|
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Oceanic Languages
The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by . Classification The West Oceanic linkage is made up of three sub-linkages:. * North New Guinea linkage * Meso-Melanesian linkage * Papuan Tip linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Willaumez Peninsula The Willaumez Peninsula is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province. It was named after Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez (7 August 1763 – 17 May 1845) was a French sailor, ... on the north coast of New Britain. Notes References * * {{Austronesian languages Oceanic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
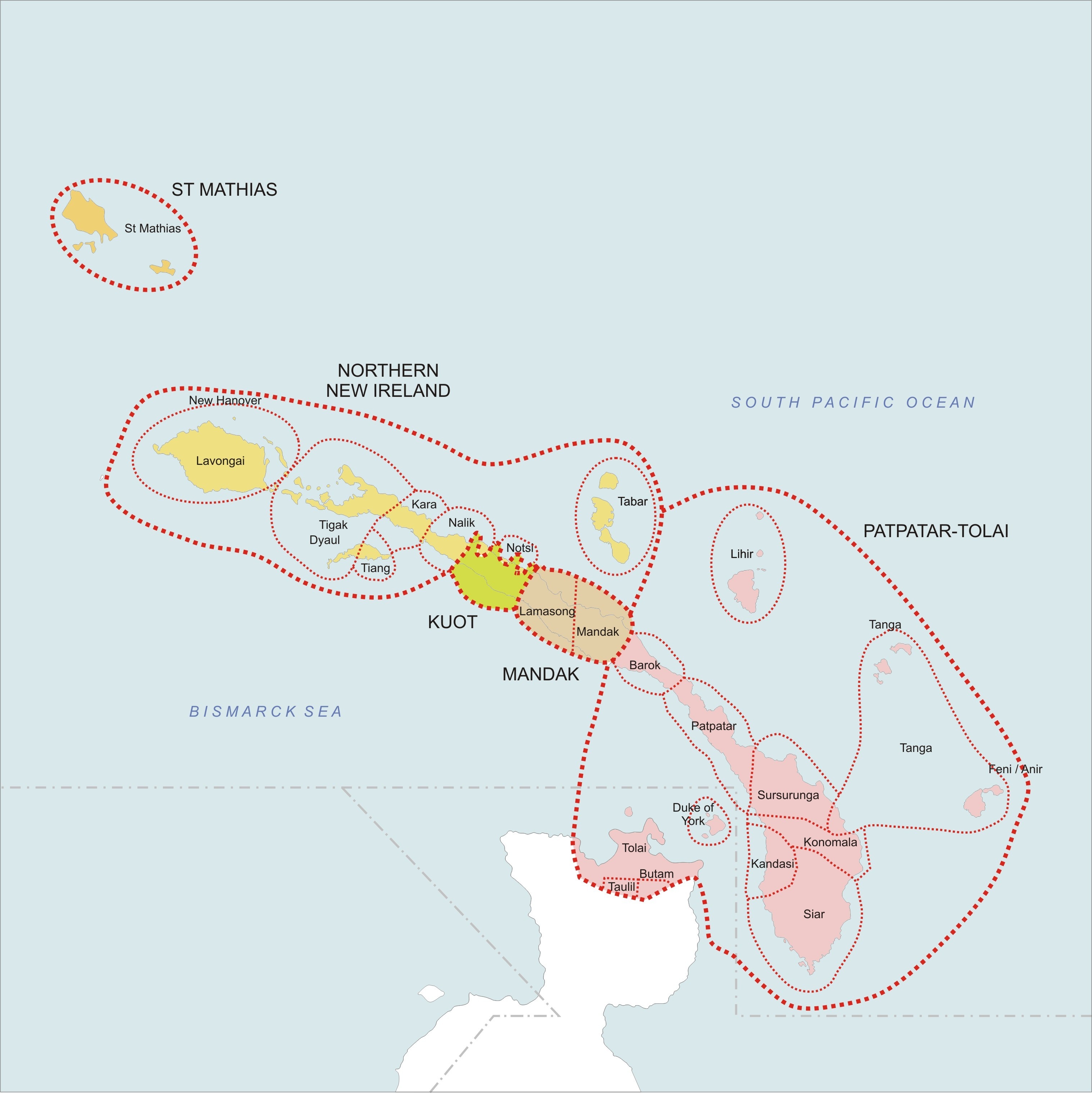
Meso-Melanesian Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a Linkage (linguistics), linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Uneapa language, Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: *Willaumez Peninsula, Willaumez linkage: Bola language (Austronesian), Bola, Bulu language (Oceanic), Bulu, Meramera language, Meramera, Nakanai language, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Uneapa language, Bali (Uneapa), Vitu language, Vitu (Muduapa) [may be a single language] *New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak language, Tigak, Tungag language, Tungag, Nalik language, Nalik, Laxudumau language, Laxudumau, Kara language (Papua New Guinea), Kara, Tiang language, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Mandara language, Madara (Tabar), Lihir language, Lihir, Notsi language, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok language, Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong language, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willaumez Languages
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: * Willaumez linkage: Bola, Bulu, Meramera, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Bali (Uneapa), Vitu (Muduapa) ay be a single language*New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak ** Tomoip **St George linkage *** Niwer Mil *** Warwar Feni *** Fanamaket *** Sursurunga *** Konomala ***Patpatar–Tolai: Patpatar, Lungalunga (Minigir), Tolai (Kuanua) ***Label–Bilur: Label, Bilur ***Kandas–Ramoaaina: Kandas, Ramoaaina *** Siar *** Northwest Solomonic linkage ''Ethnologue'' adds Guramalum to the St George linkage. The Willaumez Peninsula on the north coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Language
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West New Britain
West New Britain is a province of Papua New Guinea on the islands of New Britain. The provincial capital is Kimbe. The area of the province is 20,387 km² with a population of 264,264 as of the 2011 census. The province's only land border is with East New Britain. There are seven major tribes, the Nakanai, Bakovi, Kove, Unea, Maleu, Arowe, speaking about 25 languages. People from West New Britain are referred to as "Kombes" in Papua New Guinea, in metonymic reference to the significant Kove (or Kombe) people. The Kove people were reported on by the anthropologist Ann Chowning in ''National Geographic'' magazine during the 1960s. Within Papua New Guinea they are noted for their practice of superincision of the penis — circumcision is generally though inaccurately referred to among Papua New Guineans as "the Kombe cut" — but was formerly practiced in other northern coastal regions of New Guinea island and the New Guinea Islands. The predominant religious affiliation is Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |