Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pathology is the study of the
 The study of pathology, including the detailed examination of the body, including dissection and inquiry into specific maladies, dates back to antiquity. Rudimentary understanding of many conditions was present in most early societies and is attested to in the records of the earliest
The study of pathology, including the detailed examination of the body, including dissection and inquiry into specific maladies, dates back to antiquity. Rudimentary understanding of many conditions was present in most early societies and is attested to in the records of the earliest
 The modern practice of pathology is divided into a number of subdisciplines within the discrete but deeply interconnected aims of biological research and
The modern practice of pathology is divided into a number of subdisciplines within the discrete but deeply interconnected aims of biological research and
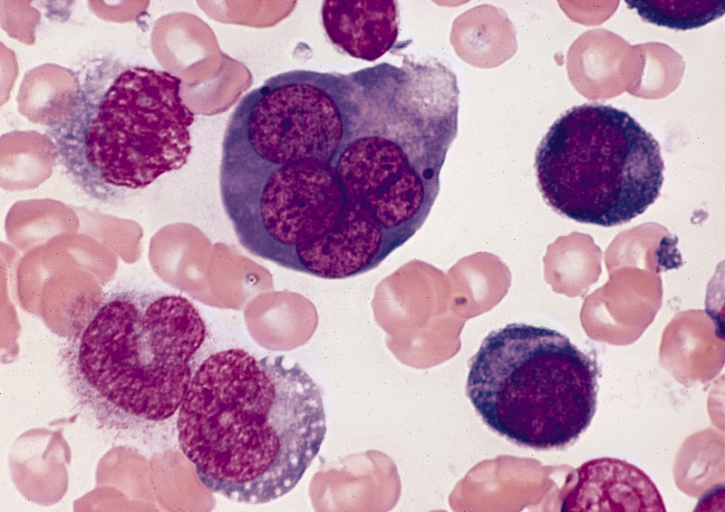 Cytopathology (sometimes referred to as "cytology") is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. It is usually used to aid in the diagnosis of cancer, but also helps in the diagnosis of certain infectious diseases and other inflammatory conditions as well as thyroid lesions, diseases involving sterile body cavities (peritoneal, pleural, and cerebrospinal), and a wide range of other body sites. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments (in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues) and cytopathologic tests are sometimes called smear tests because the samples may be smeared across a glass microscope slide for subsequent staining and microscopic examination. However, cytology samples may be prepared in other ways, including
Cytopathology (sometimes referred to as "cytology") is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. It is usually used to aid in the diagnosis of cancer, but also helps in the diagnosis of certain infectious diseases and other inflammatory conditions as well as thyroid lesions, diseases involving sterile body cavities (peritoneal, pleural, and cerebrospinal), and a wide range of other body sites. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments (in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues) and cytopathologic tests are sometimes called smear tests because the samples may be smeared across a glass microscope slide for subsequent staining and microscopic examination. However, cytology samples may be prepared in other ways, including
 Dermatopathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that focuses on the skin and the rest of the
Dermatopathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that focuses on the skin and the rest of the
 Forensic pathology focuses on determining the cause of death by
Forensic pathology focuses on determining the cause of death by
 Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of various forms of
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of various forms of
 Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either surgical biopsies or sometimes whole brains in the case of autopsy. Neuropathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology,
Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either surgical biopsies or sometimes whole brains in the case of autopsy. Neuropathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology,
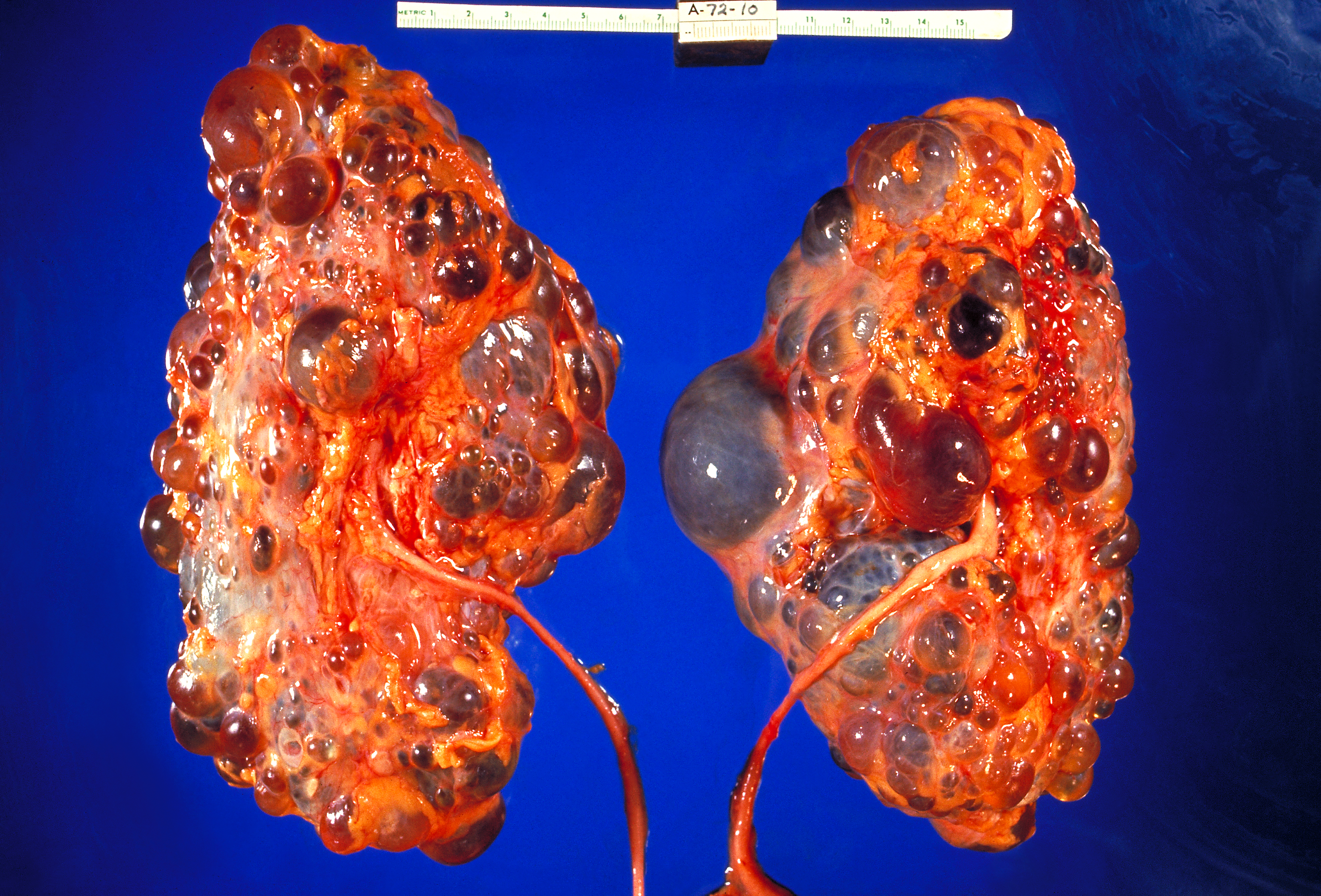 Renal pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that deals with the diagnosis and characterization of disease of the
Renal pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that deals with the diagnosis and characterization of disease of the
 Surgical pathology is one of the primary areas of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves the gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and non-surgeons such as general internists, medical subspecialists,
Surgical pathology is one of the primary areas of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves the gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and non-surgeons such as general internists, medical subspecialists,
 Hematopathology is the study of diseases of blood cells (including constituents such as
Hematopathology is the study of diseases of blood cells (including constituents such as
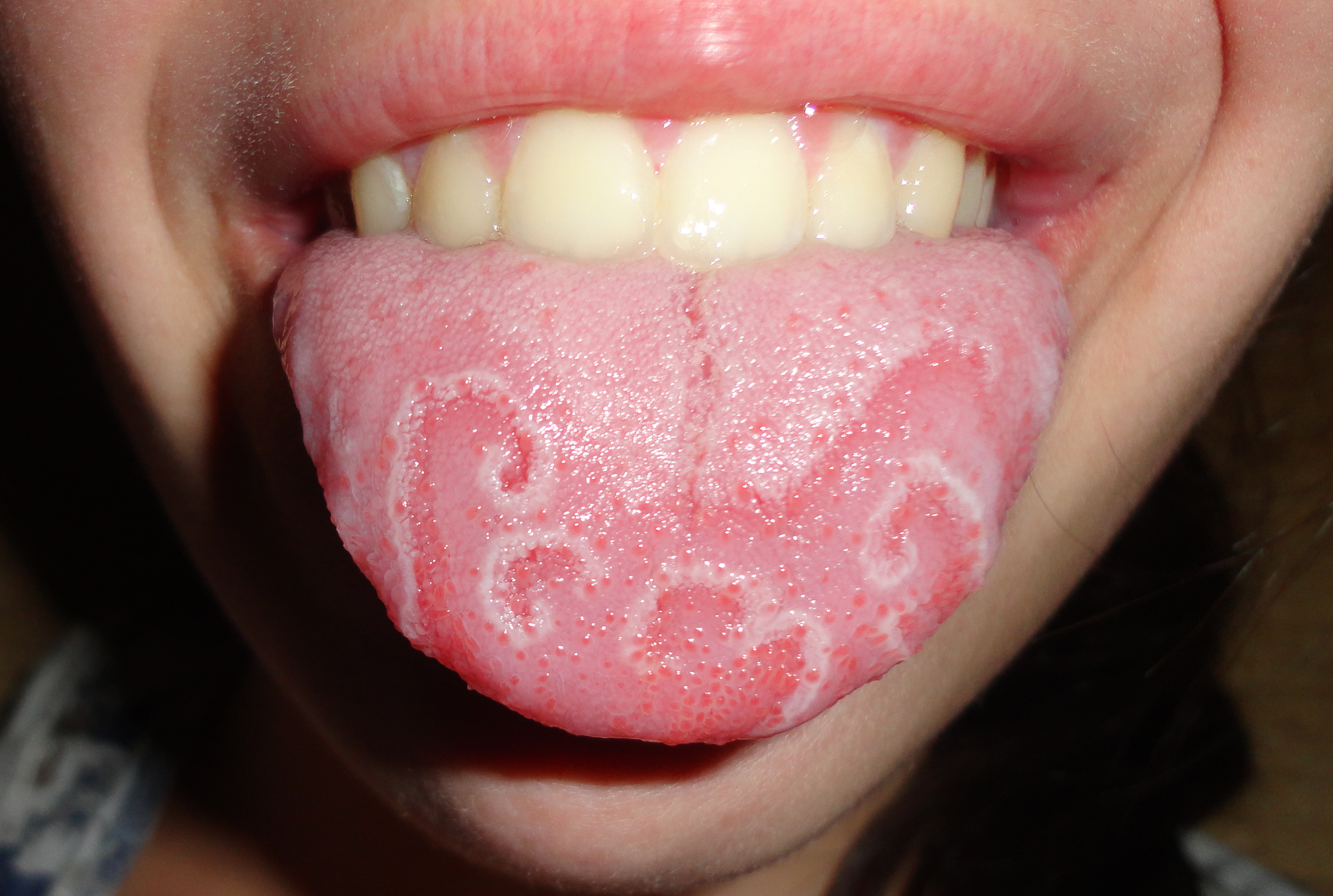 Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology is one of nine dental specialties recognized by the
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology is one of nine dental specialties recognized by the
 Becoming a pathologist generally requires specialty-training after
Becoming a pathologist generally requires specialty-training after
Moving towards ICD-11 and DSM-5: Concept and evolution of psychiatric classification.
Indian Journal of Psychiatry, Volume 51, Issue 4, Page 310-319.—the field is also heavily, and increasingly, informed upon by
 Although the vast majority of lab work and research in pathology concerns the development of disease in humans, pathology is of significance throughout the biological sciences. Two main catch-all fields exist to represent most complex organisms capable of serving as host to a pathogen or other form of disease: veterinary pathology (concerned with all non-human species of
Although the vast majority of lab work and research in pathology concerns the development of disease in humans, pathology is of significance throughout the biological sciences. Two main catch-all fields exist to represent most complex organisms capable of serving as host to a pathogen or other form of disease: veterinary pathology (concerned with all non-human species of

American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP)American Society for Investigative Pathology (ASIP) Pathpedia online pathology resource
Comprehensive pathology website with numerous resources.
College of American Pathologistshumpath.com
(Atlas in Human Pathology)
Intersociety Council for Pathology Training (ICPI)Pathological Society of Great Britain and IrelandRoyal College of Pathologists (UK)Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia (Australia & Oceania)United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology
* ttp://atlases.muni.cz Atlases: High Resolution Pathology Images {{Authority control Branches of biology
causes Causes, or causality, is the relationship between one event and another. It may also refer to:
* Causes (band), an indie band based in the Netherlands
* Causes (company)
Causes.com is a civic-technology app and website that enables users to orga ...
and effects of disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
or injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (paediatrics), cancer (oncology), ...
that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
, and body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total Human body weight, body weight; it is usually slightly lower ...
samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They ar ...
''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
) and psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
conditions (such as psychopathy
Psychopathy, sometimes considered synonymous with sociopathy, is characterized by persistent Anti-social behaviour, antisocial behavior, impaired empathy and remorse, and Boldness, bold, Disinhibition, disinhibited, and Egotism, egotistical B ...
). A physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
practicing pathology is called a ''pathologist''.
As a field of general inquiry and research, pathology addresses components of disease: cause, mechanisms of development (pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
), structural alterations of cells (morphologic changes), and the consequences of changes (clinical manifestations). In common medical practice, general pathology is mostly concerned with analyzing known clinical abnormalities that are markers or precursors for both infectious
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
and non-infectious disease, and is conducted by experts in one of two major specialties, anatomical pathology
Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or Anatomic pathology (''U.S.'') is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination ...
and clinical pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, ...
. Further divisions in specialty exist on the basis of the involved sample types (comparing, for example, cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , '' -logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1 ...
, hematopathology
Hematopathology or hemopathology (both also spelled haem-, see spelling differences) is the study of diseases and disorders affecting and found in blood cells, their production, and any organs and tissues involved in hematopoiesis, such as bone m ...
, and histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
), organs (as in renal pathology
Renal pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that deals with the diagnosis and characterization of medical diseases (non-tumor) of the kidneys. In the academic setting, renal pathologists work closely with nephrologists and transplant ...
), and physiological systems (oral pathology
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth ("oral cavity" or "stoma"), jaws ("maxillae" or "gnath") and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin (the skin arou ...
), as well as on the basis of the focus of the examination (as with forensic pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases an ...
).
Pathology is a significant field in modern medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information re ...
and medical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called ''bench science'' or ''bench research''), – involving fundamental scientif ...
.
History
 The study of pathology, including the detailed examination of the body, including dissection and inquiry into specific maladies, dates back to antiquity. Rudimentary understanding of many conditions was present in most early societies and is attested to in the records of the earliest
The study of pathology, including the detailed examination of the body, including dissection and inquiry into specific maladies, dates back to antiquity. Rudimentary understanding of many conditions was present in most early societies and is attested to in the records of the earliest historical societies
This is a partial List of historical and heritage societies from around the world. The sections provided are not mutually exclusive. Many historical societies websites are their museums' websites. List is organized by location and later by special ...
, including those of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. By the Hellenic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 ...
of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, a concerted causal study of disease was underway (see Medicine in ancient Greece
Ancient Greek medicine was a compilation of theories and practices that were constantly expanding through new ideologies and trials. Many components were considered in ancient Greek medicine, intertwining the spiritual with the physical. Specifi ...
), with many notable early physicians (such as Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
, for whom the modern Hippocratic Oath
The Hippocratic Oath is an oath of ethics historically taken by physicians. It is one of the most widely known of Greek medical texts. In its original form, it requires a new physician to swear, by a number of healing gods, to uphold specific e ...
is named) having developed methods of diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
and prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
for a number of diseases. The medical practices of the Romans and those of the Byzantines continued from these Greek roots, but, as with many areas of scientific inquiry, growth in understanding of medicine stagnated some after the Classical Era
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, but continued to slowly develop throughout numerous cultures. Notably, many advances were made in the medieval era of Islam (see Medicine in medieval Islam
In the history of medicine, "Islamic medicine" is the science of medicine developed in the Middle East, and usually written in Arabic, the '' lingua franca'' of Islamic civilization.
Islamic medicine adopted, systematized and developed the med ...
), during which numerous texts of complex pathologies were developed, also based on the Greek tradition. Even so, growth in complex understanding of disease mostly languished until knowledge and experimentation again began to proliferate in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, Enlightenment, and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
eras, following the resurgence of the empirical method at new centers of scholarship. By the 17th century, the study of rudimentary microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
was underway and examination of tissues had led British Royal Society member Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
to coin the word "cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
", setting the stage for later germ theory
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
.
Modern pathology began to develop as a distinct field of inquiry during the 19th Century through natural philosophers
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
and physicians that studied disease and the informal study of what they termed "pathological anatomy" or "morbid anatomy". However, pathology as a formal area of specialty was not fully developed until the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with the advent of detailed study of microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, prot ...
. In the 19th century, physicians had begun to understand that disease-causing pathogens, or "germs" (a catch-all for disease-causing, or pathogenic, microbes, such as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, amoebae
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopo ...
, molds, protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s, and prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It ...
s) existed and were capable of reproduction and multiplication, replacing earlier beliefs in humors
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
or even spiritual agents, that had dominated for much of the previous 1,500 years in European medicine. With the new understanding of causative agents, physicians began to compare the characteristics of one germ's symptoms as they developed within an affected individual to another germ's characteristics and symptoms. This approach led to the foundational understanding that diseases are able to replicate themselves, and that they can have many profound and varied effects on the human host. To determine causes of diseases, medical experts used the most common and widely accepted assumptions or symptoms of their times, a general principal of approach that persists into modern medicine.
Modern medicine was particularly advanced by further developments of the microscope to analyze tissues, to which Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
gave a significant contribution, leading to a slew of research developments.
By the late 1920s to early 1930s pathology was deemed a medical specialty. Combined with developments in the understanding of general physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
, by the beginning of the 20th century, the study of pathology had begun to split into a number of distinct fields, resulting in the development of a large number of modern specialties within pathology and related disciplines of diagnostic medicine
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information re ...
.
Etymology
The terms ''pathology'' comes from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
roots of ''pathos'' (), meaning "experience" or "suffering" and ''-logia
''-logy'' is a suffix in the English language, used with words originally adapted from Ancient Greek ending in ('). The earliest English examples were anglicizations of the French '' -logie'', which was in turn inherited from the Latin '' -logi ...
'' (), "study of". The Latin term is of early sixteenth-century origin and became increasingly popularized after the 1530s.
General pathology
 The modern practice of pathology is divided into a number of subdisciplines within the discrete but deeply interconnected aims of biological research and
The modern practice of pathology is divided into a number of subdisciplines within the discrete but deeply interconnected aims of biological research and medical practice
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
. Biomedical research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called ''bench science'' or ''bench research''), – involving fundamental scientif ...
into disease incorporates the work of a vast variety of life science specialists, whereas, in most parts of the world, to be licensed
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
to practice pathology as a medical specialty, one has to complete medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
and secure a license to practice medicine. Structurally, the study of disease is divided into many different fields that study or diagnose markers for disease using methods and technologies particular to specific scales, organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a f ...
, and tissue types. The information in this section mostly concerns pathology as it regards common medical practice in these systems, but each of these specialties is also the subject of voluminous pathology research as regards the disease pathways of specific pathogens and disorders that affect the tissues of these discrete organs or structures.
Anatomical pathology
Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or anatomic pathology (''United States'') is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the gross,microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens (optics), lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded a ...
, chemical, immunologic and molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
examination of organs, tissues, and whole bodies (as in a general examination or an autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any di ...
). Anatomical pathology is itself divided into subfields, the main divisions being surgical pathology
Surgical pathology is the most significant and time-consuming area of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and ...
, cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , '' -logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1 ...
, and forensic pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases an ...
. Anatomical pathology is one of two main divisions of the medical practice of pathology, the other being clinical pathology, the diagnosis of disease through the laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
analysis of bodily fluids and tissues. Sometimes, pathologists practice both anatomical and clinical pathology, a combination known as general pathology.
Cytopathology
 Cytopathology (sometimes referred to as "cytology") is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. It is usually used to aid in the diagnosis of cancer, but also helps in the diagnosis of certain infectious diseases and other inflammatory conditions as well as thyroid lesions, diseases involving sterile body cavities (peritoneal, pleural, and cerebrospinal), and a wide range of other body sites. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments (in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues) and cytopathologic tests are sometimes called smear tests because the samples may be smeared across a glass microscope slide for subsequent staining and microscopic examination. However, cytology samples may be prepared in other ways, including
Cytopathology (sometimes referred to as "cytology") is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. It is usually used to aid in the diagnosis of cancer, but also helps in the diagnosis of certain infectious diseases and other inflammatory conditions as well as thyroid lesions, diseases involving sterile body cavities (peritoneal, pleural, and cerebrospinal), and a wide range of other body sites. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments (in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues) and cytopathologic tests are sometimes called smear tests because the samples may be smeared across a glass microscope slide for subsequent staining and microscopic examination. However, cytology samples may be prepared in other ways, including cytocentrifugation
A cytocentrifuge, sometimes referred to as a cytospin, is a specialized centrifuge used to concentrate cells in fluid specimens onto a microscope slide so that they can be stained and examined. Cytocentrifuges are used in various areas of the clin ...
.
Dermatopathology
 Dermatopathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that focuses on the skin and the rest of the
Dermatopathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that focuses on the skin and the rest of the integumentary system
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves ...
as an organ. It is unique, in that there are two paths a physician can take to obtain the specialization. All general pathologists and general dermatologists train in the pathology of the skin, so the term dermatopathologist denotes either of these who has reached a certainly level of accreditation and experience; in the US, either a general pathologist or a dermatologist
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
can undergo a 1 to 2 year fellowship in the field of dermatopathology. The completion of this fellowship allows one to take a subspecialty board examination, and becomes a board certified dermatopathologist. Dermatologists are able to recognize most skin diseases based on their appearances, anatomic distributions, and behavior. Sometimes, however, those criteria do not lead to a conclusive diagnosis, and a skin biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. ...
is taken to be examined under the microscope using usual histological tests. In some cases, additional specialized testing needs to be performed on biopsies, including immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specif ...
, immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flo ...
, and molecular-pathologic analysis. One of the greatest challenges of dermatopathology is its scope. More than 1500 different disorders of the skin exist, including cutaneous eruptions ("rashes
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cra ...
") and neoplasms
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
. Therefore, dermatopathologists must maintain a broad base of knowledge in clinical dermatology, and be familiar with several other specialty areas in Medicine.
Forensic pathology
 Forensic pathology focuses on determining the cause of death by
Forensic pathology focuses on determining the cause of death by post-mortem examination
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any dis ...
of a corpse or partial remains. An autopsy is typically performed by a coroner or medical examiner, often during criminal investigations; in this role, coroner
A coroner is a government or judicial official who is empowered to conduct or order an inquest into Manner of death, the manner or cause of death, and to investigate or confirm the identity of an unknown person who has been found dead within th ...
s and medical examiners are also frequently asked to confirm the identity of a corpse. The requirements for becoming a licensed practitioner of forensic pathology varies from country to country (and even within a given nation) but typically a minimal requirement is a medical doctorate
Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated M.D., from the Latin ''Medicinae Doctor'') is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. T ...
with a specialty in general or anatomical pathology with subsequent study in forensic medicine. The methods forensic scientists use to determine death include examination of tissue specimens to identify the presence or absence of natural disease and other microscopic findings, interpretations of toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating expo ...
on body tissues and fluids to determine the chemical cause of overdoses, poisonings or other cases involving toxic agents, and examinations of physical trauma
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, ...
. Forensic pathology is a major component in the trans-disciplinary field of forensic science
Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and criminal ...
.
Histopathology
 Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of various forms of
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of various forms of human tissue
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are ...
. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. This contrasts with the methods of cytopathology, which uses free cells or tissue fragments. Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
, biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body of an organism and then placed in a fixative that stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is formalin
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Fo ...
, although frozen section
The frozen section procedure is a pathological laboratory procedure to perform rapid microscopic analysis of a specimen. It is used most often in oncological surgery. The technical name for this procedure is cryosection. The microtome device tha ...
fixing is also common. To see the tissue under a microscope, the sections are stained with one or more pigments. The aim of staining is to reveal cellular components; counterstains are used to provide contrast. Histochemistry refers to the science of using chemical reactions between laboratory chemicals and components within tissue. The histological slides are then interpreted diagnostically and the resulting pathology report describes the histological findings and the opinion of the pathologist. In the case of cancer, this represents the tissue diagnosis required for most treatment protocols.
Neuropathology
 Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either surgical biopsies or sometimes whole brains in the case of autopsy. Neuropathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology,
Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either surgical biopsies or sometimes whole brains in the case of autopsy. Neuropathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology, neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of co ...
, and neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peri ...
. In many English-speaking countries, neuropathology is considered a subfield of anatomical pathology. A physician who specializes in neuropathology, usually by completing a fellowship after a residency in anatomical or general pathology, is called a neuropathologist. In day-to-day clinical practice, a neuropathologist is a consultant for other physicians. If a disease of the nervous system is suspected, and the diagnosis cannot be made by less invasive methods, a biopsy of nervous tissue is taken from the brain or spinal cord to aid in diagnosis. Biopsy is usually requested after a mass is detected by medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
. With autopsies, the principal work of the neuropathologist is to help in the post-mortem diagnosis of various conditions that affect the central nervous system. Biopsies can also consist of the skin. Epidermal nerve fiber density testing (ENFD) is a more recently developed neuropathology test in which a punch skin biopsy is taken to identify small fiber neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
by analyzing the nerve fibers of the skin. This test is becoming available in select labs as well as many universities; it replaces the traditional nerve biopsy test as less invasive.
Pulmonary pathology
Pulmonary pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic (and especially surgical) pathology that deals with diagnosis and characterization ofneoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
and non-neoplastic diseases of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s and thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
pleura
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls.
The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips bet ...
. Diagnostic specimens are often obtained via bronchoscopic
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopy, endoscopic medical procedure, technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, o ...
transbronchial biopsy, CT-guided percutaneous biopsy, or video-assisted thoracic surgery. These tests can be necessary to diagnose between infection, inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
, or fibrotic
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
conditions.
Renal pathology
 Renal pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that deals with the diagnosis and characterization of disease of the
Renal pathology is a subspecialty of anatomic pathology that deals with the diagnosis and characterization of disease of the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
s. In a medical setting, renal pathologists work closely with nephrologists
Nephrology (from Greek'' nephros'' "kidney", combined with the suffix ''-logy'', "the study of") is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (ren ...
and transplant surgeons
Transplant or Transplantation may refer to:
Sciences
*Transplanting a plant from one location to another
*Organ transplantation, moving an organ from one body to another
*Transplant thought experiment, an experiment similar to Trolley problem
*Tra ...
, who typically obtain diagnostic specimens via percutaneous renal biopsy. The renal pathologist must synthesize findings from traditional microscope histology, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, and immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specif ...
to obtain a definitive diagnosis. Medical renal diseases may affect the glomerulus
''Glomerulus'' () is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn".
''Glomerulus'' may refer to:
* the filter ...
, the tubules
In biology, a tubule is a general term referring to small tube or similar type of structure. Specifically, tubule can refer to:
* a small tube or fistular structure
* a minute tube lined with glandular epithelium
* any hollow cylindrical body stru ...
and interstitium
The interstitium is a contiguous fluid-filled space existing between a structural barrier, such as a cell membrane or the skin, and internal structures, such as organs, including muscles and the circulatory system. The fluid in this space is cal ...
, the vessels, or a combination of these compartments.
Surgical pathology
 Surgical pathology is one of the primary areas of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves the gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and non-surgeons such as general internists, medical subspecialists,
Surgical pathology is one of the primary areas of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves the gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and non-surgeons such as general internists, medical subspecialists, dermatologists
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
, and interventional radiologists
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
. Often an excised tissue sample
In medicine, sampling is gathering of matter from the body to aid in the process of a medical diagnosis and/or evaluation of an indication for treatment, further medical tests or other procedures. In this sense, the sample is the gathered matter ...
is the best and most definitive evidence of disease (or lack thereof) in cases where tissue is surgically removed from a patient. These determinations are usually accomplished by a combination of gross (i.e., macroscopic) and histologic (i.e., microscopic) examination of the tissue, and may involve evaluations of molecular properties of the tissue by immunohistochemistry or other laboratory tests.
There are two major types of specimens submitted for surgical pathology analysis: biopsies and surgical resections. A biopsy is a small piece of tissue removed primarily for surgical pathology analysis, most often in order to render a definitive diagnosis. Types of biopsies include core biopsies, which are obtained through the use of large-bore needles, sometimes under the guidance of radiological techniques such as ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
, CT scan, or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
. Incisional biopsies are obtained through diagnostic surgical procedures that remove part of a suspicious lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
, whereas excisional biopsies remove the entire lesion, and are similar to therapeutic surgical resections. Excisional biopsies of skin lesions
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this sy ...
and gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
polyps
A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral (opposite to oral) end i ...
are very common. The pathologist's interpretation of a biopsy is critical to establishing the diagnosis of a benign or malignant tumor, and can differentiate between different types and grades of cancer, as well as determining the activity of specific molecular pathways in the tumor. Surgical resection specimens are obtained by the therapeutic surgical removal of an entire diseased area or organ (and occasionally multiple organs). These procedures are often intended as definitive surgical treatment of a disease in which the diagnosis is already known or strongly suspected, but pathological analysis of these specimens remains important in confirming the previous diagnosis.
Clinical pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on thelaboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
analysis of bodily fluids such as blood and urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excretion, excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cel ...
, as well as tissues, using the tools of chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, clinical microbiology
Medical microbiology, the large subset of microbiology that is applied to medicine, is a branch of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. In addition, this field of science studies various ...
, hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the produc ...
and molecular pathology. Clinical pathologists work in close collaboration with medical technologist
A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) or clinical laboratory scientist (CLS) or medical technologist (MT) performs diagnostic testing of blood and body fluids in clinical laboratories. The scope of a medical laboratory scientist's work begins wit ...
s, hospital administrations, and referring physicians. Clinical pathologists learn to administer a number of visual and microscopic tests and an especially large variety of tests of the biophysical
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Bi ...
properties of tissue samples involving automated analyser An automated analyser is a medical laboratory instrument designed to measure different chemicals and other characteristics in a number of biological samples quickly, with minimal human assistance. These measured properties of blood and other fluids ...
s and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
s. Sometimes the general term "laboratory medicine specialist" is used to refer to those working in clinical pathology, including medical doctors, Ph.D.s and doctors of pharmacology. Immunopathology Immunopathology is a branch of medicine that deals with immune responses associated with disease. It includes the study of the pathology of an organism, organ system, or disease with respect to the immune system, immunity, and immune responses. In ...
, the study of an organism's immune response to infection, is sometimes considered to fall within the domain of clinical pathology.
Hematopathology
 Hematopathology is the study of diseases of blood cells (including constituents such as
Hematopathology is the study of diseases of blood cells (including constituents such as white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
, red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek language, Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''k ...
, and platelets
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
) and the tissues, and organs comprising
the hematopoietic system. The term hematopoietic system refers to tissues and organs that produce and/or primarily host hematopoietic cells and includes bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
, the lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
, thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
, spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, and other lymphoid tissues. In the United States, hematopathology is a board certified subspecialty (licensed under the American Board of Pathology) practiced by those physicians who have completed a general pathology residency (anatomic, clinical, or combined) and an additional year of fellowship training in hematology. The hematopathologist reviews biopsies of lymph nodes, bone marrows and other tissues involved by an infiltrate of cells of the hematopoietic system. In addition, the hematopathologist may be in charge of flow cytometric and/or molecular hematopathology studies.
Molecular pathology
Molecular pathology is focused upon the study and diagnosis of disease through the examination of molecules within organs, tissues orbodily fluids
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the human body. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52-55%). ...
. Molecular pathology is multidisciplinary by nature and shares some aspects of practice with both anatomic pathology and clinical pathology, molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In ...
and genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
. It is often applied in a context that is as much scientific as directly medical and encompasses the development of molecular and genetic approaches to the diagnosis and classification of human diseases, the design and validation of predictive biomarkers for treatment response and disease progression, and the susceptibility of individuals of different genetic constitution to particular disorders. The crossover between molecular pathology and epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
is represented by a related field "molecular pathological epidemiology Molecular pathological epidemiology (MPE, also molecular pathologic epidemiology) is a discipline combining epidemiology and pathology. It is defined as "epidemiology of molecular pathology and heterogeneity of disease". Pathology and epidemiology s ...
". Molecular pathology is commonly used in diagnosis of cancer and infectious diseases. Molecular Pathology is primarily used to detect cancers such as melanoma, brainstem glioma, brain tumors as well as many other types of cancer and infectious diseases. Techniques are numerous but include quantitative polymerase chain reaction
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real ...
(qPCR), multiplex PCR Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (Multiplex PCR) refers to the use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify several different DNA sequences simultaneously (as if performing many separate PCR reactions all together in one reaction). This process ...
, DNA microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to ...
, in situ hybridization
''In situ'' hybridization (ISH) is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acids strand (i.e., probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (''in situ'') or ...
, DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Th ...
, antibody-based immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specif ...
tissue assays, molecular profiling of pathogens, and analysis of bacterial genes for antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
. Techniques used are based on analyzing samples of DNA and RNA. Pathology is widely used for gene therapy and disease diagnosis.
Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology is one of nine dental specialties recognized by the
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology is one of nine dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association
The American Dental Association (ADA) is an American professional association established in 1859 which has more than 161,000 members. Based in the American Dental Association Building in the Near North Side of Chicago, the ADA is the world's ...
, and is sometimes considered a specialty of both dentistry and pathology. Oral Pathologists must complete three years of post doctoral training in an accredited program and subsequently obtain diplomate status from the American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. The specialty focuses on the diagnosis, clinical management and investigation of diseases that affect the oral cavity and surrounding maxillofacial structures including but not limited to odontogenic
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stag ...
, infectious, epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
, salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary gla ...
, bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
and soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
pathologies. It also significantly intersects with the field of dental pathology
Tooth pathology is any condition of the tooth, teeth that can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes a congenital tooth diseases are called ''tooth abnormalities''. These are among the most common diseases in humans The preventive medicine, preventi ...
. Although concerned with a broad variety of diseases of the oral cavity, they have roles distinct from otorhinolaryngologists ("ear, nose, and throat" specialists), and speech pathologists, the latter of which helps diagnose many neurological or neuromuscular
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation t ...
conditions relevant to speech phonology or swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing i ...
. Owing to the availability of the oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
to non-invasive examination, many conditions in the study of oral disease can be diagnosed, or at least suspected, from gross examination, but biopsies, cell smears, and other tissue analysis remain important diagnostic tools in oral pathology.
Medical training and accreditation
 Becoming a pathologist generally requires specialty-training after
Becoming a pathologist generally requires specialty-training after medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
, but individual nations vary some in the medical licensing
A medical license is an occupational license that permits a person to legally practice medicine. In most countries, a person must have a medical license bestowed either by a specified government-approved professional association or a governm ...
required of pathologists. In the United States, pathologists are physicians (D.O.
Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO or D.O., or in Australia DO USA) is a medical degree conferred by the 38 osteopathic medical schools in the United States. DO and Doctor of Medicine (MD) degrees are equivalent: a DO graduate may become licens ...
or M.D.
Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated M.D., from the Latin ''Medicinae Doctor'') is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. T ...
) who have completed a four-year undergraduate program, four years of medical school training, and three to four years of postgraduate training in the form of a pathology residency
Residency may refer to:
* Domicile (law), the act of establishing or maintaining a residence in a given place
** Permanent residency, indefinite residence within a country despite not having citizenship
* Residency (medicine), a stage of postgrad ...
. Training may be within two primary specialties, as recognized by the American Board of Pathology: anatomical pathology
Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or Anatomic pathology (''U.S.'') is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination ...
and clinical Pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, ...
, each of which requires separate board certification. The American Osteopathic Board of Pathology
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
also recognizes four primary specialties: anatomic pathology, dermatopathology, forensic pathology, and laboratory medicine
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical labor ...
. Pathologists may pursue specialised fellowship training within one or more subspecialties of either anatomical or clinical pathology. Some of these subspecialties permit additional board certification, while others do not.
In the United Kingdom, pathologists are physicians licensed by the UK General Medical Council
The General Medical Council (GMC) is a public body that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within the United Kingdom. Its chief responsibility is to "protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public" by c ...
. The training to become a pathologist is under the oversight of the Royal College of Pathologists
The Royal College of Pathologists (RCPath) is a professional membership organisation.
Its main function is the overseeing of postgraduate training, and its Fellowship Examination (FRCPath) is recognised as the standard assessment of fitness to pr ...
. After four to six years of undergraduate medical study, trainees proceed to a two-year foundation program. Full-time training in histopathology currently lasts between five and five and a half years and includes specialist training in surgical pathology, cytopathology, and autopsy pathology. It is also possible to take a Royal College of Pathologists
The Royal College of Pathologists (RCPath) is a professional membership organisation.
Its main function is the overseeing of postgraduate training, and its Fellowship Examination (FRCPath) is recognised as the standard assessment of fitness to pr ...
diploma in forensic pathology, dermatopathology, or cytopathology, recognising additional specialist training and expertise and to get specialist accreditation in forensic pathology, pediatric pathology Pediatric pathology is the sub-specialty of surgical pathology which deals with the diagnosis and characterization of neoplastic and non-neoplastic diseases of children. The duties of pediatric pathologists can be divided into two categories: the ex ...
, and neuropathology. All postgraduate medical training and education in the UK is overseen by the General Medical Council.
In France, pathology is separated into two distinct specialties, anatomical pathology, and clinical pathology. Residencies for both lasts four years. Residency in anatomical pathology is open to physicians only, while clinical pathology is open to both physicians and pharmacist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
s. At the end of the second year of clinical pathology residency, residents can choose between general clinical pathology and a specialization in one of the disciplines, but they can not practice anatomical pathology, nor can anatomical pathology residents practice clinical pathology.
Overlap with other diagnostic medicine
Though separate fields in terms of medical practice, a number of areas of inquiry in medicine and medical science either overlap greatly with general pathology, work in tandem with it, or contribute significantly to the understanding of the pathology of a given disease or its course in an individual. As a significant portion of all general pathology practice is concerned withcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, the practice of oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
makes extensive use of both anatomical and clinical pathology in diagnosis and treatment. In particular, biopsy, resection, and blood tests are all examples of pathology work that is essential for the diagnoses of many kinds of cancer and for the staging
Staging may refer to:
Computing
* Staging (cloud computing), a process used to assemble, test, and review a new solution before it is moved into production and the existing solution is decommissioned
* Staging (data), intermediately storing data ...
of cancerous masses. In a similar fashion, the tissue and blood analysis techniques of general pathology are of central significance to the investigation of serious infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
and as such inform significantly upon the fields of epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
, etiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, e ...
, immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there ...
, and parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it fo ...
. General pathology methods are of great importance to biomedical research into disease, wherein they are sometimes referred to as "experimental" or "investigative" pathology.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
is the generating of visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging reveals details of internal
Internal may refer to:
*Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism
*''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016
...
physiology that help medical professionals plan appropriate treatments for tissue infection and trauma. Medical imaging is also central in supplying the biometric
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify in ...
data necessary to establish baseline features of anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
so as to increase the accuracy with which early or fine-detail abnormalities are detected. These diagnostic techniques are often performed in combination with general pathology procedures and are themselves often essential to developing new understanding of the pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
of a given disease and tracking the progress of disease in specific medical cases. Examples of important subdivisions in medical imaging include radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
(which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeut ...
) magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
, medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal ...
(or ultrasound), endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
, elastography
Elastography is any of a class of medical imaging modalities that map the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue.Sarvazyan A, Hall TJ, Urban MW, Fatemi M, Aglyamov SR, Garra BSOverview of elastography–an emerging branch of medical im ...
, tactile imaging
Elastography is any of a class of medical imaging modalities that map the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue.Sarvazyan A, Hall TJ, Urban MW, Fatemi M, Aglyamov SR, Garra BSOverview of elastography–an emerging branch of medical im ...
, thermography
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a Thermographic camera, thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are ...
, medical photography
Medical photography is a specialized area of photography that concerns itself with the documentation of the clinical presentation of patients, medical and surgical procedures, medical devices and specimens from autopsy. The practice requires a high ...
, nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting ...
and functional imaging
Functional imaging (or physiological imaging) is a medical imaging technique of detecting or measuring changes in metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption.
As opposed to structural imaging, functional imaging center ...
techniques such as positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bl ...
. Though they do not strictly relay images, readings from diagnostics tests involving electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
, magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (su ...
, and electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the hear ...
often give hints as to the state and function of certain tissues in the brain and heart respectively.
Psychopathology
Psychopathology is the study ofmental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
, particularly of severe disorders. Informed heavily by both psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries betwe ...
and neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of co ...
, its purpose is to classify mental illness, elucidate its underlying causes, and guide clinical psychiatric
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry.
Initial psy ...
treatment accordingly. Although diagnosis and classification of mental norms and disorders is largely the purview of psychiatry—the results of which are guidelines such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common langua ...
, which attempt to classify mental disease mostly on behavioural evidence, though not without controversyDalal PK, Sivakumar T. (2009Moving towards ICD-11 and DSM-5: Concept and evolution of psychiatric classification.
Indian Journal of Psychiatry, Volume 51, Issue 4, Page 310-319.—the field is also heavily, and increasingly, informed upon by
neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, development ...
and other of the biological cognitive sciences. Mental or social disorders or behaviours seen as generally unhealthy or excessive in a given individual, to the point where they cause harm or severe disruption to the person's lifestyle, are often called "pathological" (e.g., pathological gambling
Problem gambling or ludomania is repetitive gambling behavior despite harm and negative consequences. Problem gambling may be diagnosed as a mental disorder according to ''DSM-5'' if certain diagnostic criteria are met. Pathological gambling is ...
or pathological liar
Pathological lying, also known as ''mythomania'' and ''pseudologia fantastica'', is a chronic behavior in which the person habitually or compulsively lies. These lies often serve no obvious purpose other than to paint oneself as a hero or victi ...
).
Non-humans
 Although the vast majority of lab work and research in pathology concerns the development of disease in humans, pathology is of significance throughout the biological sciences. Two main catch-all fields exist to represent most complex organisms capable of serving as host to a pathogen or other form of disease: veterinary pathology (concerned with all non-human species of
Although the vast majority of lab work and research in pathology concerns the development of disease in humans, pathology is of significance throughout the biological sciences. Two main catch-all fields exist to represent most complex organisms capable of serving as host to a pathogen or other form of disease: veterinary pathology (concerned with all non-human species of kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
of Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
) and phytopathology
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomyc ...
, which studies disease in plants.
Veterinary pathology
Veterinary pathology covers a vast array of species, but with a significantly smaller number of practitioners, so understanding of disease in non-human animals, especially as regards veterinary practice, varies considerably by species. Nonetheless, significant amounts of pathology research are conducted on animals, for two primary reasons: 1) The origins of diseases are typicallyzoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. ...
in nature, and many infectious pathogens have animal vectors and, as such, understanding the mechanisms of action for these pathogens in non-human hosts is essential to the understanding and application of epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
and 2) those animals that share physiological and genetic traits with humans can be used as surrogates for the study of the disease and potential treatments as well as the effects of various synthetic products. For this reason, as well as their roles as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
and companion animals
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive appearances, intelligence, ...
, mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
generally have the largest body of research in veterinary pathology. Animal testing remains a controversial practice, even in cases where it is used to research treatment for human disease. As in human medical pathology, the practice of veterinary pathology is customarily divided into the two main fields of anatomical and clinical pathology.

Plant pathology
Although the pathogens and their mechanics differ greatly from those of animals, plants are subject to a wide variety of diseases, including those caused byfungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, oomycete
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the resul ...
s, bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
es, viroid
Viroids are small single-stranded, circular RNAs that are infectious pathogens. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms (flowering plants), and most cause diseases, whose respective economi ...
s, virus-like organisms, phytoplasma
Phytoplasmas are obligate intracellular parasites of plant phloem tissue and of the insect vectors that are involved in their plant-to-plant transmission. Phytoplasmas were discovered in 1967 by Japanese scientists who termed them mycoplasma-lik ...
s, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
, nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s and parasitic plant
A parasitic plant is a plant that derives some or all of its nutritional requirements from another living plant. They make up about 1% of angiosperms and are found in almost every biome. All parasitic plants develop a specialized organ called the ...
s. Damage caused by insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of j ...
, mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
s, vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
, and other small herbivores is not considered a part of the domain of plant pathology. The field is connected to plant disease epidemiology
Plant disease epidemiology is the study of disease in plant populations. Much like diseases of humans and other animals, plant diseases occur due to pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, oomycetes, nematodes, phytoplasmas, protozoa, and paras ...
and especially concerned with the horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
of species that are of high importance to the human diet
Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutrition ...
or other human utility.
See also
*Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
* Causal inference
Causal inference is the process of determining the independent, actual effect of a particular phenomenon that is a component of a larger system. The main difference between causal inference and inference of association is that causal inference ana ...
* Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients a ...
* Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
* Environmental pathology
* Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
* Etiology (medicine)
Cause, also known as etiology () and aetiology, is the reason or origination of something.
The word ''etiology'' is derived from the Greek , ''aitiologia'', "giving a reason for" (, ''aitia'', "cause"; and , '' -logia'').
Description
In medicine ...
* Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the produc ...
* Histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
* Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there ...
* List of pathologists
A list of people notable in the field of pathology.
A
* John Abercrombie, Scottish physician, neuropathologist and philosopher.
* Maude Abbott (1869–1940), Canadian pathologist, one of the earliest women graduated in medicine, expert in co ...
* Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information re ...
* Medical jurisprudence
Medical jurisprudence or legal medicine is the branch of science and medicine involving the study and application of scientific and medical knowledge to legal problems, such as inquests, and in the field of law. As modern medicine is a legal c ...
* Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
* Microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, prot ...
* Micrography
Micrography (from Greek, literally small-writing – "Μικρογραφία"), also called microcalligraphy, is a Jewish form of calligrams developed in the 9th century, with parallels in Christianity and Islam,Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
* Minimally-invasive procedures
* Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
* Parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it fo ...
* Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
* Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
* Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology ( physiopathology) – a convergence of pathology with physiology – is the study of the disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is the ...
* Precision medicine
Precision, precise or precisely may refer to:
Science, and technology, and mathematics Mathematics and computing (general)
* Accuracy and precision, measurement deviation from true value and its scatter
* Significant figures, the number of digit ...
* Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
* Speech–language pathology
Speech-language pathology (or speech and language pathology) is a healthcare field of expertise practiced globally. Speech-language pathology (SLP) specializes in the evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of communication disorders ( ...
* Telepathology
Telepathology is the practice of pathology at a distance. It uses telecommunications technology to facilitate the transfer of image-rich pathology data between distant locations for the purposes of diagnosis, education, and research. Performance o ...
References
External links
*American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP)
Comprehensive pathology website with numerous resources.
College of American Pathologists
(Atlas in Human Pathology)
Intersociety Council for Pathology Training (ICPI)
* ttp://atlases.muni.cz Atlases: High Resolution Pathology Images {{Authority control Branches of biology