|
Kingdom Of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania () was a constitutional monarchy that existed from with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King of Romania, King Carol I of Romania, Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian royal family), until 1947 with the abdication of King Michael I of Romania, Michael I and the Romanian parliament's proclamation of the Socialist Republic of Romania, Romanian People's Republic. From 1859 to 1877, Romania evolved from a personal union of two Principality, principalities: (Moldavia and Wallachia) called the Unification of Moldavia and Wallachia also known as "The Little Union" under a single prince to an autonomous principality with a House of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern monarchy. The country gained its independence from the Ottoman Empire during the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), 1877–1878 Russo-Turkish War (known locally as the Romanian War of Independence), after which it was forced to cede the southern part of Bessarabia in exchange for Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carol I Of Romania
Carol I or Charles I of Romania (born Karl Eitel Friedrich Zephyrinus Ludwig von Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen; 20 April 1839 – ), was the monarch of Romania from 1866 to his death in 1914, ruling as Prince (''Domnitor'') from 1866 to 1881, and as King from 1881 to 1914. He was elected Prince of the Romanian United Principalities on 20 April 1866 after the overthrow of Alexandru Ioan Cuza by a palace coup d'état. In May 1877, Romania was proclaimed an independent and sovereign nation. The defeat of the Ottoman Empire (1878) in the Russo-Turkish War secured Romanian independence, and he was proclaimed King on . He was the first ruler of the Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen dynasty, which ruled the country until the proclamation of a socialist republic in 1947. During his reign, Carol I personally led Romanian troops during the Russo-Turkish War and assumed command of the Russo/Romanian army during the siege of Plevna. The country achieved internationally recognized independence via the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle Époque
The Belle Époque () or La Belle Époque () was a period of French and European history that began after the end of the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and continued until the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era of the French Third Republic, it was a period characterised by optimism, enlightenment, romanticism, regional peace, economic prosperity, conservatism, nationalism, colonial expansion, and technological, scientific and cultural innovations. In this era of France's cultural and artistic climate (particularly in Paris of that time), the arts markedly flourished, and numerous masterpieces of literature, music, theatre and visual art gained extensive recognition. The Belle Époque was so named in retrospect, when it began to be considered a continental European " Golden Age" in contrast to the horrors of the Napoleonic Wars and World War I. The Belle Époque was a period in which, according to historian R. R. Palmer, " European civilisation a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Italo-Western languages, Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called ''#Dialects, Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Romanians in Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Romanians in Hungary, Hungary, Romanians in Serbia, Serbia and Romanians in Ukraine, Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand I Of Romania
Ferdinand I (Ferdinand Viktor Albert Meinrad; 24 August 1865 – 20 July 1927), nicknamed ''Întregitorul'' ("the Unifier"), was King of Romania from 10 October 1914 until his death in 1927. Ferdinand was the second son of Leopold, Prince of Hohenzollern, and Infanta Antónia of Portugal, (daughter of Queen Maria II of Portugal and of Ferdinand II of Portugal, Prince Ferdinand of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha-Kohary). His Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, family was part of the Catholic branch of the Prussian royal family Hohenzollern. In 1886, Ferdinand became heir presumptive to the Romanian throne, following the renunciation of his father (in 1880) and William, Prince of Hohenzollern, older brother. From the moment he settled in Romania, he continued his military career, gaining a series of honorary commands and being promoted to the rank of corps general. He married in 1893 Marie of Romania, Princess Marie of Edinburgh, granddaughter of both Queen Victoria and Alexander II of Russia, Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Romania
The King of Romania () or King of the Romanians () was the title of the monarch of the Kingdom of Romania from 1881 until 1947, when the Romanian Workers' Party proclaimed the Romanian People's Republic following Michael I's forced abdication. History The state had been internationally recognized as a principality since 1862, after the creation of the United Principalities, a personal union between Moldavia and Wallachia, at that time vassal states of the Ottoman Empire. Alexander I became '' domnitor'' (ruling prince) after the official unification of the two formerly separate states, being elected prince of both states in 1859. He was deposed in 1866 by a broad coalition of the main political parties, after which parliament offered the throne to Prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen who subsequently became the new "Domnitor of Romania" (as Carol I). Romania's independence from the Ottoman Empire was recognized in 1878 by the Treaty of Berlin. In an expression of ful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies (in which a monarch is the only decision-maker) in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework. A constitutional monarch in a parliamentary democracy is a hereditary symbolic head of state (who may be an emperor, king or queen, prince or grand duke) who mainly performs representative and civic roles but does not exercise executive or policy-making power. Constitutional monarchies range from countries such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait, Bahrain and Bhutan, where the constitution grants substantial discretionary powers to the sovereign, to countries such as the United Kingdom and other Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
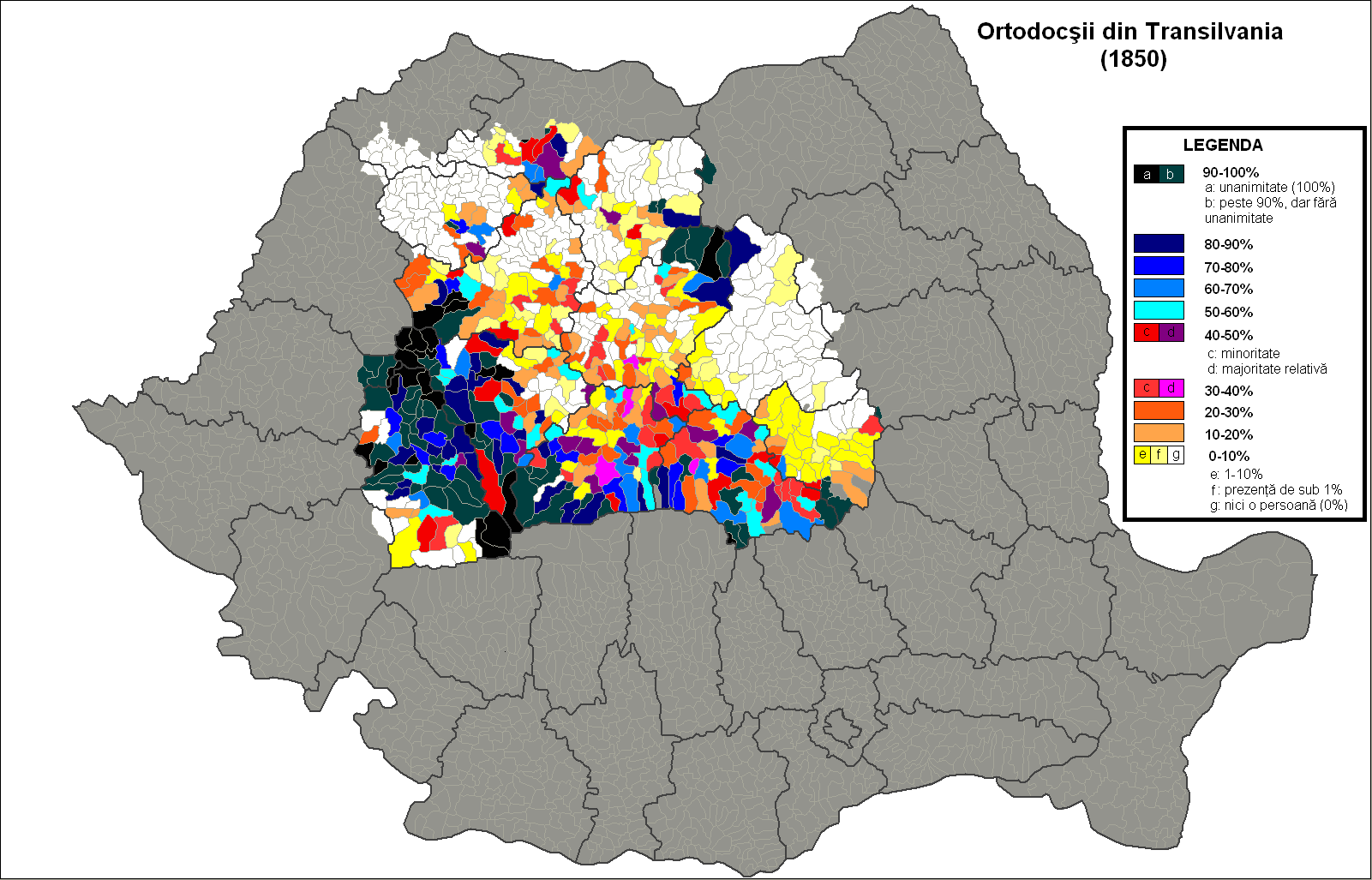
Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; , ), or Romanian Patriarchate, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the Eastern Orthodox Church organization, Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 1925, the church's Primate (bishop), Primate has borne the title of Patriarch. Its jurisdiction covers the territories of Romania and Moldova, with additional dioceses for Romanians living in nearby Ukraine, Serbia and Hungary, as well as for diaspora communities in Central Europe, Central and Western Europe, North America and Oceania. It is the only autocephalous church within Eastern Orthodoxy to have a Romance languages, Romance language for liturgical use. The majority of Romania's population (16,367,267, or 85.9% of those for whom data were available, according to the 2011 census data), as well as some 720,000 Moldovans, belong to the Romanian Orthodox Church. Members o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gagauz Language
Gagauz (; or ) is a Turkic language spoken by the Gagauz people of Moldova, Ukraine, Russia and Turkey and it is an official language of the Autonomous Region of Gagauzia in Moldova. Gagauz belongs to the Oghuz branch of Turkic languages, alongside Azerbaijani, Turkmen, and Turkish. Gagauz is a distinct language from Balkan Gagauz Turkish to some degree. Though it was established as a written language in 1957, Gagauz was not used in schools until 1959. Gagauz is a language derived from Balkan Gagauz Turkish; Balkan linguistics was the first to view the consequences of language contact as normal rather than corrupt. The term "Gagauz language" and the identification of one's language as "Gagauz" were established concurrently with or even after the creation of national self-awareness. About 150,000 Gagauz resided in Moldova in 1986, where they lived in settlements within the Comrat, Ceadîr-Lunga and Vulcănești Rayons. Along with the majority of the Gagauz living in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Language
Turkish ( , , also known as 'Turkish of Turkey') is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, a member of Oghuz languages, Oghuz branch with around 90 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey and one of two official languages of Cyprus. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers also exist in Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Greece, other parts of Europe, the South Caucasus, and some parts of Central Asia, Iraqi Turkmen, Iraq, and Syrian Turkmen, Syria. Turkish is the List of languages by total number of speakers, 18th-most spoken language in the world. To the west, the influence of Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish—the variety of the Turkish language that was used as the administrative and literary language of the Ottoman Empire—spread as the Ottoman Empire expanded. In 1928, as one of Atatürk's reforms in the early years of the Republic of Turkey, the Persian alphabet, Perso-Arabic script-based Ottoman Turkish alphabet was repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani Language
Romani ( ; also Romanes , Romany, Roma; ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani people. The largest of these are Vlax Romani language, Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself. The differences between the various varieties can be as large as, for example, the differences between the Slavic languages. Name Speakers of the Romani language usually refer to the language as ' "the Romani language" or '' (adverb)'' "in a Rom way". This derives from the Romani word ', meaning either "a member of the (Romani) group" or "husband". This is also the origin of the term "Roma" in English, although some Roma groups refer to themselves using other demonyms (e.g. 'Kaale', 'Sinti'). C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Language
Bulgarian (; , ) is an Eastern South Slavic, Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic languages, South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of grammatical case, case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidentiality, evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official Languages of Bulgaria, language of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |