Nevis Reformation Party Politicians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Nevis is a small island in the
Nevis is a small island in the
 Due to the profitable
Due to the profitable
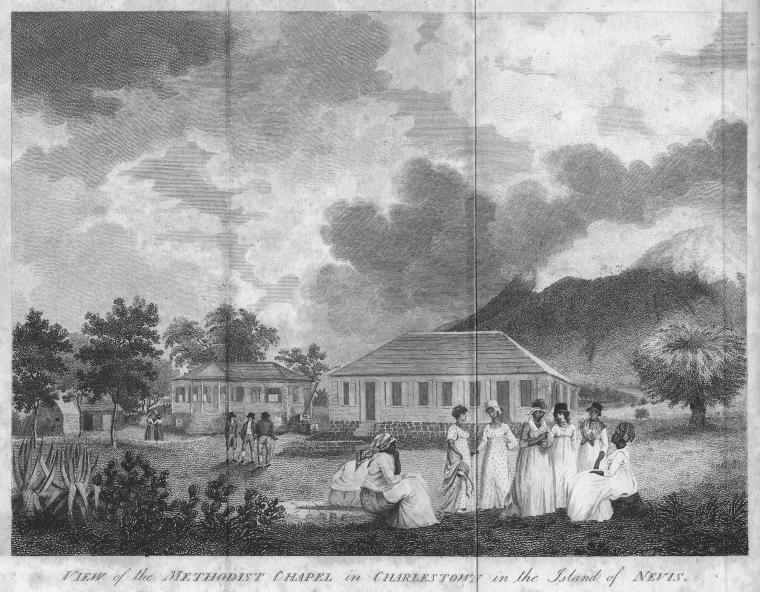 In 1706,
In 1706,  One consequence of the French attack was a collapsed sugar industry and during the ensuing hardship on Nevis, small plots of land on the plantations were made available to the enslaved families in order to control the loss of life due to starvation. With less profitability for the absentee plantation owners, the import of food supplies for the plantation workers dwindled. Between 1776 and 1783, when the food supplies failed to arrive altogether due to the rebellion in North America, 300–400 enslaved Nevisians starved to death. On 1 August 1834, slavery was abolished in the
One consequence of the French attack was a collapsed sugar industry and during the ensuing hardship on Nevis, small plots of land on the plantations were made available to the enslaved families in order to control the loss of life due to starvation. With less profitability for the absentee plantation owners, the import of food supplies for the plantation workers dwindled. Between 1776 and 1783, when the food supplies failed to arrive altogether due to the rebellion in North America, 300–400 enslaved Nevisians starved to death. On 1 August 1834, slavery was abolished in the
In ''Bristol and Transatlantic Slavery'', a project by City Museum and the University of the West of England's Faculty of Humanities. Retrieved 8 May 2007. Because of the early distribution of plots and because many of the planters departed from the island when sugar cultivation became unprofitable, a relatively large percentage of Nevisians already owned or controlled land at emancipation.Baker Motley, Constance (1998). ''Equal Justice Under Law. An Autobiography.'' New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux. . An excerpt from the autobiography, describing her search in Nevis church records for her family's history during the era of slavery, is available online a
Retrieved 8 August 2006. Others settled on crown land. This early development of a society with a majority of small, landowning farmers and entrepreneurs created a stronger middle class in Nevis than in Saint Kitts, where the sugar industry continued until 2006. Even though the 15 families in the wealthy planter elite no longer control the arable land, Saint Kitts still has a large, landless working class population.
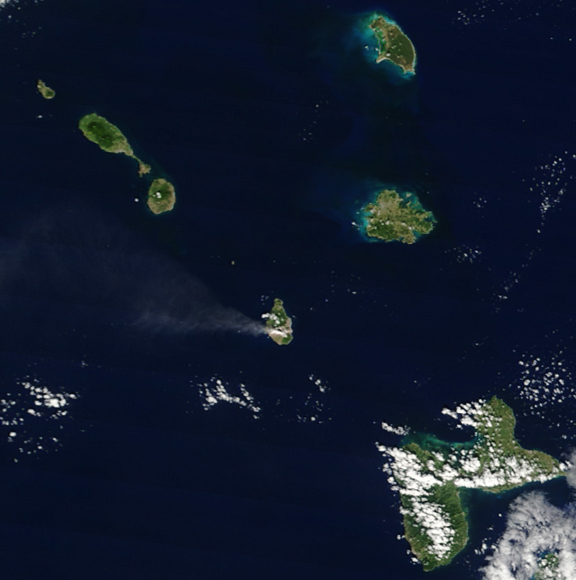 The formation of the island began in mid-Pliocene times, approximately 3.45 million years ago. Nine distinct eruptive centres from different geological ages, ranging from mid-Pliocene to
The formation of the island began in mid-Pliocene times, approximately 3.45 million years ago. Nine distinct eruptive centres from different geological ages, ranging from mid-Pliocene to
 During the 17th and 18th centuries, massive
During the 17th and 18th centuries, massive
 Nevis has several natural freshwater springs (including Nelson's Spring). The island also has numerous non-potable volcanic
Nevis has several natural freshwater springs (including Nelson's Spring). The island also has numerous non-potable volcanic
"Chapter 9: St. Kitts and Nevis"
. In Programme of Action for the sustainable development of small island developing States (SIDS POA). United Nations, 2003-09-29. Retrieved 28 August 2007.
 The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean estimates the annual per capita
The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean estimates the annual per capita
. The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
 The political structure for the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is based on the Westminster Parliamentary system, but it is a unique structure in that Nevis has its own unicameral legislature, consisting of His Majesty's representative (the Deputy Governor General) and members of the Nevis Island Assembly. Nevis has considerable autonomy in its legislative branch. The constitution actually empowers the Nevis Island Legislature to make laws that cannot be abrogated by the National Assembly.See section 3 and 4 about Nevis Island Legislature and Administration in ''The Saint Christopher and Nevis Constitution Order 1983''. Published online b
The political structure for the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is based on the Westminster Parliamentary system, but it is a unique structure in that Nevis has its own unicameral legislature, consisting of His Majesty's representative (the Deputy Governor General) and members of the Nevis Island Assembly. Nevis has considerable autonomy in its legislative branch. The constitution actually empowers the Nevis Island Legislature to make laws that cannot be abrogated by the National Assembly.See section 3 and 4 about Nevis Island Legislature and Administration in ''The Saint Christopher and Nevis Constitution Order 1983''. Published online b
Georgetown University
and also b
Retrieved 8 August 2006. Nevis has a constitutionally protected right to secede from the federation, should a two-thirds majority of the island's population vote for independence in a local referendum. Section 113.(1) of the constitution states: "The Nevis Island Legislature may provide that the island of Nevis shall cease to be federated with the island of Saint Christopher and accordingly that this Constitution shall no longer have effect in the island of Nevis." Nevis has its own
"The Way Forward For The Island Of Nevis." ''Nevis, Queen of the Caribees''.
Nevis Island Administration, September 1996. Retrieved 8 August 2006. There is also substantial support in Nevis for
Nevis Financial Services Departments and the Ministry of Finance, Nevis
. Retrieved 8 August 2006. but calls for secession are often based on concerns that the legislative authority of the Nevis Island Administration might be challenged again in the future.
 The island of Nevis is divided into five administrative subdivisions called
The island of Nevis is divided into five administrative subdivisions called
 A series of earthquakes during the 18th century severely damaged most of the colonial-era stone buildings of Charlestown. The
A series of earthquakes during the 18th century severely damaged most of the colonial-era stone buildings of Charlestown. The
"Willett for Nevis Sports Hall of Fame"
''West Indies Cricket Board'', 27 February 2005. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
Nevis Island Administration
Nevis Island Tourism Authority
{{Coord, 17, 09, N, 62, 35, W, type:isle, display=title Autonomous regions Islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis Pleistocene stratovolcanoes Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Saint Kitts and Nevis



 Nevis is a small island in the
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
chain of the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of ...
. Nevis is located near the northern end of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
, about east-southeast of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
and west of Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
. Its area is and the capital is Charlestown.
Saint Kitts and Nevis are separated by a shallow channel known as " The Narrows". Nevis is roughly conical in shape, with a volcano known as Nevis Peak at its centre. The island is fringed on its western and northern coastlines by sandy beaches composed of a mixture of white coral sand with brown and black sand eroded and washed down from the volcanic rocks that make up the island. The gently-sloping coastal plain ( wide) has natural freshwater springs as well as non-potable volcanic hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s, especially along the western coast.
The island was named ''Oualie'' ("Land of Beautiful Waters") by the Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language ...
and ''Dulcina'' ("Sweet Island") by the early British settlers. The name ''Nevis'' is derived from the Spanish ''Nuestra Señora de las Nieves'' (which means Our Lady of the Snows); the name was given by its Spanish discoverers and first appeared on maps in the 16th century.Hubbard, Vincent K. (2002). ''Swords, Ships & Sugar: History of Nevis''. Corvallis, Oregon: Premiere, , pp. 20–23 (Captain Gilbert, Captain Smith), 25 (pearl diving), 41–44 (name Dulcina, treaty with Spain, first settlement), 69–70 (privateers, Captain Francis), 79–85 (slave trade, Royal African Company, Queen of the Caribees), 86–102 (Caribs), 113–120 (d'Iberville, buccaneers), 138–139 (Great Britain's wealth derived from West Indian sugar and slave trade, 1776 starvation), 194–195 (Alexandra Hospital), 211–223 (electricity, Anguilla in 1967, OECD blacklist). Nevis is also known by the sobriquet "Queen of the Caribees", which it earned in the 18th century from sugar plantations.
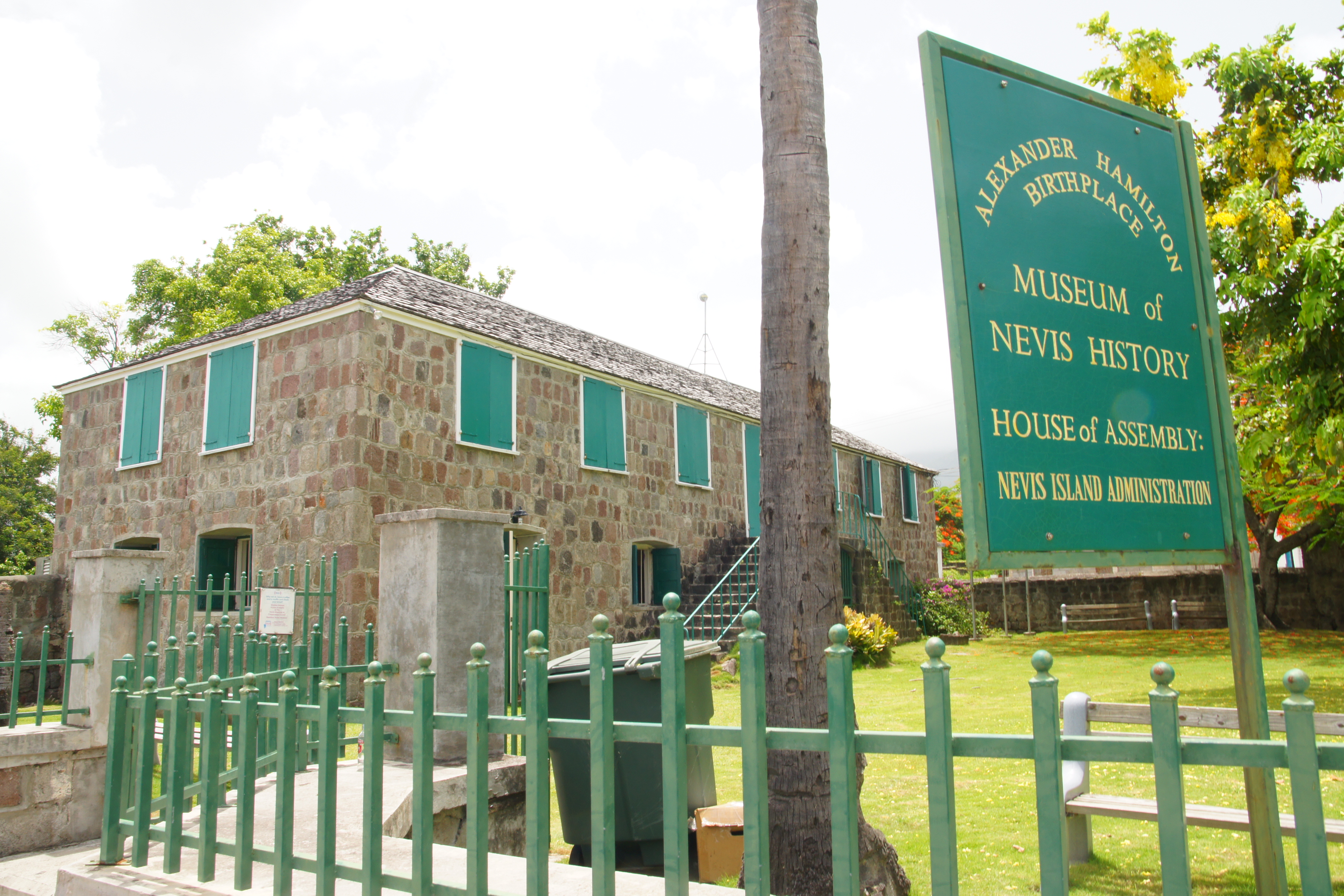
Nevis is of particular historical significance to Americans because it was the birthplace and early childhood home of Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
. For the British, Nevis is the place where Horatio Nelson
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte (29 September 1758 – 21 October 1805) was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought abo ...
was stationed as a young sea captain, and is where he met and married a Nevisian, Frances Nisbet
Frances "Fanny" Nelson, Viscountess Nelson ( Frances Herbert Woolward, formerly Nisbet; (1758 4 May 1831), is best known as the wife of Horatio Nelson, the British naval officer who won several victories over the French during the French Rev ...
, the young widow of a plantation-owner.
The majority of the approximately 12,000 Nevisians are of primarily African descent, with notable British, Portuguese and Lebanese minority communities. English is the official language, and the literacy rate, 98 percent, is one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere.
Etymology
In 1498,Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
gave the island the name ''San Martín'' (Saint Martin). However, the confusion of numerous poorly-charted small islands in the Leeward Island chain meant that this name ended up being accidentally transferred to another island, which is still known as Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten.
The current name ''Nevis'' was derived from a Spanish name ''Nuestra Señora de las Nieves'' by process of abbreviation and anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influen ...
. The Spanish name means Our Lady of the Snows. It is not known who chose this name for the island, but it is a reference to the story of a 4th-century Catholic miracle: a snowfall on the Esquiline Hill in Rome. Presumably the white clouds that usually cover the top of Nevis Peak reminded someone of this story of a miraculous snowfall in a hot climate.
Nevis was part of the Spanish claim to the Caribbean islands; a claim pursued until the 1670 Treaty of Madrid, even though there were no Spanish settlements on the island. According to Vincent Hubbard, author of ''Swords, Ships & Sugar: History of Nevis'', the Spanish ruling caused many of the Arawak groups who were not ethnically Caribs to "be redefined as Kalinago overnight". Records indicate that the Spanish enslaved large numbers of the native inhabitants on the more accessible of the Leeward Islands and sent them to Cubagua
Cubagua Island or Isla de Cubagua () is the smallest and least populated of the three islands constituting the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, after Margarita Island and Coche Island. It is located north of the Araya Peninsula, the closest ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
to dive for pearls. Hubbard suggests that the reason the first European settlers found so few "Kalinago" on Nevis is that they had already been rounded up by the Spanish and shipped off to be used as slaves.
History
Amerindians
Nevis had been settled for more than two thousand years by Amerindian people prior to having been sighted by Columbus in 1493. The indigenous people of Nevis during these periods belonged to the Leeward Island Amerindian groups popularly referred to asArawaks
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, wh ...
and Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language ...
, a complex mosaic of ethnic groups with similar culture and language.Wilson, Samuel (1990). "The Prehistoric Settlement Pattern of Nevis, West Indies". ''Journal of Field Archaeology'', Vol. 16, No. 4 (Winter 1989), p. 427-450. Dominican anthropologist Lennox Honychurch traces the European use of the term "Carib" to refer to the Leeward Island aborigines to Columbus, who picked it up from the Taínos on Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
. It was not a name the Kalinago called themselves.Honychurch, Lennox (1997). "Crossroads in the Caribbean: A Site of Encounter and Exchange on Dominica". ''World Archaeology'' Vol. 28(3): 291–304. "Carib Indians" was the generic name used for all groups believed involved in cannibalistic war rituals, more particularly, the consumption of parts of a killed enemy's body.
The Amerindian name for Nevis was ''Oualie'', land of beautiful waters. The structure of the Kalinago language has been linguistically identified as Arawakan
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branch ...
.
Colonial era
Despite the Spanish claim, Nevis continued to be a popular stop-over point for English and Dutch ships on their way to theNorth America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
. Captain Bartholomew Gilbert of Plymouth visited the island in 1603, spending two weeks to cut twenty tons of lignum vitae wood. Gilbert sailed on to Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
to seek out survivors of the Roanoke settlement
Roanoke Island () is an island in Dare County, bordered by the Outer Banks of North Carolina, United States. It was named after the historical Roanoke, a Carolina Algonquian people who inhabited the area in the 16th century at the time of Engl ...
in what is now North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. Captain John Smith visited Nevis on his way to Virginia in 1607. This was the voyage that founded Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in the New World.
On 30 August 1620 James VI and I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
of Scotland and England asserted sovereignty over Nevis by giving a Royal Patent for colonisation to the Earl of Carlisle. However, actual European settlement did not happen until 1628, when Anthony Hilton moved from nearby Saint Kitts following a murder plot against him. 80 other settlers accompanied him, soon boosted by a further 100 settlers from London who had initially hoped to settle Barbuda. Hilton became the first Governor of Nevis.
After the Treaty of Madrid (1670) between Spain and England, Nevis became the seat of the British colony and the Admiralty Court
Admiralty courts, also known as maritime courts, are courts exercising jurisdiction over all maritime contracts, torts, injuries, and offences.
Admiralty courts in the United Kingdom England and Wales
Scotland
The Scottish court's earliest ...
also sat in Nevis. Between 1675 and 1730, the island was the headquarters for the slave trade for the Leeward Islands, with approximately 6,000–7,000 enslaved West Africans passing through en route to other islands each year. The Royal African Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile (trade, trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal House of Stuart, Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the West Africa, west coast of Africa. It was led by the J ...
brought all its ships through Nevis. A 1678 census shows a community of Irish people
The Irish ( ga, Muintir na hÉireann or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common history and culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years, and it has been c ...
– 22% of the population – existing as either indentured servants or freemen.
 Due to the profitable
Due to the profitable Slave Trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and the high quality of Nevisian sugar cane, Nevis soon became a dominant source of wealth for Great Britain and the slave-owning British plantocracy. When the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
were separated from Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
in 1671, Nevis became the seat of the Leeward Islands colony and was given the nickname "Queen of the Caribees". It remained the colonial capital for the Leeward Islands until the seat was transferred to Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
for military reasons in 1698. During this period, Nevis was the richest of the British Leeward Islands.
Nevis outranked larger islands like Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
in sugar production in the late 17th century. The planters' wealth on the island is evident in the tax records preserved at the Calendar State Papers in the British Colonial Office Public Records, where the amount of tax collected on the Leeward Islands was recorded. The sums recorded for 1676 as "head tax on slaves", a tax payable in sugar, amounted to 384,600 pounds in Nevis, as opposed to 67,000 each in Antigua and Saint Kitts, 62,500 in Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, and 5,500 total in the other five islands.
The profits on sugar cultivation in Nevis was enhanced by the fact that the cane juice from Nevis yielded an unusually high amount of sugar. A gallon (3.79 litres) of cane juice from Nevis yielded 24 ounces (0.71 litres) of sugar, whereas a gallon from Saint Kitts yielded 16 ounces (0.47 litres). Twenty percent of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
's total sugar production in 1700 was derived from Nevisian plantations. Exports from West Indian colonies like Nevis were worth more than all the exports from all the mainland Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
of North America combined at the time of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
.
The enslaved families formed the large labour force required to work the sugar plantations. After the 1650s, the supply of white indentured servants began to dry up due to increased wages in England and less incentive to migrate to the colonies. By the end of the 17th century, the population of Nevis consisted of a small, wealthy planter elite in control, a marginal population of poor Whites, a great majority of African-descended slaves, and an unknown number of Maroons
Maroons are descendants of African diaspora in the Americas, Africans in the Americas who escaped from slavery and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples, eventually ethnogenesi ...
, escaped slaves living in the mountains. In 1780, 90 percent of the 10,000 people living on Nevis were Black. Some of the maroons joined with the few remaining Kalinago in Nevis to form a resistance force. Memories of the Nevisian maroons' struggle under the plantation system are preserved in place names such as Maroon Hill, an early centre of resistance.
The great wealth generated by the colonies of the West Indies led to wars among Spain, Britain, and France. The formation of the United States can be said to be a partial by-product of these wars, and the strategic trade aims that often ignored North America. Three privateers
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
(William Kidd
William Kidd, also known as Captain William Kidd or simply Captain Kidd ( – 23 May 1701), was a Scottish sea captain who was commissioned as a privateer and had experience as a pirate. He was tried and executed in London in 1701 for murder a ...
being one of them) were employed by the British Crown to help protect ships in Nevis' waters.
During the 17th century, the French, based on Saint Kitts, launched many attacks on Nevis, sometimes assisted by the Kalinago, who in 1667 sent a large fleet of canoes along in support. In the same year, a Franco–Dutch invasion fleet was repelled off Nevis by an English fleet. Letters and other records from the era indicate that the English on Nevis hated and feared the Amerindians. In 1674 and 1683, they participated in attacks on Kalinago villages in Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
and St. Vincent
Saint Vincent may refer to:
People Saints
* Vincent of Saragossa (died 304), a.k.a. Vincent the Deacon, deacon and martyr
* Saint Vincenca, 3rd century Roman martyress, whose relics are in Blato, Croatia
* Vincent, Orontius, and Victor (died 305) ...
, despite a lack of official approval from the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
for the attack.
On Nevis, the English built Fort Charles and a series of smaller fortifications to aid in defending the island. This included Saddle Hill Battery, built in 1740 to replace a deodand
A deodand is a thing forfeited or given to God, specifically, in law, an object or instrument that becomes forfeited because it has caused a person's death.
The English common law of deodands traces back to the 11th century and was applied, on a ...
on Mount Nevis.
Emancipation
 In 1706,
In 1706, Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
, the French Canadian founder of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
in North America, decided to drive the English out of Nevis and thus also stop pirate attacks on French ships; he considered Nevis the region's headquarters for piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
against French trade. During d'Iberville's invasion of Nevis, French buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from Stuart Restoration, the Restoration in 16 ...
s were used in the front line, infamous for being ruthless killers after the pillaging during the wars with Spain where they gained a reputation for torturing and murdering non-combatants. In the face of the invading force, the English militiamen of Nevis fled.
Some planters burned the plantations, rather than letting the French have them, and hid in the mountains. It was the enslaved Africans who held the French at bay by taking up arms to defend their families and the island. The slave quarters had been looted and burned as well, as the main reward promised the men fighting on the French side in the attack was the right to capture as many slaves as possible and resell them in Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in th ...
.
During the fighting, 3,400 enslaved Nevisians were captured and sent off to Martinique, but about 1,000 more, poorly armed and militarily untrained, held the French troops at bay, by "murderous fire" according to an eyewitness account by an English militiaman. He wrote that "the slaves' brave behaviour and defence there shamed what some of their masters did, and they do not shrink to tell us so." After 18 days of fighting, the French were driven off the island. Among the Nevisian men, women and children carried away on d'Iberville's ships, six ended up in Louisiana, the first persons of African descent to arrive there.
 One consequence of the French attack was a collapsed sugar industry and during the ensuing hardship on Nevis, small plots of land on the plantations were made available to the enslaved families in order to control the loss of life due to starvation. With less profitability for the absentee plantation owners, the import of food supplies for the plantation workers dwindled. Between 1776 and 1783, when the food supplies failed to arrive altogether due to the rebellion in North America, 300–400 enslaved Nevisians starved to death. On 1 August 1834, slavery was abolished in the
One consequence of the French attack was a collapsed sugar industry and during the ensuing hardship on Nevis, small plots of land on the plantations were made available to the enslaved families in order to control the loss of life due to starvation. With less profitability for the absentee plantation owners, the import of food supplies for the plantation workers dwindled. Between 1776 and 1783, when the food supplies failed to arrive altogether due to the rebellion in North America, 300–400 enslaved Nevisians starved to death. On 1 August 1834, slavery was abolished in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
. In Nevis, 8,815 slaves were freed. The first Monday in August is celebrated as Emancipation Day
Emancipation Day is observed in many former European colonies in the Caribbean and areas of the United States on various dates to commemorate the emancipation of slaves of African descent.
On August 1, 1985, Trinidad and Tobago became the fir ...
and is part of the annual Nevis Culturama festival.
A four-year apprenticeship programme followed the abolishment of slavery on the plantations. In spite of the continued use of the labour force, the Nevisian slave owners were paid over £150,000 in compensation from the British Government for the loss of property, whereas the enslaved families received nothing for 200 years of labour. One of the wealthiest planter families in Nevis, the Pinneys of Mountravers Plantation, claimed £36,396 () in compensation for the slaves on the family-owned plantations around the Caribbean.Personal stories: Traders and Merchants – John PinneyIn ''Bristol and Transatlantic Slavery'', a project by City Museum and the University of the West of England's Faculty of Humanities. Retrieved 8 May 2007. Because of the early distribution of plots and because many of the planters departed from the island when sugar cultivation became unprofitable, a relatively large percentage of Nevisians already owned or controlled land at emancipation.Baker Motley, Constance (1998). ''Equal Justice Under Law. An Autobiography.'' New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux. . An excerpt from the autobiography, describing her search in Nevis church records for her family's history during the era of slavery, is available online a
Retrieved 8 August 2006. Others settled on crown land. This early development of a society with a majority of small, landowning farmers and entrepreneurs created a stronger middle class in Nevis than in Saint Kitts, where the sugar industry continued until 2006. Even though the 15 families in the wealthy planter elite no longer control the arable land, Saint Kitts still has a large, landless working class population.
1800 to the present day
The population had reached 7,470 by 1842. Nevis was united with Saint Kitts andAnguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territo ...
in 1882, and they became an associated state with full internal autonomy in 1967, though Anguilla seceded in 1971. Together, Saint Kitts and Nevis became independent on 19 September 1983. On 10 August 1998, a referendum on Nevis to separate from Saint Kitts had 2,427 votes in favour and 1,498 against, falling short of the two-thirds majority needed.
Before 1967, the local government of Saint Kitts was also the government of Nevis and Anguilla. Nevis had two seats and Anguilla one seat in the government. The economic and infrastructural development of the two smaller islands was not a priority to the colonial federal government.
When the hospital in Charlestown was destroyed in a hurricane in 1899, planting of trees in the squares of Saint Kitts and refurbishing of government buildings, also in Saint Kitts, took precedence over the rebuilding of the only hospital in Nevis. After five years without any proper medical facilities, the leaders in Nevis initiated a campaign, threatening to seek independence from Saint Kitts. The British Administrator in Saint Kitts, Charles Cox, was unmoved. He stated that Nevis did not need a hospital since there had been no significant rise in the number of deaths during the time Nevisians had been without a hospital. Therefore, no action was needed on behalf of the government, and besides, Cox continued, the Legislative Council regarded "Nevis and Anguilla as a drag on St. Kitts and would willingly see a separation".
A letter of complaint to the metropolitan British Foreign Office gave result and the federal government in Saint Kitts was ordered by their superiors in London to take speedy action. The Legislative Council took another five years to consider their options. The final decision by the federal government was to not rebuild the old hospital after all but to instead convert the old Government House in Nevis into a hospital, named Alexandra Hospital after Queen Alexandra, wife of King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
. A majority of the funds assigned for the hospital could thus be spent on the construction of a new official residence in Nevis.
After d'Iberville's invasion in 1704, records show Nevis' sugar industry in ruins and a decimated population begging the English Parliament and relatives for loans and monetary assistance to stave off island-wide starvation. The sugar industry on the island never fully recovered and during the general depression that followed the loss of the West Indian sugar monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situati ...
, Nevis fell on hard times and the island became one of the poorest in the region. The island remained poorer than Saint Kitts until 1991, when the fiscal performance of Nevis edged ahead of the fiscal performance of Saint Kitts for the first time since the French invasion.
Electricity was introduced in Nevis in 1954 when two generators were shipped in to provide electricity to the area around Charlestown. In this regard, Nevis fared better than Anguilla, where there were no paved roads, no electricity and no telephones until 1967. However, electricity did not become available island-wide on Nevis until 1971.
An ambitious infrastructure development programme was introduced in the early 2000s which included a transformation of the Charlestown port, construction of a new deep-water harbour, resurfacing and widening the Island Main Road, a new airport terminal and control tower, and a major airport expansion, which required the relocation of an entire village in order to make room for the runway extension.
Modernised classrooms and better-equipped schools, as well as improvements in the educational system, have contributed to a leap in academic performance on the island. The pass rate among the Nevisian students sitting for the Caribbean Examination Council
The Caribbean Examinations Council (CXC) is an examination board in the Caribbean. It was established in 1972 under agreement by the participating governments in the Caribbean Community to conduct such examinations as it may think appropriate an ...
(CXC) exams, the Cambridge General Certificate of Education Examination (GCE) and the Caribbean Advance Proficiency Examinations is now consistently among the highest in the English-speaking Caribbean.
Hurricanes
* September 1989: there was a considerable amount of damage fromHurricane Hugo
Hurricane Hugo was a powerful Cape Verde tropical cyclone that inflicted widespread damage across the northeastern Caribbean and the Southeastern United States in September 1989. Across its track, Hugo affected approximately 2 million peop ...
.
* September 1998, there was a great deal of damage from Hurricane Georges
Hurricane Georges () was a powerful and long-lived Cape Verde Category 4 hurricane which caused severe destruction as it traversed the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico in September 1998, making eight landfalls along its path. Georges was the sevent ...
.
* November 1999: Nevis was hit by Hurricane Lenny, which caused some heavy damage to the island's infrastructure on the western coast, because of the storm's unusual track from west to east.
* October 2008: Nevis was brushed with the edge of Hurricane Omar
Hurricane Omar was a powerful tropical cyclone that took an unusual southwest to northeast track through the eastern Caribbean Sea during mid-October 2008. Forming out of a tropical disturbance on October 13, Omar initially moved slowly in t ...
. Among other establishments, The Four Seasons Resort Nevis was forced to close to undergo repairs. Hurricane Omar thus caused the loss of 600 jobs for over 2 years; the resort reopened on 15 December 2010.
* August 2010: there was some damage on Nevis from Hurricane Earl.
* September 2010, there was some damage from Hurricane Igor.
* September 2017, there was damage from Hurricane Irma.
Geography
 The formation of the island began in mid-Pliocene times, approximately 3.45 million years ago. Nine distinct eruptive centres from different geological ages, ranging from mid-Pliocene to
The formation of the island began in mid-Pliocene times, approximately 3.45 million years ago. Nine distinct eruptive centres from different geological ages, ranging from mid-Pliocene to Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
, have contributed to the formation. No single model of the island's geological evolution can, therefore, be ascertained.
Nevis Peak ( high) is the dormant remnant of one of these ancient stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and per ...
es. The last activity took place about 100,000 years ago, but active fumaroles
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcani ...
and hot springs are still found on the island, the most recent formed in 1953. The composite cone of Nevis volcano has two overlapping summit craters that are partially filled by a lava dome, created in recent, pre-Columbian time. Pyroclastic flows and mudflows were deposited on the lower slopes of the cone simultaneously.
Nevis Peak is located on the outer crater rim. Four other lava domes were constructed on the flanks of the volcano, one on the northeast flank (Madden's Mount), one on the eastern flank (Butlers Mountain), one on the northwest coast (Mount Lily) and one on the south coast (Saddle Hill, with a height of ). The southernmost point on the island is Dogwood Point
Dogwood Point is the southernmost point of Saint Kitts and Nevis. It is located in the southwest of the island of Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the ...
which is also the southernmost point of the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of ...
.
During the last ice age, when the sea level was 60 m lower, the three islands of Saint Kitts, Nevis and Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
(also known as Statia) were connected as one island. Saba, however, is separated from these three by a deeper channel.
There are visible wave-breaking reefs along the northern and eastern shorelines. To the south and west, the reefs are located in deeper water and are suitable for scuba diving. The most developed beach on Nevis is the Pinney's Beach
Pinney's Beach, also spelled Pinneys Beach, is a very long sandy beach on the western Caribbean coast of the island of Nevis, in Saint Kitts and Nevis, Leeward Islands in the West Indies. The southern end of Pinneys Beach starts just outside th ...
, on the western or Caribbean coast. There are sheltered swimming beaches in Oualie Bay and Cades Bay. The eastern coast of the island faces into the Atlantic Ocean and can have strong surf in parts of the shore which are unprotected by fringing coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s.
The colour of the sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of s ...
on the beaches of Nevis is variable: on a lot of the bigger beaches the sand is a yellow-grey in colour, but some beaches on the southern coast have darker, reddish, or even black sand. Under a microscope it becomes clear that Nevis sand is a mixture of tiny fragments of coral, many foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and ot ...
, and small crystals of the various mineral constituents of the volcanic rock of which the island is made.
Geology
Seven volcanic centers make up Nevis. These include Round Hill (3.43 Ma), Cades Bay (3.22 Ma), Hurricane Hill (2.7 Ma), Saddle Hill (1.8 Ma), Butlers Mountain (1.1 Ma), Red Cliff and Nevis Peak (0.98 Ma). These are mainlyandesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomi ...
and dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite. ...
lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
s, with associated block and ash flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of bu ...
s, plus lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extreme ...
s. Nevis Peak has the highest elevation, at 984 m. Cades Bay and Farm Estate Soufriere are noted areas of hydrothermal activity.
Water has been piped since 1911 from a spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a ...
called the "Source", located up the mountain, to storage tanks at Rawlins Village, and since 1912, to Butler's Village. Additional drinking water comes from Nelson's Spring near Cotton Ground and Bath Spring. Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
has been extracted since the 1990s, and mixed with the Source water.
Colonial deforestation
 During the 17th and 18th centuries, massive
During the 17th and 18th centuries, massive deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
was undertaken by the planters as the land was initially cleared for sugar cultivation. This intense land exploitation by the sugar and cotton industry lasted almost 300 years, and greatly changed the island's ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
.
In some places along the windswept southeast or "Windward" coast of the island, the landscape is radically altered compared with how it used to be in pre-colonial times. Due to extreme land erosion, the topsoil was swept away, and in some places at the coast, sheer cliffs as high as have developed.
Thick forest once covered the eastern coastal plain, where the Amerindians built their first settlements during the Aceramic period, complementing the ecosystem surrounding the coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
just offshore. It was the easy access to fresh water on the island and the rich food source represented by the ocean life sheltered by the reef that made it feasible for the Amerindians to settle this area around 600 BC. With the loss of the natural vegetation, the balance in runoff nutrients to the reef was disturbed, eventually causing as much as 80 percent of the large eastern fringing reef to become inactive. As the reef broke apart, it, in turn, provided less protection for the coastline.
During times of maximum cultivation, sugar cane fields stretched from the coastline of Nevis up to an altitude at which the mountain slopes were too steep and rocky to farm. Nonetheless, once the sugar industry was finally abandoned, vegetation on the leeward side of the island regrew reasonably well, as scrub and secondary forest.
Water resources
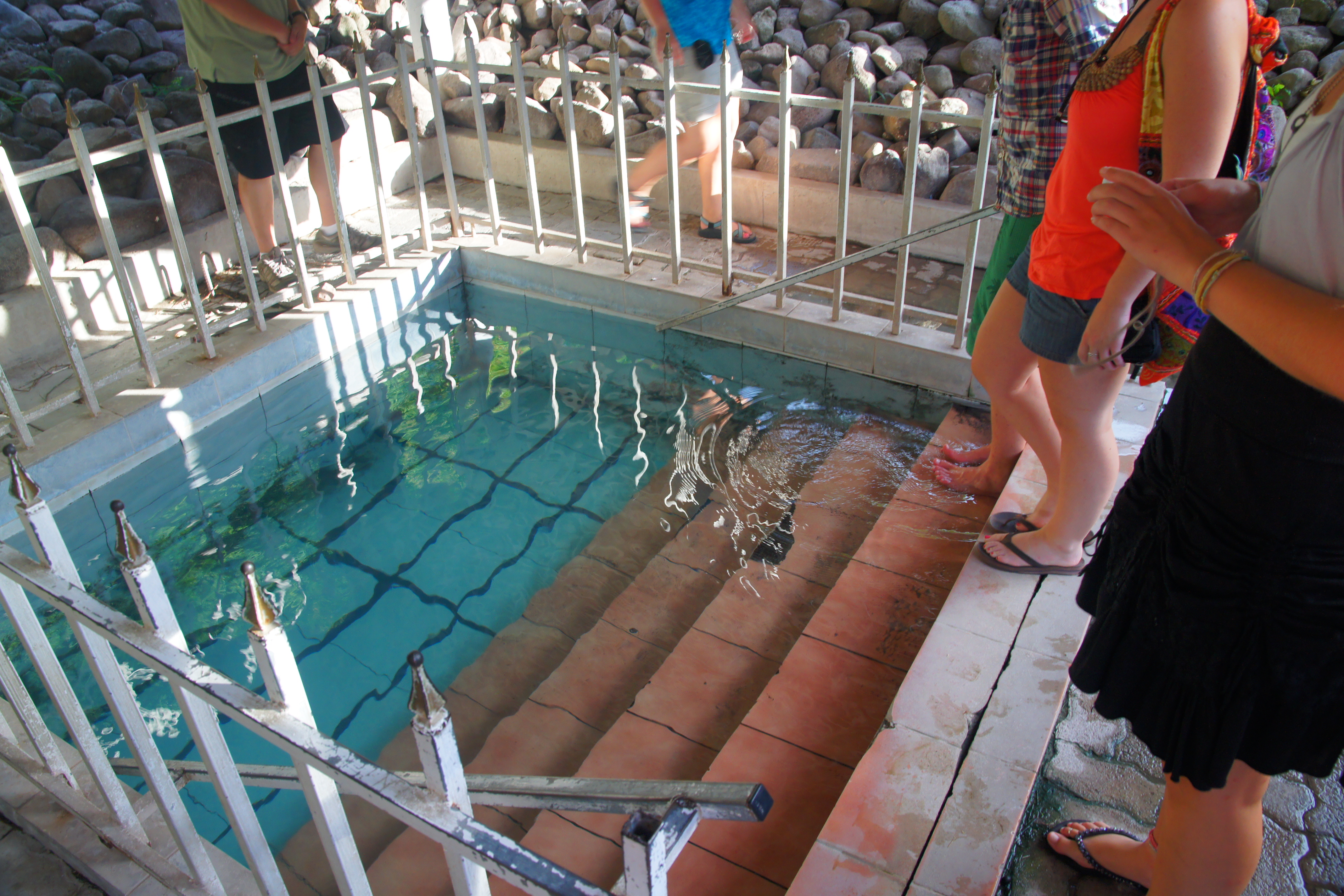
 Nevis has several natural freshwater springs (including Nelson's Spring). The island also has numerous non-potable volcanic
Nevis has several natural freshwater springs (including Nelson's Spring). The island also has numerous non-potable volcanic hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s, including most notably the Bath Spring near Bath village, just south of the capital Charlestown.
After heavy rains, powerful rivers of rainwater pour down the numerous ravines (known as ghauts). When the water reaches the coastline, the corresponding coastal ponds, both freshwater and brackish, fill to capacity and beyond, spilling over into the sea.
With modern development, the existing freshwater springs are no longer enough to supply water to the whole island. The water supply now comes mostly from Government wells. The major source of potable water for the island is groundwater, obtained from 14 active wells. Water is pumped from the wells, stored and allowed to flow by gravity to the various locations.The Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC)"Chapter 9: St. Kitts and Nevis"
. In Programme of Action for the sustainable development of small island developing States (SIDS POA). United Nations, 2003-09-29. Retrieved 28 August 2007.
Climate
The climate is tropical with little variation, tempered all year round (but particularly from December through February) by the steady north-easterly winds, called thetrade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
. There is a slightly hotter and somewhat rainier season from May to November.
Nevis lies within the track area of tropical storms and occasional hurricanes. These storms can develop between August and October. This time of year has the heaviest rainfalls.
Nevis also experiences many fires, including the devastating Nevisian Fire of 1876.
Economy
The official currency is theEastern Caribbean dollar
The Eastern Caribbean dollar (symbol: EC$; code: XCD) is the currency of all seven full members and one associate member of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). The successor to the British West Indies dollar, it has existed sinc ...
(EC$), which is shared by eight other territories in the region.
 The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean estimates the annual per capita
The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean estimates the annual per capita Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP) on Nevis to be about 10 percent higher than on St. Kitts."EU & the Eastern Caribbean: St Kitts and Nevis Overview". The European Commission's Delegation in Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
Tourism
The major source of revenue for Nevis today is tourism. During the 2003–2004 season, approximately 40,000 tourists visited the island. A five-star hotel ''(The Four Seasons Resort Nevis, West Indies)'', four exclusive restored plantation inns, and several smaller hotels including Oualie Beach Resort are currently in operation. Larger developments along the west coast have recently been approved and are in the process of being developed.Offshore banking
The introduction of secrecy legislation has made offshore financial services a rapidly growing economic sector in Nevis. Incorporation of companies, international insurance and reinsurance, as well as several international banks, trust companies, asset management firms, have created a boost in the economy. During 2005, the Nevis Island Treasury collected $94.6 million in annual revenue, compared to $59.8 million during 2001. In 1998, 17,500 international banking companies were registered in Nevis. Registration and annual filing fees paid in 1999 by these entities amounted to over 10 percent of Nevis' revenues. The offshore financial industry gained importance during the financial disaster of 1999 when Hurricane Lenny damaged the major resort on the island, causing the hotel to be closed down for a year and 400 of the 700 employees to be laid off. In 2000, the Financial Action Task Force, part of theOrganisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries ...
(OECD), issued a blacklist of 35 nations which were said to be non-cooperative in the campaign against tax evasion and money laundering
Money laundering is the process of concealing the origin of money, obtained from illicit activities such as drug trafficking, corruption, embezzlement or gambling, by converting it into a legitimate source. It is a crime in many jurisdictions ...
. The list included the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of ...
.
Politics
 The political structure for the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is based on the Westminster Parliamentary system, but it is a unique structure in that Nevis has its own unicameral legislature, consisting of His Majesty's representative (the Deputy Governor General) and members of the Nevis Island Assembly. Nevis has considerable autonomy in its legislative branch. The constitution actually empowers the Nevis Island Legislature to make laws that cannot be abrogated by the National Assembly.See section 3 and 4 about Nevis Island Legislature and Administration in ''The Saint Christopher and Nevis Constitution Order 1983''. Published online b
The political structure for the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is based on the Westminster Parliamentary system, but it is a unique structure in that Nevis has its own unicameral legislature, consisting of His Majesty's representative (the Deputy Governor General) and members of the Nevis Island Assembly. Nevis has considerable autonomy in its legislative branch. The constitution actually empowers the Nevis Island Legislature to make laws that cannot be abrogated by the National Assembly.See section 3 and 4 about Nevis Island Legislature and Administration in ''The Saint Christopher and Nevis Constitution Order 1983''. Published online bGeorgetown University
and also b
Retrieved 8 August 2006. Nevis has a constitutionally protected right to secede from the federation, should a two-thirds majority of the island's population vote for independence in a local referendum. Section 113.(1) of the constitution states: "The Nevis Island Legislature may provide that the island of Nevis shall cease to be federated with the island of Saint Christopher and accordingly that this Constitution shall no longer have effect in the island of Nevis." Nevis has its own
premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of governm ...
and its own government, the Nevis Island Administration
The Nevis Island Administration is the devolved government of the island of Nevis within the Saint Kitts and Nevis, Federation of St Kitts and Nevis.
Ministers
The ministers within the Nevis Island Administration are as follows:
See also
*Nev ...
. It collects its own taxes and has a separate budget, with a current account surplus. According to a statement released by the Nevis Ministry of Finance in 2005, Nevis had one of the highest growth rates in gross national product and per capita income in the Caribbean at that point.
Elections
Nevis elections are scheduled every five years. The Nevis elections of 2013, called on 23 January 2013, was won by the party in opposition, theConcerned Citizens Movement
The Concerned Citizens' Movement (CCM) is a Nevis-based political party in Saint Kitts and Nevis. Led by Mark Brantley, it is currently the largest party in Nevis, holding all three seats Nevisian seats in the National Assembly and three out of f ...
(CCM), led by Vance Amory
Vance Winkworth Amory (22 May 1949 – 2 April 2022) was a Saint Kitts and Nevis politician and cricketer. He served two stints as Premier of Nevis, from 1992 to 2006 and from 2013 to 2017, and served as the Minister of Sports in the Nevis Isl ...
. The CCM won three of the five seats in the Nevis Island Assembly, while the incumbent party, the Nevis Reformation Party
The Nevis Reformation Party is a Nevis-based political party in Saint Kitts and Nevis. The party currently holds none of the eleven seats in the National Assembly of Saint Kitts and Nevis, National Assembly. It is the official opposition party on ...
(NRP), won two.
In the federal elections of 2010, the CCM won two of the three Nevis assigned Federal seats, while the NRP won one. Of the eight Saint Kitts assigned federal seats, the St Kitts-Nevis Labour Party won six and the People's Action Movement (PAM) two.
Movement for constitutional reform
Joseph Parry, leader of the opposition, has indicated that he favours constitutional reform over secession for Nevis. His party, the NRP, has historically been the strongest and most ardent proponent for Nevis independence; the party came to power with secession as the main campaign issue. In 1975, the NRP manifesto declared that: "The Nevis Reformation Party will strive at all costs to gain secession for Nevis from St. Kitts – a privilege enjoyed by the island of Nevis prior to 1882." A cursory proposal for constitutional reform was presented by the NRP in 1999, but the issue was not prominent in the 2006 election campaign and it appears a detailed proposal has yet to be worked out and agreed upon within the party. In ''Handbook of Federal Countries'' published byForum of Federations
The Forum of Federations is an international organization based in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It develops and shares comparative expertise on the practice of federal and decentralized governance through a global network. The Forum and its partners ...
, the authors consider the constitution problematic because it does not "specifically outline" the federal financial arrangements or the means by which the central government and Nevis Island Administration can raise revenue: "In terms of the NIA, the constitution only states (in s. 108(1)) that 'all revenues...raised or received by the Administration...shall be paid into and form a fund styled the Nevis Island Consolidated Fund.' ..Section 110(1) states that the proceeds of all 'takes' collected in St. Kitts and Nevis under any law are to be shared between the federal government and the Nevis Island Administration based on population. The share going to the NIA, however, is subject to deductions (s. 110(2)), such as the cost of common services and debt charges, as determined by the Governor-General (s.110(3)) on the advice of the Prime Minister who can also take advice from the Premier of Nevis (s.110(4))."Griffiths, Ann Lynn and Karl Nerenberg (2002). ''Handbook of Federal Countries''. Ed. Karl Nerenberg. Published McGill-Queen's Press – MQUP, 2002. , p. 274.
According to a 1995 report by the Commonwealth Observer Group of the Commonwealth Secretariat
The Commonwealth Secretariat is the main intergovernmental agency and central institution of the Commonwealth of Nations. It is responsible for facilitating co-operation between members; organising meetings, including the Commonwealth Heads o ...
, "the federal government is also the local government of St Kitts and this has resulted in a perception among the political parties in Nevis that the interests of the people of Nevis are being neglected by the federal government which is more concerned with the administration of St Kitts than with the federal administration."
Secession movement
Simeon Daniel, Nevis' first Premier and former leader of theNevis Reformation Party
The Nevis Reformation Party is a Nevis-based political party in Saint Kitts and Nevis. The party currently holds none of the eleven seats in the National Assembly of Saint Kitts and Nevis, National Assembly. It is the official opposition party on ...
(NRP) and Vance Amory
Vance Winkworth Amory (22 May 1949 – 2 April 2022) was a Saint Kitts and Nevis politician and cricketer. He served two stints as Premier of Nevis, from 1992 to 2006 and from 2013 to 2017, and served as the Minister of Sports in the Nevis Isl ...
, Premier and leader of the Concerned Citizens Movement
The Concerned Citizens' Movement (CCM) is a Nevis-based political party in Saint Kitts and Nevis. Led by Mark Brantley, it is currently the largest party in Nevis, holding all three seats Nevisian seats in the National Assembly and three out of f ...
(CCM), made sovereign independence for Nevis from the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of ...
part of their parties' agenda. Since independence from the United Kingdom in 1983, the Nevis Island Administration and the Federal Government have been involved in several conflicts over the interpretation of the new constitution which came into effect at independence. During an interview on Voice of America
Voice of America (VOA or VoA) is the state-owned news network and international radio broadcaster of the United States of America. It is the largest and oldest U.S.-funded international broadcaster. VOA produces digital, TV, and radio content ...
in March 1998, repeated in a government-issued press release headlined "PM Douglas Maintains 1983 Constitution is Flawed", Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Denzil Douglas called the constitution a "recipe for disaster and disharmony among the people of both islands".
A crisis developed in 1984 when the People's Action Movement
The People's Action Movement (PAM) is a political party in Saint Kitts and Nevis. The party currently holds four (largest share) of the 11 seats in the National Assembly. PAM operates only in Saint Kitts and for the 2022 general election is in a ...
(PAM) won a majority in the Federal elections and temporarily ceased honouring the Federal Government's financial obligations to Nevis. Consequently, cheques issued by the Nevis Administration were not honoured by the Bank, public servants in Nevis were not paid on time and the Nevis Island Administration experienced difficulties in meeting its financial obligations.The Concerned Citizens Movement (1996)"The Way Forward For The Island Of Nevis." ''Nevis, Queen of the Caribees''.
Nevis Island Administration, September 1996. Retrieved 8 August 2006. There is also substantial support in Nevis for
British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
status similar to Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territo ...
's, which was formerly the third of the tri-state Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla colony.
Legislative motivation for secession
In 1996, four new bills were introduced in the National Assembly in Saint Kitts, one of which made provisions to have revenue derived from activities in Nevis paid directly to the treasury in Saint Kitts instead of to the treasury in Nevis. Another bill, The Financial Services Committee Act, contained provisions that all investments in Saint Kitts and Nevis would require approval by an investment committee in Saint Kitts. This was controversial, because ever since 1983 the Nevis Island Administration had approved all investments for Nevis, on the basis that the constitution vests legislative authority for industries, trades and businesses and economic development in Nevis to the Nevis Island Administration.Phillips, Fred (2002). Commonwealth Caribbean Constitutional Law. Cavendish Publishing, 2002, . All three representatives from Nevis, including the leader of the opposition in the Nevis Island Assembly, objected to the introduction of these bills into the National Assembly in Saint Kitts, arguing that the bills would affect the ability of Nevis to develop its offshore financial services sector and that the bills would be detrimental to the Nevis economy. All the representatives in opposition in the National Assembly shared the conviction that the bills if passed into law, would be unconstitutional and undermine the constitutional and legislative authority of the Nevis Island Administration, as well as result in the destruction of the economy of Nevis. The constitutional crisis initially developed when the newly appointed Attorney General refused to grant permission for the Nevis Island Administration to assert its legal right in the Courts. After a decision of the High Court in favour of the Nevis Island Administration, the Prime Minister gave newspaper interviews stating that he "refused to accept the decision of the High Court". Due to the deteriorating relationship between the Nevis Island Administration and the Federal Government, a Constitutional Committee was appointed in April 1996 to advise on whether or not the present constitutional arrangement between the islands should continue. The committee recommended constitutional reform and the establishment of an island administration for Saint Kitts, separate from the Federal Government. The Federal Government in Saint Kitts fills both functions today and Saint Kitts does not have an equivalent to the Nevis Island Administration. Disagreements between the political parties in Nevis and between the Nevis Island Administration and the Federal Government have prevented the recommendations by the electoral committee from being implemented. The problematic political arrangement between the two islands, therefore, continues to date. Nevis has continued developing its own legislation, such as The Nevis International Insurance Ordinance and the Nevis International Mutual Funds Ordinance of 2004,As reported by the Premier at the official Web site foNevis Financial Services Departments and the Ministry of Finance, Nevis
. Retrieved 8 August 2006. but calls for secession are often based on concerns that the legislative authority of the Nevis Island Administration might be challenged again in the future.
Fiscal motivation for secession
The issues of political dissension between Saint Kitts and Nevis are often centred around perceptions of imbalance in the economic structure. As noted by many scholars, Nevisians have often referred to a structural imbalance in Saint Kitts' favour in how funds are distributed between the two islands and this issue has made the movement for Nevis secession a constant presence in the island's political arena, with many articles appearing in the local press expressing concerns such as those compiled by Everton Powell in "What Motivates Our Call for Independence": * Many of the businesses that operate in Nevis are headquartered in Saint Kitts and pay the corporate taxes to Saint Kitts, despite the fact that profits for those businesses are derived from Nevis. * The vast majority of Nevisians and residents of Nevis depart the Federation from Saint Kitts. This meant that departure taxes are paid in Saint Kitts. * The bulk of cargo destined for Nevis enters the Federation through Saint Kitts. Custom duties are therefore paid in Saint Kitts. * The largest expenditure for Nevis, approximately 29 percent of the Nevis Island Administration's recurrent budget, is education and health services, but the Nevis Island Legislature has no power to legislate over these two areas. * Police, defense and coast guard are a federal responsibility. Charlestown Police Station, which served as the Headquarters for police officers in Nevis, was destroyed by fire in December 1991. Police officers initially had to operate out of the ruin, until the Nevis Island Administration managed to raise the resources to re-house the police. * Nevis experiences an economic disadvantage because of preferential treatment by the federal government for development of Saint Kitts. The division of foreign aid and various forms of international assistance toward development and infrastructure are especially contentious issues. Lists showing the disparities in sharing have been compiled by Dr. Everson Hull, a former Economics professor of Howard University, and are available online.1998 referendum
A referendum on secession from the Federation of St. Kitts and Nevis was held in 1998. Although 62% voted in favor of a secession, a two-thirds majority would have been necessary for the referendum to succeed.Government
 The island of Nevis is divided into five administrative subdivisions called
The island of Nevis is divided into five administrative subdivisions called parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or m ...
es, each of which has an elected representative in the Nevis Island Assembly. The division of this almost round island into parishes was done in a circular sector pattern, so each parish is shaped like a pie slice, reaching from the highest point of Nevis Peak down to the coastline.
The parishes have double names, for example Saint George Gingerland
Saint George Gingerland, also known as St. George's Gingerland, is a parish in the southeastern part of the island of Nevis, Leeward Islands, West Indies. It is one of five parishes on the island, and has a total population of about 2,500. The f ...
. The first part of the name is the name of the patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
of the parish church, and the second part of the name is the traditional common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrast ...
of the parish. Often the parishes are referred to simply by their common names. The religious part of a parish name is sometimes written or pronounced in the possessive: Saint George's Gingerland.
The five parishes of Nevis are:
* Saint George Gingerland
Saint George Gingerland, also known as St. George's Gingerland, is a parish in the southeastern part of the island of Nevis, Leeward Islands, West Indies. It is one of five parishes on the island, and has a total population of about 2,500. The f ...
* Saint James Windward
Saint James Windward is the largest of five parishes on the island of Nevis. These five parishes are in turn part of the 14 administrative parishes making up the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Saint James Parish is located in the northeast ...
* Saint John Figtree
Saint John Figtree is one of five administrative parishes which make up the small Caribbean island of Nevis. These five parishes are part of the fourteen parishes that exist within the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis, a two-island country in ...
* Saint Paul Charlestown
* Saint Thomas Lowland
Saint Thomas Lowland is one of 5 Nevis parishes which are in turn part of the 14 administrative parishes that make up the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Leeward Islands, Lesser Antilles, West Indies.
The coast of this parish consists prim ...
Culture
''Culturama'', the annual cultural festival of Nevis, is celebrated during the Emancipation Day weekend, the first week of August. The festivities include many traditional folk dances, such as themasquerade
Masquerade or Masquerader may refer to:
Events
* Masquerade ball, a costumed dance event
* Masquerade ceremony, a rite or cultural event in many parts of the world, especially the Caribbean and Africa
* Masqueraders, the performers in the West ...
, the Moko jumbie
In the mythology of Mangaia in the Cook Islands, Moko is a wily character and grandfather of the heroic Ngaru.
Moko is a ruler or king of the lizards, and he orders his lizard subjects to climb into the basket of the sky demon Amai-te-rangi Acco ...
s on stilts, Cowboys and Indians, and Plait the Ribbon, a May pole dance. The celebration was given a more organised form in 1974, including a Miss Culture Show and a Calypso Competition, as well as drama performances, old fashion Troupes (including Johnny Walkers, Giant and Spear, Bulls, Red Cross and Blue Ribbon), arts and crafts exhibitions and recipe competitions. According to the Nevis Department of Culture, the aim is to protect and encourage indigenous folklore, in order to make sure that the uniquely Caribbean culture can "reassert itself and flourish".
Language
The official language is English, yetSaint Kitts Creole
Saint Kitts Creole is a dialect of Leeward Caribbean Creole English spoken in Saint Kitts and Nevis by around 40,000 people. Saint Kitts Creole does not have the status of an official language.
Saint Kitts Creole has much the same history as ot ...
(known on the island as 'Nevisian' or 'Nevis creole') is also widely spoken. The local creole is actually more widely spoken on Nevis than on the neighbouring island.
Music, theatre and dance
Nevisian culture has since the 17th century incorporated African, European and East Indian cultural elements, creating a distinct Afro-Caribbean culture. Several historical anthropologists have done field research Nevis and in Nevisian migrant communities in order to trace the creation and constitution of a Nevisian cultural community. Karen Fog Olwig published her research about Nevis in 1993, writing that the areas where the Afro-Caribbean traditions were especially strong and flourishing relate tokinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
and subsistence farming. However, she adds, Afro-Caribbean cultural impulses were not recognised or valued in the colonial society and were therefore often expressed through Euro-Caribbean cultural forms.
Examples of European forms appropriated to express Afro-Caribbean culture are the Nevisian and Kittitian ''Tea Meetings'' and ''Christmas Sports''. According to anthropologist Roger D. Abrahams Roger David Abrahams (June 12, 1933 – June 20, 2017) was an American folklorist whose work focused on the expressive cultures and cultural histories of the Americas, with a specific emphasis on African American peoples and traditions.
Abrahams ...
, these traditional performance art forms are "Nevisian approximation of British performance codes, techniques, and patterns". He writes that the Tea Meetings were staged as theatrical "battles between decorum and chaos", decorum represented by the ceremony chairmen and chaos the hecklers in the audience, with a diplomatic King or a Queen presiding over the battle to ensure fairness.
The Christmas Sports included a form of comedy and satire based on local events and gossip. They were historically an important part of the Christmas celebrations in Nevis, performed on Christmas Eve by small troupes consisting of five or six men accompanied by string bands from different parts of the island. One of the men in the troupe was dressed as a woman, playing all the female parts in the dramatisations. The troupes moved from yard to yard to perform their skits, using props, face paint and costumes to play the roles of well-known personalities in the community.
Examples of gossip about undesired behaviour that could surface in the skits for comic effect were querulous neighbours, adulterous affairs, planters mistreating workers, domestic disputes or abuse, crooked politicians and any form of stealing or cheating experienced in the society. Even though no names were mentioned in these skits, the audience would usually be able to guess who the heckling message in the troupe's dramatised portrayals was aimed at, as it was played out right on the person's own front yard. The acts thus functioned as social and moral commentaries on current events and behaviours in Nevisian society. This particular form is called "Bazzarding" by many locals. Abrahams theorises that Christmas Sports are rooted in the pre-emancipation Christmas and New Year holiday celebrations, when the enslaved population had several days off.Abrahams, Roger D. (1973). "Christmas Mummings on Nevis." North Carolina Folklore Journal (1973): pp. 120–31.
American folklorist and musicologist Alan Lomax
Alan Lomax (; January 31, 1915 – July 19, 2002) was an American ethnomusicologist, best known for his numerous field recordings of folk music of the 20th century. He was also a musician himself, as well as a folklorist, archivist, writer, sch ...
visited Nevis in 1962 in order to conduct long-term research into the black folk culture of the island. His field trip to Nevis and surrounding islands resulted in the anthology ''Lomax Caribbean Voyage'' series.
Among the Nevisians recorded were chantey-singing fishermen in a session organised in a rum shop in Newcastle; Santoy, the Calypsonian, performing calypsos by Nevisian ballader and local legend Charles Walters to guitar and cuatro; and string bands, fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
players and drummers from Gingerland, performing quadrilles.
The island is also known for "Jamband music", which is the kind of music performed by local bands during the "Culturama Festival" and is key to "Jouvert" dancing. The sounds of the so-called "Iron Band" are also popular within the culture; many locals come together using any old pans, sinks, or other kits of any sort; which they use to create sounds and music. This form of music is played throughout the villages during the Christmas and carnival seasons.
Architecture
 A series of earthquakes during the 18th century severely damaged most of the colonial-era stone buildings of Charlestown. The
A series of earthquakes during the 18th century severely damaged most of the colonial-era stone buildings of Charlestown. The Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
stone buildings in Charlestown that are visible today had to be partially rebuilt after the earthquakes, and this led to the development of a new architectural style, consisting of a wooden upper floor over a stone ground floor; the new style resisted earthquake damage much more effectively.
Two famous Nevisian buildings from the 18th century are Hermitage Plantation, built of lignum vitae wood in 1740, the oldest surviving wooden house still in use in the Caribbean today, and the Bath Hotel, the first hotel in the Caribbean, a luxury hotel and spa built by John Huggins in 1778. The soothing waters of the hotel's hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
and the lively social life on Nevis attracted many famous Europeans including Antigua-based Admiral Nelson, and Prince William Henry, Duke of Clarence
Duke of Clarence is a substantive title which has been traditionally awarded to junior members of the British Royal Family. All three creations were in the Peerage of England.
The title was first granted to Lionel of Antwerp, the second son ...
, (future William IV of the United Kingdom
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded h ...
), who attended balls and private parties at the Bath Hotel. Today, the building serves as government offices, and there are two outdoor hot-spring bathing spots which were specially constructed in recent years for public use.
An often repeated legend appears to suggest that a destructive 1680 or 1690 earthquake and tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
destroyed the buildings of the original capital Jamestown on the west coast. Folk tales
Oral literature, orature or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung as opposed to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used vary ...
say that the town sank beneath the ocean, and the tsunami is blamed for the escape of (possibly fictional) pirate Red Legs Greaves
"Red Legs" Greaves was a Scottish buccaneer active in the Caribbean and the West Indies during the 1670s. His nickname came from the term ''Redlegs'' used to refer to the class of poor whites who lived on colonial Barbados.
Although considered ...
. However, archaeologists from the University of Southampton
, mottoeng = The Heights Yield to Endeavour
, type = Public research university
, established = 1862 – Hartley Institution1902 – Hartley University College1913 – Southampton University Coll ...
who have done excavations in the area, have found no evidence to indicate that the story is true. They state that this story may originate with an over-excited Victorian letter writer sharing somewhat exaggerated accounts of his exotic life in the tropical colony with a British audience back home.
One such letter recounts that so much damage was done to the town that it was completely evacuated, and was engulfed by the sea. Early maps do not, however, actually show a settlement called "Jamestown", only "Morton's Bay", and later maps show that all that was left of Jamestown/Morton's Bay in 1818 was a building labelled "Pleasure House". Very old bricks that wash up on Pinney's Beach after storms may have contributed to this legend of a sunken town; however, these bricks are thought to be dumped ballast from 17th and 18th century sailing ships.
Notable people
*Arthur Anslyn
Captain Roy Arthur Anslyn (23 December 1944–7 October 2017), formally known as Arthur Anslyn or Captain Anslyn, and informally known as "Brother" Anslyn, was a recognized expert in marine knowledge who, from 1999 to his death, served as Mar ...
MBE, marine expert
* Keith Arthurton
Keith Lloyd Thomas Arthurton (born 21 February 1965) is a former West Indian cricketer. Having become only the third player to hail from Nevis, the middle order batsman/left-arm orthodox bowler played in 33 Tests between July 1988 and August 19 ...
, cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
player
* Bertram L. Baker
Bertram Llewellyn Baker (January 10, 1898 – March 8, 1985) was a member of the New York State Assembly from 1948 to 1970, representing central Brooklyn, New York. He was the first Black person elected to any office by voters in Brooklyn.
Early ...
, Majority Whip of the New York State Assembly (1966–1970)
* Stephen Breyer
Stephen Gerald Breyer ( ; born August 15, 1938) is a retired American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the U.S. Supreme Court from 1994 until his retirement in 2022. He was nominated by President Bill Clinton, and repl ...
, United States Supreme Court Justice
* John Cleese
John Marwood Cleese ( ; born 27 October 1939) is an English actor, comedian, screenwriter, and producer. Emerging from the Cambridge Footlights in the 1960s, he first achieved success at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe and as a scriptwriter and ...
, actor/comedian, founding member of the British comedy group Monty Python
Monty Python (also collectively known as the Pythons) were a British comedy troupe who created the sketch comedy television show '' Monty Python's Flying Circus'', which first aired on the BBC in 1969. Forty-five episodes were made over four ...
* Rupert Crosse
Rupert may refer to:
People
* Rupert (name), various people known by the given name or surname "Rupert"
Places Canada
*Rupert, Quebec, a village
*Rupert Bay, a large bay located on the south-east shore of James Bay
*Rupert River, Quebec
*Rupert' ...
, first African American to be nominated for an Academy Award
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
as Best Supporting Actor
* Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
, statesman and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States, known simply as the Founding Fathers or Founders, were a group of late-18th-century American Revolution, American revolutionary leaders who United Colonies, united the Thirteen Colonies, oversaw the Am ...
* Runako Morton
Runako Shakur Morton (22 July 1978 – 4 March 2012) was a Nevisian cricketer who played for West Indies in all formats of the game. He was a right-handed batsman and a right-handed offbreak bowler.
Domestic career
A lively, often unpredicta ...
, cricket player
* Frances Nelson
Frances "Fanny" Nelson, Viscountess Nelson ( Frances Herbert Woolward, formerly Nisbet; (1758 4 May 1831), is best known as the wife of Horatio Nelson, the British naval officer who won several victories over the French during the French Rev ...
, wife of Admiral Lord Horatio Nelson
* Eulalie Spence
Eulalie Spence (June 11, 1894 – March 7, 1981) was a writer, teacher, director, actress and playwright from the British West Indies. She was an influential member of the Harlem Renaissance, writing fourteen plays, at least five of which were pu ...
, pioneer playwright of the Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the t ...
* Elquemedo Willett
Elquemedo Tonito Willett (born 1 May 1953) is a former West Indian international cricketer who played in five Test matches in 1973 and 1974.
He made his first-class debut for Leeward Islands in 1970–71 at the age of 17, and played his last ...
, cricket player, inducted into the Nevis Sports Museum Hall of Fame in 2005CMC (2005)"Willett for Nevis Sports Hall of Fame"
''West Indies Cricket Board'', 27 February 2005. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
See also
* Chief Justice of the Leeward Islands *Nevis Historical and Conservation Society
The Nevis Historical and Conservation Society is a nonprofit, non-governmental organisation (NGO) based in the Caribbean island of Nevis, founded in 1980 to protect the cultural and natural heritage of the island.
Mission and funding
The Societ ...
References
Further reading
* Michener, James, A. 1989. ''Caribbean''. Secker & Warburg. London. (Especially Chap. VIII. "A Wedding on Nevis", pp. 289–318). The book is a fictionalised account of Caribbean history, but according to the publisher, "...everything said about Nelson and his frantic search for a wealthy life is based on fact." * Ordnance Survey, Government of the United Kingdom, 1984. ''Nevis, with part of St. Christopher (Saint Kitts). Series E803 (D.O.S. 343), Sheet NEVIS, Edition 5 O.S.D. 1984''. Reprinted in 1995, published by the Government of the United Kingdom (Ordnance Survey) for the Government of Saint Christopher (St. Kitts) and Nevis. * Robinson, David and Jennifer Lowery (Editors), 2000. ''The natural history of the island of Nevis''.Nevis Historical and Conservation Society
The Nevis Historical and Conservation Society is a nonprofit, non-governmental organisation (NGO) based in the Caribbean island of Nevis, founded in 1980 to protect the cultural and natural heritage of the island.
Mission and funding
The Societ ...
Press, Ithaca, New York.
* Keith C. Simmonds. "Political and Economic Factors Influencing the St. Kitts-Nevis Polity: An Historical Perspective." Phylon Vol. 48, No. 4 (4th Qtr., 1987), pp. 277–286
External links
Nevis Island Administration
Nevis Island Tourism Authority
{{Coord, 17, 09, N, 62, 35, W, type:isle, display=title Autonomous regions Islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis Pleistocene stratovolcanoes Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Saint Kitts and Nevis