|
Zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. Typically, the first infected human transmits the infectious agent to at least one other human, who, in turn, infects others. Major modern diseases such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Most strains of influenza that infect humans are human diseases, although many strains of bird flu and swine flu are zoonoses; these viruses occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 1918 Spanish flu or the 2009 swine flu. ''Taenia solium'' infection is one of the neglected tropical diseases with public health and veterinary concern in ende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergent Virus
An emergent virus (or emerging virus) is a virus that is either newly Viral evolution, appeared, notably increasing in incidence (epidemiology), incidence/geographic range limit, geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious diseases and raise public health challenges globally, given their potential to cause disease outbreak, outbreaks of disease which can lead to epidemics and pandemics. As well as causing disease, emergent viruses can also have severe economy, economic implications. Recent examples include the SARS-related coronaviruses, which have caused the 2002-2004 SARS outbreak, 2002-2004 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV-1) and the COVID-19 pandemic, 2019–21 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-CoV-2). Other examples include the human immunodeficiency vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Zoonosis
A reverse zoonosis, also known as a zooanthroponosis (Greek "animal", "man", ''"''disease") or anthroponosis, is a pathogen reservoired in humans that is capable of being transmitted to non-human animals. Terminology Anthroponosis refers to pathogens sourced from humans and can include human to non-human animal transmission but also human to human transmission. The term zoonosis technically refers to disease transferred between any animal and another animal, human or non-human, without discretion, and also been defined as disease transmitted from animals to humans ''and vice versa''. Yet because of human-centered medical biases, zoonosis tends to be used in the same manner as anthropozoonosis which specifically refers to pathogens reservoired in non-human animals that are transmissible to humans. Additional confusion due to frequency of scientists using "anthropozoonosis" and "zooanthroponosis" interchangeably was resolved during a 1967 Joint Food and Agriculture and World He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
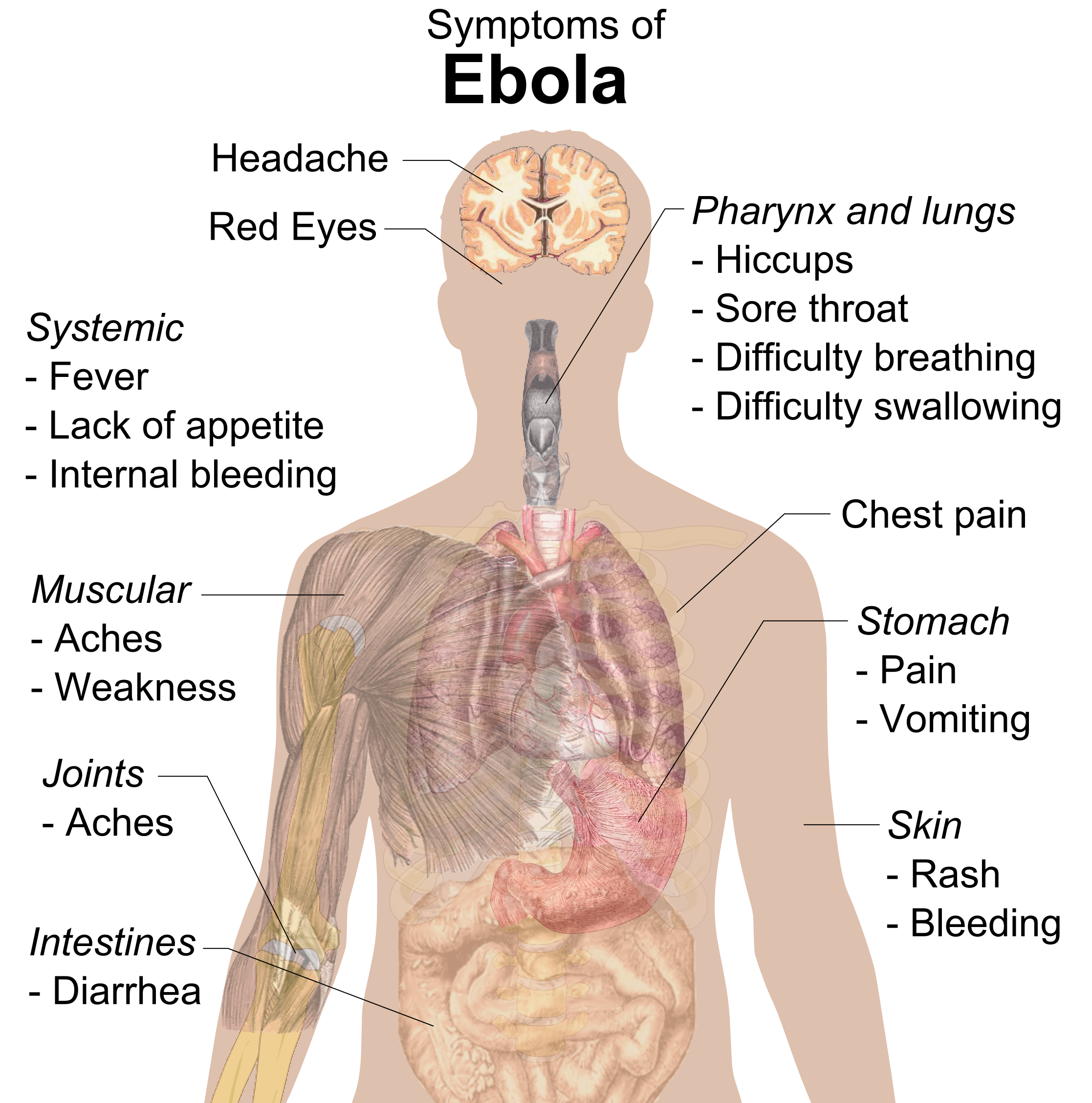
Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease with a stable number of infected individuals is not a pandemic. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide. Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The most fatal pandemic in recorded history was the Black Death—also known as Plague (disease), The Plague—which killed an estimated 75–200 million people in the 14th century. The term had not been used then but was used for later epidemics, including the 1918 influenza pandemic—more commonly known as the Spanish flu. Current pandemics include Epide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, violent movements, uncontrolled excitement, fear of water, an inability to move parts of the body, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Once symptoms appear, the result is virtually always death, regardless of treatment. The time period between contracting the disease and the start of symptoms is usually one to three months but can vary from less than one week to more than one year. The time depends on the distance the virus must travel along peripheral nerves to reach the central nervous system. Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including the rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus. It is spread when an infected animal bites or scratches a human or other animals. Saliva from an infected animal can also transmit rabies if the saliva come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect to a defined target popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-species Transmission
Cross-species transmission (CST), also called interspecies transmission, host jump, or spillover, is the transmission of an infectious pathogen, such as a virus, between hosts belonging to different species. Once introduced into an individual of a new host species, the pathogen may cause disease for the new host and/or acquire the ability to infect other individuals of the same species, allowing it to spread through the new host population. The phenomenon is most commonly studied in virology, but cross-species transmission may also occur with bacterial pathogens or other types of microorganisms. Steps involved in the transfer of pathogens to new hosts include contact between the pathogen and the host; the successful infection of an initial individual host, which may lead to amplification and an outbreak; and the adaptation of the pathogen, within either the original or new host, which may render it capable of spreading efficiently between individuals in populations of the new host. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis, more commonly known as food poisoning is a symptomatic infection caused by bacteria of the ''Salmonella'' type. It is also a food-borne disease and are defined as diseases, usually either infectious or toxic in nature, caused by agents that enter the body through the ingestion of food. In humans, the most common symptoms are diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, and vomiting. Symptoms typically occur between 12 hours and 36 hours after exposure, and last from two to seven days. Occasionally more significant disease can result in dehydration. The old, young, and others with a weakened immune system are more likely to develop severe disease. Specific types of ''Salmonella'' can result in typhoid fever or paratyphoid fever. There are two species of ''Salmonella'': ''Salmonella bongori'' and ''Salmonella enterica'' with many subspecies. However, subgroups and serovars within a species may be substantially different in their ability to cause disease. This suggests that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabid Dog
Rabies is a viral zoonotic neuroinvasive disease which causes inflammation in the brain and is usually fatal. Rabies, caused by the rabies virus, primarily infects mammals. In the laboratory it has been found that birds can be infected, as well as cell cultures from birds, reptiles and insects. The brains of animals with rabies deteriorate. As a result, they tend to behave bizarrely and often aggressively, increasing the chances that they will bite another animal or a person and transmit the disease. Most cases of humans contracting the disease from infected animals are in developing nations. In 2010, an estimated 26,000 people died from rabies, down from 54,000 in 1990. Stages of disease Three stages of rabies are recognized in dogs and other animals. # The first stage is a one- to three-day period characterized by behavioral changes and is known as the prodromal stage. # The second stage is the excitative stage, which lasts three to four days. It is this stage that is of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
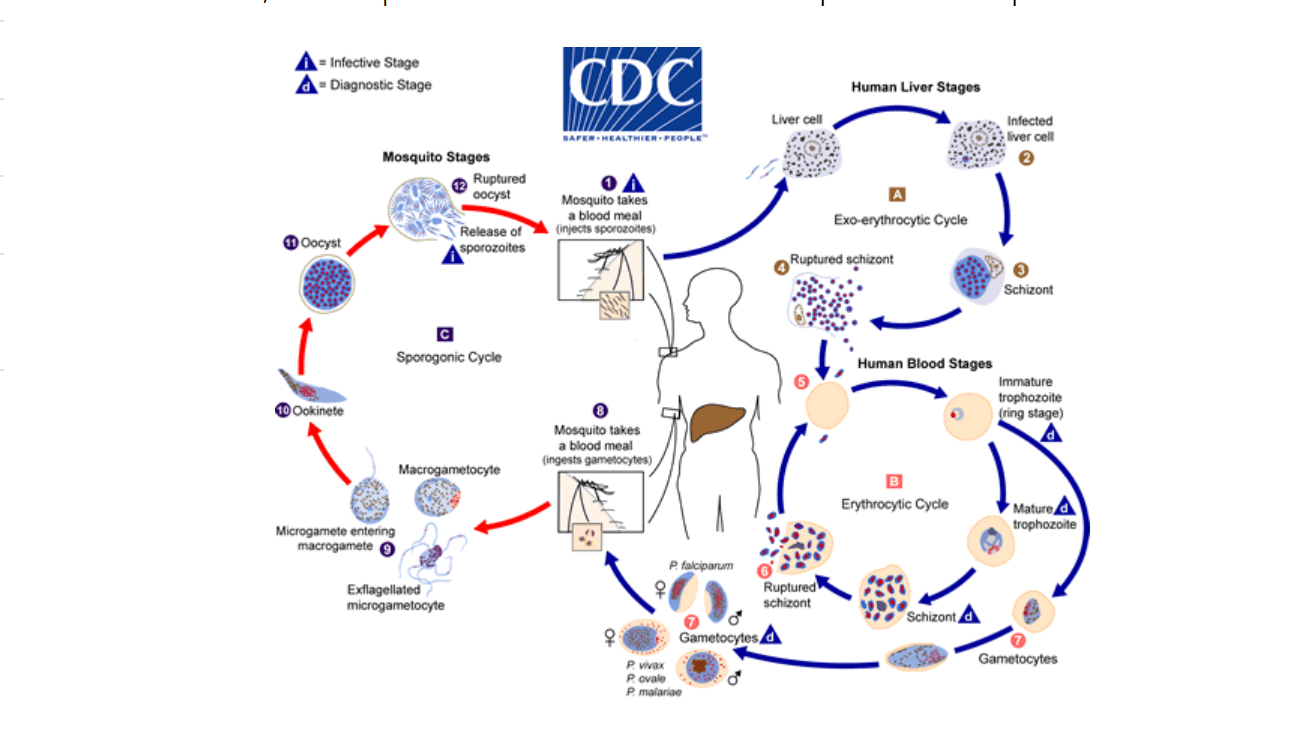
Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The ''Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its salivary gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Disease
Tropical diseases are Infectious disease, diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropics, tropical and subtropics, subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, which controls the insect population by forcing hibernation. However, many were present in northern Europe and northern America in the 17th and 18th centuries before modern understanding of disease causation. The initial impetus for tropical medicine was to protect the health of colonial settlers, notably in India under the British Raj. Insects such as mosquitoes and flies are by far the most common disease carrier, or Vector (epidemiology), vector. These insects may carry a parasite, bacterium or virus that is infectious to humans and animals. Most often disease is transmitted by an insect bite, which causes transmission of the infectious agent through subcutaneous blood exchange. Vaccines are not available for most of the diseases listed here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)