PoznaŇĄ District on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the
 The earliest surviving references to the city are found in the chronicles of Thietmar of Merseburg written between 1012 and 1018: (" bishop of PoznaŇĄ", in an entry for 970) and ''ab urbe Posnani'' ("from the city of PoznaŇĄ", for 1005). The city's name appears in documents in the Latin nominative case as ''Posnania'' in 1236 and ''Poznania'' in 1247. The phrase ''in Poznan'' appears in 1146 and 1244.
The city's full official name is ''StoŇāeczne Miasto PoznaŇĄ'' (The Capital City of PoznaŇĄ), in reference to its role as a centre of political power in the early Polish state under the
The earliest surviving references to the city are found in the chronicles of Thietmar of Merseburg written between 1012 and 1018: (" bishop of PoznaŇĄ", in an entry for 970) and ''ab urbe Posnani'' ("from the city of PoznaŇĄ", for 1005). The city's name appears in documents in the Latin nominative case as ''Posnania'' in 1236 and ''Poznania'' in 1247. The phrase ''in Poznan'' appears in 1146 and 1244.
The city's full official name is ''StoŇāeczne Miasto PoznaŇĄ'' (The Capital City of PoznaŇĄ), in reference to its role as a centre of political power in the early Polish state under the

 In about 1249, Duke PrzemysŇā I began constructing what would become the Royal Castle on a hill on the left bank of the Warta. Then in 1253, PrzemysŇā issued a charter to Thomas of Guben (Gubin) for the founding of a town under Magdeburg law, between the castle and the river. Thomas brought a large number of German settlers to aid in the building and settlement of the city ‚Äď this is an example of the German eastern migration (''
In about 1249, Duke PrzemysŇā I began constructing what would become the Royal Castle on a hill on the left bank of the Warta. Then in 1253, PrzemysŇā issued a charter to Thomas of Guben (Gubin) for the founding of a town under Magdeburg law, between the castle and the river. Thomas brought a large number of German settlers to aid in the building and settlement of the city ‚Äď this is an example of the German eastern migration (''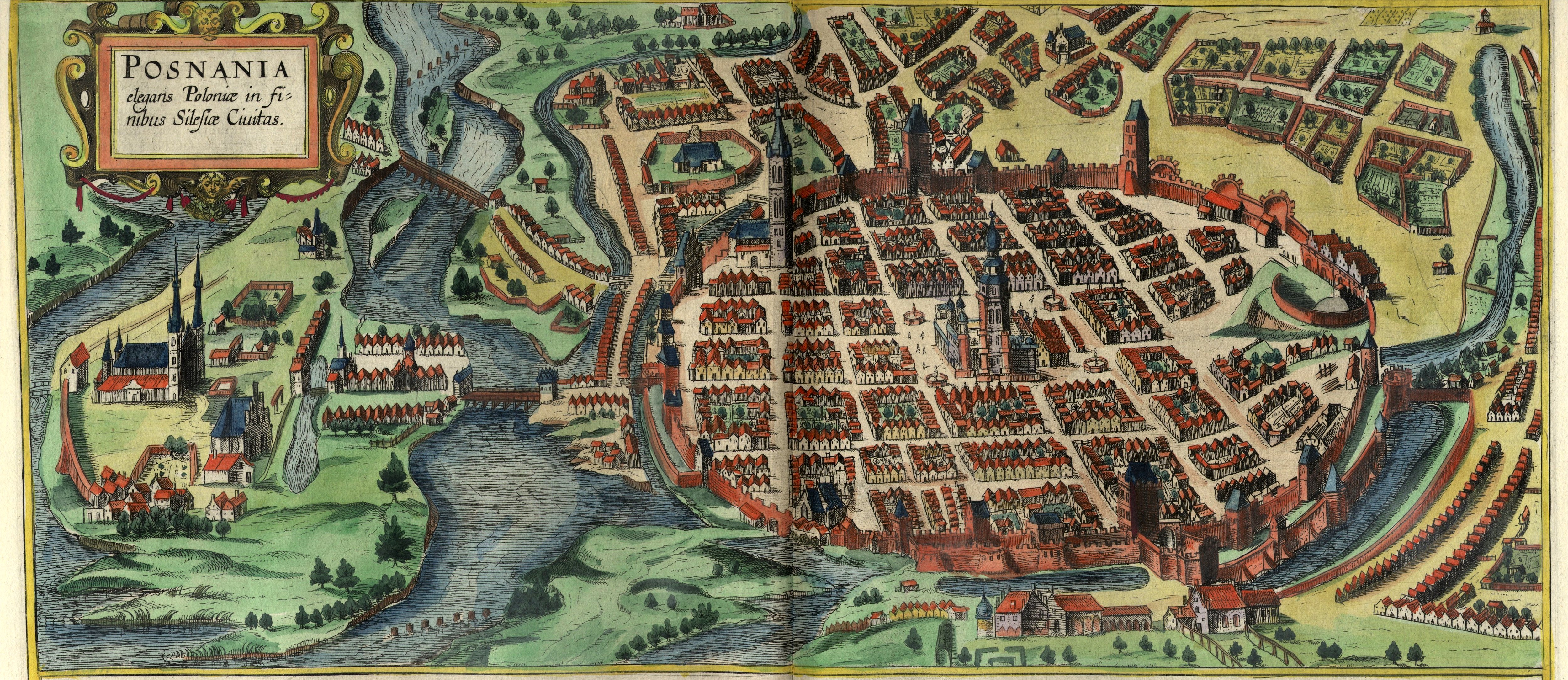
 The city continued to expand, and various projects were funded by Polish philanthropists, such as the
The city continued to expand, and various projects were funded by Polish philanthropists, such as the
 At the end of World War I, the final Greater Poland Uprising in 1918‚Äď1919 brought PoznaŇĄ and most of the region back to newly reborn Poland, which was confirmed by the Treaty of Versailles. The local German populace had to acquire Polish citizenship or leave the country. This led to a wide emigration of the ethnic Germans of the town's population ‚Äď the town's German population decreased from 65,321 in 1910 to 5,980 in 1926 and further to 4,387 in 1934. In the interwar
At the end of World War I, the final Greater Poland Uprising in 1918‚Äď1919 brought PoznaŇĄ and most of the region back to newly reborn Poland, which was confirmed by the Treaty of Versailles. The local German populace had to acquire Polish citizenship or leave the country. This led to a wide emigration of the ethnic Germans of the town's population ‚Äď the town's German population decreased from 65,321 in 1910 to 5,980 in 1926 and further to 4,387 in 1934. In the interwar
 PoznaŇĄ covers an area of , and has coordinates in the range 52¬į17'34
PoznaŇĄ covers an area of , and has coordinates in the range 52¬į17'34'' ‚Äď52¬į30'27'' N, 16¬į44'08'' ‚Äď17¬į04'28'' E. Its highest point, with an altitude of , is the summit of Morasko hill within the Morasko meteorite nature reserve in the north of the city. The lowest altitude is , in the Warta valley.
PoznaŇĄ's main river is the Warta, which flows through the city from south to north. As it approaches the city centre it divides into two branches, flowing west and east of Ostr√≥w Tumski Cathedral island, and meeting again further north. The smaller  PoznaŇĄ's largest lake is Kiekrz in the north-west end of the city. Other large lakes include Malta, an artificial lake formed in 1952 on the lower Cybina river, Strzeszyn on the Bogdanka, and RusaŇāka, an artificial lake formed in 1943 further down the Bogdanka river. The latter two are popular bathing places. Kiekrz lake is much used for sailing, while Malta is a competitive rowing and
PoznaŇĄ's largest lake is Kiekrz in the north-west end of the city. Other large lakes include Malta, an artificial lake formed in 1952 on the lower Cybina river, Strzeszyn on the Bogdanka, and RusaŇāka, an artificial lake formed in 1943 further down the Bogdanka river. The latter two are popular bathing places. Kiekrz lake is much used for sailing, while Malta is a competitive rowing and
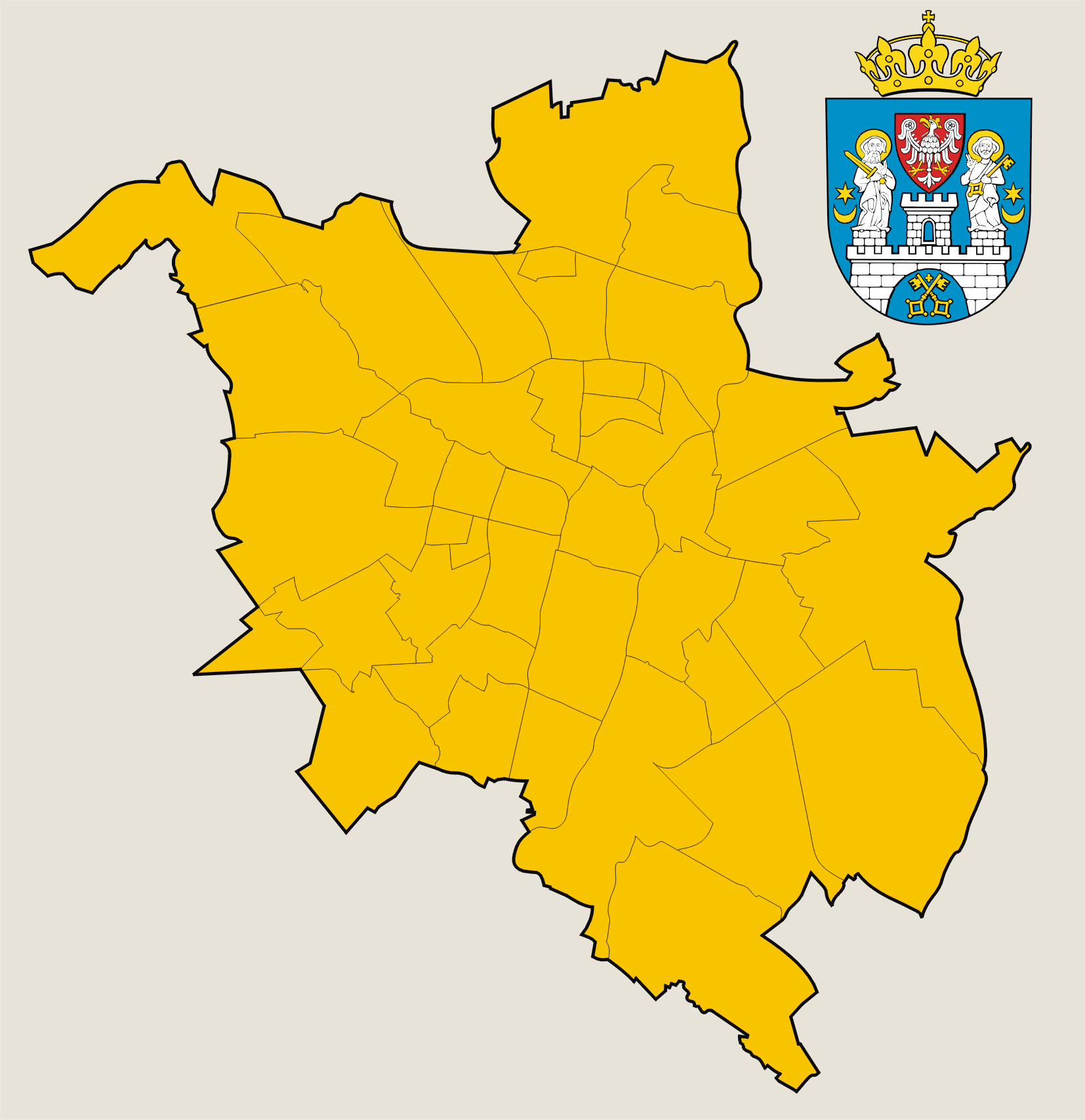
 PoznaŇĄ is divided into 42 neighbourhoods called '' osiedle'', each of which has its own elected council with certain decision-making and spending powers. The first uniform elections for these councils covering the whole area of the city were held on 20 March 2011.
For certain administrative purposes, the old division into five districts called '' dzielnica'' is used ‚Äď although these ceased to be governmental units in 1990. These were:
*
PoznaŇĄ is divided into 42 neighbourhoods called '' osiedle'', each of which has its own elected council with certain decision-making and spending powers. The first uniform elections for these councils covering the whole area of the city were held on 20 March 2011.
For certain administrative purposes, the old division into five districts called '' dzielnica'' is used ‚Äď although these ceased to be governmental units in 1990. These were:
*
 PoznaŇĄ has been an important trade centre since the Middle Ages. Starting in the 19th century, local heavy industry began to grow. Several major factories were built, including the
PoznaŇĄ has been an important trade centre since the Middle Ages. Starting in the 19th century, local heavy industry began to grow. Several major factories were built, including the  Many Western European companies have established their Polish headquarters in PoznaŇĄ or in nearby towns such as
Many Western European companies have established their Polish headquarters in PoznaŇĄ or in nearby towns such as
 The main PoznaŇĄ railway station is called ''
The main PoznaŇĄ railway station is called ''
New PoznaŇĄ GŇā√≥wny (1).JPG, ''
 PoznaŇĄ possesses many historic buildings and heritage sites, mostly concentrated around the
PoznaŇĄ possesses many historic buildings and heritage sites, mostly concentrated around the  Classical music events include the Henryk Wieniawski Violin Competition which is held every 5 years, and classical music concerts by the
Classical music events include the Henryk Wieniawski Violin Competition which is held every 5 years, and classical music concerts by the  PoznaŇĄ has several museums as well as cinemas, including
PoznaŇĄ has several museums as well as cinemas, including
PL-Posen-Freiheitsplatz-3.jpg, Freedom Square (''Plac WolnoŇõci'')
Imperial Castle Poznan (cropped).jpg, Imperial Castle, now the ''Zamek'' Culture Centre
PoznaŇĄ, zesp√≥Ňā urbanistyczno-architektoniczny Starego Rynku,(domki budnicze) nr. rej. A-195-72 z 10.11.1972 (cropped).JPG, Merchant houses, originally 16th century's herring stalls, at the Old Market Square
Bamberka blisko.jpg, ''

 PoznaŇĄ is one of the four largest academic centres in Poland. The number of students in the city is about 140,000, which ranks it the third or fourth after Warsaw and Krak√≥w and about equal to WrocŇāaw in student population. Every one in four inhabitants of PoznaŇĄ is a student. Since PoznaŇĄ is smaller than Warsaw or Krak√≥w still having a very large number of students it makes the city even more vibrant and dense academic hub than both former and current capital of Poland ‚Äď Krak√≥w and Warsaw respectively. PoznaŇĄ with its almost 30 universities and colleges has the second richest educational offering in the country after Warsaw.
PoznaŇĄ is one of the four largest academic centres in Poland. The number of students in the city is about 140,000, which ranks it the third or fourth after Warsaw and Krak√≥w and about equal to WrocŇāaw in student population. Every one in four inhabitants of PoznaŇĄ is a student. Since PoznaŇĄ is smaller than Warsaw or Krak√≥w still having a very large number of students it makes the city even more vibrant and dense academic hub than both former and current capital of Poland ‚Äď Krak√≥w and Warsaw respectively. PoznaŇĄ with its almost 30 universities and colleges has the second richest educational offering in the country after Warsaw.
 There are several multi-sport clubs in PoznaŇĄ.
There are several multi-sport clubs in PoznaŇĄ.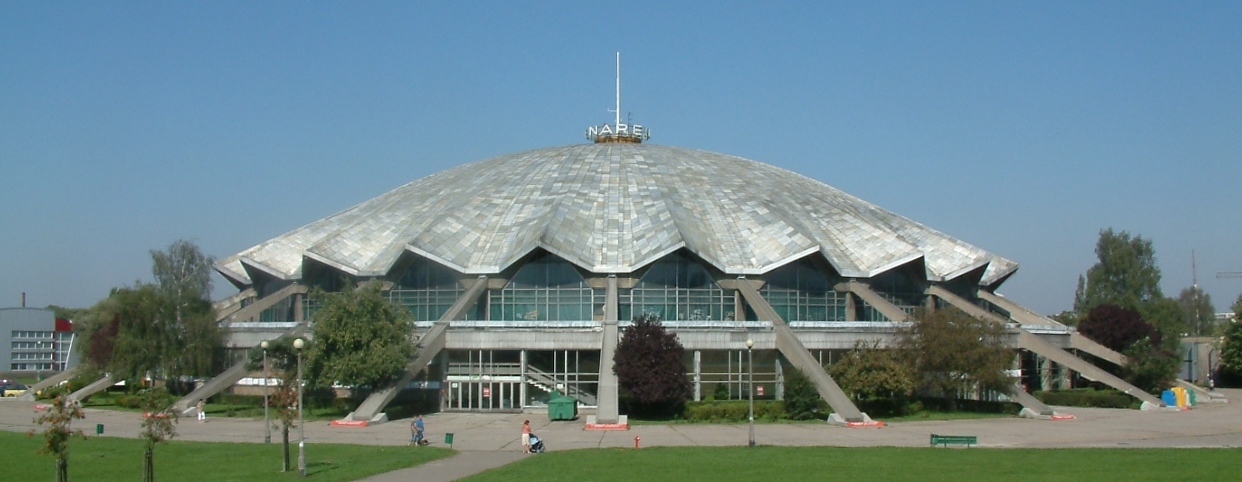  PoznaŇĄ's indoor sporting arena is simply called ''Hala Arena, Arena''. Located west of city centre and built in 1974, it originally seated about 5,500 people and is used for many different indoor sports and cultural events such as volleyball and concerts, among others. The facility has since been modernized, including lowering the level of the ground floor to increase arena capacity to about 9,200. PoznaŇĄ has experience as a host for international sporting events such as the 2009 EuroBasket.
The city has the largest motorsport race track in Poland, Tor PoznaŇĄ, located at the west city's suburbs in PrzeŇļmierowo.
PoznaŇĄ is also considered to be the hotbed of Polish field hockey, with several top teams of Warta PoznaŇĄ (field hockey), Warta PoznaŇĄ, Grunwald PoznaŇĄ (sports club), Grunwald PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď multi-sport club which also has Shooting sports, shooting, wrestling, team handball, handball and tennis sections, Pocztowiec PoznaŇĄ, and AZS AWF PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď an academic club which also fields professional teams in women's volleyball and basketball. Other clubs include: Posnania PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď one of the best rugby union teams in the country, Polonia PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď formerly a multi-sport club achieving many successes in rugby with only a football section remaining, KKS Wiara Lecha ‚Äď football club formed by the supporters of Lech PoznaŇĄ, and Odlew PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď arguably the most famous amateur club in the country due to their extensive media coverage and humorous exploits. There are also numerous rhythmic gymnastics and synchronised swimming clubs, as well as numerous less notable amateur football teams.
The E11 European long distance path for hikers passes through PoznaŇĄ.
PoznaŇĄ bid for the 2014 Summer Youth Olympics but lost to Nanjing, with the Chinese city receiving 47 votes over PoznaŇĄ's 42.
PoznaŇĄ's indoor sporting arena is simply called ''Hala Arena, Arena''. Located west of city centre and built in 1974, it originally seated about 5,500 people and is used for many different indoor sports and cultural events such as volleyball and concerts, among others. The facility has since been modernized, including lowering the level of the ground floor to increase arena capacity to about 9,200. PoznaŇĄ has experience as a host for international sporting events such as the 2009 EuroBasket.
The city has the largest motorsport race track in Poland, Tor PoznaŇĄ, located at the west city's suburbs in PrzeŇļmierowo.
PoznaŇĄ is also considered to be the hotbed of Polish field hockey, with several top teams of Warta PoznaŇĄ (field hockey), Warta PoznaŇĄ, Grunwald PoznaŇĄ (sports club), Grunwald PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď multi-sport club which also has Shooting sports, shooting, wrestling, team handball, handball and tennis sections, Pocztowiec PoznaŇĄ, and AZS AWF PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď an academic club which also fields professional teams in women's volleyball and basketball. Other clubs include: Posnania PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď one of the best rugby union teams in the country, Polonia PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď formerly a multi-sport club achieving many successes in rugby with only a football section remaining, KKS Wiara Lecha ‚Äď football club formed by the supporters of Lech PoznaŇĄ, and Odlew PoznaŇĄ ‚Äď arguably the most famous amateur club in the country due to their extensive media coverage and humorous exploits. There are also numerous rhythmic gymnastics and synchronised swimming clubs, as well as numerous less notable amateur football teams.
The E11 European long distance path for hikers passes through PoznaŇĄ.
PoznaŇĄ bid for the 2014 Summer Youth Olympics but lost to Nanjing, with the Chinese city receiving 47 votes over PoznaŇĄ's 42.
Official website of the City
{{DEFAULTSORT:Poznan PoznaŇĄ, Cities and towns in Greater Poland Voivodeship City counties of Poland Former capitals of Poland Populated places established in the 8th century PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship (1921‚Äď1939) Magdeburg rights 8th-century establishments in Europe Holocaust locations in Poland Nazi war crimes in Poland
Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Gro√üpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is PoznaŇĄ followed ...
region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark ŇöwińôtojaŇĄski''), traditional Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance Old Town, Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
and Gothic Cathedral.
PoznaŇĄ is the fifth-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. As of 2021, the city's population is 529,410, while the PoznaŇĄ metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
(''Metropolia PoznaŇĄ'') comprising PoznaŇĄ County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.1 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Gro√üpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is PoznaŇĄ followed ...
region, currently the administrative capital of the province called Greater Poland Voivodeship.
PoznaŇĄ is a center of trade, sports, education, technology and tourism. It is an important academic site, with about 130,000 students and Adam Mickiewicz University, the third largest Polish university. The city serves as the seat of the oldest Polish diocese, now being one of the most populous Catholic archdioceses in the country. The city also hosts the PoznaŇĄ International Fair ‚Äď the biggest industrial fair in Poland and one of the largest fairs in Europe. The city's other renowned landmarks include the National Museum
A national museum is a museum maintained and funded by a national government. In many countries it denotes a museum run by the central government, while other museums are run by regional or local governments. In other countries a much greater numb ...
, Grand Theatre, Fara Church and the Imperial Castle.
PoznaŇĄ is classified as a Gamma- global city by Globalization and World Cities Research Network. According to several rankings it is one of the most business-friendly cities in Poland. It also ranks highly in safety and healthcare quality
Health care quality is a level of value provided by any health care resource, as determined by some measurement. As with quality in other fields, it is an assessment of whether something is good enough and whether it is suitable for its purpose. T ...
. The city of PoznaŇĄ has also, many times, won the prize awarded by " Superbrands" for a very high quality city brand. In 2012, the PoznaŇĄ's Art and Business Center "Stary Browar
Shopping, Arts and Business Center "Stary Browar" is the center of commerce and art, built in November 2003, located in the center of PoznaŇĄ, Poland at 42 P√≥Ňāwiejska Street.
The center is a combination of retail space and an art gallery. The s ...
" won a competition organised by National Geographic Traveler and was given the first prize as one of the seven "New Polish Wonders". Companies headquartered in the city include energy provider Enea and e-commerce company Allegro
Allegro may refer to:
Common meanings
* Allegro (music), a tempo marking indicate to play fast, quickly and bright
* Allegro (ballet), brisk and lively movement
Artistic works
* L'Allegro (1645), a poem by John Milton
* ''Allegro'' (Satie), an ...
.
The official patron saints of PoznaŇĄ are Saint Peter and Paul of Tarsus
Paul; grc, ő†őĪŠŅ¶őĽőŅŌā, translit=Paulos; cop, ‚≤°‚≤Ā‚≤©‚≤ó‚≤ü‚≤•; hbo, ◊§◊ź◊ē◊ú◊ē◊° ◊Ē◊©◊ú◊ô◊ó (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, ō®ŔąŔĄō≥ ōßŔĄō∑ōĪō≥Ŕąō≥Ŕä; grc, ő£őĪŠŅ¶őĽőŅŌā ő§őĪŌĀŌÉőĶŌćŌā, SaŇ©los Tarse√ļs; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
, the patrons of the cathedral. Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 ‚Äď 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
‚Äď the patron of the main street Ňöwińôty Marcin
Ňöwińôty Marcin ("Saint Martin"), in full ''ulica Ňöwińôty Marcin'' ("Saint Martin Street"), is a main central street in the city of PoznaŇĄ in western Poland. It runs from south of the old town district, westwards past the church of St. Mart ...
‚Äď is also regarded as one of the patron saints of the city.
Names
The name PoznaŇĄ probably comes from a personal name ''Poznan'', which was in turn derived from the Polish participle ‚Äď "one who is known/recognized", and would mean "Poznan's town". It is also possible that the name comes directly from the verb ''poznańá'', which means "to get to know" or "to recognize", so it may simply mean "known town".Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930‚Äď992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branch ...
. PoznaŇĄ is known as ''Posen'' in German, and was officially called ''Haupt- und Residenzstadt Posen'' (Capital and Residence City of PoznaŇĄ) between 20 August 1910 and 28 November 1918. The Latin names of the city are ''Posnania'' and ''Civitas Posnaniensis''. Its Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
name is , or ''Poyzn''.
In Polish, the city's name has masculine grammatical gender.
History
Early Middle Ages
For centuries before the Christianization of Poland (an event that essentially is credited as the creation of the very first Polish state, the Duchy of Poland), PoznaŇĄ was an important cultural and political centre of theWestern Polans Polans may refer to two Slavic tribes:
* Polans (eastern), an East Slavic tribe which inhabited both sides of the Dnieper river from the 6th to the 9th century
* Polans (western)
The Western Polans (also known as Polanes, Polanians; , derived ...
. It consisted of a fortified stronghold between the Warta and Cybina
Cybina is a river in Greater Poland, a right affluent of Warta. It starts near village Iwno and after 43 km falls into the right branch of Warta, which is also called Cybina or KanaŇā Ulgi, in PoznaŇĄ. Cybina flows through two big lakes: Sw ...
rivers on what is now Ostrów Tumski. Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; ‚Äď 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of SiemomysŇā and ...
, the first historically recorded ruler of the West Polans and of the early Polish state which they dominated, built one of his main stable headquarters in PoznaŇĄ. Mieszko's baptism in AD 966, seen as a defining moment in the Christianization of the Polish state, may have taken place in PoznaŇĄ.

11th to 16th centuries
Following the baptism, construction began of PoznaŇĄ's cathedral, the first in Poland. PoznaŇĄ was probably the main seat of the first missionary bishop sent to Poland, Bishop Jordan. TheCongress of Gniezno
The Congress of Gniezno ( pl, Zjazd gnieŇļnieŇĄski, german: Akt von Gnesen or ''Gnesener √úbereinkunft'') was an amicable meeting between the Polish Duke BolesŇāaw I the Brave and Emperor Otto III, which took place at Gniezno in Poland on 11 Ma ...
in 1000 led to the country's first permanent archbishopric being established in Gniezno (which is generally regarded as Poland's capital in that period), although PoznaŇĄ continued to have independent bishops of its own. PoznaŇĄ's cathedral was the place of burial of the early Piast monarchs, among them Mieszko I, Boleslaus I, Mieszko II Lambert, Casimir I, and later of PrzemysŇā I and PrzemysŇā II.
The pagan reaction that followed Mieszko II's death (probably in PoznaŇĄ) in 1034 left the region weak, and in 1038, Duke Bretislaus I
Bretislav I ( cs, BŇôetislav I.; 1002/1005 ‚Äď 10 January 1055), known as the "Bohemian Achilles", of the PŇôemyslid dynasty, was Duke of Bohemia from 1034 until his death.
Youth
Bretislav was the son of Duke OldŇôich and his low-born concubine ...
of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, ńĆechy ; ; hsb, ńĆńõska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
sacked and destroyed both PoznaŇĄ and Gniezno. Poland was reunited under Casimir I the Restorer in 1039, but the capital was moved to Krak√≥w, which had been relatively unaffected by the troubles. In 1138, by the testament of Boleslaus III, Poland was divided into separate duchies under the late king's sons, and PoznaŇĄ and its surroundings became the domain of Mieszko III the Old, the first of the Dukes of Greater Poland. This period of fragmentation lasted until 1320. Duchies frequently changed hands; control of PoznaŇĄ, Gniezno and Kalisz sometimes lay with a single duke, but at other times these constituted separate duchies.
 In about 1249, Duke PrzemysŇā I began constructing what would become the Royal Castle on a hill on the left bank of the Warta. Then in 1253, PrzemysŇā issued a charter to Thomas of Guben (Gubin) for the founding of a town under Magdeburg law, between the castle and the river. Thomas brought a large number of German settlers to aid in the building and settlement of the city ‚Äď this is an example of the German eastern migration (''
In about 1249, Duke PrzemysŇā I began constructing what would become the Royal Castle on a hill on the left bank of the Warta. Then in 1253, PrzemysŇā issued a charter to Thomas of Guben (Gubin) for the founding of a town under Magdeburg law, between the castle and the river. Thomas brought a large number of German settlers to aid in the building and settlement of the city ‚Äď this is an example of the German eastern migration (''Ostsiedlung
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had al ...
'') characteristic of that period. The city, which covered the area of today's Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins after thorough renovations. There are ma ...
neighbourhood, was surrounded by a defensive wall, integrated with the castle. The royal chancery and the University ensured a first flourishing of Polish literary culture in the city.
In reunited Poland, and later in the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth, PoznaŇĄ was the seat of a voivodeship. The city's importance began to grow in the Jagiellonian period, due to its position on trading routes from Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, –†—É—ā–Ķ–Ĺ—Ė—Ź, translit=Rutenia or uk, –†—É—Ā—Ć, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, RuŇõ, be, –†—É—ā—ć–Ĺ—Ė—Ź, –†—É—Ā—Ć, russian: –†—É—ā–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź, –†—É—Ā—Ć is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
to western Europe. It would become a major center for the fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
by the late 16th century. Suburban settlements developed around the city walls, on the river islands, and on the right bank, with some (Ostr√≥w Tumski, Ňör√≥dka, Chwaliszewo, Ostr√≥wek) obtaining their own town charters. However, the city's development was hampered by regular major fires and floods. On 2 May 1536 a fire destroyed 175 buildings, including the castle, the town hall, the monastery, and the suburban settlement called St. Martin. In 1519, the LubraŇĄski Academy had been established in PoznaŇĄ as an institution of higher education, but without the right to award degrees, which was reserved to Krak√≥w's Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University (Polish: ''Uniwersytet JagielloŇĄski'', UJ) is a public research university in Krak√≥w, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
. However, the Jesuits' college, founded in the city in 1571 during the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545‚Äď1563) a ...
, had the right to award degrees from 1611 until 1773, when it was combined with the Academy.

17th and 18th centuries
In the second half of the 17th century and most of the 18th, PoznaŇĄ was severely affected by a series of wars, attendant military occupations, lootings and destruction ‚Äď theSecond
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day ‚Äď this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
and Third Northern Wars, the War of the Polish Succession, the Seven Years' War and the Bar Confederation
The Bar Confederation ( pl, Konfederacja barska; 1768‚Äď1772) was an association of Polish nobles (szlachta) formed at the fortress of Bar in Podolia (now part of Ukraine) in 1768 to defend the internal and external independence of the Polish‚ ...
rebellion. It was also hit by frequent outbreaks of plague, and by floods, particularly that of 1736, which destroyed most of the suburban buildings. The population of the conurbation declined from 20,000 around 1600 to 6,000 around 1730, and Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. C ...
ian and Dutch settlers ('' Bambrzy'' and '' Olńôdrzy'') were brought in to rebuild the devastated suburbs. In 1778, a "Committee of Good Order" (''Komisja Dobrego PorzńÖdku'') was established in the city, which oversaw rebuilding efforts and reorganized the city's administration. However, in 1793, in the Second Partition of Poland, PoznaŇĄ came under the control of the Kingdom of Prussia, becoming part of (and initially the seat of) the province of South Prussia.
19th century to World War I
The Prussian authorities expanded the city boundaries, making the walled city and its closest suburbs into a single administrative unit. Left-bank suburbs were incorporated in 1797, and Ostr√≥w Tumski, Chwaliszewo, Ňör√≥dka, Ostr√≥wek and ŇĀacina (St. Roch) in 1800. The old city walls were taken down in the early 19th century, and major development took place to the west of the old city, with many of the main streets of today's city center being laid out. In theGreater Poland uprising of 1806
Greater Poland uprising of 1806 was a Polish military insurrection which occurred in the region of Wielkopolska, also known as Greater Poland, against the occupying"In 1772, before the Prussian occupation, only four Jewish families had lived t ...
, Polish soldiers and civilian volunteers assisted the efforts of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 ‚Äď 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
by driving out Prussian forces from the region. The city became a part of the Duchy of Warsaw in 1807, and was the seat of PoznaŇĄ Department
PoznaŇĄ Department (Polish: ''Departament PoznaŇĄski'') was a unit of administrative division and local government in Polish Duchy of Warsaw in years 1806-1815.
Capital city: PoznaŇĄ
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the River Warta in west-central ...
‚Äď a unit of administrative division and local government. However, in 1815, following the Congress of Vienna, the region was returned to Prussia, and PoznaŇĄ became the capital of the semi-autonomous Grand Duchy of Posen. Around 1820, PoznaŇĄ had over 20,000 inhabitants, 70% of whom were Poles, 20% Jews, and 10% Germans.
 The city continued to expand, and various projects were funded by Polish philanthropists, such as the
The city continued to expand, and various projects were funded by Polish philanthropists, such as the RaczyŇĄski Library
The RaczyŇĄski Library (Polish: ''Biblioteka RaczyŇĄskich w Poznaniu'') is a public library founded by Count Edward RaczyŇĄski in PoznaŇĄ. The library's building was erected in 1822‚Äď1828 with the financial support of Edward RaczyŇĄski Found ...
and the Bazar hotel. The city's first railway, running north-west to Stargard
Stargard (; 1945: ''Starogr√≥d'', 1950‚Äď2016: ''Stargard SzczeciŇĄski''; formerly German language, German: ''Stargard in Pommern'', or ''Stargard an der Ihna''; csb, St√īrgard) is a city in northwestern Poland, located in the West Pomeranian V ...
, opened in 1848. Due to its strategic location, the Prussian authorities intended to make PoznaŇĄ into a fortress city, building a ring of defensive fortifications around it. Work began on the citadel with '' Fort Winiary'' in 1828, and in subsequent years the entire set of defenses called ''Festung Posen
''Festung'' is a generic German language, German word for a fortress. Although it is not in common usage in English, it is used in a number of historical contexts involving German speakers:
* For historical fortresses in Austria, Germany or Switze ...
'' was completed.
A Greater Poland Uprising during the Revolutions of 1848 was ultimately unsuccessful, and the Grand Duchy lost its remaining autonomy, PoznaŇĄ becoming simply the capital of the Prussian Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (german: Provinz Posen, pl, Prowincja PoznaŇĄska) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920. Posen was established in 1848 following the Greater Poland Uprising as a successor to the Grand Duchy of Posen, w ...
. It would become part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire ‚Äď particularly a hereditary ...
with the unification of German states in 1871. Polish patriots continued to form societies such as the Central Economic Society for the Grand Duchy of PoznaŇĄ
The Central Economic Society for the Grand Duchy of PoznaŇĄ ( pl, Centralne Towarzystwo Gospodarcze dla Wielkiego Ksińôstwa PoznaŇĄskiego) was a social-economic organization of Poland, Polish landowners in the Greater Poland region (at this time ca ...
, and a Polish theatre
In common with other European countries, the most frequent and most popular form of theatre in Poland is dramatic theatre, based on the existence of relatively stable artistic companies. It is above all a theatre of directors, who decide on the ...
opened in 1875. However, the authorities made efforts to Germanize
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
the region, particularly through the Prussian Settlement Commission The Prussian Settlement Commission, officially known as the Royal Prussian Settlement Commission in the Provinces West Prussia and Posen (german: Königlich Preußische Ansiedlungskommission in den Provinzen Westpreußen und Posen; pl, Królewska K ...
founded in 1886. Germans accounted for 38% of the city's population in 1867, though this percentage would later decline somewhat, particularly after the region returned to Poland.
Another expansion of ''Festung Posen'' was planned, with an outer ring of more widely spaced forts around the perimeter of the city. Building of the first nine forts began in 1876, and nine intermediate forts were built from 1887. The inner ring of fortifications was now considered obsolete and came to be mostly taken down by the early 20th century, although the citadel remained in use. This made space for further civilian construction, particularly the Imperial Castle (''Zamek'') which was completed in 1910, and other grand buildings around it, including today's central university buildings and the opera house. The city's boundaries were also significantly extended to take in former suburban villages: Piotrowo and Berdychowo in 1896, ŇĀazarz, G√≥rczyn, JeŇľyce and Wilda in 1900, and SoŇāacz in 1907.
In 1910, PoznaŇĄ had 156,696 inhabitants, of which nearly 60% were Poles (over 91,000 Polish inhabitants of the city), and around 40% were Germans (over 65,000 German inhabitants of the city). Other nationalities accounted for 1-2% of the population (mainly Jews).
End of World War I to World War II
 At the end of World War I, the final Greater Poland Uprising in 1918‚Äď1919 brought PoznaŇĄ and most of the region back to newly reborn Poland, which was confirmed by the Treaty of Versailles. The local German populace had to acquire Polish citizenship or leave the country. This led to a wide emigration of the ethnic Germans of the town's population ‚Äď the town's German population decreased from 65,321 in 1910 to 5,980 in 1926 and further to 4,387 in 1934. In the interwar
At the end of World War I, the final Greater Poland Uprising in 1918‚Äď1919 brought PoznaŇĄ and most of the region back to newly reborn Poland, which was confirmed by the Treaty of Versailles. The local German populace had to acquire Polish citizenship or leave the country. This led to a wide emigration of the ethnic Germans of the town's population ‚Äď the town's German population decreased from 65,321 in 1910 to 5,980 in 1926 and further to 4,387 in 1934. In the interwar Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
, the city again became the capital of PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship. PoznaŇĄ's university, today called Adam Mickiewicz University, was founded in 1919, and in 1924 the PoznaŇĄ International Fair began. In 1929, the fair site was the venue for a major National Exhibition (''Powszechna Wystawa Krajowa'', popularly ''PeWuKa'') marking the tenth anniversary of independence; it attracted around 4.5 million visitors. In the 1930s, the fair ranked as Europe's fourth largest organiser of international trade events. The city's boundaries were again expanded in 1925 to include GŇā√≥wna, Komandoria, Rataje, StaroŇāńôka, Dńôbiec, SzelńÖg and Winogrady
Winogrady is a part of the Stare Miasto district of the city of PoznaŇĄ in western Poland. It is situated north of the ''Cytadela'' park (the former PoznaŇĄ citadel). The name refers to the vineyards which formerly existed in the area ‚Äď histo ...
, and in 1933: Golńôcin and Podolany.
During the German occupation of 1939‚Äď1945, PoznaŇĄ was incorporated into the Nazi Germany as the capital of '' Reichsgau Wartheland''. Many Polish inhabitants were executed, arrested, expelled to the General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, –ď–Ķ–Ĺ–Ķ—Ä–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–į –≥—É–Ī–Ķ—Ä–Ĺ—Ė—Ź), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement f√ľr die be ...
or used as forced labour; at the same time, many Germans and '' Volksdeutsche'' were settled in the city. The German population increased from around 5,000 in 1939 (some 2% of the inhabitants) to around 95,000 in 1944.
The Jewish community's history in the city dates back to the 13th century. In the past, the Jewish council in Poznan became one of the oldest and most important Jewish councils in Poland. The pre-war Jewish population of at least about 2,000 were mostly murdered in the Holocaust. A concentration camp was set up in Fort VII, one of the 19th-century perimeter forts. The camp was later moved to ŇĽabikowo south of PoznaŇĄ.
The Nazi authorities significantly expanded PoznaŇĄ's boundaries to include most of the present-day area of the city; these boundaries were retained after the war. PoznaŇĄ was captured by the Red Army, assisted by Polish volunteers, on 23 February 1945 following the Battle of PoznaŇĄ, in which the German army conducted a last-ditch defense in line with Hitler's designation of the city as a '' Festung''. The Citadel was the last point to be taken, and the fighting left much of the city, particularly the Old Town, in ruins. Many monuments were also destroyed, including Gutzon Borglum's statue of Woodrow Wilson in Poznan.
1945‚Äďpresent
Due to the expulsion and flight of German population PoznaŇĄ's post-war population was almost uniformly Polish. The city again became a voivodeship capital. In 1950, the size of PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship was reduced, and the city itself was given separate voivodeship status. This status was lost in the 1975 reforms, which also significantly reduced the size of PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship. The PoznaŇĄ 1956 protests are seen as an early instance of discontent with communist rule. In June 1956, a protest by workers at the city's Cegielski locomotive factory developed into a series of strikes and popular protests against the policies of the government. After a protest march on 28 June was fired on, crowds attacked the communist party and secret police headquarters, where they were repulsed by gunfire. Riots continued for two days until being quelled by the army; 67 people were killed according to official figures. A monument to the victims was erected in 1981 at Plac Mickiewicza. The post-war years had seen much reconstruction work on buildings damaged in the fighting. From the 1960s onwards intensive housing development took place, consisting mainly of pre-fabricated concrete blocks of flats, especially in Rataje andWinogrady
Winogrady is a part of the Stare Miasto district of the city of PoznaŇĄ in western Poland. It is situated north of the ''Cytadela'' park (the former PoznaŇĄ citadel). The name refers to the vineyards which formerly existed in the area ‚Äď histo ...
, and later PińÖtkowo, following its incorporation into the city in 1974. Another infrastructural change, which was completed in 1968, was the rerouting of the river Warta to follow two straight branches either side of Ostr√≥w Tumski.
The most recent expansion of the city's boundaries took place in 1987, with the addition of new areas mainly to the north, including Morasko, Radojewo and Kiekrz. The first free local elections following the fall of communism took place in 1990. With the Polish local government reforms of 1999, PoznaŇĄ again became the capital of a larger province entitled Greater Poland Voivodeship. It also became the seat of a '' powiat'' PoznaŇĄ County, with the city itself gaining separate ''powiat'' status.
Post-communism
Post-communism is the period of political and economic transformation or transition in former communist states located in Eastern Europe and parts of Africa and Asia in which new governments aimed to create free market-oriented capitalist economi ...
infrastructural developments include the opening of the ''Pestka'' Fast Tram route in 1997, and PoznaŇĄ's first motorway connections in 2003 as Poland's east-west A2 highway runs south of the city centre, serving also as a bypass. In 2006 country's first F-16 Fighting Falcons came to be stationed at the 31st Air Base
The 31st Air Base ( pl, 31. Baza Lotnicza), commonly known as PoznaŇĄ-Krzesiny Airport is a Polish Air Force base and military airport, located in Krzesiny, part of the Nowe Miasto district of PoznaŇĄ.
The base was officially constituted on ...
in Krzesiny in the south-east of the city.
PoznaŇĄ continues to host regular trade fairs and international events, including the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2008. It was one of the host cities for UEFA Euro 2012.
Geography
 PoznaŇĄ covers an area of , and has coordinates in the range 52¬į17'34
PoznaŇĄ covers an area of , and has coordinates in the range 52¬į17'34Cybina
Cybina is a river in Greater Poland, a right affluent of Warta. It starts near village Iwno and after 43 km falls into the right branch of Warta, which is also called Cybina or KanaŇā Ulgi, in PoznaŇĄ. Cybina flows through two big lakes: Sw ...
river flows through eastern PoznaŇĄ to meet the east branch of the Warta, which is also called Cybina ‚Äď its northern section was originally a continuation of that river, while its southern section has been artificially widened to form a main stream of the Warta. Other tributaries of the Warta within PoznaŇĄ are the Junikowo Stream ''(StrumieŇĄ Junikowski)'', which flows through southern PoznaŇĄ from the west, meeting the Warta just outside the city boundary in LuboŇĄ; the Bogdanka and Wierzbak, formerly two separate tributaries flowing from the north-west and along the north side of the city centre, now with their lower sections diverted underground; the GŇā√≥wna, flowing through the neighbourhood of the same name in north-east PoznaŇĄ; and the Rose Stream ''(StrumieŇĄ R√≥Ňľany)'' flowing east from Morasko in the north of the city. The course of the Warta in central PoznaŇĄ was formerly quite different from today: the main stream ran between Grobla and Chwaliszewo, which were originally both islands. The branch west of Grobla (the ''ZgniŇāa Warta'' ‚Äď "rotten Warta") was filled in late in the 19th century, and the former main stream west of Chwaliszewo was diverted and filled in during the 1960s. This was done partly to prevent floods, which did serious damage to PoznaŇĄ frequently throughout history.
canoeing
Canoeing is an activity which involves paddling a canoe with a single-bladed paddle. Common meanings of the term are limited to when the canoeing is the central purpose of the activity. Broader meanings include when it is combined with other acti ...
venue.
The city centre ‚Äď including the Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins after thorough renovations. There are ma ...
, the former islands of Grobla and Chwaliszewo, the main street Ňöwińôty Marcin
Ňöwińôty Marcin ("Saint Martin"), in full ''ulica Ňöwińôty Marcin'' ("Saint Martin Street"), is a main central street in the city of PoznaŇĄ in western Poland. It runs from south of the old town district, westwards past the church of St. Mart ...
and many other important buildings and districts ‚Äď lies on the west side of the Warta. Opposite it between the two branches of the Warta is Ostr√≥w Tumski, containing Cathedral and other ecclesiastical buildings, as well as housing and industrial facilities. Facing the cathedral on the east bank of the river is the historic district of Ňör√≥dka. Large areas of apartment blocks, built from the 1960s onwards, include Rataje in the east, and Winogrady
Winogrady is a part of the Stare Miasto district of the city of PoznaŇĄ in western Poland. It is situated north of the ''Cytadela'' park (the former PoznaŇĄ citadel). The name refers to the vineyards which formerly existed in the area ‚Äď histo ...
and PińÖtkowo north of the centre. Older residential and commercial districts include those of Wilda, ŇĀazarz and G√≥rczyn to the south, and JeŇľyce to the west. There are also significant areas of forest within the city boundaries, particularly in the east adjoining Swarzńôdz
Swarzńôdz (German: ''Schwersenz'') is a town in west-central Poland with 29,766 inhabitants. It is the seat of a mixed urban-rural commune called Gmina Swarzńôdz with 40,166 inhabitants. The town is situated in the PoznaŇĄ metropolitan area, in ...
, and around the lakes in the north-west.
For more details on PoznaŇĄ's geography, see the articles on its five main districts: Stare Miasto Stare Miasto means "Old Town" in Polish. It may refer to the following places:
City districts
* Stare Miasto, GdaŇĄsk
* Stare Miasto, Kraków (for the specific neighbourhood, see Kraków Old Town)
* Stare Miasto, Police
* Stare Miasto, PoznaŇĄ ...
, Nowe Miasto, JeŇľyce, Grunwald, and Wilda.
Climate
The climate of PoznaŇĄ is within the transition zone between a humid continental andoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
( K√∂ppen: ''Cfb'' to ''Dfb'' although it just fits in the second in the 0 ¬įC isotherm) and with relatively cold winters and warm summers. Snow is common in winter, when night-time temperatures are typically below zero. In summer temperatures may often reach . Annual rainfall is more than , among the lowest in Poland. The rainiest month is July, mainly due to short but intense cloudbursts and thunderstorms. The number of hours of sunshine are among the highest in the country. Climate in this area has mild differences between highs and lows, and there is adequate rainfall year-round. The K√∂ppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is " humid continental climate). The warmest temperature was recorded on 11 July 1959 at 38.7 ¬įC (101 ¬įF)
Administrative division

 PoznaŇĄ is divided into 42 neighbourhoods called '' osiedle'', each of which has its own elected council with certain decision-making and spending powers. The first uniform elections for these councils covering the whole area of the city were held on 20 March 2011.
For certain administrative purposes, the old division into five districts called '' dzielnica'' is used ‚Äď although these ceased to be governmental units in 1990. These were:
*
PoznaŇĄ is divided into 42 neighbourhoods called '' osiedle'', each of which has its own elected council with certain decision-making and spending powers. The first uniform elections for these councils covering the whole area of the city were held on 20 March 2011.
For certain administrative purposes, the old division into five districts called '' dzielnica'' is used ‚Äď although these ceased to be governmental units in 1990. These were:
* Stare Miasto Stare Miasto means "Old Town" in Polish. It may refer to the following places:
City districts
* Stare Miasto, GdaŇĄsk
* Stare Miasto, Kraków (for the specific neighbourhood, see Kraków Old Town)
* Stare Miasto, Police
* Stare Miasto, PoznaŇĄ ...
(Old Town), population 161,200, area , covering the central and northern parts of the city
* Nowe Miasto (New Town), population 141,424, area , including all parts of the city on the east bank of the Warta
* Grunwald, population 125,500, area , covering the south-western parts of the city
* JeŇľyce, population 81,300, area , covering the north-western parts of the city
* Wilda, population 62,290, area , in the southern part of the city
Many citizens of PoznaŇĄ thanks to the strong economy of the city and high salaries started moving to suburbs of the PoznaŇĄ County ( powiat) in the 1990s. Although the number of inhabitants in PoznaŇĄ itself was decreasing for the past two decades, the suburbs gained almost twice as many inhabitants. The PoznaŇĄ metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
''Metropolia PoznaŇĄ'' comprising PoznaŇĄ County and several other communities is home to over 1 million inhabitants. The complex infrastructure, population density, number of companies and gross product per capita of PoznaŇĄ suburbs may be only compared to Warsaw suburbs. Many parts of closer suburbs such as Tarnowo Podgorne Tarnowo may refer to the following places:
* Tarnowo, Oborniki County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland)
* Tarnowo, PiŇāa County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland)
* Tarnowo, Podlaskie Voivodeship (north-east Poland ...
, Komorniki
Komorniki is a village in Poland, located in Greater Poland Voivodeship, PoznaŇĄ County, Gmina Komorniki (PoznaŇĄ metropolitan area), with approximately 5,500 inhabitants. The gmina (municipality) of Komorniki, including the village of Komornik ...
, Suchy Las
Suchy Las is a village in PoznaŇĄ County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Suchy Las. It lies just north of the regional capital PoznaŇĄ
PoznaŇĄ () is ...
, and Dopiewo produce more in terms of GDP per capita than the city itself.
Economy
 PoznaŇĄ has been an important trade centre since the Middle Ages. Starting in the 19th century, local heavy industry began to grow. Several major factories were built, including the
PoznaŇĄ has been an important trade centre since the Middle Ages. Starting in the 19th century, local heavy industry began to grow. Several major factories were built, including the Hipolit Cegielski
Hipolit Cegielski (6 January 1813, ŇĀawki ‚Äď 30 November 1868, Posen (PoznaŇĄ), Kingdom of Prussia) was a Polish businessman and social and cultural activist. He founded H. Cegielski ‚Äď PoznaŇĄ in 1846.
References
* Witold Jakóbczyk
Wit ...
's steel mill and railway factory, popularly called ''Ceglorz''.
Nowadays, PoznaŇĄ is one of the major trade centres in Poland. It is regarded as the second most prosperous city in Poland after its capital Warsaw. The city of PoznaŇĄ produced PLN 31.8 billion of Poland's gross domestic product in 2006.
 Many Western European companies have established their Polish headquarters in PoznaŇĄ or in nearby towns such as
Many Western European companies have established their Polish headquarters in PoznaŇĄ or in nearby towns such as Tarnowo Podg√≥rne
Tarnowo Podg√≥rne is an urbanized village in PoznaŇĄ County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Tarnowo Podg√≥rne. It lies approximately north-west of the regiona ...
and Swarzńôdz
Swarzńôdz (German: ''Schwersenz'') is a town in west-central Poland with 29,766 inhabitants. It is the seat of a mixed urban-rural commune called Gmina Swarzńôdz with 40,166 inhabitants. The town is situated in the PoznaŇĄ metropolitan area, in ...
. Most foreign investors are German (36%) and Dutch companies (14%). The best known examples of corporation who have their headquarters in PoznaŇĄ and the surrounding areas are that of Volkswagen, GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the ten ...
, Amazon, Bridgestone
is a Japanese multinational tire manufacturer founded in 1931 by Shojiro Ishibashi (1889‚Äď1976) in the city of Kurume, Fukuoka, Japan. The name Bridgestone comes from a calque translation and transposition of , meaning 'stone bridge' in Japan ...
, Beiersdorf, Raben Group Raben Group is a Dutch logistics company group. Its operations include contract logistics, warehousing, international road forwarding, domestic distribution, sea and air freight, intermodal transport and logistics services for fresh products (Fresh ...
(near K√≥rnik) and Kuehne + Nagel (near GńÖdki
GńÖdki () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina K√≥rnik, within PoznaŇĄ County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately north of K√≥rnik and south-east of the regional capital PoznaŇĄ
Pozna ...
). There are also several shared services centers, and IT branch offices. Investors are mostly from the food processing, furniture, automotive and transport and logistics industries. Foreign companies are primarily attracted by relatively low labour costs, good road and railway network, good vocational skills of workers, and relatively liberal employment laws.
Some of the best-known major corporations founded and still based in PoznaŇĄ and the city's metropolitan area include Allegro
Allegro may refer to:
Common meanings
* Allegro (music), a tempo marking indicate to play fast, quickly and bright
* Allegro (ballet), brisk and lively movement
Artistic works
* L'Allegro (1645), a poem by John Milton
* ''Allegro'' (Satie), an ...
‚Äď owner of the Poland's biggest e-commerce site, H. Cegielski-PoznaŇĄ SA
H is the eighth letter of the Latin alphabet.
H may also refer to:
Musical symbols
* H number, Harry Halbreich reference mechanism for music by Honegger and MartinŇĮ
* H, B (musical note)
* H, B major
People
* H. (noble) (died after 127 ...
‚Äď a historic manufacturer, Solaris Bus & Coach ‚Äď a modern bus and coach maker based in Bolechowo, and Enea S.A.
Enea is a Polish power industry company based in PoznaŇĄ. Enea is the fourth largest energy group in Poland. As of December 2017, its share in the domestic electricity sales market was 13%.
Enea Group is the vice-leader in electricity production ...
‚Äď one of the country's biggest energy firms. Kompania Piwowarska based in PoznaŇĄ produces some of Poland's best known beers, and includes not only the local Lech Brewery's products but also Tyskie from Tychy and Dojlidy Brewery
Dojlidy Brewery ( pl, Browar Dojlidy ) is a brewery located in BiaŇāystok, Poland, and owned by Kompania Piwowarska SA, the Polish subsidiary of Asahi Breweries. The brewery was modernized between 1997 and 1999, then in 2003 it was purchased b ...
from BiaŇāystok
BiaŇāystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
BiaŇāystok is located in the BiaŇāystok Up ...
among many others.
In 2008, three PoznaŇĄ students founded Netguru, a software development
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development invol ...
and digital consultancy company. It grew fast to employ about 600 people in 2019.
''Stary Browar
Shopping, Arts and Business Center "Stary Browar" is the center of commerce and art, built in November 2003, located in the center of PoznaŇĄ, Poland at 42 P√≥Ňāwiejska Street.
The center is a combination of retail space and an art gallery. The s ...
'', the center of commerce and art opened in 2003, won several awards for its architecture. Other notable shopping centers include ''Posnania'', the biggest commerce facility in Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Gro√üpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is PoznaŇĄ followed ...
, ''Galeria Malta'', and the shops at the Hotel Bazar ‚Äď a historical hotel and commercial center in the Old Town.
Transport
PoznaŇĄ GŇā√≥wny
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
'', and is located just southwest of the city centre. There are also the smaller '' East PoznaŇĄ'' and '' PoznaŇĄ Garbary'' stations northeast of the centre, and a number of other stations on the outskirts of the city. The main east-west A2 motorway runs south of the city centre connecting it with Berlin in the west and ŇĀ√≥dŇľ and Warsaw in the east, serving also as a centre bypass. Other main roads run in the direction of Warsaw, Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz ( , , ; german: Bromberg) is a city in northern Poland, straddling the meeting of the River Vistula with its left-bank tributary, the Brda. With a city population of 339,053 as of December 2021 and an urban agglomeration with more ...
, WńÖgrowiec, Oborniki, Katowice
Katowice ( , , ; szl, Katowicy; german: Kattowitz, yi, ◊ß◊ź÷∑◊ė◊Ę◊ē◊ē◊ô◊•, Kattevitz) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Upper Silesian metropolitan area. It is the 11th most popul ...
, WrocŇāaw, Buk
Buk or BUK may refer to:
Places Czech Republic
* Buk (Prachatice District), a municipality and village in the South Bohemian Region
* Buk (PŇôerov District), a municipality and village in the Olomouc Region
*Buk, a village and part of JindŇôichŇĮ ...
and Berlin.
PoznaŇĄ has one of the biggest airports in the west of Poland called ''ŇĀawica'' Airport. In 2016 it handled approximately 1.71 million passengers.
Since the bend of the communist era in 1989, city investments into transportation have been mostly into public transport. While the number of cars since 1989 has at least doubled, municipal policy concentrated on improving public transport, which mostly consists of trams and both urban and suburban buses. New tram lines are planned and built, including ''Pestka'' Fast Tram sections, and the rolling stock is being replaced for modern low-floor vehicles such as trams Solaris
Solaris may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film
* ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by StanisŇāaw Lem
** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg
** ''Solaris'' (1972 film), directed by ...
Tramino / Combino and Moderus Gamma
The Moderus Gamma is an articulated tram manufactured in Biskupice, Poland, since 2016 by , a subsidiary of transport operator . Planning began in 2008 and the prototype was completed in 2016.
Variants
Multiple variants of the Gamma tram exist ...
, and buses such as Solaris Urbino
Solaris Urbino is a series of low-floor buses and low-entry doorway intercity buses, powered by diesel drive engines and alternative fuel (CNG, gas and biogas, hybrid and electric), produced by the Polish company Solaris Bus & Coach in Bo ...
.
Paid parking zones in the city centre were established, and Park & Ride car parks have been built to encourage commuters to leave their car on the outskirts of the city and continue their journey by public transport, as well as to allow safe and legal parking outside the city centre. Limiting car access to the strict centre actually increased the level of ridership.
PoznaŇĄ GŇā√≥wny
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
'' ‚Äď main railway station
EN76 029 in Poznan Glowny (cropped).JPG, Greater Poland Railways train at the ''PoznaŇĄ GŇā√≥wny''
WńôzeŇā PoznaŇĄ-Wilda A2 i DW430 RB1.JPG, A2 motorway before the six-lane expansion done in 2019
Moderus Gamma PoznaŇĄ (cropped).jpg, Moderus Gamma
The Moderus Gamma is an articulated tram manufactured in Biskupice, Poland, since 2016 by , a subsidiary of transport operator . Planning began in 2008 and the prototype was completed in 2016.
Variants
Multiple variants of the Gamma tram exist ...
tram, which is produced near PoznaŇĄ, in city's eastern underground section
Poznanski Rower Miejski 9.jpg, City Bike's station
Witosa Wiadukt bus stop in Poznan.JPG, Solaris
Solaris may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film
* ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by StanisŇāaw Lem
** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg
** ''Solaris'' (1972 film), directed by ...
bus; they are also produced near PoznaŇĄ
PoznaŇĄ ŇĀawica.jpg, Eurocopter EC135
The Eurocopter EC135 (now Airbus Helicopters H135) is a twin-engine civil light utility helicopter produced by Airbus Helicopters (formerly known as Eurocopter). It is capable of flight under instrument flight rules (IFR) and is outfitted with ...
Lifeguard 9 waiting for an emergency dispatch at the ŇĀawica Airport
Culture and heritage
 PoznaŇĄ possesses many historic buildings and heritage sites, mostly concentrated around the
PoznaŇĄ possesses many historic buildings and heritage sites, mostly concentrated around the Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins after thorough renovations. There are ma ...
and other parts of the city centre. Many of these lie on the tourist Royal-Imperial Route ‚Äď a walk leading through the most important parts of the city showing its history, culture and identity. Parts of the city centre are listed as one of Poland's official national historic monuments, as designated 28 November 2008, along with other portions of the city's historic core. Its listing is maintained by the National Heritage Board of Poland.
Apart from traditional theatres with a long history such as '' Teatr Wielki'', ''Teatr Polski
Polish Theatre in Warsaw ( pl, Teatr Polski im. Arnolda Szyfmana w Warszawie) is a theatre in Warsaw, Poland. It is located at ul. Karasia 2. The current artistic director is Andrzej Seweryn.
The theatre was initiated by Arnold Szyfman and design ...
'', ''Teatr Nowy'', and others like ''Teatr Animacji'', ''Teatr Muzyczny'' and Polish Dance Theatre, PoznaŇĄ is also home to a growing number of different kind of alternative theatre
Fringe theatre is theatre that is produced outside of the main theatre institutions, and that is often small-scale and non-traditional in style or subject matter. The term comes from the Edinburgh Festival Fringe.Kemp, Robert, ''More that is Fre ...
groups. It is believed that even up to 30 more or less known groups may work in the city, and thus, the city has recently become a new Polish off-theatre performance centre.
 Classical music events include the Henryk Wieniawski Violin Competition which is held every 5 years, and classical music concerts by the
Classical music events include the Henryk Wieniawski Violin Competition which is held every 5 years, and classical music concerts by the PoznaŇĄ Philharmonic
Tadeusz Szeligowski PoznaŇĄ Philharmonic is a regional cultural institution founded in 1947 on the initiative of Tadeusz Szeligowski as the State Philharmonic in PoznaŇĄ; one of the two philharmonics in the Greater Poland Voivodeship.
History
T ...
orchestra held each month in the Hall of the Adam Mickiewicz University, considered to be one of the best in terms of acoustics in Poland. Especially popular are concerts by the PoznaŇĄ Nightingales The PoznaŇĄskie SŇāowiki (en: PoznaŇĄ Nightingales fr: Rossignols de Poznan de: Posener Nachtigallen) is a leading Polish choir founded in 1939.
When the Germans expelled the priest of PoznaŇĄ Cathedral, WacŇāaw Gieburowski (1878‚Äď1943), a choirb ...
.
Every year on 11 November, city residents celebrate the Day of St. Martin. A procession of horses, with Saint Martin at its head, parades along Saint Martin Street (''ulica Ňöwińôty Marcin''), in front of the Imperial Castle. The renowned St. Martin's Croissant, a regional product of PoznaŇĄ, are widely sold during the festivities.
An important cultural event in PoznaŇĄ is the annual Malta Festival
Lake Malta, known also as the MaltaŇĄski Reservoir,GoŇādyn R., Kozak A., Kostka K. 1994. Causes of changes in the water quality of the restored MaltaŇĄski Reservoir in PoznaŇĄ. In: GoŇādyn R. (ed.) Protection of the water of the catchment area of ...
, which takes place at many city venues, usually in late June and early July. It hosts mainly modern experimental off-theatre performances often taking place on squares and other public spaces. It also includes cinema, visual, music and dancing events. PoznaŇĄ also stages the Ale Kino! International Young Audience Film Festival in December, and Off Cinema festival of independent films. Other festivals: Animator
An animator is an artist who creates multiple images, known as frames, which give an illusion of movement called animation when displayed in rapid sequence. Animators can work in a variety of fields including film, television, and video gam ...
(animated film festival), Ethno Port festival of traditional world's ethnic music, Maski Theater Festival, Dance International Workshops by Polish Dance Theater, Made in Chicago (jazz festival), Festival of Ice Sculpture, Science and Art Festival, Tzadik (Jewish music festival), and Meditations Biennale (modern art).
multiplexes
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource - a ...
and art-house institutions. The Rozbrat social centre, a squatted former factory in JeŇľyce, serves as a home for independent and open-minded culture. It hosts frequent gigs, an anarchist library, vernissages, exhibitions, annual birthday festival in October, poetry evenings and graffiti festivals. The city centre has many clubs, pubs and coffee houses.
A popular venue is '' Malta'', a park with an artificial lake situated in its centre. On one south bank of the lake there are ski and sleigh slopes of Malta Ski centre, and on the opposite bank a large complex of ''Termy MaltaŇĄskie'' swimming pools.
PoznaŇĄ Zoological Garden has two facilities. The Old Zoo is one of the oldest in Poland, established in 1874 just west of the city centre. The large New Zoo was opened to the public in 1974, becoming second largest in Poland in terms of area. It is located on a hilly forest area with six large ponds at the eastern city's wedge of greenery, beyond the Malta lake. There is a dedicated and adored by children '' Maltanka'' mini-railway, that starts the route near the '' Ňör√≥dka'' roundabout.
Bamberka
Bambers, also known as PoznaŇĄ Bambergians, are Poles who are partly descended from Germans who moved from the area of Bamberg (Upper Franconia, Germany) to villages surrounding PoznaŇĄ, Poland. They settled in villages which had been destroyed du ...
'' fountain at the Old Market Square
PoznaŇĄ Ňör√≥dka 96P-82.jpg, '' Ňör√≥dka's'' Tale Mural in 2015
Stary Browar 05.jpg, ''Stary Browar
Shopping, Arts and Business Center "Stary Browar" is the center of commerce and art, built in November 2003, located in the center of PoznaŇĄ, Poland at 42 P√≥Ňāwiejska Street.
The center is a combination of retail space and an art gallery. The s ...
'', ''Kufel'' by Wojciech Kujawski (Guinness ratified largest beer mug in the world), and Art Stations Foundation gallery in the background
PoznaŇĄ Goat.jpg, PoznaŇĄ Goat mascot, Old Market Square
PaŇāac w Rogalinie (4).jpg, Rogalin's RaczyŇĄski Palace within Rogalin Landscape Park, some 8 mi south of PoznaŇĄ. Rear view
Population
In 1600, approximately 20,000 inhabitants resided in the whole PoznaŇĄ conurbation. By 1732 the population had dropped to 4,000 due to wars, floods and plague. Historically, its growth rate was high throughout the 19th and 20th centuries; in the year 1900 approximately 110,000 people were registered as residents and by 1939 there was already 274,155 people. The population of PoznaŇĄ has declined steadily since 1990, when it reached a maximum of 590,101. This phenomenon, which also affected other European cities, is caused in part by the growth of satellite suburbs at the expense of the downtown region within the city proper. In 2020, PoznaŇĄ had 532,048 registered inhabitants being the fifth most populous town in Poland, while the metropolitan area had a population of more than 1,200,000 people. The city's population density was 5,300 people per square mile (2,040/km2). Contemporary PoznaŇĄ has one of the highest concentration of foreigners in Poland alongside Warsaw and WrocŇāaw; a significant majority are migrant workers from Ukraine; others came from Italy, Spain, Belarus, Russia and Serbia. No exact statistic exists on the number of temporary residents from abroad. Many are students studying at PoznaŇĄ's schools and institutions of higher learning.Education and science

 PoznaŇĄ is one of the four largest academic centres in Poland. The number of students in the city is about 140,000, which ranks it the third or fourth after Warsaw and Krak√≥w and about equal to WrocŇāaw in student population. Every one in four inhabitants of PoznaŇĄ is a student. Since PoznaŇĄ is smaller than Warsaw or Krak√≥w still having a very large number of students it makes the city even more vibrant and dense academic hub than both former and current capital of Poland ‚Äď Krak√≥w and Warsaw respectively. PoznaŇĄ with its almost 30 universities and colleges has the second richest educational offering in the country after Warsaw.
PoznaŇĄ is one of the four largest academic centres in Poland. The number of students in the city is about 140,000, which ranks it the third or fourth after Warsaw and Krak√≥w and about equal to WrocŇāaw in student population. Every one in four inhabitants of PoznaŇĄ is a student. Since PoznaŇĄ is smaller than Warsaw or Krak√≥w still having a very large number of students it makes the city even more vibrant and dense academic hub than both former and current capital of Poland ‚Äď Krak√≥w and Warsaw respectively. PoznaŇĄ with its almost 30 universities and colleges has the second richest educational offering in the country after Warsaw.
Public universities
The city has eight state-owned universities. Adam Mickiewicz University (AMU, ''UAM'' in Polish) is one of the most influential and biggest universities in Poland. PoznaŇĄ University of Technology (PUT, ''PP'' in Polish) is one of the most influential and biggest technical universities in Poland. * Adam Mickiewicz University * PoznaŇĄ University of Technology *PoznaŇĄ University of Economics and Business
The PoznaŇĄ University of Economics and Business is a business school in Poland.
The PoznaŇĄ University of Economics and Business (PUEB) is an academic institution in the western part of the country attracting students from many parts of Poland. ...
* PoznaŇĄ University of Medical Sciences
* University of Life Sciences in PoznaŇĄ
The University of Life Sciences in PoznaŇĄ ( pl, Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy w Poznaniu, literally "University of Nature in PoznaŇĄ") is a higher-education institution in PoznaŇĄ, Poland. It officially gained university status on 11 April 2008. Its pr ...
* PoznaŇĄ University School of Physical Education
* University of Fine Arts in PoznaŇĄ
* Academy of Music in PoznaŇĄ
Adam Mickiewicz University is one of the three best universities in Poland after University of Warsaw and University of Kraków. They all have a very high number of international student and scientist exchange, research grants and top publications.
In northern suburbs of PoznaŇĄ a very large "Morasko Campus" has been built (Faculty of Biology, Physics, Mathematics, Chemistry, Political Sciences, Geography). The majority of faculties are already open, although a few more facilities will be constructed. The campus infrastructure belongs to the most impressive among Polish universities. Also, there are plans for "Uniwersytecki Park Historii Ziemii" (Earth History Park), one of the reason for the park construction is a " Morasko meteorite nature reserve" situated close by, it is one of the rare sites of Europe where a number of meteorites fell and some traces may be still seen.
PoznaŇĄ University of Technology was ranked fifth among all universities in Poland, and third among Polish technical universities, in the 2018 international Scimago Institutions Ranking. In the 2019 Academic Ranking of World Universities
The ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (''ARWU''), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, is one of the annual publications of world university rankings. The league table was originally compiled and issued by Shanghai Jiao Tong University ...
, known also as the Shanghai Ranking, PUT was classified among the 500 best universities in the world in two disciplines, i.e. "Computer Science & Engineering" and "Mechanical Engineering". PUT was ranked third among all Polish universities in the 2019‚Äď20 Ministry of Science and Higher Education popularity ranking. Recent years have brought extensive development of university infrastructure at the "Warta campus", located on the right side of Warta river between Malta lake and PoznaŇĄ city center. Location of this campus belongs to the most impressive among Polish universities.
Private universities
There is also a great number of smaller, mostly private-run colleges and institutions of higher education, including SWPS University of Social Sciences and Humanities,Collegium Da Vinci
Collegium Da Vinci is a Polish private university in Poznan.
History
June 10, 1996 the Minister of Education granted permission for the establishment of the Higher School of Humanities and Journalism in Poznan, where the initiator and founder ...
, and WSB University
, image = Akademia WSB w DńÖbrowie G√≥rniczej - 002.jpg
, image_size = 320
, latin_name =
, former_names = University of DńÖbrowa G√≥rnicza
, type = Private
, establi ...
.
High schools
PoznaŇĄ has numerous high schools, which have different programmes focusing on different subjects. Some of the most notable are: * Adam Mickiewicz High School * Karol Marcinkowski High School * St. John Cantius High School * St. Mary Magdalene High SchoolResearch
* Polish Academy of Sciences, the branch in PoznaŇĄ *PoznaŇĄ Society of Friends of Arts and Sciences
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint ...
* PoznaŇĄ Supercomputing and Networking Center
* Western Institute
Sports
 There are several multi-sport clubs in PoznaŇĄ.
There are several multi-sport clubs in PoznaŇĄ. Warta PoznaŇĄ
Warta PoznaŇĄ () is a multi-sports club based in PoznaŇĄ, Poland. The name means ''the Guard'' in Polish and also the name of the river Warta on which PoznaŇĄ is located.
Founded in 1912, the association football club are two-time winners of the ...
was one of the most successful clubs in pre-World War II history, and Lech PoznaŇĄ
Kolejowy Klub Sportowy Lech PoznaŇĄ S.A., commonly referred to as KKS Lech PoznaŇĄ or simply Lech PoznaŇĄ (), is a Polish professional association football, football club based in PoznaŇĄ and currently competing in the Ekstraklasa, the nation' ...
football team frequently plays in European cups. Lech plays at the Municipal Stadium, which hosted the 2012 European Championship group stages as well as the opening game and the final of the 2006 under-19 Euro Championship. Warta usually plays at the small DńôbiŇĄska Road Stadium, a former training ground for Edmund Szyc Stadium, however, since the latter fell into disrepair in 1998 and was sold in 2001, it became the team's main ground. The club was planning to rebuild Szyc Stadium with historical 60,000-seat capacity. In 2019/2020 season, Warta played their I liga matches at the stadium in Grodzisk Wielkopolski, as DńôbiŇĄska Road Stadium did not fulfill the requirements of the I liga's authorities.
The city's third professional football team of multi-sport Olimpia PoznaŇĄ club ceased activity in 2004, and the club focused on other sports, achieving good results in judo and tennis. Olimpia is hosting the annual tennis PoznaŇĄ Open tournament at its Olimpia Tennis Park. The club owns a large sports complex near RusaŇāka lake, and apart from the tennis facilities boasts a large city recreation areas: mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and pe ...
facilities with a four-cross track, an athletics stadium with 3,000 capacity, and a football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
- speedway stadium with 20,000 capacity. The latter had fallen into vast disrepair until it was acquired by the City Council from the Police in 2013 and was renovated. The football-speedway stadium hosts speedway club PSŇĽ PoznaŇĄ
PoznaŇĄskie Stowarzyszenie ŇĽuŇľlowe (''PoznaŇĄ Speedway Association'') is a Polish Motorcycle speedway, speedway team based in PoznaŇĄ who currently race in Polish Speedway Second League (2. Liga). The club have never ridden in the Polish top di ...
, rugby union side NKR Chaos, American football team the Armia PoznaŇĄ, and football team Poznaniak PoznaŇĄ.
The artificial Malta lake, which was formed in 1952 and is about long, hosted the 2009 World Rowing Championships
The 2009 World Rowing Championships were World Rowing Championships that were held from 23 to 30 August 2009 at Lake Malta, PoznaŇĄ, Poland. The annual week-long rowing regatta was organized by FISA (the International Rowing Federation), and held ...
and some regattas of the World Rowing Cup. It also held the ICF Canoe Sprint World Championships in 1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of Humankind, humanity on Earth, Astroph ...
, 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which Casualties of the September 11 attacks, killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a Participants in ...
, and 2010 ICF Canoe Sprint World Championships, 2010.
''Termy MaltaŇĄskie'', big water sports and recreation complex featuring Olympic-size swimming pool, is located at the north bank of the lake. A 50-metre pool can be divided into two 25-metre pools. The other pool with a diving tower also fulfils all requirements necessary for organizing sports competitions. ''Termy MaltaŇĄskie'' consists of as many as 18 sports and recreational swimming pools with a total water surface area of as well as many other attractions such as different kind of saunas and spa, among others. The complex uses natural geothermal waters drawn nearby from a depth of and saturated with beneficial minerals and elements, for some of the swimming pools.
At the south bank of the lake, Malta-Ski Dry slope skiing, year-round skiing complex is situated, and is hosting minor sport competitions, equipped with a toboggan run and a minigolf course. There is also a roller rink with a roller skating club nearby.
Since 2000, the city has been the host of the PoznaŇĄ Marathon, one of the largest such races in the country.
International relations
Twin towns ‚Äď Sister cities
PoznaŇĄ is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:' * Assen, Drenthe, Netherlands, since 1992 * Brno, South Moravia, Czech Republic, since 1966 * Kharkiv, Sloboda Ukraine, Ukraine, since 1998 * GyŇĎr, Western Transdanubia, Hungary, since 2008 * Hannover, Lower Saxony, Germany, since 1979 * Nottinghamshire, England, United Kingdom, since 1994 * Jyv√§skyl√§, Finnish Lakeland, Central Finland, Finland, since 1979 * Kutaisi, Imereti, Georgia, since 2009 * Nablus, West Bank, State of Palestine, Palestine, since 1997 * Pozuelo de Alarc√≥n, Community of Madrid, Spain, since 1992 * Ra'anana, Central District (Israel), Central District, Sharon Plain, Israel, since 2010 * Rennes, Brittany, France, since 1998 * Shenzhen, Guangdong, China, since 1993 * Toledo, Ohio, Toledo, Ohio, United States, since 1991 * Bay City, Michigan, Bay City, Michigan, United States, since 1977 * S√£o Jos√© dos Pinhais, Paran√°, Brazil,Notable people
* Anna Anderson (c. 1900‚Äď1984), pretender of Grand Duchess Anastasia of Russia * Peja (musician), Ryszard "Peja" Andrzejewski (born 1976), rapper * Lothar von Arnauld de la Peri√®re (1886‚Äď1941), German U-boat commander * Isidor Ascheim (1891‚Äď1968), painter and printmaker * StanisŇāaw BaraŇĄczak (1946‚Äď2014), poet * Hanna Banaszak (born 1957), singer, poet * Herbert Baum (1912‚Äď1942) resistance fighter * Zygmunt Bauman (1925‚Äď2017), sociologist * Judah Loew ben Bezalel (1512 or 1526‚Äď1609), important Talmudic scholar, Jewish mystic, and philosopher * Heinrich Caro (1834‚Äď1910), chemist *Hipolit Cegielski
Hipolit Cegielski (6 January 1813, ŇĀawki ‚Äď 30 November 1868, Posen (PoznaŇĄ), Kingdom of Prussia) was a Polish businessman and social and cultural activist. He founded H. Cegielski ‚Äď PoznaŇĄ in 1846.
References
* Witold Jakóbczyk
Wit ...
(1815‚Äď1868), businessman
* Dezydery ChŇāapowski (1788‚Äď1848), general
* August Cieszkowski (1814‚Äď1894), philosopher
* Antoni CzubiŇĄski (1928‚Äď2003), historian
* Leopold Damrosch (1832‚Äď1885), conductor
*Kurt Demmler (1943‚Äď2009), songwriter; accused of sexual abuse he hanged himself in his jail cell
* Ludwig Dessoir, (1810‚Äď1874), actor
* Tomasz Dietl (born 1950), physicist
* Franciszek Dobrowolski (1830‚Äď1896), theater director
* Tytus DziaŇāyŇĄski (1796‚Äď1861), political activist
* Margo Dydek, MaŇāgorzata Dydek (1974‚Äď2011), basketball player
* Akiva Eiger (1761‚Äď1837), Rabbi of PoznaŇĄ (1815‚Äď1837)
* Ewaryst Estkowski (1820‚Äď1856), teacher
* Gerard Ettinger (1909‚Äď2002), designer and manufacturer of leather goods.
* Krystyna Feldman (1916‚Äď2007), actress
* Wojciech Fibak (born 1952), tennis player
* Gerhard Flesch (1909‚Äď1948), German Nazi Gestapo and SS officer executed for war crimes
* Fredrak Fraske (1872‚Äď1973), the last surviving United States veteran of the Indian Wars
* Johannes Gad (1842‚Äď1926), neurophysiologist
* Jean Gebser (1905‚Äď1973), human consciousness scientist
* Eduard Gerhard (1795‚Äď1867), archaeologist.
* Arkadiusz GŇāowacki (born 1979), footballer
* Friedrich Goltz (1834‚Äď1902), physiologist
* Konstanty Gorski (1859‚Äď1924), composer and violinist
* Kasper Goski (died 1576), Mayor of PoznaŇĄ, astrologer and medical doctor
* Heinrich Graetz (1817‚Äď1891) historian, wrote a history of the Jewish people from a Jewish perspective.
* Paul von Hindenburg (1847‚Äď1934), Field Marshal and President of the Weimar Republic
* Joanna Hoffmann-Dietrich (born 1968), artist and academic
* Piotr HofmaŇĄski (born 1956), jurist and current International Criminal Court President
* Samuel Holdheim (1806‚Äď1860), a German rabbi and author.
* Maksymilian Jackowski (1815‚Äď1905), activist
* Anna Jantar (1950‚Äď1980), a popular Polish singer, who perished in a plane crash.
* Alfred Jodl (1890‚Äď1946), German WW2 military commander executed for war crimes
* John Jonston (1603‚Äď1675), naturalist and physician
* Jan A.P. Kaczmarek (born 1954), composer
* Maria and Bogdan Kalinowski, (1945‚Äď2020) & (1939‚Äď2017) filmgoing couple
* Richard Kandt (1867‚Äď1918), doctor and explorer
* Ernst Hartwig Kantorowicz (1895‚Äď1963), historian
* Marek Karpinski, computer scientist
* G√ľnther von Kluge (1882‚Äď1944), Field Marshal
* Krzysztof Komeda (1931‚Äď1969), jazz musician
* Leo K√∂nigsberger (1837‚Äď1921), mathematician
* Kazimierz Kordylewski (1903-1981), Polish astronomer, claimed discovery of Kordylewski Clouds
* Antoni Kraszewski (1797‚Äď1870), politician
* Germaine Krull (1897‚Äď1985), photographer
* Jakub Kucner (born 1988), male model
* Gerard Labuda (born 1916), historian
* Arthur Liebehenschel (1901‚Äď1948), Nazi commandant of Auschwitz and Majdanek executed for war crimes
* JarosŇāaw Leitgeber (1848‚Äď1933), purveyor of Polish books Partitions of Poland, under partitions
* Paul Leonhardt (1877‚Äď1934), chess master
* Karol Libelt (1807‚Äď1875), philosopher
* Magda Linette (born 1992), tennis player
* Erich Ludendorff (1865‚Äď1937), general and politician
* Karol Marcinkowski (1800‚Äď1848), physician and social activist
* WŇāadysŇāaw Markiewicz (born 1920), sociologist
* Teofil Matecki (1810‚Äď1886), philosopher
* Heinrich Mendelssohn (1881‚Äď1959), building tycoon
* Karl-Friedrich Merten (1905‚Äď1993), U-boat commander
* MaŇāgorzata Musierowicz (born 1945), novelist
* Andrzej Niegolewski (1787‚Äď1857), colonel
* WŇāadysŇāaw Niegolewski (1814‚Äď1880), politician
* Grzegorz Nowak (conductor), Grzegorz Nowak (born 1951), conductor
* WŇāadysŇāaw OleszczyŇĄski (1809‚Äď1866), sculptor
* Catherine OpaliŇĄska (1680‚Äď1747), Queen consort of Poland, Grand Duchess consort of Lithuania
* Lilli Palmer (1914‚Äď1986), actress
* Janusz PaŇāubicki (born 1948), politician
* Kazimierz Piwarski, (1903‚Äď1968), historian
* Gustaw Potworowski, (1800‚Äď1860), activist
* Ignacy Posadzy, (1898‚Äď1984), priest
* Edward RaczyŇĄski (1786‚Äď1845), Edward RaczyŇĄski (1786‚Äď1845), politician
* Cyryl Ratajski (1875‚Äď1942), mayor of PoznaŇĄ
* Antoni RadziwiŇāŇā (1775‚Äď1833), aristocrat
* Marian Rejewski (1905‚Äď1980), cryptoanalist, Enigma codemachine codebreaker
* Richard Rothe (1799‚Äď1867), Lutheran theologian.
* Marcin RoŇľek (1885‚Äď1944), sculptor and painter
* Jerzy R√≥Ňľycki (1909‚Äď1942), cryptoanalist, Enigma codemachine codebreaker
* Dame Elisabeth Schwarzkopf (1915‚Äď2006), operatic and concert lyric soprano, born in Jarocin
* MichaŇā Sczaniecki (1910‚Äď1977), historian
* Urszula Sipinska (born 1947), singer-songwriter, pianist and architect
* Bohdan SmoleŇĄ (born 1947), comedian and actor
* J√≥zef StruŇõ (1510‚Äď1568), scientist and mayor of PoznaŇĄ
* Sir PaweŇā Edmund Strzelecki (1797‚Äď1873), Polish explorer and geologist
* Anna Suszczynska (1877-1931), composer
* RafaŇā SzukaŇāa (born 1971), butterfly swimmer
* Jan SzymaŇĄski (speed skater), Jan SzymaŇĄski (born 1989), speed skater and Olympic medalist
* MirosŇāaw Szymkowiak (born 1976) football player
* Jerzy Topolski (1928‚Äď1998), historian
* Lech Trzeciakowski (1931‚Äď2017), historian
* Jorge Veytia (born 1981), jurist
* Hubert Wagner (1941‚Äď2002), volleyball player and head coach of Poland men's national volleyball team
* Jan Wńôglarz (born 1947), computer scientist
* Leon Wegner (1824‚Äď1873), economist
* Roman Wilhelmi (1936‚Äď1991), actor
* Ray Wilson (musician), Ray Wilson (born 1968), former vocalist of Genesis (band), Genesis
* Tommy Wiseau (born 1955), director, script writer, movie maker, and actor, speculated to be born here
* Zygmunt Wojciechowski, (1900‚Äď1955), historian and founder of the Western Institute
* Anna Wolff-Powńôska (born 1941), historian
* Barbara Maria Zakrzewska-Nikiporczyk (born 1946), composer
* Maciej Zaremba (born 1951), a Swedish journalist
* Szymon Zi√≥Ňākowski (born 1976), hammer thrower, Olympic champion
* Henryk Zygalski (1906‚Äď1978), cryptoanalist, Enigma codemachine codebreaker
See also
* Tourism in Poland * History of Poland * Royal coronations in Poland including in PoznaŇĄ cathedral * PoznaŇĄ Fortress * The PoznaŇĄ * 15th PoznaŇĄ Uhlans RegimentNotes
References
Bibliography
* Frieder Monzer: ''Posen, Thorn, Bromberg (mit Gro√üpolen, Kujawien und S√ľdostpommern)'', Trescher Reisef√ľhrer, Berlin 2011 * Gotthold Rhode: ''Geschichte der Stadt Posen'', Neuendettelsau 1953 * Collective work, ''PoznaŇĄ. Dzieje, ludzie kultura'', PoznaŇĄ 1953 * Robert Alvis, ''Religion and the Rise of Nationalism: A Profile of an East-Central European City'', Syracuse University Press, Syracuse 2005 * K. Malinowski (red.), ''Dziesińôńá wiek√≥w Poznania (in three volumes)'', PoznaŇĄ 1956 * Collective work, ''PoznaŇĄ'', PoznaŇĄ 1958 * Collective work, ''PoznaŇĄ. Zarys historii'', PoznaŇĄ 1963 * Cz. ŇĀuczak, ''ŇĽycie spoŇāeczno-gospodarcze w Poznaniu 1815‚Äď1918'', PoznaŇĄ 1965 * J. Topolski (red.), ''PoznaŇĄ. Zarys dziej√≥w'', PoznaŇĄ 1973 * Zygmunt Boras, ''KsińÖŇľńôta Piastowscy Wielkopolski'', Wydawnictwo PoznaŇĄskie, PoznaŇĄ 1983 * Jerzy Topolski (red.), ''Dzieje Poznania'', Wydawnictwo PWN, Warszawa, PoznaŇĄ 1988 * Alfred Kaniecki, ''Dzieje miasta wodńÖ pisane'', Wydawnictwo Aquarius, PoznaŇĄ 1993 * Witold Maisel (red.), ''Przywileje miasta Poznania XIII-XVIII wieku. Privilegia civitatis Posnaniensis saeculorum XIII-XVIII''. WŇāadze Miasta Poznania, PoznaŇĄskie Towarzystwo Przyjaci√≥Ňā Nauk, Wydawnictwa ŇĽr√≥dŇāowe Komisji Historycznej, Tom XXIV, Wydawnictwo PTPN, PoznaŇĄ 1994 * Wojciech Stankowski, ''Wielkopolska'', Wydawnictwo WSiP, Warszawa 1999External links
*Official website of the City
{{DEFAULTSORT:Poznan PoznaŇĄ, Cities and towns in Greater Poland Voivodeship City counties of Poland Former capitals of Poland Populated places established in the 8th century PoznaŇĄ Voivodeship (1921‚Äď1939) Magdeburg rights 8th-century establishments in Europe Holocaust locations in Poland Nazi war crimes in Poland