|
Guramalum Language
Guramalum is a presumed extinct Oceanic language spoken on New Ireland in Papua New Guinea. References Critically endangered languages Languages of New Ireland Province Meso-Melanesian languages Extinct languages of Oceania {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland (Tok Pisin: ''Niu Ailan'') or Latangai, is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately in area with 120,000 people. It is named after the island of Ireland. It is the largest island of New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by Saint George's Channel. The administrative centre of the island and of New Ireland province is the town of Kavieng located at the northern end of the island. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neumecklenburg ("New Mecklenburg"). Geography The island is part of the Bismarck Archipelago and is often described as having the shape of a musket. New Ireland is surrounded by the Bismarck Sea in the southwest and by the Pacific Ocean in the northeast. For much of its in length, the island's width varies between less than to , yet the central mountainous spine is very steep an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland Languages
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz (South Korean band), The Boyz Albums and EPs * New (album), ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * New (EP), ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * New (Daya song), "New" (Daya song), 2017 * New (Paul McCartney song), "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * New (No Doubt song), "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from ''Yves (single album), Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
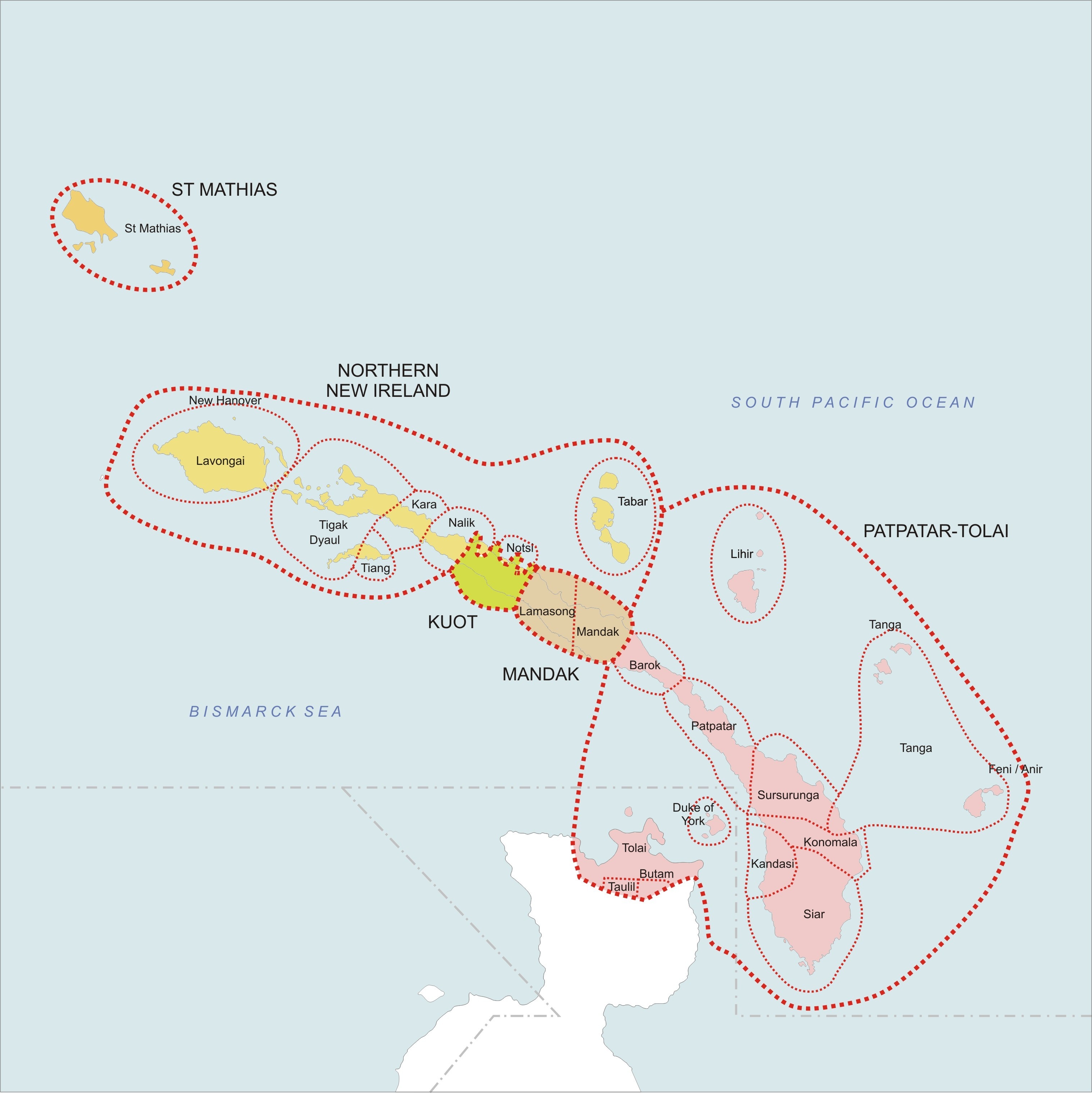
Patpatar–Tolai Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: * Willaumez linkage: Bola, Bulu, Meramera, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Bali (Uneapa), Vitu (Muduapa) ay be a single language*New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak ** Tomoip **St George linkage *** Niwer Mil *** Warwar Feni *** Fanamaket *** Sursurunga *** Konomala ***Patpatar–Tolai: Patpatar, Lungalunga (Minigir), Tolai (Kuanua) ***Label–Bilur: Label, Bilur ***Kandas–Ramoaaina: Kandas, Ramoaaina *** Siar *** Northwest Solomonic linkage ''Ethnologue'' adds Guramalum to the St George linkage. The Willaumez Peninsula on the north coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Of The World's Languages In Danger
The UNESCO ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' is an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' as a title in print after a brief period of overlap before being transferred to an online only publication. History In 1992 the International Congress of Linguists (CIPL) meeting in Canada discussed the topic of endangered languages, as a result of which it formed the Endangered Languages Committee. It held an international meeting also in 1992 in Paris to place the topic before the world and initiate action. The meeting was considered important enough to come under the authority of UNESCO. At the instigation of Stephen Wurm the committee resolved to create a research center, the International Clearing House for Endangered Languages (ICHEL) and to publish the UNESCO ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' based on the data it collected, the title being derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Language
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of New Ireland Province
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken language, spoken, sign language, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, and rely on Convention (norm), social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are speech, spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Melanesian Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a Linkage (linguistics), linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Uneapa language, Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: *Willaumez Peninsula, Willaumez linkage: Bola language (Austronesian), Bola, Bulu language (Oceanic), Bulu, Meramera language, Meramera, Nakanai language, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Uneapa language, Bali (Uneapa), Vitu language, Vitu (Muduapa) [may be a single language] *New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak language, Tigak, Tungag language, Tungag, Nalik language, Nalik, Laxudumau language, Laxudumau, Kara language (Papua New Guinea), Kara, Tiang language, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Mandara language, Madara (Tabar), Lihir language, Lihir, Notsi language, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok language, Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong language, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |