Kangxi emperor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third
 Before the Kangxi Emperor came to the throne, Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang (in the name of
Before the Kangxi Emperor came to the throne, Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang (in the name of
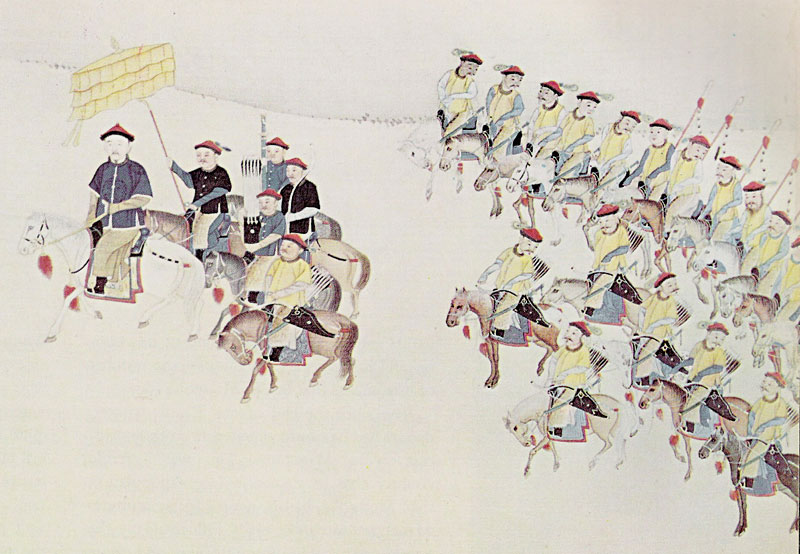
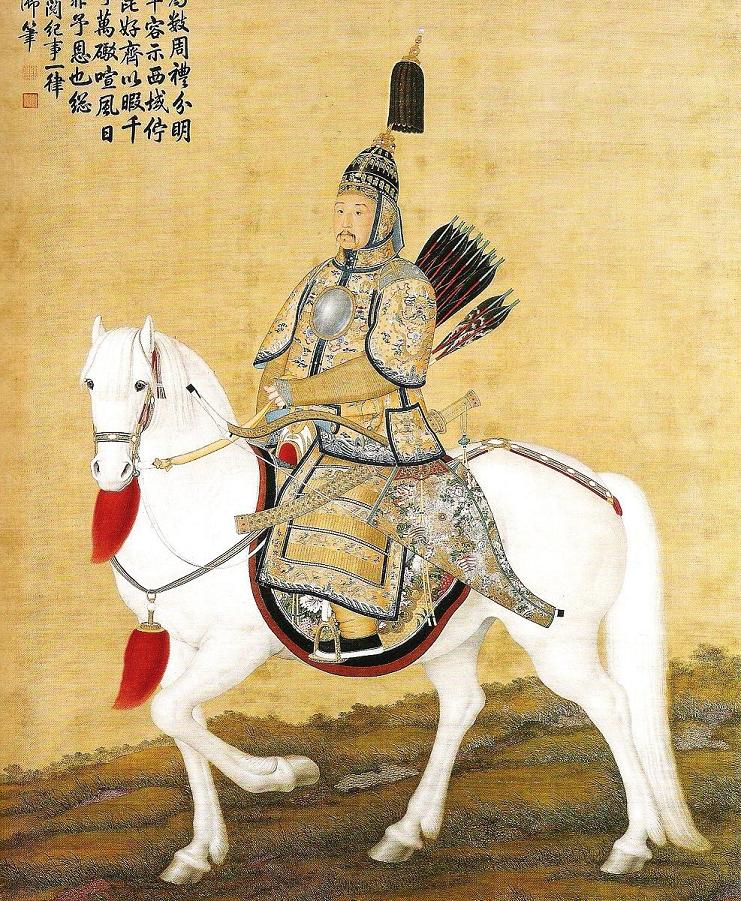
 The main army of the Qing Empire, the Eight Banners Army, was in decline under the Kangxi Emperor. It was smaller than it had been at its peak under
The main army of the Qing Empire, the Eight Banners Army, was in decline under the Kangxi Emperor. It was smaller than it had been at its peak under
 In the 1650s, the Qing Empire engaged the
In the 1650s, the Qing Empire engaged the
 The Outer
The Outer
 In 1700, some 20,000 Qiqihar Xibe were resettled in
In 1700, some 20,000 Qiqihar Xibe were resettled in
 The contents of the national treasury during the Kangxi Emperor's reign were:
:1668 (7th year of Kangxi): 14,930,000
The contents of the national treasury during the Kangxi Emperor's reign were:
:1668 (7th year of Kangxi): 14,930,000
emperor of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty (1636–1912) was a Manchu-led imperial Chinese dynasty and the last orthodox dynasty of China. It was officially founded in 1636 in what is now Northeast China, but only succeeded the Ming dynasty in China proper in 1644. Th ...
, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1722.
The Kangxi Emperor's reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history (although his grandson, the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
, had the longest period of ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' power, ascending as an adult and maintaining effective power until his death) and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. However, since he ascended the throne at the age of seven, actual power was held for six years by four regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
s and his grandmother, the Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang.
The Kangxi Emperor is considered one of China's greatest emperors. He suppressed the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
and assorted Mongol rebels in the North and Northwest to submit to Qing rule, and blocked Tsarist Russia on the Amur River, retaining Outer Manchuria.
The Kangxi Emperor's reign brought about long-term stability and relative wealth after years of war and chaos. He initiated the period known as the "Prosperous Era of Kangxi and Qianlong" or "High Qing", which lasted for several generations after his death. His court also accomplished such literary feats as the compilation of the '' Kangxi Dictionary'' and '' Quan Tangshi'' poetry anthology.
Early reign
Born on 4 May 1654 to theShunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
and Empress Xiaokangzhang in Jingren Palace, the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrific ...
, Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, the Kangxi Emperor was originally given the personal name
A personal name, or full name, in onomastic terminology also known as prosoponym (from Ancient Greek πρόσωπον / ''prósōpon'' - person, and ὄνομα / ''onoma'' - name), is the set of names by which an individual person is known ...
Xuanye (; Manchu transliteration: ''hiowan yei''). He was enthroned at the age of seven (or eight by East Asian age reckoning), on 7 February 1661. However, his era name "Kangxi", only started to be used on 18February 1662, the first day of the following lunar year.
Sinologist Herbert Giles, drawing on contemporary sources, described the Kangxi Emperor as "fairly tall and well proportioned, he loved all manly exercises, and devoted three months annually to hunting. Large bright eyes lighted up his face, which was pitted with smallpox."
 Before the Kangxi Emperor came to the throne, Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang (in the name of
Before the Kangxi Emperor came to the throne, Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang (in the name of Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
) had appointed the powerful men Sonin, Suksaha, Ebilun, and Oboi as regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
s. Sonin died after his granddaughter became Empress Xiaochengren, leaving Suksaha at odds with Oboi in politics. In a fierce power struggle, Oboi had Suksaha put to death and seized absolute power as sole regent. The Kangxi Emperor and the rest of the imperial court acquiesced to this arrangement.
In the spring of 1662, the regents ordered a Great Clearance in southern China that evacuated the entire population from the seacoast to counter a resistance movement started by Ming loyalists under the leadership of Taiwan-based Ming general Zheng Chenggong
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
, also titled Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
.
In 1669, the Kangxi Emperor had Oboi arrested with the help of his grandmother Grand Dowager Empress Xiaozhuang, who had raised him. and began taking personal control of the empire. He listed three issues of concern: flood control of the Yellow River; repair of the Grand Canal; the Revolt of the Three Feudatories in south China. The Grand Empress Dowager influenced him greatly and he took care of her himself in the months leading up to her death in 1688.
Kangxi's relatives from the Han Chinese Banner Tong 佟 clan of Fushun in Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmos ...
falsely claimed to be related to the Jurchen Manchu Tunggiya 佟佳 clan of Jilin, using this false claim to get themselves transferred to a Manchu banner in the reign of Kangxi emperor.
Military achievements
Army


 The main army of the Qing Empire, the Eight Banners Army, was in decline under the Kangxi Emperor. It was smaller than it had been at its peak under
The main army of the Qing Empire, the Eight Banners Army, was in decline under the Kangxi Emperor. It was smaller than it had been at its peak under Hong Taiji
Hong Taiji (28 November 1592 – 21 September 1643), also rendered as Huang Taiji and sometimes referred to as Abahai in Western literature, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizong of Qing, was the second khan of the Later Jin ...
and in the early reign of the Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
; however, it was larger than in the Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors' reigns. In addition, the Green Standard Army was still powerful with generals such as Tuhai, Fei Yanggu, Zhang Yong, Zhou Peigong, Shi Lang
Shi Lang (1621–1696), Marquis Jinghai, also known as Secoe or Sego, was a Chinese admiral who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties in the 17th century. He was the commander-in-chief of the Qing fleets which destroyed the power of Zheng Che ...
, Mu Zhan, Shun Shike and Wang Jingbao.
The main reason for this decline was a change in system between the Kangxi and Qianlong emperors' reigns. The Kangxi Emperor continued using the traditional military system implemented by his predecessors, which was more efficient and stricter. According to the system, a commander who returned from a battle alone (with all his men dead) would be put to death, and likewise for a foot soldier. This was meant to motivate both commanders and soldiers alike to fight valiantly in war because there was no benefit for the sole survivor in a battle.
By the Qianlong Emperor's reign, military commanders had become lax and the training of the army was deemed less important as compared to during the previous emperors' reigns.
Revolt of the Three Feudatories
After the Qing takeover of China in 1644, large parts of the south and west were given as fiefs to three Ming generals who aided the Qing; in 1673 the three feudatories were controlled byWu Sangui
Wu Sangui (; 8 June 1612 – 2 October 1678), courtesy name Changbai () or Changbo (), was a notorious Ming Dynasty military officer who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty in China. In Chinese ...
, Geng Jingzhong, and Shang Zhixin
Shang Zhixin (; 1636 – 1680) was a major figure in the early Qing Dynasty, known for his role in the Revolt of the Three Feudatories. He was Prince of Pingnan (平南王, "Prince who Pacifies the South"), inheriting his position from his father ...
. Going against the advice of most of his advisors, Kangxi attempted to force the feudal princes to give up their lands and retire to Manchuria, sparking a rebellion that lasted eight years. For years afterwards Kangxi ruminated on his mistakes and blamed himself in part for the loss of life during the revolt.
Wu Sangui's forces overran most of southwest China and he tried to ally himself with local generals such as Wang Fuchen. The Kangxi Emperor employed generals including Zhou Peigong and Tuhai to suppress the rebellion, and also granted clemency to common people caught up in the war. He intended to personally lead the armies to crush the rebels but his subjects advised him against it. The Kangxi Emperor used mainly Han Chinese Green Standard Army soldiers to crush the rebels while the Manchu Banners took a backseat. The revolt ended with victory for Qing forces in 1681.
Taiwan
In 1683, the naval forces of the Ming loyalists onTaiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
—organized under the Zheng dynasty
The House of Koxinga or the Zheng dynasty was the reigning family of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan. They played a significant role in the history of East Asia and Southeast Asia, particularly in the seventeenth century.
Names
In Chinese, ...
as the Kingdom of Tungning—were defeated off Penghu by 300-odd ships under the Qing admiral Shi Lang
Shi Lang (1621–1696), Marquis Jinghai, also known as Secoe or Sego, was a Chinese admiral who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties in the 17th century. He was the commander-in-chief of the Qing fleets which destroyed the power of Zheng Che ...
. Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
's grandson Zheng Keshuang
Zheng Keshuang, Prince of Yanping (; 13 August 1670 – 22 September 1707), courtesy name Shihong, art name Huitang, was the third and last ruler of the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan in the 17th century. He was the second son of Zheng Jing and a ...
surrendered Tungning a few days later and Taiwan became part of the Qing Empire. Zheng Keshuang moved to Beijing, joined the Qing nobility
The Qing dynasty (1636–1912) of China developed a complicated peerage system for royal and noble ranks.
Rule of inheritance
In principle, titles were downgraded one grade for each generation of inheritance.
* Direct imperial princes with ...
as the "Duke Haicheng" (), and was inducted into the Eight Banners as a member of the Han Plain Red Banner
The Plain Red Banner () was one of the Eight Banners (lower five Banners) of Manchu military and society organization during the Later Jin and Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial ...
. His soldiers—including the rattan-shield troops (, ''tengpaiying'')—were similarly entered into the Eight Banners, notably serving against Russian Cossacks at Albazin.
A score of Ming princes had joined the Zheng dynasty on Taiwan, including Prince Zhu Shugui of Ningjing and Prince Honghuan ( 朱弘桓), the son of Zhu Yihai. The Qing sent most of the 17 Ming princes still living on Taiwan back to mainland China, where they spent the rest of their lives. The Prince of Ningjing and his five concubines, however, committed suicide rather than submit to capture. Their palace was used as Shi Lang's headquarters in 1683, but he memorialized the emperor to convert it into a Mazu temple as a propaganda measure in quieting remaining resistance on Taiwan. The emperor approved its dedication as the Grand Matsu Temple
The Grand Matsu Temple,. & also known as the Datianhou or ,. is a temple to the Chinese Goddess Mazu, who is the Goddess of Sea and Patron Deity of fishermen, sailors and any occupations related to sea/ocean. The temple is located in the West Cen ...
the next year and, honoring the goddess Mazu for her supposed assistance during the Qing invasion, promoted her to "Empress of Heaven" ( ''Tianhou'') from her previous status as a "heavenly consort" ( ''Tianfei'')... Belief in Mazu remains so widespread on Taiwan that her annual celebrations can gather hundreds of thousands of people; she is sometimes even syncretized
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
with Guanyin
Guanyin () is a Bodhisattva associated with compassion. She is the East Asian representation of Avalokiteśvara ( sa, अवलोकितेश्वर) and has been adopted by other Eastern religions, including Chinese folk religion. Sh ...
and the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jews, Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Jose ...
.
The end of the rebel stronghold and capture of the Ming princes allowed the Kangxi Emperor to relax the Sea Ban
The Haijin () or sea ban was a series of related isolationism, isolationist policies in China restricting private maritime trading and coastal settlement during most of the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty. Despite official proclamations the M ...
and permit resettlement of the Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its c ...
and Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
coasts. The financial and other incentives to new settlers particularly drew the Hakka
The Hakka (), sometimes also referred to as Hakka Han, or Hakka Chinese, or Hakkas are a Han Chinese subgroup whose ancestral homes are chiefly in the Hakka-speaking provincial areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hun ...
, who would have continuous low-level conflict with the returning Punti people for the next few centuries.
Russia
 In the 1650s, the Qing Empire engaged the
In the 1650s, the Qing Empire engaged the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
in a series of border conflicts along the Amur River region, which concluded with the Qing gaining control of the area after the Siege of Albazin.
The Russians invaded the northern frontier again in the 1680s. A series of battles and negotiations culminated in the Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689, by which a border was agreed between Russia and China.
Mongolia
The Inner Mongolian Chahar leader Ligdan Khan, a descendant of Genghis Khan, opposed and fought against the Qing until he died of smallpox in 1634. Thereafter, the Inner Mongols under his son Ejei Khan surrendered to the Qing and he was given the title of Prince (Qin Wang, 親王). The Inner Mongolian nobility now became closely tied to the Qing royal family and intermarried with them extensively. Ejei Khan died in 1661 and was succeeded by his brother Abunai. After Abunai showed disaffection with Manchu Qing rule, he was placed under house arrest in 1669 in Shenyang and the Kangxi Emperor gave his title to his son Borni. Abunai bided his time then, with his brother Lubuzung, revolted against the Qing in 1675 during the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, with 3,000 Chahar Mongol followers joining in on the revolt. The revolt was put down within two months, the Qing defeating the rebels in battle on 20 April 1675, killing Abunai and all his followers. Their title was abolished, all Chahar Mongol royal males were executed even if they were born to Manchu Qing princesses, and all Chahar Mongol royal females were sold into slavery except the Manchu Qing princesses. The Chahar Mongols were then put under the direct control of the Qing Emperor unlike the other Inner Mongol leagues which maintained their autonomy. The Outer
The Outer Khalkha Mongols
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin ...
had preserved their independence, and only paid tribute to the Qing Empire. However, a conflict between the houses of Tümen Jasagtu Khan and Tösheetü Khan led to a dispute between the Khalkha and the Dzungars over the influence of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in maj ...
. In 1688, the Dzungar chief, Galdan Boshugtu Khan, attacked the Khalkha from the west and invaded their territory. The Khalkha royal families and the first Jebtsundamba Khutuktu crossed the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert ( Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast ...
and sought help from the Qing Empire in return for submission to Qing authority. In 1690, the Dzungars and Qing forces clashed at the Battle of Ulan Butung in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
, in which the Qing eventually emerged as the victor.
In 1696 and 1697 the Kangxi Emperor personally led campaigns against the Dzungars in the early Dzungar–Qing War. The western section of the Qing army defeated Galdan's forces at the Battle of Jao Modo and Galdan died in the following year.
Manchu Hoifan and Ula rebellion against the Qing
 In 1700, some 20,000 Qiqihar Xibe were resettled in
In 1700, some 20,000 Qiqihar Xibe were resettled in Guisui
Hohhot,; abbreviated zh, c=呼市, p=Hūshì, labels=no formerly known as Kweisui, is the capital of Inner Mongolia in the north of the People's Republic of China, serving as the region's administrative, economic and cultural center.''The Ne ...
, modern Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for ...
, and 36,000 Songyuan Xibe were resettled in Shenyang, Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmos ...
. The relocation of the Xibe from Qiqihar is believed by Liliya M. Gorelova to be linked to the Qing's annihilation of the Manchu clan Hoifan (Hoifa) in 1697 and the Manchu tribe Ula in 1703 after they rebelled against the Qing; both Hoifan and Ula were wiped out.
Tibet
In 1701, the Kangxi Emperor ordered the reconquest of Kangding and other border towns in westernSichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of th ...
that had been taken by the Tibetans. The Manchu forces stormed Dartsedo and secured the border with Tibet and the lucrative tea-horse trade.
The Tibetan ''desi'' (regent) Sangye Gyatso concealed the death of the 5th Dalai Lama
Ngawang Lobsang Gyatso (; ; 1617–1682) was the 5th Dalai Lama and the first Dalai Lama to wield effective temporal and spiritual power over all Tibet. He is often referred to simply as the Great Fifth, being a key religious and temporal leader ...
in 1682, and only informed the emperor in 1697. He moreover kept relations with Dzungar enemies of the Qing. All this evoked the great displeasure of the Kangxi Emperor. Eventually Sangye Gyatso was toppled and killed by the Khoshut
The Khoshut ( Mongolian: Хошууд,, qoşūd, ; literally "bannermen," from Middle Mongolian ''qosighu'' "flag, banner") are one of the four major tribes of the Oirat people. Originally, Khoshuuds were one of the Khorchin tribes in southeast ...
ruler Lha-bzang Khan in 1705. As a reward for ridding him of his old enemy the Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama (, ; ) is a title given by the Tibetan people to the foremost spiritual leader of the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" school of Tibetan Buddhism, the newest and most dominant of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. The 14th and current Dal ...
, the Kangxi Emperor appointed Lha-bzang Khan Regent of Tibet (). The Dzungar Khanate, a confederation of Oirat tribes based in parts of what is now Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, continued to threaten the Qing Empire and invaded Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
in 1717. They took control of Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhas ...
with a 6,000 strong army and killed Lha-bzang Khan. The Dzungars held on to the city for three years and at the Battle of the Salween River defeated a Qing army sent to the region in 1718. The Qing did not take control of Lhasa until 1720, when the Kangxi Emperor sent a larger expedition force there to defeat the Dzungars.
Muslims
Manchu emperor Kangxi incited anti-Muslim sentiment among the Mongols of Qinghai (Kokonor) in order to gain support against the Dzungar Oirat Mongol leaderGaldan
Erdeniin Galdan (1644–1697, mn, Галдан Бошигт хаан, , ), known as Galdan Boshugtu Khan (in Mongolian script: ) was a Choros Dzungar- Oirat Khan of the Dzungar Khanate. As fourth son of Erdeni Batur, founder of the Dzungar Kha ...
. Kangxi claimed that Chinese Muslims inside China such as Turkic Muslims in Qinghai (Kokonor) were plotting with Galdan
Erdeniin Galdan (1644–1697, mn, Галдан Бошигт хаан, , ), known as Galdan Boshugtu Khan (in Mongolian script: ) was a Choros Dzungar- Oirat Khan of the Dzungar Khanate. As fourth son of Erdeni Batur, founder of the Dzungar Kha ...
, who he falsely claimed converted to Islam. Kangxi falsely claimed that Galdan had spurned and turned his back on Buddhism and the Dalai Lama and that he was plotting to install a Muslim as ruler of China after invading it in a conspiracy with Chinese Muslims. Kangxi also distrusted Muslims of Turfan and Hami.
Chinese nobility
The Kangxi Emperor granted the title of Wujing Boshi ( 五經博士; ''Wǔjīng Bóshì'') to the descendants of Shao Yong, Zhu Xi, Zhuansun Shi, Ran family ( Ran Qiu, Ran Geng, Ran Yong), Bu Shang, Yan Yan (disciple of Confucius), and theDuke of Zhou
Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou (), commonly known as the Duke of Zhou (), was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting ...
's offspring.
Economic achievements
 The contents of the national treasury during the Kangxi Emperor's reign were:
:1668 (7th year of Kangxi): 14,930,000
The contents of the national treasury during the Kangxi Emperor's reign were:
:1668 (7th year of Kangxi): 14,930,000 tael
Tael (),"Tael" entry
at the The reasons for the declining trend in the later years of the Kangxi Emperor's reign were a huge expenditure on military campaigns and an increase in corruption. To fix the problem, the Kangxi Emperor gave Prince Yong (the future
 During his reign, the Kangxi Emperor ordered the compilation of a dictionary of
During his reign, the Kangxi Emperor ordered the compilation of a dictionary of
 In the early decades of the Kangxi Emperor's reign, Jesuits played a large role in the imperial court. With their knowledge of
In the early decades of the Kangxi Emperor's reign, Jesuits played a large role in the imperial court. With their knowledge of


 A prolonged struggle between various princes emerged during the Kangxi Emperor's reign over who should inherit the throne – the Nine Lords' War ().
In 1674 the Kangxi Emperor's first spouse, Empress Xiaochengren, died while giving birth to his second surviving son Yinreng, who at the age of two was named
A prolonged struggle between various princes emerged during the Kangxi Emperor's reign over who should inherit the throne – the Nine Lords' War ().
In 1674 the Kangxi Emperor's first spouse, Empress Xiaochengren, died while giving birth to his second surviving son Yinreng, who at the age of two was named  In 1712, during the Kangxi Emperor's last inspection tour of the south, Yinreng, who was put in charge of state affairs during his father's absence, tried to vie for power again with his supporters. He allowed an attempt at forcing the Kangxi Emperor to abdicate when his father returned to
In 1712, during the Kangxi Emperor's last inspection tour of the south, Yinreng, who was put in charge of state affairs during his father's absence, tried to vie for power again with his supporters. He allowed an attempt at forcing the Kangxi Emperor to abdicate when his father returned to
 The Kangxi Emperor was a great consolidator of the
The Kangxi Emperor was a great consolidator of the
at the The reasons for the declining trend in the later years of the Kangxi Emperor's reign were a huge expenditure on military campaigns and an increase in corruption. To fix the problem, the Kangxi Emperor gave Prince Yong (the future
Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
) advice on how to make the economy more efficient.
Cultural achievements
 During his reign, the Kangxi Emperor ordered the compilation of a dictionary of
During his reign, the Kangxi Emperor ordered the compilation of a dictionary of Chinese character
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as '' kan ...
s, which became known as the Kangxi Dictionary. This was seen as an attempt by the emperor to gain support from the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
scholar-bureaucrats, as many of them initially refused to serve him and remained loyal to the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
. However, by persuading the scholars to work on the dictionary without asking them to formally serve the Qing imperial court, the Kangxi Emperor led them to gradually taking on greater responsibilities until they were assuming the duties of state officials.
In 1705, on the Kangxi Emperor's order, a compilation of Tang poetry
Tang poetry () refers to poetry written in or around the time of or in the characteristic style of China's Tang dynasty, (June 18, 618 – June 4, 907, including the 690–705 reign of Wu Zetian) and/or follows a certain style, often considered as ...
, the Quan Tangshi, was produced.
The Kangxi Emperor also was interested in Western technology and wanted to import them to China. This was done through Jesuit missionaries, such as Ferdinand Verbiest
Father Ferdinand Verbiest (9 October 1623 – 28 January 1688) was a Flemish Jesuit missionary in China during the Qing dynasty. He was born in Pittem near Tielt in the County of Flanders (now part of Belgium). He is known as Nan Huairen () in Chi ...
, whom the Kangxi Emperor frequently summoned for meetings, or Karel Slavíček, who made the first precise map of Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
on the emperor's order.
From 1711 to 1723, Matteo Ripa, an Italian priest sent to China by the Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples
A congregation is a large gathering of people, often for the purpose of worship.
Congregation may also refer to:
* Church (congregation), a Christian organization meeting in a particular place for worship
* Congregation (Roman Curia), an adminis ...
, worked as a painter and copper-engraver at the Qing court. In 1723, he returned to Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
from China with four young Chinese Christians, in order to groom them to become priests and send them back to China as missionaries. This marked the beginning of the Collegio dei Cinesi, sanctioned by Pope Clement XII
Pope Clement XII ( la, Clemens XII; it, Clemente XII; 7 April 16526 February 1740), born Lorenzo Corsini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 July 1730 to his death in February 1740.
Clement presided over the ...
to help the evangelization of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
in China. This Chinese Institute was the first school of Sinology
Sinology, or Chinese studies, is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of China primarily through Chinese philosophy, language, literature, culture and history and often refers to Western scholarship. Its origin "may be traced to t ...
in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
, which would later develop to become the Istituto Orientale and the present day Naples Eastern University.
The Kangxi Emperor was also the first Chinese emperor to play a western musical instrument. Thomas Pereira
Thomas Pereira or Tomás Pereira (1 November 1645 – 1708), also known as Tomé Pereira, was a Portuguese Jesuit, mathematician and scientist who worked as a missionary in Qing China.
Pereira was born in Vila Nova de Famalicão. He arrived in ...
taught him how to play the harpsichord, and he employed Karel Slavíček as court musician. Slavíček was playing Spinet
A spinet is a smaller type of harpsichord or other keyboard instrument, such as a piano or organ.
Harpsichords
When the term ''spinet'' is used to designate a harpsichord, typically what is meant is the ''bentside spinet'', described in this s ...
; later the emperor would play on it himself. China's famed blue and white porcelain probably reached its zenith during the Kangxi Emperor's reign.
Christianity
 In the early decades of the Kangxi Emperor's reign, Jesuits played a large role in the imperial court. With their knowledge of
In the early decades of the Kangxi Emperor's reign, Jesuits played a large role in the imperial court. With their knowledge of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
, they ran the imperial observatory. Jean-François Gerbillon and Thomas Pereira
Thomas Pereira or Tomás Pereira (1 November 1645 – 1708), also known as Tomé Pereira, was a Portuguese Jesuit, mathematician and scientist who worked as a missionary in Qing China.
Pereira was born in Vila Nova de Famalicão. He arrived in ...
served as translators for the negotiations of the Treaty of Nerchinsk. The Kangxi Emperor was grateful to the Jesuits for their contributions, the many languages they could interpret, and the innovations they offered his military in gun manufacturingMantienne, p. 180 and artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieg ...
, the latter of which enabled the Qing Empire to conquer the Kingdom of Tungning.''Les Missions Etrangeres'', p. 83
The Kangxi Emperor was also fond of the Jesuits' respectful and unobtrusive manner; they spoke the Chinese language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the ...
well, and wore the silk robes of the elite.Manteigne, p. 178 In 1692, when Pereira requested tolerance for Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, the Kangxi Emperor was willing to oblige, and issued the Edict of Toleration, which recognized Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, barred attacks on their churches, and legalized their missions and the practice of Christianity by the Chinese people
The Chinese people or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.
Chinese people are known as Zhongguoren () or as Huaren () by speakers of sta ...
.
However, controversy arose over whether Chinese Christians could still take part in traditional Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
ceremonies and ancestor worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune o ...
, with the Jesuits arguing for tolerance and the Dominicans taking a hard-line against foreign " idolatry". The Dominican position won the support of Pope Clement XI
Pope Clement XI ( la, Clemens XI; it, Clemente XI; 23 July 1649 – 19 March 1721), born Giovanni Francesco Albani, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 23 November 1700 to his death in March 1721.
Clement XI w ...
, who in 1705 sent Charles-Thomas Maillard de Tournon as his representative to the Kangxi Emperor, to communicate the ban on Chinese rites. Through de Tournon, the Pope insisted on sending his own representative to Beijing to oversee Jesuit missionaries in China. Kangxi refused, wanting to keep missionary activities in China under his final oversight, managed by one of the Jesuits who had been living in Beijing for years.
On 19 March 1715, Pope Clement XI issued the papal bull ''Ex illa die'', which officially condemned Chinese rites. In response, the Kangxi Emperor officially forbade Christian missions in China, as they were "causing trouble".
Succession disputes


 A prolonged struggle between various princes emerged during the Kangxi Emperor's reign over who should inherit the throne – the Nine Lords' War ().
In 1674 the Kangxi Emperor's first spouse, Empress Xiaochengren, died while giving birth to his second surviving son Yinreng, who at the age of two was named
A prolonged struggle between various princes emerged during the Kangxi Emperor's reign over who should inherit the throne – the Nine Lords' War ().
In 1674 the Kangxi Emperor's first spouse, Empress Xiaochengren, died while giving birth to his second surviving son Yinreng, who at the age of two was named crown prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife ...
– a Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
custom, to ensure stability during a time of chaos in the south. Although the Kangxi Emperor left the education of several of his sons to others, he personally oversaw the upbringing of Yinreng, grooming him to be a perfect successor. Yinreng was tutored by the mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
Wang Shan, who remained devoted to him, and spent the later years of his life trying to persuade the Kangxi Emperor to restore Yinreng as the crown prince.
Yinreng proved to be unworthy of the succession despite his father showing favoritism towards him. He was said to have beaten and killed his subordinates, and was alleged to have had sexual relations with one of his father's concubines, which was deemed incest
Incest ( ) is human sexual activity between family members or close relatives. This typically includes sexual activity between people in consanguinity (blood relations), and sometimes those related by affinity ( marriage or stepfamily), ado ...
and a capital offence. Yinreng also purchased young children from Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its c ...
to satisfy his pedophilia
Pedophilia ( alternatively spelt paedophilia) is a psychiatric disorder in which an adult or older adolescent experiences a primary or exclusive sexual attraction to prepubescent children. Although girls typically begin the process of pubert ...
c pleasure. In addition, Yinreng's supporters, led by Songgotu, gradually formed a "Crown Prince Party" (太子黨), that aimed to help Yinreng get the throne as soon as possible, even if it meant using unlawful methods.
Over the years, the Kangxi Emperor kept constant watch over Yinreng and became aware of his son's many flaws, while their relationship gradually deteriorated. In 1707, the emperor decided that he could no longer tolerate Yinreng's behavior, which he partially mentioned in the imperial edict as "never obeying ancestors' virtues, never obliged to my order, only doing inhumanity and devilry, only showing maliciousness and lust", and decided to strip Yinreng of his position as crown prince. The Kangxi Emperor placed his oldest surviving son, Yinzhi, in charge of overseeing Yinreng's house arrest
In justice and law, house arrest (also called home confinement, home detention, or, in modern times, electronic monitoring) is a measure by which a person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted, if ...
. Yinzhi, an unfavored Shu son, knowing he had no chance of being selected, recommended the eighth prince, Yinsi, and requested his father to order Yinreng's execution. The Kangxi Emperor was enraged and stripped Yinzhi of his titles. The emperor then commanded his subjects to cease debating the succession issue, but despite this and attempts to reduce rumours and speculation as to who the new crown prince might be, the imperial court's daily activities were disrupted. Yinzhi's actions caused the Kangxi Emperor to suspect that Yinreng might have been framed, so he restored Yinreng as crown prince in 1709, with the support of the 4th and 13th princes, and on the excuse that Yinreng had previously acted under the influence of mental illness.
 In 1712, during the Kangxi Emperor's last inspection tour of the south, Yinreng, who was put in charge of state affairs during his father's absence, tried to vie for power again with his supporters. He allowed an attempt at forcing the Kangxi Emperor to abdicate when his father returned to
In 1712, during the Kangxi Emperor's last inspection tour of the south, Yinreng, who was put in charge of state affairs during his father's absence, tried to vie for power again with his supporters. He allowed an attempt at forcing the Kangxi Emperor to abdicate when his father returned to Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
. However, the emperor received news of the planned coup d'etat, and was so angry that he deposed Yinreng and placed him under house arrest again. After the incident, the emperor announced that he would not appoint any of his sons as crown prince for the remainder of his reign. He stated that he would place his Imperial Valedictory Will inside a box in the Palace of Heavenly Purity, which would only be opened after his death.
Seeing that Yinreng was completely disavowed, Yinsi and some other princes turned to support the 14th prince, Yinti, while the 13th prince supported Yinzhen. They formed the so-called "Eighth Lord Party" () and "Fourth Lord Party" ().
Death and succession
Following the deposition of the crown prince, the Kangxi Emperor implemented groundbreaking changes in the political landscape. The 13th prince, Yinxiang, was placed underhouse arrest
In justice and law, house arrest (also called home confinement, home detention, or, in modern times, electronic monitoring) is a measure by which a person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted, if ...
as well for cooperating with Yinreng. The eighth prince Yinsi was stripped of all his titles and only had them restored years later. The 14th prince Yinti, whom many considered to be the most likely candidate to succeed the Kangxi Emperor, was sent on a military campaign during the political conflict. Yinsi, along with the ninth and tenth princes, Yintang and Yin'e, pledged their support to Yinti.
In the evening of 20 December 1722 before his death, the Kangxi Emperor called seven of his sons to assemble at his bedside. They were the third, fourth, eighth, ninth, tenth, sixteenth and seventeenth princes. After the Kangxi Emperor died, Longkodo announced that the emperor had selected the fourth prince, Yinzhen, as the new emperor. Yinzhen ascended to the throne and became known as the Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
. The Kangxi Emperor was entombed at the Eastern Tombs in Zunhua, Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
.
A legend concerning the Kangxi Emperor's will states that he chose Yinti as his heir, but Yinzhen forged the will in his own favour. It has, however, long been refuted by serious historians. Yinzhen, later the Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
, has attracted many rumours, and some novel-like private books claim he did not die of illness but was assassinated by a swordswoman, Lü Siniang (), the granddaughter of Lü Liuliang, though this is never treated seriously by scholars.
Personality and achievements
 The Kangxi Emperor was a great consolidator of the
The Kangxi Emperor was a great consolidator of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. The transition from the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
to the Qing was a cataclysm whose central event was the fall of the capital Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
to the peasant rebels led by Li Zicheng
Li Zicheng (22 September 1606 – 1645), born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-liv ...
, then to the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
s in 1644, and the installation of the five-year-old Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
on their throne. By 1661, when the Shunzhi Emperor died and was succeeded by the Kangxi Emperor, the Qing conquest of China proper was almost complete. Leading Manchus were already using Chinese institutions and mastering Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
ideology, while maintaining Manchu culture among themselves. The Kangxi Emperor completed the conquest, suppressed all significant military threats and revived the central government system inherited from the Ming with important modifications.
The Kangxi Emperor was a workaholic, rising early and retiring late, reading and responding to numerous memorials
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of a ...
every day, conferring with his councilors and giving audiences – and this was in normal times; in wartime, he might be reading memorials from the warfront until after midnight or even, as with the Dzungar conflict, away on campaign in person.
The Kangxi Emperor devised a system of communication that circumvented the scholar-bureaucrats, who had a tendency to usurp the power of the emperor. This Palace Memorial System involved the transfer of secret messages between him and trusted officials in the provinces, where the messages were contained in locked boxes that only he and the official had access to. This started as a system for receiving uncensored extreme-weather reports, which the emperor regarded as divine comments on his rule. However, it soon evolved into a general-purpose secret "news channel." Out of this emerged a Grand Council, which dealt with extraordinary, especially military, events. The council was chaired by the emperor and manned by his more elevated Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
and Manchu household staff. From this council, the mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
civil servants were excluded – they were left only with routine administration.
The Kangxi Emperor managed to woo the Confucian intelligentsia into co-operating with the Qing government, despite their deep reservations about Manchu rule and loyalty to the Ming. He appealed to this very sense of Confucian values, for instance, by issuing the Sacred Edict
In 1670, when the Kangxi Emperor of China's Qing dynasty was sixteen years old, he issued the Sacred Edict (), consisting of sixteen maxims, each seven characters long, to instruct the average citizen in the basic principles of Confucian orthodoxy ...
in 1670. He encouraged Confucian learning and made sure that the civil service examinations were held every three years even during times of stress. When some scholars, out of loyalty to the Ming, refused to take the exams, he hit upon the expedient of a special exam to be taken by nomination. He personally sponsored the writing of the Ming Official History, the Kangxi Dictionary, a phrase-dictionary, a vast encyclopedia and an even vaster compilation of Chinese literature. To promote his image as a "sage ruler," he appointed Manchu and Chinese tutors with whom he studied the Confucian classics and worked intensively on Chinese calligraphy.
In the one military campaign in which he actively participated, against the Dzungar Mongols, the Kangxi Emperor showed himself an effective military commander. According to Finer, the emperor's own written reflections allow one to experience "how intimate and caring was his communion with the rank-and-file, how discriminating and yet masterful his relationship with his generals".
As a result of the scaling down of hostilities as peace returned to China after the Manchu conquest, and also as a result of the ensuing rapid increase of population, land cultivation and therefore tax revenues based on agriculture, the Kangxi Emperor was able first to make tax remissions, then in 1712 to freeze the land tax and corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid, forced labour, that is intermittent in nature lasting for limited periods of time: typically for only a certain number of days' work each year.
Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state for the purposes of ...
altogether, without embarrassing the state treasury (although the dynasty eventually suffered from this fiscal policy).Finer (1997), pp. 1156–7.
Family
Empress * Empress Xiaochengren, of the Heseri clan (孝誠仁皇后 赫舍里氏; 3 February 1654 – 6 June 1674) ** Chenghu (承祜; 4 January 1670 – 3 March 1672), second son ** Yunreng, Prince Limi of the First Rank (理密親王 允礽; 6 June 1674 – 27 January 1725), seventh (second) son * Empress Xiaozhaoren, of theNiohuru
The Niohuru (Manchu: ; in Manchu) were a prominent Manchu clan during the Qing dynasty. The clan had inhabited the Changbai Mountains since as early as the Liao dynasty. The clan was well known during the Qing dynasty for producing a variety o ...
clan (孝昭仁皇后 鈕祜祿氏; 1659 – 18 March 1678), second cousin
* Empress Xiaoyiren of the Tunggiya clan (孝懿仁皇后 佟佳氏; d. 24 August 1689), first cousin
** Eighth Daughter (13 July 1683 – 6 August 1683)
** Miscarriage (August 1689)
* Empress Xiaogongren of the Uya clan (孝恭仁皇后 烏雅氏; 28 April 1660 – 25 June 1723)
** Yinzhen, the Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name =
, posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi ()
, temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung ()
, house = Aisin Gioro ...
(世宗 胤禛; 13 December 1678 – 8 October 1735), 11th (fourth) son
** ''Yinzuo'' (胤祚; 5 March 1680 – 15 June 1685), 14th (sixth) son
** ''Seventh daughter'' (5 July 1682 – September 1682)
** Princess Wenxian of the First Rank (固倫溫憲公主; 10 November 1683 – August/September 1702), ninth daughter
*** Married Shun'anyan (舜安顏; d. 1724) of the Manchu Tunggiya clan in October/November 1700.
** ''12th daughter'' (14 June 1686 – February/March 1697)
** Yunti, Prince Xunqin of the Second Rank (恂勤郡王 允禵; 10 February 1688 – 16 February 1755), 23rd (14th) son
Imperial Noble Consort
* Imperial Noble Consort Quehui, of the Tunggiya clan (愨惠皇貴妃 佟佳氏; September/October 1668 – 24 April 1743), first cousin
* Imperial Noble Consort Jingmin, of the Janggiya clan (敬敏皇貴妃 章佳氏; d. 20 August 1699)
** Yinxiang, Prince Yixian of the First Rank (怡賢親王 胤祥; 16 November 1686 – 18 June 1730), 22nd (13th) son
** Princess Wenke of the Second Rank (和碩溫恪公主; 31 December 1687 – 27 July 1709), 13th daughter
*** Married Cangjin (蒼津) of the Onnigud Borjigit clan in August/September 1706
** Princess Dunke of the Second Rank (和碩敦恪公主; 3 February 1691 – 2 January 1710), 15th daughter
*** Married Dorji (多爾濟; d. 1720) of the Khorchin Borjigit clan in January/February 1709, and had issue (one daughter)
* Imperial Noble Consort Dunyi, of the Gūwalgiya clan (惇怡皇貴妃 瓜爾佳氏; 3 December 1683 – 30 April 1768).
** ''18th daughter'' (17 November 1701 – November 1701)
Noble Consort
* Noble Consort Wenxi, of the Niohuru
The Niohuru (Manchu: ; in Manchu) were a prominent Manchu clan during the Qing dynasty. The clan had inhabited the Changbai Mountains since as early as the Liao dynasty. The clan was well known during the Qing dynasty for producing a variety o ...
clan (溫僖貴妃 鈕祜祿氏; 14 February 1661 – 19 December 1694), second cousin
** Yun'e, Duke of the Second Rank (輔國公 允䄉; 28 November 1683 – 18 October 1741), 18th (tenth) son
** ''11th daughter'' (24 October 1685 – June/July 1686)
Consort
* Consort Hui, of the Khorchin Borjigit clan (慧妃 博爾濟吉特氏; d. 30 May 1670), first cousin twice removed
* Consort Hui, of the Ula Nara clan (惠妃 葉赫那拉氏; d. 1 May 1732).
** ''Chengqing'' (承慶; 21 March 1670 – 26 May 1671), third son
** Yunzhi, Prince of the Fourth Rank (貝子 允禔; 12 March 1672 – 7 January 1735), fifth (first) son
* Consort Yi, of the Gorolo clan (宜妃 郭絡羅氏; 1660 – 2 October 1733)
** Yunqi, Prince Hengwen of the First Rank (恆溫親王 允祺; 5 January 1680 – 10 July 1732), 13th (fifth) son
** Yuntang, Prince of the Fourth Rank (貝子 允禟; 17 October 1683 – 22 September 1726), 17th (ninth) son
** ''Yinzi'' (胤禌; 8 June 1685 – 22 August 1696), 20th (11th) son
* Consort Rong, of the Magiya clan (榮妃 馬佳氏; d. 26 April 1727)
** ''Chengrui'' (承瑞; 5 November 1667 – 10 July 1670), first son
** ''Saiyinchahun'' (賽音察渾; 24 January 1672 – 6 March 1674), fourth son
** Princess Rongxian of the First Rank (固倫榮憲公主; 20 June 1673 – 29 May 1728), third daughter
*** Married Örgen (烏爾袞; d. 1721) of the Barin Borjigit clan in June/July 1691 and had issue (a son)
** ''Changhua'' (長華; 11 May 1674), sixth son
** ''Changsheng'' (長生; 10 September 1675 – 27 April 1677), eighth son
** Yunzhi, Prince Chengyin of the Second Rank (誠隱郡王 允祉; 23 March 1677 – 10 July 1732), tenth (third) son
* Consort Ping __NOTOC__
Consort may refer to:
Music
* "The Consort" (Rufus Wainwright song), from the 2000 album ''Poses''
* Consort of instruments, term for instrumental ensembles
* Consort song (musical), a characteristic English song form, late 16th–earl ...
, of the Hešeri
Hešeri (Chinese: 赫舍里; Pinyin: Hesheli; Manchu: ''Hešeri''), is a clan of Manchu nobility with Jianzhou Jurchens roots, originally hailing from the area which is now the modern Chinese provinces of Jilin and Liaoning. It was once one of t ...
clan (平妃 赫舍里氏; d. 18 July 1696)
** ''Yinji'' (胤禨; 23 February 1691 – 30 March 1691), 24th son
* Consort Liang
Consort Liang (梁貴人, personal name unknown) (62(?)-83?), posthumous title Empress Gonghuai (恭懷皇后, literally, "empress of reverent recollection"), was an imperial consort to Emperor Zhang of Han. She gave birth to his son Liu Zhao (劉 ...
, of the Wei clan (良妃 衛氏; 1662 – 29 December 1711).
** Yunsi, Prince Lian of the First Rank (廉親王 允禩; 29 March 1681 – 5 October 1726), 16th (eighth) son
* Consort Xuan, of the Khorchin Borjigit clan (宣妃 博爾濟吉特氏; d. 12 September 1736), third cousin, personal name Chenglian (成蓮)
* Consort Cheng, of the Daigiya clan (成妃 戴佳氏; d. 18 December 1740)
** Yunyou, Prince Chundu of the First Rank (淳度親王 允佑; 19 August 1680 – 18 May 1730), 15th (seventh) son
* Consort Shunyimi, of the Wang clan (順懿密妃 王氏; d. 19 November 1744)
** Yunxu, Prince Yuke of the Second Rank (愉恪郡王 允禑; 24 December 1693 – 8 March 1731), 25th (15th) son
** Yunlu, Prince Zhuangke of the First Rank (莊恪親王 允祿; 28 July 1695 – 20 March 1767), 26th (16th) son
** ''Yinxie'' (胤祄; 15 May 1701 – 17 October 1708), 28th (18th) son
* Consort Chunyuqin, of the Chen clan (純裕勤妃 陳氏; d. 12 January 1754)
** Yunli, Prince Guoyi of the First Rank (果毅親王 允禮; 24 March 1697 – 21 March 1738), 27th (17th) son
* Consort Ding, of the Wanlioha clan (定妃 萬琉哈氏; January/February 1661 – 24 May 1757).
** Yuntao, Prince Lüyi of the First Rank (履懿親王 允祹; 18 January 1686 – 1 September 1763), 21st (12th) son
Imperial Concubine
* Imperial Concubine An, of the Li clan (安嬪 李氏)
* Imperial Concubine Jing, of the Wanggiya clan (敬嬪 王佳氏)
* Imperial Concubine Duan, of the Dong clan (端嬪 董氏; d. 1702)
** ''Second daughter'' (17 April 1671 – March/April 1673)
* Imperial Concubine Xi, of the Hešeri
Hešeri (Chinese: 赫舍里; Pinyin: Hesheli; Manchu: ''Hešeri''), is a clan of Manchu nobility with Jianzhou Jurchens roots, originally hailing from the area which is now the modern Chinese provinces of Jilin and Liaoning. It was once one of t ...
clan (僖嬪 赫舍里氏; d. 31 October 1702)
* Imperial Concubine Tong of the Ula Nara clan (通嬪 那拉氏; 1664 – 1 August 1744).
** Princess Chunque of the First Rank (固倫純慤公主; 20 March 1685 – 22 April 1710), tenth daughter
*** Married Ts'ering (策棱; d. 1750) of the Khalkha Borjigit clan in June/July 1706, and had issue (one son)
* Imperial Concubine Xiang of the Gao clan (襄嬪 高氏; d. 14 August 1746).
** ''Yinji'' (胤禝; 25 October 1702 – 28 March 1704), 29th (19th) son
** ''19th daughter'' (30 March 1703 – February/March 1705)
** Yunyi, Prince Jianjing of the Third Rank (簡靖貝勒 允禕; 1 September 1706 – 30 June 1755), 30th (20th) son
* Imperial Concubine Jin, of the Sehetu clan (謹嬪 色赫圖氏; 2 August 1682 – 23 April 1739)
** Yunhu, Prince Gongqin of the Third Rank (恭勤貝勒 允祜; 10 January 1712 – 12 February 1744), 32nd (22nd) son
* Imperial Concubine Jing, of the Shi clan (靜嬪 石氏; 13 December 1689 – 10 July 1758)
** Yunqi, Prince Cheng of the Third Rank (誠貝勒 允祁; 14 January 1714 – 31 August 1785), 33rd (23rd) son
* Imperial Concubine Xi, of the Chen clan (熙嬪 陳氏; April/May 1690 – 1 February 1737)
** Yunxi, Prince Shenjing of the Second Rank (慎靖郡王 允禧; 27 February 1711 – 26 June 1758), 31st (21st) son
* Imperial Concubine Mu, of the Chen clan (穆嬪 陳氏; d. 1727)
** Yunbi, Prince Xianke of the First Rank (𫍯恪親王 允秘; 5 July 1716 – 3 December 1773), 34th (24th) son
** ''Yinyuan'' (胤禐; 2 March 1718), 35th son
Noble Lady
* Noble Lady Yi, of the Yi clan (伊貴人 易氏; d. 1728)
* Noble Lady Bu, of the Joogiya clan (布貴人 兆佳氏; d. 21 February 1717)
** Princess Duanjing of the Second Rank (和碩端靜公主; 9 June 1674 – March/April 1710), fifth daughter
*** Married Ga'erzang (噶爾臧; 1675–1722) of the Kharchin Ulanghan (烏梁罕) clan in November/December 1692, and had issue (one daughter)
* Noble Lady, of the Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
clan (貴人 那拉氏)
** ''Wanfu'' (萬黼; 4 December 1675 – 11 March 1679), ninth son
** ''Yinzan'' (胤禶; 10 April 1679 – 30 April 1680), 12th son
* Noble Lady, of the Gorolo clan (貴人 郭絡羅氏)
** Princess Kejing of the First Rank (固倫恪靖公主; 4 July 1679 – March/April 1735), sixth daughter
*** Married Dondob Dorji (敦多布多爾濟; d. 1743) of the Khalkha Borjigit clan in December 1697 or January 1698 and had issue (three sons)
** ''Yinju'' (胤䄔; 13 September 1683 – 17 July 1684), 19th son
* Noble Lady, of the Yuan clan (貴人 袁氏; d. 25 September 1719)
** Princess Quejing of the Second Rank (和碩愨靖公主; 16 January 1690 – 1736), 14th daughter
*** Married Sun Chengyun (孫承運; d. 1719) in 1706
Mistress
* Mistress, of the Zhang clan (張氏)
** ''First daughter'' (23 December 1668 – November 1671)
** ''Fourth daughter'' (16 March 1674 – January/February 1679)
* Mistress, of the Wang clan (王氏)
** ''16th daughter'' (27 November 1695 – October/November 1707)
* Mistress, of the Liu clan (劉氏)
** ''17th daughter'' (12 January 1699 – December 1700 or January 1701)
* Mistress, of the Niohuru
The Niohuru (Manchu: ; in Manchu) were a prominent Manchu clan during the Qing dynasty. The clan had inhabited the Changbai Mountains since as early as the Liao dynasty. The clan was well known during the Qing dynasty for producing a variety o ...
clan (鈕祜祿氏)
** ''20th daughter'' (20 November 1708 – January/February 1709)
Ancestry
Popular culture
Fiction
* ''Kangxi Dadi'' (康熙大帝; ''The Great Kangxi Emperor''), ahistorical novel
Historical fiction is a literary genre in which the plot takes place in a setting related to the past events, but is fictional. Although the term is commonly used as a synonym for historical fiction literature, it can also be applied to other t ...
by Er Yuehe which romanticises the Kangxi Emperor's life.
*'' The Deer and the Cauldron'' (鹿鼎記), a ''wuxia
( ), which literally means "martial heroes", is a genre of Chinese fiction concerning the adventures of martial artists in ancient China. Although is traditionally a form of historical fiction, its popularity has caused it to be adapted f ...
'' novel by Louis Cha
Louis Cha Leung-yung (; 10 March 1924 – 30 October 2018), better known by his pen name Jin Yong (), pronounced "Gum Yoong" in Cantonese, was a Chinese wuxia ("martial arts and chivalry") novelist and essayist who co-founded the Hong Kong dail ...
. In the story, by coincidence, the Kangxi Emperor and the protagonist, Wei Xiaobao, become close friends in their childhood. Wei helps the emperor consolidate his rule over the Qing Empire and plays an important role in affecting how significant historical events during the Kangxi era unfold.
*'' Qijian Xia Tianshan'' (七劍下天山; ''Seven Swords Descend from Mount Heaven''), a ''wuxia'' novel by Liang Yusheng. In the story, the Kangxi Emperor discovers that his father, the Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
, has become a monk in a monastery on Mount Wutai
Mount Wutai, also known by its Chinese name Wutaishan and as is a sacred Buddhist site at the headwaters of the Qingshui in Shanxi Province, China. Its central area is surrounded by a cluster of flat-topped peaks roughly corresponding to the ...
. He orders a close aide to kill his father in order to consolidate power, and attempts to erase evidence of the murder later.
Film and television
Video games
* '' Age of Empires III: The Asian Dynasties'': The Kangxi Emperor is featured as the Chinese leader in thisreal-time strategy
Real-time strategy (RTS) is a subgenre of strategy video games that do not progress incrementally in turns, but allow all players to play simultaneously, in "real time". By contrast, in turn-based strategy (TBS) games, players take turns to pla ...
game.
* '' Call Me Emperor'': Kangxi is featured as a minister in this Strategy Click-RPG game.
See also
* Chinese emperors family tree (late) *Kangxi Tongbao
Kangxi Tongbao () refers to an inscription used on Chinese cash coins produced during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty. Under the Kangxi Emperor the weights and standards of the brass cash coins changed several times ...
Notes
References
Bibliography and further reading
* * . * Finer, S. E. (1997). ''The History of Government from the Earliest Times''. (three-volume set, hardback) * * * * . * . * * . * * Ch. 3, "Kangxi's Consolidation," inJonathan D. Spence
Jonathan Dermot Spence (11 August 1936 – 25 December 2021) was an English-born American historian, sinologist, and writer who specialized in Chinese history. He was Sterling Professor of History at Yale University from 1993 to 2008. His mos ...
, '' The Search for Modern China'' (New York: Norton; 3rd, 2013), pp. 48–71.
*
*
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Kangxi Emperor 1654 births 1722 deaths 17th-century Chinese monarchs 18th-century Chinese monarchs Child rulers from Asia Qing dynasty emperors Shunzhi Emperor's sons