Interwar Years on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the
In the
 Following the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November 1918 that ended World War I, the years 1918–1924 were marked by turmoil as the
Following the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November 1918 that ended World War I, the years 1918–1924 were marked by turmoil as the
 The
The
 In the
In the history of the 20th century
Following the 19th century, the 20th century changed the world in unprecedented ways. The World Wars sparked tension between countries and led to the creation of atomic bombs, the Cold War led to the Space Race and creation of space-based rocket ...
, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
to the beginning of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. The interwar period was relatively short, yet featured many significant social, political, and economic changes throughout the world. Petroleum-based energy production and associated mechanisation led to the prosperous Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, sometimes stylized as Roaring '20s, refers to the 1920s decade in music and fashion, as it happened in Western society and Western culture. It was a period of economic prosperity with a distinctive cultural edge in the ...
, a time of both social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given societ ...
and economic mobility
Economic mobility is the ability of an individual, family or some other group to improve (or lower) their economic status—usually measured in income. Economic mobility is often measured by movement between income quintiles. Economic mobility ...
for the middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Co ...
. Automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s, electric lighting, radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
, and more became common among populations in the developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruc ...
. The indulgences of the era subsequently were followed by the Great Depression, an unprecedented worldwide economic downturn that severely damaged many of the world's largest economies.
Politically, the era coincided with the rise of communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society ...
, starting in Russia with the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
and Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, at the end of World War I, and ended with the rise of fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and th ...
, particularly in Germany and in Italy. China was in the midst of half-a-century of instability and the Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on main ...
between the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
and the Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Ci ...
. The empires of Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and others faced challenges as imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power ( economic and ...
was increasingly viewed negatively in Europe, and independence movements emerged in many colonies; for example the south of Ireland became independent after much fighting.
The Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, and German Empires were dismantled, with the Ottoman territories and German colonies
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
redistributed among the Allies, chiefly Britain and France. The western parts of the Russian Empire, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
became independent nations in their own right, and Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
(now Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnist ...
and parts of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
) chose to reunify with Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
.
The Russian communists managed to regain control of the other East Slavic states, Central Asia and the Caucasus, forming the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. Ireland was partitioned between the independent Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independ ...
and the British-controlled Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. North ...
after the Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War ( ga, Cogadh Cathartha na hÉireann; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United ...
in which the Free State fought against "anti-treaty" Irish republicans, who opposed partition. In the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, both Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
gained independence. During the Great Depression, countries in Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
nationalised many foreign companies, most of which were American, in a bid to strengthen their own economies. The territorial ambitions of the Soviets, Japanese, Italians, and Germans led to the expansion of their domains.
The period ended at the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Turmoil in Europe
 Following the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November 1918 that ended World War I, the years 1918–1924 were marked by turmoil as the
Following the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November 1918 that ended World War I, the years 1918–1924 were marked by turmoil as the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
continued to rage on, and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
struggled to recover from the devastation of the First World War and the destabilising effects of not just the collapse of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
, but the destruction of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
, and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, as well. There were numerous new or restored countries in Southern, Central and Eastern Europe, some small in size, such as Lithuania or Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, and some larger, such as Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
. The United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
gained dominance in world finance. Thus, when Germany could no longer afford war reparations to Britain, France and other former members of the Entente, the Americans came up with the Dawes Plan
The Dawes Plan (as proposed by the Dawes Committee, chaired by Charles G. Dawes) was a plan in 1924 that successfully resolved the issue of World War I reparations that Germany had to pay. It ended a crisis in European diplomacy following W ...
and Wall Street invested heavily in Germany, which repaid its reparations to nations that, in turn, used the dollars to pay off their war debts to Washington. By the middle of the decade, prosperity was widespread, with the second half of the decade known as the Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, sometimes stylized as Roaring '20s, refers to the 1920s decade in music and fashion, as it happened in Western society and Western culture. It was a period of economic prosperity with a distinctive cultural edge in the ...
.
International relations
The important stages of interwar diplomacy and international relations included resolutions of wartime issues, such as reparations owed by Germany and boundaries; American involvement in European finances and disarmament projects; the expectations and failures of theLeague of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
; the relationships of the new countries to the old; the distrustful relations of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
to the capitalist world; peace and disarmament efforts; responses to the Great Depression starting in 1929; the collapse of world trade; the collapse of democratic regimes one by one; the growth of efforts at economic autarky; Japanese aggressiveness toward China, occupying large amounts of Chinese land, as well as border disputes between the Soviet Union and Japan, leading to multiple clashes along the Soviet and Japanese occupied Manchurian border; Fascist diplomacy, including the aggressive moves by Mussolini's Italy and Hitler's Germany; the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
; Italy's invasion and occupation of Abyssinia (Ethiopia) in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
; the appeasement
Appeasement in an international context is a diplomatic policy of making political, material, or territorial concessions to an aggressive power in order to avoid conflict. The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the UK governme ...
of Germany's expansionist moves against the German-speaking nation of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, the region inhabited by ethnic Germans called the Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the ...
in Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, the remilitarisation of the League of Nations demilitarised zone of the German Rhineland region, and the last, desperate stages of rearmament as the Second World War increasingly loomed.
Disarmament was a very popular public policy. However, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
played little role in this effort, with the United States and Britain taking the lead. U.S. Secretary of State Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes Sr. (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American statesman, politician and jurist who served as the 11th Chief Justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party, he previously was the ...
sponsored the Washington Naval Conference
The Washington Naval Conference was a disarmament conference called by the United States and held in Washington, DC from November 12, 1921 to February 6, 1922. It was conducted outside the auspices of the League of Nations. It was attended by nine ...
of 1921 in determining how many capital ships each major country was allowed. The new allocations were actually followed and there were no naval races in the 1920s. Britain played a leading role in the 1927 Geneva Naval Conference
The Geneva Naval Conference was a conference held to discuss naval arms limitation, held in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1927. The aim of the conference was to extend the existing limits on naval construction which had been agreed in the Washington N ...
and the 1930 London Conference that led to the London Naval Treaty, which added cruisers and submarines to the list of ship allocations. However the refusal of Japan, Germany, Italy and the USSR to go along with this led to the meaningless Second London Naval Treaty
The Second London Naval Treaty was an international treaty signed as a result of the Second London Naval Disarmament Conference held in London, the United Kingdom. The conference started on 9 December 1935 and the treaty was signed by the pa ...
of 1936. Naval disarmament had collapsed and the issue became rearming for a war against Germany and Japan.
Roaring Twenties
 The
The Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, sometimes stylized as Roaring '20s, refers to the 1920s decade in music and fashion, as it happened in Western society and Western culture. It was a period of economic prosperity with a distinctive cultural edge in the ...
highlighted novel and highly visible social and cultural trends and innovations. These trends, made possible by sustained economic prosperity, were most visible in major cities like New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
, Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, and London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. The Jazz Age began and Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
peaked. For women, knee-length skirts and dresses became socially acceptable, as did bobbed hair with a Marcel wave
Marcelling is a hair styling technique in which hot curling tongs are used to induce a curl into the hair. Its appearance was similar to that of a finger wave but it is created using a different method.
Marcelled hair was a popular style for w ...
. The young women who pioneered these trends were called "flappers
Flappers were a subculture of young Western women in the 1920s who wore short skirts (knee height was considered short during that period), bobbed their hair, listened to jazz, and flaunted their disdain for what was then considered accep ...
". Not all was new: "normalcy" returned to politics in the wake of hyper-emotional wartime passions in the United States, France, and Germany. The leftist revolutions in Finland, Poland, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and Spain were defeated by conservatives, but succeeded in Russia, which became the base for Soviet Communism
The ideology of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) was Bolshevist Marxism–Leninism, an ideology of a centralised command economy with a vanguardist one-party state to realise the dictatorship of the proletariat. The Soviet Union ...
and Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a List of communist ideologies, communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its Soviet satellite state ...
. In Italy the National Fascist Party
The National Fascist Party ( it, Partito Nazionale Fascista, PNF) was a political party in Italy, created by Benito Mussolini as the political expression of Italian Fascism and as a reorganization of the previous Italian Fasces of Combat. The p ...
came to power under Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
after threatening a March on Rome
The March on Rome ( it, Marcia su Roma) was an organized mass demonstration and a coup d'état in October 1922 which resulted in Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party (PNF) ascending to power in the Kingdom of Italy. In late October 1922, F ...
in 1922.
Most independent countries enacted women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to gran ...
in the interwar era, including Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
in 1917 (though Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
held out longer), Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
in 1918, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
in 1920. There were a few major countries that held out until after the Second World War (such as France, Switzerland and Portugal). Leslie Hume argues:
: The women's contribution to the war effort combined with failures of the previous systems' of Government made it more difficult than hitherto to maintain that women were, both by constitution and temperament, unfit to vote. If women could work in munitions factories, it seemed both ungrateful and illogical to deny them a place in the polling booth. But the vote was much more than simply a reward for war work; the point was that women's participation in the war helped to dispel the fears that surrounded women's entry into the public arena.
In Europe, according to Derek Aldcroft and Steven Morewood, "Nearly all countries registered some economic progress in the 1920s and most of them managed to regain or surpass their pre-war income and production levels by the end of the decade." The Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, and Greece did especially well, while Eastern Europe did poorly, due to the First World War and Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
. In advanced economies the prosperity reached middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Co ...
households and many in the working class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colo ...
with radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
, automobiles
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
, telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into el ...
s, and electric lighting and appliances. There was unprecedented industrial growth, accelerated consumer demand and aspirations, and significant changes in lifestyle and culture. The media began to focus on celebrities, especially sports heroes and movie stars. Major cities built large sports stadiums for the fans, in addition to palatial cinemas. The mechanisation of agriculture
Mechanised agriculture or agricultural mechanization is the use of machinery and equipment, ranging from simple and basic hand tools to more sophisticated, motorized equipment and machinery, to perform agricultural operations. In modern times, po ...
continued apace, producing an expansion of output that lowered prices, and made many farm workers redundant. Often they moved to nearby industrial towns and cities.
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwideeconomic depression
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economical downturn that is result of lowered economic activity in one major or more national economies. Economic depression maybe related to one specific country were there is some economic ...
that took place after 1929. The timing varied across nations; in most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s. It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. The depression originated in the United States and became worldwide news with the stock market crash
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often f ...
of 29 October 1929 (known as Black Tuesday
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange colla ...
). Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide GDP fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II.
The Great Depression had devastating effects in countries both rich
Rich may refer to:
Common uses
* Rich, an entity possessing wealth
* Rich, an intense taste, flavor, color, sound, texture, or feeling
**Rich (wine), a descriptor in wine tasting
Places United States
* Rich, Mississippi, an unincorporated ...
and poor
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little
 Democracy and prosperity largely went together in the 1920s. Economic disaster led to a distrust in the effectiveness of democracy and its collapse in much of Europe and Latin America, including the Baltic and Balkan countries, Poland, Spain, and Portugal. Powerful expansionary anti-democratic regimes emerged in Italy, Japan, and Germany.
While
Democracy and prosperity largely went together in the 1920s. Economic disaster led to a distrust in the effectiveness of democracy and its collapse in much of Europe and Latin America, including the Baltic and Balkan countries, Poland, Spain, and Portugal. Powerful expansionary anti-democratic regimes emerged in Italy, Japan, and Germany.
While
 The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew the
The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew the  India strongly supported the Empire in the First World War. It expected a reward, but failed to get sovereignty as the
India strongly supported the Empire in the First World War. It expected a reward, but failed to get sovereignty as the
 French census statistics from 1938 show an imperial population with France at over 150 million people, outside of France itself, of 102.8 million people living on 13.5 million square kilometers. Of the total population, 64.7 million lived in Africa and 31.2 million lived in Asia; 900,000 lived in the
French census statistics from 1938 show an imperial population with France at over 150 million people, outside of France itself, of 102.8 million people living on 13.5 million square kilometers. Of the total population, 64.7 million lived in Africa and 31.2 million lived in Asia; 900,000 lived in the
 The humiliating peace terms in the
The humiliating peace terms in the
 Hitler's diplomatic strategy in the 1930s was to make seemingly reasonable demands, threatening war if they were not met. When opponents tried to appease him, he accepted the gains that were offered, then went to the next target. That aggressive strategy worked as Germany pulled out of the
Hitler's diplomatic strategy in the 1930s was to make seemingly reasonable demands, threatening war if they were not met. When opponents tried to appease him, he accepted the gains that were offered, then went to the next target. That aggressive strategy worked as Germany pulled out of the
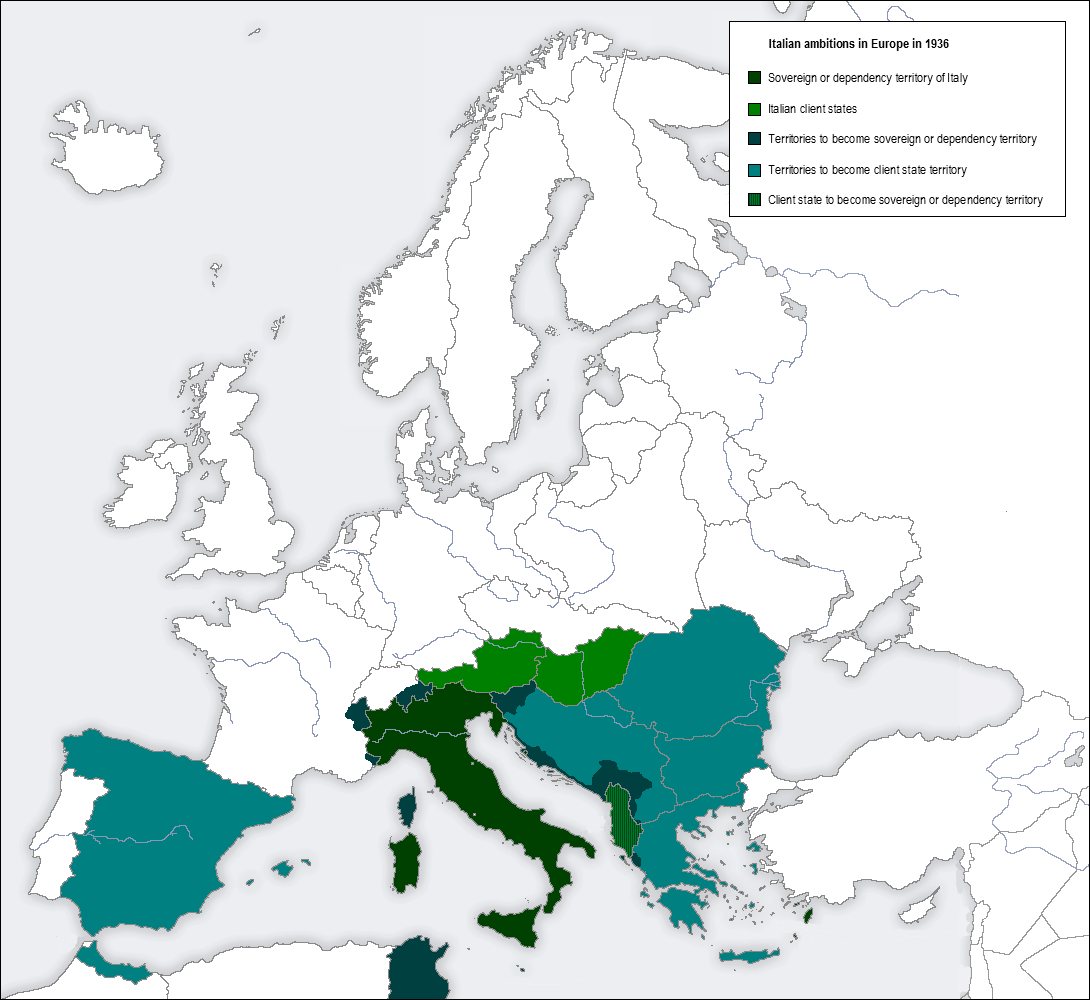
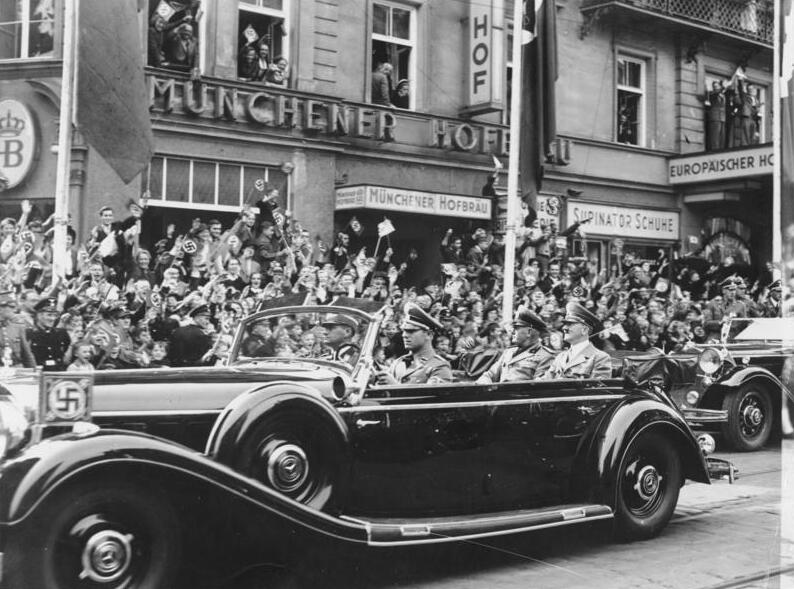
 In 1922, the leader of the Italian Fascist movement,
In 1922, the leader of the Italian Fascist movement,  After Great Britain signed the Anglo-Italian Easter Accords in 1938, Mussolini and Foreign Minister
After Great Britain signed the Anglo-Italian Easter Accords in 1938, Mussolini and Foreign Minister
 The Japanese modelled their
The Japanese modelled their
 The civilian government in Tokyo tried to minimise the Army's aggression in Manchuria, and announced it was withdrawing. On the contrary, the Army completed the conquest of Manchuria, and the civilian cabinet resigned. The political parties were divided on the issue of military expansion. Prime Minister Tsuyoshi tried to negotiate with China, but was assassinated in the May 15 Incident in 1932, which ushered in an era of
The civilian government in Tokyo tried to minimise the Army's aggression in Manchuria, and announced it was withdrawing. On the contrary, the Army completed the conquest of Manchuria, and the civilian cabinet resigned. The political parties were divided on the issue of military expansion. Prime Minister Tsuyoshi tried to negotiate with China, but was assassinated in the May 15 Incident in 1932, which ushered in an era of
ImageSize = width:800 height:200
PlotArea = width:640 height:140 left:65 bottom:20
AlignBars = late
Colors =
id:time value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) #
id:period value:rgb(1,0.7,0.5) #
id:age value:rgb(0.95,0.85,0.5) #
id:era value:rgb(1,0.85,0.5) #
id:eon value:rgb(1,0.85,0.7) #
id:filler value:gray(0.8) # background bar
id:black value:black
Period = from:1900 till:1950
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:1900
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:1900
PlotData =
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:10 mark:(line,white) width:11 shift:(0,-5)
bar:Decades color:era
from:1920 till:1929 text: Twenties
from:1929 till:1939 text: Depression
bar:Machine color:era
from:1900 till:1945 text:
online
. * Morris, Richard B. and Graham W. Irwin, eds. ''Harper Encyclopedia of the Modern World: A Concise Reference History from 1760 to the Present'' (1970
online
* Albrecht-Carrié, René. ''A Diplomatic History of Europe Since the Congress of Vienna'' (1958), 736pp; a basic introduction, 1815–195
online free to borrow
* Berg-Schlosser, Dirk, and Jeremy Mitchell, eds. ''Authoritarianism and democracy in Europe, 1919–39: comparative analyses'' (Springer, 2002). * Berman, Sheri. ''The Social Democratic Moment: Ideas and Politics in the Making of Interwar Europe'' (Harvard UP, 2009). * Bowman, Isaiah. ''The New World: Problems in Political Geography'' (4th ed. 1928) sophisticated global coverage; 215 maps
online
* Brendon, Piers. '' The Dark Valley: A Panorama of the 1930s'' (2000) a comprehensive global political history; 816p
excerpt
* Cambon, Jules, ed ''The Foreign Policy of the Powers'' (1935) Essays by experts that cover France, Germany, Great Britain, Italy, Japan, Russia and the United State
Online free
* Clark, Linda Darus, ed. ''Interwar America: 1920–1940: Primary Sources in U.S. History'' (2001) * Dailey, Andy, and David G. Williamson. (2012) ''Peacemaking, Peacekeeping: International Relations 1918–36'' (2012) 244 pp; textbook, heavily illustrated with diagrams and contemporary photographs and colour posters. * Doumanis, Nicholas, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of European History, 1914–1945'' (Oxford UP, 2016). * Duus, Peter, ed., ''The Cambridge History of Japan, vol. 6, The Twentieth Century'' (1989) pp 53–153, 217–340
online
* Feinstein, Charles H., Peter Temin, and Gianni Toniolo. ''The World Economy Between the World Wars'' (Oxford UP, 2008), a standard scholarly survey. * Freeman, Robert. ''The InterWar Years (1919–1939)'' (2014), brief survey * Garraty, John A. '' The Great Depression: An Inquiry into the Causes, Course, and Consequences of the Worldwide Depression of the Nineteen-1930s, As Seen by Contemporaries'' (1986). * Gathorne-Hardy, Geoffrey Malcolm. ''A Short History of International Affairs, 1920 to 1934'' (Oxford UP, 1952). *
Online free to borrow
* Grift, Liesbeth van de, and Amalia Ribi Forclaz, eds. ''Governing the Rural in Interwar Europe'' (2017) * Grossman, Mark ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Interwar Years: From 1919 to 1939'' (2000). * Hicks, John D. ''Republican Ascendancy, 1921-1933'' (1960) for US
online
* – a view from the Left. * Kaser, M. C. and E. A. Radice, eds. ''The Economic History of Eastern Europe 1919–1975: Volume II: Interwar Policy, The War, and Reconstruction'' (1987) * * Koshar, Rudy. ''Splintered Classes: Politics and the Lower Middle Classes in Interwar Europe'' (1990). * * Luebbert, Gregory M. ''Liberalism, Fascism, Or Social Democracy: Social Classes and the Political Origins of Regimes in Interwar Europe'' (Oxford UP, 1991). * * Matera, Marc, and Susan Kingsley Kent. ''The Global 1930s: The International Decade'' (Routledge, 2017
excerpt
* * *
also online free to borrow
* Murray, Williamson and Allan R. Millett, eds. ''Military Innovation in the Interwar Period'' (1998) * Newman, Sarah, and Matt Houlbrook, eds. ''The Press and Popular Culture in Interwar Europe'' (2015) * Overy, R.J. ''The Inter-War Crisis 1919–1939'' (2nd ed. 2007) * Rothschild, Joseph. ''East Central Europe Between the Two World Wars'' (U of Washington Press, 2017). * Seton-Watson, Hugh. (1945) ''Eastern Europe Between The Wars 1918–1941'' (1945
online
* – 550 pp; wide-ranging political, social and economic coverage of Britain, 1910–35 * Sontag, Raymond James. ''A Broken World, 1919–1939'' (1972
online free to borrow
wide-ranging survey of European history * Sontag, Raymond James. "Between the Wars." ''Pacific Historical Review'' 29.1 (1960): 1–1
online
* Steiner, Zara. ''The Lights that Failed: European International History 1919–1933''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2008. * Steiner, Zara. ''The Triumph of the Dark: European International History 1933–1939''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2011. * Toynbee, A. J. ''Survey of International Affairs 1920–1923'' (1924
online
''Survey of International Affairs'' annual 1920–193
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1924'' (1925); ''Survey of International Affairs 1925'' (1926
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1924'' (1925
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1927'' (1928
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1928'' (1929
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1929'' (1930
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1932'' (1933
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1934'' (1935), focus on Europe, Middle East, Far East; ''Survey of International Affairs 1936'' (1937
online
* Watt, D.C. et al., A History of the World in the Twentieth Century (1968) pp 301–530. * Wheeler-Bennett, John. ''Munich: Prologue To Tragedy,'' (1948) broad coverage of diplomacy of 1930s * Zachmann, Urs Matthias. ''Asia after Versailles: Asian Perspectives on the Paris Peace Conference and the Interwar Order, 1919–33'' (2017)
Mount Holyoke College edition
"Britain 1919 to the present"
Several large collections of primary sources and illustrations
{{Authority control . . Chronology of World War II Periodization
income< ...
. Personal income
In economics, personal income refers to an individual's total earnings from wages, investment enterprises, and other ventures. It is the sum of all the incomes received by all the individuals or household during a given period. Personal income i ...
, tax revenue
Tax revenue is the income that is collected by governments through taxation. Taxation is the primary source of government revenue. Revenue may be extracted from sources such as individuals, public enterprises, trade, royalties on natural resou ...
, profits, and price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in t ...
s dropped, while international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significan ...
plunged by more than 50%. Unemployment in the United States
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, auto ...
rose to 25% and in some countries rose as high as 33%. Prices fell sharply, especially for mining and agricultural commodities. Business profits fell sharply as well, with a sharp reduction in new business starts.
Cities all around the world were hit hard, especially those dependent on heavy industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); ...
. Construction was virtually halted in many countries. Farming communities and rural areas suffered as crop prices fell by about 60%. Facing plummeting demand with few alternative sources of jobs, areas dependent on primary sector industries such as mining and logging suffered the most.
The Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also r ...
in Germany gave way to two episodes of political and economic turmoil, the first culminated in the German hyperinflation of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch,Dan Moorhouse, ed schoolshistory.org.uk, accessed 2008-05-31.Known in German as the or was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party ( or NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff and oth ...
of that same year. The second convulsion, brought on by the worldwide depression and Germany's disastrous monetary policies, resulted in the further rise of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
. In Asia, Japan became an ever more assertive power, especially with regard to China.
Fascism displaces democracy
 Democracy and prosperity largely went together in the 1920s. Economic disaster led to a distrust in the effectiveness of democracy and its collapse in much of Europe and Latin America, including the Baltic and Balkan countries, Poland, Spain, and Portugal. Powerful expansionary anti-democratic regimes emerged in Italy, Japan, and Germany.
While
Democracy and prosperity largely went together in the 1920s. Economic disaster led to a distrust in the effectiveness of democracy and its collapse in much of Europe and Latin America, including the Baltic and Balkan countries, Poland, Spain, and Portugal. Powerful expansionary anti-democratic regimes emerged in Italy, Japan, and Germany.
While communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society ...
was tightly contained in the isolated Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and th ...
took control of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and ...
in 1922; as the Great Depression worsened, Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
emerged victorious in Germany, fascism spread to many other countries in Europe, and also played a major role in several countries in Latin America. Fascist parties sprang up, attuned to local right-wing traditions, but also possessing common features that typically included extreme militaristic nationalism, a desire for economic self-containment, threats and aggression toward neighbouring countries, oppression of minorities, a ridicule of democracy while using its techniques to mobilise an angry middle-class base, and a disgust with cultural liberalism
Cultural liberalism is a social philosophy which expresses the social dimension of liberalism and advocates the freedom of individuals to choose whether to conform to cultural norms. In the words of Henry David Thoreau, it is often expressed ...
. Fascists believed in power, violence, male superiority, and a "natural" hierarchy, often led by dictators such as Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
or Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
. Fascism in power meant that liberalism and human rights were discarded, and individual pursuits and values were subordinated to what the party decided was best.
Spanish Civil War (1936–1939)
To one degree or another, Spain had been unstable politically for centuries, and in 1936–1939 was wracked by one of the bloodiest civil wars of the 20th century. The real importance comes from outside countries. In Spain theconservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
and Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
elements and the army revolted against the newly elected government of the Second Spanish Republic
The Spanish Republic (), commonly known as the Second Spanish Republic (), was the form of government in Spain from 1931 to 1939. The Republic was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, after the deposition of King Alfonso XIII, and was dissolved on 1 ...
, and full-scale civil war erupted. Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany gave munitions and strong military units to the rebel Nationalist faction, led by General Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
. The Republican (or "Loyalist") government, was on the defensive, but it received significant help from the Soviet Union and Mexico. Led by Great Britain and France, and including the United States, most countries remained neutral and refused to provide armaments to either side. The powerful fear was that this localised conflict would escalate into a European conflagration that no one wanted.
The Spanish Civil War was marked by numerous small battles and sieges, and many atrocities, until the Nationalists won in 1939 by overwhelming the Republican forces. The Soviet Union provided armaments but never enough to equip the heterogeneous government militias and the "International Brigades
The International Brigades ( es, Brigadas Internacionales) were military units set up by the Communist International to assist the Popular Front government of the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War. The organization existed ...
" of outside far-left
Far-left politics, also known as the radical left or the extreme left, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single definition. Some scholars consider ...
volunteers. The civil war did not escalate into a larger conflict, but did become a worldwide ideological battleground that pitted all the Communists
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a ...
and many socialists
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
and liberals against Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, conservatives and fascists. Worldwide there was a decline in pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaig ...
and a growing sense that another world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World War I, Worl ...
was imminent, and that it would be worth fighting for.
British Empire
 The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew the
The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew the Anglo-Japanese Alliance
The first was an alliance between Britain and Japan, signed in January 1902. The alliance was signed in London at Lansdowne House on 30 January 1902 by Lord Lansdowne, British Foreign Secretary, and Hayashi Tadasu, Japanese diplomat. A d ...
and instead signed the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty
The Washington Naval Treaty, also known as the Five-Power Treaty, was a treaty signed during 1922 among the major Allies of World War I, which agreed to prevent an arms race by limiting naval construction. It was negotiated at the Washington ...
, in which Britain accepted naval parity with the United States. The issue of the empire's security was a serious concern in Britain, as it was vital to the British pride, its finance, and its trade-oriented economy.
 India strongly supported the Empire in the First World War. It expected a reward, but failed to get sovereignty as the
India strongly supported the Empire in the First World War. It expected a reward, but failed to get sovereignty as the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Q ...
kept control in British hands and feared another rebellion like that of 1857. The Government of India Act 1919
The Government of India Act 1919 (9 & 10 Geo. 5 c. 101) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was passed to expand participation of Indians in the government of India. The Act embodied the reforms recommended in the report of ...
failed to satisfy demand for independence. Mounting tension, particularly in the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, culminated in the Amritsar Massacre
The Jallianwala Bagh massacre, also known as the Amritsar massacre, took place on 13 April 1919. A large peaceful crowd had gathered at the Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar, Punjab, to protest against the Rowlatt Act and arrest of pro-independence ...
in 1919. Indian nationalism
Indian nationalism is an instance of territorial nationalism, which is inclusive of all of the people of India, despite their diverse ethnic, linguistic and religious backgrounds. Indian nationalism can trace roots to pre-colonial India, ...
surged and centred in the Congress Party led by Mohandas Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti- ...
. In Britain, public opinion was divided over the morality of the massacre between those who saw it as having saved India from anarchy and those who viewed it with revulsion. – 25 chapters; 845 pp
Egypt had been under ''de facto'' British control since the 1880s, despite its nominal ownership by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. In 1922, the Kingdom of Egypt
The Kingdom of Egypt ( ar, المملكة المصرية, Al-Mamlaka Al-Miṣreyya, The Egyptian Kingdom) was the legal form of the Egyptian state during the latter period of the Muhammad Ali dynasty's reign, from the United Kingdom's recog ...
was granted formal independence, though it continued to be a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
following British guidance. Egypt joined the League of Nations. Egypt's King Fuad and his son King Farouk
Farouk I (; ar, فاروق الأول ''Fārūq al-Awwal''; 11 February 1920 – 18 March 1965) was the tenth ruler of Egypt from the Muhammad Ali dynasty and the penultimate King of Egypt and the Sudan, succeeding his father, Fuad I, in 1936 ...
and their conservative allies stayed in power with lavish lifestyles thanks to an informal alliance with Britain who would protect them from both secular and Muslim radicalism. Mandatory Iraq
The Kingdom of Iraq under British Administration, or Mandatory Iraq ( ar, الانتداب البريطاني على العراق '), was created in 1921, following the 1920 Iraqi Revolt against the proposed British Mandate of Mesopotamia, a ...
, a British mandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also r ...
since 1920, gained official independence as the Kingdom of Iraq
The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq ( ar, المملكة العراقية الهاشمية, translit=al-Mamlakah al-ʿIrāqiyyah ʾal-Hāshimyyah) was a state located in the Middle East from 1932 to 1958.
It was founded on 23 August 1921 as the Kingdo ...
in 1932 when King Faisal agreed to British terms of a military alliance and an assured flow of oil.
In Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East J ...
, Britain was presented with the problem of mediating between the Palestinian Arabs
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
and increasing numbers of Jewish settlers
Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, overwhelmingly of Jewish ethnicity, built on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli s ...
. The Balfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
, which had been incorporated into the terms of the mandate, stated that a national home for the Jewish people
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
would be established in Palestine, and Jewish immigration allowed up to a limit that would be determined by the mandatory power. This led to increasing conflict with the Arab population, who openly revolted in 1936. As the threat of war with Germany increased during the 1930s, Britain judged the support of Arabs as more important than the establishment of a Jewish homeland, and shifted to a pro-Arab stance, limiting Jewish immigration and in turn triggering a Jewish insurgency.
The Dominions (Canada, Newfoundland, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and the Irish Free State) were self-governing and gained semi-independence in the World War, while Britain still controlled foreign policy and defence. The right of the Dominions to set their own foreign policy was recognised in 1923 and formalised by the 1931 Statute of Westminster. (Southern) Ireland effectively broke all ties with Britain in 1937, leaving the Commonwealth and becoming an independent republic.
French Empire
 French census statistics from 1938 show an imperial population with France at over 150 million people, outside of France itself, of 102.8 million people living on 13.5 million square kilometers. Of the total population, 64.7 million lived in Africa and 31.2 million lived in Asia; 900,000 lived in the
French census statistics from 1938 show an imperial population with France at over 150 million people, outside of France itself, of 102.8 million people living on 13.5 million square kilometers. Of the total population, 64.7 million lived in Africa and 31.2 million lived in Asia; 900,000 lived in the French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloup ...
or islands in the South Pacific. The largest colonies were French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
with 26.8 million (in five separate colonies), French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the ...
with 6.6 million, the French protectorate in Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco (french: Protectorat français au Maroc; ar, الحماية الفرنسية في المغرب), also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco between 1912 to 1956. The prot ...
, with 5.4 million, and French West Africa with 35.2 million in nine colonies. The total includes 1.9 million Europeans, and 350,000 "assimilated" natives.
Revolt in North Africa against Spain and France
The Berber independence leaderAbd el-Krim
Muhammad ibn Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi (; Tarifit: Muḥend n Ɛabd Krim Lxeṭṭabi, ⵎⵓⵃⵏⴷ ⵏ ⵄⴰⴱⴷⵍⴽⵔⵉⵎ ⴰⵅⵟⵟⴰⴱ), better known as Abd el-Krim (1882/1883, Ajdir, Morocco – 6 February 1963, Cairo, Egypt) ...
(1882–1963) organised armed resistance against the Spanish and French for control of Morocco. The Spanish had faced unrest off and on from the 1890s, but in 1921, Spanish forces were massacred at the Battle of Annual
The Battle of Annual was fought on 22 July 1921 at Annual, in northeastern Morocco, between the Spanish Army and Rifian Berbers during the Rif War. The Spanish suffered a major military defeat, which is almost always referred to by the Spanish a ...
. El-Krim founded an independent Rif Republic
The Republic of the Rif (Tarifit: ''Tagduda n Arrif'', ''Jumhūriyya ar-Rīf''), unofficially The Confederal Republic of the Tribes of the Rif, also recorded as the Riff, was a short-lived republic in northern Morocco that existed between 192 ...
that operated until 1926, but had no international recognition. Eventually, France and Spain agreed to end the revolt. They sent in 200,000 soldiers, forcing el-Krim to surrender in 1926; he was exiled in the Pacific until 1947. Morocco was now pacified, and became the base from which Spanish Nationalists would launch their rebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
against the Spanish Republic in 1936.
Germany
Weimar Republic
 The humiliating peace terms in the
The humiliating peace terms in the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
provoked bitter indignation throughout Germany, and seriously weakened the new democratic regime. The Treaty stripped Germany of all of its overseas colonies, of Alsace–Lorraine
Alsace–Lorraine, now called Alsace–Moselle, is a historical region located in France. It was created in 1871 by the German Empire after it had seized the region from the Second French Empire in the Franco-Prussian War with the Treaty of F ...
, and of predominantly Polish districts. The Allied armies occupied industrial sectors in western Germany including the Rhineland, and Germany was not allowed to have a real army, navy, or air force. Reparations
Reparation(s) may refer to:
Christianity
* Restitution (theology), the Christian doctrine calling for reparation
* Acts of reparation, prayers for repairing the damages of sin
History
* War reparations
** World War I reparations, made from ...
were demanded, especially by France, involving shipments of raw materials, as well as annual payments.
When Germany defaulted on its reparation payments, French and Belgian troops occupied the heavily industrialised Ruhr district (January 1923). The German government encouraged the population of the Ruhr to passive resistance
Nonviolent resistance (NVR), or nonviolent action, sometimes called civil resistance, is the practice of achieving goals such as social change through symbolic protests, civil disobedience, economic or political noncooperation, satyagraha, con ...
: shops would not sell goods to the foreign soldiers, coal mines would not dig for the foreign troops, trams in which members of the occupation army had taken seat would be left abandoned in the middle of the street. The German government printed vast quantities of paper money, causing hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as t ...
, which also damaged the French economy. The passive resistance proved effective, insofar as the occupation became a loss-making deal for the French government. But the hyperinflation caused many prudent savers to lose all the money they had saved. Weimar added new internal enemies every year, as anti-democratic Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hit ...
, Nationalists
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
, and Communists
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a ...
battled each other in the streets.
Germany was the first state to establish diplomatic relations with the new Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. Under the Treaty of Rapallo Following World War I there were two Treaties of Rapallo, both named after Rapallo, a resort on the Ligurian coast of Italy:
* Treaty of Rapallo, 1920, an agreement between Italy and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (the later Yugosla ...
, Germany accorded the Soviet Union ''de jure'' recognition, and the two signatories mutually agreed to cancel all pre-war debts and renounced war claims. In October 1925 the Treaty of Locarno
The Locarno Treaties were seven agreements negotiated at Locarno, Switzerland, during 5 to 16 October 1925 and formally signed in London on 1 December, in which the First World War Western European Allied powers and the new states of Central ...
was signed by Germany, France, Belgium, Britain, and Italy; it recognised Germany's borders with France and Belgium. Moreover, Britain, Italy, and Belgium undertook to assist France in the case that German troops marched into the demilitarised Rhineland. Locarno paved the way for Germany's admission to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
in 1926.
Nazi era, 1933–1939
Hitler came to power in January 1933, and inaugurated an aggressive power designed to give Germany economic and political domination across central Europe. He did not attempt to recover the lost colonies. Until August 1939, the Nazis denounced Communists and the Soviet Union as the greatest enemy, along with the Jews. Hitler's diplomatic strategy in the 1930s was to make seemingly reasonable demands, threatening war if they were not met. When opponents tried to appease him, he accepted the gains that were offered, then went to the next target. That aggressive strategy worked as Germany pulled out of the
Hitler's diplomatic strategy in the 1930s was to make seemingly reasonable demands, threatening war if they were not met. When opponents tried to appease him, he accepted the gains that were offered, then went to the next target. That aggressive strategy worked as Germany pulled out of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
, rejected the Versailles Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 19 ...
, and began to rearm. Retaking the Territory of the Saar Basin
The Territory of the Saar Basin (german: Saarbeckengebiet, ; french: Territoire du bassin de la Sarre) was a region of Germany occupied and governed by the United Kingdom and France from 1920 to 1935 under a League of Nations mandate. It had its ...
in the aftermath of a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
that favoured returning to Germany, Hitler's Germany remilitarised the Rhineland, formed the Pact of Steel
The Pact of Steel (german: Stahlpakt, it, Patto d'Acciaio), formally known as the Pact of Friendship and Alliance between Germany and Italy, was a military and political alliance between Italy and Germany.
The pact was initially drafted as a t ...
alliance with Mussolini's Italy, and sent massive military aid to Franco in the Spanish Civil War. Germany seized Austria, considered to be a German state, in 1938, and took over Czechoslovakia after the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
with Britain and France. Forming a non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a tr ...
with the Soviet Union in August 1939, Germany invaded Poland after Poland's refusal to cede the Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (german: Freie Stadt Danzig; pl, Wolne Miasto Gdańsk; csb, Wòlny Gard Gduńsk) was a city-state under the protection of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gda ...
in September 1939. Britain and France declared war and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
began – somewhat sooner than the Nazis expected or were ready for.
After establishing the "Rome-Berlin Axis
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were Na ...
" with Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
, and signing the Anti-Comintern Pact
The Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International was an anti-Communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936 and was directed against the Communist International ( ...
with Japan – which was joined by Italy a year later in 1937 – Hitler felt able to take the offensive in foreign policy. On 12 March 1938, German troops marched into Austria, where an attempted Nazi coup had been unsuccessful in 1934. When Austrian-born Hitler entered Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, he was greeted by loud cheers. Four weeks later, 99% of Austrians voted in favour of the annexation (Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the Nazi Germany, German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a "Ger ...
) of their country Austria to the German Reich
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty ...
. After Austria, Hitler turned to Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, where the 3.5 million-strong Sudeten German minority was demanding equal rights and self-government.Donald Cameron Watt, ''How war came: the immediate origins of the Second World War, 1938–1939'' (1989).R.J. Overy, ''The Origins of the Second World War'' (2014).
At the Munich Conference
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
of September 1938, Hitler, the Italian leader Benito Mussolini, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeasem ...
, and French Prime Minister Édouard Daladier
Édouard Daladier (; 18 June 1884 – 10 October 1970) was a French Radical-Socialist (centre-left) politician, and the Prime Minister of France who signed the Munich Agreement before the outbreak of World War II.
Daladier was born in Carp ...
agreed upon the cession of Sudeten territory to the German Reich by Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
. Hitler thereupon declared that all of German Reich's territorial claims had been fulfilled. However, hardly six months after the Munich Agreement, in March 1939, Hitler used the smouldering quarrel between Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 ...
and Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
as a pretext for taking over the rest of Czechoslovakia as the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia; cs, Protektorát Čechy a Morava; its territory was called by the Nazis ("the rest of Czechia"). was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German oc ...
. In the same month, he secured the return of Memel from Lithuania to Germany. Chamberlain was forced to acknowledge that his policy of appeasement
Appeasement in an international context is a diplomatic policy of making political, material, or territorial concessions to an aggressive power in order to avoid conflict. The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the UK governme ...
towards Hitler had failed.
Italy

Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
, was appointed Prime Minister of Italy
The Prime Minister of Italy, officially the President of the Council of Ministers ( it, link=no, Presidente del Consiglio dei Ministri), is the head of government of the Italian Republic. The office of president of the Council of Ministers is ...
after the March on Rome
The March on Rome ( it, Marcia su Roma) was an organized mass demonstration and a coup d'état in October 1922 which resulted in Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party (PNF) ascending to power in the Kingdom of Italy. In late October 1922, F ...
. Mussolini resolved the question of sovereignty over the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited ...
at the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conf ...
, which formalised Italian administration of both Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
and the Dodecanese Islands
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. ...
, in return for a payment to Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, the successor state to the Ottoman Empire, though he failed in an attempt to extract a mandate of a portion of Iraq from Britain.
The month following the ratification of the Treaty of Lausanne, Mussolini ordered the invasion of the Greek island of Corfu after the Corfu incident
The Corfu Incident was a 1923 diplomatic and military crisis between Greece and Italy. It was triggered when an Italian general heading a commission to resolve a border dispute between Albania and Greece was murdered in Greek territory along w ...
. The Italian press supported the move, noting that Corfu had been a Venetian possession for four hundred years. The matter was taken by Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
, where Mussolini was convinced by Britain to evacuate Royal Italian Army
The Royal Italian Army ( it, Regio Esercito, , Royal Army) was the land force of the Kingdom of Italy, established with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. During the 19th century Italy started to unify into one country, and in 1861 Manf ...
troops, in return for reparations from Greece. The confrontation led Britain and Italy to resolve the question of Jubaland
Jubaland ( so, Jubbaland, ar, , it, Oltregiuba), the Juba Valley ( so, Dooxada Jubba) or Azania ( so, Asaaniya, ar, ), is a Federal Member State in southern Somalia. Its eastern border lies east of the Jubba River, stretching from Gedo ...
in 1924, which was merged into Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th cent ...
.
During the late 1920s, imperial expansion became an increasingly favoured theme in Mussolini's speeches. Amongst Mussolini's aims were that Italy had to become the dominant power in the Mediterranean that would be able to challenge France or Britain, as well as attain access to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
and Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
s. Mussolini alleged that Italy required uncontested access to the world's oceans and shipping lanes to ensure its national sovereignty. This was elaborated on in a document he later drew up in 1939 called "The March to the Oceans", and included in the official records of a meeting of the Grand Council of Fascism
The Grand Council of Fascism (, also translated "Fascist Grand Council") was the main body of Mussolini's Fascist government in Italy, that held and applied great power to control the institutions of government. It was created as a body of the ...
. This text asserted that maritime position determined a nation's independence: countries with free access to the high seas were independent; while those who lacked this, were not. Italy, which only had access to an inland sea without French and British acquiescence, was only a "semi-independent nation", and alleged to be a "prisoner in the Mediterranean":
In the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, the Fascist regime claimed Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
and held ambitions over Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the ...
, Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
, and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
based on the precedent of previous Roman dominance in these regions. Dalmatia and Slovenia were to be directly annexed into Italy while the remainder of the Balkans was to be transformed into Italian client states. The regime also sought to establish protective patron-client relationships with Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
.
In both 1932 and 1935, Italy demanded a League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for adminis ...
of the former German Cameroon
Kamerun was an African colony of the German Empire from 1884 to 1916 in the region of today's Republic of Cameroon. Kamerun also included northern parts of Gabon and the Congo with western parts of the Central African Republic, southwester ...
and a free hand in the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historical ...
from France in return for Italian support against Germany in the Stresa Front. This was refused by French Prime Minister Édouard Herriot
Édouard Marie Herriot (; 5 July 1872 – 26 March 1957) was a French Radical politician of the Third Republic who served three times as Prime Minister (1924–1925; 1926; 1932) and twice as President of the Chamber of Deputies. He led the ...
, who was not yet sufficiently worried about the prospect of a German resurgence. The failed resolution of the Abyssinia Crisis
The Abyssinia Crisis (; ) was an international crisis in 1935 that originated in what was called the Walwal incident during the ongoing conflict between the Kingdom of Italy and the Empire of Ethiopia (then commonly known as "Abyssinia"). The Le ...
led to the Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression which was fought between Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy and Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethio ...
, in which Italy annexed Ethiopia to its empire.
Italy's stance towards Spain shifted between the 1920s and the 1930s. The Fascist regime in the 1920s held deep antagonism towards Spain due to Miguel Primo de Rivera
Miguel Primo de Rivera y Orbaneja, 2nd Marquess of Estella (8 January 1870 – 16 March 1930), was a dictator, aristocrat, and military officer who served as Prime Minister of Spain from 1923 to 1930 during Spain's Restoration era. He deep ...
's pro-French foreign policy. In 1926, Mussolini began aiding the Catalan separatist movement, which was led by Francesc Macià
Francesc Macià i Llussà (; 21 September 1859 – 25 December 1933) was a Spanish politician from Catalonia who served as the 122nd president of the Generalitat of Catalonia, and formerly an officer in the Spanish Army.
Politically, he evolv ...
, against the Spanish government. With the rise of the left-wing Republican government replacing the Spanish monarchy
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
, Spanish monarchists and fascists repeatedly approached Italy for aid in overthrowing the Republican government, in which Italy agreed to support them to establish a pro-Italian government in Spain. In July 1936, Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
of the Nationalist faction in the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
requested Italian support against the ruling Republican faction, and guaranteed that, if Italy supported the Nationalists, "future relations would be more than friendly" and that Italian support "would have permitted the influence of Rome to prevail over that of Berlin in the future politics of Spain". Italy intervened in the civil war with the intention of occupying the Balearic Islands and creating a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite sta ...
in Spain. Italy sought the control of the Balearic Islands due to its strategic position—Italy could use the islands as a base to disrupt the lines of communication between France and its North African colonies and between British Gibraltar and Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
. After the victory by Franco and the Nationalists in the war, Allied intelligence was informed that Italy was pressuring Spain to permit an Italian occupation of the Balearic Islands.
 After Great Britain signed the Anglo-Italian Easter Accords in 1938, Mussolini and Foreign Minister
After Great Britain signed the Anglo-Italian Easter Accords in 1938, Mussolini and Foreign Minister Galeazzo Ciano
Gian Galeazzo Ciano, 2nd Count of Cortellazzo and Buccari ( , ; 18 March 1903 – 11 January 1944) was an Italian diplomat and politician who served as Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs, Foreign Minister in the government of his father-in-law, ...
issued demands for concessions in the Mediterranean by France, particularly regarding French Somaliland, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and the French-run Suez Canal. Three weeks later, Mussolini told Ciano that he intended for an Italian takeover of Albania. Mussolini professed that Italy would only be able to "breathe easily" if it had acquired a contiguous colonial domain in Africa from the Atlantic to the Indian Oceans, and when ten million Italians had settled in them. In 1938, Italy demanded a sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal al ...
in the Suez Canal in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, specifically demanding that the French-dominated Suez Canal Company
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same b ...
accept an Italian representative on its board of directors. Italy opposed the French monopoly over the Suez Canal because, under the French-dominated Suez Canal Company, all merchant traffic to the Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa ( it, Africa Orientale Italiana, AOI) was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 through the merger of Italian Somalia, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire, conquered in the Se ...
colony was forced to pay tolls on entering the canal.
Albanian Prime Minister and President Ahmet Zogu
Zog I ( sq, Naltmadhnija e tij Zogu I, Mbreti i Shqiptarëve, ; 8 October 18959 April 1961), born Ahmed Muhtar bey Zogolli, taking the name Ahmet Zogu in 1922, was the leader of Albania from 1922 to 1939. At age 27, he first served as Albania's ...
, who had, in 1928, proclaimed himself King of Albania
While the medieval Angevin Kingdom of Albania was a monarchy, it did not encompass fully the entirety of the modern state of Albania and was ended soon by the Albanian nobles by 1282 when they understood that the Angevin king was not going to k ...
, failed to create a stable state. Albanian society was deeply divided by religion and language, with a border dispute with Greece and an undeveloped, rural economy. In 1939, Italy invaded and annexed Albania as a separate kingdom in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more State (polity), states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some e ...
with the Italian crown. Italy had long built strong links with the Albanian leadership and considered it firmly within its sphere of influence. Mussolini wanted a spectacular success over a smaller neighbour to match Germany's annexation of Austria
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a "Greater Germany ...
and Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
. Italian King Victor Emmanuel III
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
took the Albanian crown, and a fascist government under Shefqet Vërlaci
Shefqet bey Vërlaci (; 15 December 1877, Elbasan, Manastir Vilayet, Ottoman Empire – 21 July 1946, Zürich, Switzerland), also known as Shevket Verlaci, was an Albanian politician and wealthy landowner.
Biography
In 1922, Vërlaci was the ...
was established.
To one degree or another, Spain had been unstable politically for centuries, and in 1936–1939 was wracked by one of the bloodiest civil wars of the 20th century. The real importance comes from outside countries. In Spain the conservative and Catholic elements and the army revolted against the newly elected government, and full-scale civil war erupted. Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany gave munitions and strong military units to the rebel Nationalists, led by General Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 19 ...
. The Republican (or "Loyalist") government, was on the defensive, but it received significant help from the Soviet Union and Mexico. Led by Great Britain and France, and including the United States, most countries remained neutral and refused to provide armaments to either side. The powerful fear was that this localised conflict would escalate into a European conflagration that no one wanted.
Regional patterns
Balkans
The Great Depression destabilised theKingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
. The early 1930s were marked by social unrest, high unemployment, and strikes. In several instances, the Romanian government violently repressed strikes and riots, notably the 1929 miners' strike in Valea Jiului
The Jiu Valley ( ro, Valea Jiului ) is a region in southwestern Transylvania, Romania, in Hunedoara county, situated in a valley of the Jiu River between the Retezat Mountains and the Parâng Mountains. The region was heavily industrialised and t ...
and the strike in the Grivița
Grivița () is a district of Bucharest, Romania, centered on the Grivița Railway Yards (''Atelierele CFR Grivița''), which were and still are an important landmark within the manufacturing landscape of the city. Located near Gara de Nord, thei ...
railroad workshops. In the mid-1930s, the Romanian economy recovered and the industry grew significantly, although about 80% of Romanians were still employed in agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
. French economic and political influence was predominant in the early 1920s but then Germany became more dominant, especially in the 1930s.
In the Albanian Kingdom, Zog I
Zog I ( sq, Naltmadhnija e tij Zogu I, Mbreti i Shqiptarëve, ; 8 October 18959 April 1961), born Ahmed Muhtar bey Zogolli, taking the name Ahmet Zogu in 1922, was the leader of Albania from 1922 to 1939. At age 27, he first served as Albania's ...
introduced new civil codes, constitutional changes and attempted land reforms, the latter which was largely unsuccessful due to the inadequacy of the country's banking system that could not deal with advanced reformist transactions. Albania's reliance on Italy also grew as Italians exercised control over nearly every Albanian official through money and patronage, breeding a colonial-like mentality.
Ethnic integration and assimilation was a major problem faced by the newly formed post-World War I Balkan states, which were compounded by historical differences. In the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
for instance, its most influential element was the pre-war Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
but also integrated states like Slovenia and Croatia, which were part of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. With new territories came varying legal systems, social structures and political structures. Social and economic development rates also varied as for example Slovenia and Croatia was far more advanced economically than Kosovo and Macedonia. Redistribution of land led to social instability, with estate seizures generally benefiting Slavic Christians.
China
Japanese dominance in East Asia
industrial economy
In economics, industrial organization is a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure of (and, therefore, the boundaries between) firms and markets. Industrial organization adds real-world complications to the perf ...
closely on the most advanced Western European models. They started with textiles, railways, and shipping, expanding to electricity and machinery. The most serious weakness was a shortage of raw materials. Industry ran short of copper, and coal became a net importer. A deep flaw in the aggressive military strategy was a heavy dependence on imports including 100 percent of the aluminium, 85 percent of the iron ore, and especially 79 percent of the oil supplies. It was one thing to go to war with China or Russia, but quite another to be in conflict with the key suppliers, especially the United States, Britain, and the Netherlands, of oil and iron.
Japan joined the Allies of the First World War to make territorial gains. Together with the British Empire, it divided up Germany's territories scattered in the Pacific and on the Chinese coast; they did not amount to very much. The other Allies pushed back hard against Japan's efforts to dominate China through the Twenty-One Demands
The Twenty-One Demands ( ja, 対華21ヶ条要求, Taika Nijūikkajō Yōkyū; ) was a set of demands made during the First World War by the Empire of Japan under Prime Minister Ōkuma Shigenobu to the government of the Republic of China on 1 ...
of 1915. Its occupation of Siberia proved unproductive. Japan's wartime diplomacy and limited military action had produced few results, and at the Paris Versailles peace conference. At the end of the war, Japan was frustrated in its ambitions. At the Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
in 1919, its Racial Equality Proposal
The was an amendment to the Treaty of Versailles that was considered at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference. Proposed by Japan, it was never intended to have any universal implications, but one was attached to it anyway, which caused its controversy. ...
led to increasing diplomatic isolation. The 1902 alliance with Britain was not renewed in 1922 because of heavy pressure on Britain from Canada and the United States. In the 1920s Japanese diplomacy was rooted in an largely liberal democratic political system, and favoured internationalism. By 1930, however, Japan was rapidly reversing itself, rejecting democracy at home, as the Army seized more and more power, and rejecting internationalism and liberalism. By the late 1930s it had joined the Axis military alliance with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy.
In 1930, the London disarmament conference angered the Imperial Japanese Armed Forces
The Imperial Japanese Armed Forces (IJAF) were the combined military forces of the Japanese Empire. Formed during the Meiji Restoration in 1868,"One can date the 'restoration' of imperial rule from the edict of 3 January 1868." p. 334. they ...
. The Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
demanded parity with the United States, Britain and France, but was rejected and the conference kept the 1921 ratios. Japan was required to scrap a capital ship
The capital ships of a navy are its most important warships; they are generally the larger ships when compared to other warships in their respective fleet. A capital ship is generally a leading or a primary ship in a naval fleet.
Strategic i ...
. Extremists assassinated Japanese Prime Minister Inukai Tsuyoshi
Inukai Tsuyoshi ( ja, 犬養 毅, 4 June 1855 – 15 May 1932) was a Japanese politician, cabinet minister, and Prime Minister of Japan from 1931 to his assassination in 1932. Inukai was Japan's second oldest prime minister while serving, as he ...
in the May 15 Incident and the military took more power, leading to rapid democratic backsliding
Democratic backsliding, also called autocratization, is the decline in the democratic characteristics of a political system, and is the opposite of democratization. Democracy is the most popular form of government, with more than half of the nat ...
.
Japan seizes Manchuria
In September 1931, the JapaneseKwantung Army
''Kantō-gun''
, image = Kwantung Army Headquarters.JPG
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Kwantung Army headquarters in Hsinking, Manchukuo
, dates = Apri ...
—acting on its own without government approval— seized control of Manchuria, an anarchic area that China had not controlled in decades. It created the puppet government of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese in ...
. Britain and France effectively controlled the League of Nations, which issued the Lytton Report
are the findings of the Lytton Commission, entrusted in 1931 by the League of Nations in an attempt to evaluate the Mukden Incident, which led to the Empire of Japan's seizure of Manchuria.
The five-member commission headed by British politicia ...
in 1932, saying that Japan had genuine grievances, but it acted illegally in seizing the entire province. Japan quit the League, Britain and France took no action. US Secretary of State Henry L. Stimson
Henry Lewis Stimson (September 21, 1867 – October 20, 1950) was an American statesman, lawyer, and Republican Party politician. Over his long career, he emerged as a leading figure in U.S. foreign policy by serving in both Republican and De ...
announced that the United States would also not recognize Japan's conquest as legitimate. Germany welcomed Japan's actions.
Towards the conquest of China
 The civilian government in Tokyo tried to minimise the Army's aggression in Manchuria, and announced it was withdrawing. On the contrary, the Army completed the conquest of Manchuria, and the civilian cabinet resigned. The political parties were divided on the issue of military expansion. Prime Minister Tsuyoshi tried to negotiate with China, but was assassinated in the May 15 Incident in 1932, which ushered in an era of
The civilian government in Tokyo tried to minimise the Army's aggression in Manchuria, and announced it was withdrawing. On the contrary, the Army completed the conquest of Manchuria, and the civilian cabinet resigned. The political parties were divided on the issue of military expansion. Prime Minister Tsuyoshi tried to negotiate with China, but was assassinated in the May 15 Incident in 1932, which ushered in an era of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
and militarism
Militarism is the belief or the desire of a government or a people that a state should maintain a strong military capability and to use it aggressively to expand national interests and/or values. It may also imply the glorification of the mili ...
led by the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor ...
and supported by other right-wing societies. The IJA's nationalism ended civilian rule in Japan until after 1945.
The Army, however, was itself divided into cliques and factions with different strategic viewpoints. One faction viewed the Soviet Union as the main enemy; the other sought to build a mighty empire based in Manchuria and northern China. The Navy, while smaller and less influential, was also factionalised. Large-scale warfare, known as the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Thea ...
, began in August 1937, with naval and infantry attacks focused on Shanghai, which quickly spread to other major cities. There were numerous large-scale atrocities against Chinese civilians, such as the Nanjing massacre
The Nanjing Massacre (, ja, 南京大虐殺, Nankin Daigyakusatsu) or the Rape of Nanjing (formerly romanized as ''Nanking'') was the mass murder of Chinese civilians in Nanjing, the capital of the Republic of China, immediately after the Ba ...
in December 1937, with mass murder and mass rape. By 1939 military lines had stabilised, with Japan in control of almost all of the major Chinese cities and industrial areas. A puppet government was set up. In the U.S., government and public opinion—even including those who were isolationist regarding Europe—was resolutely opposed to Japan and gave strong support to China. Meanwhile, the Japanese Army fared badly in large battles with the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
in Mongolia at the Battles of Khalkhin Gol
The Battles of Khalkhin Gol (russian: Бои на Халхин-Голе; mn, Халхын голын байлдаан) were the decisive engagements of the undeclared Soviet–Japanese border conflicts involving the Soviet Union, Mongolia, J ...
in summer 1939. The USSR was too powerful. Tokyo and Moscow signed a nonaggression treaty in April 1941, as the militarists turned their attention to the European colonies to the south which had urgently-needed oil fields.
Latin America
The United States launched minor interventions into Latin America. These included military presence inCuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Panama with the Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone ( es, Zona del Canal de Panamá), also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the terr ...
, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
(1915–1935), Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
(1916–1924) and Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea, Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to ...
(1912–1933). The U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through com ...
began to specialize in long-term military occupation of these countries.
The Great Depression posed a great challenge to the region. The collapse of the world economy meant that the demand for raw materials drastically declined, undermining many of the economies of Latin America. Intellectuals and government leaders in Latin America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialisation. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the fluctuations of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration (1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a Good Neighbour policy and allowed the nationalisation of some American companies in Latin America. Mexican President Lázaro Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas del Río (; 21 May 1895 – 19 October 1970) was a Mexican army officer and politician who served as president of Mexico from 1934 to 1940.
Born in Jiquilpan, Michoacán, to a working-class family, Cárdenas joined the Me ...
nationalised American oil companies, out of which he created Pemex
Pemex (a portmanteau of Petróleos Mexicanos, which translates to ''Mexican Petroleum'' in English; ) is the Mexican state-owned petroleum company managed and operated by the Mexican government. It was formed in 1938 by nationalization and expr ...
. Cárdenas also oversaw the redistribution of a quantity of land, fulfilling the hopes of many since the start of the Mexican Revolution. The Platt Amendment
On March 2, 1901, the Platt Amendment was passed as part of the 1901 Army Appropriations Bill.Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
countries where US influence was weaker and larger German communities were at place.
The contrary ideals of ''indigenismo
''Indigenismo'' () is a political ideology in several Latin American countries which emphasizes the relationship between the nation state and indigenous nations and indigenous peoples. In some contemporary uses, it refers to the pursuit of great ...
'' and '' hispanismo'' held sway among intellectuals in Spanish-speaking America during the interwar period. In Argentina the ''gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and ...
'' genre flourished. A rejection of "Western universalist" influences was in vogue across Latin America. This last tendency was in part inspired by the translation into Spanish of the book ''Decline of the West
''The Decline of the West'' (german: Der Untergang des Abendlandes; more literally, ''The Downfall of the Occident''), is a two-volume work by Oswald Spengler. The first volume, subtitled ''Form and Actuality'', was published in the summer of 191 ...
'' in 1923.
Sports
Sports became increasingly popular, drawing enthusiastic fans to large stadiums. TheInternational Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swis ...
(IOC) worked to encourage Olympic ideals and participation. Following the 1922 Latin American Games in Rio de Janeiro, the IOC helped to establish national Olympic committees and prepare for future competition. In Brazil, however, sporting and political rivalries slowed progress as opposing factions fought for control of international sport The concept of international sport refers to sport when the participants represent at least two countries. The most well-known international sports event is the Olympic Games. Other examples include the FIFA World Cup and the Cricket World Cup. Th ...
. The 1924 Summer Olympics
The 1924 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1924), officially the Games of the VIII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIIe olympiade) and also known as Paris 1924, were an international multi-sport event held in Paris, France. The op ...
in Paris and the 1928 Summer Olympics
The 1928 Summer Olympics ( nl, Olympische Zomerspelen 1928), officially known as the Games of the IX Olympiad ( nl, Spelen van de IXe Olympiade) and commonly known as Amsterdam 1928, was an international multi-sport event that was celebrated from ...
in Amsterdam had greatly increased participation from Latin American athletes.
English and Scottish engineers had brought futebol (soccer) to Brazil in the late 19th century. The International Committee of the YMCA of North America and the Playground Association of America played major roles in training coaches. Across the globe after 1912, the Fédération Internationale de Football Association
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' (French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was founde ...
(FIFA) played the chief role in the transformation of association football into a global game, working with national and regional organisations, and setting up the rules and customs, and establishing championships such as the World Cup.
Machine Age
The Machine Age is an era that includes the early-to-mid 20th century, sometimes also including the late 19th century. An approximate dating would be about 1880 to 1945. Considered to be at its peak in the time between the first and second wo ...
bar:World.Wars color:era
from:1914 till:1918 text:WWI
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
from:1918 till:1939 text:Interwar period
from:1939 till:1946 text:WWII
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
End of an era
The interwar period ended in September 1939 with theGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
and Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
and the start of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
See also
*International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919)
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
* Aftermath of World War I
The aftermath of World War I saw drastic political, cultural, economic, and social change across Eurasia, Africa, and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Four empires collapsed due to the war, old countries were abolished, ne ...
* 1920s
File:1920s decade montage.png, From left, clockwise: Third Tipperary Brigade Flying Column No. 2 under Seán Hogan during the Irish War of Independence; Prohibition agents destroying barrels of alcohol in accordance to the 18th amendment, which ...
* Jazz age
* Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, sometimes stylized as Roaring '20s, refers to the 1920s decade in music and fashion, as it happened in Western society and Western culture. It was a period of economic prosperity with a distinctive cultural edge in the ...
* 1930s
* International relations (1919–1939)
International relations (1919–1939) covers the main interactions shaping world history in this era, known as the Interwar Period, with emphasis on diplomacy and economic relations. The coverage here follows the diplomatic history of World War I ...
* Diplomatic history of World War I
The diplomatic history of World War I covers the non-military interactions among the major players during World War I. For the domestic histories of participants see home front during World War I. For a longer-term perspective see international rel ...
* Diplomatic history of World War II
The diplomatic history of World War II includes the major foreign policies and interactions inside the opposing coalitions, the Allies of World War II and the Axis powers, between 1939 and 1945.
High-level diplomacy began as soon as the war star ...
* Causes of World War II
The causes of World War II, a global war from 1939 to 1945 that was the deadliest conflict in human history, have been given considerable attention by historians from many countries who studied and understood them. The immediate precipitating ...
* Interwar Britain
In the United Kingdom, the interwar period (1918–1939) was a period of relative stability after the division of Ireland, though of economic stagnation. In politics, the Liberal Party collapsed and the Labour Party became the main challenge ...
* European Civil War
The European Civil War is a concept meant to characterize a series of 19th- and 20th-century conflicts in Europe as segments of an overarching civil war within a supposed European society. The timeframes associated with this European Civil War var ...
* European interwar dictatorships
* Interwar United States
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
* Lost Generation
The Lost Generation was the social generational cohort in the Western world that was in early adulthood during World War I. "Lost" in this context refers to the "disoriented, wandering, directionless" spirit of many of the war's survivors in the ...
* Interbellum Generation
Interbellum Generation is a term (derived from the Latin ''inter'' "between" and ''bellum'' "war") that is sometimes used to denote people born in the United States during the first decade of the 20th century, often expressed specifically as the y ...
* Greatest Generation
* Interwar Poland
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World ...
* Interwar Belgium
The history of Belgium extends before the founding of the modern state of that name in 1830, and is intertwined with those of its neighbors: the Netherlands, Germany, France and Luxembourg. For most of its history, what is now Belgium was e ...
* Second Thirty Years' War
:''This is about the term and historiography. For history of the period see World War I, World War II, etc..''
"Second Thirty Years' War" is a periodization scheme sometimes used to encompass the wars in Europe from 1914 to 1945.
Just as the Thirty ...
* 1920s in Western fashion
Western fashion in the 1920s underwent a modernization. For women, fashion had continued to change away from the extravagant and restrictive styles of the Victorian and Edwardian periods, and towards looser clothing which revealed more of the ...
** 1930–45 in Western fashion
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 ''Ab urbe condit ...
* Great Depression
*** Great Depression in the United States
In the United States, the Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of October 1929 and then spread worldwide. The nadir came in 1931–1933, and recovery came in 1940. The stock market crash marked the beginning of a decade of high ...
*** European interwar economy The European interwar economy (the period between the First and Second World War, also known as the interbellum) began when the countries in Western Europe were struggling to recover from the devastation caused by the First World War, while also dea ...
*** Causes of the Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. The sp ...
*** Cities in the Great Depression
Throughout the industrial world, cities were hit hard during the Great Depression, beginning in 1929 and lasting through most of the 1930s. Worst hit were port cities (as world trade fell) and cities that depended on heavy industry, such as the ...
*** Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl was a period of severe dust storms that greatly damaged the ecology and agriculture of the American and Canadian prairies during the 1930s. The phenomenon was caused by a combination of both natural factors (severe drought) an ...
*** Entertainment during the Great Depression During the 1930s the United States was facing its longest and deepest economic downturn, the Great Depression. Spending money on entertainment was out of the question for most people. The United States put the nation back to work, including artists ...
*** Timeline of the Great Depression
The initial economic collapse which resulted in the Great Depression can be divided into two parts: 1929 to mid-1931, and then mid-1931 to 1933. The initial decline lasted from mid-1929 to mid-1931. During this time, most people believed that th ...
* Political history of the world
The political history of the world is the history of the various political entities created by the human race throughout their existence and the way these states define their borders. Throughout history, political systems have expanded from bas ...
* '' Apocalypse: Never-Ending War 1918–1926''
Timelines
*Timeline of the 20th century
This is a timeline of the 20th century.
1900s
1901
* January 1: The Australian colonies federate.
* January 22: Edward VII becomes King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India upon the death of Queen Victoria.
...
, since 1900
* Timeline of events preceding World War II
This timeline of events preceding World War II covers the events of the interwar period (1918–1939) after World War I that affected or led to World War II.
__NOTOC__
1910s: 19181919
1920s: 1920 1921 1922 1923 1924 1925 1926 1927 19281929
...
** Events preceding World War II in Europe
The events preceding World War II in Europe are closely tied to the bellicosity of Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany, and Imperial Japan, as well as the Great Depression. The peace movement led to appeasement and disarmament.
Aftermath of World War ...
** Events preceding World War II in Asia
This article is concerned with the events that preceded World War II in Asia.
Kuomintang and Communism in China
The revolution led by the Kuomintang (KMT, or Chinese Nationalist Party) and others ended the last Chinese dynasty, the Qing dyn ...
References
Further reading
For a guide to the reliable sources see Jacobson (1983).Jon Jacobson, "Is there a New International History of the 1920s?." ''American Historical Review'' 88.3 (1983): 617–64online
. * Morris, Richard B. and Graham W. Irwin, eds. ''Harper Encyclopedia of the Modern World: A Concise Reference History from 1760 to the Present'' (1970
online
* Albrecht-Carrié, René. ''A Diplomatic History of Europe Since the Congress of Vienna'' (1958), 736pp; a basic introduction, 1815–195
online free to borrow
* Berg-Schlosser, Dirk, and Jeremy Mitchell, eds. ''Authoritarianism and democracy in Europe, 1919–39: comparative analyses'' (Springer, 2002). * Berman, Sheri. ''The Social Democratic Moment: Ideas and Politics in the Making of Interwar Europe'' (Harvard UP, 2009). * Bowman, Isaiah. ''The New World: Problems in Political Geography'' (4th ed. 1928) sophisticated global coverage; 215 maps
online
* Brendon, Piers. '' The Dark Valley: A Panorama of the 1930s'' (2000) a comprehensive global political history; 816p
excerpt
* Cambon, Jules, ed ''The Foreign Policy of the Powers'' (1935) Essays by experts that cover France, Germany, Great Britain, Italy, Japan, Russia and the United State
Online free
* Clark, Linda Darus, ed. ''Interwar America: 1920–1940: Primary Sources in U.S. History'' (2001) * Dailey, Andy, and David G. Williamson. (2012) ''Peacemaking, Peacekeeping: International Relations 1918–36'' (2012) 244 pp; textbook, heavily illustrated with diagrams and contemporary photographs and colour posters. * Doumanis, Nicholas, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of European History, 1914–1945'' (Oxford UP, 2016). * Duus, Peter, ed., ''The Cambridge History of Japan, vol. 6, The Twentieth Century'' (1989) pp 53–153, 217–340
online
* Feinstein, Charles H., Peter Temin, and Gianni Toniolo. ''The World Economy Between the World Wars'' (Oxford UP, 2008), a standard scholarly survey. * Freeman, Robert. ''The InterWar Years (1919–1939)'' (2014), brief survey * Garraty, John A. '' The Great Depression: An Inquiry into the Causes, Course, and Consequences of the Worldwide Depression of the Nineteen-1930s, As Seen by Contemporaries'' (1986). * Gathorne-Hardy, Geoffrey Malcolm. ''A Short History of International Affairs, 1920 to 1934'' (Oxford UP, 1952). *
Online free to borrow
* Grift, Liesbeth van de, and Amalia Ribi Forclaz, eds. ''Governing the Rural in Interwar Europe'' (2017) * Grossman, Mark ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Interwar Years: From 1919 to 1939'' (2000). * Hicks, John D. ''Republican Ascendancy, 1921-1933'' (1960) for US
online
* – a view from the Left. * Kaser, M. C. and E. A. Radice, eds. ''The Economic History of Eastern Europe 1919–1975: Volume II: Interwar Policy, The War, and Reconstruction'' (1987) * * Koshar, Rudy. ''Splintered Classes: Politics and the Lower Middle Classes in Interwar Europe'' (1990). * * Luebbert, Gregory M. ''Liberalism, Fascism, Or Social Democracy: Social Classes and the Political Origins of Regimes in Interwar Europe'' (Oxford UP, 1991). * * Matera, Marc, and Susan Kingsley Kent. ''The Global 1930s: The International Decade'' (Routledge, 2017
excerpt
* * *
Mowat, C. L.
Charles Loch Mowat (4 October 1911 – 23 June 1970) was a British-born American historian.
Biography
Mowat was educated at Marlborough College and St John's College, Oxford. John Ramsden (ed.), ''The Oxford Companion to Twentieth Century B ...
ed. (1968). ''The New Cambridge Modern History, Vol. 12: The Shifting Balance of World Forces, 1898–1945'' (2nd ed.). – 25 chapters by experts; 845 pp; the first edition (1960) edited by David Thompson has the same title but numerous different chapters.
* Mowat, Charles Loch. ''Britain Between the Wars, 1918–1940'' (1955), 690pp; thorough scholarly coverage; emphasis on politics. also online free to borrow
* Murray, Williamson and Allan R. Millett, eds. ''Military Innovation in the Interwar Period'' (1998) * Newman, Sarah, and Matt Houlbrook, eds. ''The Press and Popular Culture in Interwar Europe'' (2015) * Overy, R.J. ''The Inter-War Crisis 1919–1939'' (2nd ed. 2007) * Rothschild, Joseph. ''East Central Europe Between the Two World Wars'' (U of Washington Press, 2017). * Seton-Watson, Hugh. (1945) ''Eastern Europe Between The Wars 1918–1941'' (1945
online
* – 550 pp; wide-ranging political, social and economic coverage of Britain, 1910–35 * Sontag, Raymond James. ''A Broken World, 1919–1939'' (1972
online free to borrow
wide-ranging survey of European history * Sontag, Raymond James. "Between the Wars." ''Pacific Historical Review'' 29.1 (1960): 1–1
online
* Steiner, Zara. ''The Lights that Failed: European International History 1919–1933''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2008. * Steiner, Zara. ''The Triumph of the Dark: European International History 1933–1939''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2011. * Toynbee, A. J. ''Survey of International Affairs 1920–1923'' (1924
online
''Survey of International Affairs'' annual 1920–193
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1924'' (1925); ''Survey of International Affairs 1925'' (1926
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1924'' (1925
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1927'' (1928
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1928'' (1929
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1929'' (1930
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1932'' (1933
online
''Survey of International Affairs 1934'' (1935), focus on Europe, Middle East, Far East; ''Survey of International Affairs 1936'' (1937
online
* Watt, D.C. et al., A History of the World in the Twentieth Century (1968) pp 301–530. * Wheeler-Bennett, John. ''Munich: Prologue To Tragedy,'' (1948) broad coverage of diplomacy of 1930s * Zachmann, Urs Matthias. ''Asia after Versailles: Asian Perspectives on the Paris Peace Conference and the Interwar Order, 1919–33'' (2017)
Historiography
* Cornelissen, Christoph, and Arndt Weinrich, eds. ''Writing the Great War – The Historiography of World War I from 1918 to the Present'' (2020) free download; full coverage for major countries. * Jacobson, Jon. "Is there a New International History of the 1920s?." ''American Historical Review'' 88.3 (1983): 617–645 online.Primary sources
* Keith, Arthur Berridale, ed. ''Speeches and Documents On International Affairs Vol-I'' (1938) online free vol 1 vol 2 online free; all in English translationExternal links
Mount Holyoke College edition
"Britain 1919 to the present"
Several large collections of primary sources and illustrations
{{Authority control . . Chronology of World War II Periodization