Kandas–Ramoaaina Languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a
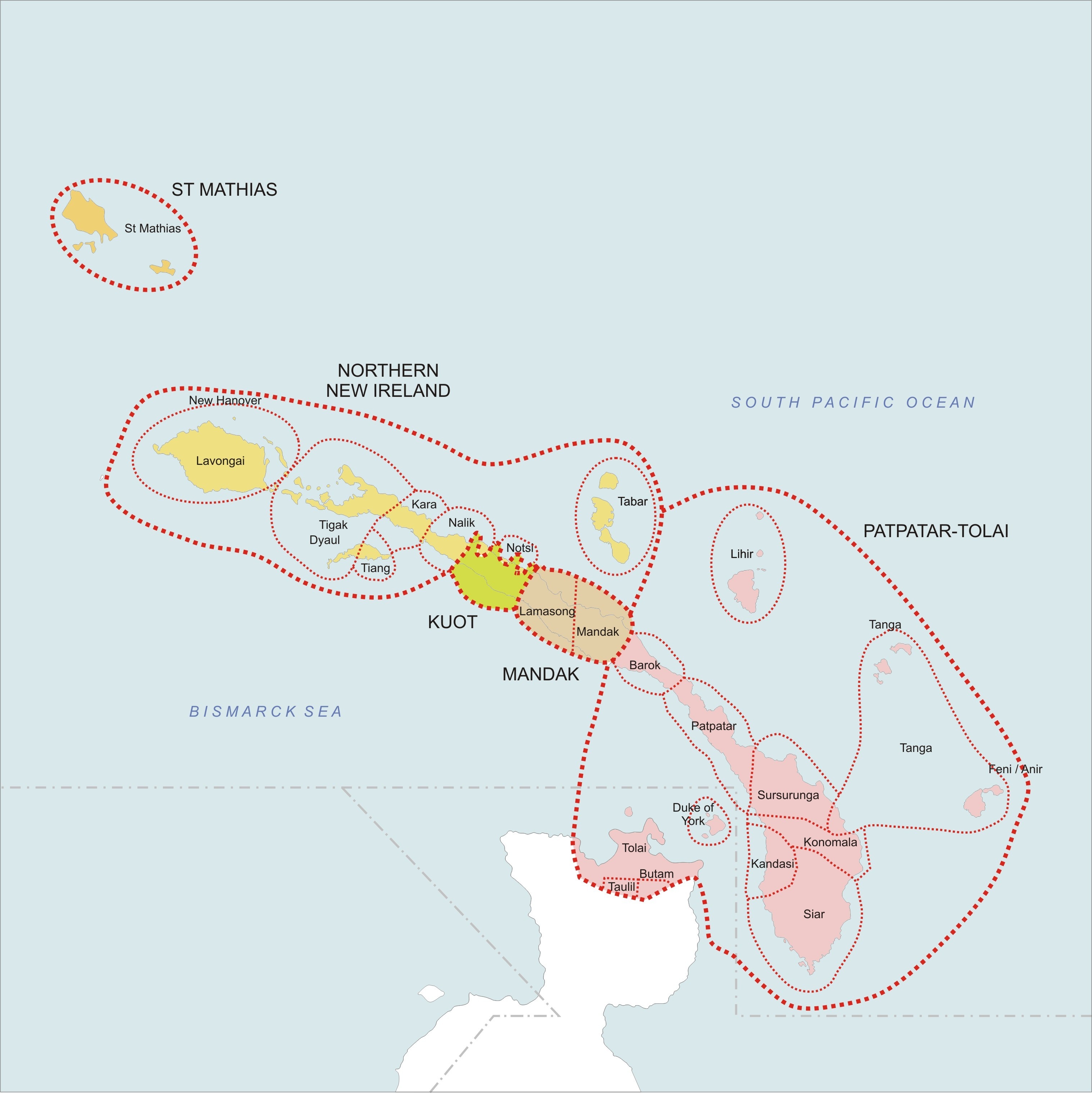 **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang
**Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi
**Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong,
**Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang
**Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi
**Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong,
linkage
Linkage may refer to:
* ''Linkage'' (album), by J-pop singer Mami Kawada, released in 2010
*Linkage (graph theory), the maximum min-degree of any of its subgraphs
*Linkage (horse), an American Thoroughbred racehorse
* Linkage (hierarchical cluster ...
of Oceanic languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ...
spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
is one of the most conservative languages.
Composition
The languages group as follows: * Willaumez linkage:Bola
Bola may refer to:
People
* Bola (name), a surname and given name
* Darrell Fitton, electronic musician from Manchester, England, AKA "Bola" and "Jello"
Geography
* Bola (volcano), a volcano on the island of New Britain in Papua New Guinea
* Bo ...
, Bulu, Meramera, Nakanai
*Bali–Vitu: Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
(Uneapa), Vitu (Muduapa) ay be a single language
Ay, AY or variants, may refer to:
People
* Ay (pharaoh), a pharaoh of the 18th Egyptian dynasty
* Merneferre Ay, a pharaoh of the 13th Egyptian dynasty
* A.Y. (musician) (born 1981), a Tanzanian "bongo flava" artist
* A.Y, stage name of Ayo M ...
*New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage
 **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang
**Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi
**Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong,
**Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang
**Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi
**Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak
Madak was a blend of opium and tobacco used as a recreational drug in 16th- and 17th-century China. It emerged in southern coastal areas in the first half of the 17th century. In the last quarter of the 18th century madak was phased out by raw opi ...
** Tomoip
**St George linkage
The St. George linkage links the North-West Solomonic and New Ireland languages under the Meso-Melanesian languages. Members of the St George linkage are Niwer Mil language, Warwar Feni, Fanamaket, Sursurunga, Konomala, Patpatar, Tolai, Ka ...
*** Niwer Mil
*** Warwar Feni
*** Fanamaket
*** Sursurunga
*** Konomala
***Patpatar–Tolai: Patpatar
Patpatar, or Gelik, is an Austronesian language spoken in New Ireland Province in Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( ...
, Lungalunga (Minigir), Tolai (Kuanua)
***Label–Bilur: Label, Bilur
***Kandas–Ramoaaina: Kandas, Ramoaaina
*** Siar
*** Northwest Solomonic linkage
''Ethnologue'' adds Guramalum to the St George linkage.
The Willaumez Peninsula on the north coast of New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dam ...
was evidently the center of dispersal.
Johnston (1982) combines the Willaumez and Bali–Vitu branches into a single Kimbe branch, for which he reconstructs Proto-Kimbe.
Language contact
Lenition in Lamasong,Madak
Madak was a blend of opium and tobacco used as a recreational drug in 16th- and 17th-century China. It emerged in southern coastal areas in the first half of the 17th century. In the last quarter of the 18th century madak was phased out by raw opi ...
, Barok, Nalik, and Kara may have diffused via influence from Kuot, the only non-Austronesian language spoken on New Ireland (Ross 1994: 566).Ross, Malcolm. 1994. Areal phonological features in north central New Ireland. In: Dutton and Tryon (eds.) Language contact and change in the Austronesian world, 551–572. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
References
{{Austronesian languages Western Oceanic languages