Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco;
Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
city-state and
microstate
A microstate or ministate is a sovereign state having a very small population or very small land area, usually both. However, the meanings of "state" and "very small" are not well-defined in international law.Warrington, E. (1994). "Lilliputs ...
on the
French Riviera
The French Riviera (known in French as the ; oc, Còsta d'Azur ; literal translation " Azure Coast") is the Mediterranean coastline of the southeast corner of France. There is no official boundary, but it is usually considered to extend fro ...
a few kilometres west of the Italian region of
Liguria, in
Western Europe, on the
Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by
France to the north, east and west. The
principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
is home to 38,682 residents, of whom 9,486 are Monégasque nationals; it is widely recognised as one of the most expensive and wealthiest places in the world. The
official language of the principality is
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
. In addition,
Monégasque (a dialect of
Ligurian),
Italian and
English are spoken and understood by many residents.
With an area of , it is the second-smallest sovereign state in the world, after
Vatican City. Its make it the
most densely-populated sovereign state in the world. Monaco has a land border of and the world's shortest coastline of approximately ; it has a width that varies between . The highest point in the state is a narrow pathway named
Chemin des Révoires
The Chemin des Révoires is a pathway within Les Révoires district of the Principality of Monaco. It is the highest point in Monaco.
Features
The highest point in Monaco, at 162 metres (528 feet) above sea level, is situated on this pathway ...
on the slopes of
Mont Agel
Mont Agel is a mountain on the border between France and Monaco. The summit of this mount, at above sea level, is on the French side, but the highest point of Monaco, lying on a pathway named Chemin des Révoires, is on its slopes, at an altitud ...
, in the
Les Révoires ward, which is
above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The principality is about from the
border with Italy. Its most populous ward is
Larvotto/Bas Moulins with a population of 5,443 as of 2008. Through
land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
, Monaco's land mass has
expanded by 20 percent. In 2005, it had an area of only .
The principality is governed under a form of
constitutional monarchy, with
Prince Albert II as
head of state, who wields immense political power despite his constitutional status. The
prime minister, who is the
head of government, can be either a Monégasque or a French citizen; the monarch consults with the
Government of France
The Government of France ( French: ''Gouvernement français''), officially the Government of the French Republic (''Gouvernement de la République française'' ), exercises executive power in France. It is composed of the Prime Minister, who ...
before an appointment. Key members of the judiciary in Monaco are detached French magistrates. The
House of Grimaldi
The House of Grimaldi ( , also , , ) is the current reigning house of the Principality of Monaco. The house was founded in 1160 by Grimaldo Canella in Genoa and became the ruling house of Monaco when Francesco Grimaldi captured Monaco in 1297 ...
has ruled Monaco, with brief interruptions, since 1297. The state's sovereignty was officially recognised by the
Franco-Monégasque Treaty of 1861, with Monaco becoming a full
United Nations voting member in 1993. Despite Monaco's independence and separate foreign policy, its defence is the responsibility of France. However, Monaco does maintain two small
military units.
Economic development was spurred in the late 19th century with the opening of the state's first casino, the
Monte Carlo Casino
The Monte Carlo Casino, officially named Casino de Monte-Carlo, is a gambling and entertainment complex located in Monaco. It includes a casino, the Opéra de Monte-Carlo, and the office of Les Ballets de Monte-Carlo.
The Casino de Monte-Carlo i ...
, and a
railway connection to Paris. Since then, Monaco's mild climate, scenery, and gambling facilities have contributed to the principality's status as a tourist destination and recreation centre for the rich. In more recent years, Monaco has become a major banking centre and has sought to diversify its economy into the services sector and small,
high-value-added, non-polluting industries. Monaco is famous as a
tax haven: the principality has no personal
income tax and
low business taxes. Over 30% of the residents are millionaires, with real estate prices reaching €100,000 ($116,374) per square metre in 2018.
Monaco is not formally a part of the
European Union (EU), but it
participates in certain EU policies, including customs and border controls. Through its relationship with France, Monaco uses the
euro as its sole currency; before, it used the
Monegasque franc, which was pegged, and exchangeable with, the
French franc until 1 January 2002. Monaco joined the
Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
in 2004 and is a member of the
Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF). It is also the host of the annual street circuit motor race, the
Monaco Grand Prix
The Monaco Grand Prix (french: Grand Prix de Monaco) is a Formula One motor racing event held annually on the Circuit de Monaco, in late May or early June. Run since 1929, it is widely considered to be one of the most important and prestigiou ...
, one of the original Grands Prix of
Formula One. The local motorsports association gives name to the
Monte Carlo Rally
The Monte Carlo Rally or Rallye Monte-Carlo (officially ''Rallye Automobile de Monte-Carlo'') is a rallying event organised each year by the Automobile Club de Monaco. The rally now takes place along the French Riviera in Monaco and southeast ...
, hosted in January in the French Alps. The principality has a club football team,
AS Monaco, which competes in the
French Ligue 1 and have become
French champions on multiple occasions, and a basketball team, which plays in the
EuroLeague. A centre of research into
marine conservation, Monaco is home to one of the world's first protected marine habitats, an
Oceanographic Museum, and the
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
Environment Labs, which is the only
marine laboratory in the
United Nations structure.
History
Monaco's name comes from the nearby 6th-century BC
Phocaean
Greek colony. Referred to by the
Ligurians as ''Monoikos'', from the Greek "μόνοικος", "single house", from "μόνος" (''monos'') "alone, single" + "οἶκος" (''oikos'') "house". According to an ancient myth,
Hercules passed through the Monaco area and turned away the previous gods. As a result, a temple was constructed there. Because this "House" of Hercules was the only temple in the area, the city was called Monoikos. It ended up in the hands of the
Holy Roman Empire, which gave it to the Genoese.
An ousted branch of a Genoese family, the
Grimaldi, contested it for a hundred years before actually gaining control. Though the
Republic of Genoa would last until the 19th century, they allowed the Grimaldi family to keep Monaco, and, likewise, both France and Spain left it alone for hundreds of years. France did not annex it until the
French Revolution, but after the defeat of Napoleon it was put under the care of the
Kingdom of Sardinia.
In the 19th century, when
Sardinia became a part of Italy, the region came under French influence but France allowed it to remain independent. Like France, Monaco was overrun by the
Axis powers during the Second World War and for a short time was administered by Italy, then the
Third Reich, before finally being liberated. Although the occupation lasted for just a short time, it resulted in the deportation of the
Jewish population and execution of several
resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
members from Monaco. Since then Monaco has been independent. It has taken some steps towards
integration with the European Union.
Arrival of the Grimaldi family

Following a grant of land from Emperor
Henry VI in 1191, Monaco was refounded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa.
Monaco was first ruled by a member of the House of Grimaldi in 1297, when
Francesco Grimaldi, known as "''Malizia''" (translated from Italian either as "The Malicious One" or "The Cunning One"), and his men captured the fortress protecting the
Rock of Monaco while dressed as
Franciscan friars – a ''monaco'' in Italian – although this is a coincidence as the area was already known by this name.
Francesco, however, was evicted only a few years after by the Genoese forces, and the struggle over "the Rock" continued for another century. The Grimaldi family was Genoese and the struggle was something of a family feud. However, the Genoese became engaged in other conflicts, and in the late 1300s Genoa lost Monaco in conflict with the
Crown of Aragon over
Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
.
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
eventually became part of a united Spain, and other parts of the land grant came to be integrated piecemeal into other states.
1400–1800

In 1419, the Grimaldi family purchased Monaco from the Crown of Aragon and became the official and undisputed rulers of "the Rock of Monaco". In 1612,
Honoré II
Honoré is a name of French origin and may refer to several people or places:
Given name
Sovereigns of Monaco
Lords of Monaco
* Honoré I of Monaco
Princes of Monaco
* Honoré II of Monaco
* Honoré III of Monaco
* Honoré IV of Monaco
* Honor� ...
began to style himself "Prince" of Monaco. In the 1630s, he sought French protection against the Spanish forces and, in 1642, was received at the court of
Louis XIII as a "duc et pair étranger".
The princes of Monaco thus became vassals of the French kings while at the same time remaining sovereign princes. Though successive princes and their families spent most of their lives in
Paris, and intermarried with French and Italian nobilities, the House of Grimaldi is Italian. The principality continued its existence as a protectorate of France until the
French Revolution.
19th century

In 1793, Revolutionary forces captured Monaco and until 1814 it was occupied by the French (in this period much of Europe had been overrun by the French armies under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte).
The principality was reestablished in 1814 under the Grimaldis, only to be designated a protectorate of the
Kingdom of Sardinia by the
Congress of Vienna in 1815.
Monaco remained in this position until 1860 when, by the
Treaty of Turin, the Sardinian forces pulled out of the principality; the surrounding
County of Nice (as well as
Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Savo ...
) was ceded to France.
Monaco became a French protectorate once again.
Before this time there was unrest in
Menton and
Roquebrune, where the townspeople had become weary of heavy taxation by the Grimaldi family. They declared their independence, hoping for annexation by Sardinia. France protested. The unrest continued until
Charles III of Monaco
Charles III (Charles Honoré Grimaldi; 8 December 1818 – 10 September 1889) was Prince of Monaco and Duke of Valentinois from 20 June 1856 to his death. He was the founder of the famous casino in Monte Carlo, as his title in Monegasque and Ita ...
gave up his claim to the two mainland towns (some 95% of the principality at the time) that had been ruled by the Grimaldi family for over 500 years.
These were ceded to France in return for 4,100,000 francs. The transfer and Monaco's sovereignty were recognised by the
Franco-Monégasque Treaty of 1861. In 1869, the principality stopped collecting income tax from its residents—an indulgence the Grimaldi family could afford to entertain thanks solely to the extraordinary success of the casino. This made Monaco not only a playground for the rich, but a favoured place for them to live.
20th century
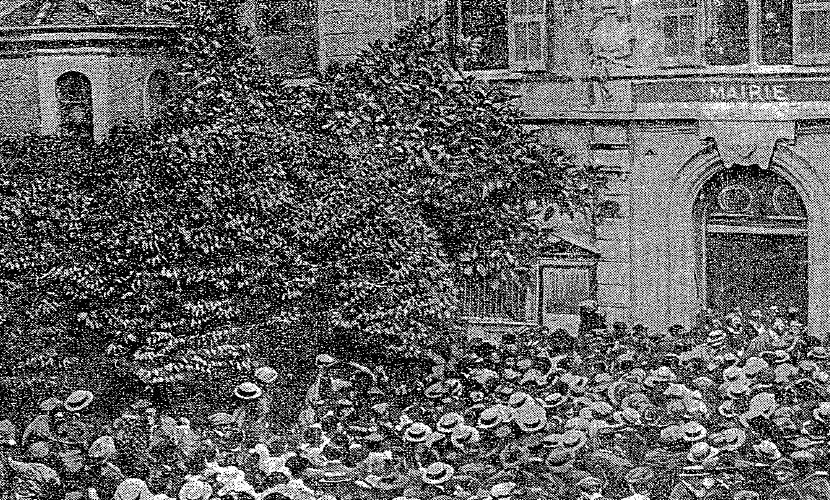
Until the
Monégasque Revolution of 1910 forced the adoption of the 1911
Constitution of Monaco, the
princes of Monaco were
absolute rulers. The new constitution, however, barely reduced the autocratic rule of the Grimaldi family and
Prince Albert I soon suspended it during the First World War.
In July 1918, a new
Franco-Monégasque Treaty was signed, providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, endorsed in 1919 by the
Treaty of Versailles, established that Monégasque international policy would be aligned with French political, military and economic interests. It also resolved the
Monaco succession crisis.

In 1943, the Italian Army
invaded and occupied Monaco, forming a
fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
administration.
In September 1943, after Mussolini's fall from power, the German
Wehrmacht occupied Italy and Monaco, and the Nazi deportation of the Jewish population began.
René Blum, the prominent French Jew who founded the Ballet de l'Opéra in Monte Carlo, was arrested in his
Paris home and held in the
Drancy
Drancy () is a commune in the northeastern suburbs of Paris in the Seine-Saint-Denis department in northern France. It is located 10.8 km (6.7 mi) from the center of Paris.
History
Toponymy
The name Drancy comes from Medieval Lati ...
deportation camp outside the French capital before being transported to
Auschwitz
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It con ...
, where he was later murdered. Blum's colleague
Raoul Gunsbourg, the director of the
Opéra de Monte-Carlo, helped by the
French Resistance, escaped arrest and fled to
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. In August 1944, the Germans executed René Borghini, Joseph-Henri Lajoux and Esther Poggio, who were Resistance leaders.
Rainier III, succeeded to the throne on the death of his grandfather, Prince
Louis II, in 1949, and then ruled until 2005. On 19 April 1956, Prince Rainier married the American actress
Grace Kelly, an event that was widely televised and covered in the popular press, focusing the world's attention on the tiny principality.
A 1962 amendment to the constitution abolished capital punishment, provided for
women's suffrage and established a
Supreme Court of Monaco to guarantee fundamental liberties. In 1963, a crisis developed when
Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
blockaded Monaco, angered by its status as a tax haven for wealthy French citizens. The 2014 film ''
Grace of Monaco
Grace Patricia Kelly (November 12, 1929 – September 14, 1982) was an American actress who, after starring in several significant films in the early to mid-1950s, became Princess of Monaco by marrying Prince Rainier III in April 1956.
Kelly ...
'' is loosely based on this crisis.
In 1993, the Principality of Monaco became a member of the
United Nations, with full voting rights.
21st century

In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco specified that, should there be no heirs to carry on the Grimaldi dynasty, the principality would still remain an independent nation rather than revert to France. Monaco's military defence, however, is still the responsibility of France.
On 31 March 2005,
Rainier III, who was too ill to exercise his duties, relinquished them to his only son and heir, Albert. He died six days later, after a reign of 56 years, with his son succeeding him as
Albert II,
Sovereign Prince of Monaco. Following a period of official mourning, Prince Albert II formally assumed the princely crown on 12 July 2005, in a celebration that began with a solemn Mass at
Saint Nicholas Cathedral, where his father had been buried three months earlier. His accession to the Monégasque throne was a two-step event with a further ceremony, drawing heads of state for an elaborate reception, held on 18 November 2005, at the historic
Prince's Palace
Princes is the plural for prince, a royal title.
Princes may also refer to:
Roads:
* Princes Highway, a major road in Australia
* Princes Motorway, New South Wales, Australia
* Princes Freeway, Victoria, Australia
* Princes Street, a major tho ...
in
Monaco-Ville. On 27 August 2015, Albert II apologised for Monaco's role during World War II in facilitating the deportation of a total of 90 Jews and resistance fighters, of whom only nine survived. "We committed the irreparable in handing over to the neighbouring authorities women, men and a child who had taken refuge with us to escape the persecutions they had suffered in France," Albert said at a ceremony in which a monument to the victims was unveiled at the Monaco cemetery. "In distress, they came specifically to take shelter with us, thinking they would find neutrality."
In 2015, Monaco unanimously approved a modest
land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
expansion intended primarily to accommodate desperately needed housing and a small green/park area.
Monaco had previously considered an expansion in 2008, but had called it off.
The plan is for about six
hectares (15 acres) of apartment buildings, parks, shops and offices to a land value of about 1 billion
euros.
The development will be adjacent to the
Larvotto district and also will include a small marina.
There were four main proposals, and the final mix of use will be finalised as the development progresses. The name for the new district is
Anse du Portier.
On 29 February 2020, Monaco announced its first case of
COVID-19, a man who was admitted to the
Princess Grace Hospital Centre then transferred to
Nice University
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative ci ...
Hospital in France. The virus was confirmed to have reached Monaco on 29 February 2020.
On 3 September 2020, the first Monégasque satellite, OSM-1 CICERO, was launched into space from French Guiana aboard a
Vega rocket. The satellite was built in Monaco by Orbital Solutions Monaco.

Government

Politics

Monaco has been governed under a
constitutional monarchy since 1911, with the
Sovereign Prince of Monaco as
head of state. The
executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a State (polity), state.
In poli ...
consists of a
Prime Minister as the
head of government, who presides over the other five members of the
Council of Government
The Council of Government of Monaco is the Prince's governing body.
It consists of six members:
Minister of State, who chairs the council, and the five members (four counsellors and one delegate); he also has voting rights, and has control of ...
. Until 2002, the Prime Minister was a French citizen appointed by the prince from among candidates proposed by the Government of France; since a constitutional amendment in 2002, the Prime Minister can be French or Monégasque.
On 1 September 2020, Prince Albert II appointed a French citizen,
Pierre Dartout, to the office.
Under the 1962
Constitution of Monaco, the prince shares his
veto power with the
unicameral National Council. The 24 members of the National Council are elected for five-year terms; 16 are chosen through a majority electoral system and 8 by proportional representation.
All legislation requires the approval of the National Council, which is dominated by the conservative
Rally and Issues for Monaco (REM) party which holds 20 seats.
holds three seats
while
Renaissance holds one seat. The principality's city affairs are directed by the
Communal Council,
which consists of 14 elected members and is presided over by a
mayor.
Georges Marsan has been mayor since 2003. Unlike the National Council, communal councillors are elected for four-year terms and are strictly
non-partisan; however,
oppositions
''Oppositions'' was an architectural journal produced by the Institute for Architecture and Urban Studies from 1973 to 1984. Many of its articles contributed to advancing architectural theory and many of its contributors became distinguished practi ...
inside the council frequently form.
[
Members of the judiciary of Monaco are appointed by the Sovereign Prince. Key positions within the judiciary are held by French magistrates, proposed by the Government of France. Monaco currently has three examining magistrates.
]
Security
 The wider defence of the nation is provided by France. Monaco has no navy or air force, but on both a per-capita and per-area basis, Monaco has one of the largest police forces (515 police officers for about 38,000 people) and police presences in the world. Its police includes a special unit which operates patrol and surveillance boats jointly with the military. Police forces in Monaco are commanded by a French officer.
There is also a small military force. This consists of a bodyguard unit for the prince and his palace in Monaco-Ville called the Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince (Prince's Company of Carabiniers); together with the militarised, armed fire and civil defence corps ( Sapeurs-Pompiers) it forms Monaco's total forces. The Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince was created by Prince Honoré IV in 1817 for the protection of the principality and the princely family. The company numbers exactly 116 officers and men; while the
The wider defence of the nation is provided by France. Monaco has no navy or air force, but on both a per-capita and per-area basis, Monaco has one of the largest police forces (515 police officers for about 38,000 people) and police presences in the world. Its police includes a special unit which operates patrol and surveillance boats jointly with the military. Police forces in Monaco are commanded by a French officer.
There is also a small military force. This consists of a bodyguard unit for the prince and his palace in Monaco-Ville called the Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince (Prince's Company of Carabiniers); together with the militarised, armed fire and civil defence corps ( Sapeurs-Pompiers) it forms Monaco's total forces. The Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince was created by Prince Honoré IV in 1817 for the protection of the principality and the princely family. The company numbers exactly 116 officers and men; while the non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s and soldiers are local, the officers have generally served in the French Army. In addition to their guard duties as described, the carabiniers patrol the principality's beaches and coastal waters.
Geography
 Monaco is a sovereign city-state, with five quarters and ten wards, located on the
Monaco is a sovereign city-state, with five quarters and ten wards, located on the French Riviera
The French Riviera (known in French as the ; oc, Còsta d'Azur ; literal translation " Azure Coast") is the Mediterranean coastline of the southeast corner of France. There is no official boundary, but it is usually considered to extend fro ...
in Western Europe. It is bordered by France's Alpes-Maritimes
Alpes-Maritimes (; oc, Aups Maritims; it, Alpi Marittime, "Maritime Alps") is a department of France located in the country's southeast corner, on the Italian border and Mediterranean coast. Part of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, it ...
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
on three sides, with one side bordering the Mediterranean Sea. Its centre is about from Italy and only northeast of Nice.Chemin des Révoires
The Chemin des Révoires is a pathway within Les Révoires district of the Principality of Monaco. It is the highest point in Monaco.
Features
The highest point in Monaco, at 162 metres (528 feet) above sea level, is situated on this pathway ...
(ward Les Révoires) from the D6007 (''Moyenne Corniche'' street) at above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The lowest point in the country is the Mediterranean Sea.
Saint-Jean brook is the longest flowing body of water, around in length, and Fontvieille is the largest lake, approximately in area. Monaco's most populated ''quartier'' is Monte Carlo, and the most populated ward is Larvotto/Bas Moulins.
Administrative divisions
 Monaco is the second-smallest country by area in the world; only Vatican City is smaller. Monaco is the most densely populated country in the world. The state consists of only one municipality (''commune''), the Municipality of Monaco. There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different.
Monaco is the second-smallest country by area in the world; only Vatican City is smaller. Monaco is the most densely populated country in the world. The state consists of only one municipality (''commune''), the Municipality of Monaco. There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different.principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
was subdivided into three municipalities:
* Monaco-Ville, the old city and seat of government of the principality on a rocky promontory extending into the Mediterranean, known as the Rock of Monaco, or simply "The Rock";
* Monte Carlo, the principal residential and resort area with the Monte Carlo Casino
The Monte Carlo Casino, officially named Casino de Monte-Carlo, is a gambling and entertainment complex located in Monaco. It includes a casino, the Opéra de Monte-Carlo, and the office of Les Ballets de Monte-Carlo.
The Casino de Monte-Carlo i ...
in the east and northeast;
* La Condamine, the southwestern section including the port area, Port Hercules.
The municipalities were merged into one in 1917, and they were accorded the status of ''Wards
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a priso ...
'' or ''Quartiers'' thereafter.
* Fontvieille was added as a fourth ward, a newly constructed area claimed from the sea in the 1970s;
* Moneghetti became the fifth ward, created from part of La Condamine;
* Larvotto became the sixth ward, created from part of Monte Carlo;
* La Rousse/Saint Roman (including Le Ténao) became the seventh ward, also created from part of Monte Carlo.
Subsequently, three additional wards were created, however all of them were dissolved in 2013:
* Saint Michel, created from part of Monte Carlo;
*La Colle
La Colle ( 1736 – 1742) was a Monsoni (a branch of the Ojibwa ) chief who is known in Canadian history for this period because of the writings of La Vérendrye.
In the fall of 1731, construction began on Fort St. Pierre at the west end of ...
, created from part of La Condamine;
* Les Révoires, also created from part of La Condamine.
Most of Saint Michel became part of Monte Carlo again in 2013. La Colle and Les Révoires were merged the same year as part of a redistricting process, where they became part of the larger Jardin Exotique ward. An additional ward was planned by new land reclamation to be settled beginning in 2014 but Prince Albert II announced in his 2009 New Year Speech that he had ended plans due to the economic climate at the time. However, Prince Albert II in mid-2010 firmly restarted the programme.
Traditional quarters and modern geographic areas
The four traditional ''quartiers'' of Monaco are Monaco-Ville, La Condamine, Monte Carlo and Fontvieille. However, the suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separate ...
of Moneghetti, the high-level part of La Condamine, is generally seen today as an effective fifth ''Quartier'' of Monaco, having a very distinct atmosphere and topography when compared with low-level La Condamine.
Wards
 For town planning purposes, a sovereign ordinance in 1966 divided the principality into reserved sectors, "whose current character must be preserved", and
For town planning purposes, a sovereign ordinance in 1966 divided the principality into reserved sectors, "whose current character must be preserved", and wards
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a priso ...
. The number and boundaries of these sectors and wards
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a priso ...
have been modified several times. The latest division dates from 2013 and created two reserved sectors and seven wards. A new 6-hectare district, Le Portier, is currently being built on the sea.
''Note: for statistical purposes, the Wards of Monaco are further subdivided into 178 city block
A city block, residential block, urban block, or simply block is a central element of urban planning and urban design.
A city block is the smallest group of buildings that is surrounded by streets, not counting any type of thoroughfare within t ...
s (îlots), which are comparable to the census blocks in the United States''.Fontvieille II Fontvieille may refer to:
* Fontvieille, Bouches-du-Rhône, a commune in the French Bouches-du-Rhône department
*Fontvieille, Monaco
Fontvieille (; lij, Funtanaveya ) is the southernmost ward in the Principality of Monaco. It was developed by a ...
Development to commence in 2013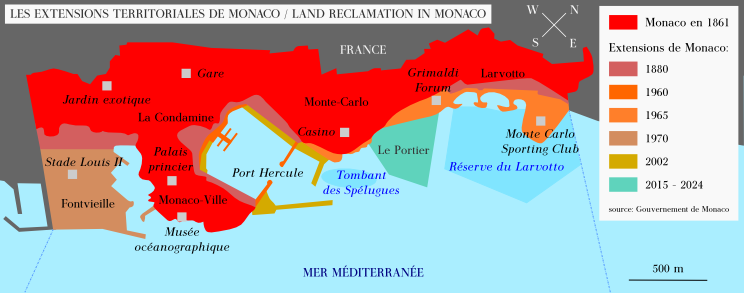
Architecture
Monaco exhibits a wide range of architecture, but the principality's signature style, particularly in Monte Carlo, is that of the Belle Époque
The Belle Époque or La Belle Époque (; French for "Beautiful Epoch") is a period of French and European history, usually considered to begin around 1871–1880 and to end with the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era ...
. It finds its most florid expression in the 1878–9 Casino and the Salle Garnier
Salle is the French word for 'hall', 'room' or 'auditorium', as in:
*Salle des Concerts Herz, a former Paris concert hall
*Salle Favart, theatre of the Paris Opéra-Comique
*Salle Le Peletier, former home of the Paris Opéra
*Salle Pleyel, a Paris ...
created by Charles Garnier and Jules Dutrou. Decorative elements include turrets, balconies, pinnacles, multi-coloured ceramics, and caryatids. These were blended to create a picturesque fantasy of pleasure and luxury, and an alluring expression of how Monaco sought and still seeks, to portray itself. This capriccio of French, Italian, and Spanish elements were incorporated into hacienda villas and apartments. Following major development in the 1970s, Prince Rainier III banned high-rise development in the principality. His successor, Prince Albert II, overturned this Sovereign Order.architectural heritage
''Architectural Heritage'' is an academic journal published by Edinburgh University Press on behalf of the Architectural Heritage Society of Scotland in November each year. It was founded in 1991. The journal focuses on architectural history and ...
, including its single-family villas, has created dismay. The principality has no heritage protection legislation.
Climate
 Monaco has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with strong maritime influences, with some resemblances to the
Monaco has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with strong maritime influences, with some resemblances to the humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa''). As a result, it has balmy warm, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. The winters are very mild considering the city's latitude, being as mild as locations located much further south in the Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and w ...
. Cool and rainy interludes can interrupt the dry summer season, the average length of which is also shorter. Summer afternoons are infrequently hot (indeed, temperatures greater than are rare) as the atmosphere is temperate because of constant sea breezes. On the other hand, the nights are very mild, due to the fairly high temperature of the sea in summer. Generally, temperatures do not drop below in this season. In the winter, frosts and snowfalls are extremely rare and generally occur once or twice every ten years. On 27 February 2018, both Monaco and Monte Carlo experienced snowfall.
Economy
 Monaco has the world's highest GDP nominal per capita at US$185,742, GDP PPP per capita at $132,571 and GNI per capita at $183,150.
Monaco has the world's highest GDP nominal per capita at US$185,742, GDP PPP per capita at $132,571 and GNI per capita at $183,150.CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
, Monaco has the world's lowest poverty rate
Gambling industry
 The plan for casino gambling was drafted during the reign of
The plan for casino gambling was drafted during the reign of Florestan I
Florestan (Tancrède Florestan Roger Louis Grimaldi; 10 October 1785, in Paris – 20 June 1856) was Prince of Monaco and Duke of Valentinois from 2 October 1841 until his death. He was the second son of Prince Honoré IV and Louise d'Aumont ...
in 1846. Under Louis-Philippe's petite-bourgeois regime, however, a dignitary such as the Prince of Monaco was not allowed to operate a gambling house.House of Grimaldi
The House of Grimaldi ( , also , , ) is the current reigning house of the Principality of Monaco. The house was founded in 1160 by Grimaldo Canella in Genoa and became the ruling house of Monaco when Francesco Grimaldi captured Monaco in 1297 ...
was in dire need of money.
The towns of Menton and Roquebrune, which had been the main sources of income for the Grimaldi family for centuries, were now accustomed to a much-improved standard of living
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
and lenient taxation thanks to the Sardinian intervention and clamoured for financial and political concession, even for separation. The Grimaldi family hoped the newly legal industry would help alleviate the difficulties they faced, above all the crushing debt the family had incurred, but Monaco's first casino would not be ready to operate until after Charles III assumed the throne in 1856.
The grantee of the princely concession (licence) was unable to attract enough business to sustain the operation and, after relocating the casino several times, sold the concession to French casino magnates François and Louis Blanc for 1.7 million francs.
The Blancs had already set up a highly successful casino (in fact the largest in Europe) in Bad-Homburg in the Grand Duchy of Hesse-Homburg, a small German principality comparable to Monaco, and quickly petitioned Charles III to rename a depressed seaside area known as "Les Spelugues (Den of Thieves)" to "Monte Carlo (Mount Charles)."Société des bains de mer de Monaco
The Société des Bains de Mer (SBM; en, Society of Sea Baths), officially the Société Anonyme des Bains de Mer et du Cercle des Etrangers à Monaco (; en, Society of Sea Baths and of the Circle of Foreigners in Monaco), is a publicly traded ...
, which owns Le Grand Casino, still operates in the original building that the Blancs constructed and has since been joined by several other casinos, including the Le Casino Café de Paris, the Monte Carlo Sporting Club & Casino and the Sun Casino. The most recent addition in Monte Carlo is the Monte Carlo Bay Casino, which sits on 4 hectares of the Mediterranean Sea; among other things, it offers 145 slot machines, all equipped with " ticket-in, ticket-out" (TITO). It is the first Mediterranean casino to use this technology.
Low taxes
Monaco has a 20% VAT plus high social-insurance taxes, payable by both employers and employees. The employers' contributions are between 28% and 40% (averaging 35%) of gross salary, including benefits, and employees pay a further 10% to 14% (averaging 13%).
Monaco has never levied income tax on individual
An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) of being a person unique from other people and possessing one's own Maslow ...
s,[ and foreigners are thus able to use it as a " tax haven" from their own country's high taxes, because as an independent country, Monaco is not obliged to pay taxes to other countries.
The absence of a personal income tax has attracted many wealthy "tax refugee" residents from European countries, who derive the majority of their income from activity outside Monaco. Celebrities, such as Formula One drivers, attract most of the attention but the vast majority are lesser-known business people.
However, due to a bilateral treaty with France, French citizens who reside in Monaco must still pay income and wealth taxes to France.]Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries ...
(OECD), issued a first report on the consequences of the financial systems of known tax havens. Monaco did not appear in the list of these territories until 2004, when the OECD became indignant regarding the Monegasque situation and denounced it in a report, along with Andorra, Liechtenstein, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
, and the Marshall Islands. The report underlined Monaco's lack of co-operation regarding financial information disclosure and availability. Later, Monaco overcame the OECD's objections and was removed from the "grey list" of uncooperative jurisdictions. In 2009, Monaco went a step further and secured a place on the "white list" after signing twelve information exchange treaties with other jurisdictions.[
In 2000, the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) stated: "The anti-money laundering system in Monaco is comprehensive. However, difficulties have been encountered with Monaco by countries in international investigations on serious crimes that appear to be linked also with tax matters. In addition, the FIU of Monaco (SICCFIN) suffers a great lack of adequate resources. The authorities of Monaco have stated that they will provide additional resources to SICCFIN."
Also in 2000, a report by French Socialist ]MPs
MPS, M.P.S., MPs, or mps may refer to:
Science and technology
* Mucopolysaccharidosis, genetic lysosomal storage disorder
* Mononuclear phagocyte system, cells in mammalian biology
* Myofascial pain syndrome
* Metallopanstimulin
* Potassium perox ...
Arnaud Montebourg and Vincent Peillon stated that Monaco had relaxed policies with respect to money laundering including within its casino and that the Government of Monaco had been placing political pressure on the judiciary so that alleged crimes were not being properly investigated. In its Progress Report of 2005, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified Monaco, along with 36 other territories, as a tax haven, but in its FATF report of the same year it took a positive view of Monaco's measures against money-laundering.
The Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
also decided to issue reports naming tax havens. Twenty-two territories, including Monaco, were thus evaluated between 1998 and 2000 on a first round. Monaco was the only territory that refused to perform the second round, between 2001 and 2003, whereas the 21 other territories had planned to implement the third and final round, planned between 2005 and 2007.
Numismatics
 Monaco issued its own coins in various devaluations connected to the écu already in the seventeenth century, but its first decimal coins of the Monégasque franc were issued in 1837 continued until 2001.
Although Monaco is not a European Union member, it is allowed to use the euro as its currency by arrangement with the Council of the European Union; it is also granted the right to use its own designs on the national side of the euro coins, which was introduced in 2002. In preparation for this date, the minting of the new euro coins started as early as 2001. Like Belgium, Finland, France, the Netherlands, and Spain, Monaco decided to put the minting date on its coins. This is why the first euro coins from Monaco have the year 2001 on them, instead of 2002, like the other countries of the Eurozone that decided to put the year of first circulation (2002) on their coins. Three different designs were selected for the Monégasque coins.
Monaco issued its own coins in various devaluations connected to the écu already in the seventeenth century, but its first decimal coins of the Monégasque franc were issued in 1837 continued until 2001.
Although Monaco is not a European Union member, it is allowed to use the euro as its currency by arrangement with the Council of the European Union; it is also granted the right to use its own designs on the national side of the euro coins, which was introduced in 2002. In preparation for this date, the minting of the new euro coins started as early as 2001. Like Belgium, Finland, France, the Netherlands, and Spain, Monaco decided to put the minting date on its coins. This is why the first euro coins from Monaco have the year 2001 on them, instead of 2002, like the other countries of the Eurozone that decided to put the year of first circulation (2002) on their coins. Three different designs were selected for the Monégasque coins.
Population
Demographics
Monaco's total population was 38,400 in 2015, and estimated by the United Nations to be 39,511 as of 1 July 2021. Monaco's population is unusual in that the native Monégasques are a minority in their own country: the largest group are French nationals at 28.4%, followed by Monégasque (21.6%), Italian (18.7%), British (7.5%), Belgian (2.8%), German (2.5%), Swiss (2.5%) and U.S. nationals (1.2%).
Language
The main and official language of Monaco is French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, while Italian is spoken by the principality's sizeable community from Italy. French and Italian are in fact more spoken in the principality today than Monégasque, its historic vernacular language. A dialect of Ligurian, Monégasque is not recognised as an official language; nevertheless, some signage appears in both French and Monégasque, and the language is taught in schools. English is also used.
Italian was the official language in Monaco until 1860, when it was replaced by French.
Religion
Christianity
Christians comprise a total of 86% of Monaco's population.
Catholicism

 The official religion is Catholicism, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution.
The official religion is Catholicism, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution.archbishop of Monaco
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Monaco ( la, Archidioecesis Monoecensis) is an exempt Latin ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Roman Catholic Church in Monaco, directly subject to the Holy See, not part of any ecclesiastical prov ...
.
The diocese, which has existed since the mid-19th century, was raised to a non-metropolitan archbishopric in 1981 as the Archdiocese of Monaco and remains exempt (i.e. immediately subject to the Holy See). The patron saint is Saint Devota.
Anglican Communion
There is one Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
church (St Paul's Church), located in the Avenue de Grande Bretagne in Monte Carlo. The church was dedicated in 1925. In 2007 this had a formal membership of 135 Anglican residents in the principality but was also serving a considerably larger number of Anglicans temporarily in the country, mostly as tourists. The church site also accommodates an English-language library of over 3,000 books. The church is part of the Anglican Diocese in Europe.
Reformed Church of Monaco
There is one Reformed church, which meets in a building located in Rue Louis Notari. The building dates from 1958-59. The church is affiliated with the United Protestant Church of France (Église Protestante Unie de France, EPUF), a group that incorporates the former Reformed Church of France (Église Réformée de France). Through this affiliation with EPUF, the church is part of the World Communion of Reformed Churches. The church acts as a host-church to some other Christian communities, allowing them to use its building.
Charismatic Episcopal Church
The Monaco Parish of the Charismatic Episcopal Church (Parish of St Joseph) dates from 2017 and meets in the Reformed Church's Rue Louis Notari building.
Christian Fellowship
The Monaco Christian Fellowship, formed in 1996, meets in the Reformed Church's Rue Louis Notari building.
Greek Orthodoxy
Monaco's 2012 International Religious Freedom Report states that there is one Greek Orthodox church in Monaco.
Russian Orthodox
The Russian Orthodox Parish of the Holy Royal Martyrs meets in the Reformed Church's Rue Louis Notari building.
Judaism
The Association Culturelle Israélite de Monaco (founded in 1948) is a converted house containing a synagogue, a community Hebrew school, and a kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, כּשר), fro ...
food shop, located in Monte Carlo. The community mainly consists of retirees from Britain (40%) and North Africa. Half of the Jewish population is Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), ...
, mainly from North Africa, while the other half is Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
.
Islam
The Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
population of Monaco consists of about 280 people, most of whom are residents, not citizens. The majority of the Muslim population of Monaco are Arabs, though there is a Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
minority as well. Monaco does not have any official mosques.
Sports
Formula One
 Since 1929, the
Since 1929, the Monaco Grand Prix
The Monaco Grand Prix (french: Grand Prix de Monaco) is a Formula One motor racing event held annually on the Circuit de Monaco, in late May or early June. Run since 1929, it is widely considered to be one of the most important and prestigiou ...
has been held annually in the streets of Monaco.Circuit de Monaco
Circuit de Monaco is a street circuit laid out on the city streets of Monte Carlo and La Condamine around the harbour of the Principality of Monaco. It is commonly, and even officially, referred to as "Monte Carlo" because it is largely inside ...
takes six weeks to complete and the removal after the race takes another three weeks.1952 Monaco Grand Prix
The 1952 Monaco Grand Prix was a non-championship sports car race held on June 2, 1952, at Monaco.
For the second time in two races, the ''Grand Prix'' suffered a multi-car pileup. In addition, it was marred by Luigi Fagioli's accident in practi ...
(run to sports car regulations that year, not Formula 1) and Lorenzo Bandini, who crashed, burned and died three days later from his injuries in 1967.["Hulme Wins Monte Carlo; Bandini Hurt", '']Sheboygan Press
''The Sheboygan Press'' is a daily newspaper based in Sheboygan, Wisconsin, United States. It is one of a number of newspapers in the state of Wisconsin owned by Gannett, including the ''Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'', ''Green Bay Press-Gazette'' a ...
'', 8 May 1967, Page 13. Two other drivers had lucky escapes after they crashed into the harbour, the most famous being Alberto Ascari in the 1955 Monaco Grand Prix and Paul Hawkins, during the 1965 race.
Monégasque Formula 1 Drivers
There have been five Formula One drivers from Monaco
There have been five Formula One drivers from Monaco.
Current drivers
Charles Leclerc (racing driver), Charles Leclerc currently competes for Scuderia Ferrari. He made his Formula One debut for Sauber at the 2018 Australian Grand Prix. In the s ...
:
* Charles Leclerc (2018–present)
*Robert Doornbos
Robert Michael Doornbos (; born 23 September 1981) is a Dutch former racing driver who also competed with a Monégasque licence. He has been test and third driver for the Jordan and Red Bull Racing Formula One teams, as well as driving for Mi ...
(2005, Dutch driver under a Monégasque license)
* Olivier Beretta (1994)
*André Testut
André Testut (13 April 1926, Lyon – 24 September 2005, Lyon) was a French-born racing driver and team owner from Monaco.
Career
Testut's debut in racing took place at the beginning of September 1956 at the Course de Cote de Vuillafans-Echevan ...
(1958–1959)
* Louis Chiron (1950–1958)
Formula E
Starting in 2015 Formula E
Formula E, officially the ABB FIA Formula E World Championship, is a single-seater motorsport championship for electric cars. The series was conceived in 2011 in Paris by FIA president Jean Todt and Spanish businessman Alejandro Agag, who is ...
started racing biennially with the Historic Grand Prix of Monaco on the Monaco ePrix and used a shorter configuration of the full Formula 1 circuit, keeping it around Port Hercules until 2021.
ROKiT Venturi Racing is the only motor racing team based in the principality, headquartered in Fontvieille. The marque competes in Formula E and was one of the founding teams of the fully-electric championship. Managed by former racing drivers Susie Wolff
Susie is a female name that can be a diminutive form of Susan, Susanne, Suzanne, Susannah, Susanna or Susana.
Susie may refer to:
Songs
* "Susie Q" (song), a 1957 song by Dale Hawkins, covered by Creedence Clearwater Revival (1968)
*"Wake Up ...
(CEO) and Jérôme d'Ambrosio (Team Principal), the outfit holds 16 podiums in the series to date including five victories. 1997 Formula One World Champion Jacques Villeneuve and eleven-time Formula One race winner Felipe Massa
Felipe Massa (, born 25 April 1981) is a Brazilian racing driver. He competed in 15 seasons of Formula One between 2002 and 2017, where he scored 11 Grand Prix victories, 41 podiums and finished as championship runner-up in 2008 by one poin ...
have raced for the team previously. Ten-time Macau winner and 2021
File:2021 collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in 2021; Protesters in Yangon, Myanmar following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état, coup d'état; A civil demonstration against the October–November 2021 ...
vice World Champion Edoardo Mortara and Season 3 Formula E champion Lucas di Grassi
Lucas Tucci di Grassi (born 11 August 1984) is a Brazilian professional racing driver who competes in the FIA Formula E World Championship for Mahindra Racing. He became the FIA Formula E Champion in 2016–2017, achieved three overall podium ...
currently race for the team.
Monte Carlo Rally
Since 1911 part of the Monte Carlo Rally
The Monte Carlo Rally or Rallye Monte-Carlo (officially ''Rallye Automobile de Monte-Carlo'') is a rallying event organised each year by the Automobile Club de Monaco. The rally now takes place along the French Riviera in Monaco and southeast ...
has been held in the principality, originally held at the behest of Prince Albert I. Like the Grand Prix, the rally is organised by Automobile Club de Monaco. It has long been considered to be one of the toughest and most prestigious events in rallying
Rally is a wide-ranging form of motorsport with various competitive motoring elements such as speed tests (often called ''rally racing),'' navigation tests, or the ability to reach waypoints or a destination at a prescribed time or average speed. ...
and from 1973 to 2008 was the opening round of the World Rally Championship (WRC). From 2009 until 2011, the rally served as the opening round of the Intercontinental Rally Challenge. The rally returned to the WRC calendar in 2012 and has been held annually since. Due to Monaco's limited size, all but the ending of the rally is held on French territory.
Football
 Monaco hosts two major football teams in the principality: the men's football club, AS Monaco FC, and the women's football club, OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in
Monaco hosts two major football teams in the principality: the men's football club, AS Monaco FC, and the women's football club, OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in Ligue 1
Ligue 1, officially known as Ligue 1 Uber Eats for sponsorship reasons, is a French professional league for men's association football clubs. At the top of the French football league system, it is the country's primary football competition. A ...
, the first division of French football. The club is historically one of the most successful clubs in the French league, having won Ligue 1 eight times (most recently in 2016–17) and competed at the top level for all but six seasons since 1953. The club reached the 2004 UEFA Champions League Final
The 2004 UEFA Champions League Final was an association football match played on 26 May 2004 to decide the winner of the 2003–04 UEFA Champions League. AS Monaco, a Monaco-based club representing the French Football Federation, faced Portugue ...
, with a team that included Dado Pršo, Fernando Morientes, Jérôme Rothen, Akis Zikos and Ludovic Giuly, but lost 3–0 to Portuguese team FC Porto
Futebol Clube do Porto, MHIH, OM (), commonly known as FC Porto or simply Porto, is a Portuguese professional sports club based in Porto. It is best known for the professional football team playing in the Primeira Liga, the top flight of Portu ...
. French World Cup-winners Thierry Henry, Fabien Barthez, David Trezeguet, and Kylian Mbappe have played for the club. The Stade Louis II also played host to the annual UEFA Super Cup from 1998–2012 between the winners of the UEFA Champions League and the UEFA Europa League.
The women's team, OS Monaco, competes in the women's French football league system. The club plays in the local regional league, deep down in the league system. It once played in the Division 1 Féminine, in the 1994–95 season, but was quickly relegated.
The Monaco national football team represents the nation in association football and is controlled by the Monégasque Football Federation, the governing body for football in Monaco. However, Monaco is one of only two sovereign states in Europe (along with the Vatican City) that is not a member of UEFA and so does not take part in any UEFA European Football Championship or FIFA World Cup competitions. They are instead affiliated with CONIFA, where they compete against other national teams that are not FIFA members. The team plays its home matches in the Stade Louis II.
Rugby
Monaco's national rugby team, as of April 2019, is 101st in the World Rugby Rankings.
Basketball
Multi-sport club AS Monaco owns AS Monaco Basket
Association Sportive de Monaco Basketball Club, commonly referred to as A.S. Monaco Basket, is a French-registered Monaco-based professional basketball club. They are a part of the Monaco-based multi-sports club of A.S. Monaco, which was foun ...
which was founded in 1928. They play in the top-tier European basketball league, the EuroLeague, and the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
top flight, the LNB Pro A
The LNB Pro A, currently known for sponsorship reasons as Betclic Élite, is the top-tier men's professional basketball league in France. The competition has existed since 1921. Since 1987, the Ligue Nationale de Basket has governed the league. ...
. They have three Pro A Leaders Cup, two Pro B
The LNB Pro B, commonly known as Pro B, is the French basketball league system, 2nd-tier level men's professional basketball league in France. It is the second division of the Ligue Nationale de Basket (LNB), which has organized the league since t ...
(2nd-tier), and one NM1
The Nationale Masculine 1, abbreviated as NM1, (English: National Male 1), is the professional level third-tier division of men's club basketball in France. The two top teams from each season of the competition are promoted to the LNB Pro B, which ...
(3rd-tier) championship. They play in Salle Gaston Médecin, which is part of Stade Louis II.
Professional boxing
Due in part to its position both as a tourist and gambling centre, Monaco has staged major professional boxing
Professional boxing, or prizefighting, is regulated, sanctioned boxing. Professional boxing bouts are fought for a purse bid, purse that is divided between the boxers as determined by contract. Most professional bouts are supervised by a regula ...
world title and non title fights from time to time; those include the Carlos Monzon versus Nino Benvenuti rematch, Monzon's rematch with Emile Griffith, Monzon's two classic fights with Rodrigo Valdes
Rodrigo is a Spanish, Portuguese and Italian name derived from the Germanic name ''Roderick'' (Gothic ''*Hroþareiks'', via Latinized ''Rodericus'' or ''Rudericus''), given specifically in reference to either King Roderic (d. 712), the last ...
, Davey Moore versus Wilfredo Benitez, the double knockout-ending classic between Lee Roy Murphy and Chisanda Mutti (won by Murphy), and Julio César Chávez, Sr. versus Rocky Lockridge. All of the aforementioned contests took place at the first Stade Louis II or the second Stade Louis II stadiums.
Other sports
 The Monte-Carlo Masters is held annually in neighbouring
The Monte-Carlo Masters is held annually in neighbouring Roquebrune-Cap-Martin
Roquebrune-Cap-Martin (; oc, Ròcabruna Caup Martin or ; it, Roccabruna-Capo Martino, ; Mentonasc: ''Rocabrüna''; Roquebrune until 1921) is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, Southeastern Fr ...
, France, as a professional tournament for men as part of tennis's ATP Masters Series. The tournament has been held since 1897. Golf's Monte Carlo Open
The Monte-Carlo Masters is an annual tennis tournament for male professional players held in Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, France, a Communes of France, commune that borders on Monaco. The event is part of the ATP Tour Masters 1000 on the Association of ...
was also held at the Monte Carlo Golf Club at Mont Agel in France between 1984 and 1992.
Monaco has a national Davis Cup team, which plays in the European/African Zone.
Monaco has also competed in the Olympic Games, although, no athlete from Monaco has ever won an Olympic medal. At the Youth Olympic Winter Games, Monaco won a bronze medal in bobsleigh.
The 2009 Tour de France, the world's premier cycle race, started from Monaco with a closed-circuit individual time trial starting and finishing there on the first day, and the second leg starting there on the following day and ending in Brignoles, France.
Monaco has also staged part of the Global Champions Tour (International Show-jumping). In 2009, the Monaco stage of the Global Champions tour took place between 25 and 27 June.
The Monaco Marathon is the only marathon in the world to pass through three countries, those of Monaco, France and Italy, before the finish at the Stade Louis II.
The Monaco Ironman 70.3 triathlon race is an annual event with over 1,000 athletes competing and attracts top professional athletes from around the world. The race includes a swim, bike ride and run.
Since 1993, the headquarters of the International Association of Athletics Federations, the world governing body of athletics, is located in Monaco. An IAAF Diamond League meet is annually held at Stade Louis II.
A municipal sports complex, the Rainier III Nautical Stadium in the Port Hercules district consists of a heated saltwater Olympic-size swimming pool, diving boards and a slide.FIA Formula 2
The FIA Formula 2 Championship is a second-tier single-seater championship organised by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). Held on racing circuits, the championship was introduced in 2017, following the rebranding of the lo ...
, Porsche Supercup and Formula Regional Europe. It has in the past also hosted Formula Three and Formula Renault
Formula Renault are classes of formula racing popular in Europe and elsewhere. Regarded as an entry-level series to motor racing, it was founded in 1971, and was a respected series where drivers can learn advanced racecraft before moving on to hig ...
.
From 10 to 12 July 2014 Monaco inaugurated the Solar1 Monte Carlo Cup, a series of ocean races exclusively for solar-powered boats.,
The women team of the chess club CE Monte Carlo won the European Chess Club Cup several times.

Culture
Cuisine
The cuisine of Monaco is a Mediterranean cuisine shaped by the cooking style of Provence and the influences of nearby northern Italian and southern French cooking, in addition to Monaco's own culinary traditions.
Music
 Monaco has an opera house, a
Monaco has an opera house, a symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, ce ...
and a classical ballet company. Monaco participated regularly in the Eurovision Song Contest
The Eurovision Song Contest (), sometimes abbreviated to ESC and often known simply as Eurovision, is an international songwriting competition organised annually by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), featuring participants representing pr ...
between 1959–1979 and 2004–2006, winning in 1971 *
The year 1971 had three partial solar eclipses ( February 25, July 22 and August 20) and two total lunar eclipses (February 10, and August 6).
The world population increased by 2.1% this year, the highest increase in history.
Events
Ja ...
, although none of the artists participating for the principality was originally Monegasque.
Visual arts
Monaco has a national museum of contemporary visual art at the New National Museum of Monaco. In 1997, the Audiovisual Institute of Monaco
Audiovisual Institute of Monaco () is a Monegasque organization aimed to list, gather, restore, conserve, protect, share and promote audiovisual archives. The Institute proposes to show how the Principality of Monaco is represented in cinema, a ...
was founded aimed to preserve audiovisual archives and show how the Principality of Monaco is represented in cinema. The country also has numerous works of public art, statues, museums, and memorials (see list of public art in Monaco).
Prince Albert of Monaco visited the Sassi di Matera on 22 April 2022, exploring the ancient districts.
Museums in Monaco
 *
*Monaco Top Cars Collection
The Exhibition of HSH The Prince of Monaco's Car Collection is an automobile museum in the La Condamine district of Monaco.
The cars were the personal collection of Prince Rainier III of Monaco (1923–2005), and assembled over a thirty-year perio ...
*Napoleon Museum (Monaco)
The Napoleon Museum in Monte Carlo, Monaco was a museum of artifacts which once belonged to the French Emperor Napoleon I.
Location and exhibits
The museum, which was attached to the Prince of Monaco's palace, contained a collection assembled by ...
* Oceanographic Museum
Events, festivals and shows
The Principality of Monaco hosts major international events such as :
* International Circus Festival of Monte-Carlo
* Mondial du Théâtre
* Monte-Carlo Television Festival
Bread Festival
Monaco also has an annual bread festival on 17 September every year.
Education
Primary and secondary schools
 Monaco has ten state-operated schools, including: seven nursery and primary schools; one
Monaco has ten state-operated schools, including: seven nursery and primary schools; one secondary school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' secondary education, lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) ...
, Collège Charles III; one ''lycée'' that provides general and technological training, Lycée Albert 1er; and one lycée that provides vocational and hotel training, Lycée technique et hôtelier de Monte-Carlo. There are also two grant-aided denominational private schools, Institution François d'Assise Nicolas Barré and Ecole des Sœurs Dominicaines, and one international school, the International School of Monaco, founded in 1994.
Colleges and universities
There is one university located in Monaco, namely the International University of Monaco (IUM), an English-language university specialising in business education and operated by the ''Institut des hautes études économiques et commerciales'' (INSEEC) group.
Flag
 The flag of Monaco is one of the world's oldest national flag designs. Adopted by Monaco on 4 April 1881, it is almost identical to the flag of Indonesia (The flag "Sang Saka Merah Putih" is an old flag from the Indonesian kingdom Majapahit in the 13th century, and also adopted by modern Indonesia) except for the ratio of height to width.
The flag of Monaco is one of the world's oldest national flag designs. Adopted by Monaco on 4 April 1881, it is almost identical to the flag of Indonesia (The flag "Sang Saka Merah Putih" is an old flag from the Indonesian kingdom Majapahit in the 13th century, and also adopted by modern Indonesia) except for the ratio of height to width.
Transport
The Monaco-Monte Carlo station is served by the SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffi ...
, the French national rail system. The Monaco Heliport provides helicopter service to the closest airport, Côte d'Azur Airport in Nice, France.
The Monaco bus company (CAM) covers all the tourist attractions, museums, Exotic garden, business centres, and the Casino or the Louis II Stadium.
Relations with other countries
 Monaco is so old that it has outlived many of the nations and institutions that it has had relations with. The Crown of Aragon and Republic of Genoa became a part of other countries, as did the Kingdom of Sardinia. Honoré II, Prince of Monaco secured recognition of his independent sovereignty from Spain in 1633, and then from Louis XIII of France by the
Monaco is so old that it has outlived many of the nations and institutions that it has had relations with. The Crown of Aragon and Republic of Genoa became a part of other countries, as did the Kingdom of Sardinia. Honoré II, Prince of Monaco secured recognition of his independent sovereignty from Spain in 1633, and then from Louis XIII of France by the Treaty of Péronne (1641)
The Treaty of Péronne was signed on September 14, 1641, in Péronne, France between Honoré II, Prince of Monaco, and Louis XIII, King of France. Based on the terms of the treaty, Prince Honoré permitted Monaco to become a French protectorate ...
.
Monaco made a special agreement with France in 1963 in which French customs laws apply in Monaco and its territorial waters. There are two embassies in Monaco: those of France and Italy.
There are two embassies in Monaco: those of France and Italy.passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that contains a person's identity. A person with a passport can travel to and from foreign countries more easily and access consular assistance. A passport certifies the personal ...
stamp is available on request at Monaco's tourist office. This is located on the far side of the gardens that face the Casino.
See also
*Japanese Garden, Monaco
The Japanese Garden is a municipal park on the Avenue Princesse Grace, in the Larvotto ward of Monaco. It is next to the Grimaldi Forum convention centre. The garden is 0.7 hectares in size, and features a stylised mountain, hill, waterfall, beach ...
* Telecommunications in Monaco
* Outline of Monaco
* Microstates and the European Union
* List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density
* List of rulers of Monaco
* List of diplomatic missions in Monaco
* List of diplomatic missions of Monaco
* ISO 3166-2:MC
Notes
References
External links
; Government
Official Government PortalOfficial website of the Prince's Palace of Monaco
Monaco Statistics Pocket – Edition 2014
; General information
Monaco
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Monaco
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
*
Monaco
from the BBC News
MonacoDailyNews – Latest Daily News
English-language Monaco news source and publisher of daily newsletter Good Morning Monaco.
Monaco
information about Monaco
History of Monaco: Primary documents
*
*
Google Earth view
; Travel
Official website for Tourism
; Other
Order of the doctors of Monaco
Monacolife.net
English news portal
The Monaco Times
nbsp;– a regular feature in The Riviera Times is the English language newspaper for the French – Italian Riviera and the Principality of Monaco provides monthly local news and information about the business, art and culture, people and lifestyle, events and also the real estate market.
Monaco-IQ
Monaco information and news aggregator
{{Authority control
Capitals in Europe
City-states
French-speaking countries and territories
Italian-speaking countries and territories
Massalian colonies
Territories of the Republic of Genoa
Member states of the Council of Europe
Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
Member states of the United Nations
Port cities of the Mediterranean Sea
Principalities
States and territories established in 1297
Countries in Europe
Christian states
Western European countries
 Following a grant of land from Emperor Henry VI in 1191, Monaco was refounded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa. Monaco was first ruled by a member of the House of Grimaldi in 1297, when Francesco Grimaldi, known as "''Malizia''" (translated from Italian either as "The Malicious One" or "The Cunning One"), and his men captured the fortress protecting the Rock of Monaco while dressed as Franciscan friars – a ''monaco'' in Italian – although this is a coincidence as the area was already known by this name.
Francesco, however, was evicted only a few years after by the Genoese forces, and the struggle over "the Rock" continued for another century. The Grimaldi family was Genoese and the struggle was something of a family feud. However, the Genoese became engaged in other conflicts, and in the late 1300s Genoa lost Monaco in conflict with the Crown of Aragon over
Following a grant of land from Emperor Henry VI in 1191, Monaco was refounded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa. Monaco was first ruled by a member of the House of Grimaldi in 1297, when Francesco Grimaldi, known as "''Malizia''" (translated from Italian either as "The Malicious One" or "The Cunning One"), and his men captured the fortress protecting the Rock of Monaco while dressed as Franciscan friars – a ''monaco'' in Italian – although this is a coincidence as the area was already known by this name.
Francesco, however, was evicted only a few years after by the Genoese forces, and the struggle over "the Rock" continued for another century. The Grimaldi family was Genoese and the struggle was something of a family feud. However, the Genoese became engaged in other conflicts, and in the late 1300s Genoa lost Monaco in conflict with the Crown of Aragon over  Until the Monégasque Revolution of 1910 forced the adoption of the 1911 Constitution of Monaco, the princes of Monaco were absolute rulers. The new constitution, however, barely reduced the autocratic rule of the Grimaldi family and Prince Albert I soon suspended it during the First World War.
In July 1918, a new Franco-Monégasque Treaty was signed, providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, endorsed in 1919 by the Treaty of Versailles, established that Monégasque international policy would be aligned with French political, military and economic interests. It also resolved the Monaco succession crisis.
Until the Monégasque Revolution of 1910 forced the adoption of the 1911 Constitution of Monaco, the princes of Monaco were absolute rulers. The new constitution, however, barely reduced the autocratic rule of the Grimaldi family and Prince Albert I soon suspended it during the First World War.
In July 1918, a new Franco-Monégasque Treaty was signed, providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, endorsed in 1919 by the Treaty of Versailles, established that Monégasque international policy would be aligned with French political, military and economic interests. It also resolved the Monaco succession crisis.
 In 1943, the Italian Army invaded and occupied Monaco, forming a
In 1943, the Italian Army invaded and occupied Monaco, forming a  In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco specified that, should there be no heirs to carry on the Grimaldi dynasty, the principality would still remain an independent nation rather than revert to France. Monaco's military defence, however, is still the responsibility of France.
On 31 March 2005, Rainier III, who was too ill to exercise his duties, relinquished them to his only son and heir, Albert. He died six days later, after a reign of 56 years, with his son succeeding him as Albert II, Sovereign Prince of Monaco. Following a period of official mourning, Prince Albert II formally assumed the princely crown on 12 July 2005, in a celebration that began with a solemn Mass at Saint Nicholas Cathedral, where his father had been buried three months earlier. His accession to the Monégasque throne was a two-step event with a further ceremony, drawing heads of state for an elaborate reception, held on 18 November 2005, at the historic
In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco specified that, should there be no heirs to carry on the Grimaldi dynasty, the principality would still remain an independent nation rather than revert to France. Monaco's military defence, however, is still the responsibility of France.
On 31 March 2005, Rainier III, who was too ill to exercise his duties, relinquished them to his only son and heir, Albert. He died six days later, after a reign of 56 years, with his son succeeding him as Albert II, Sovereign Prince of Monaco. Following a period of official mourning, Prince Albert II formally assumed the princely crown on 12 July 2005, in a celebration that began with a solemn Mass at Saint Nicholas Cathedral, where his father had been buried three months earlier. His accession to the Monégasque throne was a two-step event with a further ceremony, drawing heads of state for an elaborate reception, held on 18 November 2005, at the historic 
 Monaco has been governed under a constitutional monarchy since 1911, with the Sovereign Prince of Monaco as head of state. The
Monaco has been governed under a constitutional monarchy since 1911, with the Sovereign Prince of Monaco as head of state. The  The wider defence of the nation is provided by France. Monaco has no navy or air force, but on both a per-capita and per-area basis, Monaco has one of the largest police forces (515 police officers for about 38,000 people) and police presences in the world. Its police includes a special unit which operates patrol and surveillance boats jointly with the military. Police forces in Monaco are commanded by a French officer.
There is also a small military force. This consists of a bodyguard unit for the prince and his palace in Monaco-Ville called the Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince (Prince's Company of Carabiniers); together with the militarised, armed fire and civil defence corps ( Sapeurs-Pompiers) it forms Monaco's total forces. The Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince was created by Prince Honoré IV in 1817 for the protection of the principality and the princely family. The company numbers exactly 116 officers and men; while the
The wider defence of the nation is provided by France. Monaco has no navy or air force, but on both a per-capita and per-area basis, Monaco has one of the largest police forces (515 police officers for about 38,000 people) and police presences in the world. Its police includes a special unit which operates patrol and surveillance boats jointly with the military. Police forces in Monaco are commanded by a French officer.
There is also a small military force. This consists of a bodyguard unit for the prince and his palace in Monaco-Ville called the Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince (Prince's Company of Carabiniers); together with the militarised, armed fire and civil defence corps ( Sapeurs-Pompiers) it forms Monaco's total forces. The Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince was created by Prince Honoré IV in 1817 for the protection of the principality and the princely family. The company numbers exactly 116 officers and men; while the  Monaco is a sovereign city-state, with five quarters and ten wards, located on the
Monaco is a sovereign city-state, with five quarters and ten wards, located on the 
 Monaco is the second-smallest country by area in the world; only Vatican City is smaller. Monaco is the most densely populated country in the world. The state consists of only one municipality (''commune''), the Municipality of Monaco. There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different. According to the constitution of 1911, the
Monaco is the second-smallest country by area in the world; only Vatican City is smaller. Monaco is the most densely populated country in the world. The state consists of only one municipality (''commune''), the Municipality of Monaco. There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different. According to the constitution of 1911, the 
 Monaco has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with strong maritime influences, with some resemblances to the
Monaco has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''), with strong maritime influences, with some resemblances to the  Monaco has the world's highest GDP nominal per capita at US$185,742, GDP PPP per capita at $132,571 and GNI per capita at $183,150. It also has an unemployment rate of 2%, with over 48,000 workers who commute from France and Italy each day. According to the
Monaco has the world's highest GDP nominal per capita at US$185,742, GDP PPP per capita at $132,571 and GNI per capita at $183,150. It also has an unemployment rate of 2%, with over 48,000 workers who commute from France and Italy each day. According to the  Monaco issued its own coins in various devaluations connected to the écu already in the seventeenth century, but its first decimal coins of the Monégasque franc were issued in 1837 continued until 2001.
Although Monaco is not a European Union member, it is allowed to use the euro as its currency by arrangement with the Council of the European Union; it is also granted the right to use its own designs on the national side of the euro coins, which was introduced in 2002. In preparation for this date, the minting of the new euro coins started as early as 2001. Like Belgium, Finland, France, the Netherlands, and Spain, Monaco decided to put the minting date on its coins. This is why the first euro coins from Monaco have the year 2001 on them, instead of 2002, like the other countries of the Eurozone that decided to put the year of first circulation (2002) on their coins. Three different designs were selected for the Monégasque coins. However, in 2006, the design was changed after the death of ruling Prince Rainier to have the effigy of Prince Albert.
Monaco issued its own coins in various devaluations connected to the écu already in the seventeenth century, but its first decimal coins of the Monégasque franc were issued in 1837 continued until 2001.
Although Monaco is not a European Union member, it is allowed to use the euro as its currency by arrangement with the Council of the European Union; it is also granted the right to use its own designs on the national side of the euro coins, which was introduced in 2002. In preparation for this date, the minting of the new euro coins started as early as 2001. Like Belgium, Finland, France, the Netherlands, and Spain, Monaco decided to put the minting date on its coins. This is why the first euro coins from Monaco have the year 2001 on them, instead of 2002, like the other countries of the Eurozone that decided to put the year of first circulation (2002) on their coins. Three different designs were selected for the Monégasque coins. However, in 2006, the design was changed after the death of ruling Prince Rainier to have the effigy of Prince Albert.

 The official religion is Catholicism, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution. There are five Catholic parish churches in Monaco and one cathedral, which is the seat of the
The official religion is Catholicism, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution. There are five Catholic parish churches in Monaco and one cathedral, which is the seat of the  Since 1929, the
Since 1929, the  Monaco hosts two major football teams in the principality: the men's football club, AS Monaco FC, and the women's football club, OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in
Monaco hosts two major football teams in the principality: the men's football club, AS Monaco FC, and the women's football club, OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in  The Monte-Carlo Masters is held annually in neighbouring
The Monte-Carlo Masters is held annually in neighbouring 
 Monaco has an opera house, a
Monaco has an opera house, a  *
* Monaco has ten state-operated schools, including: seven nursery and primary schools; one
Monaco has ten state-operated schools, including: seven nursery and primary schools; one  The flag of Monaco is one of the world's oldest national flag designs. Adopted by Monaco on 4 April 1881, it is almost identical to the flag of Indonesia (The flag "Sang Saka Merah Putih" is an old flag from the Indonesian kingdom Majapahit in the 13th century, and also adopted by modern Indonesia) except for the ratio of height to width.
The flag of Monaco is one of the world's oldest national flag designs. Adopted by Monaco on 4 April 1881, it is almost identical to the flag of Indonesia (The flag "Sang Saka Merah Putih" is an old flag from the Indonesian kingdom Majapahit in the 13th century, and also adopted by modern Indonesia) except for the ratio of height to width.
 Monaco is so old that it has outlived many of the nations and institutions that it has had relations with. The Crown of Aragon and Republic of Genoa became a part of other countries, as did the Kingdom of Sardinia. Honoré II, Prince of Monaco secured recognition of his independent sovereignty from Spain in 1633, and then from Louis XIII of France by the
Monaco is so old that it has outlived many of the nations and institutions that it has had relations with. The Crown of Aragon and Republic of Genoa became a part of other countries, as did the Kingdom of Sardinia. Honoré II, Prince of Monaco secured recognition of his independent sovereignty from Spain in 1633, and then from Louis XIII of France by the  There are two embassies in Monaco: those of France and Italy. There are about another 30 or so consulates. By the 21st century Monaco maintained embassies in Belgium (Brussels), France (Paris), Germany (Berlin), the Vatican, Italy (Rome), Portugal (Lisbon), Spain (Madrid), Switzerland (Bern), United Kingdom (London) and the United States (Washington).
nearly two-thirds of the residents of Monaco were foreigners. In 2015 the immigrant population was estimated at 60% It is reported to be difficult to gain citizenship in Monaco, or at least in relative number there are not many people who do so. In 2015 an immigration rate of about 4 people per 1,000 was noted, or about 100–150 people a year. The population of Monaco went from 35,000 in 2008 to 36,000 in 2013, and of that about 20 percent were native Monegasque (see also Nationality law of Monaco).
A recurring issue Monaco encounters with other countries is the attempt by foreign nationals to use Monaco to avoid paying taxes in their own country. Monaco actually collects a number of taxes including a 20% VAT and 33% on companies unless they make over 75% of their income inside Monaco. Monaco does not allow dual citizenship but does have multiple paths to citizenship including by declaration and naturalisation. In many cases the key issue for obtaining citizenship, rather than attaining residency in Monaco, is the person's ties to their departure country. For example, French citizens must still pay taxes to France even if they live full-time in Monaco unless they resided in the country before 1962 for at least 5 years. In the early 1960s there was some tension between France and Monaco over taxation.
There are no border formalities entering or leaving France. For visitors, a souvenir
There are two embassies in Monaco: those of France and Italy. There are about another 30 or so consulates. By the 21st century Monaco maintained embassies in Belgium (Brussels), France (Paris), Germany (Berlin), the Vatican, Italy (Rome), Portugal (Lisbon), Spain (Madrid), Switzerland (Bern), United Kingdom (London) and the United States (Washington).
nearly two-thirds of the residents of Monaco were foreigners. In 2015 the immigrant population was estimated at 60% It is reported to be difficult to gain citizenship in Monaco, or at least in relative number there are not many people who do so. In 2015 an immigration rate of about 4 people per 1,000 was noted, or about 100–150 people a year. The population of Monaco went from 35,000 in 2008 to 36,000 in 2013, and of that about 20 percent were native Monegasque (see also Nationality law of Monaco).
A recurring issue Monaco encounters with other countries is the attempt by foreign nationals to use Monaco to avoid paying taxes in their own country. Monaco actually collects a number of taxes including a 20% VAT and 33% on companies unless they make over 75% of their income inside Monaco. Monaco does not allow dual citizenship but does have multiple paths to citizenship including by declaration and naturalisation. In many cases the key issue for obtaining citizenship, rather than attaining residency in Monaco, is the person's ties to their departure country. For example, French citizens must still pay taxes to France even if they live full-time in Monaco unless they resided in the country before 1962 for at least 5 years. In the early 1960s there was some tension between France and Monaco over taxation.
There are no border formalities entering or leaving France. For visitors, a souvenir