|
Winter Storms Of 2009–10 In East Asia
The East Asian snowstorms of 2009–2010 were heavy winter storms, including blizzards, ice storms, and other winter events, that affected East Asia from 8 May 2009 to 28 February 2010. The areas affected included Mongolia, China (the P.R.C.), Nepal, the Korean Peninsula, Japan, Kuril Islands, Sea of Okhotsk, Primorsky, and Sakhalin Island. The list of events An unusually cold and/or snowy weather was reported across the Northern Hemisphere, with many severe cases being reported in the United States, Canada, the UK, Poland, Finland, Russia, India, South Korea, China and Japan. As this occurred, unusually heavy rain hit Brazil, southern Bangladesh, Italy and Argentina. A heat wave and unforeseen monsoon weather also hit Australia. Guam was hit by a typhoon on December 29, 2009. 2009 May 8 =Mongolia= 21 people had died in a rural Mongolian blizzard. June 2 =Mongolia= Another 15 people and 10,000 head of cattle had died by this date in Mongolia. September 4 =Russia= A h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Storm
A winter storm is an event in which wind coincides with varieties of precipitation that only occur at freezing temperatures, such as snow, mixed snow and rain, or freezing rain. In temperate continental climates, these storms are not necessarily restricted to the winter season, but may occur in the late autumn and early spring as well. A snowstorm with strong winds and other conditions meeting certain criteria is called a blizzard. Formation Winter storms are formed when moist air rises up into the atmosphere, creating low pressure near the ground and clouds up in the air. The air can also be pushed upwards by hills or large mountains. The upward motion is called lift. The moisture is collected by the wind from large bodies of water, such as a big lake or the ocean. If temperature is below freezing, , near the ground and up in the clouds, precipitation will fall as snow, ice, rain and snow mixed (sleet), ice pellets or even graupel (soft hail). Since cold air can not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states and the Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world; and the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of . It borders all other countries and territories in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers roughly half of the continent's land area. Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulan County
Purang County or Burang County (; ) is an administrative division of Ngari Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region (''TAR'') of China. The county seat is Purang Town, known as ''Taklakot'' in Nepali. The county covers an area of , and has a population of 9,657 as of 2010. Geography Political geography Purang County has TAR's south-western border with Nepal's Sudurpashchim and Karnali province, Darchula, Bajhang and Humla District. Further west, India's Uttarakhand State, Pithoragarh district and Chamoli district borders. Buddhist, Hindu and Jain pilgrims going to Lake Manasarovar and Mount Kailash enter from Nepal via Simikot, and from India via Dharchula. The county is bounded by other counties in the Ngari Prefecture, including Zanda to the west, Gar to the northwest and Gê'gyai to the north. To the east is Zhongba County of Shigatse Prefecture. Physical geography The county covers an area of , and has a population of some 9,058 people as of 2010. The county seat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Prefecture
Ngari Prefecture () or Ali Prefecture () is a prefecture of China's Tibet Autonomous Region covering Western Tibet, whose traditional name is Ngari Khorsum. Its administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Shiquanhe. History Ngari was once the heart of the ancient kingdom of Guge. Later Ngari, along with Ü and Tsang, composed Ü-Tsang, one of the traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo and Kham. The lowlands of Ngari is known as Maryul. During the 10th century, the kingdom of Maryul was founded, taking the name Ladakh, lasted until 1842. The prefecture has close cultural links with Kinnaur and Lahaul and Spiti district of the bordering Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Geography and climate The paved Xinjiang-Tibet Highway () passes through this area. There are well-known prehistoric petroglyphs near the far western town of Rutog. The town of Ngari lies above sea level in northwest Tibet some west of the capital, Lhasa. Ngari Gunsa Airport be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named for Vitus Bering, a Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean. The Bering Sea is separated from the Gulf of Alaska by the Alaska Peninsula. It covers over and is bordered on the east and northeast by Alaska, on the west by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula, on the south by the Alaska Peninsula and the Aleutian Islands and on the far north by the Bering Strait, which connects the Bering Sea to the Arctic Ocean's Chukchi Sea. Bristol Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low-pressure area, low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortex, polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi Sea
Chukchi Sea ( rus, Чуко́тское мо́ре, r=Chukotskoye more, p=tɕʊˈkotskəjə ˈmorʲɪ), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The principal port on the Chukchi Sea is Uelen in Russia. The International Date Line crosses the Chukchi Sea from northwest to southeast. It is displaced eastwards to avoid Wrangel Island as well as the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug on the Russian mainland. Geography The sea has an approximate area of and is only navigable about four months of the year. The main geological feature of the Chukchi Sea bottom is the Hope Basin, which is bound to the northeast by the Herald Arch. Depths less than occupy 56% of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea (; french: Mer de Beaufort, Iñupiaq: ''Taġiuq'') is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores. The sea, characterized by severe climate, is frozen over most of the year. Historically, only a narrow pass up to opened in August–September near its shores, but recently due to climate change in the Arctic the ice-free area in late summer has greatly enlarged. Until recently, the Beaufort Sea was known as an important reservoir for the replenishment of Arctic sea ice. Sea ice would often rotate for several years in the Beaufort Gyre, the dominant ocean current of the Beaufort Sea, growing into sturdy and thick multi-ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
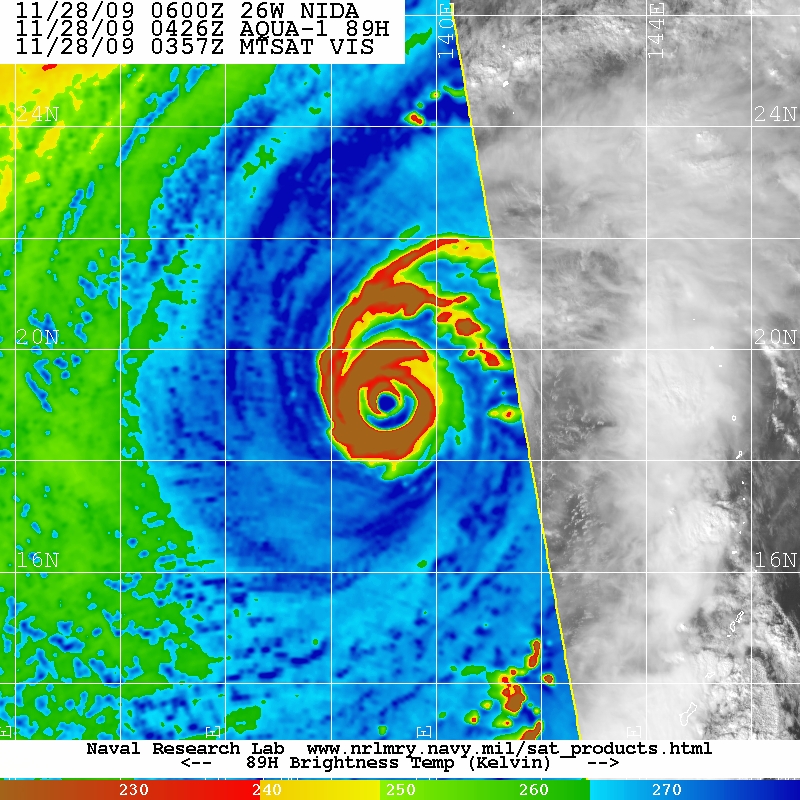
Typhoon Nida (2009)
Typhoon Nida, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Vinta, was the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2009. It was also the most intense tropical cyclone in the Northwest Pacific Ocean during the 2000s, tied with Jangmi in 2008. Meteorological history Early on November 21 the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that an area of convection had persisted within a monsoon trough about 880 km, (545 mi) to the southeast of Guam island. At this time the system was moving around the subtropical ridge of pressure, with an anticyclone over the cyclone helping the convection to consolidate over a broad and elongated low level circulation center which was located in an area of minimal vertical wind shear. Later that morning a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert was released as deep convection increased in organization with multiple bands of convection starting to wrap into the developing low level circulation center. The system was then declared as a tropical depress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic center of the U.S.); its capital Hagåtña (144°45'00"E) lies further west than Melbourne, Australia (144°57'47"E). In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. People born on Guam are American citizens but have no vote in the United States presidential elections while residing on Guam and Guam delegates to the United States House of Representatives have no vote on the floor. Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamoru, historically known as the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples of Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Taiwan, Micronesia, and Polynesia. As of 2022, Guam's popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |