Moravia Union on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with
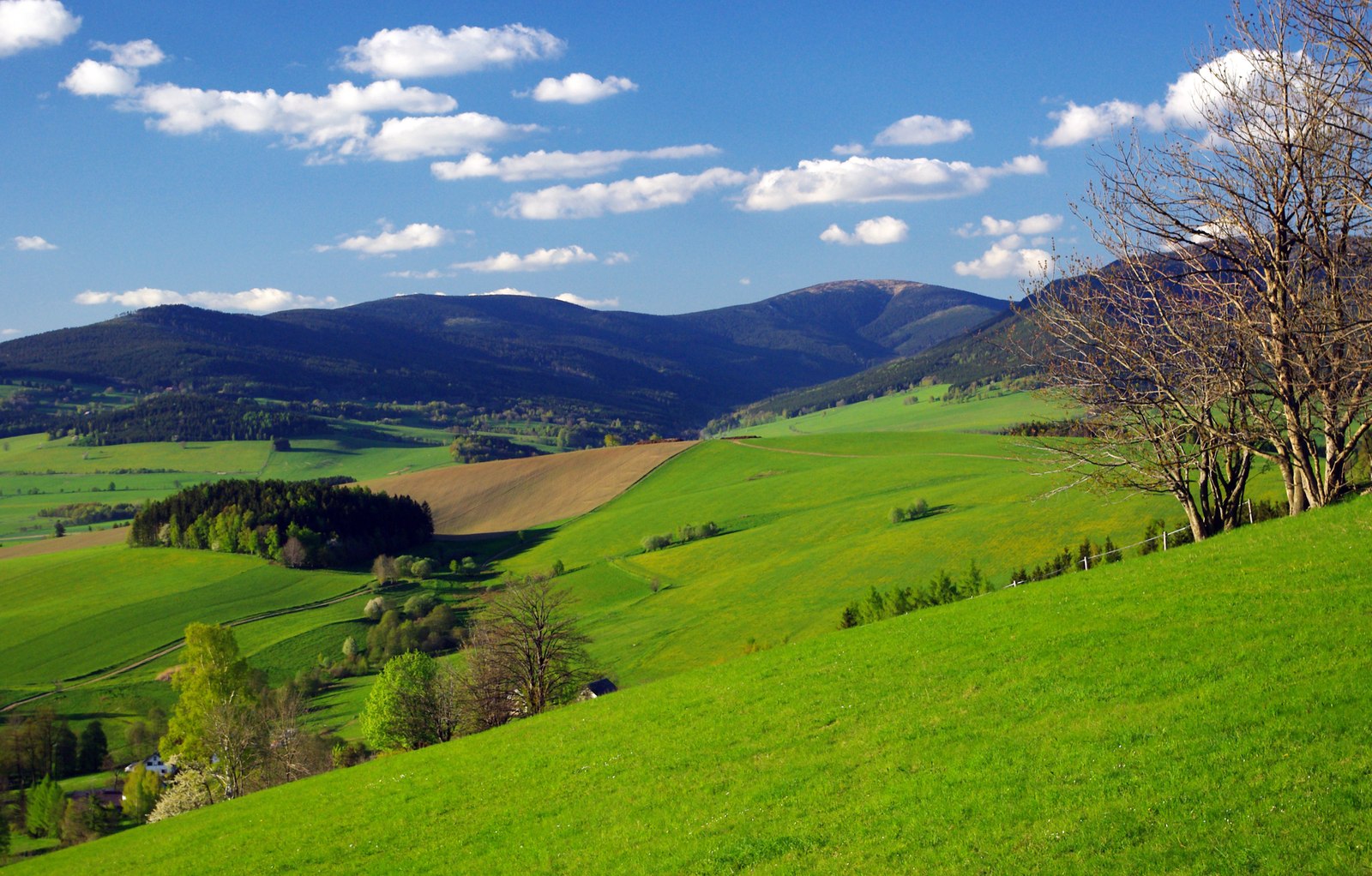


 Moravia borders
Moravia borders

 Evidence of the presence of members of the human genus, '' Homo'', dates back more than 600,000 years in the paleontological area of
Evidence of the presence of members of the human genus, '' Homo'', dates back more than 600,000 years in the paleontological area of
 A variety of Germanic and major Slavic tribes crossed through Moravia during the
A variety of Germanic and major Slavic tribes crossed through Moravia during the
Bohemia 1138–1254.jpg, Bohemia and Moravia in the 12th century
Brno - Kostel sv. Tomáše, místodžitelský palác a alegorická postava spravedlnosti.jpg, Church of St. Thomas in Brno, mausoleum of Moravian branch House of Luxembourg, rulers of Moravia; and the old governor's palace, a former Augustinian abbey
Trebic podklasteri bazilika velka apsida.jpg, 12th century Romanesque
Growth of Habsburg territories.jpg, Habsburg Empire
JanCerny.jpg,
Tatra 77.jpg, The Tatra 77 (1934)
Sportovní vůz Supersport.gif, WIKOV Supersport (1931)
Michael Thonet 14.jpg, Thonet

 The Moravians are generally a Slavic ethnic group who speak various (generally more archaic) dialects of Czech. Before the expulsion of Germans from Moravia the Moravian German minority also referred to themselves as "Moravians" (''Mährer''). Those expelled and their descendants continue to identify as Moravian.
Some Moravians assert that Moravian is a language distinct from Czech; however, their position is not widely supported by academics and the public. Some Moravians identify as an ethnically distinct group; the majority consider themselves to be ethnically Czech. In the census of 1991 (the first census in history in which respondents were allowed to claim Moravian nationality), 1,362,000 (13.2%) of the Czech population identified as being of Moravian nationality (or ethnicity). In some parts of Moravia (mostly in the centre and south), majority of the population identified as Moravians, rather than Czechs. In the census of 2001, the number of Moravians had decreased to 380,000 (3.7% of the country's population). In the census of 2011, this number rose to 522,474 (4.9% of the Czech population).
Moravia historically had a large minority of
The Moravians are generally a Slavic ethnic group who speak various (generally more archaic) dialects of Czech. Before the expulsion of Germans from Moravia the Moravian German minority also referred to themselves as "Moravians" (''Mährer''). Those expelled and their descendants continue to identify as Moravian.
Some Moravians assert that Moravian is a language distinct from Czech; however, their position is not widely supported by academics and the public. Some Moravians identify as an ethnically distinct group; the majority consider themselves to be ethnically Czech. In the census of 1991 (the first census in history in which respondents were allowed to claim Moravian nationality), 1,362,000 (13.2%) of the Czech population identified as being of Moravian nationality (or ethnicity). In some parts of Moravia (mostly in the centre and south), majority of the population identified as Moravians, rather than Czechs. In the census of 2001, the number of Moravians had decreased to 380,000 (3.7% of the country's population). In the census of 2011, this number rose to 522,474 (4.9% of the Czech population).
Moravia historically had a large minority of
Johan_amos_comenius_1592-1671.jpg, Comenius
Gregor_Mendel_oval.jpg, Gregor Mendel
Jan Vilímek - František Palacký 2.jpg, František Palacký
Jasomir Mundy.jpg, Jaromír Mundy
Tomáš_Garrigue_Masaryk_1925.PNG, Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk
Leoš_Janáček.jpg, Leoš Janáček
Sigmund Freud, by Max Halberstadt (cropped).jpg, Sigmund Freud
Edmund_Husserl_1910s.jpg, Edmund Husserl
Alfons_Mucha_LOC_3c05828u.jpg, Alphonse Mucha
Adolf Loos (1870–1933) (vor 1920; Franz Löwy).jpg, Adolf Loos
Tomas_Bata.jpg, Tomáš Baťa
Kurt_gödel.jpg, Kurt Gödel
Fotothek_df_roe-neg_0006305_003_Emil_Zátopek-2.jpg, Emil Zátopek
Milan Kundera redux.jpg, Milan Kundera
Lendl_CU.jpg, Ivan Lendl
Notable people from Moravia include (in order of birth):
* Anton Pilgram (1450–1516), architect, sculptor and woodcarver
* * Joseph Schumpeter (1883–1950), economist and political scientist
*
* Joseph Schumpeter (1883–1950), economist and political scientist
*


Moravian museum official website
Moravian gallery official website
Moravian library official website
Moravian land archive official website
Province of Moravia – Czech Catholic Church – official website
Welcome to the 2nd largest city of the CR
Welcome to Olomouc, city of good cheer...
Znojmo – City of Virtue
* {{Authority control Counties of the Holy Roman Empire Geography of Central Europe Geography of the Czech Republic Historic counties in Moravia Historical regions in the Czech Republic Historical regions Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early modern Margraviate of Moravia was a crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. ...
of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown from 1348 to 1918, an imperial state
An Imperial State or Imperial Estate ( la, Status Imperii; german: Reichsstand, plural: ') was a part of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise si ...
of the Holy Roman Empire from 1004 to 1806, a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1804 to 1867, and a part of Austria-Hungary from 1867 to 1918. Moravia was one of the five lands of Czechoslovakia founded in 1918. In 1928 it was merged with Czech Silesia, and then dissolved in 1949 during the abolition of the land system following the communist coup d'état.
Its area of 22,623.41 km2 is home to more than 3 million people.
The people are historically named Moravians
Moravians ( cs, Moravané or colloquially , outdated ) are a West Slavic ethnographic group from the Moravia region of the Czech Republic, who speak the Moravian dialects of Czech or Common Czech or a mixed form of both. Along with the Silesi ...
, a subgroup of Czechs, the other group being called Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
ns. Moravia also had been home of a large German-speaking population until their expulsion in 1945. The land takes its name from the Morava river, which runs from its north to south, being its principal watercourse. Moravia's largest city and historical capital is Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
. Before being sacked by the Swedish army
The Swedish Army ( sv, svenska armén) is the land force of the Swedish Armed Forces.
History
Svea Life Guards dates back to the year 1521, when the men of Dalarna chose 16 young able men as body guards for the insurgent nobleman Gustav Vas ...
during the Thirty Years' War, Olomouc served as the Moravian capital, and it is still the seat of the Archdiocese of Olomouc.
Toponymy
The region and former margraviate of Moravia, ''Morava'' in Czech, is named after its principal river Morava. It is theorized that the river's name is derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*mori'': "waters", or indeed any word denoting ''water'' or a ''marsh''. The German name for Moravia is ''Mähren'', from the river's German name ''March''. This could have a different etymology, as ''march'' is a term used in the Medieval times for an outlying territory, a border or a frontier (cf. English '' march'').Geography
Moravia occupies most of the eastern part of the Czech Republic. Moravian territory is naturally strongly determined, in fact, as the Morava river basin, with strong effect of mountains in the west (''de facto'' main European continental divide) and partly in the east, where all the rivers rise. Moravia occupies an exceptional position in Central Europe. All thehighland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
s in the west and east of this part of Europe run west–east, and therefore form a kind of filter, making north–south or south–north movement more difficult. Only Moravia with the depression of the westernmost Outer Subcarpathia, wide, between the Bohemian Massif and the Outer Western Carpathians (gripping the meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
at a constant angle of 30°), provides a comfortable connection between the Danubian
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and Polish regions
Polish historic regions are regions that were related to a former Polish state, or are within present-day Poland, with or without being identified in its administrative divisions.
There are several historic and cultural regions in Poland that ...
, and this area is thus of great importance in terms of the possible migration routes of large mammals – both as regards periodically recurring seasonal migrations triggered by climatic oscillations in the prehistory, when permanent settlement
Settlement may refer to:
*Human settlement, a community where people live
*Settlement (structural), the distortion or disruption of parts of a building
*Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
*Settlement (fina ...
started.


 Moravia borders
Moravia borders Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
in the west, Lower Austria in the southwest, Slovakia in the southeast, Poland very shortly in the north, and Czech Silesia in the northeast. Its natural boundary is formed by the Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consis ...
mountains in the north, the Carpathians in the east and the Bohemian-Moravian Highlands in the west (the border runs from Králický Sněžník in the north, over Suchý vrch
Suchý vrch (german: Dürrer Berg; pl, Suchy szczyt; 995 metres) is the highest (double-peaked) mountain of the southern part of the Orlické Mountains in the Czech Republic. Located on the historical border between Bohemia and Moravia, and right ...
, across Upper Svratka Highlands and Javořice Highlands
The Javořice Highlands ( cs, Javořická vrchovina, german: Jaborschützer Bergeland) is a mountain range in the Czech Republic. The highlands, together with the Jevišovice Highlands threshold, form the Western-Moravian part of Moldanubian Zone ...
to tripoint nearby Slavonice
Slavonice (; german: Zlabings) is a town in Jindřichův Hradec District in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 2,300 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation ...
in the south). The Thaya
The Thaya ( cs, Dyje ) is a river in Central Europe, the longest tributary to the river Morava. Its drainage basin is . It is ( with its longest source river German Thaya) long and meanders from west to east in the border area between Lower Au ...
river meanders along the border with Austria and the tripoint of Moravia, Austria and Slovakia is at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Thaya and Morava rivers. The northeast border with Silesia runs partly along the Moravice, Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows thr ...
and Ostravice
Ostravice (german: Ostrawitz, pl, Ostrawica) is a municipality and village in Frýdek-Místek District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 2,400 inhabitants.
Geography
Ostravice is located about south of Frýdek- ...
rivers. Between 1782 and 1850, Moravia (also thus known as ''Moravia-Silesia'') also included a small portion of the former province of Silesia – the Austrian Silesia (when Frederick the Great annexed most of ancient Silesia (the land of upper and middle Oder river) to Prussia, Silesia's southernmost part remained with the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s).
Today Moravia includes the South Moravian Region, the Zlín Region, vast majority of the Olomouc Region, southeastern half of the Vysočina Region and parts of the Moravian-Silesian, Pardubice
Pardubice (; german: Pardubitz) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 89,000 inhabitants. It is the capital city of the Pardubice Region and lies on the Elbe River. The historic centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monu ...
and South Bohemian regions.
Geologically, Moravia covers a transitive area between the Bohemian Massif and the Carpathians (from northwest to southeast), and between the Danube basin and the North European Plain (from south to northeast). Its core geomorphological features are three wide valleys, namely the Dyje-Svratka Valley (''Dyjsko-svratecký úval''), the Upper Morava Valley
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
(''Hornomoravský úval'') and the Lower Morava Valley
The Lower Morava Valley ( cs, Dolnomoravský úval, Jihomoravská pánev; sk, Dolnomoravský úval; german: Nieder March Talsenke) is a geomorphological formation (special type of valley) in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. It is formed by the ...
(''Dolnomoravský úval''). The first two form the westernmost part of the Outer Subcarpathia, the last is the northernmost part of the Vienna Basin. The valleys surround the low range of Central Moravian Carpathians
The Central Moravian Carpathians ( cs, Středomoravské Karpaty) are a mountain range within the Czech Republic belonging to the Outer Western Carpathians.
Despite the name, they stand in southern Moravia, east of Brno. In the east, they border ...
. The highest mountains of Moravia are situated on its northern border in Hrubý Jeseník, the highest peak is Praděd
Praděd (; german: Altvater; pl, Pradziad; literally " great grandfather") () is the highest mountain of the Hrubý Jeseník mountains, Moravia, Czech Silesia and Upper Silesia and is the fifth-highest mountain of the Czech Republic. The highes ...
(1491 m). Second highest is the massive of Králický Sněžník (1424 m) the third are the Moravian-Silesian Beskids
The Moravian-Silesian Beskids (Czech: , sk, Moravsko-sliezske Beskydy) is a mountain range in the Czech Republic with a small part reaching to Slovakia. It lies on the historical division between Moravia and Silesia, hence the name. It is part o ...
at the very east, with Smrk
Smrk may refer to:
* Smrk (Jizera Mountains), the highest mountain in the Jizera Mountains of Bohemia, Czech Republic at 1124m
* Smrk (Moravian-Silesian Beskids)
Smrk is a massif and a mountain in the Moravian-Silesian Beskids range in the Czec ...
(1278 m), and then south from here Javorníky (1072). The White Carpathians along the southeastern border rise up to 970 m at Velká Javořina. The spacious, but moderate Bohemian-Moravian Highlands on the west reach 837 m at Javořice
Javořice (german: Jaborschützeberg) is a mountain in the Javořice Highlands mountain range within the Bohemian-Moravian Highlands in the Czech Republic. With an elevation of , it is the highest mountain of the Bohemian-Moravian Highlands and o ...
.
The fluvial system of Moravia is very cohesive, as the region border is similar to the watershed of the Morava river, and thus almost the entire area is drained exclusively by a single stream. Morava's far biggest tributaries are Thaya (Dyje) from the right (or west) and Bečva
The Bečva (; german: Betschwa, also ''Betsch'', ''Beczwa'') is a river in the Czech Republic. It is a left tributary of the river Morava. The Bečva is created by two source streams, the northern Rožnovská Bečva (whose valley separates the Mo ...
(east). Morava and Thaya meet at the southernmost and lowest (148 m) point of Moravia. Small peripheral parts of Moravia belong to the catchment area of Elbe, Váh and especially Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows thr ...
(the northeast). The watershed line running along Moravia's border from west to north and east is part of the European Watershed. For centuries, there have been plans to build a waterway across Moravia to join the Danube and Oder river systems, using the natural route through the Moravian Gate
The Moravian Gate ( cs, Moravská brána, pl, Brama Morawska, german: Mährische Pforte, sk, Moravská brána) is a geomorphological feature in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic and the Upper Silesia region in Poland. It is formed by the ...
.
History
Pre-history

 Evidence of the presence of members of the human genus, '' Homo'', dates back more than 600,000 years in the paleontological area of
Evidence of the presence of members of the human genus, '' Homo'', dates back more than 600,000 years in the paleontological area of Stránská skála
Stránská skála is a hill and a national nature monument in Brno in the Czech Republic. It refers to a Mid-Pleistocene- Cromerian interglacial most important paleontological site in Central Europe.
Location
Stránská skála is situated in t ...
.
Attracted by suitable living conditions, early modern humans settled in the region by the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
period. The Předmostí archeological (Cro-magnon
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They ...
) site in Moravia is dated to between 24,000 and 27,000 years old. Caves in Moravský kras
The Moravian Karst ( cs, Moravský kras) is a karst landscape and protected landscape area to the north of Brno in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It encompasses a number of notable geological features, including roughly 1100 c ...
were used by mammoth hunters. Venus of Dolní Věstonice, the oldest ceramic figure in the world, was found in the excavation of Dolní Věstonice
Dolní Věstonice (german: Unterwisternitz) is a municipality and village in Břeclav District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 300 inhabitants. It is known for the eponymous archaeological site.
Geography
Dolní ...
by Karel Absolon.
Roman era
Around 60 BC, theCelt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic Volcae
The Volcae () were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found si ...
people withdrew from the region and were succeeded by the Germanic Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
. Some of the events of the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars (Latin: ''bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum'', "German and Sarmatian War") were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi ...
took place in Moravia in AD 169–180. After the war exposed the weakness of Rome's northern frontier, half of the Roman legions (16 out of 33) were stationed along the Danube. In response to increasing numbers of Germanic settlers in frontier regions like Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
, Dacia, Rome established two new frontier provinces on the left shore of the Danube, Marcomannia and Sarmatia, including today's Moravia and western Slovakia.
In the 2nd century AD, a Roman fortress stood on the vineyards hill known as german: link=no, Burgstall and cz, Hradisko (" hillfort"), situated above the former village Mušov
Mušov (german: Muschau) is a cadastral area and a defunct village in the municipality of Pasohlávky, South Moravian Region, Czech Republic. It covers an area of .
Geography and history
Mušov was the lowest-lying village in the Břeclav Dist ...
and above today's beach resort at Pasohlávky
Pasohlávky (german: Weißstätten) is a municipality and village in Brno-Country District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 700 inhabitants. It is a summer resort at the Nové Mlýny Reservoir.
Geography
Pasohlávk ...
. During the reign of the Emperor Marcus Aurelius, the 10th Legion was assigned to control the Germanic tribes who had been defeated in the Marcomannic Wars. In 1927, the archeologist Gnirs, with the support of president Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, began research on the site, located 80 km from Vindobona and 22 km to the south of Brno. The researchers found remnants of two masonry buildings, a ''praetorium
The Latin term (also and ) originally identified the tent of a general within a Roman castrum (encampment), and derived from the title praetor, which identified a Roman magistrate.Smith, William. Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities, 2 ed., ...
'' and a '' balneum'' ("bath"), including a ''hypocaustum
A hypocaust ( la, hypocaustum) is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm th ...
''. The discovery of bricks with the stamp of the Legio X Gemina and coins from the period of the emperors Antoninus Pius, Marcus Aurelius and Commodus
Commodus (; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. ...
facilitated dating of the locality.
Ancient Moravia
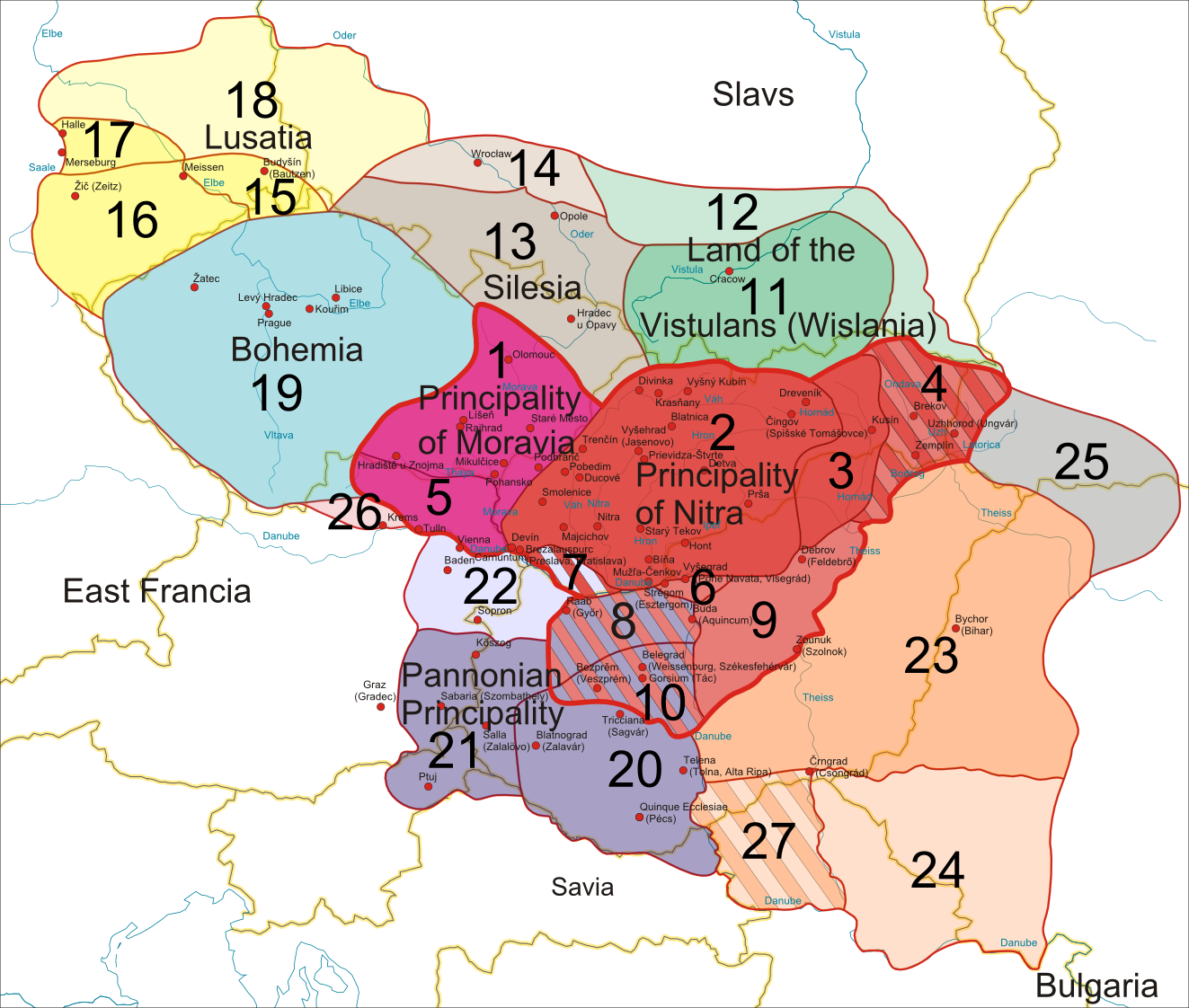
 A variety of Germanic and major Slavic tribes crossed through Moravia during the
A variety of Germanic and major Slavic tribes crossed through Moravia during the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
before Slavs established themselves in the 6th century AD. At the end of the 8th century, the Moravian Principality came into being in present-day south-eastern Moravia, Záhorie
Záhorie ( hu, Erdőhát) is a region in western Slovakia between by the Little Carpathians to the east and the Morava (river), Morava River to the west. Although not an administrative region, it is one of the List of tourism regions of Slovakia, ...
in south-western Slovakia and parts of Lower Austria. In 833 AD, this became the state of Great Moravia with the conquest of the Principality of Nitra (present-day Slovakia). Their first king was Mojmír I
Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I (Latin: ''Moimarus'', ''Moymarus'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmír I.'') was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir. In modern scholarship, the creation of t ...
(ruled 830–846). Louis the German invaded Moravia and replaced Mojmír I with his nephew Rastiz who became St. Rastislav. St. Rastislav (846–870) tried to emancipate his land from the Carolingian influence, so he sent envoys to Rome to get missionaries to come. When Rome refused he turned to Constantinople to the Byzantine emperor Michael. The result was the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius who translated liturgical books into Slavonic, which had lately been elevated by the Pope to the same level as Latin and Greek. Methodius became the first Moravian archbishop, the first archbishop in Slavic world, but after his death the German influence again prevailed and the disciples of Methodius were forced to flee. Great Moravia reached its greatest territorial extent in the 890s under Svatopluk I. At this time, the empire encompassed the territory of the present-day Czech Republic and Slovakia, the western part of present Hungary (Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
), as well as Lusatia in present-day Germany and Silesia and the upper Vistula basin in southern Poland. After Svatopluk's death in 895, the Bohemian princes defected to become vassals of the East Frankish ruler Arnulf of Carinthia
Arnulf of Carinthia ( 850 – 8 December 899) was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894 and the disputed emperor from Feb ...
, and the Moravian state ceased to exist after being overrun by invading Magyars in 907.
Union with Bohemia
Following the defeat of the Magyars by Emperor Otto I at the Battle of Lechfeld in 955, Otto's ally Boleslaus I, the Přemyslid ruler ofBohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, took control over Moravia. Bolesław I Chrobry of Poland annexed Moravia in 999, and ruled it until 1019, when the Přemyslid prince Bretislaus recaptured it. Upon his father's death in 1034, Bretislaus became the ruler of Bohemia. In 1055, he decreed that Bohemia and Moravia would be inherited together by primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
, although he also provided that his younger sons should govern parts (quarters) of Moravia as vassals to his oldest son.
Throughout the Přemyslid era, junior princes often ruled all or part of Moravia from Olomouc, Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
or Znojmo, with varying degrees of autonomy from the ruler of Bohemia. Dukes of Olomouc often acted as the "right hand" of Prague dukes and kings, while Dukes of Brno and especially those of Znojmo were much more insubordinate. Moravia reached its height of autonomy in 1182, when Emperor Frederick I elevated Conrad II Otto of Znojmo to the status of a margrave, immediately subject to the emperor, independent of Bohemia. This status was short-lived: in 1186, Conrad Otto was forced to obey the supreme rule of Bohemian duke Frederick. Three years later, Conrad Otto succeeded to Frederick as Duke of Bohemia and subsequently canceled his margrave title. Nevertheless, the margrave title was restored in 1197 when Vladislaus III of Bohemia
Vladislaus Henry ( cs, Vladislav Jindřich; – 12 August 1222), a member of the Přemyslid dynasty, was elected Duke of Bohemia (as "Vladislaus III") in 1197 and Margrave of Moravia from 1197 until his death. He only served as duke during t ...
resolved the succession dispute between him and his brother Ottokar
Ottokar is the medieval German form of the Germanic name Audovacar.
People with the name Ottokar include:
*Two kings of Bohemia, members of the Přemyslid dynasty
** Ottokar I of Bohemia (–1230)
** Ottokar II of Bohemia (–1278)
*Four Styrian m ...
by abdicating from the Bohemian throne and accepting Moravia as a vassal land of Bohemian (i.e., Prague) rulers. Vladislaus gradually established this land as Margraviate, slightly administratively different from Bohemia. After the Battle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica ( pl, bitwa pod Legnicą), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz (german: Schlacht von Liegnitz) or Battle of Wahlstatt (german: Schlacht bei Wahlstatt), was a battle between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces t ...
, the Mongols carried their raids into Moravia.
The main line of the Přemyslid dynasty became extinct in 1306, and in 1310 John of Luxembourg
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
became Margrave of Moravia and King of Bohemia. In 1333, he made his son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
the next Margrave of Moravia (later in 1346, Charles also became the King of Bohemia). In 1349, Charles gave Moravia to his younger brother John Henry who ruled in the margraviate until his death in 1375, after him Moravia was ruled by his oldest son Jobst of Moravia who was in 1410 elected the Holy Roman King but died in 1411 (he is buried with his father in the Church of St. Thomas in Brno – the Moravian capital from which they both ruled). Moravia and Bohemia remained within the Luxembourg dynasty of Holy Roman kings and emperors (except during the Hussite wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
), until inherited by Albert II of Habsburg in 1437.
After his death followed the interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
until 1453; land (as the rest of lands of the Bohemian Crown) was administered by the landfriedens (''landfrýdy''). The rule of young Ladislaus the Posthumous subsisted only less than five years and subsequently (1458) the Hussite George of Poděbrady was elected as the king. He again reunited all Czech lands (then Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Upper & Lower Lusatia) into one-man ruled state. In 1466, Pope Paul II
Pope Paul II ( la, Paulus II; it, Paolo II; 23 February 1417 – 26 July 1471), born Pietro Barbo, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States
from 30 August 1464 to his death in July 1471. When his maternal uncle Eugene IV ...
excommunicated George and forbade all Catholics (i.e. about 15% of population) from continuing to serve him. The Hungarian crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
followed and in 1469 Matthias Corvinus conquered Moravia and proclaimed himself (with assistance of rebelling Bohemian nobility Czech nobility consists of the noble families from historical Czech lands, especially in their narrow sense, i.e. nobility of Bohemia proper, Moravia and Austrian Silesia – whether these families originated from those countries or moved into them ...
) as the king of Bohemia.
The subsequent 21-year period of a divided kingdom was decisive for the rising awareness of a specific Moravian identity, distinct from that of Bohemia. Although Moravia was reunited with Bohemia in 1490 when Vladislaus Jagiellon, king of Bohemia, also became king of Hungary, some attachment to Moravian "freedoms" and resistance to government by Prague continued until the end of independence in 1620. In 1526, Vladislaus' son Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis (d ...
died in battle and the Habsburg Ferdinand I Ferdinand I or Fernando I may refer to:
People
* Ferdinand I of León, ''the Great'' (ca. 1000–1065, king from 1037)
* Ferdinand I of Portugal and the Algarve, ''the Handsome'' (1345–1383, king from 1367)
* Ferdinand I of Aragon and Sicily, '' ...
was elected as his successor.
St. Procopius Basilica in Třebíč
St. Procopius Basilica ( cs, Bazilika svatého Prokopa) is a Romanesque-Gothic Christian church in Třebíč, Czech Republic. It was built on the site of the original Virgin Mary's Chapel of the Benedictine monastery in 1240–1280. It became a ...
Moravská orlice.jpg, The Moravian banner of arms, which first appeared in the medieval era
Habsburg rule (1526–1918)
After the death of King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia in 1526,Ferdinand I Ferdinand I or Fernando I may refer to:
People
* Ferdinand I of León, ''the Great'' (ca. 1000–1065, king from 1037)
* Ferdinand I of Portugal and the Algarve, ''the Handsome'' (1345–1383, king from 1367)
* Ferdinand I of Aragon and Sicily, '' ...
of Austria was elected King of Bohemia and thus ruler of the Crown of Bohemia (including Moravia). The epoch 1526–1620 was marked by increasing animosity between Catholic Habsburg kings (emperors) and the Protestant Moravian nobility (and other Crowns') estates. Moravia, like Bohemia, was a Habsburg possession until the end of World War I. In 1573 the Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
University of Olomouc was established; this was the first university in Moravia. The establishment of a special papal seminary, Collegium Nordicum, made the University a centre of the Catholic Reformation and effort to revive Catholicism in Central and Northern Europe. The second largest group of students were from Scandinavia.
Brno and Olomouc served as Moravia's capitals until 1641. As the only city to successfully resist the Swedish invasion, Brno become the sole capital following the capture of Olomouc. The Margraviate of Moravia had, from 1348 in Olomouc and Brno, its own Diet, or parliament, ''zemský sněm'' (''Landtag'' in German), whose deputies from 1905 onward were elected separately from the ethnically separate German and Czech constituencies.
The oldest surviving theatre building in Central Europe, the Reduta Theatre
The Reduta Theatre is a theatre in Brno, Czech Republic. It was built on the city's oldest square, Zelný trh) and began its life in Renaissance times as the Taverna (Tavern) Theatre. In 1767, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart performed with his sister ...
, was established in 17th-century Moravia. Ottoman Turks and Tatars invaded the region in 1663, taking 12,000 captives. In 1740, Moravia was invaded by Prussian forces under Frederick the Great, and Olomouc was forced to surrender on 27 December 1741. A few months later the Prussians were repelled, mainly because of their unsuccessful siege of Brno in 1742. In 1758, Olomouc was besieged by Prussians again, but this time its defenders forced the Prussians to withdraw following the Battle of Domstadtl
The Battle of Domstadtl (also spelled Domstadt, cs, Domašov) was a battle between the Habsburg monarchy and the Kingdom of Prussia in the Moravian village of Domašov nad Bystřicí during the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years' Wa ...
. In 1777, a new Moravian bishopric was established in Brno, and the Olomouc bishopric was elevated to an archbishopric. In 1782, the Margraviate of Moravia was merged with Austrian Silesia into ''Moravia-Silesia'', with Brno as its capital. Moravia became a separate crown land of Austria again in 1849, and then became part of Cisleithania
Cisleithania, also ''Zisleithanien'' sl, Cislajtanija hu, Ciszlajtánia cs, Předlitavsko sk, Predlitavsko pl, Przedlitawia sh-Cyrl-Latn, Цислајтанија, Cislajtanija ro, Cisleithania uk, Цислейтанія, Tsysleitaniia it, Cislei ...
n Austria-Hungary after 1867. According to Austro-Hungarian census of 1910 the proportion of Czechs in the population of Moravia at the time (2.622.000) was 71.8%, while the proportion of Germans was 27.6%.
Crown land
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. ...
s: growth of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
territories and Moravia's status
Verwaltungsgliederung der Markgrafschaft Mähren 1893.svg, Administrative division of Moravia as crown land of Austria in 1893
20th century
Following the break-up of theAustro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
in 1918, Moravia became part of Czechoslovakia. As one of the five lands of Czechoslovakia, it had restricted autonomy. In 1928 Moravia ceased to exist as a territorial unity and was merged with Czech Silesia into the Moravian-Silesian Land (yet with the natural dominance of Moravia). By the Munich Agreement (1938), the southwestern and northern peripheries of Moravia, which had a German-speaking majority, were annexed by Nazi Germany, and during the German occupation of Czechoslovakia
Occupation commonly refers to:
*Occupation (human activity), or job, one's role in society, often a regular activity performed for payment
*Occupation (protest), political demonstration by holding public or symbolic spaces
*Military occupation, th ...
(1939–1945), the remnant of Moravia was an administrative unit within the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.
In 1945 after the end of World War II and Allied defeat of Germany, Czechoslovakia expelled the ethnic German minority of Moravia to Germany and Austria. The Moravian-Silesian Land was restored with Moravia as part of it and towns and villages that were left by the former German inhabitants, were re-settled by Czechs, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
and reemigrants. In 1949 the territorial division of Czechoslovakia was radically changed, as the Moravian-Silesian Land was abolished and Lands were replaced by "''kraje''" (regions), whose borders substantially differ from the historical Bohemian-Moravian border, so Moravia politically ceased to exist after more than 1100 years (833–1949) of its history. Although another administrative reform in 1960 implemented (among others) the North Moravian and the South Moravian regions (''Severomoravský'' and ''Jihomoravský kraj''), with capitals in Ostrava and Brno respectively, their joint area was only roughly alike the historical state and, chiefly, there was no land or federal autonomy, unlike Slovakia.
After the fall of the Soviet Union and the whole Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
, the Czechoslovak Federal Assembly condemned the cancellation of Moravian-Silesian land and expressed "firm conviction that this injustice will be corrected" in 1990. However, after the breakup
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the termination of a relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a married couple, where a brea ...
of Czechoslovakia into Czech Republic and Slovakia in 1993, Moravian area remained integral to the Czech territory, and the latest administrative division of Czech Republic (introduced in 2000) is similar to the administrative division of 1949. Nevertheless, the federalist
The term ''federalist'' describes several political beliefs around the world. It may also refer to the concept of parties, whose members or supporters called themselves ''Federalists''.
History Europe federation
In Europe, proponents of de ...
or separatist
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greate ...
movement in Moravia is completely marginal.
The centuries-lasting historical Bohemian-Moravian border has been preserved up to now only by the Czech Roman Catholic Administration, as the Ecclesiastical Province of Moravia corresponds with the former Moravian-Silesian Land. The popular perception of the Bohemian-Moravian border's location is distorted by the memory of the 1960 regions (whose boundaries are still partly in use).
Jan Černý
Jan Černý (4 March 1874, in Uherský Ostroh, Moravia, Austria-Hungary – 10 April 1959, in Uherský Ostroh, Czechoslovakia) was a Czechoslovak civil servant and politician. He was the prime minister of Czechoslovakia from 1920 to 1921 and in ...
, president of Moravia in 1922–1926, later also Prime Minister of Czechoslovakia
Map of Moravia.jpg, A general map of Moravia in the 1920s
First Czechoslovak Republic.SVG, In 1928, Moravia was merged into Moravia-Silesia, one of four lands of Czechoslovakia, together with Bohemia, Slovakia and Subcarpathian Rus.
Economy
An area in South Moravia, around Hodonín andBřeclav
Břeclav (; german: Lundenburg) is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 24,000 inhabitants.
Administrative parts
Town parts of Charvátská Nová Ves and Poštorná are administrative parts of Břeclav.
Etymol ...
, is part of the Viennese Basin. Petroleum and lignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35%, and is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat ...
are found there in abundance. The main economic centres of Moravia are Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
, Olomouc and Zlín, plus Ostrava lying directly on the Moravian–Silesian border. As well as agriculture in general, Moravia is noted for its viticulture; it contains 94% of the Czech Republic's vineyards and is at the centre of the country's wine industry. Wallachia have at least a 400-year-old tradition of slivovitz making.
The Czech automotive industry also had a large role in the industry of Moravia in the 20th century; the factories of Wikov Wichterle & Kovářik was a Czechoslovakian machinery manufacturer based in Prostějov. They produced cars and trucks from 1925 to 1937.
Development
František Wichterle founded a small factory in Prostějov, 1878 where he built agricultural veh ...
in Prostějov and Tatra in Kopřivnice produced many automobiles.
Moravia is also the centre of the Czech firearm industry, as the vast majority of Czech firearms manufacturers (e.g. CZUB, Zbrojovka Brno, Czech Small Arms
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
*Czech, ...
, Czech Weapons
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
*Czech ...
, ZVI Zvi ( he, צְבִי and , ''Tzvi'', Ṣvi, "gazelle") is a Jewish name, Jewish masculine given name. Notable people with this name include:
* Zvi Aharoni (1921–2012), Israeli Mossad agent
* Zvi Arad (1942–2018), Israeli mathematician, acting p ...
, Great Gun
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
) are found in Moravia. Almost all the well-known Czech sporting, self-defence, military and hunting firearms are made in Moravia. Meopta
Meopta - optika, s.r.o. is a Czech Republic based company that manufactures various products mainly in the field of optics. The company was once well-known for its still and movie cameras, although it no longer manufactures such products.
Histo ...
rifle scopes are of Moravian origin. The original Bren gun was conceived here, as were the assault rifles the CZ-805 BREN
The CZ 805 BREN is a gas-operated modular assault rifle designed and manufactured by Česká zbrojovka Uherský Brod. The modular design enables users to change the calibre of the weapon to 5.56×45mm NATO or 7.62×39mm intermediate cartridges by ...
and Sa vz. 58
The vz. 58 (or Sa vz. 58) is a 7.62×39mm assault rifle designed and manufactured in Czechoslovakia and accepted into service in the late 1950s as the 7,62 mm samopal vzor 58 ("7.62mm submachine gun model 58"), replacing the vz. 52 self-lo ...
, and the handguns CZ 75 and ZVI Kevin
Kevin ZP98 (usually just Kevin) is a 9 mm/.380 ACP sub-compact semi-automatic pistol manufactured in the Czech Republic. It is manufactured and sold in the United States by Magnum Research as the Micro Desert Eagle (ME380).
Descriptio ...
(also known as the "Micro Desert Eagle").
The Zlín Region hosts several aircraft manufacturers, namely Let Kunovice (also known as Aircraft Industries, a.s.), ZLIN AIRCRAFT a.s. Otrokovice (formerly known under the name Moravan Otrokovice), Evektor-Aerotechnik
Evektor-Aerotechnik is a Czech aircraft manufacturer based in Kunovice, Czech Republic. The company produces range of light sport aircraft, training, advanced ultralight aircraft and electric aircraft.
Evektor-Aerotechnik is also developin ...
and Czech Sport Aircraft
Czech Sport Aircraft, a.s. (successor of Czech Aircraft Works) is an aircraft manufacturer based in the Czech Republic. Czech Sport Aircraft company formally entered the market in 2009.
In 2011 the company's aircraft line included the amphibio ...
. Sport aircraft are also manufactured in Jihlava by Jihlavan Airplanes
Skyleader a.s. is a Chinese-owned aircraft manufacturer based in Jihlava, Czech Republic. The company specializes in the design and manufacture of ultralight aircraft in the form of ready-to-fly aircraft in the Fédération Aéronautique Inter ...
/Skyleader
Skyleader a.s. is a Chinese-owned aircraft manufacturer based in Jihlava, Czech Republic. The company specializes in the design and manufacture of ultralight aircraft in the form of ready-to-fly aircraft in the Fédération Aéronautique Inter ...
.
Aircraft production in the region started in 1930s; after a period of low production post-1989, there are signs of recovery post-2010, and production is expected to grow from 2013 onwards.
No. 14 chair
The No. 14 chair is the most famous chair made by the Thonet chair company. Also known as the 'bistro chair', it was designed by Michael Thonet and introduced in 1859, becoming the world's first mass-produced item of furniture. It is made using ...
M 290.002 Slovenská strela, Žleby zastávka – Žleby 02.jpg, The speed train Tatra M 290.0 Slovenská strela 1936
Zlin XIII OK-TBZ (8190833921).jpg, Zlín XIII
The Zlín XIII was a fast single or two seat aircraft, designed and built in Czechoslovakia in the late 1930s. Its development was ended by the disruption of Czechoslovakia in the approach to World War II.
Design and development
The Zlín XIII ...
aircraft on display at the National Technical Museum in Prague
Zetor 25A.jpg, Zetor 25A tractor
Electron microscope Mamut at the Institute of Scientific Instruments of the Czech Academy of Science in Brno (4).jpg, Electron microscope Brno
File:LET L-410NG OK-NGA ILA Berlin 2016 09.jpg, Aeroplane L 410 NG by Let Kunovice
File:Rifle scope.jpg, Precise rifle scope by MeOpta
File:CZ BREN 2.jpg, The (modern) BREN gun M 2 11
File:Czech Raildays 2012, Evo2 (01).jpg, The modern street car EVO 2
File:Czech Raildays 2012, ČD Bfhpvee295, 80-30 020-9 (03).jpg, Diesel railway coach class Bfhpvee295
Machinery industry
The machinery industry has been the most important industrial sector in the region, especially in South Moravia, for many decades. The main centres of machinery production are Brno ( Zbrojovka Brno, Zetor, První brněnská strojírna,Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
), Blansko (ČKD Blansko
ČKD (Českomoravská Kolben-Daněk) () was one of the largest engineering companies in the former Czechoslovakia and today's Czech Republic. It is famous for the Tatra T3, a tramcar that sold 13,991 units worldwide.
History
ČKD was formed in ...
, Metra), Kuřim
Kuřim (; german: Gurein) is a town in Brno-Country District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 11,000 inhabitants. It is the most populated town of Brno-Country District.
Geography
Kuřim is located about north of B ...
(TOS Kuřim
TOS may refer to:
General
* Terms of service
* The original series of a particular media, in contrast to a spin-off
Chemistry
* Tosyl, a chemical group
* Gy's sampling theory (abbreviation)
Entertainment
* ''Star Trek: The Original Seri ...
), Boskovice (Minerva, Novibra) and Břeclav
Břeclav (; german: Lundenburg) is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 24,000 inhabitants.
Administrative parts
Town parts of Charvátská Nová Ves and Poštorná are administrative parts of Břeclav.
Etymol ...
( Otis Elevator Company). A number of other, smaller machinery and machine parts factories, companies and workshops are spread over Moravia.
Electrical industry
The beginnings of the electrical industry in Moravia date back to 1918. The biggest centres of electrical production are Brno ( VUES, ZPA Brno,EM Brno
EM, Em or em may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* EM, the E major musical scale
* Em, the E minor musical scale
* Electronic music, music that employs electronic musical instruments and electronic music technology in its production
* Enc ...
), Drásov, Frenštát pod Radhoštěm
Frenštát pod Radhoštěm (; german: Frankstadt (unter dem Radhoscht)) is a town in Nový Jičín District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 11,000 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is p ...
and Mohelnice (currently Siemens).
Cities and towns
Cities
*Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
, c. 381,000 inhabitants, former land capital and nowadays capital of South Moravian Region; industrial, judicial, educational and research centre; railway and motorway junction
* Ostrava, c. 288,000 inh. (central part, Moravská Ostrava
Ostrava (; pl, Ostrawa; german: Ostrau ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic, and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 280,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rive ...
, lies historically in Moravia, most of the outskirts are in Czech Silesia), capital of Moravian-Silesian Region, centre of heavy industry
* Olomouc, c. 101,000 inh., capital of Olomouc Region, medieval land capital, seat of Roman Catholic archbishop, cultural centre of Hanakia and Central Moravia
* Zlín, c. 75,000 inh., capital of Zlín Region, modern city developed after World War I by the Bata Shoes
The Bata Corporation (known as Bata, and in the Czech Republic and Slovakia, known as Baťa) is a multinational footwear, apparel and fashion accessories manufacturer and retailer of Moravian (Czech) origin, headquartered in Lausanne, Switzer ...
company
*Frýdek-Místek
Frýdek-Místek (, pl, Frydek-Mistek; german: Friede(c)k-Mistek) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 54,000 inhabitants. The historic centres of both Frýdek and Místek are well preserved and are protecte ...
, c. 56,000 inh., twin-city lying directly on the old Moravian-Silesian border (the western part, Místek, is Moravian), in the industrial area around Ostrava
* Jihlava, c. 51,000 inh. (mostly in Moravia, northwestern periphery lies in Bohemia), capital of Vysočina Region, centre of the Moravian Highlands
Moravian is the adjective form of the Czech Republic region of Moravia, and refers to people of ancestry from Moravia.
Moravian may also refer to:
* a member or adherent of the Moravian Church, one of the oldest Protestant denominations
* Moravia ...
* Prostějov, c. 44,000 inh., former centre of clothing and fashion industry, birthplace of Edmund Husserl
*Přerov
Přerov (; german: Prerau) is a city in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 41,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Bečva River. In the past it was a major crossroad in the heart of Moravia in the Czech Republic. The historic centre ...
, c. 43,000 inh., important railway hub and archeological site ( Předmostí)
Towns
*Třebíč
Třebíč (; german: Trebitsch; yi, טרייביטש Treybitsh) is a town in the Vysočina Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 34,000 inhabitants.
The beginnings of the town's history are connected with the establishment of a Benedictine ...
(35,000), another centre in the Highlands, with exceptionally preserved Jewish quarter
* Znojmo (34,000), historical and cultural centre of southwestern Moravia
* Kroměříž (29,000), historical town in southern Hanakia
*Vsetín
Vsetín () is a town in the Zlín Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 25,000 inhabitants.
Originally a small town, Vsetín has become an important centre of industrial, economic, cultural and sports life during the 20th century.
Administr ...
(26,000), centre of the Moravian Wallachia
* Šumperk (26,000), centre of the north of Moravia, at the foot of Hrubý Jeseník
* Uherské Hradiště (25,000), cultural centre of the Moravian Slovakia
*Břeclav
Břeclav (; german: Lundenburg) is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 24,000 inhabitants.
Administrative parts
Town parts of Charvátská Nová Ves and Poštorná are administrative parts of Břeclav.
Etymol ...
(25,000), important railway hub in the very south of Moravia
* Hodonín (25,000), another town in the Moravian Slovakia, the birthplace of Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk
* Nový Jičín (23,000), historical town with hatting industry
* Valašské Meziříčí (22,000), centre of chemical industry in Moravian Wallachia
* Kopřivnice (22,000), centre of automotive industry ( Tatra), south from Ostrava
* Vyškov (21,000), local centre at a motorway junction halfway between Brno and Olomouc
*Žďár nad Sázavou
Žďár nad Sázavou (; german: Saar) is a town in the Vysočina Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 20,000 inhabitants. It is situated on a major rail link between Prague and Brno. The town both industrial and tourist centre. It is known f ...
(21,000), industrial town in the Highlands, near the border with Bohemia
* Blansko (20,000), industrial town north from Brno, at the foot of the Moravian Karst
People
 The Moravians are generally a Slavic ethnic group who speak various (generally more archaic) dialects of Czech. Before the expulsion of Germans from Moravia the Moravian German minority also referred to themselves as "Moravians" (''Mährer''). Those expelled and their descendants continue to identify as Moravian.
Some Moravians assert that Moravian is a language distinct from Czech; however, their position is not widely supported by academics and the public. Some Moravians identify as an ethnically distinct group; the majority consider themselves to be ethnically Czech. In the census of 1991 (the first census in history in which respondents were allowed to claim Moravian nationality), 1,362,000 (13.2%) of the Czech population identified as being of Moravian nationality (or ethnicity). In some parts of Moravia (mostly in the centre and south), majority of the population identified as Moravians, rather than Czechs. In the census of 2001, the number of Moravians had decreased to 380,000 (3.7% of the country's population). In the census of 2011, this number rose to 522,474 (4.9% of the Czech population).
Moravia historically had a large minority of
The Moravians are generally a Slavic ethnic group who speak various (generally more archaic) dialects of Czech. Before the expulsion of Germans from Moravia the Moravian German minority also referred to themselves as "Moravians" (''Mährer''). Those expelled and their descendants continue to identify as Moravian.
Some Moravians assert that Moravian is a language distinct from Czech; however, their position is not widely supported by academics and the public. Some Moravians identify as an ethnically distinct group; the majority consider themselves to be ethnically Czech. In the census of 1991 (the first census in history in which respondents were allowed to claim Moravian nationality), 1,362,000 (13.2%) of the Czech population identified as being of Moravian nationality (or ethnicity). In some parts of Moravia (mostly in the centre and south), majority of the population identified as Moravians, rather than Czechs. In the census of 2001, the number of Moravians had decreased to 380,000 (3.7% of the country's population). In the census of 2011, this number rose to 522,474 (4.9% of the Czech population).
Moravia historically had a large minority of ethnic Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, some of whom had arrived as early as the 13th century at the behest of the Přemyslid dynasty. Germans continued to come to Moravia in waves, culminating in the 18th century. They lived in the main city centres and in the countryside along the border with Austria (stretching up to Brno) and along the border with Silesia at Jeseníky, and also in two language islands, around Jihlava and around Moravská Třebová
Moravská Třebová (; german: Mährisch Trübau) is a town in Svitavy District in the Pardubice Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 9,700 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument ...
. After the World War II, the Czechoslovak government almost fully expelled them in retaliation for their support of Nazi Germany's invasion and dismemberment of Czechoslovakia (1938–1939) and subsequent German war crimes (1938–1945) towards the Czech, Moravian, and Jewish populations.
Moravians
Jan Ámos Komenský
John Amos Comenius (; cs, Jan Amos Komenský; pl, Jan Amos Komeński; german: Johann Amos Comenius; Latinized: ''Ioannes Amos Comenius''; 28 March 1592 – 15 November 1670) was a Czech philosopher, pedagogue and theologian who is consider ...
(Comenius) (1592–1670), educator and theologian, last bishop of Unity of the Brethren Unity of the Brethren (Latin ''Unitas Fratrum'') may refer to:
*Unity of the Brethren (Czech Republic), the province of the Moravian Church in the Czech Republic
*Unity of the Brethren (Texas), a Protestant church formed in the 1800s by Czech immig ...
* Georg Joseph Camellus (1661–1706), Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
missionary to the Philippines, pharmacist and botanist
* David Zeisberger (1717–1807) Moravian missionary to the Leni Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory includ ...
, "Apostle to the Indians"
* Georgius Prochaska (1749–1820), ophthalmologist and physiologist
*František Palacký
František Palacký (; June 17, 1798 – May 26, 1876) was a Czech historian and politician, the most influential person of the Czech National Revival, called "Father of the Nation".
Life
František Palacký was born on June 17, 1798 at Hodslavi ...
(1798–1876), historian and politician, "The Father of the Czech nation"
* Gregor Mendel (1822–1884), founder of genetics
*Ernst Mach
Ernst Waldfried Josef Wenzel Mach ( , ; 18 February 1838 – 19 February 1916) was a Moravian-born Austrian physicist and philosopher, who contributed to the physics of shock waves. The ratio of one's speed to that of sound is named the Mach ...
(1838–1916), physicist and philosopher
* Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk (1850–1937), philosopher and politician, first president of Czechoslovakia
* Leoš Janáček (1854–1928), composer
* Sigmund Freud (1856–1939), founder of psychoanalysis
* Edmund Husserl (1859–1938), philosopher
*Alfons Mucha
Alfons Maria Mucha (; 24 July 1860 – 14 July 1939), known internationally as Alphonse Mucha, was a Czech painter, illustrator and graphic artist, living in Paris during the Art Nouveau period, best known for his distinctly stylized and decora ...
(1860–1939), painter
*Zdeňka Wiedermannová-Motyčková
Zdeňka Wiedermannová-Motyčková (17 April 1868 – 16 October 1915) was a Moravians, Moravian teacher, journal editor, and women's rights activist. Born into a family of progressive educators, she studied to become a teacher, graduating in 18 ...
(1868–1915), women's rights activist
* Adolf Loos (1870–1933), architect, pioneer of functionalism
* Karl Renner (1870–1950), Austrian statesman, co-founder of Friends of Nature movement
* Tomáš Baťa (1876–1932), entrepreneur, founder of Bata Shoes
The Bata Corporation (known as Bata, and in the Czech Republic and Slovakia, known as Baťa) is a multinational footwear, apparel and fashion accessories manufacturer and retailer of Moravian (Czech) origin, headquartered in Lausanne, Switzer ...
company
 * Joseph Schumpeter (1883–1950), economist and political scientist
*
* Joseph Schumpeter (1883–1950), economist and political scientist
*Marie Jeritza
Maria Jeritza (born Marie Jedličková; 6 October 1887 – 10 July 1982) was a dramatic soprano, long associated with the Vienna State Opera (1912–1934 and 1950-1953) and the Metropolitan Opera (1921–1932 and 1951). Her rapid rise to fame, ...
(1887–1982), soprano singer
* Hans Krebs (1888–1947), Nazi SS ''Brigadeführer'' executed for war crimes
* Ludvík Svoboda (1895–1979), general of I Czechoslovak Army Corps, seventh president of Czechoslovakia
* Klement Gottwald (1896–1953), first Czechoslovak communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
president
* Erich Wolfgang Korngold (1897–1957), composer
*George Placzek
George Placzek (; September 26, 1905 – October 9, 1955) was a Moravian physicist.
Biography
Placzek was born into a wealthy Jewish family in Brünn, Moravia (now Brno, Czech Republic), the grandson of Chief Rabbi Baruch Placzek.PDF He studied ...
(1905–1955), physicist, participant in Manhattan Project
*Kurt Gödel
Kurt Friedrich Gödel ( , ; April 28, 1906 – January 14, 1978) was a logician, mathematician, and philosopher. Considered along with Aristotle and Gottlob Frege to be one of the most significant logicians in history, Gödel had an imme ...
(1906–1978), theoretical mathematician
* Oskar Schindler (1908–1974), Nazi Germany entrepreneur, saviour of almost 1,200 Jews during the WWII
*Jan Kubiš
Jan Kubiš (24 June 1913 – 18 June 1942) was a Czech soldier, one of a team of Czechoslovak British-trained paratroopers sent to eliminate acting Reichsprotektor (Realm-Protector) of Bohemia and Moravia, SS-Obergruppenführer Reinhard Heydri ...
(1913–1942), paratrooper who assassinated Nazi despot R. Heydrich
*Bohumil Hrabal
Bohumil Hrabal (; 28 March 1914 – 3 February 1997) was a Czech writer, often named among the best Czech writers of the 20th century.
Early life
Hrabal was born in Židenice (suburb of Brno) on 28 March 1914, in what was then the province ...
(1914–1997), writer
*Thomas J. Bata
Tomáš Jan Baťa, (; anglicised to Thomas J. Bata; September 17, 1914 – September 1, 2008), also known as Thomas Bata Jr. and Tomáš Baťa ml., was a Czech-Canadian businessman and philanthropist. He ran the Bata Shoe Company from the 1940s ...
(1914–2008), entrepreneur, son of Tomáš Baťa and former head of the Bata shoe company
*Emil Zátopek
Emil Zátopek (; 19 September 1922 – 21 November 2000) was a Czech long-distance runner best known for winning three gold medals at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. He won gold in the 5,000 metres and 10,000 metres runs, but his final m ...
(1922–2000), long-distance runner, multiple Olympic gold medalist
* Karel Reisz (1926–2002), filmmaker, pioneer of the British Free Cinema movement
*Milan Kundera
Milan Kundera (, ; born 1 April 1929) is a Czech writer who went into exile in France in 1975, becoming a naturalised French citizen in 1981. Kundera's Czechoslovak citizenship was revoked in 1979, then conferred again in 2019. He "sees himself ...
(born 1929), writer
* Václav Nedomanský (born 1944), ice hockey player
*Karel Kryl
Karel Kryl (12 April 1944 – 3 March 1994) was an iconic Czechoslovak (Moravian born and Czech speaking) poet, singer-songwriter and author of many hit protest songs in which he identified and attacked the hypocrisy, stupidity and inhumanity of ...
(1944–1994), poet and protest singer-songwriter
* Karel Loprais (1949–2021), truck race driver, multiple winner of the Dakar Rally
* Ivana Trump (1949–2022), socialite and business magnate, former wife of Donald Trump
* Ivan Lendl (born 1959), tennis player
* Petr Nečas (born 1964), politician, Czech Prime Minister
The prime minister of the Czech Republic (Czech: ''Předseda vlády České republiky'') is the head of the government of the Czech Republic. The prime minister is the de-facto leader of the executive branch, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ...
2010–2013
* Jana Novotná (1968–2017), tennis player
*Jiří Šlégr
Jiří Šlégr (; born 30 May 1971) is a Czech former professional ice hockey defenceman, and was a member of the 2001–02 Detroit Red Wings Stanley Cup championship team after being acquired in a late-season trade. Šlégr was inducted into th ...
(born 1971), ice hockey player, member of the Triple Gold Club
* Bohuslav Sobotka (born 1971), social-democratic
Social democracy is a Political philosophy, political, Social philosophy, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocati ...
politician, Czech Prime Minister
The prime minister of the Czech Republic (Czech: ''Předseda vlády České republiky'') is the head of the government of the Czech Republic. The prime minister is the de-facto leader of the executive branch, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ...
2014–2017
* Magdalena Kožená (born 1973), mezzo-soprano
*Markéta Irglová
Markéta Irglová () (born 28 February 1988) is a Czech-Icelandic singer-songwriter, musician and actress, who starred in the film ''Once'', which earned her a number of major awards, including the Academy Award for Best Original Song for "Falli ...
(born 1988), Academy awarded singer-songwriter
* Petra Kvitová (born 1990), tennis player
* Adam Ondra (born 1993), rock climber
Rock climbing is a sport in which participants climb up, across, or down natural rock formations. The goal is to reach the summit of a formation or the endpoint of a usually pre-defined route without falling. Rock climbing is a physically and ...
* Barbora Krejčíková (born 1996), tennis player
Ethnographic regions
Moravia can be divided on dialectal and lore basis into several ethnographic regions of comparable significance. In this sense, it is more heterogenous than Bohemia. Significant parts of Moravia, usually those formerly inhabited by the German speakers, are dialectally indifferent, as they have been resettled by people from various Czech (and Slovak) regions. The principal cultural regions of Moravia are: * Hanakia (''Haná'') in the central and northern part * Lachia (''Lašsko'') in the northeastern tip * Highlands (''Horácko'') in the west * Moravian Slovakia (''Slovácko'') in the southeast * Moravian Wallachia (''Valašsko'') in the eastPlaces of interest


World Heritage Sites
*Gardens and Castle at Kroměříž
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate both ...
*Historic Centre of Telč
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
* Holy Trinity Column in Olomouc
*Jewish Quarter and St Procopius' Basilica in Třebíč
Jewish Quarter and St Procopius' Basilica in Třebíč is the official name of the UNESCO World Heritage site in Třebíč, Czech Republic.
It consists of:
* the Jewish Quarter of Třebíč
The Jewish Quarter of Třebíč ( cs, Židovská čtvr� ...
* Lednice-Valtice Cultural Landscape
*Pilgrimage Church of St John of Nepomuk at Zelená Hora
The Pilgrimage Church of Saint John of Nepomuk ( cs, Poutní kostel svatého Jana Nepomuckého) at Zelená hora (meaning "Green Hill", german: Grünberg) is a religious building at the edge of Žďár nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, near the histori ...
*Tugendhat Villa in Brno
Villa Tugendhat is an architecturally significant building in Brno, Czech Republic. It is one of the pioneering prototypes of modern architecture in Europe, and was designed by the German architects Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and Lilly Reich. It ...
Other
*Hranice Abyss
Hranice Abyss ( cs, Hranická propast) is the deepest flooded pit cave in the world. It is a karst sinkhole near the town of Hranice, Czech Republic. The greatest confirmed depth is , of which is underwater. In 2020, a scientific expedition to ...
, the deepest known underwater cave in the world
See also
* Extreme points of Moravia * Flag of Moravia * German South Moravia * Moravian traditional musicNotes
References
Further reading
* ''The Penny Cyclopaedia
''The Penny Cyclopædia'' published by the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge was a multi-volume encyclopedia edited by George Long and published by Charles Knight alongside the ''Penny Magazine''. Twenty-seven volumes and three sup ...
of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful ...'' (1877), volume 15. London, Charles Knight. Moravia. pp. 397–398.
* ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in En ...
'' (2003). Chicago, New Delhi, Paris, Seoul, Sydney, Taipei, Tokyo. Volume 8. p. 309. Moravia. .
* Filip, Jan (1964). ''The Great Moravia exhibition''. ČSAV ( Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences).
* Galuška, Luděk, Mitáček Jiří, Novotná, Lea (eds.) (2010) ''Treausures of Moravia: story of historical land''. Brno, Moravian Museum. .
* National Geographic Society. Wonders of the Ancient World; National Geographic Atlas of Archaeology, Norman Hammond, consultant, Nat'l Geogr. Soc., (multiple staff authors), (Nat'l Geogr., R. H. Donnelley & Sons, Willard, OH), 1994, 1999, Reg or Deluxe Ed., 304 pp. Deluxe ed. photo (p. 248): "Venus, Dolni Věstonice, 24,000 B.C." In section titled: "The Potter's Art", pp. 246–253.
* Dekan, Jan (1981). Moravia Magna
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
: The Great Moravian Empire, Its Art and Time, Minneapolis: Control Data Arts. .
* Hugh, Agnew (2004). ''The Czechs and the Lands of the Bohemian Crown''.Hoower Press, Stanford
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considere ...
. .
* Róna-Tas, András (1999) ''Hungarians & Europe in the Early Middle Ages: An Introduction to Early Hungarian History'' translated by Nicholas Bodoczky, Central European University Press
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center (disambiguation), center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa ...
, Budapest, .
* Wihoda, Martin (2015), '' Vladislaus Henry: The Formation of Moravian Identity''. Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 27 ...
.
* Kirschbaum, Stanislav J. (1996) ''A History of Slovakia: The Struggle for Survival'' St. Martin's Press
St. Martin's Press is a book publisher headquartered in Manhattan, New York City, in the Equitable Building. St. Martin's Press is considered one of the largest English-language publishers, bringing to the public some 700 titles a year under si ...
, New York, .
* Constantine Porphyrogenitus De Administrando Imperio
''De Administrando Imperio'' ("On the Governance of the Empire") is the Latin title of a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is ("To yown son Romanos"). It is a domes ...
edited by Gy. Moravcsik, translated by R. J. H. Jenkins
Romilly James Heald Jenkins (1907 – 30 September 1969) was a British scholar in Byzantine and Modern Greek studies. He occupied the prestigious seat of ''Koraes Professor of Modern Greek and Byzantine History, Language and Literature'' at King's ...
, Dumbarton Oaks Edition, Washington, D.C. (1993)
* Hlobil, Ivo, Daniel, Ladislav (2000), ''The last flowers of the middle ages: from the gothic to the renaissance in Moravia and Silesia''. Olomouc/Brno, Moravian Galery, Muzeum umění Olomouc
* David, Jiří (2009). "Moravian estatism and provincial councils in the second half of the 17th century". ''Folia historica Bohemica. 1 2''4: 111–165. .
* Svoboda, Jiří A. (1999), ''Hunters between East and West: the paleolithic of Moravia''. New York: Plenum Press, .
* Absolon, Karel (1949), ''The diluvial anthropomorphic statuettes and drawings, especially the so-called Venus statuettes, discovered in Moravia'' New York, Salmony 1949. .
* Musil, Rudolf (1971), ''G. Mendel's Discovery and the Development of Agricultural and Natural Sciences in Moravia''. Brno, Moravian Museum.
* Šimsa, Martin (2009), ''Open-Air Museum of Rural Architecture in South-East Moravia''. Strážnice
Strážnice (german: Straßnitz) is a town in Hodonín District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 5,400 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone.
Etym ...
, National Institute of Folk Culture. .
* Miller, Michael R. (2010), ''The Jews of Moravia in the Age of Emancipation'', Cover of Rabbis and Revolution edition. Stanford University Press. .
* Bata, Thomas J. (1990), ''Bata: Shoemaker to the World''. Stoddart Publishers Canada. .
* Procházka, Jiří (2009), "Vienna obsessa. Thesaurus Moraviae". Brno, ITEM, .
External links
Moravian museum official website
Moravian gallery official website
Moravian library official website
Moravian land archive official website
Province of Moravia – Czech Catholic Church – official website
Welcome to the 2nd largest city of the CR
Welcome to Olomouc, city of good cheer...
Znojmo – City of Virtue
* {{Authority control Counties of the Holy Roman Empire Geography of Central Europe Geography of the Czech Republic Historic counties in Moravia Historical regions in the Czech Republic Historical regions Subdivisions of Austria-Hungary