|
Orochs
Orochs ( Russian ''О́рочи''), Orochons, or Orochis (self-designation: ''Nani'') are a people of Russia that speak the Oroch (''Orochon'') language of the Southern group of Tungusic languages. According to the 2002 census there were 686 Orochs in Russia. According to the 2010 census there were 596 Orochs in Russia. Orochs traditionally settled in the southern part of the Khabarovsk Krai, Russia and on the Amur and Kopp rivers. In the 19th century, some of them migrated to Sakhalin. In the early 1930s, the Orochi National District was created, but was cancelled shortly thereafter "due to lack of native population". Because the people never had a written language, they were educated in the Russian language. Their language, Oroch, is on the verge of extinction. They follow Shamanism Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In Russia
Russia, as the largest country in the world, has great ethnic diversity, is a multinational state, and is home to over 190 ethnic groups nationwide. However, demographically; ethnic Russians dominate the country's population. In the 2010 Census, roughly 81% of the population were ethnic Russians, and the remaining 19% of the population were ethnic minorities. The 83 (or 85) federal subjects which together constitute the Russian Federation include: * 21 national republics (intended as homes to a specific ethnic minority) * 4 autonomous okrugs (usually with substantial or predominant ethnic minority) * 1 autonomous oblast Ethnic groups of Russia, 1926–2010 Future projections The ethnic demographic mix of the Russian Federation is projected to change far into the future. The majority population, ethnic Russians, who have been in slight decline since the 1950's will decline further due to a below replacement fertility rate and population ageing. In 2010, rough population pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The city of Vladivostok is the administrative center of the krai, and the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk. The krai has the largest economy among the federal subjects in the Russian Far East, and a population of 1,956,497 as of the 2010 Census. The krai shares Russia's only border with North Korea, along the Tumen River in Khasansky District in the southwestern corner of the krai. Peter the Great Gulf, the largest gulf in the Sea of Japan, is located along the south coast. Historically part of Manchuria, Primorsky Krai was ceded to the Russian Empire by Qing China in 1860 as part of a region known as Outer Manchuria, forming most of the territory of Primorskay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroch Language
The Oroch language is an critically endangered language spoken by the Oroch people in Siberia. It is a member of the southern group of the Tungusic languages and is closely related to the Nanai language and Udege language. It is or was spoken in the Khabarovsk Krai ( Komsomolsky, Sovetskaya Gavan, and Ulchsky districts). The language is split into three dialects: Tumninsky, Khadinsky, and Hungarisky. At the beginning of the 21st century, a written form of the language was created. The Russian government and the scientific field disagree on whether the language is living or extinct. Genealogical and areal characteristics According to the 2002 Census, there were 257 speakers of the Oroch language, however, this data is known to be erroneous due to confusion with the similarly-named Orok language Uilta ( oaa, ульта, also called Ulta, Uilta, Ujlta, or Orok) is a Tungusic language spoken in the Poronaysky and Nogliksky Administrative Divisions of Sakhalin Oblas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Small-numbered Peoples Of The North, Siberia And The Far East
The indigenous small-numbered peoples of the North, Siberia and the Far East (russian: коренные малочисленные народы Севера, Сибири и Дальнего Востока) is a Russian census classification of indigenous peoples, assigned to groups with fewer than 50,000 members, living in the Russian Far North, Siberia or Russian Far East. They are frequently referred as indigenous small-numbered peoples of the North or indigenous peoples of the North. Definition Today, 40 indigenous peoples are officially recognised by Russia as indigenous small-numbered peoples and are listed in the unified register of indigenous small-numbered peoples (единый перечень коренных, малочисленных народов Российской Федерации). This register includes 46 indigenous peoples. Six of these peoples do not live in either the Extreme North or territories equated to it, so that the total number of recognised indige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadan Oblast
Magadan Oblast ( rus, Магаданская область, r=Magadanskaya oblast, p=məgɐˈdanskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Far East region of the country, and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Magadan Oblast has a population of 156,996 ( 2010 Census), making it the least populated oblast and the third-least populated federal subject in Russia. Magadan is the largest city and the capital of Magadan Oblast. The majority of the Oblast's inhabitants live in the city. The coastline has a less severe climate than the interiors, although both are very cold for its latitude. It borders Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the north, Kamchatka Krai in the east, Khabarovsk Krai in the south and the Sakha Republic in the west. The economy is primarily based on mining, particularly gold, silver and other non-ferrous metals. History Magadan Oblast was established on December 3, 1953D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabarovsk Krai
Khabarovsk Krai ( rus, Хабаровский край, r=Khabarovsky kray, p=xɐˈbarəfskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative centre of the krai is the city of Khabarovsk, which is home to roughly half of the krai's population and the largest city in the Russian Far East (just ahead of Vladivostok). Khabarovsk Krai is the fourth-largest federal subject by area, and has a population of 1,343,869 as of 2010. The southern region lies mostly in the basin of the lower Amur River, with the mouth of the river located at Nikolaevsk-on-Amur draining into the Strait of Tartary, which separates Khabarovsk Krai from the island of Sakhalin. The north occupies a vast mountainous area along the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk, a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. Khabarovsk Krai is bordered by Magadan Oblast to the north, Amur Oblast, Jewi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of North Asia
Indigenous may refer to: *Indigenous peoples *Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention * Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band * Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse * ''Indigenous'' (film), Australian, 2016 See also *Disappeared indigenous women *Indigenous Australians *Indigenous language *Indigenous religion Indigenous religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the religious belief systems of communities described as being " indigenous". This category is often juxtaposed against others such as the " world religions" and "new ... * Indigenous peoples in Canada * Native (other) * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungusic Peoples
Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia and Northeast Asia. The Tungusic phylum is divided into two main branches, northern (Evenic or Tungus) and southern ( Jurchen– Nanai). An intermediate group ( Oroch– Udege) is sometimes recognized. Name The name ''Tungusic'' is artificial, and properly refers just to the postulated linguistic phylum ( Tungusic languages). It is derived from Russian (), a Russian exonym for the Evenks (Ewenki). English usage of ''Tungusic'' was introduced by Friedrich Max Müller in the 1850s, based on earlier use of German by Heinrich Julius Klaproth. The alternative term ''Manchu–Tungus'' is also in use ( 'Tunguso-Manchurian'). The name ''Tunguska'', a region of eastern Siberia bounded on the west by the Tunguska rivers and on the east by the Pacific Ocean, has its origin from the Tungus people (Evenks). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Red Book Of The Peoples Of The Russian Empire
''The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire'' is a book about the small nations of the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union, and Russia and some other post-Soviet states of today. It was published in Estonian in 1991 and in English in 2001. The foreword of the book explains the book's approach by saying, "the authors of the present book, who come from a country (Estonia) which has shared the fate of nations in the Russian and Soviet empires, endeavour to publicize the plight of the small nations whose very existence is threatened as a result of recent history." Described peoples The authors' intention for the book was to include the peoples according to the following criteria: * are not yet extinct, * whose main area of settlement is on ex-Soviet territory, * whose numbers are below 30,000, * of whom less than 70% speak their native language, * who form a minority on their ancient territory, * whose settlement is scattered rather than compact, * who have no vernacular school, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
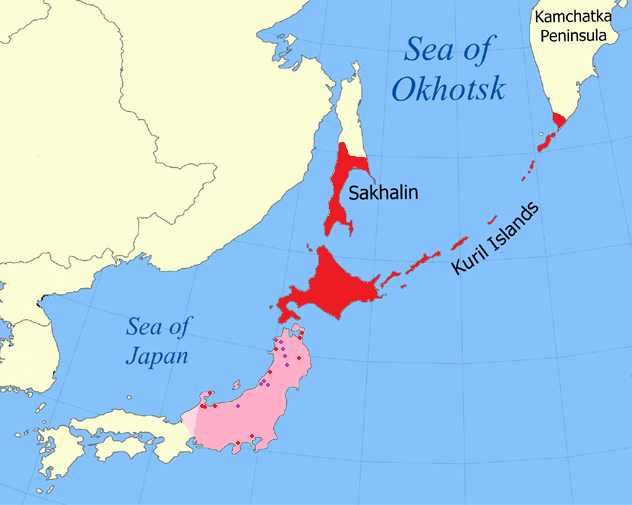
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |