Primorsky Krai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the  The krai shares Russia's only border with North Korea, along the Tumen River in Khasansky District in the southwestern corner of the krai. Peter the Great Gulf, the largest gulf in the Sea of Japan, is located along the south coast.
Historically part of
The krai shares Russia's only border with North Korea, along the Tumen River in Khasansky District in the southwestern corner of the krai. Peter the Great Gulf, the largest gulf in the Sea of Japan, is located along the south coast.
Historically part of


(Parallel report submitted to the UN Committee for the Elimination of Racial Discrimination, During the latter part of the 19th century, there was a significant resource, industrial and resulting economic development in Primorye. Coal mining became a prominent industry, as did the export of
During the latter part of the 19th century, there was a significant resource, industrial and resulting economic development in Primorye. Coal mining became a prominent industry, as did the export of
 Primorsky Krai's economy, the most balanced in the Russian Far East, is also the largest in absolute terms. Food production is the most important sector, represented mainly by fish processing. Annual catch exceeds two million
Primorsky Krai's economy, the most balanced in the Russian Far East, is also the largest in absolute terms. Food production is the most important sector, represented mainly by fish processing. Annual catch exceeds two million
2009 - 1.51 , 2010 - 1.49 , 2011 - 1.53 , 2012 - 1.65 , 2013 - 1.68 , 2014 - 1.73 , 2015 - 1.76 , 2016 - 1.73(e) Average
 In the 2010 Census, the following ethnic groups were listed:
* Russian 92.5%
* Ukrainian 2.8%
* Korean 1%
* Tatar 0.6%
* Uzbek 0.5%
* Belarusians 0.3%
* Armenian 0.3%
* Azeri 0.2%
* Chinese 0.2%
* Mordvin 0.1%
*others 1.5%
*144,927 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Birthrate (2012): 12.4
*Deathrate (2012): 13.7 Russian demographics#Population statistics
In the 2010 Census, the following ethnic groups were listed:
* Russian 92.5%
* Ukrainian 2.8%
* Korean 1%
* Tatar 0.6%
* Uzbek 0.5%
* Belarusians 0.3%
* Armenian 0.3%
* Azeri 0.2%
* Chinese 0.2%
* Mordvin 0.1%
*others 1.5%
*144,927 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Birthrate (2012): 12.4
*Deathrate (2012): 13.7 Russian demographics#Population statistics
(A. R. Artyomyev et al. ''History of Russian Primorye''. Vladivostok: Dalnauka, 1998)
Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The te ...
region of the country and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be de ...
of Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
is the administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, L ...
of the krai, and the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of th ...
. The krai has the largest economy among the federal subjects in the Russian Far East, and a population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using ...
of 1,956,497 as of the 2010 Census.
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym "Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East ( Outer ...
, Primorsky Krai was ceded to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
by Qing China in 1860 as part of a region known as Outer Manchuria, forming most of the territory of Primorskaya Oblast. During the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
it became part of the Far Eastern Republic before joining the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, going through numerous changes until reaching its current form in 1938. Primorsky Krai is home to the Russian Navy's Russian Pacific Fleet.
Etymology
The name of the krai is derived from the Russian words (), meaning "littoral" or "coastal", and (), meaning "region" or "area". It is informally known as Primorye (, ) in Russian, and is occasionally translated as Maritime Territory in English.Geography
*Border length — over , including of the sea borders. *Highest peak — Anik Mountain, *Rail network length — (of which are electrified). *Automobile road length — Primorsky Krai, bordered byChina
China (), officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zo ...
( Jilin and Heilongjiang), North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
( Rason) and Khabarovsk Krai, and the relatively warm—although freezing in winter—waters of the Sea of Japan, is the southeasternmost region of Russia, located between the 42° and 48° north latitude and 130° and 139° east longitude. It is stretched in the meridianal direction, the distance from its extreme northern point to its most southerly point being about .
Topography
Highlands dominate the territory of the krai. Most of the territory is mountainous, and almost 80% of it is forested. The average elevation is about . Sikhote-Alin is a mountainous formation, extending for the most part of the Krai. It consists of a number of parallel ranges: the Partizansky (Partisan), the Siny (Blue), the Kholodny (Cold), and others. There are many karst caves in the South of Primorye. The relatively accessible Spyashchaya Krasavitsa cave (the Sleeping Beauty) in the Ussuriysky Nature Preserve could be recommended for tourists. There are comparatively well-preserved fragments of the ancient volcanoes in the area. The ranges are cut by the picturesque narrow and deep valleys of the rivers and by large brooks, such as the Partizanskaya, the Kiyevka, the Zerkalnaya, the Cheryomukhovaya, the Yedinka, the Samarga, the Bikin, and the Bolshaya Ussurka. Most rivers in the Krai have rocky bottoms and limpid water. The largest among them is theUssuri
The Ussuri or Wusuli (russian: Уссури; ) is a river that runs through Khabarovsk and Primorsky Krais, Russia and the southeast region of Northeast China. It rises in the Sikhote-Alin mountain range, flowing north and forming part of th ...
, with a length of . The head of the Ussuri River originates to the East of Oblachnaya Mountain. The vast Khanka Lowlands extends into the West and the South-West of Primorye, carpeted by coniferous-deciduous forest. A part of the Lowland surrounding the largest lake in the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
, Khanka Lake, is occupied by a forest-steppe.
Coast and islands
The krai's coastline is fairly straight, except for the southernmost section around Vladivostok which contains the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula. There are numerous islands in this area, the main ones being Lisy Island, Askold Island, Putyatin Island,Skrebtsov island
Skrebtsova Island, popularly known as Kovrizhka ("honey-cake"), is an island in the Amur Bay, Sea of Japan, 2 km north-west of the coast of Vladivostok. Named in 1863 in honor of M. L. Skrebtsova who participated in hydrographic research of ...
, Sibiryakov Island, the Eugénie Archipelago (the largest island of which being Russky Island), the Rimsky-Korsakov Archipelago and Furugelm Island.
Flora and fauna
The geographic location of Primorye accounts for the variety of itsflora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
. The territory of Primorye has not been subjected to the ice cover in the past in contrast to the rest of Siberia during the ice ages. The specifics of the geographical situation and the specific features of climate, determine the unique, diversity of the plant world at species and genetic levels and the richness of plant resources. In the flora of Primorye, there are more than two thousand species of higher plants, of which are about 250 species of trees, bushes, and ligneous lianas. Flora of mosses and lichens are very diverse. As part of the coastal flora, there are many valuable medicinal, technical and food plants, many relict and endemic species. About 200 species are listed in the IUCN Red List as rare and threatened extermination.
There are mountainous tundra areas, conifers and coniferous-deciduous forests, and forest-steppe, which is sometimes called the Far Eastern Prairie, where many ancient plant species have been preserved, including fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except ...
s, lotus
Lotus may refer to:
Plants
*Lotus (plant), various botanical taxa commonly known as lotus, particularly:
** ''Lotus'' (genus), a genus of terrestrial plants in the family Fabaceae
**Lotus flower, a symbolically important aquatic Asian plant also ...
, and the '' Chosenia'' willow. The flora of the territory contains such plants as '' Taxus cuspidata'', '' Juniperus rigida'', '' Phellodendron amurense'', '' Kalopanax'', '' Aralia elata'', '' Maackia amurensis'', '' Alnus japonica'', ''Actinidia kolomikta
''Actinidia kolomikta'', the kolomikta, miyamatatabi, variegated-leaf hardy kiwi, is a species of flowering plant in the family Actinidiaceae, native to temperate mixed forests of the Russian Far East, Korea, Japan and China (Eastern Asiatic Regi ...
'', '' Schisandra chinensis'', ''Celastrus orbiculatus
''Celastrus orbiculatus'' is a woody vine of the family Celastraceae. It is commonly called Oriental bittersweet, as well as Chinese bittersweet, Asian bittersweet, round-leaved bittersweet, and Asiatic bittersweet. It is native to China, whe ...
'', '' Thladiantha dubia'', '' Weigela'', '' Eleutherococcus'', '' Flueggea suffruticosa'', '' Deutzia'', '' Nelumbo nucifera'', '' Betula schmidtii'', ''Carpinus cordata'', '' Acer mandshuricum'', ''Parthenocissus tricuspidata
''Parthenocissus tricuspidata'' is a flowering plant in the grape family (Vitaceae) native to eastern Asia in Korea, Japan, and northern and eastern China. Although unrelated to true ivy, it is commonly known as Boston ivy, grape ivy, and Japa ...
'', '' Vitis amurensis'', '' Panax ginseng'' and many others.
The fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''biota''. Zoo ...
of Primorye is also diverse. The following animals are found in the Krai: Ussuri black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), Amur tiger, Amur leopard (''Panthera pardus orientalis''), Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx''), wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
(''Sus scrofa''), Manchurian deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
(''Cervus elaphus xanthopygos''), Siberian roe deer (''Capreolus pygargus''), musk deer (''Moschus moschiferus''), long-tailed goral (''Naemorhedus caudatus''), sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), sable (''Martes zibellina''), Blakiston's fish owl (''Bubo blakistoni''), mandarinka duck
The mandarin duck (''Aix galericulata'') is a perching duck species native to the East Palearctic. It is medium-sized, at long with a wingspan. It is closely related to the North American wood duck, the only other member of the genus ''Aix'' ...
(''Aix galericulata''), black stork (''Ciconia nigra''), scaly goosander (''Mergus squamatus''), chestnut-cheeked starling (''Sturnia philippensis''), black griffon (''Aegypius monachus''), large-winged cuckoo (family Cuculidae), and others. Among 690 species of birds inhabiting the territory of the former USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
, 350 are found in Primorye. Rich fisheries of salmon
Salmon () is the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of ...
, Hucho taimen, lenok and marine fisheries of crab, pollock and other species make the aquatic and maritime environment a valuable resource for the region. However, the rich diversity of wildlife in Primorye is threatened by poaching and the illegal wildlife trade. Wildlife Conservation Society, World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor ...
, Wild Salmon Center
The Wild Salmon Center (WSC) is an international conservation organization that works to protect wild salmon, Rainbow trout, steelhead, Salvelinus, char, trout and the ecosystems on which these species depend. Headquartered in Portland, Oregon, P ...
, and Russian NGOs including Phoenix Fund are active in the region's wildlife and habitat conservation.

Climate
*Primorsky Krai is dominated by a four-seasonhumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
.
*Average annual temperature — near in the north of the krai; on the southern coast.
*Average annual precipitation — .
History
The area was settled by several Tungusic and Mongolic tribes, such as the Sushen, the proto-MongolShiwei Shiwei may refer to:
*Shiwei people, a historic Mongolic people
*Shiwei, Inner Mongolia, a township in Ergun City, Inner Mongolia
Given names
*Che Shiwei (born 1996), Chinese footballer
*Chen Shiwei, Chinese track and field athlete
*Pan Shiwei (bo ...
and the Mohe.
The Udege people are said to have traditionally settled in territories along the Bikin River long ago, however, they are possibly of Jianzhou Jurchen origin.Discrimination against indigenous small-numbered peoples of the North, Siberia and the Far East of the Russian Federation(Parallel report submitted to the UN Committee for the Elimination of Racial Discrimination,
RAIPON
The Russian Association of Indigenous Peoples of the North (RAIPON) (russian: Ассоциация коренных, малочисленных народов Севера, Сибири и Дальнего Востока Российской Фе� ...
, June 13, 2008)
During the Bohai Kingdom, most of the krai was within the boundaries of the provinces of Dingli, Anbian and Anyuan. After Bohai was conquered by the Khitans, the territory became part of Liao dynasty's Eastern Circuit and Jin dynasty's Supin Circuit. It then came under Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
and Manchu rule.
The acquisition of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
by the Tsardom of Russia and the subsequent Russian expansion to the Far East brought the Russians into direct contact with China. The Nerchinsk Treaty of 1689 demarcating the borders of the two states gave all lands lying south of the Stanovoy Mountains, including Primorye, to the Qing Empire. However, with the weakening of the Qing Empire in the second half of the 19th century, Russia began its expansion into the area. In 1858, the towns of Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of th ...
and Blagoveshchensk were founded. In 1858, Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky signed the Aigun Treaty with China, followed by the Beijing Treaty two years later. As a result of the two treaties, the Sino–Russian border shifted south in the Amur Annexation to the Amur
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
and Ussuri Rivers, granting Russia full control of Primorye.
Primorskaya Oblast was established as the easternmost division of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
in 1856. It included the territory of modern Primorsky Krai as well as the territories of modern Khabarovsk Krai and Magadan Oblast
Magadan Oblast ( rus, Магаданская область, r=Magadanskaya oblast, p=məgɐˈdanskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Far East region of the country, and is admin ...
, stretching from Vladivostok to the Chukchi Peninsula in the far north.
In the period from 1859 to 1882, ninety-five settlements were established in the Primorye region, including Vladivostok, Ussuriysk, Razdolnoye, Vladimiro-Aleksandrovskoye, Shkotovo
Shkotovo (russian: Шко́тово) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) and a railway station in Shkotovsky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia. Population:
History
It was founded in 1865 as a village at the mouth of the Tsymukhe Ri ...
, Pokrovka, Tury Rog, and Kamen-Rybolov. The population was primarily engaged in hunting, fishing and cultivation. More than two-thirds of the territory's inhabitants followed these occupations.
 During the latter part of the 19th century, there was a significant resource, industrial and resulting economic development in Primorye. Coal mining became a prominent industry, as did the export of
During the latter part of the 19th century, there was a significant resource, industrial and resulting economic development in Primorye. Coal mining became a prominent industry, as did the export of sea-kale
''Crambe maritima'', common name sea kale, seakale or crambe, is a species of halophytic (salt-tolerant) flowering plant in the genus ''Crambe'' of the family Brassicaceae. It grows wild along the coasts of mainland Europe and the British I ...
, velvet antlers, timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including Beam (structure), beams and plank (wood), planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as fini ...
, crab, dried fish
Fresh fish rapidly deteriorates unless some way can be found to preserve it. Drying (food), Drying is a method of food preservation that works by removing water from the food, which inhibits the growth of microorganisms. Open air drying using sun ...
, and trepangs. The rapid economic expansion of Primorye was financed in large measure by Russian and foreign capital investment.
After the Russian Revolution and the victory of the communists, the new government renamed Primorskaya Oblast as the Zemstvo of Maritime Territory
Regional government of Primorye Zemstvo (russian: Приморская областная земская управа) was a local government that existed in the eastern part of Russia during the Russian Civil War between January 31, 1920 and ...
. It was defined as the Far-Eastern Republic
The Far Eastern Republic ( rus, Дальневосто́чная Респу́блика, ДВР, r=Dalnevostochnaya Respublika, DVR, p=dəlʲnʲɪvɐˈstotɕnəjə rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə), sometimes called the Chita Republic, was a nominally indep ...
(1920–1922). Within the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
, this became Far-Eastern Oblast (1922–1926) and then Far-Eastern Krai (1926–1938).
The area became a battleground for allied and Bolshevik troops during the Siberian Intervention. In 1922, shortly before the end of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polic ...
, Primorye came under Bolshevik control. The new government directed the economic, scientific, and cultural development of the territory. The Soviet Government spent the following ten years combating "bourgeois ideology" in many areas of life and culture. As a result, the music, theater, literature, and the fine arts of Primorye were censored.
Primorsky was the center of the ethnic Korean minority of Russia. The Pos'et Korean National Raion was created under the policy of Korenizatsiya
Korenizatsiya ( rus, коренизация, p=kərʲɪnʲɪˈzatsɨjə, , "indigenization") was an early policy of the Soviet Union for the integration of non-Russian nationalities into the governments of their specific Soviet republics. In th ...
. The Krai had 105 both fully and mixed Korean towns where residents used the Korean language as an official language. Nearly 200,000 ethnic Koreans were living in the Krai by the time of their deportation in 1938. The Soviet Union had earlier deported ethnic Chinese from western Siberia.
During this period, the Soviet government emphasized centralized planning of the economy. As in the rest of the Soviet Union, priority was given to heavy industry, with a special emphasis on mining and commercial fishing. There was a widespread investment in the construction of rail and sea transit, and new port facilities were constructed.
Primorsky Krai was formed by further subdivision of Far-Eastern Krai in 1938, as part of the Stalin-era policy of "unbundling". Primorsky Krai, as defined in 1938, corresponds to the northeastern part of the historical region of Outer Manchuria.
On April 18, 1942, the region became accidentally involved in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, which the United States had entered after Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in December 1941. Primorsky Krai was the location where one of 16 United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical ri ...
B-25 Mitchell medium bombers landed. The group had been launched from USS ''Hornet'' to carry out the Doolittle Raid on Japan. Japan and the Soviet Union were not then at war. The landing occurred 40 miles (65 km) west of Vladivostok; the bomber's crew could not return to their base, the aircraft carrier ''Hornet,'' by the mission plan. The crew later returned home via Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
.
During the 1970s, the Soviet Union expanded scientific institutions in Primorye, especially in the city of Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
. Several large research institutions are located here, such as the Institute of Biology and Agriculture, the Pacific Institute of Bio-organic Chemistry, the Institute of Marine Biology, the Pacific Institute of Geography, the Pacific Oceanological Institute, as well as several Institutes affiliated with the Far Eastern Division of the Russian Academy of Science.
By the early 1990s, once-small enterprises in the city had developed into large companies. Some of the most prominent include the DVMP (FESCO) shipping company, the Dalmoreprodukt , Progress Arsenyev Aircraft Works, and Vostok Mining. Commercial fishing plays an important part in the economy of the Primorye and includes firms like Vladivostok Trawling and Refrigerating Fleet (VBTRF), the Active Marine Fisheries Base of Nakhodka, and the Fishing and Marine Transport Fleet of Primorye. Numerous enterprises of the Russian military-industrial complex were also established in Primorye.
The Udege people, led by Pavel Sulyandziga, are trying to gain control over their traditional territories along the Bikin River and in particular a Territory of Traditional Natural Resource Use of federal status.
Politics
During the Soviet period, the high authority in the oblast was shared between three persons: The first secretary of the Primorsky CPSU Committee (who in reality had the biggest authority), the chairman of the oblast Soviet (legislative power), and the chairman of the oblast Executive Committee (executive power). After 1991, the head of the Oblast administration and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside elected regional parliament. The Charter of Primorsky Krai is the fundamental law of the region. The Legislative Assembly of Primorsky Krai is the province's regional standing legislative (representative) body. The Legislative Assembly exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. The highest executive body is the Oblast Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters of the province. The Oblast administration supports the activities of the Governor who is the highest official and acts as the guarantor of the observance of the krai Charter in accordance with the Constitution of Russia.Administrative divisions
Economy
 Primorsky Krai's economy, the most balanced in the Russian Far East, is also the largest in absolute terms. Food production is the most important sector, represented mainly by fish processing. Annual catch exceeds two million
Primorsky Krai's economy, the most balanced in the Russian Far East, is also the largest in absolute terms. Food production is the most important sector, represented mainly by fish processing. Annual catch exceeds two million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s, or one half of the Russian Far East total. Second is machine building, where half of the output is geared toward the fishing industry and shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance ...
s. Defense is another important sector, producing naval vessels and military aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
. The construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and ...
materials industry here provides for the whole Russian Far East. Lead smelting is conducted in Rudnaya Pristan on the coast.
The timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including Beam (structure), beams and plank (wood), planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as fini ...
industry, though in recession, is still second only to Khabarovsk Krai's with an annual yield of about 3 million cubic meters of timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including Beam (structure), beams and plank (wood), planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as fini ...
. Primorsky Krai is the largest coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
producer in the Russian Far East and generates more electricity than any other Russian Far East administrative division, but power shortages are common. Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
is also important; the krai produces rice, milk, eggs, and vegetables.
Primorsky Krai is the Russian Far East's banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
and finance center. It has more than 100 bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Becau ...
s and affiliates and well-developed futures
Futures may mean:
Finance
*Futures contract, a tradable financial derivatives contract
*Futures exchange, a financial market where futures contracts are traded
* ''Futures'' (magazine), an American finance magazine
Music
* ''Futures'' (album), a ...
and stock exchanges.
The krai's proximity to Pacific Rim markets gives it an edge over most other Russian Far East administrative divisions in developing foreign trade. Major trade items are seafood products, timber products, and ferrous metals. Major trading partners are Japan, China, and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
.The economy will be further diversified with the addition of as many as 8 government sanctioned casinos to be built in the Primorye Gambling Zone, which encompasses the entire Primorsky Krai. Primorsky Entertainment Resort City, under development by NagaCorp Ltd. of Phnom Penh, Kingdom of Cambodia, will be the largest. The development is expected to cost in the region of RUB11.6 billion (approximately HK$2.7 billion, US$350 million) and have a total footprint of 214.89 hectares.
Primorsky Krai's compact territory is well endowed with infrastructure. Its railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
density is twice the Russian average. Railroads connect it with China and North Korea. Vladivostok, the eastern terminus of the Trans-Siberian Railway, was surpassed as a port by the nearby Nakhodka- Vostochny Port container, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
and timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including Beam (structure), beams and plank (wood), planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as fini ...
terminals. Primorsky Krai-based shipping companies provide 80% of marine shipping services in the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
. All the krai's significant ports are now open to international shipping.
The largest companies in the region include Far-Eastern Energy Company, NNK-Bunker, Mazda Sollers, and Vostochny Port.
Natural resources
Coal
More than 100 deposits ofcoal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
are known in Primorsky Krai. The commercial deposits of coal are connected to the Partizansky and Razdolnensky coal basins, the Podgorodnensky deposit, the Uglovsky basin, and the Shkotovsky, Pavlovsky, Bikinsky, Rettikhovsky, and Suputinsky deposits.
Partizansky Basin: The city of Partizansk is located in the southern part of the basin. The total area of the basin is . The basin has been known since the 19th century and has been explored since 1902. Five coal-bearing regions—Staropartizansky, Melnikovsky, Belopadinsky, Molchanovsky, and Sergeyevsky—are within the limits of the basin. The coal is anthracite coal. By the output of volatile substances and caking ability, rich coals prevail. The reserves of coal in the basin total 193.6 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s. The deposits are maintained by the mines of the Partizanskugol Association. A coal-mining factory also operates in this area.
Razdolnensky Basin: The total area of this basin is about . The basin is located to the north and the west of the city of Ussuriysk. The basin includes the following deposits: Ussuriysky, Lipovetsky, Verkhne-Razdolnensky, Konstantinovsky, and Alekseye-Nikolsky. The deposits were prospected as early as 1868. The mining of coal has been conducted since 1909. By the output of volatile substances and coking ability, long-flame coals prevail. The reserves of coal in the basin total of 66.7 million tons. The deposits are maintained by the mines and the open-pit coal mines of the Lipovetskoye Mine Administration.
Uglovsky Basin: Located northeast of Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
, the basin's band extends about to the northeast of Amursky Bay and ranges from in width. Coals in the basin have been known since 1859. The mining of coal has been executed since 1867 in the Tavrichansky deposit, and since 1911 in the Artyomovsky deposit. The coal is brown coal, which is used as a power fuel. In the long years of operation, the stocks of coal in the basin have been considerably depleted. The reserves of coal in the basin total 233.7 million tons. The mines of the Tavrichansky Mine Administration and the Artyomugol Association operate on the basis of the deposits.
Podgrodnensko-Surazhevsky: This coal-bearing region is located close to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
. The stocks of the Podgrodnensky deposit are estimated to be a total of 19.6 million tons. The coal is anthracite coal. By the output of volatile substances and caking ability, the coal is hard (non-bituminous). The deposits are maintained by the Podgorodenka mine of the Artyomugol Association.
The Paleogene-Neogene deposits of Primorsky Krai are the Bikinsky, Pavlovsky, Shkotovsky, Rettikhovsky, Rakovsky, and Khasansky deposits. The deposits are the major sources of fuel for the largest heat and power stations of Primorye: Luchegorskaya and Vladivostokskaya. The coal is brown coal.
The Bikinsky Deposit is the largest brown coal deposit in Primorsky Krai. Its total area is . The reserves total 1,113.9 million tons. The coal-bearing thickness is . The Luchegorsky Open-Pit Coal Mine maintains the mine and provides fuel to the largest power station in the krai, the Luchegorsky Hydro-Electric Power Station.
Pavlovsky Deposit: The total area is . The reserves total 400 million tons. The coal-bearing thickness is up to . The mining is maintained by the Pavlovsky-1 and Pavlovsky-2 Open-Pit Coal Mines. Coal is used as fuel for the Vladivostok Heat and Power Plant-2.
Skotovsky Deposit: The total area is . The reserves total 251.6 million tons. The coal-bearing thickness ranges from . Maintenance is by the open-pit mine of the Artyomugol Association.
The coal of the Pavlovsky, Skotovsky, and Bikinsky deposits contains germanium and non-ferrous metals.
Tin
The major areas of occurrence of commercial tin stocks are Kavalerovsky, Krasnoarmeysky, and Dalnegorsky Districts. There are more than 30 deposits of tin in Primorsky Krai. The extraction of tin ore is maintained by Khrustalnenskaya Tin Extracting Company, Dalpolimetal Stock Company, and Vostok Mining Company. All tin-extracting enterprises of the krai have a 30-year supply of ore.Tungsten
There are four major commercial deposits of tungsten in Krasnoarmeysky and Pozharsky Districts. The mining of only two of them is currently maintained, at Vostok-2 and Lermontovskoye by the Primorsky Mining Group and Lermontovskoye Mining Company. The enterprises have a 10-year reserve supply. The ores are complex, containingcopper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, bismuth, and other metals besides tungsten.
Lead and zinc
There are more than 10 commercial deposits oflead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
in the territories of Dalnegorsky, Kavalerovsky, and Krasnoarmeysky Districts. The mining of the deposits of lead and zinc is maintained by Dalpolimetal Stock Company. The enterprise has a 40-year supply of ore.
Silver
Among the deposits of precious metals in Primorsky Krai,silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
and gold-silver deposits predominate. Ten deposits of silver are found in the Krai. The majority of silver-polymetal ore deposits are located in Dalnegorsky District and are maintained by Dalpolimetal Stock Company. Silver is extracted simultaneously with tungsten from tungsten ores deposits in Krasnoarmeysky and Pozharsky Districts.
Gold
More than 60 deposits ofgold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
are found in the territory of the krai. Most of them are placer deposits. The southern part of the krai is the richest in placer deposits. Significant gold placer sites are at Kommisarovsky (the Pogranichnaya river), Fadeyevsky (the Fadeyevka river), Krinichny (the Bolshaya Rudnevka river), Nakhodkinsky (the Korobkovka river), and Soboliny (the Sobolinaya river). Okean Artel and Primorsky Mine are engaged in gold extraction. Gold is also extracted from complex deposits of tungsten ores.
Fluorspar
The Voznesenovsky and Pogranichny deposits of rare-metal- fluorspar ore are located in Khorolsky District. The Voznesenovskoye deposit was prospected in 1948. It is maintained by the Yaroslavsky Mining Group Stock Company and there is a 20-year supply of ore. The ore is a complex ore. Fluorspar totals 10 percent of the mineral content of the ore. The ore contains such rare metals as beryllium, lithium, tantalum, and niobium. TheUsuglinskoye mine
The Usuglinskoye mine is a large mine located in the south-eastern Russia in Primorsky Krai. Usuglinskoye represents one of the largest fluorite reserves in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country s ...
is one of the largest fluorite mines in Russia, having estimated reserves of 2.9 million tonnes of ore.
Boron
Russia's largest deposit of boron-containing ore (boron silicates) is located in Dalnegorsky District. The deposit is operated by ''Bor Stock Company''. The enterprise has 50 years' supply of borosilicates stocks.Limestone
There are more than 100 large deposits of various construction materials. The Spasskaya group includes the Spasskoye and Dlinnogorskoyelimestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
deposits. The stocks total more than 100 million tons and are maintained by Spassktsement Stock Company.
The Suchanskaya group includes the Novitskoye and Chandolazskoye limestone deposits, which are located in Partizansky District. These deposits are suitable for the production of Portland cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel (aggregate) together. Cement m ...
of 400 and 500 types. The stocks total approximately more than 1 billion tons.
The Maikhinskaya group includes the Maikhinskoye and Glubinnogorskoye deposits located in Shkotovsky District. The estimated stocks of limestone in both deposits total about 60 million tons.
Ashlar stones
There are numerous deposits ofgranite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
s, porphyrites, and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
s which, when polished, acquire a smooth surface of beautiful color. These deposits are located in Lesozavodsky, Khorolsky, Khasansky, Spassky, Chernigovsky, Partizansky, and other districts.
The Ambinskoye deposit of marble is located in Khasanky District. This marble is highly decorative and is easily polished. The estimated stocks total more than 2 million m3 (70.6 million ft3).
The Knorringskoye deposit of ashlar stones is located in Chernigovsky District. The estimated stocks total about 10 million m3 (35.3 million ft3). They are similar in color to the famous American ashlar stones.
Brick earth
There are more than 100 deposits of fusible clay which is used in brick production in the krai. Fusible clay deposits are found almost everywhere in the krai, except its northeastern parts. The Uglovskaya, Ussuriyskaya, and Spasskaya group of fusible clay deposits are noteworthy in this area. The krai's largest stocks, a total of more than fifteen million tons, is the Uglovskaya group of deposits located inUglovoye
Uglovoye (russian: Угловое) is a rural locality (a selo) and the administrative center of Uglovskiy Selsoviet of Mazanovsky District, Amur Oblast, Russia. The population was 530 as of 2018. There are 24 streets.
Geography
Uglovoye is lo ...
settlement. The deposits provide raw material to the brick factories in Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
and Artyom.
There are more than twenty deposits of refractory clay
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase ...
and fireclay. The clay is suitable for the manufacture of bricks and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelai ...
s. The largest deposits are located in Oktyabrsky and Chernigovsky District, and in Artyom.
The Lipovetskoye Deposit of refractory clay is located in Oktyabrsky District. The estimated stocks total about 1.5 million tons and are maintained by the Lipovetsky Brick Factory.
The Ozernovskoye deposit of fireclay is located in Uglovoye settlement. The estimated stocks total about 2 million tons and have been used for the manufacture of bricks since 1964.
Porcelain stones
Primorsky krai's best-known Gusevskoye deposit of porcelain stone is located in Khasansky District. The material is used by the Vladivostok and Artyom Porcelain Factories. The estimated stocks total about 3 million tons.Feldspar rhyolites
The Sergeyevskoye deposit of ceramic rhyolites is located in Partizansky District. It may be used for the manufacture of porcelain.Demographics

Demographics in the past
SeveralTungusic Tungusic may refer to:
*The Tungusic languages
*The Tungusic peoples, people who speak a Tungusic language
{{dab ...
and Paleosiberian peoples lived here before Russian colonization: Udeges, Nanais, Nivkhs, Orochs
Orochs ( Russian ''О́рочи''), Orochons, or Orochis (self-designation: ''Nani'') are a people of Russia that speak the Oroch (''Orochon'') language of the Southern group of Tungusic languages. According to the 2002 census there were 68 ...
, Ulchs, Oroks, and Manchus.
Contemporary demographics
''Population'': According to the 2010 Census, the population of the krai was 1,956,497, down from 2,071,210 recorded in the 2002 Census, and further down from 2,258,391 recorded in the 1989 Census. Due to its geographical location, the krai boasts a mixture of not only ethnic Russians, but also Ukrainians,Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
, Volga German
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
s, Buriats, Nanais, Japanese, Chinese and Orochs. The indigenous Udege and their sub-minority, the Taz, are the region's aboriginals.
Total fertility rate: 2009 - 1.51 , 2010 - 1.49 , 2011 - 1.53 , 2012 - 1.65 , 2013 - 1.68 , 2014 - 1.73 , 2015 - 1.76 , 2016 - 1.73(e) Average
life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
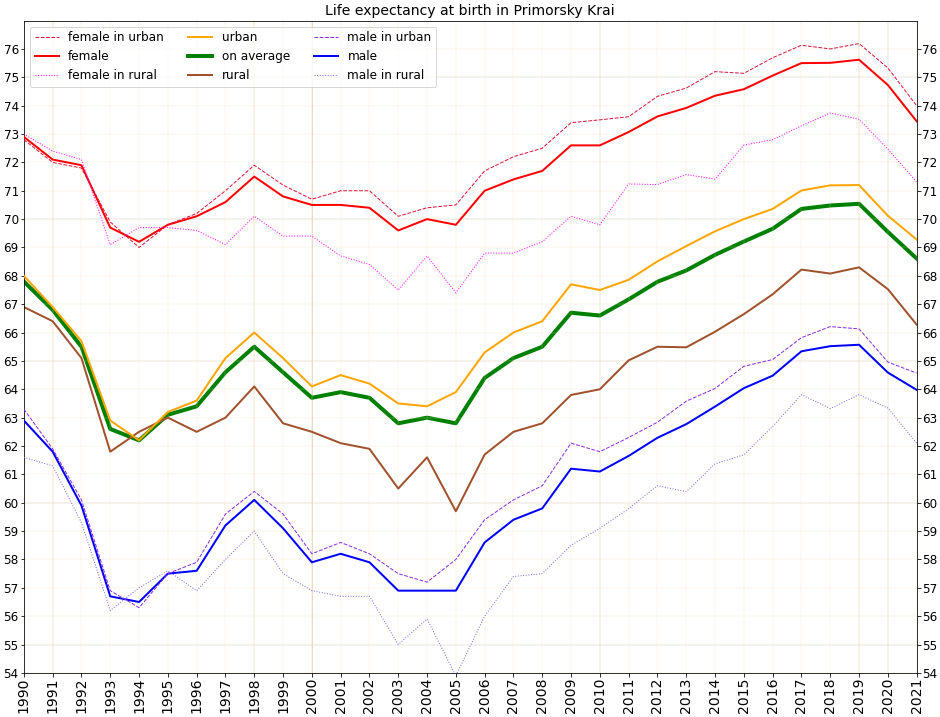
in 1994 — 62.5 years (male — 56.8, female — 69.4).
Settlements
Ethnic groups
 In the 2010 Census, the following ethnic groups were listed:
* Russian 92.5%
* Ukrainian 2.8%
* Korean 1%
* Tatar 0.6%
* Uzbek 0.5%
* Belarusians 0.3%
* Armenian 0.3%
* Azeri 0.2%
* Chinese 0.2%
* Mordvin 0.1%
*others 1.5%
*144,927 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Birthrate (2012): 12.4
*Deathrate (2012): 13.7 Russian demographics#Population statistics
In the 2010 Census, the following ethnic groups were listed:
* Russian 92.5%
* Ukrainian 2.8%
* Korean 1%
* Tatar 0.6%
* Uzbek 0.5%
* Belarusians 0.3%
* Armenian 0.3%
* Azeri 0.2%
* Chinese 0.2%
* Mordvin 0.1%
*others 1.5%
*144,927 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Birthrate (2012): 12.4
*Deathrate (2012): 13.7 Russian demographics#Population statistics
Religion
According to a 2012 survey 26.6% of the population of Primorsky Krai adheres to theRussian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
, 6% are unaffiliated generic Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, 1% adheres to other Eastern Orthodox church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
es or is an Eastern Orthodox believer without belonging to any church, and 1% of the population adheres to the Slavic native faith (Rodnovery) or to local Siberian native faiths. In addition, 24% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious
"Spiritual but not religious" (SBNR), also known as "spiritual but not affiliated" (SBNA), is a popular phrase and initialism used to self-identify a life stance of spirituality that does not regard organized religion as the sole or most valuable ...
, 35% is atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
, and 6.4% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question. This is one of the least religious regions in Russia.
Meteorite
The krai is the location of the massive Sikhote-Alin meteorite, which fell February 12, 1947, in the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, near the village of Paseka (approximately 440 km northeast of Vladivostok).Sister districts
* Gangwon-do,South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
* Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea
* Gyeongsangnam-do, South Korea
* Osaka Prefecture, Japan
* Toyama Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Toyama Prefecture has a population of 1,044,588 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 4,247.61 km2 (1,640.01 sq mi). Toyama Prefecture borders Ishikawa Prefecture to th ...
, Japan
See also
* Outer Manchuria * Geography of Primorsky Krai *List of cities in Primorsky Krai * Winter storms of 2009–10 in East Asia * Primorsky Krai Police *Green Ukraine
Green Ukraine, also known as Zelenyi Klyn ( uk, Зелений клин, Zelenyi Klyn, russian: Зелёный Клин, Zelyonyy Klin, literally: 'the green gore/wedge') or Zakytaishchyna (Ukrainian and Russian: , literally: 'Trans China'), is ...
– a formerly proposed country in the Russian Far East
References
Sources
* *(A. R. Artyomyev et al. ''History of Russian Primorye''. Vladivostok: Dalnauka, 1998)
External links
* {{Authority control Manchuria Pacific Coast of Russia States and territories established in 1938 1938 establishments in the Soviet Union Inner Asia Russian Far East Far Eastern Federal District Krais of Russia Russian-speaking countries and territories