Natural Disasters In Georgia (U.S. State) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Nature, in the broadest sense, is the
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the
 Earth is the only
Earth is the only
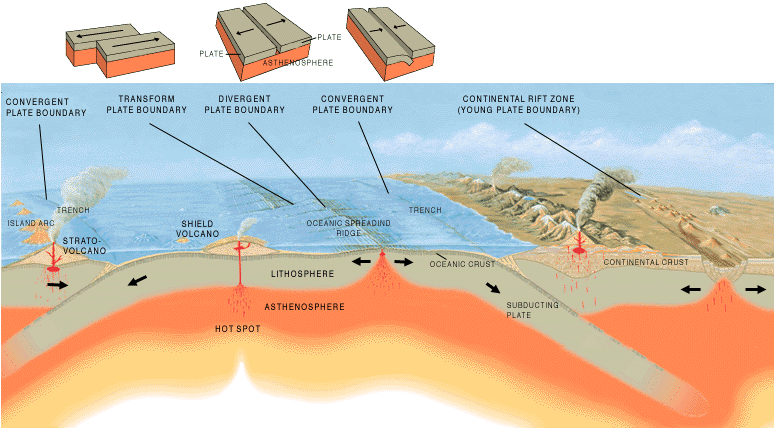 The geology of an area evolves through time as rock units are deposited and inserted and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by
The geology of an area evolves through time as rock units are deposited and inserted and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by
 Earth is estimated to have formed 4.54 billion years ago from the
Earth is estimated to have formed 4.54 billion years ago from the  Continents formed, then broke up and reformed as the surface of Earth reshaped over hundreds of millions of years, occasionally combining to make a
Continents formed, then broke up and reformed as the surface of Earth reshaped over hundreds of millions of years, occasionally combining to make a
 The Earth's atmosphere is a key factor in sustaining the
The Earth's atmosphere is a key factor in sustaining the  Weather can have both beneficial and harmful effects. Extremes in weather, such as
Weather can have both beneficial and harmful effects. Extremes in weather, such as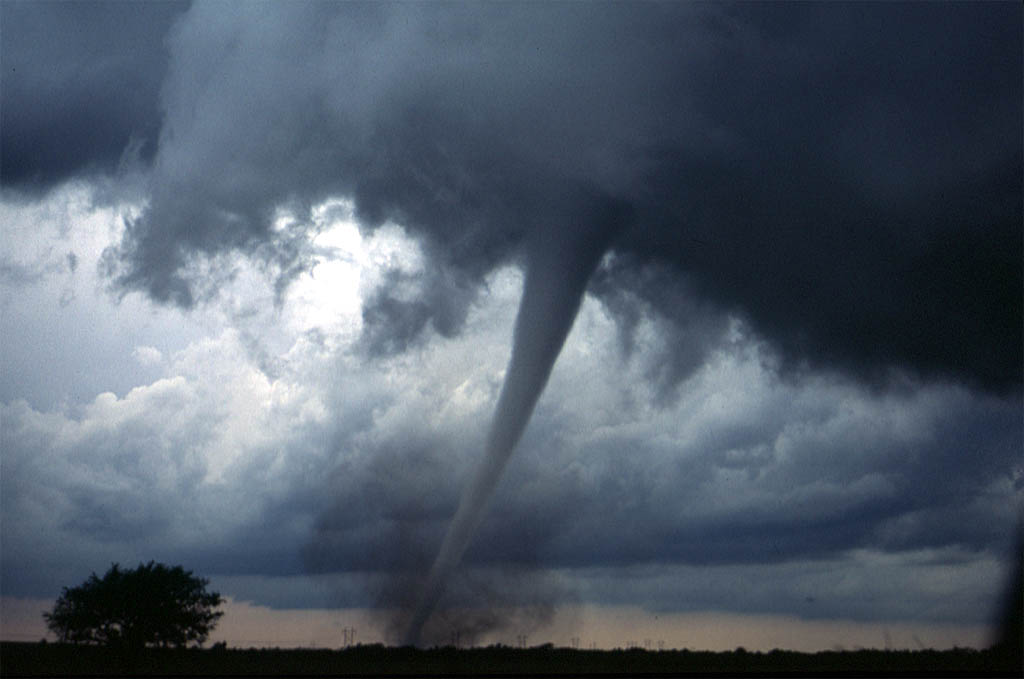  The climate of a region depends on a number of factors, especially
The climate of a region depends on a number of factors, especially
 Water is a
Water is a
 An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35
"
UN Atlas of the Oceans
This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to oceanography. The major oceanic divisions are defined in part by the
 A lake (from Latin word ''lacus'') is a
A lake (from Latin word ''lacus'') is a
 A pond is a
A pond is a
 A river is a natural
A river is a natural
 A stream is a flowing body of water with a
A stream is a flowing body of water with a

 Ecosystems are composed of a variety of biotic and
Ecosystems are composed of a variety of biotic and
 Wilderness is generally defined as areas that have not been significantly modified by human activity. Wilderness areas can be found in preserves, estates, farms, conservation preserves, ranches, national forests, national parks, and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches, or otherwise undeveloped areas. Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain
Wilderness is generally defined as areas that have not been significantly modified by human activity. Wilderness areas can be found in preserves, estates, farms, conservation preserves, ranches, national forests, national parks, and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches, or otherwise undeveloped areas. Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain
 Although there is no universal agreement on the definition of life, scientists generally accept that the biological manifestation of life is characterized by
Although there is no universal agreement on the definition of life, scientists generally accept that the biological manifestation of life is characterized by
 The
The
 The first form of life to develop on the Earth were microbes, and they remained the only form of life until about a billion years ago when multi-cellular organisms began to appear. Microorganisms are single-celled organisms that are generally
The first form of life to develop on the Earth were microbes, and they remained the only form of life until about a billion years ago when multi-cellular organisms began to appear. Microorganisms are single-celled organisms that are generally

 Originally
Originally
of plant life from a previous era. People in many regions and countries take great pride in their individual arrays of characteristic flora, which can vary widely across the globe due to differences in climate and

 Beauty in nature has historically been a prevalent theme in art and books, filling large sections of libraries and bookstores. That nature has been depicted and celebrated by so much art, photography, poetry, and other literature shows the strength with which many people associate nature and beauty. Reasons why this association exists, and what the association consists of, are studied by the branch of philosophy called
Beauty in nature has historically been a prevalent theme in art and books, filling large sections of libraries and bookstores. That nature has been depicted and celebrated by so much art, photography, poetry, and other literature shows the strength with which many people associate nature and beauty. Reasons why this association exists, and what the association consists of, are studied by the branch of philosophy called
BC Spaces for Nature. Accessed: May 20, 2006. This artistic movement also coincided with the Transcendentalist movement in the Western world. A common classical idea of beautiful art involves the word mimesis, the imitation of nature. Also in the realm of ideas about beauty in nature is that the perfect is implied through perfect mathematical
 Some fields of science see nature as matter in motion, obeying certain laws of nature which science seeks to understand. For this reason the most fundamental science is generally understood to be "
Some fields of science see nature as matter in motion, obeying certain laws of nature which science seeks to understand. For this reason the most fundamental science is generally understood to be "

 Outer space, also simply called ''space'', refers to the relatively empty regions of the
Outer space, also simply called ''space'', refers to the relatively empty regions of the
"Naturalism"
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Edward N. Zalta (ed.), > this includes the ''methodological naturalism'' of natural science, which makes the
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (iucnredlist.org)
* {{Authority control Environmental science Environmental social science concepts Main topic articles
 Nature, in the broadest sense, is the
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical
Physical may refer to:
* Physical examination, a regular overall check-up with a doctor
* ''Physical'' (Olivia Newton-John album), 1981
** "Physical" (Olivia Newton-John song)
* ''Physical'' (Gabe Gurnsey album)
* "Physical" (Alcazar song) (2004)
* ...
world or universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried ...
of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.
The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intel ...
''nature'' and is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis
Fusis, Phusis or Physis (; grc, φύσις ) is a Greek philosophical, theological, and scientific term, usually translated into English—according to its Latin translation "natura"—as "nature". The term originated in ancient Greek philosophy ...
'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord.
The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers (though this word had a dynamic dimension then, especially for Heraclitus
Heraclitus of Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἡράκλειτος , "Glory of Hera"; ) was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.
Little is known of Heraclitus's life. He wrot ...
), and has steadily gained currency ever since.
During the advent of modern scientific method
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientifi ...
in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
, American transcendentalism
Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that developed in the late 1820s and 1830s in New England. "Transcendentalism is an American literary, political, and philosophical movement of the early nineteenth century, centered around Ralph Wald ...
) or a mere decorum for divine providence
In theology, Divine Providence, or simply Providence, is God's intervention in the Universe. The term ''Divine Providence'' (usually capitalized) is also used as a title of God. A distinction is usually made between "general providence", which ...
or human history (Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends a ...
, Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
). However, a vitalist
Vitalism is a belief that starts from the premise that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things." Wher ...
vision of nature, closer to the presocratic one, got reborn at the same time, especially after Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
.
Within the various uses of the word today, "nature" often refers to geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology ...
and wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects—the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
. It is often taken to mean the "natural environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to the Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses t ...
" or wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
—wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, "human nature" or "the whole of nature". This more traditional concept of natural things that can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
or a human mind
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for various m ...
. Depending on the particular context, the term "natural" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
.
Earth
 Earth is the only
Earth is the only planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
known to support life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
, and its natural features are the subject of many fields of scientific research. Within the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
, it is third closest to the Sun; it is the largest terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
and the fifth largest overall. Its most prominent climatic features are its two large polar regions, two relatively narrow temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
zones, and a wide equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
ial tropical to subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
region. Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
varies widely with location, from several metres of water per year to less than a millimetre. 71 percent of the Earth's surface is covered by salt-water oceans. The remainder consists of continents and islands, with most of the inhabited land in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
.
Earth has evolved through geological and biological processes that have left traces of the original conditions. The outer surface is divided into several gradually migrating tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
s. The interior remains active, with a thick layer of plastic mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
and an iron-filled core that generates a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
. This iron core is composed of a solid inner phase, and a fluid outer phase. Convective motion in the core generates electric currents through dynamo action, and these, in turn, generate the geomagnetic field.
The atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
conditions have been significantly altered from the original conditions by the presence of life-forms, which create an ecological balance that stabilizes the surface conditions. Despite the wide regional variations in climate by latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
and other geographic factors, the long-term average global climate is quite stable during interglacial periods, and variations of a degree or two of average global temperature have historically had major effects on the ecological balance, and on the actual geography of the Earth.
Geology
Geology is the science and study of the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth. The field of geology encompasses the study of the composition,structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such a ...
, physical properties
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are ...
, dynamics, and history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
of Earth materials, and the processes by which they are formed, moved, and changed. The field is a major academic discipline
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
, and is also important for mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
and hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
extraction, knowledge about and mitigation of natural hazard
A natural hazard is a natural phenomenon that might have a negative effect on humans and other animals, or the environment. Natural hazard events can be classified into two broad categories: geophysical and biological.
An example of the distinc ...
s, some Geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics for the solution of its respective engineering problems. It ...
fields, and understanding past climates and environments.
Geological evolution
 The geology of an area evolves through time as rock units are deposited and inserted and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by
The geology of an area evolves through time as rock units are deposited and inserted and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by deposition
Deposition may refer to:
* Deposition (law), taking testimony outside of court
* Deposition (politics), the removal of a person of authority from political power
* Deposition (university), a widespread initiation ritual for new students practiced f ...
onto the surface or intrude into the overlying rock
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the l ...
. Deposition can occur when sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
s settle onto the surface of the Earth and later lithify into sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
, or when as volcanic material
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
such as volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
or lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
flows, blanket the surface. Igneous intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s such as batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, s ...
s, laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apar ...
s, dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
, and sills, push upwards into the overlying rock, and crystallize as they intrude.
After the initial sequence of rocks has been deposited, the rock units can be deformed and/or metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
. Deformation typically occurs as a result of horizontal shortening, horizontal extension, or side-to-side (strike-slip
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
) motion. These structural regimes broadly relate to convergent boundaries
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a ...
, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries, respectively, between tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
.
Historical perspective
 Earth is estimated to have formed 4.54 billion years ago from the
Earth is estimated to have formed 4.54 billion years ago from the solar nebula
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened int ...
, along with the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
and other planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s. The Moon formed roughly 20 million years later. Initially molten, the outer layer of the Earth cooled, resulting in the solid crust. Outgassing and volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, most or all of which came from ice delivered by comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, produced the oceans and other water sources. The highly energetic chemistry is believed to have produced a self-replicating molecule around 4 billion years ago.
 Continents formed, then broke up and reformed as the surface of Earth reshaped over hundreds of millions of years, occasionally combining to make a
Continents formed, then broke up and reformed as the surface of Earth reshaped over hundreds of millions of years, occasionally combining to make a supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leav ...
. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia which broke apart about 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
, which broke apart about 180 million years ago.
During the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is prec ...
era, freezing temperatures covered much of the Earth in glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s and ice sheets. This hypothesis has been termed the " Snowball Earth", and it is of particular interest as it precedes the Cambrian explosion in which multicellular life forms began to proliferate about 530–540 million years ago.
Since the Cambrian explosion there have been five distinctly identifiable mass extinctions
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It ...
. The last mass extinction occurred some 66 million years ago, when a meteorite collision probably triggered the extinction of the non-avian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s and other large reptiles, but spared small animals such as mammals. Over the past 66 million years, mammalian life diversified.
Several million years ago, a species of small African ape
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and as well as Europe in prehistory), which together with its sister g ...
gained the ability to stand upright. The subsequent advent of human life, and the development of agriculture and further civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
allowed humans to affect the Earth more rapidly than any previous life form, affecting both the nature and quantity of other organisms as well as global climate. By comparison, the Great Oxygenation Event, produced by the proliferation of algae during the Siderian
The Siderian Period (; grc, σίδηρος, sídēros, meaning "iron") is the first geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Ma to Ma (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chr ...
period, required about 300 million years to culminate.
The present era is classified as part of a mass extinction event, the Holocene extinction event, the fastest ever to have occurred. Some, such as E. O. Wilson
Edward Osborne Wilson (June 10, 1929 – December 26, 2021) was an American biologist, naturalist, entomologist and writer. According to David Attenborough, Wilson was the world's leading expert in his specialty of myrmecology, the study of an ...
of Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
, predict that human destruction of the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
could cause the extinction of one-half of all species in the next 100 years. The extent of the current extinction event is still being researched, debated and calculated by biologists.
Atmosphere, climate, and weather
 The Earth's atmosphere is a key factor in sustaining the
The Earth's atmosphere is a key factor in sustaining the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
. The thin layer of gases that envelops the Earth is held in place by gravity. Air is mostly nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, with much smaller amounts of carbon dioxide, argon, etc. The atmospheric pressure declines steadily with altitude. The ozone layer plays an important role in depleting the amount of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
(UV) radiation that reaches the surface. As DNA is readily damaged by UV light, this serves to protect life at the surface. The atmosphere also retains heat during the night, thereby reducing the daily temperature extremes.
Terrestrial weather occurs almost exclusively in the lower part of the atmosphere, and serves as a convective system for redistributing heat. Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours ...
s are another important factor in determining climate, particularly the major underwater thermohaline circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to temp ...
which distributes heat energy from the equatorial oceans to the polar regions. These currents help to moderate the differences in temperature between winter and summer in the temperate zones. Also, without the redistributions of heat energy by the ocean currents and atmosphere, the tropics would be much hotter, and the polar regions much colder.
 Weather can have both beneficial and harmful effects. Extremes in weather, such as
Weather can have both beneficial and harmful effects. Extremes in weather, such as tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
es or hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s and cyclones, can expend large amounts of energy along their paths, and produce devastation. Surface vegetation has evolved a dependence on the seasonal variation of the weather, and sudden changes lasting only a few years can have a dramatic effect, both on the vegetation and on the animals which depend on its growth for their food.
Climate is a measure of the long-term trends in the weather. Various factors are known to influence the climate, including ocean currents, surface albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that refl ...
, greenhouse gases, variations in the solar luminosity, and changes to the Earth's orbit. Based on historical records, the Earth is known to have undergone drastic climate changes in the past, including ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
s.
 The climate of a region depends on a number of factors, especially
The climate of a region depends on a number of factors, especially latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
. A latitudinal band of the surface with similar climatic attributes forms a climate region. There are a number of such regions, ranging from the tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
at the equator to the polar climate in the northern and southern extremes. Weather is also influenced by the seasons, which result from the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
being tilted relative to its orbital plane
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) an ...
. Thus, at any given time during the summer or winter, one part of the Earth is more directly exposed to the rays of the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. This exposure alternates as the Earth revolves in its orbit. At any given time, regardless of season, the Northern and Southern Hemispheres experience opposite seasons.
Weather is a chaotic system
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have ...
that is readily modified by small changes to the environment, so accurate weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th cent ...
is limited to only a few days. Overall, two things are happening worldwide: (1) temperature is increasing on the average; and (2) regional climates have been undergoing noticeable changes.
Water on the Earth
 Water is a
Water is a chemical substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
that is composed of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
(H2O) and is vital for all known forms of life. In typical usage, ''water'' refers only to its liquid form or state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
, but the substance also has a solid state, ice, and a gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
eous state, water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, or steam. Water covers 71% of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's surface. On Earth, it is found mostly in oceans and other large bodies of water, with 1.6% of water below ground in aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteris ...
s and 0.001% in the air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
as vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (British English and Canadian English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Her ...
, clouds, and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. Oceans hold 97% of surface water, glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s, and polar ice caps 2.4%, and other land surface water such as rivers, lakes, and ponds 0.6%. Additionally, a minute amount of the Earth's water is contained within biological bodies and manufactured products.
Oceans
 An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35 parts per thousand
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they ...
(ppt) (3.5%), and nearly all seawater has a salinity in the range of 30 to 38 ppt. Though generally recognized as several 'separate' oceans, these waters comprise one global, interconnected body of salt water often referred to as the World Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the worl ...
or global ocean.Distribution of land and water on the planet"
UN Atlas of the Oceans
This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to oceanography. The major oceanic divisions are defined in part by the
continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas t ...
s, various archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
s, and other criteria: these divisions are (in descending order of size) the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
, the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-small ...
, and the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays and other names. There are also salt lakes, which are smaller bodies of landlocked saltwater that are not interconnected with the World Ocean. Two notable examples of salt lakes are the Aral Sea and the Great Salt Lake.
Lakes
 A lake (from Latin word ''lacus'') is a
A lake (from Latin word ''lacus'') is a terrain feature
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surf ...
(or physical feature), a body of liquid on the surface of a world that is localized to the bottom of basin (another type of landform or terrain feature; that is, it is not global) and moves slowly if it moves at all. On Earth, a body of water is considered a lake when it is inland, not part of the ocean, is larger and deeper than a pond, and is fed by a river. The only world other than Earth known to harbor lakes is Titan, Saturn's largest moon, which has lakes of ethane
Ethane ( , ) is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petroc ...
, most likely mixed with methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ...
. It is not known if Titan's lakes are fed by rivers, though Titan's surface is carved by numerous river beds. Natural lakes on Earth are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zone
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed t ...
s, and areas with ongoing or recent glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
. Other lakes are found in endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
s or along the courses of mature rivers. In some parts of the world, there are many lakes because of chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice age. All lakes are temporary over geologic time scales, as they will slowly fill in with sediments or spill out of the basin containing them.
Ponds
 A pond is a
A pond is a body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anima ...
of standing water
Water stagnation occurs when water stops flowing. Stagnant water can be a major environmental hazard.
Dangers
Malaria and dengue are among the main dangers of stagnant water, which can become a breeding ground for the mosquitoes that transmi ...
, either natural or man-made, that is usually smaller than a lake. A wide variety of man-made bodies of water are classified as ponds, including water garden
Water garden or aquatic garden, is a term sometimes used for gardens, or parts of gardens, where any type of water feature is a principal or dominant element. The primary focus is on plants, but they will sometimes also house waterfowl, or orn ...
s designed for aesthetic ornamentation, fish ponds designed for commercial fish breeding, and solar ponds designed to store thermal energy. Ponds and lakes are distinguished from streams via current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
speed. While currents in streams are easily observed, ponds and lakes possess thermally driven micro-currents and moderate wind driven currents. These features distinguish a pond from many other aquatic terrain features, such as stream pool
A stream pool, in hydrology, is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is below average.
Formation
A stream pool may be bedded with sediment or armoured with gravel, and in some cases t ...
s and tide pool
A tide pool or rock pool is a shallow pool of seawater that forms on the rocky intertidal shore. Many of these pools exist as separate bodies of water only at low tide.
Many tide pool habitats are home to especially adaptable animals that ...
s.
Rivers
 A river is a natural
A river is a natural watercourse
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams a ...
, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including stream, creek, brook, rivulet, and rill; there is no general rule that defines what can be called a river. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; one example is ''Burn'' in Scotland and North-east England. Sometimes a river is said to be larger than a creek, but this is not always the case, due to vagueness in the language. A river is part of the hydrological cycle. Water within a river is generally collected from precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
through surface runoff, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
recharge, springs, and the release of stored water in natural ice and snowpacks (i.e., from glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s).
Streams
 A stream is a flowing body of water with a
A stream is a flowing body of water with a current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
, confined within a bed
A bed is an item of furniture that is used as a place to sleep, rest, and relax.
Most modern beds consist of a soft, cushioned mattress on a bed frame. The mattress rests either on a solid base, often wood slats, or a sprung base. Many beds ...
and stream banks. In the United States, a stream is classified as a watercourse less than wide. Streams are important as conduits in the water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
, instruments in groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs ...
, and they serve as corridors for fish and wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
migration. The biological habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
in the immediate vicinity of a stream is called a riparian zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
. Given the status of the ongoing Holocene extinction, streams play an important corridor role in connecting fragmented habitats and thus in conserving biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
. The study of streams and waterways in general involves many branches of inter-disciplinary natural science and engineering, including hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is call ...
, fluvial geomorphology
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluv ...
, aquatic ecology
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The tw ...
, fish biology, riparian ecology, and others.
Ecosystems
 Ecosystems are composed of a variety of biotic and
Ecosystems are composed of a variety of biotic and abiotic component
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them un ...
s that function in an interrelated way. The structure and composition is determined by various environmental factors that are interrelated. Variations of these factors will initiate dynamic modifications to the ecosystem. Some of the more important components are soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
, atmosphere, radiation from the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, water, and living organisms.
Central to the ecosystem concept is the idea that living organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fungi ...
s interact with every other element in their local environment. Eugene Odum, a founder of ecology, stated: "Any unit that includes all of the organisms (ie: the "community") in a given area interacting with the physical environment so that a flow of energy leads to clearly defined trophic structure, biotic diversity, and material cycles (i.e.: exchange of materials between living and nonliving parts) within the system is an ecosystem."Odum, EP (1971) ''Fundamentals of ecology'', 3rd edition, Saunders New York Within the ecosystem, species are connected and dependent upon one another in the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), de ...
, and exchange energy and matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic part ...
between themselves as well as with their environment. The human ecosystem concept is based on the human/nature dichotomy and the idea that all species are ecologically dependent on each other, as well as with the abiotic constituents of their biotope.
A smaller unit of size is called a microecosystem
Microecosystems can exist in locations which are precisely defined by critical environmental factors within small or tiny spaces.
Such factors may include temperature, pH, chemical milieu, nutrient supply, presence of symbionts or solid substrate ...
. For example, a microsystem can be a stone and all the life under it. A ''macroecosystem'' might involve a whole ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
, with its drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
.
Wilderness
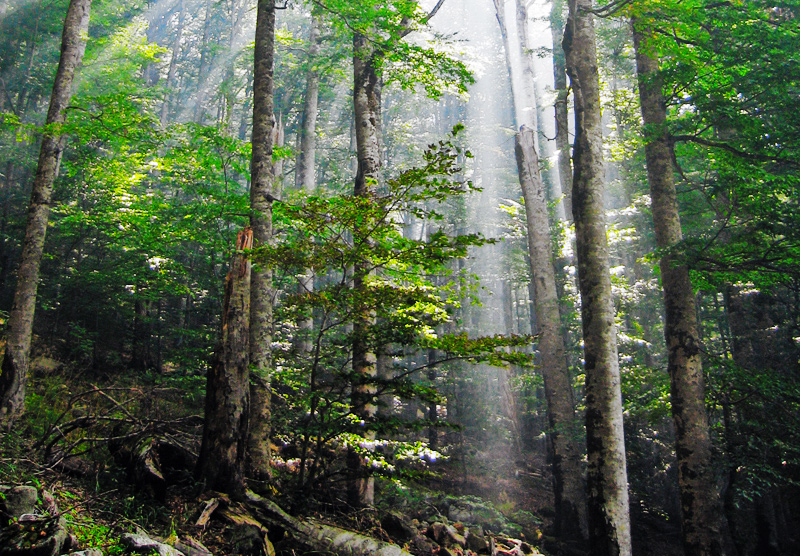
 Wilderness is generally defined as areas that have not been significantly modified by human activity. Wilderness areas can be found in preserves, estates, farms, conservation preserves, ranches, national forests, national parks, and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches, or otherwise undeveloped areas. Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain
Wilderness is generally defined as areas that have not been significantly modified by human activity. Wilderness areas can be found in preserves, estates, farms, conservation preserves, ranches, national forests, national parks, and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches, or otherwise undeveloped areas. Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, ecological studies, conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
, and solitude. Some nature writers believe wilderness areas are vital for the human spirit and creativity,Botkin, Daniel B. (2000) ''No Man's Garden'', Island Press, pp. 155–57, . and some ecologists consider wilderness areas to be an integral part of the Earth's self-sustaining natural ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
(the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
). They may also preserve historic genetic traits and that they provide habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
for wild flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology ...
that may be difficult or impossible to recreate in zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zoo ...
s, arboretums, or laboratories
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physici ...
.
Life
 Although there is no universal agreement on the definition of life, scientists generally accept that the biological manifestation of life is characterized by
Although there is no universal agreement on the definition of life, scientists generally accept that the biological manifestation of life is characterized by organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
, growth, adaptation, response to stimuli
A stimulus is something that causes a physiological response. It may refer to:
* Stimulation
** Stimulus (physiology), something external that influences an activity
** Stimulus (psychology), a concept in behaviorism and perception
* Stimulus (eco ...
, and reproduction. Life may also be said to be simply the characteristic state of organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
s.
Properties common to terrestrial organisms (plants, animals, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s, archaea, and bacteria) are that they are cellular, carbon-and-water-based with complex organization, having a metabolism, a capacity to grow, respond to stimuli, and reproduce. An entity with these properties is generally considered life. However, not every definition of life considers all of these properties to be essential. Human-made analogs of life may also be considered to be life.
The biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
is the part of Earth's outer shell—including land, surface rocks, water, air and the atmosphere—within which life occurs, and which biotic processes in turn alter or transform. From the broadest geophysiological point of view, the biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere (rocks), hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
(water), and atmosphere (air). The entire Earth contains over 75 billion tons (150 ''trillion'' pounds or about 6.8×1013 kilograms) of biomass (life), which lives within various environments within the biosphere.
Over nine-tenths of the total biomass on Earth is plant life, on which animal life depends very heavily for its existence. More than 2 million species of plant and animal life have been identified to date, and estimates of the actual number of existing species range from several million to well over 50 million. The number of individual species of life is constantly in some degree of flux, with new species appearing and others ceasing to exist on a continual basis. The total number of species is in rapid decline.
Evolution
 The
The origin of life
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothes ...
on Earth is not well understood, but it is known to have occurred at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the hadean or archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth during the Arc ...
eons on a primordial Earth that had a substantially different environment than is found at present. These life forms possessed the basic traits of self-replication and inheritable traits. Once life had appeared, the process of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
resulted in the development of ever-more diverse life forms.
Species that were unable to adapt to the changing environment and competition from other life forms became extinct. However, the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
record retains evidence of many of these older species. Current fossil and DNA evidence shows that all existing species can trace a continual ancestry back to the first primitive life forms.
When basic forms of plant life developed the process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
the sun's energy could be harvested to create conditions which allowed for more complex life forms. The resultant oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
accumulated in the atmosphere and gave rise to the ozone layer. The incorporation of smaller cells within larger ones resulted in the development of yet more complex cells called eukaryotes. Cells within colonies became increasingly specialized, resulting in true multicellular organisms. With the ozone layer absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, life colonized the surface of Earth.
Microbes
 The first form of life to develop on the Earth were microbes, and they remained the only form of life until about a billion years ago when multi-cellular organisms began to appear. Microorganisms are single-celled organisms that are generally
The first form of life to develop on the Earth were microbes, and they remained the only form of life until about a billion years ago when multi-cellular organisms began to appear. Microorganisms are single-celled organisms that are generally microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale be ...
, and smaller than the human eye can see. They include Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
, Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, Archaea, and Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
a.
These life forms are found in almost every location on the Earth where there is liquid water, including in the Earth's interior.
Their reproduction is both rapid and profuse. The combination of a high mutation rate and a horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). H ...
ability makes them highly adaptable, and able to survive in new environments, including outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
. They form an essential part of the planetary ecosystem. However, some microorganisms are pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
ic and can post health risk to other organisms.
Plants and animals

 Originally
Originally Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
divided all living things between plants, which generally do not move fast enough for humans to notice, and animals. In Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
' system, these became the kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
Vegetabilia (later Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclu ...
ae) and Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
ia. Since then, it has become clear that the Plantae as originally defined included several unrelated groups, and the fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
and several groups of alga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
e were removed to new kingdoms. However, these are still often considered plants in many contexts. Bacterial life is sometimes included in flora, and some classifications use the term ''bacterial flora'' separately from ''plant flora''.
Among the many ways of classifying plants are by regional flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
s, which, depending on the purpose of study, can also include ''fossil flora'', remnantsof plant life from a previous era. People in many regions and countries take great pride in their individual arrays of characteristic flora, which can vary widely across the globe due to differences in climate and
terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin wo ...
.
Regional floras commonly are divided into categories such as ''native flora'' and ''agricultural and garden flora'', the lastly mentioned of which are intentionally grown and cultivated. Some types of "native flora" actually have been introduced centuries ago by people migrating from one region or continent to another, and become an integral part of the native, or natural flora of the place to which they were introduced. This is an example of how human interaction with nature can blur the boundary of what is considered nature.
Another category of plant has historically been carved out for ''weeds''. Though the term has fallen into disfavor among botanists
This is a list of botanists who have Wikipedia articles, in alphabetical order by surname. The List of botanists by author abbreviation is mostly a list of plant taxonomists because an author receives a standard abbreviation only when that auth ...
as a formal way to categorize "useless" plants, the informal use of the word "weeds" to describe those plants that are deemed worthy of elimination is illustrative of the general tendency of people and societies to seek to alter or shape the course of nature. Similarly, animals are often categorized in ways such as ''domestic'', ''farm animals'', ''wild animals'', ''pests'', etc. according to their relationship to human life.
Animals as a category have several characteristics that generally set them apart from other living things. Animals are eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
and usually multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially un ...
(although see Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. O ...
), which separates them from bacteria, archaea, and most protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s. They are heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
ic, generally digesting food in an internal chamber, which separates them from plants and alga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
e. They are also distinguished from plants, algae, and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
by lacking cell walls.
With a few exceptions—most notably the two phyla consisting of sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate throug ...
s and placozoa
The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', '' Hoilungia hongkongensis'', a ...
ns—animals have bodies that are differentiated into tissues. These include muscles, which are able to contract and control locomotion, and a nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
, which sends and processes signals. There is also typically an internal digestive chamber. The eukaryotic cells possessed by all animals are surrounded by a characteristic extracellular matrix composed of collagen and elastic glycoproteins. This may be calcified to form structures like shells, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, and spicules, a framework upon which cells can move about and be reorganized during development and maturation, and which supports the complex anatomy required for mobility.
Human interrelationship

Human impact
Althoughhumans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
comprise only a minuscule proportion of the total living biomass on Earth, the human effect on nature is disproportionately large. Because of the extent of human influence, the boundaries between what humans regard as nature and "made environments" is not clear cut except at the extremes. Even at the extremes, the amount of natural environment that is free of discernible human influence is diminishing at an increasingly rapid pace. A 2020 study published in ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' found that anthropogenic mass (human-made materials) outweighs all living biomass on earth, with plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
alone exceeding the mass of all land and marine animals combined. And according to a 2021 study published in ''Frontiers in Forests and Global Change'', only about 3% of the planet's terrestrial surface is ecologically and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology ...
lly intact, with a low human footprint and healthy populations of native animal species.
The development of technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and Reproducibility, reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in me ...
by the human race has allowed the greater exploitation of natural resources
The exploitation of natural resources is the use of natural resources for economic growth, sometimes with a negative connotation of accompanying environmental degradation. It started to emerge on an industrial scale in the 19th century as the e ...
and has helped to alleviate some of the risk from natural hazards
A natural hazard is a natural phenomenon that might have a negative effect on humans and other animals, or the environment. Natural hazard events can be classified into two broad categories: geophysical and biological.
An example of the distincti ...
. In spite of this progress, however, the fate of human civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
remains closely linked to changes in the environment. There exists a highly complex feedback loop
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled c ...
between the use of advanced technology and changes to the environment that are only slowly becoming understood. Man-made threats to the Earth's natural environment include pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
, and disasters such as oil spills. Humans have contributed to the extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
of many plants and animals, with roughly 1 million species threatened with extinction within decades. The loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
and ecosystem functions over the last half century have impacted the extent that nature can contribute to human quality of life, and continued declines could pose a major threat to the continued existence of human civilization, unless a rapid course correction is made. The value of natural resources to human society is not reflected in market prices
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the ...
because mostly natural resources are available free of charge. This distorts market pricing of natural resources and at the same time leads to underinvestment in our natural assets. The annual global cost of public subsidies that damage nature is conservatively estimated at $4–$6 trillion (million million). Institutional protections of these natural goods, such as the oceans and rainforests, are lacking. Governments have not prevented these economic externalities
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either co ...
.
Humans employ nature for both leisure and economic activities. The acquisition of natural resources for industrial use remains a sizable component of the world's economic system. Some activities, such as hunting and fishing, are used for both sustenance and leisure, often by different people. Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
was first adopted around the 9th millennium BCE. Ranging from food production to energy, nature influences economic wealth.
Although early humans gathered uncultivated plant materials for food and employed the medicinal properties of vegetation for healing, most modern human use of plants is through agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
. The clearance of large tracts of land for crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydropon ...
growth has led to a significant reduction in the amount available of forestation
Forestation is either growing existing forests ( proforestation) or establishing forest growth on areas that either had forest or lacked it naturally. In the first case, the process is called reforestation, or reafforestation while the second is c ...
and wetlands, resulting in the loss of habitat for many plant and animal species as well as increased erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
.
Aesthetics and beauty
 Beauty in nature has historically been a prevalent theme in art and books, filling large sections of libraries and bookstores. That nature has been depicted and celebrated by so much art, photography, poetry, and other literature shows the strength with which many people associate nature and beauty. Reasons why this association exists, and what the association consists of, are studied by the branch of philosophy called
Beauty in nature has historically been a prevalent theme in art and books, filling large sections of libraries and bookstores. That nature has been depicted and celebrated by so much art, photography, poetry, and other literature shows the strength with which many people associate nature and beauty. Reasons why this association exists, and what the association consists of, are studied by the branch of philosophy called aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed t ...
. Beyond certain basic characteristics that many philosophers agree about to explain what is seen as beautiful, the opinions are virtually endless. Nature and wildness have been important subjects in various eras of world history. An early tradition of landscape art
Landscape painting, also known as landscape art, is the depiction of natural scenery such as mountains, valleys, trees, rivers, and forests, especially where the main subject is a wide view—with its elements arranged into a coherent composi ...
began in China during the Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
(618–907). The tradition of representing nature ''as it is'' became one of the aims of Chinese painting
Chinese painting () is one of the oldest continuous artistic traditions in the world. Painting in the traditional style is known today in Chinese as ''guó huà'' (), meaning "national painting" or "native painting", as opposed to Western style ...
and was a significant influence in Asian art.
Although natural wonders are celebrated in the Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
and the Book of Job, wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
portrayals in art became more prevalent in the 1800s, especially in the works of the Romantic movement
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
. British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
artists John Constable and J. M. W. Turner turned their attention to capturing the beauty of the natural world in their paintings. Before that, paintings had been primarily of religious scenes or of human beings. William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication '' Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's ' ...
's poetry described the wonder of the natural world, which had formerly been viewed as a threatening place. Increasingly the valuing of nature became an aspect of Western culture.History of ConservationBC Spaces for Nature. Accessed: May 20, 2006. This artistic movement also coincided with the Transcendentalist movement in the Western world. A common classical idea of beautiful art involves the word mimesis, the imitation of nature. Also in the realm of ideas about beauty in nature is that the perfect is implied through perfect mathematical
forms
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form also refers to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter data
* ...
and more generally by patterns in nature
Patterns in nature are visible regularities of form found in the natural world. These patterns recur in different contexts and can sometimes be modelled mathematically. Natural patterns include symmetries, trees, spirals, meanders, waves, ...
. As David Rothenburg writes, "The beautiful is the root of science and the goal of art, the highest possibility that humanity can ever hope to see".
Matter and energy
 Some fields of science see nature as matter in motion, obeying certain laws of nature which science seeks to understand. For this reason the most fundamental science is generally understood to be "
Some fields of science see nature as matter in motion, obeying certain laws of nature which science seeks to understand. For this reason the most fundamental science is generally understood to be "physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
"—the name for which is still recognizable as meaning that it is the "''study of nature''".
Matter is commonly defined as the substance of which physical objects are composed. It constitutes the observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these ob ...
. The visible components of the universe are now believed to compose only 4.9 percent of the total mass. The remainder is believed to consist of 26.8 percent cold dark matter and 68.3 percent dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univ ...
. The exact arrangement of these components is still unknown and is under intensive investigation by physicists.
The behaviour of matter and energy throughout the observable universe appears to follow well-defined physical law
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) ...
s. These laws have been employed to produce cosmological
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
models that successfully explain the structure and the evolution of the universe we can observe. The mathematical expressions of the laws of physics employ a set of twenty physical constants that appear to be static across the observable universe. The values of these constants have been carefully measured, but the reason for their specific values remains a mystery.
Beyond Earth
 Outer space, also simply called ''space'', refers to the relatively empty regions of the
Outer space, also simply called ''space'', refers to the relatively empty regions of the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies. ''Outer'' space is used to distinguish it from airspace (and terrestrial locations). There is no discrete boundary between Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
and space, as the atmosphere gradually attenuates with increasing altitude. Outer space within the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
is called interplanetary space
Interplanetary may refer to:
* Interplanetary space, the space between the planets of the Solar System
*Interplanetary spaceflight, travel between planets
*The interplanetary medium, the material that exists in interplanetary space
*The InterPlane ...
, which passes over into interstellar space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predo ...
at what is known as the heliopause.
Outer space is sparsely filled with several dozen types of organic molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s discovered to date by microwave spectroscopy
Microwave spectroscopy is the spectroscopy method that employs microwaves, i.e. electromagnetic radiation at GHz frequencies, for the study of matter.
History
The ammonia molecule NH3 is shaped like a pyramid 0.38 Å in height, with an equilatera ...
, blackbody radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous spe ...
left over from the Big Bang and the origin of the universe, and cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s, which include ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
ized atomic nuclei
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron ...
and various subatomic particles. There is also some gas, plasma and dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ho ...
, and small meteor
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s. Additionally, there are signs of human life in outer space today, such as material left over from previous crewed and uncrewed launches which are a potential hazard to spacecraft. Some of this debris
Debris (, ) is rubble, wreckage, ruins, litter and discarded garbage/refuse/trash, scattered remains of something destroyed, or, as in geology, large rock fragments left by a melting glacier, etc. Depending on context, ''debris'' can refer to ...
re-enters the atmosphere periodically.
Although Earth is the only body within the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
known to support life, evidence suggests that in the distant past the planet Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
possessed bodies of liquid water on the surface. For a brief period in Mars' history, it may have also been capable of forming life. At present though, most of the water remaining on Mars is frozen.
If life exists at all on Mars, it is most likely to be located underground where liquid water can still exist.
Conditions on the other terrestrial planets, Mercury and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, appear to be too harsh to support life as we know it. But it has been conjectured that Europa, the fourth-largest moon of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
, may possess a sub-surface ocean of liquid water and could potentially host life.
Astronomers have started to discover extrasolar Earth analog
An Earth analog, also called an Earth analogue, Earth twin, or second Earth, is a planet or moon with environmental conditions similar to those found on Earth. The term Earth-like planet is also used, but this term may refer to any terrestrial pl ...
s – planets that lie in the habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kast ...
of space surrounding a star, and therefore could possibly host life as we know it.
See also
*Force of nature Forces of nature are literally natural phenomena.
Figuratively, the term is also used to describe a thing or person that exhibits qualities which appear to be beyond outside control.
Force or Forces of Nature may also refer to:
Science
*Fundamen ...
* Human nature
Human nature is a concept that denotes the fundamental dispositions and characteristics—including ways of thinking, feeling, and acting—that humans are said to have naturally. The term is often used to denote the essence of humankind, or ...
* Natural history
* Naturalism
* Natural landscape
* Natural law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacte ...
* Natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
* Natural science
* Natural theology
* Nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
* Nature versus nurture
* Nature worship
* Naturism
* Rewilding
Rewilding may refer to:
*Rewilding (conservation biology), the return of habitats to a natural state
**Rewilding Europe
Rewilding Europe is a non-profit organisation based in Nijmegen, Netherlands, working to create rewilded landscapes through ...
Media:
* '' National Wildlife'', a publication of the National Wildlife Federation
* '' Natural History'', by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
* ''Natural World
''Natural World'' is a strand of British wildlife documentary programmes broadcast on BBC Two and BBC Two HD and regarded by the BBC as its flagship natural history series. It is the longest-running documentary in its genre on British televis ...
'' (TV series)
* ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'', by Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
* ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'', a prominent scientific journal
* ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'' (TV series)
* ''The World We Live In (Life magazine)
''The World We Live In'' appeared in the pages of LIFE magazine from December 8, 1952, to December 20, 1954. A science series, it comprised 13 parts published on an average of every eight weeks. Written by Lincoln Barnett, ''The World We Live In'' ...
''
Organizations:
* Nature Detectives
* The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
Philosophy:
* Balance of nature (biological fallacy), a discredited concept of natural equilibrium in predator–prey dynamics
* Mother Nature
* Naturalism, any of several philosophical stances, typically those descended from materialism and pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that considers words and thought as tools and instruments for prediction, problem solving, and action, and rejects the idea that the function of thought is to describe, represent, or mirror reality. ...
that do not distinguish the supernatural from nature;Papineau, David (2016"Naturalism"
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Edward N. Zalta (ed.), > this includes the ''methodological naturalism'' of natural science, which makes the
methodological
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
assumption that observable
In physics, an observable is a physical quantity that can be measured. Examples include position and momentum. In systems governed by classical mechanics, it is a real-valued "function" on the set of all possible system states. In quantum phy ...
events in nature are explained only by natural causes, without assuming either the existence or non-existence of the supernatural
* Nature (philosophy)
Nature has two inter-related meanings in philosophy and natural philosophy. On the one hand, it means the set of all things which are natural, or subject to the normal working of the laws of nature. On the other hand, it means the essential prope ...
Notes and references
Further reading
* * * * Farber, Paul Lawrence (2000), ''Finding Order in Nature: The Naturalist Tradition from Linnaeus to E. O. Wilson''. Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore. * * *External links
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (iucnredlist.org)
* {{Authority control Environmental science Environmental social science concepts Main topic articles