L'Orient on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lorient (; ) is a town (''
 In 1664,
In 1664,
 The town experienced a period of growth when
The town experienced a period of growth when
 Maritime activities slowed at the start of the 19th century. Activity at the shipyards and naval base reached a low that would last until the
Maritime activities slowed at the start of the 19th century. Activity at the shipyards and naval base reached a low that would last until the
 In April 1945, the Reconstruction Ministry advocated the use of temporary wooden shacks. These shelters were shipped as a kit to be built on site. In 1948, there were 28 settlements under the city's authority, and 20 more in the
In April 1945, the Reconstruction Ministry advocated the use of temporary wooden shacks. These shelters were shipped as a kit to be built on site. In 1948, there were 28 settlements under the city's authority, and 20 more in the
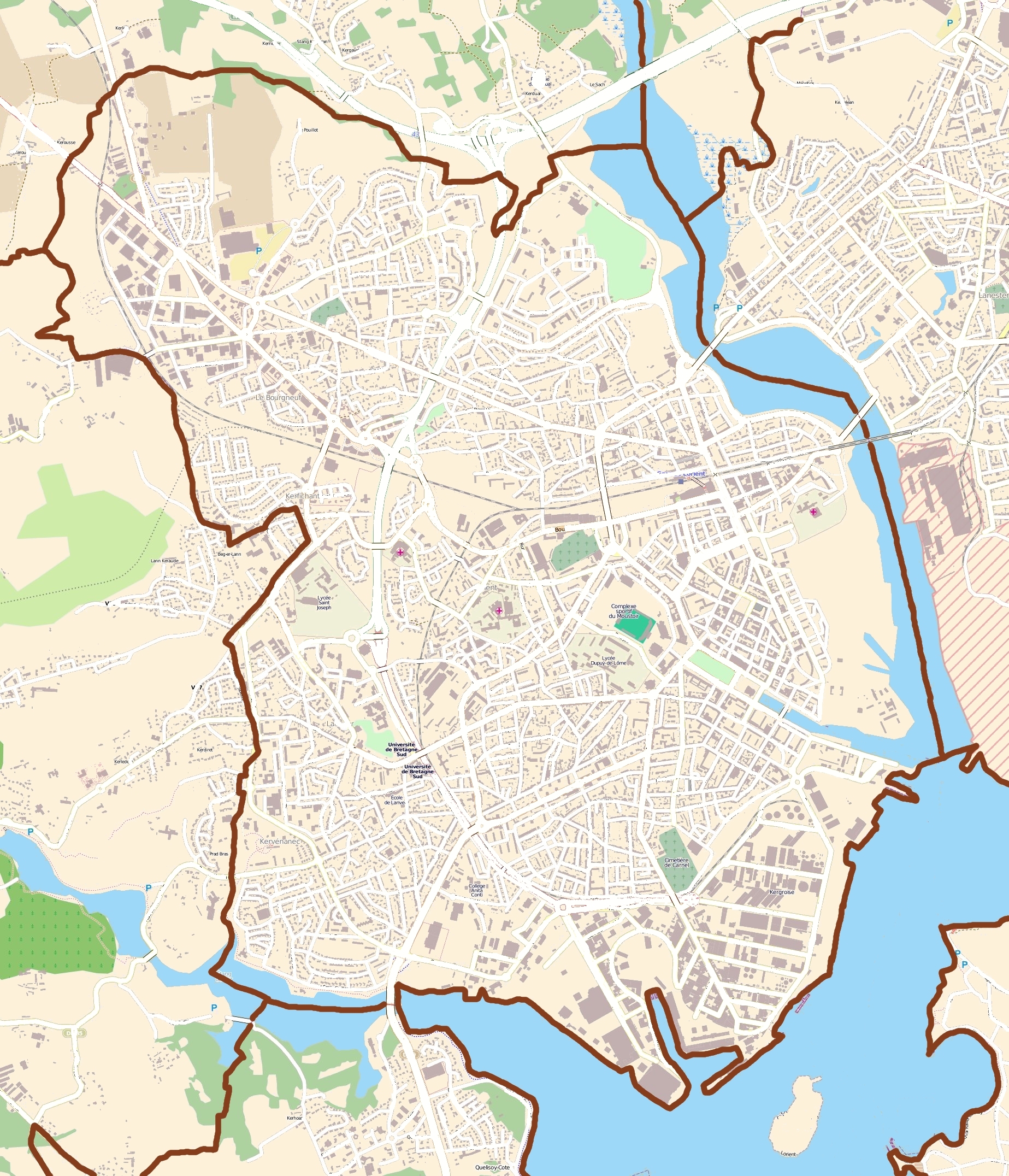 Lorient is located on the south coast of
Lorient is located on the south coast of



 Active units based near Lorient:
* Naval Commandos (''Commando Marine''): the
Active units based near Lorient:
* Naval Commandos (''Commando Marine''): the
 Lorient was the location of an extensive
Lorient was the location of an extensive

Official website
(in French)
Ville de Lorient et Festival Interceltique Images
Festival Interceltique de Lorient
*
See pictures on Antonio Mucherino's web site
Tourism office
(in French) {{Authority control Lorient, Subprefectures in France German Navy submarine bases Communes of Morbihan Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast
commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
'') and seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
in the Morbihan
Morbihan ( , ; br, Mor-Bihan ) is a department in the administrative region of Brittany, situated in the northwest of France. It is named after the Morbihan (''small sea'' in Breton), the enclosed sea that is the principal feature of the coastli ...
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
in western France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
History
Prehistory and classical antiquity
Beginning around 3000 BC, settlements in the area of Lorient are attested by the presence of megalithic architecture. Ruins ofRoman roads
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
(linking Vannes
Vannes (; br, Gwened) is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany in north-western France. It was founded over 2,000 years ago.
History Celtic Era
The name ''Vannes'' comes from the Veneti, a seafaring Celtic people who lived ...
to Quimper
Quimper (, ; br, Kemper ; la, Civitas Aquilonia or ) is a commune and prefecture of the Finistère department of Brittany in northwestern France.
Administration
Quimper is the prefecture (capital) of the Finistère department.
Geography
The ...
and Port-Louis
Port Louis (french: Port-Louis; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Polwi or , ) is the capital city of Mauritius. It is mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's eco ...
to Carhaix
Carhaix-Plouguer (; br, Karaez-Plougêr ), commonly known as just Carhaix (), is a Communes of France, commune in the Departments of France, French department of Finistère, region of Brittany (administrative region), Brittany, France.
) confirm Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
presence.
Founding
 In 1664,
In 1664, Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the countr ...
founded the French East Indies Company
The French East India Company (french: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a colonial commercial enterprise, founded on 1 September 1664 to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in th ...
. In June 1666, an ordinance
Ordinance may refer to:
Law
* Ordinance (Belgium), a law adopted by the Brussels Parliament or the Common Community Commission
* Ordinance (India), a temporary law promulgated by the President of India on recommendation of the Union Cabinet
* ...
of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
granted lands of Port-Louis
Port Louis (french: Port-Louis; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Polwi or , ) is the capital city of Mauritius. It is mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's eco ...
to the company, along with Faouédic on the other side of the roadstead
A roadstead (or ''roads'' – the earlier form) is a body of water sheltered from rip currents, spring tides, or ocean swell where ships can lie reasonably safely at anchor without dragging or snatching.United States Army technical manual, TM 5- ...
. One of its directors, Denis Langlois, bought lands at the confluence of the Scorff
The Scorff (; br, Skorf) River flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast in Lorient.
The Scorff rises north of Langoëlan, in the Morbihan department, and flows through the towns of Guémené-sur-Scorff and Pon ...
and the Blavet
The Blavet (; br, Blavezh) river flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast near Lorient. It is long. The river is canalised for most of its length, forming one of the links in the Brittany canal system. It con ...
rivers, and built slipway
A slipway, also known as boat ramp or launch or boat deployer, is a ramp on the shore by which ships or boats can be moved to and from the water. They are used for building and repairing ships and boats, and for launching and retrieving small ...
s. At first, it only served as a subsidiary of Port-Louis, where offices and warehouses were located. The following years, the operation was almost abandoned, but in 1675, during the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
, the French East Indies Company
The French East India Company (french: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a colonial commercial enterprise, founded on 1 September 1664 to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in th ...
scrapped its base in Le Havre
Le Havre (, ; nrf, Lé Hâvre ) is a port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the river Seine on the Channel southwest of the Pays de Caux, very cl ...
since it was too exposed during wartime, and transferred its infrastructures to l'Enclot, out of which Lorient grew. The company then erected a chapel, workshops, forges, and offices, leaving Port-Louis permanently.
The city's name is derived from ''Le Soleil d'Orient'', the first ship constructed at the site, in 1669. Workers gave the site the name of the ship, which, by contraction, became simply ''L'Orient'' and finally ''Lorient''.
The French Royal Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
opened a base there in 1690, under the command of Colbert de Seignelay, who inherited his father's position as Secretary of State of the Navy. At the same time, privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s from Saint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, on the English Channel coast.
The walled city had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth from local extortion and overseas adventures. In 1944, the Alli ...
took shelter there. In 1700, the town grew out of l'Enclot following a law forcing people to leave the domain to move to the Faouédic heath. In 1702, there were about 6,000 inhabitants in Lorient, though activities slowed, and the town began to decline.
Growth under the Company of the Indies
 The town experienced a period of growth when
The town experienced a period of growth when John Law
John Law may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* John Law (artist) (born 1958), American artist
* John Law (comics), comic-book character created by Will Eisner
* John Law (film director), Hong Kong film director
* John Law (musician) (born 1961) ...
formed the Perpetual Company of the Indies by absorbing other chartered companies
A chartered company is an association with investors or shareholders that is incorporated and granted rights (often exclusive rights) by royal charter (or similar instrument of government) for the purpose of trade, exploration, and/or coloniza ...
(including the French East India Company
The French East India Company (french: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a colonial commercial enterprise, founded on 1 September 1664 to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in the ...
), and chose Lorient as its operations base. Despite the economic bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be c ...
caused by the Company in 1720, the city was still growing as it took part in the Atlantic triangular slave trade. From 1720 to 1790, 156 ships deported an estimated 43,000 slaves. In 1732, the Company decided to transfer its sales headquarters from Nantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabita ...
to Lorient, and asked architect Jacques Gabriel
Ancient and noble French family names, Jacques, Jacq, or James are believed to originate from the Middle Ages in the historic northwest Brittany region in France, and have since spread around the world over the centuries. To date, there are over ...
to raise new buildings out of dimension stone
Dimension stone is natural stone or rock that has been selected and finished (e.g., trimmed, cut, drilled, ground, or other) to specific sizes or shapes. Color, texture and pattern, and surface finish of the stone are also normal requirements. A ...
s to host these new activities, and to embellish the L'Enclos domain. Sales began in 1734, peaking up to 25 million ''livres tournois
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France.
The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 gr ...
''. In 1769, the Company's monopoly ended with the scrapping of the company itself, under the influence of the physiocrats
Physiocracy (; from the Greek for "government of nature") is an economic theory developed by a group of 18th-century Age of Enlightenment French economists who believed that the wealth of nations derived solely from the value of "land agricultur ...
.
Until the Company's closure, the city took advantage of its prosperity. In 1738, there were 14,000 inhabitants, or 20,000 considering the outlying villages of Kerentrech, Merville, La Perrière, Calvin, and Keryado, which are now neighbourhoods within the present-day city limits. In 1735, new streets were laid out and in 1738, it was granted city status. Further work was undertaken as the streets began to be paved, wharves and slipways were built along the Faouédic river, and thatched
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of ...
houses were replaced with stone buildings following 18th-century classical architecture style as it was the case for l'Enclos. In 1744, the city walls were erected, and proved quickly useful as Lorient was raided in September 1746. Following the demise of the Company, the city lost one-seventh of its population.
In 1769, the city evolved into a full-scale naval base
A naval base, navy base, or military port is a military base, where warships and naval ships are docked when they have no mission at sea or need to restock. Ships may also undergo repairs. Some naval bases are temporary homes to aircraft that us ...
for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
when the King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
bought out the Company's infrastructures for 17,500,000 ''livres tournois
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France.
The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 gr ...
''. From 1775 on, the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
brought a surge in activity, as many privateers
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
hailed from Lorient. When the war ended, transatlantic lines opened to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, and in 1785, a new commercial company started under Calonne's tutelage (then Controller-General of Finances The Controller-General or Comptroller-General of Finances (french: Contrôleur général des finances) was the name of the minister in charge of finances in France from 1661 to 1791. It replaced the former position of Superintendent of Finances (''S ...
) with the same goal as the previous entities, i.e. conducting trade in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, with again Lorient standing as its operative base.
The French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
and the subsequent Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
put an end to trade for nearly two decades.
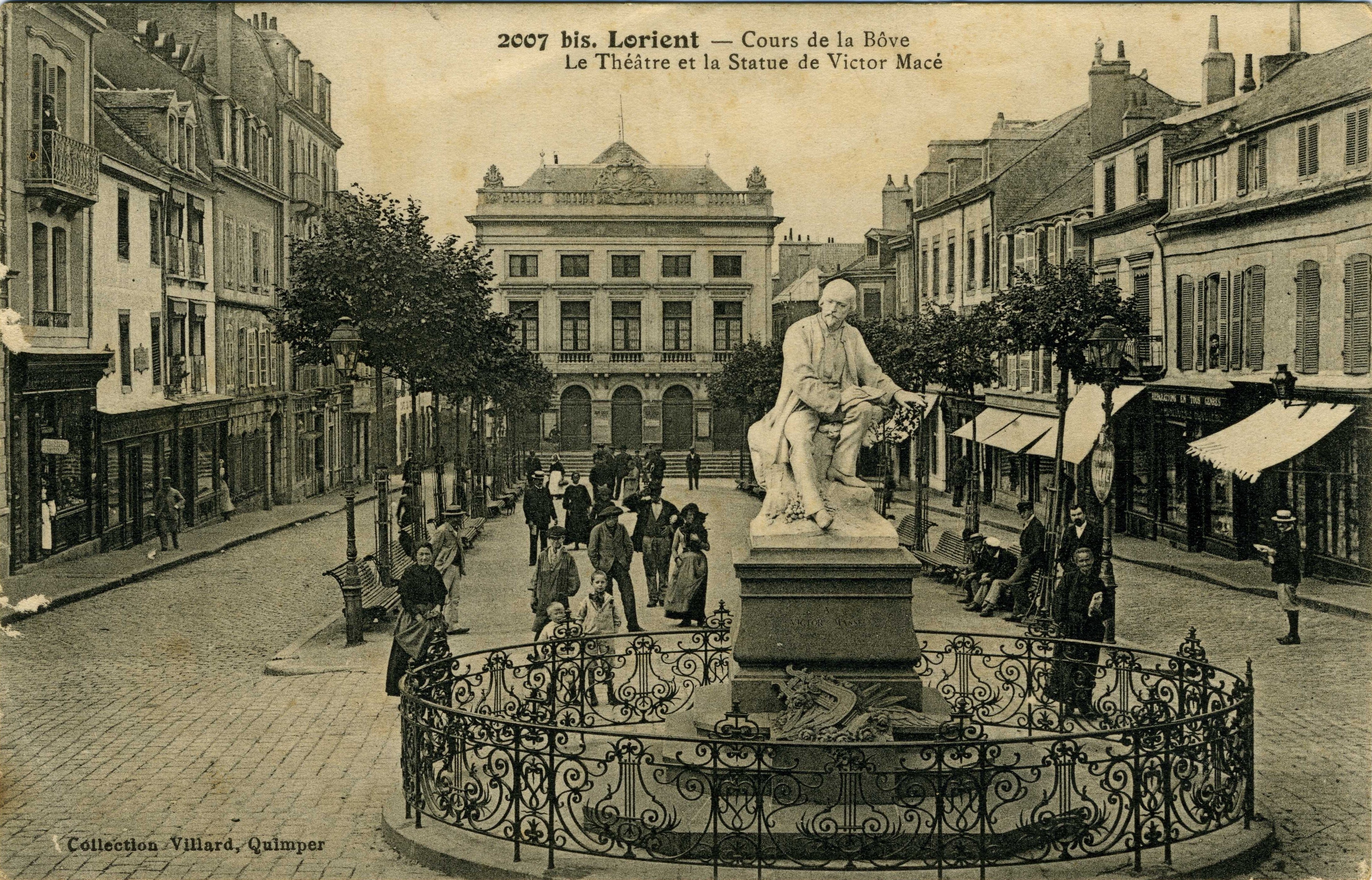
19th and early 20th centuries

 Maritime activities slowed at the start of the 19th century. Activity at the shipyards and naval base reached a low that would last until the
Maritime activities slowed at the start of the 19th century. Activity at the shipyards and naval base reached a low that would last until the July Monarchy
The July Monarchy (french: Monarchie de Juillet), officially the Kingdom of France (french: Royaume de France), was a liberal constitutional monarchy in France under , starting on 26 July 1830, with the July Revolution of 1830, and ending 23 F ...
. During this period, the city was more of an administrative center. The first secondary school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' secondary education, lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) ...
opened in 1822, a lazaretto
A lazaretto or lazaret (from it, lazzaretto a diminutive form of the Italian word for beggar cf. lazzaro) is a quarantine station for maritime travellers. Lazarets can be ships permanently at anchor, isolated islands, or mainland buildings ...
in 1823, and barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
in 1839.
The city began to modernize in the second quarter of the century; in 1825, a roofed slipway and a drydock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
were added to the shipyards. A sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
cannery
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although un ...
opened the same year. The first gasworks
A gasworks or gas house is an industrial plant for the production of flammable gas. Many of these have been made redundant in the developed world by the use of natural gas, though they are still used for storage space.
Early gasworks
Coal ...
was built in 1845.
In the second half of the 19th century, the steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
allowed the ports to strengthen their output. The first locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
reached the city in 1865. In 1861, the original drydock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
was enlarged as a second one was dug out. The same year, the ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
'' Couronne'' was built on a design directly inspired by the '' Gloire'' class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
, though unlike her wooden-hull predecessors, she was entirely made of iron. She was followed in 1876 by the ironclad '' Redoutable'', the first ship in the world with a steel structure.
In 1889, fishing expanded following the creation of the municipal fish market, and the arrival of steam-powered
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tra ...
fishing trawler
A fishing trawler is a commercial fishing vessel designed to operate Trawling, fishing trawls. Trawling is a method of fishing that involves actively dragging or pulling a trawl through the water behind one or more trawlers. Trawls are fishing ...
s in 1900. The Keroman fishing port construction started in 1920.
World War II
In1941
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Eu ...
, the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, then occupying France, chose to establish a U-boat base at Lorient. The submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
facilities quickly became targets of constant bombing from Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
air forces. The Germans decided to build a complex of bomb-proof submarine pen
A submarine pen (''U-Boot-Bunker'' in German) is a type of submarine base that acts as a bunker to protect submarines from air attack.
The term is generally applied to submarine bases constructed during World War II, particularly in Germany and ...
s, their largest U-boat base, which would house the 2nd
A second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI).
Second, Seconds or 2nd may also refer to:
Mathematics
* 2 (number), as an ordinal (also written as ''2nd'' or ''2d'')
* Second of arc, an angular measurement unit ...
and the 10th
10 (ten) is the even natural number following 9 and preceding 11. Ten is the base of the decimal numeral system, by far the most common system of denoting numbers in both spoken and written language. It is the first double-digit number. The rea ...
U-boat flotillas for the bulk of the Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade ...
. Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
, then supreme commander of the U-boat Arm, moved his staff into the Kernevel villa, just across the water from Keroman, in Larmor-Plage
Larmor-Plage (; br, An Arvor) is a commune in the Morbihan department of Brittany in north-western France.
History
Larmor-Plage was created as a new commune in 1925. Before that, it came within the administrative area of the town of Ploemeur ...
.
In 1943–1944, Lorient was nearly razed to the ground by Allied bombing
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanica ...
, though failing to destroy the submarine pens despite 4,000 tons of bombs dropped. According to the book ''Steel Boats, Iron Hearts'' (by former crewman Hans Goebeler
Hans may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People
* Hans (name), a masculine given name
* Hans Raj Hans, Indian singer and politician
** Navraj Hans, Indian singer, actor, entrepreneur, cricket player and performer, son of Hans Raj Hans
** Yuvraj Hans, Punjabi ...
), after the Allies failed to damage the U-boat bunkers the bombing shifted to the city itself to deny the Germans workers and other resources. Before tse bombings, thousands of leaflets were dropped on the population instructing the inhabitants to evacuate. Between 14 January 1943 and 17 February 1943, as many as 500 high-explosive aerial bomb
An aerial bomb is a type of explosive or incendiary weapon intended to travel through the air on a predictable trajectory. Engineers usually develop such bombs to be dropped from an aircraft.
The use of aerial bombs is termed aerial bombing.
...
s and more than 60,000 incendiary bombs
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires or destroy sensitive equipment using fire (and sometimes used as anti-personnel weaponry), that use materials such as napalm, th ...
were dropped on Lorient.
After the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
in June 1944 and the subsequent breakout, Lorient was surrounded by Allied troops on 12 August 1944. Its usefulness as a naval base gone, Lorient was left in a state of siege, surrounded by the American Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
. On 10 May 1945, the German garrison surrendered, two days after the official final unconditional surrender of Germany. In 1949, the city of Lorient was awarded the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon, ...
and the ''Croix de guerre 1939–1945
The ''Croix de Guerre 1939–1945'' (English: War Cross 1939–1945) is a French military decoration, a version of the ''Croix de Guerre'' created on 26 September 1939 to honour people who fought with the Allies against the Axis forces at any ti ...
''.
Reconstruction
urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, t ...
, distributed among the neighboring towns of Ploemeur
Ploemeur (; br, Plañvour), sometimes written instead as Plœmeur, is a commune in the Morbihan department in the region of Brittany in north-western France. It is a western suburb of Lorient.
Population
The inhabitants are called the ''Ploeme ...
, Lanester
Lanester (; br, Lannarstêr) is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany, in north-western France.
It is the largest suburb of the city of Lorient, across the river Scorff to the east.
Demographics
Inhabitants of Lanester are called ' ...
, Hennebont
Hennebont (; ) is a commune in the Morbihan department in the region of Brittany in north-western France.
Geography
Hennebont is situated about ten miles from the mouth of the River Blavet, which divides it into two parts: the ''Ville Close'', ...
and Quéven
Quéven (; ) is a commune in the Morbihan department of Brittany in north-western France.
History
During World War I, Quéven lost one hundred and one of its children.
85% of the town was destroyed in World War II. In January 1945, the cit ...
. Each of these neighbourhoods could hold up to 280 houses.
This temporary housing would stand from 10 to 40 years depending on the location. The last shack in the largest settlement, Soye, was torn down in 1991. Today, only a few buildings dating to the 18th century still stand.
Geography
Location
 Lorient is located on the south coast of
Lorient is located on the south coast of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
, where the rivers Scorff
The Scorff (; br, Skorf) River flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast in Lorient.
The Scorff rises north of Langoëlan, in the Morbihan department, and flows through the towns of Guémené-sur-Scorff and Pon ...
and Blavet
The Blavet (; br, Blavezh) river flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast near Lorient. It is long. The river is canalised for most of its length, forming one of the links in the Brittany canal system. It con ...
join to form the roadstead of Lorient
The roadstead of Lorient (, ) is a roadstead located to the west of Morbihan in Brittany, France.
Geography
The harbor of Lorient constitutes the mouths of the rivers Blavet, Scorff and the Ter in the Atlantic Ocean. It has several port facil ...
( fr), before discharging into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. The river Ter used to flow into the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
to the south of the city, however, a dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
was constructed in 1967, stopping the flow. The city is south-west of Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, south-west of Rennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department ...
and north-west of Nantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabita ...
.
The city comprises different neighbourhoods:
* Bois du Château
* Keryado
* Saint-Armel
* Kerentrech
* Le Gaillec
* Le Manio
* Kerdual
* Kervénanec
* Lanveur
* Keroman
* Kergroise
* Carnel
* Kerfichant
* Kerolay
* Kerguestenen
* Le Mir
* La Perrière
* La Ville Neuve
* La Ville en Bois
* Kermélo
* Le Ter
* Kerlin
* Merville
* La Nouvelle Ville
* Le « bout du monde »
* Saint-Maudé
* Frébault-Polygone
* Quehélio
* Kervaric
* Keryvalant
* La Fontaine des Anglais
* Kerforn
* Le petit et le grand Batteur
* Le Kreisker
* Kerguillet
* Le Parco
* Soye
Adjacent towns:
Climate
Under theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, Lorient experiences an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(Cfb), with mild winters and cool to warm summers. Precipitation is evenly distributed throughout the year. Frost is rare in winter, as are days over during summer.
Population
In 2017, Lorient had a population of 57,149. In 2017, itsintercommunality
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equiv ...
Lorient Agglomération
Communauté d'agglomération Lorient Agglomération is the ''communauté d'agglomération'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the city of Lorient. It is located in the Morbihan department, in the Brittany region, northwestern France. It was ...
had 203,309 inhabitants. Lorient is the most populous commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
in Morbihan
Morbihan ( , ; br, Mor-Bihan ) is a department in the administrative region of Brittany, situated in the northwest of France. It is named after the Morbihan (''small sea'' in Breton), the enclosed sea that is the principal feature of the coastli ...
''département
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the regions of France, admin ...
'', although the ''préfecture
In France, a prefecture (french: préfecture) may be:
* the ''chef-lieu de département'', the commune in which the administration of a department is located;
* the ''chef-lieu de région'', the commune in which the administration of a region is l ...
'' is the slightly smaller commune of Vannes
Vannes (; br, Gwened) is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany in north-western France. It was founded over 2,000 years ago.
History Celtic Era
The name ''Vannes'' comes from the Veneti, a seafaring Celtic people who lived ...
. Inhabitants of Lorient are called ''Lorientais''.
The population data in the table and graph below refer to the commune of Lorient proper, in its geography at the given years. The commune of Lorient absorbed the former commune of Keryado in 1947.
Breton language
The municipality launched a linguistic plan throughYa d'ar brezhoneg
(french: Oui au breton, en, Yes to Breton) is a campaign started in the 21st century by the ( en, Office of the Breton language) to promote and stimulate the use of the Breton language in daily life in Brittany, northwestern France. Breton is a ...
on 25 January 2007.
In 2008, 2.71% of the children attended the bilingual schools in primary education.
Economy


Ports
Lorient is commonly referred to as ''La ville aux cinq ports'' ("the city of five ports"): military, fishing, commercial, passengers and yachting. In 2010, the sector represented 9,600 direct jobs for a total 12,000 jobs (with indirect jobs accounted for), or 12% of local employment. * Keroman fishing port ( fr): In 2010, with a catch of 27,000 tons, it was second only toBoulogne-sur-Mer
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
regarding catch tonnage among French fishing ports, but first considering the cash value. It accounts for 3,000 jobs (including 700 fishermen) and 130 fishing vessels.
* Kergroise cargo port : With 2.6 million tons of cargo per year (including oil, cattle fodder, sand, containers), it ranks first in Brittany.
* Marinas
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : ''marina'', "coast" or "shore") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats.
A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ship ...
: mooring berths are dispatched on Lorient (370), Kernevel (1,000), Port-Louis
Port Louis (french: Port-Louis; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Polwi or , ) is the capital city of Mauritius. It is mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's eco ...
(450), Gâvres
Gâvres (; ) is a commune in the Morbihan department of Brittany in north-western France. French Navy Minister Hyde de Neuville chose this place as a military testing area in 1829 for heavy marine ordnance.See the governmental directions of Jun ...
(57) and Guidel
Guidel (; ) is a commune in the Morbihan department of Brittany in north-western France. Inhabitants of Guidel are called in French ''Guidélois''.
Population
Cemetery
The communal cemetery, containing 108 tombs from the World War II, has bee ...
(102). Additionally, there is an long dock dedicated to offshore competitive sailing (''Pôle course au large''), recently built within the former submarine base.
* Passenger ships : each year, more 457,500 passengers set sail to the nearby islands of Groix
Groix (; br, Enez Groe) is an island and a commune in the Morbihan department of the region of Brittany in north-western France.
Groix lies a few kilometres off the coast of Lorient. Several ferries a day run from Lorient to Groix.
There are a ...
and Belle-Île-en-Mer.
* Military : though no longer a French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
base, new warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster a ...
s are still built at DCNS, docking temporarily on wharves
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths (mooring location ...
along the Scorff
The Scorff (; br, Skorf) River flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast in Lorient.
The Scorff rises north of Langoëlan, in the Morbihan department, and flows through the towns of Guémené-sur-Scorff and Pon ...
river.

Industry
From its founding,shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
has always been of great importance to the city. DCNS continues the legacy of the formerly state-owned shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance a ...
s (colloquially known as ''l'Arsenal'') that began operation in 1690. It still builds warships, mainly frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
s. There is also a substantial industrial base in Keroman to support the fishing fleet.
Transport
Lorient South Brittany Airport
Lorient South Brittany Airport or ''Aéroport de Lorient Bretagne Sud'' , also known as Lorient-Lann-Bihoué Airport, is the airport serving the city of Lorient. It is situated 5 kilometre, km west-northwest of Lorient, a ''Communes of the Morbiha ...
is situated just west of the city at Lann Bihoue, and it has direct flights to Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
. There are also direct flights to London and Porto in the Summer.
The Gare de Lorient is the railway station, offering connections to Quimper, Nantes, Rennes, Paris (less than three hours by TGV) and several regional destinations.
Education
Schools in Lorient belong to the Academy ofRennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department ...
.
Tertiary
* CPGE at ''Dupuy-de-Lôme'' and ''Saint Joseph-La salle''lycée
In France, secondary education is in two stages:
* ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 15.
* ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for children between ...
s.
* '' Université de Bretagne Sud''.
* '' Institut universitaire de technologie de Lorient''
* ''École nationale supérieure d'ingénieurs de Bretagne Sud
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by Secondary education in France, secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région ...
''
* ''École supérieure d'art''.
* ''École nationale de musique et de danse''.
Military
 Active units based near Lorient:
* Naval Commandos (''Commando Marine''): the
Active units based near Lorient:
* Naval Commandos (''Commando Marine''): the special forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
of the French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
. Accordingly, it is one of the most selective units among the French armed forces
The French Armed Forces (french: Forces armées françaises) encompass the Army, the Navy, the Air and Space Force and the Gendarmerie of the French Republic. The President of France heads the armed forces as Chief of the Armed Forces.
Franc ...
, equivalent in their mission and affiliation to Navy SEALs
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the United States Navy, U.S. Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the United States Naval Special Warfare Command, Naval Special Wa ...
or British Special Boat Service
The Special Boat Service (SBS) is the special forces unit of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. The SBS can trace its origins back to the Second World War when the Army Special Boat Section was formed in 1940. After the Second World War, the Roya ...
. Five out of the six existing naval commandos are based in Lanester
Lanester (; br, Lannarstêr) is a commune in the Morbihan department in Brittany, in north-western France.
It is the largest suburb of the city of Lorient, across the river Scorff to the east.
Demographics
Inhabitants of Lanester are called ' ...
, just across the Scorff
The Scorff (; br, Skorf) River flows from central Brittany and enters the Atlantic Ocean on the south coast in Lorient.
The Scorff rises north of Langoëlan, in the Morbihan department, and flows through the towns of Guémené-sur-Scorff and Pon ...
river from Lorient. The Naval Fusilier & Commando Training School is also based here.
*Lann-Bihoué
Lorient South Brittany Airport or ''Aéroport de Lorient Bretagne Sud'' , also known as Lorient-Lann-Bihoué Airport, is the airport serving the city of Lorient. It is situated 5 km west-northwest of Lorient, a ''commune'' of the Morbihan ''dépa ...
Naval Aviation Base: Five squadrons ("'' flottilles''") are based in Ploemeur
Ploemeur (; br, Plañvour), sometimes written instead as Plœmeur, is a commune in the Morbihan department in the region of Brittany in north-western France. It is a western suburb of Lorient.
Population
The inhabitants are called the ''Ploeme ...
. Their tasks include airborne early warning
Airborne or Airborn may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''Airborne'' (1962 film), a 1962 American film directed by James Landis
* ''Airborne'' (1993 film), a comedy–drama film
* ''Airborne'' (1998 film), an action film sta ...
, maritime patrol {{Unreferenced, date=March 2008
Maritime patrol is the task of monitoring areas of water. Generally conducted by military and law enforcement agencies, maritime patrol is usually aimed at identifying human activities.
Maritime patrol refers to ac ...
and air-sea rescue
Air-sea rescue (ASR or A/SR, also known as sea-air rescue), and aeronautical and maritime search and rescue (AMSAR) by the ICAO and International Maritime Organization, IMO, is the coordinated search and rescue (SAR) of the survivors of emergenc ...
.
Lorient Submarine Base
 Lorient was the location of an extensive
Lorient was the location of an extensive submarine base
A submarine base is a military base that shelters submarines and their personnel.
Examples of present-day submarine bases include HMNB Clyde, Île Longue (the base for France's Force océanique stratégique), Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, Na ...
, built by the Germans
"The Germans" (named on some releases as "Fire Drill") is the sixth episode of the BBC sitcom ''Fawlty Towers''. In the episode, while suffering the effects of concussion, Basil Fawlty repeatedly offends some German guests. Despite warning his ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and used subsequently by the French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
. Head of the U-Boat Arm Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
decided to construct the base on 28 June 1940. Between November 1940 and January 1942 a number of gigantic reinforced concrete structures were built. including three on the Keroman peninsula. They are called K1, K2 and K3. In 1944 work began on a fourth structure. The base was capable of sheltering thirty submarines. Lorient was damaged by Allied bombing raids but the naval base survived the war.
Following the German surrender the base was used by the French Navy, named for Jacques Stosskopf
Jacques Stosskopf (27 November 1898 – 1 September 1944) held the post of deputy director of naval construction at the German-held Lorient U-boat arsenal, but was a member of the French Resistance and war hero killed by the Nazis.
Military care ...
, a hero of the French Resistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
who had worked there. The base was decommissioned in 1995 and turned over to civilian use.
Culture

Events
Each year in August since 1970, Lorient hosts the Festival interceltique, bringing together artists from all the Celtic world (Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
, Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, Galicia, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in nor ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and early ...
and Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
). Each year, a Celtic nation is chosen as honored guest. It is one of the biggest festival in Europe by attendance (800,000 people for the 40th edition)
Media
Lorient is home to TébéSud (formerly TyTélé), a local TV channel covering Morbihan through DTT.Religion
Catholic churches are among the main religious landmarks of Lorient. While the Church of Our Lady of the Assumption was built in 1850 in a revivalist neo-Gothic style, the church of Saint Joan of Arc was built in a neo-Roman style in the 1930s by French architectJean Desbois
Jean Desbois was a French architect who rose to fame during the 20th century and left significant landmarks in France and in Cambodia such as the Central Market in Phnom Penh.
He was a member of the French Society of Architects (''Société des A ...
and a few years later in 1955, and the modernist church of Notre-Dame-de-Victoire is the highest point of Lorient with its 4-meter-high concrete bell tower though the population never really accepted this new style. Major Catholic festivals such as Christmas, Carnaval, Easter and the ''Pardon'' are celebrated as major feasts of the city.
Sports
Football
The most popular club in Lorient isFC Lorient
Football Club Lorient Bretagne Sud (; commonly referred to FC Lorient or simply Lorient) is a French association football club based in Lorient, Brittany. The club was founded in 1926 and currently competes in Ligue 1, the top flight of French ...
, which currently play in Ligue 1
Ligue 1, officially known as Ligue 1 Uber Eats for sponsorship reasons, is a French professional league for men's association football clubs. At the top of the French football league system, it is the country's primary football competition. A ...
, after winning Ligue 2
Ligue 2 (, League 2), also known as Ligue 2 BKT due to sponsor (commercial), sponsorship by Balkrishna Industries, is a French professional football league. The league serves as the second division of French football and is one of two divisions ...
in 2020. They are nicknamed '' les Merlus''. They play their home fixtures at Stade du Moustoir
The Stade du Moustoir - Yves Allainmat, known as the Stade du Moustoir, is a multi-use stadium in Lorient, France. It is currently used mostly for football matches and is the home stadium of FC Lorient. The stadium can hold up to 18,110 with the ...
.
Christian Gourcuff
Christian Jean Gourcuff (born 5 April 1955) is a French professional Manager (association football), football manager and former Football player, player who was most recently the manager of Ligue 1 club FC Nantes, Nantes.
Club career
During his ...
has managed the team for over 20 years (aggregate years).
Sailing
The convertedsubmarine base
A submarine base is a military base that shelters submarines and their personnel.
Examples of present-day submarine bases include HMNB Clyde, Île Longue (the base for France's Force océanique stratégique), Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, Na ...
has been home port to several skippers and their sailing teams:
*Jérémie Beyou (Delta Dore),
*Pascal Bidégorry
Pascal Bidegorry (born 15 January 1968, in Bayonne) is a French sailor.
Life
He has raced across the Atlantic Ocean over 30 times and has set records in many classes. He has won the Solitaire du Figaro and the Transat Jacques Vabre; apart from ...
(Banque Populaire),
*Franck Cammas
Franck Cammas (born 22 December 1972 in Aix-en-Provence) is a French yachtsman. He has lived in Brittany since his victory in the Challenge Espoir Crédit Agricole in 1994. After completing a two-year maths course for the ‘Grandes écoles’, ...
(Groupama), winner of the 2011–12 Volvo Ocean Race
* Samantha Davies (Roxy),
*Jean-Baptiste Dejeanty (Maisonneuve),
*Jean-Pierre Dick (Paprec-Virbac),
*Yann Elies (Generali),
*Alain Gautier (Foncia),
*Sébastien Josse (British Telecom),
*Marc Thiercelin (DCNS)
Lorient was also a staging port during the 2011–12 Volvo Ocean Race, as well as the starting point of ''la Solitaire du Figaro
The Solitaire du Figaro, previously called the Course de l'Aurore, is a solo multi-stage sailing race created in 1970 by Jean-Louis Guillemard and . The unique character of the race, the presence of great solo sailors and its being open to amateu ...
'' (2009 edition).
Eric Tabarly
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization).
The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* ain ...
built three out of his six ''Pen Duick'' boats in Lorient.
Notable ''Lorientais''
Arts and literature
*Marie-Léontine Bordes-Pène
Marie-Léontine Bordes-Pène (Léontine-Marie Pène) was a notable French pianist, who premiered major works by César Franck, Vincent d'Indy and others. She married a brother of the composer Charles Bordes, and was known by the surname Bordes-Pè ...
(1858–1924), pianist
* Charles Delioux
Jean-Charles Delioux (de) Savignac (17 April 1825 – 12 November 1915) was a French composer, a pupil of Halévy and potentially Chopin, who was quite popular in the Paris salons of the nineteenth century.
Life
Charles Delioux was born in the B ...
(1825–1915), composer and pianist
* Marie Dorval
Marie Dorval (6 January 1798, Lorient, Morbihan – 20 May 1849) was a French actress in the Romantic style.
Early life and first marriage
Marie Thomase Amélie Delauney was born on 6 January 1798 to Marie Bourdais, who was sixteen yea ...
(1798–1849), actress
* Irène Frain (b. 1950), writer
* Ernest Hello
Ernest Hello (4 November 182814 July 1885) was a French Roman Catholic writer, who produced books and articles on philosophy, theology, and literature.
Life
Born at Lorient, in Brittany, he was the son of a lawyer who held posts of great impor ...
(1828-1885), writer
* Viktor Lazlo
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* Victor (1951 film), ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* Victor (1993 film), ...
(b. 1960), singer
* Rita Strohl (1865–1941), pianist and composer
* Jacques Vaché Jacques Vaché
Jacques Vaché (7 September 1895 – 6 January 1919) was a friend of André Breton, the founder of surrealism. Vaché was one of the chief inspirations behind the Surrealist movement. As Breton said:
:"''En littérature, je me suis ...
(1895–1919), writer and artist
Sailors
* Jean-Baptiste Bompard (1757–1842), took part in theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
as a privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
, later rose to the rank of admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
.
* François Joseph Bouvet
François Joseph Bouvet (1753–1832) was a French admiral.
Early life
Son of René Joseph Bouvet de Précourt, a captain in the service of the French East India Company and of the French Royal Navy under Suffren, François Joseph Bouvet wen ...
(1753–1832), vice admiral and Maritime Prefect, maritime prefect
* Jean-Baptiste Chaigneau (1769–1832), sailor, French consulate, consul in Cochinchina
* Pierre-François Forissier, b. 1951, admiral, Chief of Staff of the French Navy (2008–2011)
* Raymond Rallier du Baty (1881–1978), explorer of the Kerguelen islands.
Politics
* Henri Dupuy de Lôme (1816–1885), naval architect, chief designer of the ''French ship Napoléon (1850), Napoléon'', ''French ironclad Gloire, La Gloire'' and ''French submarine Gymnote (Q1), Gymnote'', which were breakthroughs in naval technology, also designed airships, National Assembly (France), deputy representingMorbihan
Morbihan ( , ; br, Mor-Bihan ) is a department in the administrative region of Brittany, situated in the northwest of France. It is named after the Morbihan (''small sea'' in Breton), the enclosed sea that is the principal feature of the coastli ...
, member of the French Academy of Sciences, Academy of Sciences, senator for life.
* Pierre-Paul Guieysse (1841–1914), Morbihan deputy, Minister of the Colonies.
* Jean-Yves Le Drian, b. 1947, former mayor of Lorient, former Morbihan deputy, current Minister of Defence
* Jules Simon (1814–1896), philosopher, List of Prime Ministers of France, President of the Council of Ministers, senator for life, member of ''l'Académie française''.
Sports
* Georges Eo, b. 1948, former association football, football player and manager *Christian Gourcuff
Christian Jean Gourcuff (born 5 April 1955) is a French professional Manager (association football), football manager and former Football player, player who was most recently the manager of Ligue 1 club FC Nantes, Nantes.
Club career
During his ...
, b. 1955, former manager of FC Lorient
Football Club Lorient Bretagne Sud (; commonly referred to FC Lorient or simply Lorient) is a French association football club based in Lorient, Brittany. The club was founded in 1926 and currently competes in Ligue 1, the top flight of French ...
*Yoann Gourcuff, b. 1986, son of the former, French national football team, international midfielder, currently plays for Stade Rennais F.C.
* Ronan Le Crom, b. 1974, goalkeeper
* Jérémy Morel, b. 1984, left-back for Olympique de Marseille
*Illan Meslier, b. 2000, goalkeeper for Leeds United F.C., Leeds United
Sciences
* Pierre Fatou (1878–1929), mathematician and astronomer * Nicole Marthe Le Douarin, Nicole Le Douarin, b. 1930, biologistOthers
* Jacques Andrieux (1917–2005), WWII fighter ace and Compagnon de la Libération. *Jacques Stosskopf
Jacques Stosskopf (27 November 1898 – 1 September 1944) held the post of deputy director of naval construction at the German-held Lorient U-boat arsenal, but was a member of the French Resistance and war hero killed by the Nazis.
Military care ...
(1898–1944), naval engineer, ''French Resistance, résistant''. Mistaken for being a traitor, in 1946 the submarine base was renamed "Base Ingénieur Général Stosskopf" in his honour.
International relations
Lorient is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Galway, Ireland * Vigo, Spain * Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Wirral, England, United Kingdom * Ventspils, Latvia * Ludwigshafen, Germany * České Budějovice, Czech Republic * Denizli, TurkeySee also
* Mississippi Company *FC Lorient
Football Club Lorient Bretagne Sud (; commonly referred to FC Lorient or simply Lorient) is a French association football club based in Lorient, Brittany. The club was founded in 1926 and currently competes in Ligue 1, the top flight of French ...
* Festival Interceltique de Lorient
* Arrondissement of Lorient
*Communes of the Morbihan department
* Raid on Lorient (1746)
References
;NotesExternal links
Official website
(in French)
Ville de Lorient et Festival Interceltique Images
*
See pictures on Antonio Mucherino's web site
Tourism office
(in French) {{Authority control Lorient, Subprefectures in France German Navy submarine bases Communes of Morbihan Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast