Mysooru on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12┬░ 18ŌĆ▓ 26ŌĆ│ north latitude and 76┬░ 38ŌĆ▓ 59ŌĆ│ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of above mean sea level.
Mysore is situated at the foothills of Chamundi Hills about towards the southwest of Bangalore and spread across an area of . Mysore City Corporation is responsible for the civic administration of the city, which is also the headquarters of Mysore district and
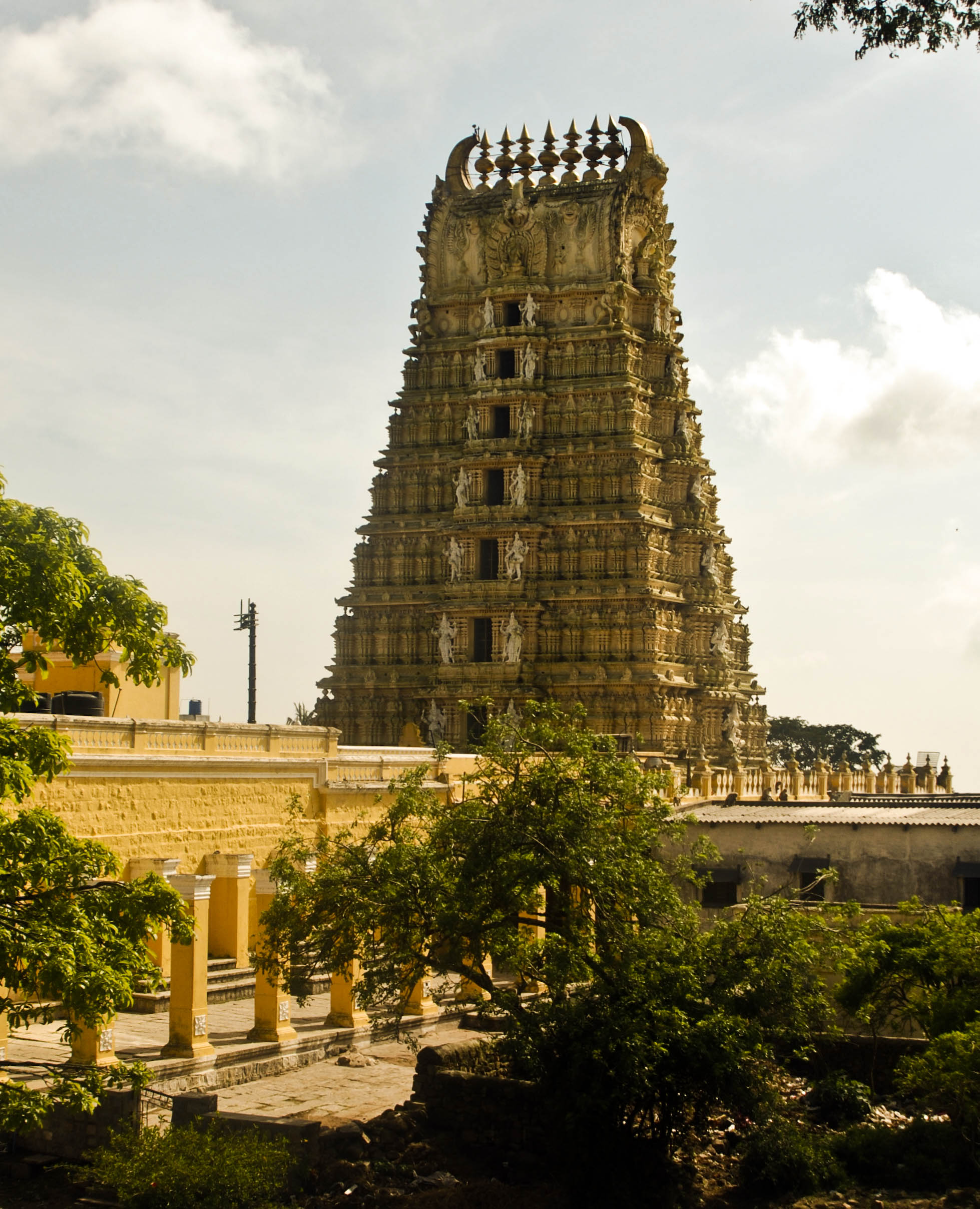

 The site where Mysore Palace now stands was occupied by a village named Puragere at the beginning of the 16th century. The Mahishūru Fort was constructed in 1524 by
The site where Mysore Palace now stands was occupied by a village named Puragere at the beginning of the 16th century. The Mahishūru Fort was constructed in 1524 by
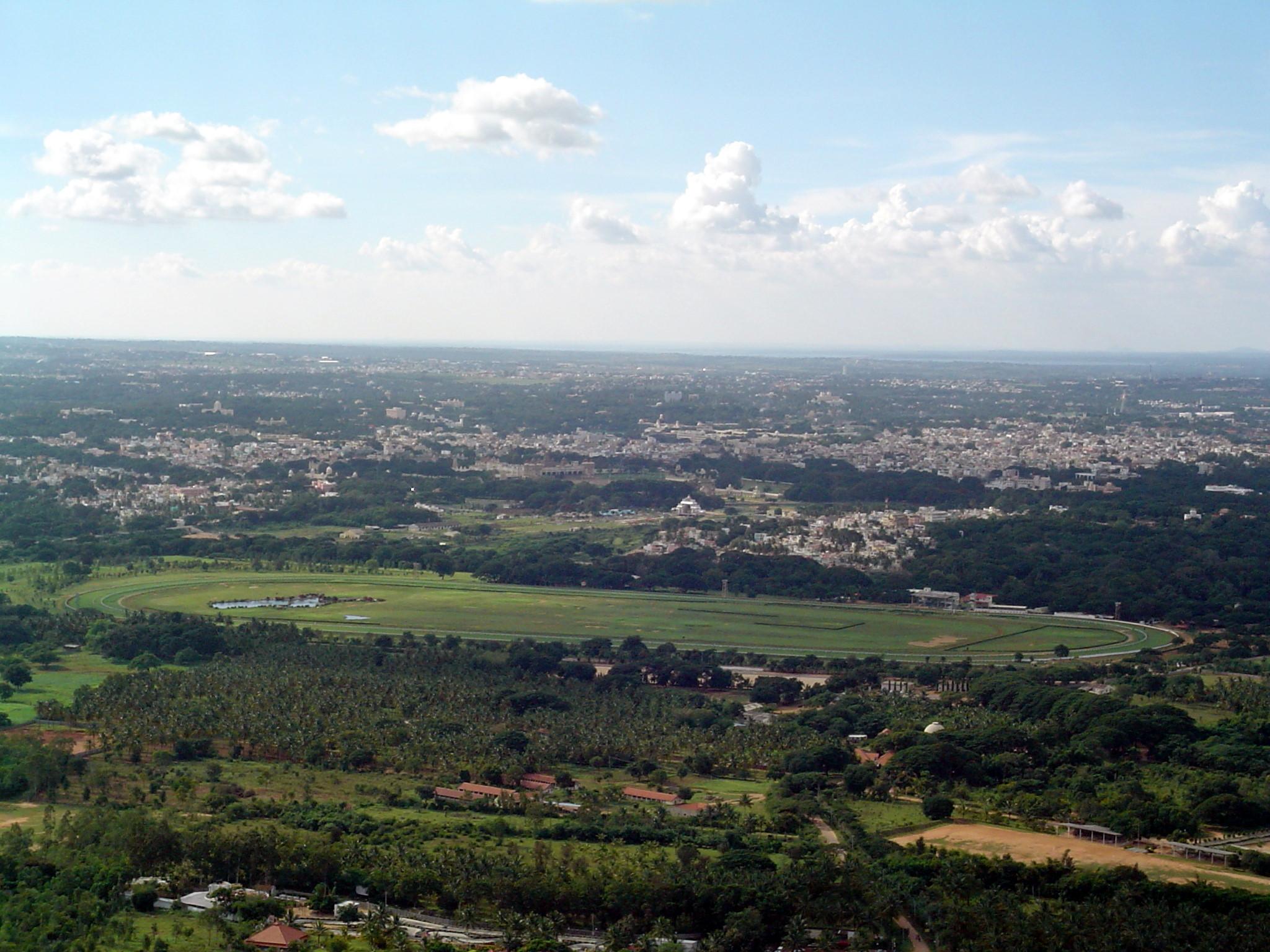


 Mysore is located at and has an average altitude of . It is spread across an area of at the base of the
Mysore is located at and has an average altitude of . It is spread across an area of at the base of the

 The civic administration of the city is managed by the Mysore City Corporation, which was established as a municipality in 1888 and converted into a corporation in 1977. Overseeing engineering works, health, sanitation, water supply, administration and taxation, the corporation is headed by a Mayor, who is assisted by commissioners and council members. The city is divided into 65 wards and the council members (also known as ''corporators'') are elected by the citizens of Mysore every five years. The council members, in turn, elect the mayor. The annual budget of the corporation for the year 2011ŌĆō2012 was . Among 63 cities covered under the
The civic administration of the city is managed by the Mysore City Corporation, which was established as a municipality in 1888 and converted into a corporation in 1977. Overseeing engineering works, health, sanitation, water supply, administration and taxation, the corporation is headed by a Mayor, who is assisted by commissioners and council members. The city is divided into 65 wards and the council members (also known as ''corporators'') are elected by the citizens of Mysore every five years. The council members, in turn, elect the mayor. The annual budget of the corporation for the year 2011ŌĆō2012 was . Among 63 cities covered under the
 Before the advent of the European system of education in Mysore, '' Agraharas'' ( Brahmin quarters) provided Vedic education to Hindus, and ''
Before the advent of the European system of education in Mysore, '' Agraharas'' ( Brahmin quarters) provided Vedic education to Hindus, and ''
 Tourism and IT are the major industries in Mysore. The city attracted about 3.15 million tourists in 2010. Mysore has traditionally been home to industries such as weaving, sandalwood carving, bronze work and the production of lime and salt. It has many big IT companies like Infosys and Wipro. The planned industrial growth of the city and the state was first envisaged at the ''Mysore economic conference'' in 1911. This led to the establishment of industries such as the Mysore Sandalwood Oil Factory in 1917 and the Sri Krishnarajendra Mills in 1920. Mysore has emerged as an industrial hub in Karnataka next to Bangalore. Mysore is part of the Bidar-Mysore Industrial Corridor. Major drivers of the economy are tourism, finance, manufacturing and industry which includes chemicals, petrochemicals, machinery, automobile, engineering, textiles and food processing sectors. A new industrial corridor plan is underway between Mysore and Bangalore.
For the industrial development of the city, the Karnataka Industrial Areas Development Board (KIADB) has established four industrial areas in and around Mysore, in the Belagola,
Tourism and IT are the major industries in Mysore. The city attracted about 3.15 million tourists in 2010. Mysore has traditionally been home to industries such as weaving, sandalwood carving, bronze work and the production of lime and salt. It has many big IT companies like Infosys and Wipro. The planned industrial growth of the city and the state was first envisaged at the ''Mysore economic conference'' in 1911. This led to the establishment of industries such as the Mysore Sandalwood Oil Factory in 1917 and the Sri Krishnarajendra Mills in 1920. Mysore has emerged as an industrial hub in Karnataka next to Bangalore. Mysore is part of the Bidar-Mysore Industrial Corridor. Major drivers of the economy are tourism, finance, manufacturing and industry which includes chemicals, petrochemicals, machinery, automobile, engineering, textiles and food processing sectors. A new industrial corridor plan is underway between Mysore and Bangalore.
For the industrial development of the city, the Karnataka Industrial Areas Development Board (KIADB) has established four industrial areas in and around Mysore, in the Belagola,
 Referred to as the ''cultural capital'' of Karnataka, Mysore is well known for the festivities that take place during the period of '' Dasara''; the state festival of Karnataka. The ''Dasara'' festivities, which are celebrated over a ten-day period, were first introduced by King Raja Wodeyar I in 1610. On the ninth day of ''Dasara'', called ''Mahanavami'', the royal sword is worshipped and is taken on a procession of decorated elephants, camels and horses. On the tenth day, called '' Vijayadashami'', the traditional ''Dasara'' procession (locally known as ''Jumboo Savari'') is held on the streets of Mysore which usually falls in the month of September or October. The idol of the goddess Chamundeshwari is placed on a golden ''
Referred to as the ''cultural capital'' of Karnataka, Mysore is well known for the festivities that take place during the period of '' Dasara''; the state festival of Karnataka. The ''Dasara'' festivities, which are celebrated over a ten-day period, were first introduced by King Raja Wodeyar I in 1610. On the ninth day of ''Dasara'', called ''Mahanavami'', the royal sword is worshipped and is taken on a procession of decorated elephants, camels and horses. On the tenth day, called '' Vijayadashami'', the traditional ''Dasara'' procession (locally known as ''Jumboo Savari'') is held on the streets of Mysore which usually falls in the month of September or October. The idol of the goddess Chamundeshwari is placed on a golden '' The
The
 Mysore is connected by
Mysore is connected by
 A public bicycle sharing system, Trin Trin, funded partially by the United Nations is popular mode of transport. It is a government project. It is the first public bike-sharing system throughout India. The key objective of Trin Trin is to encourage local commuters, as well as visitors, to use the bicycle in preference to motorized modes of travel and thereby help scale down the multifarious environmental and road-traffic hazards, enhance conveyance convenience, and make local daily commutes economical for the common citizen.
A public bicycle sharing system, Trin Trin, funded partially by the United Nations is popular mode of transport. It is a government project. It is the first public bike-sharing system throughout India. The key objective of Trin Trin is to encourage local commuters, as well as visitors, to use the bicycle in preference to motorized modes of travel and thereby help scale down the multifarious environmental and road-traffic hazards, enhance conveyance convenience, and make local daily commutes economical for the common citizen.

 Mysore Airport is a domestic airport and is located near the village of Mandakalli, 10 kilometres south of the centre of the city. It was built by the kings of Mysore in early 1940s. Mysore Airport currently serves the city of Mysore and is connected to multiple domestic locations including Bangalore, Chennai, Goa, Hubli, Hyderabad, Kochi and Mangalore. The current runway is not able to handle big flights and hence a runway expansion is about to take place expanding the runway from 1.7 km to 2.8 km and will be upgraded to international airport after the expansion. The nearest International airport is Kannur International Airport in Kannur which lies about away from Mysore city but considering that the only international destinations from this airport are in the Middle East,
Mysore Airport is a domestic airport and is located near the village of Mandakalli, 10 kilometres south of the centre of the city. It was built by the kings of Mysore in early 1940s. Mysore Airport currently serves the city of Mysore and is connected to multiple domestic locations including Bangalore, Chennai, Goa, Hubli, Hyderabad, Kochi and Mangalore. The current runway is not able to handle big flights and hence a runway expansion is about to take place expanding the runway from 1.7 km to 2.8 km and will be upgraded to international airport after the expansion. The nearest International airport is Kannur International Airport in Kannur which lies about away from Mysore city but considering that the only international destinations from this airport are in the Middle East,
 Newspaper publishing in Mysore started in 1859 when Bhashyam Bhashyacharya began publishing a weekly newspaper in Kannada called the ''Mysooru Vrittanta Bodhini'', the first of a number of weekly newspapers published in the following three decades. A well-known Mysore publisher during Wodeyar rule was
Newspaper publishing in Mysore started in 1859 when Bhashyam Bhashyacharya began publishing a weekly newspaper in Kannada called the ''Mysooru Vrittanta Bodhini'', the first of a number of weekly newspapers published in the following three decades. A well-known Mysore publisher during Wodeyar rule was

 Mysore is a major tourist destination in its own right and serves as a base for other tourist attractions in the vicinity. The city receives many tourists during the ten-day ''Dasara'' festival. One of the most visited monuments in India, the Amba Vilas Palace, or Mysore Palace, is the centre of the ''Dasara'' festivities. The Jaganmohana Palace, The Sand Sculpture Museum the Jayalakshmi Vilas and the Lalitha Mahal are other palaces in the city. Chamundeshwari Temple, atop the Chamundi Hills, and St. Philomena's Church, Wesley's Cathedral are notable religious places in Mysore.
Mysore is a major tourist destination in its own right and serves as a base for other tourist attractions in the vicinity. The city receives many tourists during the ten-day ''Dasara'' festival. One of the most visited monuments in India, the Amba Vilas Palace, or Mysore Palace, is the centre of the ''Dasara'' festivities. The Jaganmohana Palace, The Sand Sculpture Museum the Jayalakshmi Vilas and the Lalitha Mahal are other palaces in the city. Chamundeshwari Temple, atop the Chamundi Hills, and St. Philomena's Church, Wesley's Cathedral are notable religious places in Mysore.
 The Mysore Zoo, established in 1892, the Karanji, Kukkarahalli and the Blue Lagoon Lake are popular recreational destinations. Blue Lagoon is a lake with a mini island located behind the KRS water dam, from which it is mesmerising to watch the sunset and sunrise. Mysore has the Regional Museum of Natural History, the Folk Lore Museum, the Railway Museum and the Oriental Research Institute. The city is a centre for yoga-related health tourism that attracts domestic and foreign visitors, particularly those who, for years, came to study with the late Ashtanga vinyasa yoga guru K. Pattabhi Jois.
A short distance from Mysore city is the neighbouring Mandya District's Krishnarajasagar Dam and the adjoining
The Mysore Zoo, established in 1892, the Karanji, Kukkarahalli and the Blue Lagoon Lake are popular recreational destinations. Blue Lagoon is a lake with a mini island located behind the KRS water dam, from which it is mesmerising to watch the sunset and sunrise. Mysore has the Regional Museum of Natural History, the Folk Lore Museum, the Railway Museum and the Oriental Research Institute. The city is a centre for yoga-related health tourism that attracts domestic and foreign visitors, particularly those who, for years, came to study with the late Ashtanga vinyasa yoga guru K. Pattabhi Jois.
A short distance from Mysore city is the neighbouring Mandya District's Krishnarajasagar Dam and the adjoining
Mysore division
Mysore division, officially Mysuru division, is an administrative division in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is one of four administrative divisions in Karnataka, the others being Bangalore division, Belgaum division, and Gulbarg ...
.
It served as the capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
city of the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
for nearly six centuries from 1399 until 1956. The Kingdom was ruled by the Wadiyar dynasty
The Wadiyar dynasty (formerly spelt Wodeyer or Odeyer, also referred to as the Wadiyars of Mysore), is a late-medieval/ early-modern South Indian Hindu royal family of former kings of Mysore from the Urs clan originally based in Mysore city. ...
, with a brief period of interregnum in the late 18th century when Hyder Ali and Tipu Sultan were in power. The Wadiyars were patrons of art and culture. Tipu Sultan and Hyder Ali also contributed significantly to the cultural and economic growth of the city and the state by planting mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identif ...
trees introducing silk in the region and fighting four wars against the British. The cultural ambience and achievements of Mysore earned it the sobriquet of '' Cultural Capital of Karnataka''.
Mysore is noted for its heritage structures and palaces, including the Mysore Palace, and for the festivities that take place during the '' Dasara'' festival when the city receives hundreds of thousands of tourists from around the world. It lends its name to various art forms and culture, such as Mysore Dasara, Mysore painting
Mysore painting ( kn, Ó▓«Ó│łÓ▓ĖÓ│éÓ▓░Ó│ü Ó▓ÜÓ▓┐Ó▓żÓ│ŹÓ▓░Ó▓ĢÓ▓▓Ó│å) is an important form of classical South Indian painting style that originated in and around the town of Mysore in Karnataka encouraged and nurtured by the Mysore rulers. Painti ...
; the sweet dish Mysore Pak, Mysore ''Masala Dosa''; brands such as Mysore Sandal Soap
Mysore Sandal Soap is a brand of soap manufactured by the Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Limited (KSDL), a company owned by the government of Karnataka in India. This soap has been manufactured since 1916, when Krishna Raja Wadiyar IV, the king ...
, Mysore Paints and Varnish Limited
Mysore Paints and Varnish Limited, formerly Mysore Lac and Paints Limited, is a company located in the southern Indian city of Mysore, Karnataka. It is the only company in India authorised to produce indelible ink, which is used in elections to p ...
; and styles and cosmetics such as Mysore Peta
The ''Mysuru peta'' (''peta'' is a Kannada word which means turban in English) is the classical royal Indian attire worn by the erstwhile Kings of Mysore. Wodeyars wore a richly bejeweled turban made of silk and jari (gold threaded lace) to mat ...
(a traditional silk turban) and the Mysore silk
Karnataka produces 9,000 metric tons of mulberry silk of a total of 20,000 metric tons of mulberry silk produced in the country, thus contributing to nearly 45% of the country's total mulberry silk. In Karnataka, silk is mainly produced in the ...
''saris''. Mysore is also known for betel leaves
The betel (''Piper betle'') is a vine of the family Piperaceae, which includes pepper and kava. The betel plant is native to Southeast Asia. It is an evergreen, dioecious perennial, with glossy heart-shaped leaves and white catkins. Betel plant ...
and own its special variety of jasmine
Jasmine ( taxonomic name: ''Jasminum''; , ) is a genus of shrubs and vines in the olive family (Oleaceae). It contains around 200 species native to tropical and warm temperate regions of Eurasia, Africa, and Oceania. Jasmines are widely cultiva ...
flower fondly referred as "Mysore Mallige". Tourism is the major industry alongside the traditional industries. Mysore's inter-city public transportation includes rail, bus and air.
Etymology
The name ''Mysore'' is an anglicised version of ''Mahishūru'', which means the abode of ''Mahisha'' in the vernacular Kannada. The common noun ''Mahisha,'' in Sanskrit, means buffalo; in this context, however, ''Mahisha'' refers to Mahishasura, a mythical demon who could assume the form of either a human or a buffalo, and who, according toHindu mythology
Hindu mythology is the body of myths and literature attributed to, and espoused by, the adherents of the Hindu religion, found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'', the Puranas, and reg ...
, ruled the ancient parts of Mysore Kingdom, known in Sanskrit as ''Mah├Ł┼Īhaka'', centred at ''Mahishapura''. He was killed by the goddess Chamundeshwari
Chamunda (Sanskrit: ÓżÜÓżŠÓż«ÓźüÓżŻÓźŹÓżĪÓżŠ, ISO-15919: C─ümuß╣ćßĖŹ─ü), also known as Chamundeshwari, Chamundi or Charchika, is a fearsome form of Chandi, the Hindu Divine Mother Shakti and is one of the seven Matrikas (mother goddesses).W ...
, whose temple is situated atop the Chamundi Hills, after whom it is named. 'Mahishapura' later became ''Mahisūru'' (a name which, even now, the royal family uses), and finally came to be anglicised as ''Mysore'' by the British and Maisūru/Mysuru in the vernacular Kannada language
Kannada (; Ó▓ĢÓ▓©Ó│ŹÓ▓©Ó▓Ī, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native sp ...
.Deve Gowda Javare Gowda (1998), p. 82.
In December 2005, the Government of Karnataka announced its intention to change the anglicised name of the city to ''Mysuru''. This was approved by the Government of India in October 2014, and Mysore was renamed, along with twelve other cities, on 1 November 2014.
History

 The site where Mysore Palace now stands was occupied by a village named Puragere at the beginning of the 16th century. The Mahishūru Fort was constructed in 1524 by
The site where Mysore Palace now stands was occupied by a village named Puragere at the beginning of the 16th century. The Mahishūru Fort was constructed in 1524 by Chamaraja Wodeyar III
Chamaraja Wodeyar III (29 September 1492 ŌĆō 17 February 1553) was fifth raja of the Kingdom of Mysore and the last one to rule as feudal king under the Vijayanagara Empire. He reigned after his father's demise in 1513 until his death in 1553 ...
(1513ŌĆō1553), who passed on the dominion of ''Puragere'' to his son Chamaraja Wodeyar IV
Chamaraja Wodeyar IV (25 July 1507 ŌĆō 9 November 1576) was the seventh maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore. He was youngest son of Chamaraja Wodeyar III, the fifth raja of Mysore. He took over the kingdom at the age of 65 after his older brothe ...
(1572ŌĆō1576). Since the 16th century, the name of ''Mahish┼½ru'' has commonly been used to denote the city. The Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
, governed by the Wodeyar family, initially served as a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Vijayanagara Empire. With the decline of that empire after the Battle of Talikota in 1565, the Mysore Kingdom gradually achieved independence, and by the time of King Narasaraja Wodeyar (1637), it had become a sovereign state. Seringapatam, near Mysore, the present-day Srirangapatna, was the capital of the kingdom beginning in 1610. The 17th century saw a steady expansion of its territory and, under Narasaraja Wodeyar I and Chikka Devaraja Wodeyar, the kingdom annexed large areas of what is now southern Karnataka and parts of Tamil Nadu, to become a powerful state in the southern Deccan.
The kingdom reached the height of its military power and dominion in the latter half of the 18th century, under the de facto rulers Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan. The latter demolished parts of Mysore to remove legacies of the Wodeyar dynasty. During this time, the kingdom of Mysore came into conflict with the Marathas, the British, and the Nizam of Hyderabad
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niß║ō─üm ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, leading to the four Anglo-Mysore wars, success in the first two of which was followed by defeat in the third and fourth. After Tipu Sultan's death in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War in 1799, the capital of the kingdom was moved back to Mysore from Seringapatam, and the kingdom was distributed by the British to their allies of the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War. Part of the kingdom was annexed into the Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including the ...
, another to the Nizam of Hyderabad. The landlocked interior of the defeated kingdom of Mysore was turned into a princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
under the suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
of the British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
, with the five-year-old Wodeyar Krishnaraja III as titular ruler and with Purnaiah, who had served under Tipu, as chief minister or '' Diwan'' and Lt. Col. Barry Close
Sir Barry Close, 1st Baronet (3 December 1756 ŌĆō 12 April 1813) was an army general in the East India Company and a political officer.
Life
Barry Close was born at Elm Park in Armagh, the third son of Maxwell Close and his wife Mary. The fami ...
as Resident. The British took control of Mysore's foreign policy and insisted on an annual tribute for maintaining a standing British army at Mysore. Purnaiah is credited with improving Mysore's public works. In 1831, claiming there was maladministration, the British took direct control of the princely state. For the next fifty years, the kingdom of Mysore was under the direct rule of British Commissioners, and in 1831 the city of Mysore lost its status as the administrative centre, when the British Commissioner moved the capital to Bangalore.
In 1876ŌĆō77, towards the end of the period of direct British rule, Mysore suffered from the Great Famine of 1876ŌĆō1878
The Great Famine of 1876ŌĆō1878 was a famine in British Raj, India under Crown rule. It began in 1876 after an intense drought resulted in crop failure in the Deccan Plateau. It affected South India, south and West India, Southwestern IndiaŌĆöth ...
, in which nearly a fifth of the population died. In 1881, Maharaja Chamaraja Wadiyar X was given control of Mysore, in a process called rendition, but with a resident British officer and a diwan to handle the Maharaja's administration,Kamath (2001), pp. 250ŌĆō254 and the city of Mysore regained its status as the capital. The Mysore municipality was established in 1888 and the city was divided into eight wards. In 1897 an outbreak of bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
killed nearly half of the population of the city. With the establishment of the City Improvement Trust Board (CITB) in 1903, Mysore became one of the first cities in Asia to undertake planned urban development. Public demonstrations and meetings were held there during the Quit India movement
The Quit India Movement, also known as the August Kranti Movement, was a movement launched at the Bombay session of the All India Congress Committee by Mahatma Gandhi on 8th August 1942, during World War II, demanding an end to British rule in ...
and other phases of the Indian independence movement.
Until the independence of British India (which did not include Mysore) in 1947, Mysore remained a Princely State within the British Indian Empire, with the Wodeyars continuing their rule. After Indian Independence, Mysore city remained as part of the Mysore State, now known as Karnataka. Jayachamarajendra Wodeyar, then king of Mysore, was allowed to retain his titles and was nominated as the '' Rajapramukh'' (appointed governor) of the state. He died in September 1974 and was cremated in Mysore. Over the years, Mysore became well known as a centre for tourism; the city remained largely peaceful, except for occasional riots related to the Kaveri River Water Dispute. Among the events that took place in Mysore and made national headlines were a fire at a television studio that claimed 62 lives in 1989, and the sudden deaths of many animals at the Mysore Zoo
Mysore Zoo (Now Mysuru Zoo) (officially the Sri Chamarajendra Zoological Gardens) is a zoo located near the palace in Mysore, India. It is one of the oldest and most popular zoos in India, and is home to a wide range of species (168). Mysore Z ...
.
Geography
Area and extent

 Mysore is located at and has an average altitude of . It is spread across an area of at the base of the
Mysore is located at and has an average altitude of . It is spread across an area of at the base of the Chamundi Hill
The Chamundi Hills are located 13 km east of Mysore, Karnataka, India. The name comes from the Chamundeshwari Temple at the peak. The average elevation is .
Attractions
The Chamundeshwari Temple is located atop the Chamundi Hills. Patro ...
s in the southern region of Karnataka. Mysore is the southernmost city of Karnataka and is a neighbouring city of the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu in the south, flanked by the state cities Mercara
Madikeri is a hill station town in Madikeri taluk and headquarters of Kodagu district in Karnataka, India.
Etymology
Madikeri was known as ''Muddu Raja Keri'', which meant Mudduraja's town, was named after the prominent Haleri king Mudduraj ...
, Chamarajanagara, and Mandya. People in and around Mysore extensively use Kannada as a medium of language. Mysore has several lakes, such as the Kukkarahalli, the Karanji Karanji may refer to:
* ''Karanji'' (film), a 2009 Kannada-language Indian film
* Karanji Lake, a lake in the Mysore city of Karnataka, India
* Karanji, Maharashtra, a village, List of villages in Pathardi taluka, in Pathardi taluka, Ahmednagar ...
, and the Lingambudhi lakes. Mysore has The Biggest 'Walk-Through Aviary' called Karanji Lake in India. In 2001, total land area usage in Mysore city was 39.9% residential, 16.1% roads, 13.74% parks and open spaces, 13.48% industrial, 8.96% public property, 3.02% commercial, 2.27% agriculture and 2.02 water. The city is located between two rivers: the Kaveri River
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dist ...
that flows through the north of the city and the Kabini River, a tributary of the Kaveri, that lies to the south.
Climate
Mysore has a tropical savanna climate (''Aw'') bordering on ahot semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(''BSh'') under the K├Čppen climate classification. The main seasons are Summer from March to May, the monsoon season from June to October and winter from November to February. The highest temperature recorded in Mysore was on 4 April 1917, and the lowest was on 16 January 2012. The city's average annual rainfall is .
Administration and utilities

 The civic administration of the city is managed by the Mysore City Corporation, which was established as a municipality in 1888 and converted into a corporation in 1977. Overseeing engineering works, health, sanitation, water supply, administration and taxation, the corporation is headed by a Mayor, who is assisted by commissioners and council members. The city is divided into 65 wards and the council members (also known as ''corporators'') are elected by the citizens of Mysore every five years. The council members, in turn, elect the mayor. The annual budget of the corporation for the year 2011ŌĆō2012 was . Among 63 cities covered under the
The civic administration of the city is managed by the Mysore City Corporation, which was established as a municipality in 1888 and converted into a corporation in 1977. Overseeing engineering works, health, sanitation, water supply, administration and taxation, the corporation is headed by a Mayor, who is assisted by commissioners and council members. The city is divided into 65 wards and the council members (also known as ''corporators'') are elected by the citizens of Mysore every five years. The council members, in turn, elect the mayor. The annual budget of the corporation for the year 2011ŌĆō2012 was . Among 63 cities covered under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission
Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM) was a massive city-modernization scheme launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Urban Development. It envisaged a total investment of over $20 billion over seven years. ...
, Mysore City Corporation was adjudged the second best city municipal corporation and was given the ''"Nagara Ratna"'' award in 2011.
Urban growth and expansion is managed by the Mysore Urban Development Authority (MUDA), which is headed by a commissioner. Its activities include developing new layouts and roads, town planning and land acquisition. One of the major projects undertaken by MUDA is the creation of an Outer Ring Road to ease traffic congestion. Citizens of Mysore have criticised MUDA for its inability to prevent land mafias and ensure lawful distribution of housing lands among city residents. The Chamundeshwari Electricity Supply Corporation is responsible for electric supply to the city.
Drinking water for Mysore is sourced from the Kaveri and Kabini
The Kabini River is one of the major tributaries of the river Cauvery in southern India. It originates near Kavilumpara in Kozhikode district of Kerala state by the confluence of the Panamaram River and the Mananthavady River. It flows eastw ...
rivers. The city got its first piped water supply when the Belagola project was commissioned in 1896. , Mysore gets of water per day. Mysore sometimes faces water crises, mainly during the summer months (MarchŌĆōJune) and in years of low rainfall. The city has had an underground drainage system since 1904. The entire sewage from the city drains into four valleys: Kesare, Malalavadi, Dalavai and Belavatha. In an exercise carried out by the Urban Development Ministry under the national urban sanitation policy, Mysore was rated the second cleanest city in India in 2010 and the cleanest in Karnataka.
The citizens of Mysore elect five representatives to the Legislative assembly of Karnataka
The Karnataka Legislative Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral legislature of the Indian state of Karnataka. Karnataka is one of the six states in India where the state legislature is bicameral, comprising two houses. The two houses are ...
through the constituencies of Chamaraja, Krishnaraja, Narasimharaja, Hunsur and Chamundeshwari. Mysore city, being part of the larger Mysore Lok Sabha constituency, also elects one member to the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Indian Parliament. The politics in the city is dominated by three political parties: the Indian National Congress (INC), the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), and the Janata Dal (Secular)
The Janata Dal (Secular) is an Indian political party led by former prime minister of India, H. D. Deve Gowda. The party is recognized as a State Party in the states of Karnataka, Kerala and Arunachal Pradesh. It was formed in July 1999 by the ...
(JDS).
Demographics
, Mysore city had an estimated population of 920,550 consisting of 461,042 males and 459,508 females, making it the third most populous city in Karnataka Mysore urban agglomeration is the second largest urban agglomeration in the state and is home to 1,060,120 people, consisting of 497,132 males and 493,762 females. According to 2011 census, Mysore was the largest non-metropolitan city in India and had the highest basic infrastructure index of 2.846. Mysore is estimated to have crossed 1 million in 2017 making it a Metropolitan city. For the year 2022, the projected population of Mysuru Metropolitan Area, which includes Mysore City Corporation,Hootagalli
Hootagalli or Hutagalli is a city and a Suburb of Mysore , situated in Mysuru metropolitan area Ó▓«Ó│łÓ▓ĖÓ│éÓ▓░Ó│ü Ó▓£Ó▓┐Ó▓▓Ó│ŹÓ▓▓Ó│å of Karnataka, India. Hootagalli is located in the outskirts of the city of Mysuru and forms a continuous urba ...
City Municipal Council, and Bogadi, Srirampura, Rammanahalli and Kadakola Town Panchayats is 1,261,000, as per the United Nation's World Urbanization Prospects - 2018. The gender ratio of the city is 1000 females to every 1000 males and the population density is . According to the census of 2001, 73.65% of the city population are Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
s, 21.92% are Muslim
Muslims ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘å, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, 2.71% are Christians, 1.13% are Jains and the remainder belong to other religions. The population exceeded 100,000 in the census of 1931 and grew by 20.5 per cent in the decade 1991ŌĆō2001. , the literacy rate of the city is 86.84 per cent, which is higher than the state's average of 75.6 per cent.
Kannada is the most widely spoken language in the city. Approximately 19% of the population live below the poverty line, and 9% live in slum
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily inh ...
s. According to the 2001 census, 35.75% of the population in the urban areas of Karnataka are workers, but only 33.3% of the population of Mysore are. Members of Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes constitute 15.1% of the population. According to the National Crime Records Bureau of India, the number of cognizable crime incidents reported in Mysore during 2010 was 3,407 (second in the state, after Bangalore's 32,188), increasing from 3,183 incidents reported in 2009.
The residents of the city are known as ''Mysoreans'' in English and ''Mysoorinavaru'' in Kannada. The dispute between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu over the sharing of Kaveri river water often leads to minor altercations and demonstrations in the city. Growth in the information technology industry in Mysore has led to a change in the city's demographic profile; likely strains on the infrastructure and haphazard growth of the city resulting from the demographic change have been a cause of concern for some of its citizens.
Education
 Before the advent of the European system of education in Mysore, '' Agraharas'' ( Brahmin quarters) provided Vedic education to Hindus, and ''
Before the advent of the European system of education in Mysore, '' Agraharas'' ( Brahmin quarters) provided Vedic education to Hindus, and ''madrassas
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: ┘ģž»ž▒ž│ž® , Plural, pl. , ) is the Arabs, Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. T ...
'' provided schooling for Muslims. Modern education began in Mysore when a free English school was established in 1833. Maharaja's College was founded in 1864. A high school exclusively for girls was established in 1881 and was later renamed ''Maharani's Women's College''. The ''Industrial School'', the first institute for technical education in the city, was established in 1892; this was followed by the Chamarajendra Technical Institute in 1913. While the modern system of education have made inroads, colleges such as the ''Mysore Sanskrit P─ütha┼øh─üla'', established in 1876, still continue to provide Vedic education.
The education system was enhanced by the establishment of the University of Mysore in 1916. This was the sixth university to be established in India and the first in Karnataka. It was named ''Manasagangotri'' ("fountainhead of the Ganges of the mind") by the poet Kuvempu
Kuppali Venkatappa Puttappa (29 December 1904 ŌĆō 11 November 1994), popularly known by his pen name Kuvempu, was an Indian poet, playwright, novelist and critic. He is widely regarded as the greatest Kannada poet of the 20th century. He was ...
. The university caters to the districts of Mysore, Mandya, Hassan Hassan, Hasan, Hassane, Haasana, Hassaan, Asan, Hassun, Hasun, Hassen, Hasson or Hasani may refer to:
People
*Hassan (given name), Arabic given name and a list of people with that given name
*Hassan (surname), Arabic, Jewish, Irish, and Scottis ...
and Chamarajanagar
Chamarajanagar or Chamarajanagara is a town in the southern part of Karnataka, India. Named after Chamaraja Wodeyar IX, the erstwhile king of Mysore, previously known as 'Arikottara'. Chamarajanagara is the headquarters of Chamarajanagar distr ...
in Karnataka. About 127 colleges, with a total of 53,000 students, are affiliated with the university. Its alumni include Kuvempu, Gopalakrishna Adiga
Mogeri Gopalakrishna Adiga (1918ŌĆō1992) was a modern Kannada poet. He is known by some commentators as the "pioneer of New style" poetry. The Hindu - 26 September 2002
Biography
He was born in an orthodox brahmin family in coastal village of ...
, S. L. Bhyrappa
Santeshivara Lingannaiah Bhyrappa (born 20 June 1931) is an Indian novelist, philosopher and screenwriter who writes in Kannada. His work is popular in the state of Karnataka and he is widely regarded as one of modern India's popular novelists. ...
, U. R. Ananthamurthy and N.R. Narayana Murthy
Nāgavārā Rāmarāo Nārāyana Mūrthy (born 21 August 1946) is an Indian billionaire businessman. He is the founder of Infosys, and has been the chairman, chief executive officer (CEO), president, and chief mentor of the company before ret ...
. Engineering education began in Mysore with the establishment in 1946 of the National Institute of Engineering
National Institute of Engineering (NIE) is a private engineering college located in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It was established in 1946 and granted autonomy in 2007 from Visvesvaraya Technological University.
History
NIE was started in 1946 ...
, the second oldest engineering college in the state. The Mysore Medical College, founded in 1924, was the first medical college to be started in Karnataka and the seventh in India. National institutes in the city include te Central Food Technological Research Institute, the Central Institute of Indian Languages, the Defence Food Research Laboratory, and the All India Institute of Speech and Hearing
The All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, commonly known as AIISH (AYE-SH), is located in Manasagangotri (Mysore University Campus), Mysore, India. It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The institu ...
. The city houses a campus multi-campus, multi-disciplinary private deemed university, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (or Amrita University) is a private deemed university based in Coimbatore, India. It currently has 7 campuses with 16 constituent schools across the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka ...
.
Universities
Autonomous institutes
Economy
Belawadi
Belawadi is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India.Village code= 101100 It is located in the Bailhongal taluk of Belgaum district in Karnataka.
Demographics
India census, Belawadi had a population of 8061 with 4089 males and ...
, Hebbal Hebbal may refer to several places in Karnataka, India:
* Hebbal, Bangalore, a neighborhood in Bangalore
** Hebbal Lake, Bangalore
** Hebbal-Kittayya inscription
** Hebbal (Vidhana Sabha constituency)
** University of Agricultural Sciences, Banga ...
and Hootagalli
Hootagalli or Hutagalli is a city and a Suburb of Mysore , situated in Mysuru metropolitan area Ó▓«Ó│łÓ▓ĖÓ│éÓ▓░Ó│ü Ó▓£Ó▓┐Ó▓▓Ó│ŹÓ▓▓Ó│å of Karnataka, India. Hootagalli is located in the outskirts of the city of Mysuru and forms a continuous urba ...
areas. One of the major industrial areas near Mysore is Nanjangud which will be a satellite town to Mysore. Nanjangud industrial area hosts a number of industries like AT&S India Pvt Ltd, Nestle India ltd, Reid and Taylor, Jubiliant, TVS TVS may refer to:
Mathematics
* Topological vector space
Television
* Television Sydney, TV channel in Sydney, Australia
* Television South, ITV franchise holder in the South of England between 1982 and 1992
* TVS Television Network, US dis ...
, and Asian Paints. Nanjangud Industrial area also boasts being 2nd highest VAT / Sales Taxpayer which is more than after Peenya which is in state capital Bangalore. JK Tyre has its manufacturing facility in Mysore. The city has emerged as a hub of automobile industries in Karnataka.
The major software companies in Mysore are Infosys, ArisGlobal, Larsen & Toubro Infotech, Excelsoft Technologies and Triveni Engineering. The growth of the information technology industry in the first decade of the 21st century has resulted in the city emerging as the second largest software exporter in Karnataka (), next to Bangalore. Mysore also has many shopping malls, including the Mall of Mysore
Mall of Mysore is a shopping mall which is one of the largest and the first of its kind in the Indian city of Mysore, Karnataka. It is located next to the Mysore Race Course with the Chamundi hills
The Chamundi Hills are located 13 k ...
which is one of the largest malls in India and Karnataka. Retail is also a major part of the economy in Mysore.
Mysore also hosts many central government organizations like CFTRI, DFRL, CIPET, BEML, RMP (Rare Material Project), RBI Note printing Press and RBI Paper Printing Press.
Culture
 Referred to as the ''cultural capital'' of Karnataka, Mysore is well known for the festivities that take place during the period of '' Dasara''; the state festival of Karnataka. The ''Dasara'' festivities, which are celebrated over a ten-day period, were first introduced by King Raja Wodeyar I in 1610. On the ninth day of ''Dasara'', called ''Mahanavami'', the royal sword is worshipped and is taken on a procession of decorated elephants, camels and horses. On the tenth day, called '' Vijayadashami'', the traditional ''Dasara'' procession (locally known as ''Jumboo Savari'') is held on the streets of Mysore which usually falls in the month of September or October. The idol of the goddess Chamundeshwari is placed on a golden ''
Referred to as the ''cultural capital'' of Karnataka, Mysore is well known for the festivities that take place during the period of '' Dasara''; the state festival of Karnataka. The ''Dasara'' festivities, which are celebrated over a ten-day period, were first introduced by King Raja Wodeyar I in 1610. On the ninth day of ''Dasara'', called ''Mahanavami'', the royal sword is worshipped and is taken on a procession of decorated elephants, camels and horses. On the tenth day, called '' Vijayadashami'', the traditional ''Dasara'' procession (locally known as ''Jumboo Savari'') is held on the streets of Mysore which usually falls in the month of September or October. The idol of the goddess Chamundeshwari is placed on a golden ''mantapa
A mandapa or mantapa () is a pillared hall or pavilion for public rituals in Indian architecture, especially featured in Hindu temple architecture.
Mandapas are described as "open" or "closed" depending on whether they have walls. In temples, ...
'' on the back of a decorated elephant and taken on a procession, accompanied by tabla, dance groups, music bands, decorated elephants, horses and camels. The procession starts from the Mysore Palace and culminates at a place called Bannimantapa, where the ''banni'' tree (''Prosopis spicigera
''Prosopis cineraria'', also known as ghaf, is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. It is native to arid portions of Western Asia and the Indian Subcontinent, including Afghanistan, Bahrain, Iran, India, Oman, Pakistan, Saud ...
'') is worshipped. The ''Dasara'' festivities culminate on the night of ''Vijayadashami'' with a torchlight parade, known locally as ''Panjina Kavayatthu''.
Mysore is called the ''City of Palaces'' because of several ornate examples in the city. Among the most notable are Amba Vilas, popularly known as Mysore Palace; Jaganmohana Palace, which also serves as an art gallery; Rajendra Vilas
The Rajendra Vilas is a palace-hotel atop Chamundi Hills in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It is now closed and in a state of neglect and can only be visited with prior permission.
Description
The Rajendra Vilas palace is located on top of Chamundi H ...
, also known as the summer palace; Lalitha Mahal, which has been converted into a hotel; and Jayalakshmi Vilas. The palace of Mysore burned down in 1897, and the present structure was built on the same site. Amba Vilas palace exhibits an Indo-Saracenic style of architecture on the outside, but a distinctly Hoysala style in the interior. Even though the Government of Karnataka maintains the Mysore palace, a small portion has been allocated for the erstwhile royal family to live in. The Jayalakshmi Vilas Mansion was constructed by Sri Chamaraja Wodeyar for his daughter Jayalakshammanni. It is now a museum dedicated to folk culture and artifacts of the royal family.
 The
The Mysore painting
Mysore painting ( kn, Ó▓«Ó│łÓ▓ĖÓ│éÓ▓░Ó│ü Ó▓ÜÓ▓┐Ó▓żÓ│ŹÓ▓░Ó▓ĢÓ▓▓Ó│å) is an important form of classical South Indian painting style that originated in and around the town of Mysore in Karnataka encouraged and nurtured by the Mysore rulers. Painti ...
style is an offshoot of the Vijayanagar school of painting, and King Raja Wodeyar (1578ŌĆō1617 CE) is credited with having been its patron. The distinctive feature of these paintings is the '' gesso'' work, to which gold foil is applied. Mysore is known for rosewood inlay work; around 4,000 craftsmen were involved in this art in 2002. The city lends its name to the Mysore silk sari, a women's garment made with pure silk and gold ''zari
''Zari'' (or ''jari'') is an even thread traditionally made of fine gold or silver used in traditional Indian, Bangladeshi and Pakistani garments, especially as brocade in saris etc. This thread is woven into fabrics, primarily silk, to make in ...
'' (thread). ''Mysore Peta
The ''Mysuru peta'' (''peta'' is a Kannada word which means turban in English) is the classical royal Indian attire worn by the erstwhile Kings of Mysore. Wodeyars wore a richly bejeweled turban made of silk and jari (gold threaded lace) to mat ...
'', the traditional indigenous turban worn by the erstwhile rulers of Mysore, is worn by men in some traditional ceremonies. A notable local dessert that traces its history to the kitchen in the Mysore palace is '' Mysore pak''.
Mysore is the location of the International Ganjifa Research Centre, which researches the ancient card game '' Ganjifa'' and the art associated with it. The Chamarajendra Academy of Visual Arts
Chamarajendra Academy of Visual Arts (CAVA) is a visual art school in Mysore, in the state of Karnataka in India. The academy is affiliated to the University of Mysore and offers courses in drawing, painting, sculpture, graphics, applied arts, p ...
(CAVA) offers education in visual art forms such as painting, graphics, sculpture, applied art, photography, photojournalism and art history. The Rangayana repertory company performs plays and offers certificate courses in subjects related to theatre. Kannada writers Kuvempu
Kuppali Venkatappa Puttappa (29 December 1904 ŌĆō 11 November 1994), popularly known by his pen name Kuvempu, was an Indian poet, playwright, novelist and critic. He is widely regarded as the greatest Kannada poet of the 20th century. He was ...
, Gopalakrishna Adiga
Mogeri Gopalakrishna Adiga (1918ŌĆō1992) was a modern Kannada poet. He is known by some commentators as the "pioneer of New style" poetry. The Hindu - 26 September 2002
Biography
He was born in an orthodox brahmin family in coastal village of ...
and U. R. Ananthamurthy were educated in Mysore and served as professors at the Mysore University. R. K. Narayan
Rasipuram Krishnaswami Iyer Narayanaswami (10 October 1906 ŌĆō 13 May 2001) was an Indian writer known for his work set in the fictional South Indian town of Malgudi. He was a leading author of early Indian literature in English along with Mul ...
, a popular English-language novelist and creator of the fictional town of Malgudi
Malgudi is a fictional town located in Agumbe in Karnataka in the novels and short stories of R. K. Narayan. It forms the setting for most of Narayan's works. Starting with his first novel, ''Swami and Friends'', all but one of his fifteen nov ...
, and his cartoonist brother R. K. Laxman
Rasipuram Krishnaswami Laxman ''Pg. 11 in the source says that Laxman & his brother Narayan were Tamil Iyer Brahmins.'' (24 October 1921 ŌĆō 26 January 2015) was an Indian cartoonist, illustrator, and humorist. He is best known for his creation ...
spent much of their life in Mysore.
Transport
Road
 Mysore is connected by
Mysore is connected by National Highway National highway or National Highway may refer to:
* National Highways (England)
* National Highway (Australia)
* List of National Roads in Belgium
* Brunei National Roads System
* National Highway System (Canada)
* Trans-Ca ...
NH-212 to the state border town of Gundlupet
Gundlupet also known as Land of Tigers (''Gundlup─ōt─ō'' in Kannada) is a municipal town situated in the Chamarajanagar district of Karnataka, India. It is also known as "''The flower pot of India''". It is situated 60 km away from NH 766 and ...
, where the road forks into the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. State Highway 17, which connects Mysore to Bangalore, was upgraded to a four-lane highway in 2006, reducing travel time between the two cities. A project was planned in 1994 to construct a new expressway to connect Bangalore and Mysore. After numerous legal hurdles, it remains unfinished . State Highway 33 and National Highway 275
Route 275 or Highway 275 may refer to:
Canada
* Manitoba Provincial Road 275
* New Brunswick Route 275
* Quebec Route 275
India
* National Highway 275 (India)
* State Highway 275 (Maharashtra)
Japan
* Japan National Route 275
United States
...
which connect Mysore to H D Kote
Heggadadevanakote or H.D.Kote is a town and a taluk headquarters in Mysore district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Kakana kote forest lies in Heggadadevana kote taluk. H.D Kote city is divided into 13 wards for which elections are held every ...
and Mangalore respectively. The Karnataka State Road Transport Corporation (KSRTC) and other private agencies operate buses both within the city and between cities. A new division of KSRTC called Mysore City Transport Corporation (MCTC) has been proposed. Within the city, buses are cheap and popular means of transport, auto-rickshaw
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many terms in various countries including auto, auto rickshaw, baby taxi, mototaxi, pigeon, jonnybee, bajaj ...
s are also available and ''tongas
A tonga or tanga is a light carriage or curricle drawn by one horse (compare ekka) used for transportation in the Indian subcontinent. They have a canopy over the carriage with a single pair of large wheels. The passengers reach the seats fro ...
'' (horse-drawn carriages) are popular with tourists.
Mysore also has a long ring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop, bypass or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city, or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist i ...
that is being upgraded to six lanes by the MUDA
Muda or MUDA or MuDA may refer to:
People
* Sultan Muda (1579ŌĆō1579), nominal Sultan of Aceh
* Tycho Muda (born 1988), Dutch rower
* Vincent Muda (born 1988), Dutch rower
Places
* Muda, Estonia, a village
* Mud├Ī, Spain
*Muda River, Malaysi ...
. Mysore has implemented Intelligent Transport System (ITS) to manage its city buses and ferrying commuters.
Trin Trin PBS
 A public bicycle sharing system, Trin Trin, funded partially by the United Nations is popular mode of transport. It is a government project. It is the first public bike-sharing system throughout India. The key objective of Trin Trin is to encourage local commuters, as well as visitors, to use the bicycle in preference to motorized modes of travel and thereby help scale down the multifarious environmental and road-traffic hazards, enhance conveyance convenience, and make local daily commutes economical for the common citizen.
A public bicycle sharing system, Trin Trin, funded partially by the United Nations is popular mode of transport. It is a government project. It is the first public bike-sharing system throughout India. The key objective of Trin Trin is to encourage local commuters, as well as visitors, to use the bicycle in preference to motorized modes of travel and thereby help scale down the multifarious environmental and road-traffic hazards, enhance conveyance convenience, and make local daily commutes economical for the common citizen.
Rail

Mysore railway station
Mysore Junction railway station, re-christened as Mysuru Junction railway station (station code: MYS) is a railway station on MysoreŌĆōBangalore railway line serving the city of Mysore, Karnataka, India. Previously Mysore was connected to Bangal ...
has three lines, connecting it to Bangalore, Mangalore, and Chamarajanagar
Chamarajanagar or Chamarajanagara is a town in the southern part of Karnataka, India. Named after Chamaraja Wodeyar IX, the erstwhile king of Mysore, previously known as 'Arikottara'. Chamarajanagara is the headquarters of Chamarajanagar distr ...
. The first railway line established in the city was the BengaloreŌĆōMysore Junction metre gauge
Metre-gauge railways are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
The metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires. In Europe, la ...
line, which was commissioned in 1882. Railway lines that connect the city to Chamarajanagara and Mangalore are unelectrified single track and the track that connects to Bengaluru
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
is electrified double track
A double-track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single-track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.
Overview
In the earliest days of railways in the United Kingdom, most lin ...
. Mysore Railway Junction comes under the jurisdiction of South Western Railway Zone. Within the city limits of Mysore, there are two small stations in the line which connects Chamarajanagara. They are Ashokpuram and Chamarajapuram
Chamarajapuram is one of the earliest settlements and localities in Mysore, Karnataka, India, located in the centre of Mysore city. Initially an agraharam inhabited by the Mysore nobility, parts of it were later allotted other local dwellers as ...
. The fastest train to serve the city is the Shatabdi Express which goes to Chennai via Bangalore. A satellite terminal is planned at Naganahalli to reduce congestion in the main railway station. On 20 June 2022, Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation to upgrade the present city railway junction with , to construct another 3 platforms, 4 pit lines and 4 stabiling line to make 9 platforms in the city junction and Naganahali station to built coach complex and MEMU hub and two more platforms to solve congestion in the city railway junction.
Air
 Mysore Airport is a domestic airport and is located near the village of Mandakalli, 10 kilometres south of the centre of the city. It was built by the kings of Mysore in early 1940s. Mysore Airport currently serves the city of Mysore and is connected to multiple domestic locations including Bangalore, Chennai, Goa, Hubli, Hyderabad, Kochi and Mangalore. The current runway is not able to handle big flights and hence a runway expansion is about to take place expanding the runway from 1.7 km to 2.8 km and will be upgraded to international airport after the expansion. The nearest International airport is Kannur International Airport in Kannur which lies about away from Mysore city but considering that the only international destinations from this airport are in the Middle East,
Mysore Airport is a domestic airport and is located near the village of Mandakalli, 10 kilometres south of the centre of the city. It was built by the kings of Mysore in early 1940s. Mysore Airport currently serves the city of Mysore and is connected to multiple domestic locations including Bangalore, Chennai, Goa, Hubli, Hyderabad, Kochi and Mangalore. The current runway is not able to handle big flights and hence a runway expansion is about to take place expanding the runway from 1.7 km to 2.8 km and will be upgraded to international airport after the expansion. The nearest International airport is Kannur International Airport in Kannur which lies about away from Mysore city but considering that the only international destinations from this airport are in the Middle East, Bangalore Airport
Kempegowda International Airport is an international airport serving Bangalore, the capital of Karnataka, India. Spread over , it is located about north of the city near the suburb of Devanahalli. It is owned and operated by Bengaluru Inte ...
is more commonly used to reach more destinations globally.
Media
 Newspaper publishing in Mysore started in 1859 when Bhashyam Bhashyacharya began publishing a weekly newspaper in Kannada called the ''Mysooru Vrittanta Bodhini'', the first of a number of weekly newspapers published in the following three decades. A well-known Mysore publisher during Wodeyar rule was
Newspaper publishing in Mysore started in 1859 when Bhashyam Bhashyacharya began publishing a weekly newspaper in Kannada called the ''Mysooru Vrittanta Bodhini'', the first of a number of weekly newspapers published in the following three decades. A well-known Mysore publisher during Wodeyar rule was M. Venkatakrishnaiah
M. Venkatakrishnaiah (1844ŌĆō1933) was pioneer of journalism, author, social reformer, educator, civil servant and philanthropist based in the city of Mysore, India. He was often referred to as the grand-old man of Mysore or Tataiah. His achieve ...
, known as the father of Kannada journalism, who started several news magazines. Many local newspapers are published in Mysore and carry news mostly related to the city and its surroundings, and national and regional dailies in English and Kannada are available, as in the other parts of the state. Sudharma
''Sudharma'' ( sa, ÓżĖÓźüÓż¦Óż░ÓźŹÓż«ÓżŠ) is the daily newspaper printed in Sanskrit in India. The paper is published from the city of Mysore in the Indian state of Karnataka. Established in 1970, the paper is mainly distributed via mail, a met ...
, the only Indian daily newspaper in Sanskrit, is published in Mysore.
Mysore was the location of the first private radio broadcasting station in India when ''Akashavani'' (voice from the sky) was established in the city on 10 September 1935 by M.V. Gopalaswamy, a professor of psychology, at his house in the Vontikoppal area of Mysore, using a 50-watt transmitter. The station was taken over by the princely state of Mysore in 1941 and was moved to Bangalore in 1955. In 1957, ''Akashvani'' was chosen as the official name of All India Radio (AIR), the radio broadcaster of the Government of India. The AIR station at Mysore broadcasts an FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is cap ...
channel at 100.6 MHz, and Gyan Vani
Gyan Vani is an educational FM radio station in several cities of India.
Description
Gyan Vani is an educational FM radio station in several cities of India. Gyan Vani stations operate as a media cooperative with the day-to-day programmes being ...
broadcasts on 105.6. BIG FM, Radio Mirchi and Red FM are the three private FM channels operating in the city.
Mysore started receiving television broadcasts in the early 1980s, when Doordarshan
Doordarshan (abbreviated as DD; Hindi: , ) is an Indian public service broadcaster founded by the Government of India, owned by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting and one of Prasar Bharati's two divisions. One of India's largest bro ...
( public service broadcaster of the Indian government) started broadcasting its national channel all over India. This was the only channel available to Mysoreans until Star TV started satellite channels in 1991. Direct-to-home channels are now available in Mysore.
Sports
The Wodeyar kings of Mysore were patrons of games and sports. KingKrishnaraja Wodeyar III
Krishnaraja Wadiyar III (14 July 1794 ŌĆō 27 March 1868) was the twenty-second maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore. Also known as Mummadi Krishnaraja Wadiyar, the maharaja belonged to the Wadiyar dynasty and ruled the kingdom for nearly seventy y ...
had a passion for indoor games. He invented new board games and popularised the ''ganjifa'' card game. Malla-yuddha (traditional wrestling) has a history in Mysore dating back to the 16th century. The wrestling competition held in Mysore during the ''Dasara'' celebrations attracts wrestlers from all over India. An annual sports meeting is organised there during the ''Dasara'' season too.
In 1997 Mysore and Bangalore co-hosted the city's biggest sports event ever, the National Games of India
The National Games of India consist of various disciplines in which athletes from the different states of India participate against each other.
The country's first few Olympic Games, now renamed as National Games, were held in North India (De ...
. Mysore was the venue for six sports: archery, gymnastics, equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, Driving (horse), driving, and Equestrian vaulting, vaulting ...
, handball, table tennis and wrestling. Cricket is by far the most popular sport in Mysore. The city has five established cricket grounds. Javagal Srinath
Javagal Srinath, (, born 31 August 1969) is a former Indian cricketer and currently an ICC match referee. He is considered among India's finest fast bowlers, and was the first Indian fast bowler to take more than 300 wickets in One Day Inter ...
, who represented India for several years as its frontline fast bowler, comes from Mysore. Other prominent sportsmen from the city are Prahlad Srinath
Srinath Prahlad (born 8 January 1973) is a tennis player from India. He won two bronze medals at the 1998 Asian Games and competed in the Davis Cup. He reached one ATP doubles final partnering fellow Indian Saurav Panja at the 2000 Chennai Op ...
, who has represented India in Davis Cup
The Davis Cup is the premier international team event in men's tennis. It is run by the International Tennis Federation (ITF) and is contested annually between teams from competing countries in a knock-out format. It is described by the organis ...
tennis tournaments; Reeth Abraham
Reeth Abraham is an athlete from Bengaluru, India and former Asian medalist in long jump and 100 meters hurdles and the former national champion in heptathlon. She won the Arjuna Award in 1997 and the Rajyotsava Award in 1983. Reeth had a long ...
, a national champion in the heptathlon
A heptathlon is a track and field combined events contest made up of seven events. The name derives from the Greek ╬ĄŽĆŽä╬¼ (hepta, meaning "seven") and ß╝ä╬Ė╬╗╬┐Žé (├Īthlos, or ß╝ä╬Ė╬╗╬┐╬Į, ├Īthlon, meaning "competition"). A competitor in a hept ...
and a long jump record holder; Sagar Kashyap
Sagar Kashyap is a former under-18 tennis player from Mysore, Karnataka, India, and the youngest Indian to officiate at the Wimbledon Championship.
Biography
Kashyap, hailing from Mysore started playing tennis at the age of 12. He is a forme ...
, the youngest Indian to officiate at the Wimbledon Championships; and Rahul Ganapathy, a national amateur golf champion. The Mysore race course hosts a racing season each year from August through October. India's first youth hostel was formed in the Maharaja's College Hostel in 1949.
Tourism
 Mysore is a major tourist destination in its own right and serves as a base for other tourist attractions in the vicinity. The city receives many tourists during the ten-day ''Dasara'' festival. One of the most visited monuments in India, the Amba Vilas Palace, or Mysore Palace, is the centre of the ''Dasara'' festivities. The Jaganmohana Palace, The Sand Sculpture Museum the Jayalakshmi Vilas and the Lalitha Mahal are other palaces in the city. Chamundeshwari Temple, atop the Chamundi Hills, and St. Philomena's Church, Wesley's Cathedral are notable religious places in Mysore.
Mysore is a major tourist destination in its own right and serves as a base for other tourist attractions in the vicinity. The city receives many tourists during the ten-day ''Dasara'' festival. One of the most visited monuments in India, the Amba Vilas Palace, or Mysore Palace, is the centre of the ''Dasara'' festivities. The Jaganmohana Palace, The Sand Sculpture Museum the Jayalakshmi Vilas and the Lalitha Mahal are other palaces in the city. Chamundeshwari Temple, atop the Chamundi Hills, and St. Philomena's Church, Wesley's Cathedral are notable religious places in Mysore.
 The Mysore Zoo, established in 1892, the Karanji, Kukkarahalli and the Blue Lagoon Lake are popular recreational destinations. Blue Lagoon is a lake with a mini island located behind the KRS water dam, from which it is mesmerising to watch the sunset and sunrise. Mysore has the Regional Museum of Natural History, the Folk Lore Museum, the Railway Museum and the Oriental Research Institute. The city is a centre for yoga-related health tourism that attracts domestic and foreign visitors, particularly those who, for years, came to study with the late Ashtanga vinyasa yoga guru K. Pattabhi Jois.
A short distance from Mysore city is the neighbouring Mandya District's Krishnarajasagar Dam and the adjoining
The Mysore Zoo, established in 1892, the Karanji, Kukkarahalli and the Blue Lagoon Lake are popular recreational destinations. Blue Lagoon is a lake with a mini island located behind the KRS water dam, from which it is mesmerising to watch the sunset and sunrise. Mysore has the Regional Museum of Natural History, the Folk Lore Museum, the Railway Museum and the Oriental Research Institute. The city is a centre for yoga-related health tourism that attracts domestic and foreign visitors, particularly those who, for years, came to study with the late Ashtanga vinyasa yoga guru K. Pattabhi Jois.
A short distance from Mysore city is the neighbouring Mandya District's Krishnarajasagar Dam and the adjoining Brindavan Gardens
The Brindavan Gardens is a garden located 12 k.ms from the city of Mysore in the Mandya District of the Indian State of Karnataka. It lies adjoining the Krishnarajasagara Dam which is built across the river Kaveri. The work on laying out t ...
, where a musical fountain show is held every evening. Places of historic importance close to Mysore are Mandya District's Ranganathaswamy Temple, Srirangapatna. And other historical places are Somanathapura
Somanathapura, also spelled Somanathpur, Somnathpur, or Somanathpura, is a town and Grama Panchayat in Tirumakudalu Narasipura, Mysore district in the state of Karnataka in India.Talakad. B R Hills,
Popular Museums in Mysore
ĆöIxigo * * * * * * *
Mysore Palace ŌĆō Govt of Karnataka
Mysore City Corporation
Mysore District Information
MysoreMedia
* {{Authority control Former capital cities in India Cities in Karnataka 1888 establishments in India
Himavad Gopalaswamy Betta
Himavad Gopalaswamy Betta, is a hill (betta in Kannada) located in the Gundlupete Taluk, Chamarajanagar district of the state of Karnataka, India at a height of 1450m and is extensively wooded. It is also the highest peak in the Bandipur Na ...
hill and the hill station
A hill station is a town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The term was used mostly in colonial Asia (particularly in India), but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by European colonialists as refuges ...
s of Ooty, Sultan Bathery and Madikeri are close to Mysore. Popular destinations for wildlife enthusiasts near Mysore include the Nagarahole National Park, the wildlife sanctuaries at Melkote, Mandya and B R Hills and the bird sanctuaries at Ranganathittu, Mandya and Kokrebellur, Mandya. Bandipur National Park
Bandipur National Park is a national park covering in Chamarajnagar district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It was established as a tiger reserve under Project Tiger in 1973.
It is part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve since 1986.
History
...
and Mudumalai National Park in Tamil Nadu, which are sanctuaries for gaur, chital, elephants, tigers, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s and other threatened species, lie between to the south. Other tourist spots near Mysore include the religious locations of Nanjanagud
Nanjangud, officially known as Nanjanagudu, is a town in the Mysuru district of Indian state of Karnataka. Nanjangud lies on the banks of the river Kapila (also called Kabini), 23 km from the city of Mysore. Nanjangud is famous for the S ...
and Bylakuppe
Bylakuppe is an area in Karnataka which is home to the Indian town Bylakuppe and several Tibetan settlements (there are several Tibetan settlements in India), established by Lugsum Samdupling (in 1961) and Dickyi Larsoe (in 1969). Bylakuppe ...
and the waterfalls at neighbouring districts of Mandya's Shivanasamudra.
Sister cities
* Cincinnati, Ohio, United States (2012) *Nashua, New Hampshire
Nashua is a city in southern New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it had a population of 91,322, the second-largest in northern New England after nearby Manchester, New Hampshire, Manchester. Along with Manc ...
, United States (2016)
See also
*C V Rangacharlu Memorial Hall
The Rangacharlu Memorial Hall, commonly known as Mysore Town Hall and colloquially referred to simply as the Town Hall, is a Neoclassical-styled public building that was constructed in 1884 in memory of the 14th Diwan of Mysore Sir C. V. Runga ...
* List of Heritage Buildings in Mysore
This article lists heritage and monumental edifices built before the Indian Independence in and around Mysore City in the first section, and then tabulates modern buildings. The history of Mysore city, in particular, and of the Deccan Plateau ...
* List of million-plus cities in India
The following tables are the list of cities in India by population. Often cities are bifurcated into multiple regions (municipalities) which results in creation of cities within cities which may figure in the list. The entire work of this article ...
* Maharaja of Mysore
* Mahisha Kingdom
Mahisha or Mahishaka was a kingdom in ancient India. The capital, Mahishuru, is currently known as Mysore, a city in Karnataka. This kingdom is mentioned in Mahabharata, though Puranas (especially Markandeya Purana) gives more information. The ...
* Mysore Dasara
* Mysore Kingdom
* Tourist attractions in Mysore
Mysore was the previous capital city in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the headquarters of the Mysore district and Mysore division and lies about southwest of Bengaluru, the capital of Karnataka. The city covers an area of and is situ ...
* Mysore Sandal Soap
Mysore Sandal Soap is a brand of soap manufactured by the Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Limited (KSDL), a company owned by the government of Karnataka in India. This soap has been manufactured since 1916, when Krishna Raja Wadiyar IV, the king ...
* Vijayanagara Kingdom
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana and Maharas ...
* Mysuru Local Planning Area
Mysuru Local Planning Area is the metropolitan area limit defined in City Development Plan 2031 by Mysore Urban Development Authority. Mysuru Planning Area is divided into 45 planning districts spanning across the Taluks of Mysore, Nanjangud and ...
References
Bibliography
Popular Museums in Mysore
ĆöIxigo * * * * * * *
External links
Mysore Palace ŌĆō Govt of Karnataka
Mysore City Corporation
Mysore District Information
MysoreMedia
* {{Authority control Former capital cities in India Cities in Karnataka 1888 establishments in India