the first electric trains, which in Germany operated at 15,000 V on overhead lines
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as:
* Overhead catenary
* Overhead contact system (OCS)
* Overhead equipmen ...
. The '' Berliner Stadt-, Ring- und Vorortbahn'' instead implemented direct current multiple unit
A multiple-unit train or simply multiple unit (MU) is a self-propelled train composed of one or more carriages joined together, which when coupled to another multiple unit can be controlled by a single driver, with multiple-unit train contr ...
s running on 750 V from a third rail. In 1924, the first electrified route went into service. The third rail was chosen because it made both the modifications of the rail tracks (especially in tunnels and under bridges) and the side-by-side use of electric and steam trains easier.
To set it apart from the subterranean '' U-Bahn'', the term ''S-Bahn'' replaced ''Stadt-, Ring- und Vorortbahn'' in 1930.
The Hamburg service had established an alternating current line in 1907 with the use of multiple units with slam door
A slam-door train or slammer is a set of diesel multiple units (DMUs) or electric multiple units (EMUs) that were designed before the introduction of automatic doors on railway carriages in the United Kingdom and other countries, which featur ...
s. In 1940 a new system with 1200 V DC third rail and modern electric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a numbe ...
s with sliding doors was integrated on this line (on the same tracks). The old system with overhead wire remained up to 1955. The other lines of the network still used steam and later Diesel power.
In 1934, the ''Hamburg-Altonaer Stadt- und Vorortbahn'' was renamed as S-Bahn.
Comparable systems




Austria
Euroregion
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two (or more) contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region. ...
S-Bahn, crossing the border to the neighbouring towns of Freilassing and Berchtesgaden
Berchtesgaden () is a municipality in the district Berchtesgadener Land, Bavaria, in southeastern Germany, near the border with Austria, south of Salzburg and southeast of Munich. It lies in the Berchtesgaden Alps, south of Berchtesgaden; the ...
in Bavaria. The network is served by three corporations: the ''Berchtesgadener Land Bahn'' (BLB)(S4), the Austrian Federal Railways (German: ''Österreichischen Bundesbahn'' / ÖBB)(S2 and S3) and the ''Salzburger Lokalbahn'' (SLB)(S1 and S11) and . The Salzburg S-Bahn logo is only different one, it is a white S on a light blue circle.
In 2006 the regional train line in the Rhine Valley
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
in the state of Vorarlberg has been renamed to '' S-Bahn Vorarlberg''. It is a three lines network, operated by the '' Montafonerbahn'' and the ÖBB.
The '' S-Bahn Steiermark'' has been inaugurated in December 2007 in Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
, built to connect its capital city Graz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the popul ...
with the rest of the metropolitan area, currently the following lines are active: S1, S11, S3, S31, S5, S51, S6, S61, S7, S8 and S9. The network is operated by three railway companies: the ''Graz-Köflacher Bahn'' (GKB) (lines: S6, S61 and S7), the ÖBB (lines: S1, S3, S5, S51, S8 and S9) and the ''Steiermärkische Landesbahnen'' (StB) (lines: S11 and S31).
In December 2007 as well the Tyrol S-Bahn
The Tyrol S-Bahn provides regional rail services in metropolitan Innsbruck, Austria and its hinterlands in the state of Tyrol. At present, it is only a nominally an S-Bahn in that it only operates on the lines of the Austrian Federal Railways. Expa ...
opened, running from Hall in Tirol
Hall in Tyrol is a town in the Innsbruck-Land district of Tyrol, Austria. Located at an altitude of 574 m, about 5 km (3 mi) east of the state's capital Innsbruck in the Inn valley, it has a population of about 13,000 (Jan 2013).
History ...
in the east to Innsbruck Central Station and Telfs in the west and from Innsbruck to Steinach am Brenner. Class 4024 EMUs are used as rolling stock on this network.
In 2010 the '' S-Bahn Kärnten'' was opened in the state of Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost States of Austria, Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German language, German. Its regional dialects belong to t ...
and currently consists of 4 lines operated by ÖBB.
The youngest network is the '' S-Bahn Oberösterreich'' in the Greater Linz area of the state of Upper Austria, which was inaugurated in December 2016. It is a 5 line system operated by '' Stern und Hafferl'' and the ÖBB.
Belgium
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Ghent, Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
and Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.
.
Czech Republic
Esko Moravian-Silesian Region
Esko Moravian-Silesian Region is a commuter rail system in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. The integrated system began on 14 December 2008. Esko is part of the ODIS Integrated Transport system serving the Moravian-Silesian Regi ...
began operating on 14 December 2008 as a part of the ODIS Integrated Transport system serving the Moravian-Silesian Region. Both systems are primarily operated by České dráhy. Several shorter lines are operated by other companies.
Denmark
Amager
Amager ( or, especially among older speakers, ) in the Øresund is Denmark's most densely populated island, with more than 212,000 inhabitants (January 2021) a small appendage to Zealand. The protected natural area of ''Naturpark Amager'' (includi ...
have a local service that equals the S-trains'.
The Copenhagen Metro opened in 2002 as a complement to the already existing S-train system. Copenhagen's S-train system is the only one in the country. Outside Denmark, in cities where both exist, is it far from unusual that a metro system later has been complemented with S-trains. The branch towards Køge (the southernmost S-train station in Copenhagen's S-network) has a rather unique history, as it was built in the 1970s where no previous railway ever had existed.
Germany
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
are terminal stations, so all four cities have monocentric S-Bahn networks. The S-Bahn trains use a tunnel under the central station and the city centre.
The high number of large cities in the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
area promotes a polycentric network connecting all cities and suburbs. The ''S-Bahn Rhein-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn Rhein-Ruhr) is a polycentric and electrically driven S-train network covering the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region in the German federated state of North Rhine-Westphalia. This includes most of the Ruhr (and ci ...
'', as it is called, features few tunnels, and its routes are longer than those of other networks. The Ruhr S-Bahn is the only S-Bahn network to be run by more than one corporation in Germany, and the Salzburg S-Bahn holds a similar distinction in Austria. Most Swiss S-Bahn systems are multi-corporation networks, however.
Most German S-Bahn networks have a unique ticket system, separated from the ''Deutsche Bahn
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the se ...
'' rates, instead connected to the city ticket system used for U-bahns and local buses. The S-Bahn of Hanover, however, operates under five different rates due to its large expanse.
One S-Bahn system is no longer in operation: the Erfurt S-Bahn which operated from 1976 until 1993 and was an single-line system which consisted of four stations from Erfurt Central Station to Erfurt Berliner Straße station in the then newly built northern suburbs of Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits in ...
.
There are several S-Bahn or S-Bahn-like systems in planning, such as the Danube-Iller S-Bahn and the Augsburg S-Bahn
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
. The S-Bahn system in Lübeck is under discussion (see network plan).
The Stadtbahn Karlsruhe (a tram-train network) uses the green "S" logo, but does not refer to itself as ''S-Bahn''. The blue '' U-Bahn'' logo is not used either, due to the lack of subterranean lines.
Despite its name, the ''Ortenau S-Bahn
Ortenau-S-Bahn (''OSB'') is a brand name of the Südwestdeutsche Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft (SWEG), a transport company owned by the state of Baden-Württemberg. It is employed for regional railway services in the Ortenau area, centering on . Be ...
'' ( Offenburg) is a Regionalbahn service.
The following networks are currently in operation:
Switzerland and Liechtenstein
''S-Bahn'' is also used in theGerman-speaking
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is a ...
part of Switzerland. While French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
publications of those networks translate it as '' RER'', the line numbers are still prefixed with an S (e.g., as S2), except for the '' Léman Express'', which uses the prefix "L" (e.g., as L2). S-Bahn-style services in the Italian and Romansh speaking parts of Switzerland also use the "S" prefix, although in Italian such networks are called ''rete celere'' (lit. fast network) instead of S-Bahn.

 The oldest network in Switzerland is the Bern S-Bahn, which was established in stages from 1974 onward and has adopted the term S-Bahn since 1995. It is also the only one in Switzerland to use a coloured "S" logo. In 1990, the Zürich S-Bahn, went into service. As of 2022, this network comprises 32 services, covering a large area in Switzerland (and parts of southern Germany). Further S-Bahn services were set up in the course of the '' Bahn 2000'' initiative in Central Switzerland (a collaborative network of ''
The oldest network in Switzerland is the Bern S-Bahn, which was established in stages from 1974 onward and has adopted the term S-Bahn since 1995. It is also the only one in Switzerland to use a coloured "S" logo. In 1990, the Zürich S-Bahn, went into service. As of 2022, this network comprises 32 services, covering a large area in Switzerland (and parts of southern Germany). Further S-Bahn services were set up in the course of the '' Bahn 2000'' initiative in Central Switzerland (a collaborative network of ''S-Bahn Luzern
The Lucerne S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn Luzern) is an S-Bahn-style commuter rail network focusing on Lucerne, Switzerland.
Opened on 12 December 2004, the network forms part of the Central Switzerland S-Bahn project (german: S-Bahn Zentralschweiz, link ...
'' and ''Stadtbahn Zug
The Zug Stadtbahn (german: Stadtbahn Zug) is an S-Bahn-style commuter rail network centred on Zug, Switzerland.
Opened on 12 December 2004, the network forms part of the Central Switzerland S-Bahn project (german: S-Bahn Zentralschweiz, links=no) ...
''), and Eastern Switzerland ('' S-Bahn St. Gallen'').
The ''Basel trinational S-Bahn ,french: RER trinational de Bâle
, image = Logo trireno black.svg
, alt = logo trireno
, imagesize = 180
, image2 = Basel 2012-08 Mattes 1 (283).JPG
, alt2 = S-Bahn train at B ...
'' services the Basel metropolitan area, thus providing cross-border transportation into both France and Germany. A tunnel connecting Basel's two large intercity stations ( Basel Badischer Bahnhof and Basel SBB) is planned as '' Herzstück Regio-S-Bahn Basel'' (lit. heart-piece Regio-S-Bahn Basel).
An international S-Bahn network also existsts across the Swiss-Italian border
The Swiss people (german: die Schweizer, french: les Suisses, it, gli Svizzeri, rm, ils Svizzers) are the citizens of Switzerland or people of Swiss ancestry.
The number of Swiss nationals has grown from 1.7 million in 1815 to 8.7 million ...
, in the Swiss Canton of Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and the Italian state
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional ...
of Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
. Services are operated by Treni Regionali Ticino Lombardia (TILO), a joint venture between Italian railway company Trenord and Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS).
The '' RER Vaud'' of Lausanne and the '' Léman Express'' of Geneva serve the area around Lake Geneva (''fr. Lac Léman''). The ''Léman express'' network expands across the Swiss-French border
Swiss French (french: français de Suisse or ') is the variety of French spoken in the French-speaking area of Switzerland known as Romandy. French is one of the four official languages of Switzerland, the others being German, Italian, and ...
. It is the largest cross-country S-Bahn network of Europe. ''Léman express'' was launched in December 2019 and is operated by Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS) and SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffi ...
.
Another transborder network for the Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
(''Bodensee'') area, connecting up to four nations, is under discussion. This network would extend across the German states Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria, the Austrian state
Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states (German: ''Länder''). Since ''Land'' is also the German word for "country", the term ''Bundesländer'' (literally ''federal states'') is often used instead to avoid ambiguity. The Constitutio ...
Vorarlberg, the Principality of Liechtenstein (''S-Bahn FL.A.CH
The S-Bahn is the name of hybrid urban- suburban rail systems serving a metropolitan region in German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit systems, while smaller ones often resemble co ...
''), and the Swiss cantons
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confe ...
of Appenzell Ausserrhoden
Appenzell Ausserrhoden (; in English sometimes Appenzell Outer Rhodes) (german: Kanton Appenzell Ausserrhoden; rm, Chantun Appenzell Dadora; french: Canton d'Appenzell Rhodes-Extérieures; it, Canton Appenzello Esterno) is one of the 26 canton ...
, Appenzell Innerrhoden
Appenzell Innerrhoden (; in English sometimes Appenzell Inner-Rhodes) (german: Kanton Appenzell Innerrhoden rm, Chantun Appenzell Dadens; french: Canton d'Appenzell Rhodes-Intérieures; it, Canton Appenzello Interno) is one of the 26 cantons ...
, Schaffhausen, St. Gallen and Thurgau. Possible names are ''Bodensee-S-Bahn'' and '' Alpenrhein-Bahn''. Presently, an hourly service, S3 of Vorarlberg S-Bahn
The Vorarlberg S-Bahn is a label for regional rail services in the Austrian state of Vorarlberg. It is integrated into the which manages ticket pricing, and is operated by the state-owned ÖBB and privately owned Montafonerbahn (mbs). In addit ...
( ÖBB), connects Bregenz ( A) with St. Margrethen
St. Margrethen (Saint Margrethen/Sankt Margrethen) is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Rheintal in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Geography
St. Margrethen has an area, , of . Of this area, 28.3% is used for agric ...
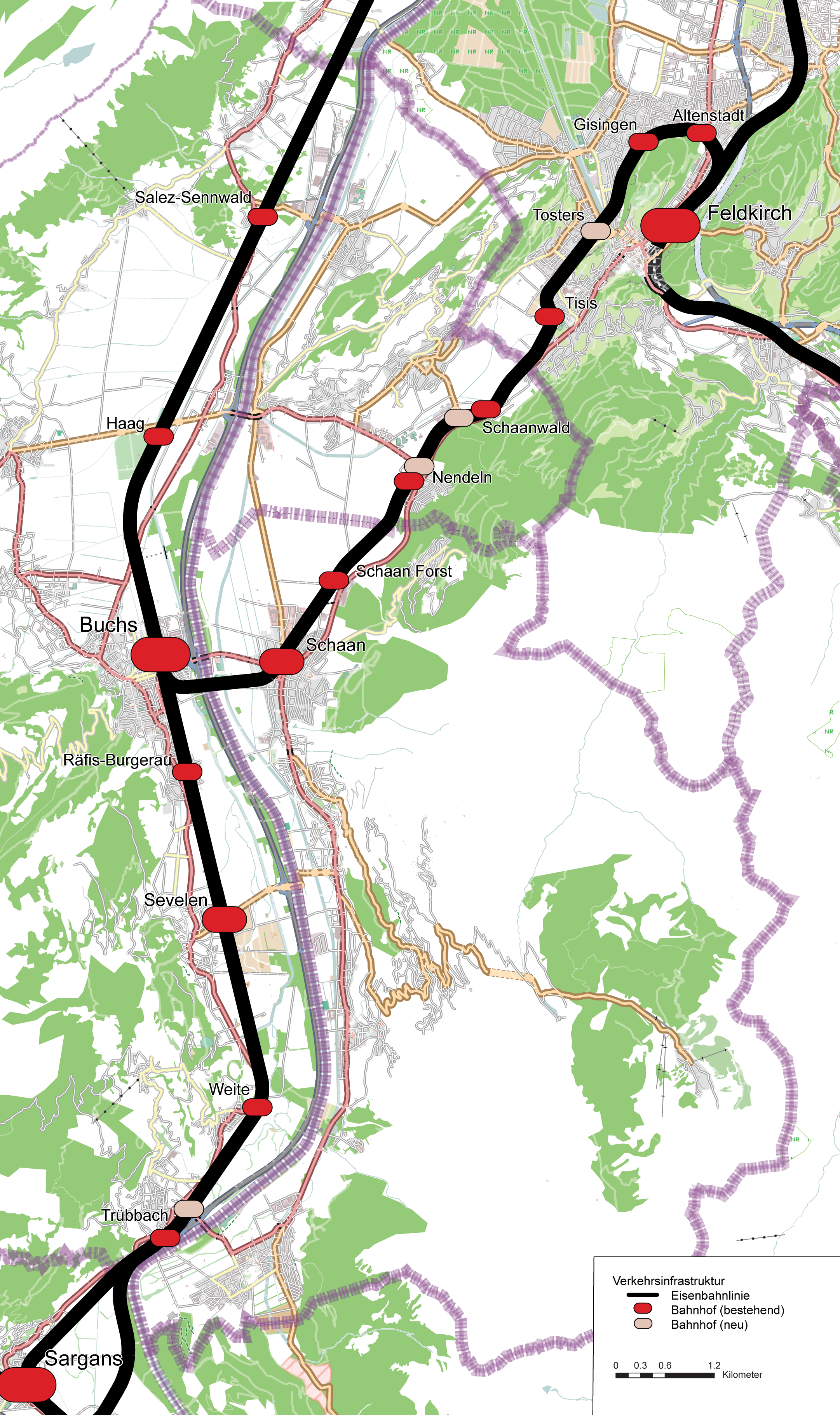
( CH), and a less frequent service (S2) operates between Feldkirch Feldkirch may refer to:
Places
* Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, a medieval city and capital of an administrative district in Austria
** Feldkirch (district), an administrative division of Vorarlberg, Austria
* Feldkirch (Hartheim), a village in the municip ...
(A), Schaan ( FL) and Buchs SG (CH). The S14 and S44 services of S-Bahn St. Gallen both connect Konstanz ( D) with Kreuzlingen
Kreuzlingen is a municipality in the district of Kreuzlingen in the canton of Thurgau in north-eastern Switzerland. It is the seat of the district and is the second-largest city of the canton, after Frauenfeld, with a population of about 22,000. ...
and Weinfelden (both CH), and since 2022, some S7 services continue from Rorschach Rorschach may refer to:
* Hermann Rorschach, a Swiss psychiatrist
** Rorschach test, his psychological evaluation method involving inkblots
* Rorschach (character), a character from the comics ''Watchmen''
* Rorschach (comic book), a 2020 comic
* ...
(CH) to Bregenz and Lindau-Reutin (D). Additional transborder services are planned. The future of ''S-Bahn Liechtenstein'' is uncertain since a voter referendum in 2020.
The Chur S-Bahn provides services around Chur, the capital of the alpine Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ent ...
of Graubünden (Grisons) in south-eastern Switzerland.
The Aargau S-Bahn is a small network that services stations in the cantons of Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capita ...
, Lucerne
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic German, High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking po ...
and Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
.
The '' RER Fribourg'' is an S-Bahn-style service centered at Fribourg/Freiburg and Bulle in the Canton of Fribourg
The canton of Fribourg, also canton of Freiburg (french: Canton de Fribourg ; german: Kanton Freiburg ; frp, Canton de Fribôrg rm, Chantun Friburg it, Canton Friburgo) is located in western Switzerland. The canton is bilingual, with French ...
, and extending into the cantons of Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), ...
and Vaud.
Two unnumbered S-Bahn services (designated only with an "S"), one between Schaffhausen and Erzingen (D), running on railway tracks owned by Deutsche Bahn
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the se ...
(DB), and one between Schaffhausen and Jestetten (D), opened in 2013. They are operated by SBB GmbH
SBB GmbH, also known as SBB Deutschland, is a railway company that operates services in Germany and the cantons of Basel-City and Schaffhausen in Switzerland. It is a subsidiary of Swiss Federal Railways, the state railway company of Switzerla ...
and THURBO, respectively. Since December 2022, the Schaffhausen– Singen am Hohentwiel line is also serviced by SBB GmbHSBB GmbH website: https://www.sbb-deutschland.de/strecken-und-tarife/s-bahn-schaffhausen/ ().
Additionally, there are services designated "S" that are not part of any formal S-Bahn network. These include the S20, S21, and S22 operated by Swiss Federal Railways in Solothurn or the S27 operated by Südostbahn (SOB) between Siebnen-Wangen and Ziegelbrücke.
Swiss S-Bahn services are operated mostly by the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
(SBB CFF FFS) but also by private railway companies, such as '' Appenzeller Bahnen'' (AB), BLS AG, '' Forchbahn'' (FB), '' Regionalverkehr Bern-Solothurn'' (RBS), '' Rhätische Bahn'' (RhB), '' Sihltal Zürich Uetliberg Bahn'' (SZU), '' Südostbahn'' (SOB) or '' Zentralbahn'' (ZB).
Rail transport in Switzerland, including S-Bahn systems, is noteworthy for its coordination between services due to the clock-face schedule. Due to the proximity of the various S-Bahn systems in Switzerland, services of one network often offer connections to services of neighboring networks. S-Bahn services are used by commuters and tourists (some services call nearby tourist attractions, such as the Rhine Falls or the Swiss Museum of Transport).
See also
* Commuter rail * U-Bahn * Urban rail transit * Train categories in Europe * List of suburban and commuter rail systemsReferences
External links
* {{S-Bahn systems in Switzerland * * * *