|
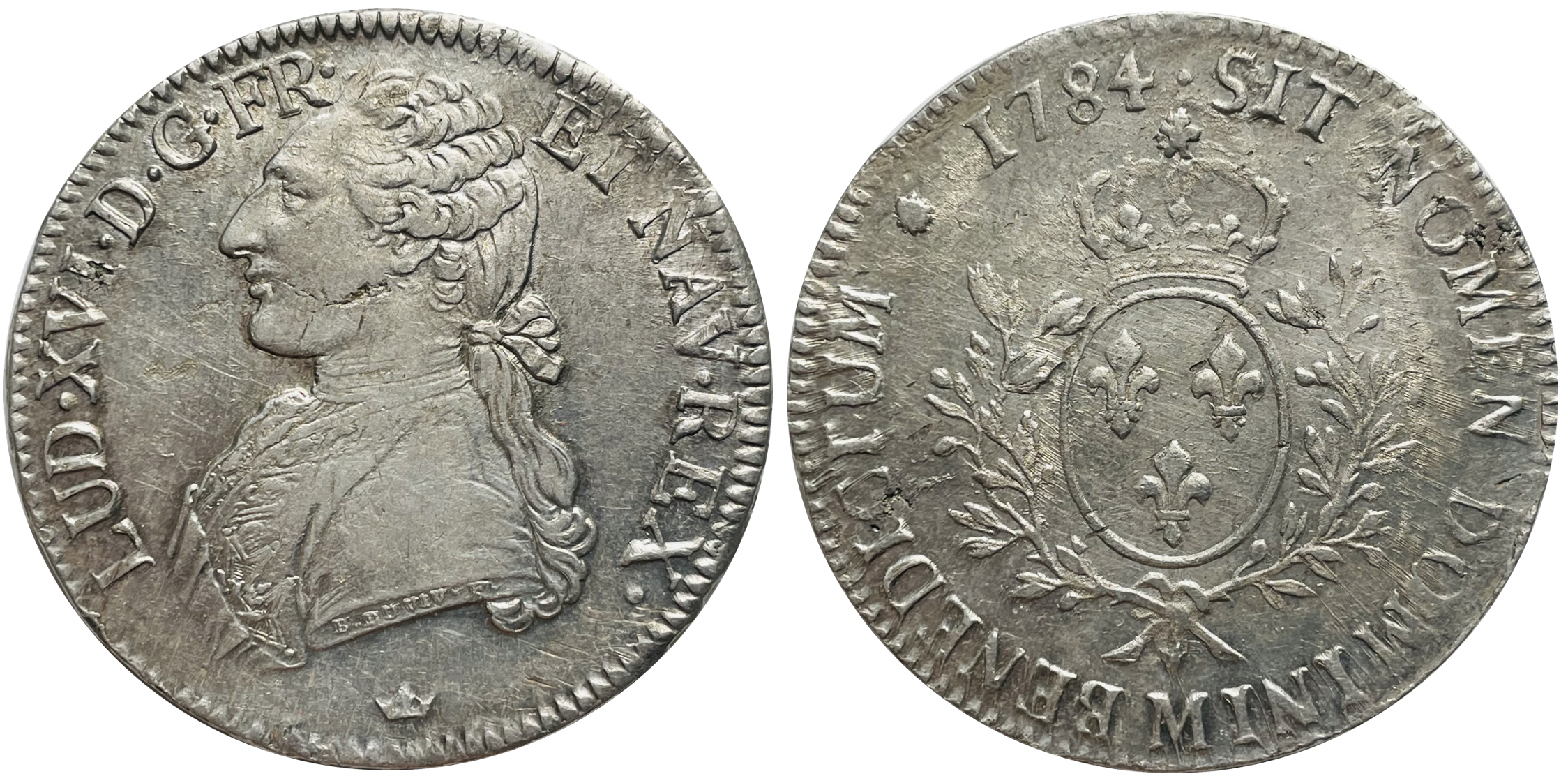
ĂŠcu
The term ''ĂŠcu'' () may refer to one of several France, French coins. The first ''ĂŠcu'' was a gold coin (the ''ĂŠcu d'or'') minted during the reign of Louis IX of France, in 1266. The value of the ''ĂŠcu'' varied considerably over time, and silver coins (known as ''ĂŠcu d'argent'') were also introduced. ''Ăcu'' (from Latin ''scutum'') means shield, and the coin was so called because its design included the coat of arms of France. The word is related to the Catalan language, Catalan ''escut'', Italian language, Italian ''scudo (other), scudo,'' or Portuguese language, Portuguese and Castilian language, Castilian ''escudo''. In English, the ''ĂŠcu'' was often referred to as the crown, or the French crown in the eras of the crown (English coin), English crown, crown (British coin), British crown, and crown (currency), other crowns. History Origin When Louis IX took the throne, France still used small silver French denier, deniers (abbreviated ''d''.), which had circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ăcu Louis XII
The term ''ĂŠcu'' () may refer to one of several French coins. The first ''ĂŠcu'' was a gold coin (the ''ĂŠcu d'or'') minted during the reign of Louis IX of France, in 1266. The value of the ''ĂŠcu'' varied considerably over time, and silver coins (known as ''ĂŠcu d'argent'') were also introduced. ''Ăcu'' (from Latin ''scutum'') means shield, and the coin was so called because its design included the coat of arms of France. The word is related to the Catalan '' escut'', Italian '' scudo,'' or Portuguese and Castilian '' escudo''. In English, the ''ĂŠcu'' was often referred to as the crown, or the French crown in the eras of the English crown, British crown, and other crowns. History Origin When Louis IX took the throne, France still used small silver deniers (abbreviated ''d''.), which had circulated since the time of Charlemagne to the exclusion of larger silver or gold coins. Over the years, French kings had granted numerous nobles and bishops the right to strike co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Livre
The livre (abbreviation: Pound sign, ÂŁ or Livre tournois, âś., French language, French for (pound)) was the currency of Kingdom of France and its predecessor states of Francia and West Francia from 781 to 1794. Several different livres existed, some concurrently. The livre was the name of coins and of units of account. History Origin and etymology The livre was established by Charlemagne as a unit of account equal to one Pound (mass), pound of silver. It was subdivided into 20 ''French sol, sous'' (also ''sols''), each sou equalling 12 ''French denier, deniers''. The word ''livre'' came from the Latin word ''Ancient Roman units of measurement#Weight, libra'', a Roman unit of weight and still the name of a Pound (mass), pound in modern French, and the denier comes from the Roman denarius. This system and the denier itself served as the model for many of Europe's currencies, including the British pound, Italian lira, Spanish dinero and the Portuguese dinheiro. This first l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis D'or
The Louis d'or () is any number of French coins first introduced by Louis XIII in 1640. The name derives from the depiction of the portrait of King Louis on one side of the coin; the French royal coat of arms is on the reverse. The coin was replaced by the French franc at the time of the revolution and later the similarly valued NapolĂŠon. The actual value of the coins fluctuated according to monetary and fiscal policy (see livre tournois), but in 1726 the value was stabilized. The 1640 issue of Louis dâor contained five denominations: a half Louis and a one, two, four, and eight Louis. All subsequent issues through 1793 were only denominated in half, one, and two Louis. Louis XIII The Louis d'or (a gold coin) replaced the franc which had been in circulation (in theory) since John II. In actual practice the principal gold coin circulating in France in the earlier 17th century had been Spanish: the 6.7-gram double ''escudo'' or "doubloon", of which the ''Louis d'or'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livre Tournois
The (; ; abbreviation: âś or ÂŁ) was one of numerous currencies used in France in the Middle Ages, medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in early modern France. The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 grams of Fineness, fine silver. The was a gold coin of one minted in large numbers from 1360. In 1549, the was decreed a unit of account, and in 1667 it officially replaced the . In 1720, the was redefined as 0.31 grams of pure gold, and in 1726, in a devaluation under Louis XV, as 4.50516 grams of fine silver. It was the basis of the revolutionary French franc of 1795, defined as 4.5 grams of fine silver exactly. Circulating currency In France, the was worth 240 French denier, deniers (the "Tours penny"). These deniers were first minted by the Basilica of Saint Martin, Tours, abbey of Saint Martin, in the Provinces of France, province of Touraine. Soon after Philip II of France seized the counties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or ) is a Western Romance language of the Indo-European language family originating from the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the official language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and SĂŁo TomĂŠ and PrĂncipe, and has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau. Portuguese-speaking people or nations are known as Lusophone (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Gallaecian language, Celtic phonology. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 17 million second language speakers, Portuguese has approximately 267 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the List of languages by number of native speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escudo
The escudo ( Portuguese: 'shield') is a unit of currency which is used in Cape Verde, and which has been used by Portugal, Spain and their colonies. The original coin was worth 16 silver . The Cape Verdean escudo is, and the Portuguese escudo was, subdivided into 100 . Its symbol is the , a letter S with two vertical bars superimposed used between the units and the subdivision (for example, ). In Spain and its colonies, the '' escudo'' refers to a gold coin worth sixteen '' reales de plata'' or forty ''reales de vellĂłn''. Currencies named "escudo" Circulating * Cape Verdean escudo Obsolete *Angolan escudo *Chilean escudo * French ĂŠcu *Mozambican escudo *Portuguese escudo *Portuguese Guinean escudo *Portuguese Indian escudo *Portuguese Timorese escudo *SĂŁo TomĂŠ and PrĂncipe escudo *Spanish escudo The escudo was either of two distinct Spanish currency denominations. Gold escudo The first escudo was a gold coin introduced in 1535/1537, with coins denominated in esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France 1644-A Quarter Ecu (Louis14)
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its eighteen integral regionsâfive of which are overseasâspan a combined area of and have an estimated total population of over 68.6 million . France is a semi-presidential republic and its capital, List of commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regionsâfive of which are overseasâspan a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sou (French Coin)
The sol, later called a sou, is the name of a number of different coins, for accounting or payment, dating from Antiquity to today. The name is derived from the late-Roman and Byzantine solidus. Its longevity of use anchored it in many expressions of the French language. Roman antiquity The ''solidus'' is a coin made of 4.5 g of gold, created by emperor Constantine to replace the ''aureus''. Early Middle Ages Doing honour to its name, the new currency earned the reputation of unalterability, crossing almost unchanged the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire, and the great invasions and the creation of Germanic kingdoms throughout Europe. Not only was it issued in the Byzantine Empire until the 11th century under the name of ''nomisma'', but the ''solidus'' was imitated by the barbarian kings, particularly the Merovingians, albeit most often in the form of a "third of a sou" (''tremissis''). Facing a shortage of gold, Charlemagne introduced a new "stabilization" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Denier
The denier (; , , ; . d.) or penny was a medieval coin which takes its name from the Frankish empire, Frankish coin first issued in the late seventh century; in English it is sometimes referred to as a silver penny. Its appearance represents the end of gold coinage, which, at the start of Frankish rule, had either been Roman (Byzantine) or "pseudo-imperial" (minted by the Franks in imitation of Byzantine coinage). Silver would be the basis for Frankish coinage from then on. The ''denier'' was minted in France, Cyprus and parts of the Italian peninsula for the whole of the Middle Ages, in states such as the Patriarchate of Aquileia (state), patriarchate of Aquileia, the Kingdom of Sicily, the Republic of Genoa, the Republic of Siena, Kingdom of Cyprus, and the crusader state Kingdom of Jerusalem, among others. History Coin Around 755, amid the Carolingian Renaissance, Carolingian Reforms, Pepin the Short introduced a new French currency, currency system which was eventually a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337â1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by English claims to the French throne, a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival Dynasty, dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |