Han period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring
 At the beginning of the Western Han (), also known as the Former Han () dynasty, thirteen centrally-controlled
At the beginning of the Western Han (), also known as the Former Han () dynasty, thirteen centrally-controlled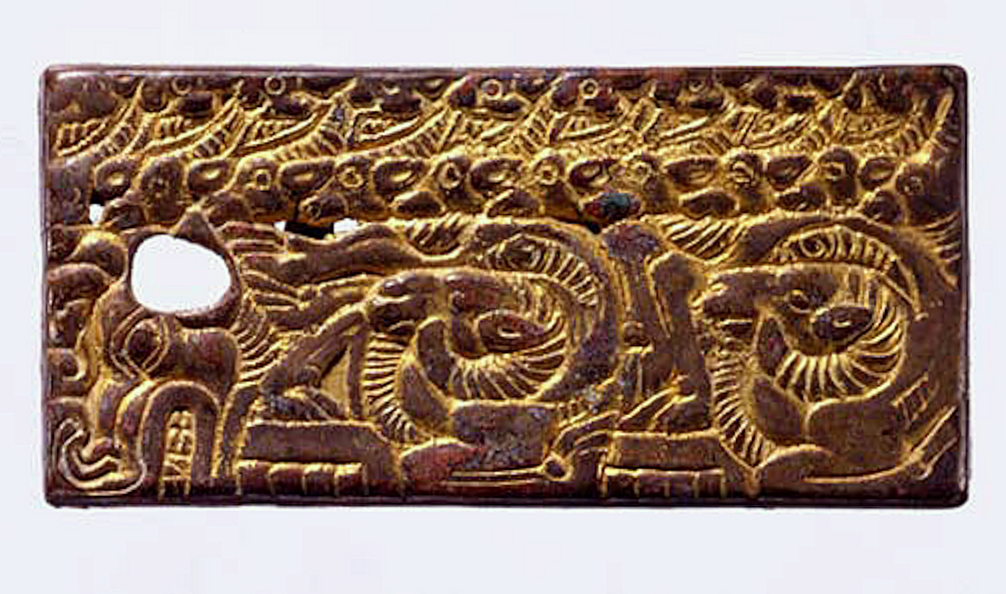  Despite the tribute and negotiation between Laoshang Chanyu ( BC) and Emperor Wen ( BC) to reopen border markets, many of the
Despite the tribute and negotiation between Laoshang Chanyu ( BC) and Emperor Wen ( BC) to reopen border markets, many of the  In 121 BC, Han forces expelled the Xiongnu from a vast territory spanning the Hexi Corridor to
In 121 BC, Han forces expelled the Xiongnu from a vast territory spanning the Hexi Corridor to
 Wang Zhengjun (71 BC – 13 AD) was first empress, then
Wang Zhengjun (71 BC – 13 AD) was first empress, then
 The Eastern Han (), also known as the Later Han (), formally began on 5 August AD 25, when Liu Xiu became Emperor Guangwu of Han. During the widespread rebellion against Wang Mang, the state of Goguryeo was free to raid Han's Korean commanderies; Han did not reaffirm its control over the region until AD 30.
The Trưng Sisters of Vietnam rebelled against Han in AD 40. Their rebellion was crushed by Han general
The Eastern Han (), also known as the Later Han (), formally began on 5 August AD 25, when Liu Xiu became Emperor Guangwu of Han. During the widespread rebellion against Wang Mang, the state of Goguryeo was free to raid Han's Korean commanderies; Han did not reaffirm its control over the region until AD 30.
The Trưng Sisters of Vietnam rebelled against Han in AD 40. Their rebellion was crushed by Han general
interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurp
A usurper is an illegitimate or controversial claimant to power, often but not always in a monarchy. In other words, one who takes the power of a country, city, or established region for oneself, without any formal or legal right to claim it as ...
ing regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the " Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as " Han characters".
The emperor
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in E ...
was at the pinnacle of Han society. He presided over the Han government but shared power with both the nobility and appointed ministers who came largely from the scholarly gentry class. The Han Empire was divided into areas directly controlled by the central government called commanderies
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Gr ...
, as well as a number of semi-autonomous kingdoms. These kingdoms gradually lost all vestiges of their independence, particularly following the Rebellion of the Seven States. From the reign of Emperor Wu ( BC) onward, the Chinese court officially sponsored Confucianism in education and court politics, synthesized with the cosmology of later scholars such as Dong Zhongshu
Dong Zhongshu (; 179–104 BC) was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and writer of the Han Dynasty. He is traditionally associated with the promotion of Confucianism as the official ideology of the Chinese imperial state. He apparently favored ...
. This policy endured until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912 AD.
The Han dynasty saw an age of economic prosperity and witnessed a significant growth of the money economy first established during the Zhou dynasty ( BC). The coinage issued by the central government mint in 119 BC remained the standard coinage of China until the Tang dynasty (618–907 AD). The period saw a number of limited institutional innovations. To finance its military campaigns and the settlement of newly conquered frontier territories, the Han government nationalized the private salt and iron industries in 117 BC, though these government monopolies were later repealed during the Eastern Han dynasty. Science and technology during the Han period saw significant advances, including the process of papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
, the nautical steering ship rudder, the use of negative number
In mathematics, a negative number represents an opposite. In the real number system, a negative number is a number that is less than zero. Negative numbers are often used to represent the magnitude of a loss or deficiency. A debt that is owed m ...
s in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, the raised-relief map, the hydraulic-powered armillary sphere
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of ...
for astronomy, and a seismometer employing an inverted pendulum that could be used to discern the cardinal direction of distant earthquakes.
The Han dynasty is known for the many conflicts it had with the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
, a nomadic steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
confederation to the dynasty's north. The Xiongnu initially had the upper hand in these conflicts. They defeated the Han in 200 BC and forced the Han to submit as a ''de facto'' inferior and vassal partner for several decades, while continuing their military raids on the dynasty's borders. This changed in 133 BC, during the reign of Emperor Wu, when Han forces began a series of intensive military campaigns and operations against the Xiongnu. The Han ultimately defeated the Xiongnu in these campaigns, and the Xiongnu were forced to accept vassal status as Han tributaries. Additionally, the campaigns brought the Hexi Corridor and the Tarim Basin of Central Asia under Han control, split the Xiongnu into two separate confederations, and helped establish the vast trade network known as the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, which reached as far as the Mediterranean world
The history of the Mediterranean region and of the cultures and people of the Mediterranean Basin is important for understanding the origin and development of the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Canaanite, Phoenician, Hebrew, Carthaginian, Minoan, Gre ...
. The territories north of Han's borders were later overrun by the nomadic Xianbei confederation. Emperor Wu also launched successful military expeditions in the south, annexing Nanyue in 111 BC and Dian in 109 BC. He expanded Han territory into the northern Korean Peninsula as well, where Han forces conquered Gojoseon and established the Xuantu and Lelang Commanderies in 108 BC.
After 92 AD, the palace eunuchs
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium ...
increasingly involved themselves in the dynasty's court politics, engaging in violent power struggles between the various consort clans of the empresses and empresses dowager, causing the Han's ultimate downfall. Imperial authority was also seriously challenged by large Daoist religious societies which instigated the Yellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, alternatively translated as the Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a List of peasant revolts, peasant revolt in China against the Eastern Han dynasty. The uprising broke out in 184 CE during the reign of Emperor Ling of ...
and the Five Pecks of Rice Rebellion
The Way of the Five Pecks of Rice () or the Way of the Celestial Master, commonly abbreviated to simply The Celestial Masters, was a Chinese Taoist movement founded by the first Celestial Master Zhang Daoling in 142 CE. At its height, the mov ...
. Following the death of Emperor Ling ( AD), the palace eunuchs suffered wholesale massacre by military officers, allowing members of the aristocracy and military governors to become warlords and divide the empire. When Cao Pi, king of Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
, usurped the throne from Emperor Xian, the Han dynasty ceased to exist.
Etymology
According to the '' Records of the Grand Historian'', after the collapse of the Qin dynasty the hegemon Xiang Yu appointed Liu Bang as prince of the small fief of Hanzhong, named after its location on the Han River (in modern southwest Shaanxi). Following Liu Bang's victory in theChu–Han Contention
The Chu–Han Contention ( zh, , lk=on) or Chu–Han War () was an interregnum period in ancient China between the fallen Qin dynasty and the subsequent Han dynasty. After the third and last Qin ruler, Ziying, unconditionally surrendered t ...
, the resulting Han dynasty was named after the Hanzhong fief.
History
Western Han
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
's first imperial dynasty was the Qin dynasty (221–207 BC). The Qin united the Chinese Warring States by conquest, but their regime became unstable after the death of the first emperor Qin Shi Huang. Within four years, the dynasty's authority had collapsed in the face of rebellion. Two former rebel leaders, Xiang Yu (d. 202 BC) of Chu
Chu or CHU may refer to:
Chinese history
* Chu (state) (c. 1030 BC–223 BC), a state during the Zhou dynasty
* Western Chu (206 BC–202 BC), a state founded and ruled by Xiang Yu
* Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty) (201 BC–70 AD), a kingdom of the Ha ...
and Liu Bang (d. 195 BC) of Han, engaged in a war to decide who would become hegemon of China, which had fissured into 18 kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.� ...
, each claiming allegiance to either Xiang Yu or Liu Bang. Although Xiang Yu proved to be an effective commander, Liu Bang defeated him at the Battle of Gaixia (202 BC), in modern-day Anhui. Liu Bang assumed the title "emperor" (''huangdi'') at the urging of his followers and is known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu ( BC). Chang'an (known today as Xi'an) was chosen as the new capital of the reunified empire under Han.
 At the beginning of the Western Han (), also known as the Former Han () dynasty, thirteen centrally-controlled
At the beginning of the Western Han (), also known as the Former Han () dynasty, thirteen centrally-controlled commanderies
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Gr ...
—including the capital region—existed in the western third of the empire, while the eastern two-thirds were divided into ten semi-autonomous kingdoms. To placate his prominent commanders from the war with Chu, Emperor Gaozu enfeoffed some of them as kings.
By 196 BC, the Han court had replaced all but one of these kings (the exception being in Changsha) with royal Liu family members, since the loyalty of non-relatives to the throne was questioned. After several insurrections by Han kings—the largest being the Rebellion of the Seven States in 154 BC—the imperial court enacted a series of reforms beginning in 145 BC limiting the size and power of these kingdoms and dividing their former territories into new centrally-controlled commanderies. Kings were no longer able to appoint their own staff; this duty was assumed by the imperial court. Kings became nominal heads of their fiefs and collected a portion of tax revenues as their personal incomes. The kingdoms were never entirely abolished and existed throughout the remainder of Western and Eastern Han.
To the north of China proper, the nomadic Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
chieftain Modu Chanyu ( BC) conquered various tribes inhabiting the eastern portion of the Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistri ...
. By the end of his reign, he controlled Manchuria, Mongolia, and the Tarim Basin, subjugating over twenty states east of Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
. Emperor Gaozu was troubled about the abundant Han-manufactured iron weapons traded to the Xiongnu along the northern borders, and he established a trade embargo against the group.
In retaliation, the Xiongnu invaded what is now Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
province, where they defeated the Han forces at Baideng in 200 BC. After negotiations, the '' heqin'' agreement in 198 BC nominally held the leaders of the Xiongnu and the Han as equal partners in a royal marriage alliance, but the Han were forced to send large amounts of tribute items such as silk clothes, food, and wine to the Xiongnu.
 Despite the tribute and negotiation between Laoshang Chanyu ( BC) and Emperor Wen ( BC) to reopen border markets, many of the
Despite the tribute and negotiation between Laoshang Chanyu ( BC) and Emperor Wen ( BC) to reopen border markets, many of the Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling L ...
's Xiongnu subordinates chose not to obey the treaty and periodically raided Han territories south of the Great Wall for additional goods. In a court conference assembled by Emperor Wu ( BC) in 135 BC, the majority consensus of the ministers was to retain the ''heqin'' agreement. Emperor Wu accepted this, despite continuing Xiongnu raids.
However, a court conference the following year convinced the majority that a limited engagement at Mayi involving the assassination of the Chanyu would throw the Xiongnu realm into chaos and benefit the Han. When this plot failed in 133 BC, Emperor Wu launched a series of massive military invasions into Xiongnu territory. The assault culminated in 119 BC at the Battle of Mobei, when Han commanders Huo Qubing (d. 117 BC) and Wei Qing (d. 106 BC) forced the Xiongnu court to flee north of the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
, and Han forces reached as far north as Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
.
After Wu's reign, Han forces continued to fight the Xiongnu. The Xiongnu leader Huhanye Chanyu ( BC) finally submitted to the Han as a tributary vassal in 51 BC. Huhanye's rival claimant to the throne, Zhizhi Chanyu ( BC), was killed by Han forces under Chen Tang and Gan Yanshou () at the Battle of Zhizhi, in modern Taraz, Kazakhstan.
 In 121 BC, Han forces expelled the Xiongnu from a vast territory spanning the Hexi Corridor to
In 121 BC, Han forces expelled the Xiongnu from a vast territory spanning the Hexi Corridor to Lop Nur
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (from a Mongolian name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a former salt lake, now largely dried up, located in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin, between the Taklamakan and Kumtag deserts ...
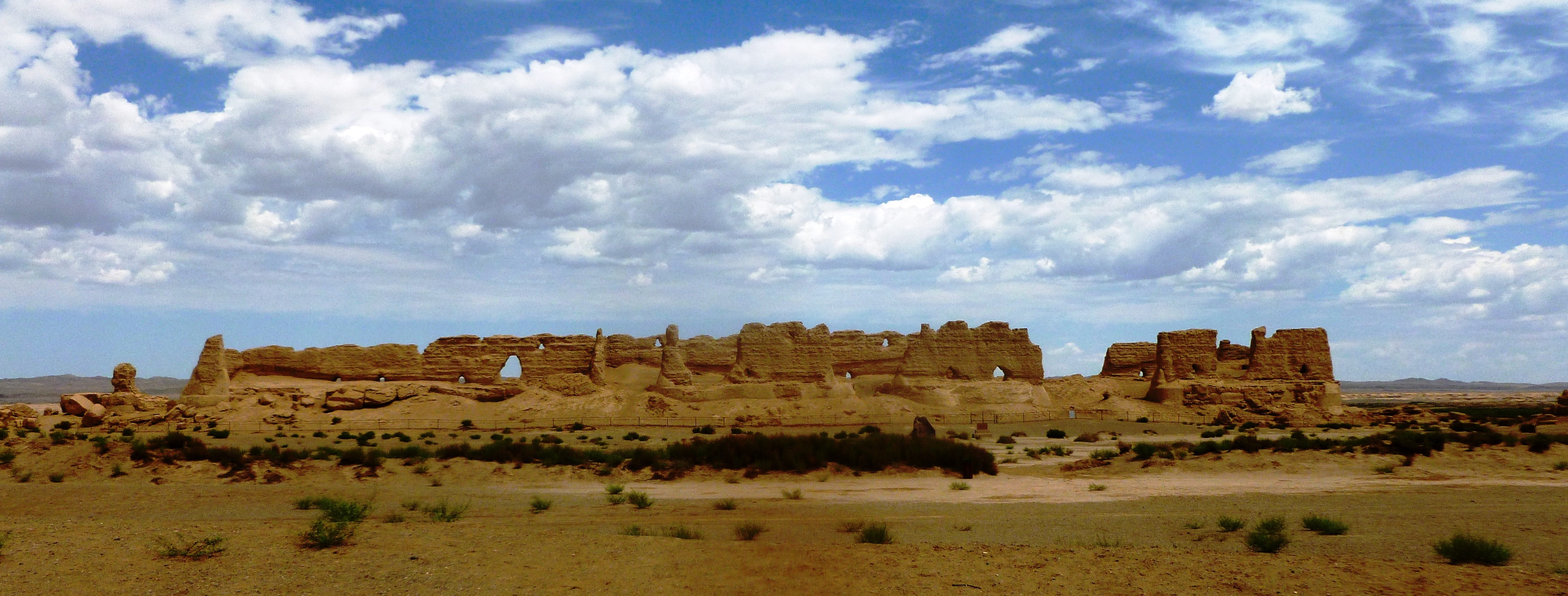
. They repelled a joint Xiongnu- Qiang invasion of this northwestern territory in 111 BC. In that same year, the Han court established four new frontier commanderies in this region to consolidate their control: Jiuquan, Zhangyi
Zhangyi () is a town under the administration of Yuanzhou District, Guyuan, Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the Pe ...
, Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major ...
, and Wuwei. The majority of people on the frontier were soldiers. On occasion, the court forcibly moved peasant farmers to new frontier settlements, along with government-owned slaves and convicts who performed hard labor. The court also encouraged commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
s, such as farmers, merchants, landowners, and hired laborers, to voluntarily migrate to the frontier.
Even before the Han's expansion into Central Asia, diplomat Zhang Qian's travels from 139 to 125 BC had established Chinese contacts with many surrounding civilizations. Zhang encountered Dayuan ( Fergana), Kangju ( Sogdiana), and Daxia (Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
, formerly the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Hellenistic Greece, Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Helleni ...
); he also gathered information on Shendu (Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
valley of North India) and Anxi (the Parthian Empire). All of these countries eventually received Han embassies. These connections marked the beginning of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
trade network that extended to the Roman Empire, bringing Han items like silk to Rome and Roman goods such as glasswares to China.
From roughly 115 to 60 BC, Han forces fought the Xiongnu over control of the oasis city-states in the Tarim Basin. The Han was eventually victorious and established the Protectorate of the Western Regions in 60 BC, which dealt with the region's defense and foreign affairs. The Han also expanded southward. The naval conquest of Nanyue in 111 BC expanded the Han realm into what are now modern Guangdong, Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
, and northern Vietnam. Yunnan was brought into the Han realm with the conquest of the Dian Kingdom in 109 BC, followed by parts of the Korean Peninsula with the Han conquest of Gojoseon and colonial establishments of Xuantu Commandery and Lelang Commandery in 108 BC. In China's first known nationwide census taken in 2 AD, the population was registered as having 57,671,400 individuals in 12,366,470 households.
To pay for his military campaigns and colonial expansion, Emperor Wu nationalized several private industries. He created central government monopolies administered largely by former merchants. These monopolies included salt, iron, and liquor
Liquor (or a spirit) is an alcoholic drink produced by distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar, that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit drink, distilled beverage or hard ...
production, as well as bronze-coin currency. The liquor monopoly lasted only from 98 to 81 BC, and the salt and iron monopolies were eventually abolished in the early Eastern Han. The issuing of coinage remained a central government monopoly throughout the rest of the Han dynasty.
The government monopolies were eventually repealed when a political faction known as the Reformists gained greater influence in the court. The Reformists opposed the Modernist faction that had dominated court politics in Emperor Wu's reign and during the subsequent regency of Huo Guang (d. 68 BC). The Modernists argued for an aggressive and expansionary foreign policy supported by revenues from heavy government intervention in the private economy. The Reformists, however, overturned these policies, favoring a cautious, non-expansionary approach to foreign policy, frugal budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environmenta ...
reform, and lower tax-rates imposed on private entrepreneurs.
Wang Mang's reign and civil war
 Wang Zhengjun (71 BC – 13 AD) was first empress, then
Wang Zhengjun (71 BC – 13 AD) was first empress, then empress dowager
Empress dowager (also dowager empress or empress mother) () is the English language translation of the title given to the mother or widow of a Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese emperor in the Chinese cultural sphere.
The title was also g ...
, and finally grand empress dowager during the reigns of the Emperors Yuan ( BC), Cheng ( BC), and Ai ( BC), respectively. During this time, a succession of her male relatives held the title of regent. Following the death of Ai, Wang Zhengjun's nephew Wang Mang (45 BC – 23 AD) was appointed regent as Marshall of State on 16 August under Emperor Ping ( AD).
When Ping died on 3 February 6 AD, Ruzi Ying (d. 25 AD) was chosen as the heir and Wang Mang was appointed to serve as acting emperor for the child. Wang promised to relinquish his control to Liu Ying once he came of age. Despite this promise, and against protest and revolts from the nobility, Wang Mang claimed on 10 January that the divine Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, ''Tian'') – which embodies the natural ...
called for the end of the Han dynasty and the beginning of his own: the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD).
Wang Mang initiated a series of major reforms that were ultimately unsuccessful. These reforms included outlawing slavery, nationalizing
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
land to equally distribute between households, and introducing new currencies, a change which debased the value of coinage. Although these reforms provoked considerable opposition, Wang's regime met its ultimate downfall with the massive floods of AD and 11 AD. Gradual silt buildup in the Yellow River had raised its water level and overwhelmed the flood control works. The Yellow River split into two new branches: one emptying to the north and the other to the south of the Shandong Peninsula, though Han engineers managed to dam the southern branch by 70 AD.
The flood dislodged thousands of peasant farmers, many of whom joined roving bandit and rebel groups such as the Red Eyebrows to survive. Wang Mang's armies were incapable of quelling these enlarged rebel groups. Eventually, an insurgent mob forced their way into the Weiyang Palace and killed Wang Mang.
The Gengshi Emperor ( AD), a descendant of Emperor Jing ( BC), attempted to restore the Han dynasty and occupied Chang'an as his capital. However, he was overwhelmed by the Red Eyebrow rebels who deposed, assassinated, and replaced him with the puppet monarch Liu Penzi. Gengshi's distant cousin Liu Xiu, known posthumously as Emperor Guangwu
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC – 29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han (Later ...
( AD), after distinguishing himself at the Battle of Kunyang in 23 AD, was urged to succeed Gengshi as emperor.
Under Guangwu's rule the Han Empire was restored. Guangwu made Luoyang his capital in 25 AD, and by 27 AD his officers Deng Yu
Deng Yu (2–58 CE), courtesy name Zhonghua, was a Chinese statesman and military commander of the early Eastern Han dynasty who was instrumental in Emperor Guangwu's reunification of China. Although acquainted during his childhood with Liu Xiu, ...
and Feng Yi
Feng Yi (?- A.D. 34) was a Chinese general of the Eastern Han Dynasty, who helped Emperor Guangwu of Han establish the Eastern Han dynasty. One of his greatest contributions was the final defeat of the Red Eyebrows rebels.
He was famous for hi ...
had forced the Red Eyebrows to surrender and executed their leaders for treason. From 26 until 36 AD, Emperor Guangwu had to wage war against other regional warlords who claimed the title of emperor; when these warlords were defeated, China reunified under the Han.
The period between the foundation of the Han dynasty and Wang Mang's reign is known as the Western Han () or Former Han () (206 BC – 9 AD). During this period the capital was at Chang'an (modern Xi'an). From the reign of Guangwu the capital was moved eastward to Luoyang. The era from his reign until the fall of Han is known as the Eastern Han or Later Han (25–220 AD).
Eastern Han
 The Eastern Han (), also known as the Later Han (), formally began on 5 August AD 25, when Liu Xiu became Emperor Guangwu of Han. During the widespread rebellion against Wang Mang, the state of Goguryeo was free to raid Han's Korean commanderies; Han did not reaffirm its control over the region until AD 30.
The Trưng Sisters of Vietnam rebelled against Han in AD 40. Their rebellion was crushed by Han general
The Eastern Han (), also known as the Later Han (), formally began on 5 August AD 25, when Liu Xiu became Emperor Guangwu of Han. During the widespread rebellion against Wang Mang, the state of Goguryeo was free to raid Han's Korean commanderies; Han did not reaffirm its control over the region until AD 30.
The Trưng Sisters of Vietnam rebelled against Han in AD 40. Their rebellion was crushed by Han general Ma Yuan Ma Yuan may refer to:
* Ma Yuan (Han dynasty) (馬援; 14 BC – 49 AD), general of the Han dynasty
* Ma Yuan (painter) (馬遠; 1160–1225), painter of the Song dynasty
* Ma Yuan (judge) (馬原), a former Vice President of the Supreme People's ...
(d. AD 49) in a campaign from AD 42–43. Wang Mang renewed hostilities against the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
, who were estranged from Han until their leader Bi (比), a rival claimant to the throne against his cousin Punu (蒲奴), submitted to Han as a tributary vassal in AD 50. This created two rival Xiongnu states: the Southern Xiongnu led by Bi, an ally of Han, and the Northern Xiongnu led by Punu, an enemy of Han.
During the turbulent reign of Wang Mang, China lost control over the Tarim Basin, which was conquered by the Northern Xiongnu in AD 63 and used as a base to invade the Hexi Corridor in Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
. Dou Gu (d. 88 AD) defeated the Northern Xiongnu at the Battle of Yiwulu in AD 73, evicting them from Turpan and chasing them as far as Lake Barkol before establishing a garrison at Hami. After the new Protector General of the Western Regions Chen Mu
Chen Mu (, d. 75) was a governor and general during the Han Dynasty who served the first Protector General of the Western Regions under Eastern Han between 74–75. During his service, he was killed by the rebels in Karasahr
Karasahr or Karashar ...
(d. AD 75) was killed by allies of the Xiongnu in Karasahr and Kucha, the garrison at Hami was withdrawn.
At the Battle of Ikh Bayan
The Battle of Altai Mountains (), was a major expedition launched against the Northern Xiongnu by the Han Dynasty in June AD 89. The battle was a success for the Han under Dou Xian (d. AD 92).''Book of Later Han'', vols. 04, 19, 23, 88, 89, ...
in AD 89, Dou Xian
Dou Xian (; died August 92) was a Chinese general and consort kin of the Eastern Han Dynasty, famous for destroying the Xiongnu nomadic empire.
Early life
A native of modern-day Xianyang, Shaanxi Province, he was part of the powerful Dou clan whi ...
(d. AD 92) defeated the Northern Xiongnu chanyu who then retreated into the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The m ...
. After the Northern Xiongnu fled into the Ili River
The Ili ( ug, ئىلى دەرياسى, Ili deryasi, Ili dəryasi, 6=Или Дәряси; kk, Ile, ; russian: Или; zh, c=伊犁河, p=Yīlí Hé, dng, Йили хә, Xiao'erjing: اِلِ حْ; mn, Ил, literally "Bareness") is a river sit ...
valley in AD 91, the nomadic Xianbei occupied the area from the borders of the Buyeo Kingdom in Manchuria to the Ili River of the Wusun
The Wusun (; Eastern Han Chinese *''ʔɑ-suən'' < (140 BCE < 436 BCE): *''Ɂâ-sûn'') were an ancient semi- people. The Xianbei reached their apogee under Tanshihuai (檀石槐) (d. AD 180), who consistently defeated Chinese armies. However, Tanshihuai's confederation disintegrated after his death.
 Foreign travelers to Eastern-Han China included Buddhist monks who translated works into Chinese, such as An Shigao from Parthia, and Lokaksema from Kushan-era
Foreign travelers to Eastern-Han China included Buddhist monks who translated works into Chinese, such as An Shigao from Parthia, and Lokaksema from Kushan-era 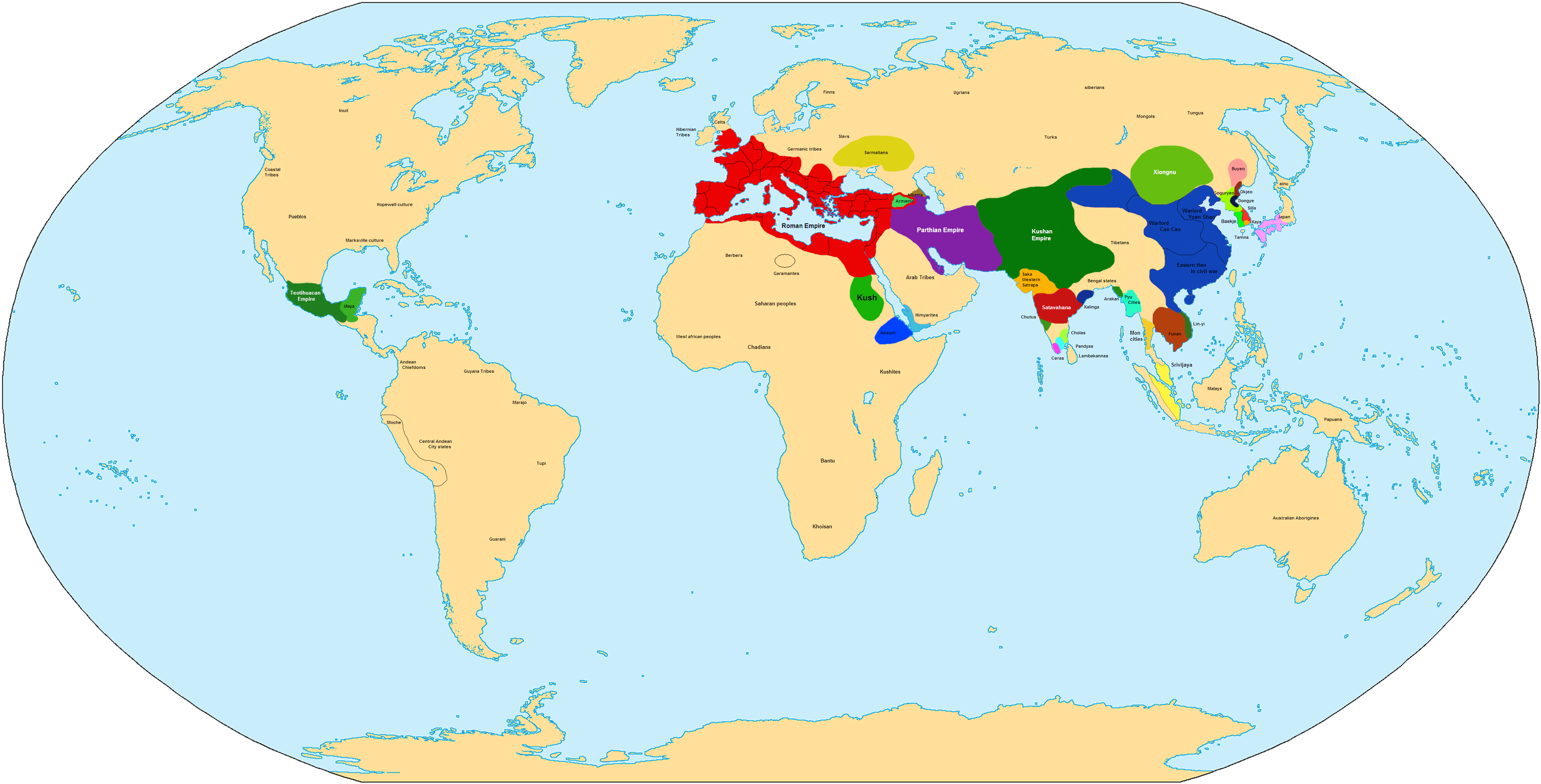 Following Huan's death, Dou Wu and the Grand Tutor Chen Fan (d. 168 AD) attempted a coup d'état against the eunuchs Hou Lan (d. 172 AD), Cao Jie (d. 181 AD), and Wang Fu (). When the plot was uncovered, the eunuchs arrested Empress Dowager Dou (d. 172 AD) and Chen Fan. General Zhang Huan () favored the eunuchs. He and his troops confronted Dou Wu and his retainers at the palace gate where each side shouted accusations of treason against the other. When the retainers gradually deserted Dou Wu, he was forced to commit suicide.
Under Emperor Ling ( AD) the eunuchs had the partisan prohibitions renewed and expanded, while also auctioning off top government offices. Many affairs of state were entrusted to the eunuchs
Following Huan's death, Dou Wu and the Grand Tutor Chen Fan (d. 168 AD) attempted a coup d'état against the eunuchs Hou Lan (d. 172 AD), Cao Jie (d. 181 AD), and Wang Fu (). When the plot was uncovered, the eunuchs arrested Empress Dowager Dou (d. 172 AD) and Chen Fan. General Zhang Huan () favored the eunuchs. He and his troops confronted Dou Wu and his retainers at the palace gate where each side shouted accusations of treason against the other. When the retainers gradually deserted Dou Wu, he was forced to commit suicide.
Under Emperor Ling ( AD) the eunuchs had the partisan prohibitions renewed and expanded, while also auctioning off top government offices. Many affairs of state were entrusted to the eunuchs
Ban Chao
Ban Chao (; 32–102 CE), courtesy name Zhongsheng, was a Chinese diplomat, explorer, and military general of the Eastern Han Dynasty. He was born in Fufeng, now Xianyang, Shaanxi. Three of his family members—father Ban Biao, elder brother ...
(d. AD 102) enlisted the aid of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
, occupying the area of modern India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan, to subdue Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
and its ally Sogdiana. When a request by Kushan ruler Vima Kadphises () for a marriage alliance with the Han was rejected in AD 90, he sent his forces to Wakhan (Afghanistan) to attack Ban Chao. The conflict ended with the Kushans withdrawing because of lack of supplies. In AD 91, the office of Protector General of the Western Regions was reinstated when it was bestowed on Ban Chao.
 Foreign travelers to Eastern-Han China included Buddhist monks who translated works into Chinese, such as An Shigao from Parthia, and Lokaksema from Kushan-era
Foreign travelers to Eastern-Han China included Buddhist monks who translated works into Chinese, such as An Shigao from Parthia, and Lokaksema from Kushan-era Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
, India. In addition to tributary relations with the Kushans, the Han Empire received gifts from the Parthian Empire, from a king in modern Burma, from a ruler in Japan, and initiated an unsuccessful mission to Daqin ( Rome) in AD 97 with Gan Ying as emissary.
A Roman embassy of Emperor Marcus Aurelius ( AD) is recorded in the '' Weilüe'' and ''Hou Hanshu
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese language, Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period ...
'' to have reached the court of Emperor Huan of Han ( AD) in AD 166, yet Rafe de Crespigny
Richard Rafe Champion de Crespigny (born 1936), also known by his Chinese name Zhang Leifu (), is an Australian sinologist and historian. He was an adjunct professor in the College of Asia and the Pacific at the Australian National University. ...
asserts that this was most likely a group of Roman merchants. In addition to Roman glasswares and coins found in China, Roman medallions from the reign of Antoninus Pius and his adopted son Marcus Aurelius have been found at Óc Eo in Vietnam. This was near the commandery of Rinan
Rinan (; vi, Nhật Nam), also rendered as Jih-nan, was the southernmost commandery of the Chinese Han dynasty. It was located in the central area of modern-day Vietnam between Quảng Bình and Bình Định provinces. It was administered by ...
(also Jiaozhi) where Chinese sources claim the Romans first landed, as well as embassies from Tianzhu (in northern India) in the years 159 and 161. Óc Eo is also thought to be the port city "Cattigara
Cattigara is the name of a major port city located on the Magnus Sinus described by various antiquity sources. Modern scholars have linked Cattigara to the archaeological site of Óc Eo in present-day Vietnam.
Ptolemy's description
Cattigara w ...
" described by Ptolemy in his '' Geography'' ( AD) as lying east of the Golden Chersonese
The Golden Chersonese or Golden Khersonese ( grc, Χρυσῆ Χερσόνησος, ''Chrysḗ Chersónēsos''; la, Chersonesus Aurea), meaning the Golden Peninsula, was the name used for the Malay Peninsula by Greek and Roman geographers in cla ...
(Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
) along the '' Magnus Sinus'' (i.e. Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around in l ...
and South China Sea), where a Greek sailor had visited.
Emperor Zhang's ( AD) reign came to be viewed by later Eastern Han scholars as the high point of the dynastic house. Subsequent reigns were increasingly marked by eunuch intervention in court politics and their involvement in the violent power struggles of the imperial consort clans. In 92 AD, with the aid of the eunuch Zheng Zhong
Zheng Zhong (鄭眾), courtesy name Jichan (季產) (died 107), was the first Han Dynasty eunuch with real power in government, thanks to the trust that Emperor He of Han, Emperor He had in him for his contributions in overthrowing the clan of Emp ...
(d. 107 AD), Emperor He ( AD) had Empress Dowager Dou (d. 97 AD) put under house arrest
In justice and law, house arrest (also called home confinement, home detention, or, in modern times, electronic monitoring) is a measure by which a person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted, if all ...
and her clan stripped of power. This was in revenge for Dou's purging of the clan of his natural mother—Consort Liang
Consort Liang (梁貴人, personal name unknown) (62(?)-83?), posthumous title Empress Gonghuai (恭懷皇后, literally, "empress of reverent recollection"), was an imperial consort to Emperor Zhang of Han. She gave birth to his son Liu Zhao (劉 ...
—and then concealing her identity from him. After Emperor He's death, his wife Empress Deng Sui (d. 121 AD) managed state affairs as the regent empress dowager during a turbulent financial crisis and widespread Qiang rebellion that lasted from 107 to 118 AD.
When Empress Dowager Deng died, Emperor An ( AD) was convinced by the accusations of the eunuchs Li Run () and Jiang Jing () that Deng and her family had planned to depose him. An dismissed Deng's clan members from office, exiled them, and forced many to commit suicide. After An's death, his wife, Empress Dowager Yan (d. 126 AD) placed the child Marquess of Beixiang on the throne in an attempt to retain power within her family. However, palace eunuch Sun Cheng
Sun Cheng () (died 132) was a eunuch at the Imperial Chinese court during the Han Dynasty. Contrary to the stereotype of Han eunuchs being corrupt and power-hungry, he was loyal to the imperial family and tried (unsuccessfully) to counter the cul ...
(d. 132 AD) masterminded a successful overthrow of her regime to enthrone Emperor Shun of Han ( AD). Yan was placed under house arrest, her relatives were either killed or exiled, and her eunuch allies were slaughtered. The regent Liang Ji
Liang Ji (梁冀) (died 9 September 159Emperor Huan's biography in ''Book of the Later Han'' recorded that Liang Ji and Sun Shou committed suicide on the ''dingchou'' day of the 8th month of the 2nd year of the ''Yanxi'' era of his reign. This co ...
(d. 159 AD), brother of Empress Liang Na
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
(d. 150 AD), had the brother-in-law of Consort Deng Mengnü (later empress) (d. 165 AD) killed after Deng Mengnü resisted Liang Ji's attempts to control her. Afterward, Emperor Huan employed eunuchs to depose Liang Ji, who was then forced to commit suicide.
Students from the Imperial University organized a widespread student protest
Campus protest or student protest is a form of student activism that takes the form of protest at university campuses. Such protests encompass a wide range of activities that indicate student dissatisfaction with a given political or academ ...
against the eunuchs of Emperor Huan's court. Huan further alienated the bureaucracy when he initiated grandiose construction projects and hosted thousands of concubines in his harem at a time of economic crisis. Palace eunuchs imprisoned the official Li Ying () and his associates from the Imperial University on a dubious charge of treason. In 167 AD, the Grand Commandant Dou Wu (d. 168 AD) convinced his son-in-law, Emperor Huan, to release them. However the emperor permanently barred Li Ying and his associates from serving in office, marking the beginning of the Partisan Prohibitions.
Zhao Zhong
The Ten Attendants, also known as the Ten Eunuchs, were a group of influential eunuch-officials in the imperial court of Emperor Ling of Han, Emperor Ling ( 168–189) in Eastern Han dynasty, Eastern Han China. Although they are often referred to ...
(d. 189 AD) and Zhang Rang (d. 189 AD) while Emperor Ling spent much of his time roleplaying with concubines and participating in military parades.
End of the Han dynasty
The Partisan Prohibitions were repealed during theYellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, alternatively translated as the Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a List of peasant revolts, peasant revolt in China against the Eastern Han dynasty. The uprising broke out in 184 CE during the reign of Emperor Ling of ...
and Five Pecks of Rice Rebellion
The Way of the Five Pecks of Rice () or the Way of the Celestial Master, commonly abbreviated to simply The Celestial Masters, was a Chinese Taoist movement founded by the first Celestial Master Zhang Daoling in 142 CE. At its height, the mov ...
in 184 AD, largely because the court did not want to continue to alienate a significant portion of the gentry class who might otherwise join the rebellions. The Yellow Turbans and Five-Pecks-of-Rice adherents belonged to two different hierarchical Daoist religious societies led by faith healers
Faith healing is the practice of prayer and gestures (such as laying on of hands) that are believed by some to elicit divine intervention in spiritual and physical healing, especially the Christian practice. Believers assert that the healing ...
Zhang Jue (d. 184 AD) and Zhang Lu (d. 216 AD), respectively.
Zhang Lu's rebellion, in modern northern Sichuan and southern Shaanxi, was not quelled until 215 AD. Zhang Jue's massive rebellion across eight provinces was annihilated by Han forces within a year, however the following decades saw much smaller recurrent uprisings. Although the Yellow Turbans were defeated, many generals appointed during the crisis never disbanded their assembled militia forces and used these troops to amass power outside of the collapsing imperial authority.
General-in-Chief He Jin
He Jin () (died 22 September 189), courtesy name Suigao, was a Chinese military general and politician. He was the military Grand Marshal and regent of the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was an elder half-brother of Empress He, the emp ...
(d. 189 AD), half-brother to Empress He (d. 189 AD), plotted with Yuan Shao (d. 202 AD) to overthrow the eunuchs by having several generals march to the outskirts of the capital. There, in a written petition to Empress He, they demanded the eunuchs' execution. After a period of hesitation, Empress He consented. When the eunuchs discovered this, however, they had her brother He Miao () rescind the order. The eunuchs assassinated He Jin on September 22, 189 AD.
Yuan Shao then besieged Luoyang's Northern Palace while his brother Yuan Shu (d. 199 AD) besieged the Southern Palace. On September 25 both palaces were breached and approximately two thousand eunuchs were killed. Zhang Rang had previously fled with Emperor Shao ( AD) and his brother Liu Xie—the future Emperor Xian of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220.
Liu Xie was a s ...
( AD). While being pursued by the Yuan brothers, Zhang committed suicide by jumping into the Yellow River.
General Dong Zhuo (d. 192 AD) found the young emperor and his brother wandering in the countryside. He escorted them safely back to the capital and was made Minister of Works, taking control of Luoyang and forcing Yuan Shao to flee. After Dong Zhuo demoted Emperor Shao and promoted his brother Liu Xie as Emperor Xian, Yuan Shao led a coalition of former officials and officers against Dong, who burned Luoyang to the ground and resettled the court at Chang'an in May 191 AD. Dong Zhuo later poisoned Emperor Shao.
Dong was killed by his adopted son Lü Bu (d. 198 AD) in a plot hatched by Wang Yun (d. 192 AD). Emperor Xian fled from Chang'an in 195 AD to the ruins of Luoyang. Xian was persuaded by Cao Cao
Cao Cao () (; 155 – 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde (), was a Chinese statesman, warlord and poet. He was the penultimate Grand chancellor (China), grand chancellor of the Eastern Han dynasty, and he amassed immense power in the End of ...
(155–220 AD), then Governor of Yan Province in modern western Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
and eastern Henan, to move the capital to Xuchang in 196 AD.
Yuan Shao challenged Cao Cao for control over the emperor. Yuan's power was greatly diminished after Cao defeated him at the Battle of Guandu in 200 AD. After Yuan died, Cao killed Yuan Shao's son Yuan Tan (173–205 AD), who had fought with his brothers over the family inheritance. His brothers Yuan Shang and Yuan Xi
Yuan Xi (died December 20711th month of the 12th year of the ''Jian'an'' era, per Emperor Xian's biography in ''Book of the Later Han''. The month corresponds to 7 Dec 207 to 5 Jan 208 in the Julian calendar.), courtesy name Xianyi or Xianyong ...
were killed in 207 AD by Gongsun Kang (d. 221 AD), who sent their heads to Cao Cao.
After Cao's defeat at the naval Battle of Red Cliffs
The Battle of Red Cliffs, also known as the Battle of Chibi, was a decisive naval battle in the winter of AD 208–209 at the end of the Han dynasty, about twelve years prior to the beginning of the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history. T ...
in 208 AD, China was divided into three spheres of influence, with Cao Cao dominating the north, Sun Quan
Sun Quan (, Chinese: 孫權) (183 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of the Eastern Wu dynasty, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime es ...
(182–252 AD) dominating the south, and Liu Bei (161–223 AD) dominating the west. Cao Cao died in March 220 AD. By December his son Cao Pi (187–226 AD) had Emperor Xian relinquish the throne to him and is known posthumously as Emperor Wen of Wei. This formally ended the Han dynasty and initiated an age of conflict between three states: Cao Wei, Eastern Wu
Wu ( Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < : ''*ŋuɑ''), known in h ...
, and Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' <
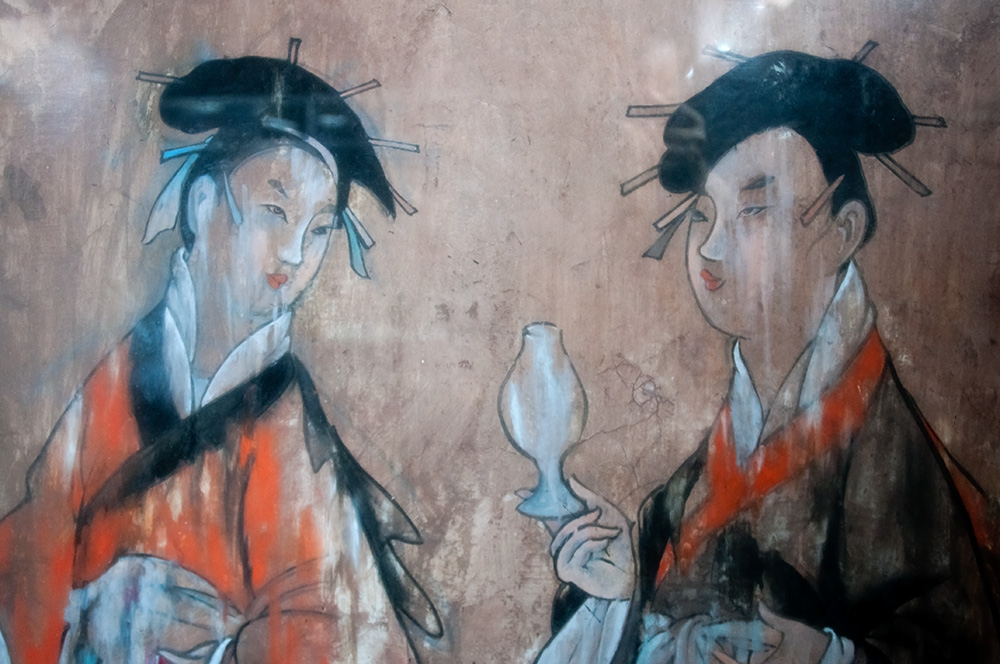
 The Han-era family was patrilineal and typically had four to five
The Han-era family was patrilineal and typically had four to five

 Some important texts were created and studied by scholars. Philosophical works written by Yang Xiong (53 BCE – 18 CE), Huan Tan (43 BCE – 28 CE), Wang Chong (27–100 CE), and Wang Fu (78–163 CE) questioned whether human nature was innately good or evil and posed challenges to Dong's universal order. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Tan (d. 110 BCE) and his son
Some important texts were created and studied by scholars. Philosophical works written by Yang Xiong (53 BCE – 18 CE), Huan Tan (43 BCE – 28 CE), Wang Chong (27–100 CE), and Wang Fu (78–163 CE) questioned whether human nature was innately good or evil and posed challenges to Dong's universal order. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Tan (d. 110 BCE) and his son
 Han scholars such as Jia Yi (201–169 BCE) portrayed the previous Qin dynasty as a brutal regime. However, archeological evidence from
Han scholars such as Jia Yi (201–169 BCE) portrayed the previous Qin dynasty as a brutal regime. However, archeological evidence from
 Families throughout Han China made ritual sacrifices of animals and food to deities, spirits, and ancestors at temples and shrines. They believed that these items could be used by those in the spiritual realm. It was thought that each person had a two-part soul: the spirit-soul (''hun'' 魂) which journeyed to the afterlife paradise of immortals ('' xian''), and the body-soul (''po'' 魄) which remained in its grave or tomb on earth and was only reunited with the spirit-soul through a ritual ceremony.
Families throughout Han China made ritual sacrifices of animals and food to deities, spirits, and ancestors at temples and shrines. They believed that these items could be used by those in the spiritual realm. It was thought that each person had a two-part soul: the spirit-soul (''hun'' 魂) which journeyed to the afterlife paradise of immortals ('' xian''), and the body-soul (''po'' 魄) which remained in its grave or tomb on earth and was only reunited with the spirit-soul through a ritual ceremony.
 In addition to his many other roles, the emperor acted as the highest priest in the land who made sacrifices to
In addition to his many other roles, the emperor acted as the highest priest in the land who made sacrifices to
 In Han government, the emperor was the supreme judge and lawgiver, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and sole designator of official nominees appointed to the top posts in central and local administrations; those who earned a 600-bushel salary-rank or higher. Theoretically, there were no limits to his power.
However, state organs with competing interests and institutions such as the court conference (''tíngyì'' )—where ministers were convened to reach majority consensus on an issue—pressured the emperor to accept the advice of his ministers on policy decisions. If the emperor rejected a court conference decision, he risked alienating his high ministers. Nevertheless, emperors sometimes did reject the majority opinion reached at court conferences.
Below the emperor were his
In Han government, the emperor was the supreme judge and lawgiver, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and sole designator of official nominees appointed to the top posts in central and local administrations; those who earned a 600-bushel salary-rank or higher. Theoretically, there were no limits to his power.
However, state organs with competing interests and institutions such as the court conference (''tíngyì'' )—where ministers were convened to reach majority consensus on an issue—pressured the emperor to accept the advice of his ministers on policy decisions. If the emperor rejected a court conference decision, he risked alienating his high ministers. Nevertheless, emperors sometimes did reject the majority opinion reached at court conferences.
Below the emperor were his  Ranked below the Three Councilors of State were the Nine Ministers (''Jiǔ qīng'' ), who each headed a specialized ministry. The Minister of Ceremonies (''Tàicháng'' ) was the chief official in charge of religious rites, rituals, prayers, and the maintenance of ancestral temples and altars. The Minister of the Household (''Guāng lù xūn'' ) was in charge of the emperor's security within the palace grounds, external imperial parks, and wherever the emperor made an outing by chariot.
Ranked below the Three Councilors of State were the Nine Ministers (''Jiǔ qīng'' ), who each headed a specialized ministry. The Minister of Ceremonies (''Tàicháng'' ) was the chief official in charge of religious rites, rituals, prayers, and the maintenance of ancestral temples and altars. The Minister of the Household (''Guāng lù xūn'' ) was in charge of the emperor's security within the palace grounds, external imperial parks, and wherever the emperor made an outing by chariot.
 The Minister of the Guards (''Wèiwèi'' ) was responsible for securing and patrolling the walls, towers, and gates of the imperial palaces. The Minister Coachman (''Tàipú'' ) was responsible for the maintenance of imperial stables, horses, carriages, and coach-houses for the emperor and his palace attendants, as well as the supply of horses for the armed forces. The Minister of Justice (''Tíngwèi'' ) was the chief official in charge of upholding, administering, and interpreting the law. The Minister Herald (''Dà hónglú'' ) was the chief official in charge of receiving honored guests at the imperial court, such as nobles and foreign ambassadors.
The Minister of the Imperial Clan (''Zōngzhèng'' ) oversaw the imperial court's interactions with the empire's nobility and extended imperial family, such as granting fiefs and titles. The Minister of Finance (''Dà sìnóng'' ) was the treasurer for the official bureaucracy and the armed forces who handled tax revenues and set standards for units of measurement. The Minister Steward (''Shǎofǔ'' ) served the emperor exclusively, providing him with entertainment and amusements, proper food and clothing, medicine and physical care, valuables and equipment.
The Minister of the Guards (''Wèiwèi'' ) was responsible for securing and patrolling the walls, towers, and gates of the imperial palaces. The Minister Coachman (''Tàipú'' ) was responsible for the maintenance of imperial stables, horses, carriages, and coach-houses for the emperor and his palace attendants, as well as the supply of horses for the armed forces. The Minister of Justice (''Tíngwèi'' ) was the chief official in charge of upholding, administering, and interpreting the law. The Minister Herald (''Dà hónglú'' ) was the chief official in charge of receiving honored guests at the imperial court, such as nobles and foreign ambassadors.
The Minister of the Imperial Clan (''Zōngzhèng'' ) oversaw the imperial court's interactions with the empire's nobility and extended imperial family, such as granting fiefs and titles. The Minister of Finance (''Dà sìnóng'' ) was the treasurer for the official bureaucracy and the armed forces who handled tax revenues and set standards for units of measurement. The Minister Steward (''Shǎofǔ'' ) served the emperor exclusively, providing him with entertainment and amusements, proper food and clothing, medicine and physical care, valuables and equipment.
 Up until the reign of
Up until the reign of
Social class
In the hierarchical social order, the emperor was at the apex of Han society and government. However, the emperor was often a minor, ruled over by a regent such as theempress dowager
Empress dowager (also dowager empress or empress mother) () is the English language translation of the title given to the mother or widow of a Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese emperor in the Chinese cultural sphere.
The title was also g ...
or one of her male relatives. Ranked immediately below the emperor were the kings who were of the same Liu family clan. The rest of society, including nobles lower than kings and all commoners excluding slave
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
s, belonged to one of twenty ranks (''ershi gongcheng'' ).
Each successive rank gave its holder greater pensions and legal privileges. The highest rank, of full marquess
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
, came with a state pension and a territorial fiefdom. Holders of the rank immediately below, that of ordinary marquess, received a pension, but had no territorial rule. Officials who served in government belonged to the wider commoner social class and were ranked just below nobles in social prestige. The highest government officials could be enfeoffed as marquesses.
By the Eastern Han period, local elites of unattached scholars, teachers, students, and government officials began to identify themselves as members of a larger, nationwide gentry class with shared values and a commitment to mainstream scholarship. When the government became noticeably corrupt in mid-to-late Eastern Han, many gentrymen even considered the cultivation of morally-grounded personal relationships more important than serving in public office.
The farmer, or specifically the small landowner-cultivator, was ranked just below scholars and officials in the social hierarchy. Other agricultural cultivators were of a lower status, such as tenants, wage laborers, and slaves. The Han dynasty made adjustments to slavery in China and saw an increase in agricultural slaves. Artisans, technicians, tradespeople
A tradesman, tradeswoman, or tradesperson is a skilled worker that specializes in a particular trade (occupation or field of work). Tradesmen usually have work experience, on-the-job training, and often formal vocational education in contrast to ...
, and craftsmen had a legal and socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's ...
between that of owner-cultivator farmers and common merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as indust ...
s.
State-registered merchants, who were forced by law to wear white-colored clothes and pay high commercial taxes, were considered by the gentry as social parasites with a contemptible status. These were often petty shopkeepers of urban marketplaces; merchants such as industrialists and itinerant traders working between a network of cities could avoid registering as merchants and were often wealthier and more powerful than the vast majority of government officials.
Wealthy landowners, such as nobles and officials, often provided lodging for retainers who provided valuable work or duties, sometimes including fighting bandits or riding into battle. Unlike slaves, retainers could come and go from their master's home as they pleased. Medical physicians, pig breeders, and butchers had a fairly high social status, while occultist diviners, runners, and messengers had low status.

Marriage, gender, and kinship
 The Han-era family was patrilineal and typically had four to five
The Han-era family was patrilineal and typically had four to five nuclear family
A nuclear family, elementary family, cereal-packet family or conjugal family is a family group consisting of parents and their children (one or more), typically living in one home residence. It is in contrast to a single-parent family, the larger ...
members living in one household. Multiple generations of extended family members did not occupy the same house, unlike families of later dynasties. According to Confucian family norms, various family members were treated with different levels of respect and intimacy. For example, there were different accepted time frames for mourning the death of a father versus a paternal uncle.
Marriages were highly ritualized, particularly for the wealthy, and included many important steps. The giving of betrothal gifts, known as bridewealth and dowry, were especially important. A lack of either was considered dishonorable and the woman would have been seen not as a wife, but as a concubine. Arranged marriage
Arranged marriage is a type of marital union where the bride and groom are primarily selected by individuals other than the couple themselves, particularly by family members such as the parents. In some cultures a professional matchmaker may be us ...
s were normal, with the father's input on his offspring's spouse being considered more important than the mother's.
Monogamous marriages were also normal, although nobles and high officials were wealthy enough to afford and support concubines as additional lovers. Under certain conditions dictated by custom, not law, both men and women were able to divorce their spouses and remarry. However, a woman who had been widowed continued to belong to her husband's family after his death. In order to remarry, the widow would have to be returned to her family in exchange for a ransom fee. Her children would not be allowed to go with her.
Apart from the passing of noble titles or ranks, inheritance practices did not involve primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
; each son received an equal share of the family property. Unlike the practice in later dynasties, the father usually sent his adult married sons away with their portions of the family fortune. Daughters received a portion of the family fortune through their marriage dowries, though this was usually much less than the shares of sons. A different distribution of the remainder could be specified in a will
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
, but it is unclear how common this was.
Women were expected to obey the will of their father, then their husband, and then their adult son in old age. However, it is known from contemporary sources that there were many deviations to this rule, especially in regard to mothers over their sons, and empresses who ordered around and openly humiliated their fathers and brothers. Women were exempt from the annual corvée labor duties, but often engaged in a range of income-earning occupations aside from their domestic chores of cooking and cleaning.
The most common occupation for women was weaving clothes for the family, for sale at market, or for large textile enterprises that employed hundreds of women. Other women helped on their brothers' farms or became singers, dancers, sorceresses, respected medical physicians, and successful merchants who could afford their own silk clothes. Some women formed spinning collectives, aggregating the resources of several different families.
Education, literature, and philosophy
The early Western Han court simultaneously accepted the philosophical teachings of Legalism, Huang-Lao Daoism, and Confucianism in making state decisions and shaping government policy. However, the Han court under Emperor Wu gave Confucianism exclusive patronage. He abolished all academic chairs or erudites (''bóshì'' 博士) not dealing with the Confucian Five Classics in 136 BCE and encouraged nominees for office to receive a Confucian-based education at the Imperial University that he established in 124 BCE. Unlike the original ideology espoused by Confucius, or Kongzi (551–479 BCE), Han Confucianism in Emperor Wu's reign was the creation ofDong Zhongshu
Dong Zhongshu (; 179–104 BC) was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and writer of the Han Dynasty. He is traditionally associated with the promotion of Confucianism as the official ideology of the Chinese imperial state. He apparently favored ...
(179–104 BCE). Dong was a scholar and minor official who aggregated the ethical Confucian ideas of ritual, filial piety, and harmonious relationships with five phases and yin-yang cosmologies. Much to the interest of the ruler, Dong's synthesis justified the imperial system of government within the natural order of the universe.
The Imperial University grew in importance as the student body grew to over 30,000 by the 2nd century CE. A Confucian-based education was also made available at commandery-level schools and private schools opened in small towns, where teachers earned respectable incomes from tuition payments. Schools were established in far southern regions where standard Chinese texts were used to assimilate the local populace.

 Some important texts were created and studied by scholars. Philosophical works written by Yang Xiong (53 BCE – 18 CE), Huan Tan (43 BCE – 28 CE), Wang Chong (27–100 CE), and Wang Fu (78–163 CE) questioned whether human nature was innately good or evil and posed challenges to Dong's universal order. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Tan (d. 110 BCE) and his son
Some important texts were created and studied by scholars. Philosophical works written by Yang Xiong (53 BCE – 18 CE), Huan Tan (43 BCE – 28 CE), Wang Chong (27–100 CE), and Wang Fu (78–163 CE) questioned whether human nature was innately good or evil and posed challenges to Dong's universal order. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Tan (d. 110 BCE) and his son Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years b ...
(145–86 BCE) established the standard model for all of imperial China's Standard Histories, such as the '' Book of Han'' written by Ban Biao (3–54 CE), his son Ban Gu
Ban Gu (AD32–92) was a Chinese historian, politician, and poet best known for his part in compiling the ''Book of Han'', the second of China's 24 dynastic histories. He also wrote a number of '' fu'', a major literary form, part prose ...
(32–92 CE), and his daughter Ban Zhao (45–116 CE). There were dictionaries
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically (or by radical and stroke for ideographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, p ...
such as the '' Shuowen Jiezi'' by Xu Shen ( – CE) and the '' Fangyan'' by Yang Xiong.
Biographies on important figures were written by various gentrymen. Han dynasty poetry was dominated by the ''fu'' genre, which achieved its greatest prominence during the reign of Emperor Wu.
Law and order
 Han scholars such as Jia Yi (201–169 BCE) portrayed the previous Qin dynasty as a brutal regime. However, archeological evidence from
Han scholars such as Jia Yi (201–169 BCE) portrayed the previous Qin dynasty as a brutal regime. However, archeological evidence from Zhangjiashan The Zhangjiashan Han bamboo texts are ancient Han Dynasty Chinese written works dated 196–186 BC. They were discovered in 1983 by archaeologists excavating tomb no. 247 at Mount Zhangjia () of Jiangling County, Hubei Province (near modern Jing ...
and Shuihudi
The Shuihudi Qin bamboo texts () are early Chinese texts written on bamboo slips, and are also sometimes called the Yúnmèng Qin bamboo texts. They were excavated in December 1975 from Tomb #11 at Shuìhǔdì () in Yunmeng County, Hubei, China. T ...
reveal that many of the statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by le ...
s in the Han law code compiled by Chancellor Xiao He (d. 193 BCE) were derived from Qin law.
Various cases for rape, physical abuse, and murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person wit ...
were prosecuted in court. Women, although usually having fewer rights by custom, were allowed to level civil and criminal charges against men. While suspects were jailed, convicted criminals were never imprisoned. Instead, punishments were commonly monetary fines, periods of forced hard labor for convicts, and the penalty of death by beheading. Early Han punishments of torturous mutilation were borrowed from Qin law. A series of reforms abolished mutilation punishments with progressively less-severe beatings by the bastinado.
Acting as a judge in lawsuits was one of the many duties of the county magistrate and Administrators of commanderies. Complex, high-profile, or unresolved cases were often deferred to the Minister of Justice in the capital or even the emperor. In each Han county was several districts, each overseen by a chief of police. Order in the cities was maintained by government officers in the marketplaces and constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in criminal law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. A constable is commonly the rank of an officer within the police. Other peop ...
s in the neighborhoods.
Food
The most common staple crops consumed during Han were wheat, barley, foxtail millet, proso millet, rice, andbean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s. Commonly eaten fruits and vegetables included chestnuts, pears, plums, peaches, melons, apricots, strawberries, red bayberries, jujubes, calabash, bamboo shoots, mustard plant
The mustard plant is any one of several plant species in the genera ''Brassica'' and ''Sinapis'' in the family Brassicaceae (the mustard family). Mustard seed is used as a spice. Grinding and mixing the seeds with water, vinegar, or other liqui ...
, and taro. Domesticated animals that were also eaten included chickens, Mandarin ducks, geese, cows, sheep, pigs, camels, and dogs (various types were bred specifically for food, while most were used as pets). Turtles and fish were taken from streams and lakes. Commonly hunted game, such as owl, pheasant, magpie, sika deer, and Chinese bamboo partridge were consumed. Seasonings included sugar, honey, salt, and soy sauce
Soy sauce (also called simply soy in American English and soya sauce in British English) is a liquid condiment of Chinese origin, traditionally made from a fermented paste of soybeans, roasted grain, brine, and '' Aspergillus oryzae'' or ''Asp ...
. Beer and wine were regularly consumed.
Clothing
The types of clothing worn and the materials used during the Han period depended upon social class. Wealthy folk could afford silk robes, skirts, socks, and mittens, coats made of badger or fox fur, duck plumes, and slippers with inlaid leather, pearls, and silk lining. Peasants commonly wore clothes made ofhemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
, wool, and ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, Domestication, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), evidenced by their Hybrid (biol ...
skins.
Religion, cosmology, and metaphysics
 In addition to his many other roles, the emperor acted as the highest priest in the land who made sacrifices to
In addition to his many other roles, the emperor acted as the highest priest in the land who made sacrifices to Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
, the main deities known as the Five Powers, and the spirits (''shen'' 神) of mountains and rivers. It was believed that the three realms of Heaven, Earth, and Mankind were linked by natural cycles of yin and yang and the five phases. If the emperor did not behave according to proper ritual, ethics, and morals, he could disrupt the fine balance of these cosmological cycles and cause calamities such as earthquakes, floods, droughts, epidemics, and swarms of locusts.
It was believed that immortality could be achieved if one reached the lands of the Queen Mother of the West or Mount Penglai. Han-era Daoists assembled into small groups of hermits who attempted to achieve immortality through breathing exercises, sexual techniques, and the use of medical elixirs.
By the 2nd century CE, Daoists formed large hierarchical religious societies such as the Way of the Five Pecks of Rice. Its followers believed that the sage-philosopher Laozi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state
...
() was a holy prophet who would offer salvation and good health if his devout followers would confess their sins, ban the worship of unclean gods who accepted meat sacrifices, and chant sections of the '' Daodejing''.
Buddhism first entered Imperial China through the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
during the Eastern Han, and was first mentioned in 65 CE. Liu Ying (d. 71 CE), a half-brother to Emperor Ming of Han ( CE), was one of its earliest Chinese adherents, although Chinese Buddhism at this point was heavily associated with Huang-Lao Daoism. China's first known Buddhist temple, the White Horse Temple, was constructed outside the wall of the capital, Luoyang, during Emperor Ming's reign. Important Buddhist canons were translated into Chinese during the 2nd century CE, including the ''Sutra of Forty-two Chapters
The ''Sutra of Forty-two Chapters'' (also called the ''Sutra of Forty-two Sections'', Chinese: 四十二章經) is often regarded as the first Indian Buddhist sutra translated into Chinese. However, this collection of aphorisms may have appeared so ...
'', ''Perfection of Wisdom
A Tibetan painting with a Prajñāpāramitā sūtra at the center of the mandala
Prajñāpāramitā ( sa, प्रज्ञापारमिता) means "the Perfection of Wisdom" or "Transcendental Knowledge" in Mahāyāna and Theravāda ...
'', '' Shurangama Sutra'', and '' Pratyutpanna Sutra''.
Government and politics
Central government
 In Han government, the emperor was the supreme judge and lawgiver, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and sole designator of official nominees appointed to the top posts in central and local administrations; those who earned a 600-bushel salary-rank or higher. Theoretically, there were no limits to his power.
However, state organs with competing interests and institutions such as the court conference (''tíngyì'' )—where ministers were convened to reach majority consensus on an issue—pressured the emperor to accept the advice of his ministers on policy decisions. If the emperor rejected a court conference decision, he risked alienating his high ministers. Nevertheless, emperors sometimes did reject the majority opinion reached at court conferences.
Below the emperor were his
In Han government, the emperor was the supreme judge and lawgiver, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and sole designator of official nominees appointed to the top posts in central and local administrations; those who earned a 600-bushel salary-rank or higher. Theoretically, there were no limits to his power.
However, state organs with competing interests and institutions such as the court conference (''tíngyì'' )—where ministers were convened to reach majority consensus on an issue—pressured the emperor to accept the advice of his ministers on policy decisions. If the emperor rejected a court conference decision, he risked alienating his high ministers. Nevertheless, emperors sometimes did reject the majority opinion reached at court conferences.
Below the emperor were his cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
members known as the Three Councilors of State (''Sān gōng'' ). These were the Chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
or Minister over the Masses (''Chéngxiāng'' or ''Dà sìtú'' ), the Imperial Counselor or Excellency of Works (''Yùshǐ dàfū'' or ''Dà sìkōng'' ), and Grand Commandant or Grand Marshal (''Tàiwèi'' or ''Dà sīmǎ'' ).
The Chancellor, whose title was changed to 'Minister over the Masses' in 8 BC, was chiefly responsible for drafting the government budget
A government budget is a document prepared by the government and/or other political entity presenting its anticipated tax revenues (Inheritance tax, income tax, corporation tax, import taxes) and proposed spending/expenditure (Healthcare, Educa ...
. The Chancellor's other duties included managing provincial registers for land and population, leading court conferences, acting as judge in lawsuits, and recommending nominees for high office. He could appoint officials below the salary-rank of 600 bushels.
The Imperial Counselor's chief duty was to conduct disciplinary procedures for officials. He shared similar duties with the Chancellor, such as receiving annual provincial reports. However, when his title was changed to Minister of Works in 8 BC, his chief duty became the oversight of public works projects.
The Grand Commandant, whose title was changed to Grand Marshal in 119 BC before reverting to Grand Commandant in 51 AD, was the irregularly posted commander of the military and then regent during the Western Han period. In the Eastern Han era he was chiefly a civil official who shared many of the same censorial powers as the other two Councilors of State.
 The Minister of the Guards (''Wèiwèi'' ) was responsible for securing and patrolling the walls, towers, and gates of the imperial palaces. The Minister Coachman (''Tàipú'' ) was responsible for the maintenance of imperial stables, horses, carriages, and coach-houses for the emperor and his palace attendants, as well as the supply of horses for the armed forces. The Minister of Justice (''Tíngwèi'' ) was the chief official in charge of upholding, administering, and interpreting the law. The Minister Herald (''Dà hónglú'' ) was the chief official in charge of receiving honored guests at the imperial court, such as nobles and foreign ambassadors.
The Minister of the Imperial Clan (''Zōngzhèng'' ) oversaw the imperial court's interactions with the empire's nobility and extended imperial family, such as granting fiefs and titles. The Minister of Finance (''Dà sìnóng'' ) was the treasurer for the official bureaucracy and the armed forces who handled tax revenues and set standards for units of measurement. The Minister Steward (''Shǎofǔ'' ) served the emperor exclusively, providing him with entertainment and amusements, proper food and clothing, medicine and physical care, valuables and equipment.
The Minister of the Guards (''Wèiwèi'' ) was responsible for securing and patrolling the walls, towers, and gates of the imperial palaces. The Minister Coachman (''Tàipú'' ) was responsible for the maintenance of imperial stables, horses, carriages, and coach-houses for the emperor and his palace attendants, as well as the supply of horses for the armed forces. The Minister of Justice (''Tíngwèi'' ) was the chief official in charge of upholding, administering, and interpreting the law. The Minister Herald (''Dà hónglú'' ) was the chief official in charge of receiving honored guests at the imperial court, such as nobles and foreign ambassadors.
The Minister of the Imperial Clan (''Zōngzhèng'' ) oversaw the imperial court's interactions with the empire's nobility and extended imperial family, such as granting fiefs and titles. The Minister of Finance (''Dà sìnóng'' ) was the treasurer for the official bureaucracy and the armed forces who handled tax revenues and set standards for units of measurement. The Minister Steward (''Shǎofǔ'' ) served the emperor exclusively, providing him with entertainment and amusements, proper food and clothing, medicine and physical care, valuables and equipment.
Local government
The Han empire, excluding kingdoms and marquessates, was divided, in descending order of size, into political units of provinces,commanderies
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Gr ...
, and counties. A county was divided into several districts (''xiang'' 鄉), the latter composed of a group of hamlets (''li'' 里), each containing about a hundred families.
The heads of provinces, whose official title was changed from Inspector to Governor and vice versa several times during Han, were responsible for inspecting several commandery-level and kingdom-level administrations. On the basis of their reports, the officials in these local administrations would be promoted, demoted, dismissed, or prosecuted by the imperial court.
A governor could take various actions without permission from the imperial court. The lower-ranked inspector had executive powers only during times of crisis, such as raising militias across the commanderies under his jurisdiction to suppress a rebellion.
A commandery consisted of a group of counties, and was headed by an Administrator. He was the top civil and military leader of the commandery and handled defense, lawsuits, seasonal instructions to farmers, and recommendations of nominees for office sent annually to the capital in a quota system first established by Emperor Wu. The head of a large county of about 10,000 households was called a Prefect, while the heads of smaller counties were called Chiefs, and both could be referred to as Magistrates. A Magistrate maintained law and order in his county, registered the populace for taxation, mobilized commoners for annual corvée duties, repaired schools, and supervised public works.
Kingdoms and marquessates
Kingdoms—roughly the size ofcommanderies
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Gr ...
—were ruled exclusively by the emperor's male relatives as semi-autonomous fiefdoms. Before 157 BC some kingdoms were ruled by non-relatives, granted to them in return for their services to Emperor Gaozu. The administration of each kingdom was very similar to that of the central government. Although the emperor appointed the Chancellor of each kingdom, kings appointed all the remaining civil officials in their fiefs.
However, in 145 BC, after several insurrections by the kings, Emperor Jing removed the kings' rights to appoint officials whose salaries were higher than 400 bushels. The Imperial Counselors and Nine Ministers (excluding the Minister Coachman) of every kingdom were abolished, although the Chancellor was still appointed by the central government.
With these reforms, kings were reduced to being nominal heads of their fiefs, gaining a personal income from only a portion of the taxes collected in their kingdom. Similarly, the officials in the administrative staff of a full marquess's fief were appointed by the central government. A marquess's Chancellor was ranked as the equivalent of a county Prefect. Like a king, the marquess collected a portion of the tax revenues in his fief as personal income.
 Up until the reign of
Up until the reign of Emperor Jing of Han
Emperor Jing of Han (Liu Qi (劉啟); 188 BC – 9 March 141 BC) was the sixth emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty from 157 to 141 BC. His reign saw the limiting of the power of the feudal kings/princes which resulted in the Rebellion of the Sev ...
, the Emperors of the Han had great difficulty bringing the vassal kings under control, as kings often switched their allegiance to the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling L ...
whenever threatened by Imperial attempts to centralize power. Within the seven years of Han Gaozu's reign, three vassal kings and one marquess either defected to or allied with the Xiongnu. Even imperial princes in control of fiefdoms would sometimes invite the Xiongnu to invade in response to threats by the Emperor to remove their power. The Han emperors moved to secure a treaty with the Chanyu to demarcate authority between them, recognizing each other as the "two masters" (兩主), the sole representatives of their respective peoples, and cemented it with a marriage alliance ('' heqin''), before eliminating the rebellious vassal kings in 154 BC. This prompted some vassal kings of the Xiongnu to switch their allegiance to the Han emperor from 147 BC. Han court officials were initially hostile to the idea of disrupting the status quo and expanding into the Xiongnu steppe territory. The surrendered Xiongnu were integrated into a parallel military and political structure under the Han Emperor, and opened the avenue for the Han dynasty to challenge the Xiongnu cavalry on the steppe. This also introduced the Han to the interstate networks in the Tarim Basin (Xinjiang), allowing for the expansion of the Han dynasty from a limited regional state to a universalist and cosmopolitan empire through further marriage alliances with another steppe power, the Wusun
The Wusun (; Eastern Han Chinese *''ʔɑ-suən'' < (140 BCE < 436 BCE): *''Ɂâ-sûn'') were an ancient semi-.
 At the beginning of the Han dynasty, every male commoner aged twenty-three was liable for
At the beginning of the Han dynasty, every male commoner aged twenty-three was liable for
 In the early Western Han, a wealthy salt or iron industrialist, whether a semi-autonomous king or wealthy merchant, could boast funds that rivaled the imperial treasury and amass a peasant workforce of over a thousand. This kept many peasants away from their farms and denied the government a significant portion of its land tax revenue. To eliminate the influence of such private entrepreneurs, Emperor Wu nationalized the salt and iron industries in 117 BC and allowed many of the former industrialists to become officials administering the state monopolies. By Eastern Han times, the central government monopolies were repealed in favor of production by commandery and county administrations, as well as private businessmen.
In the early Western Han, a wealthy salt or iron industrialist, whether a semi-autonomous king or wealthy merchant, could boast funds that rivaled the imperial treasury and amass a peasant workforce of over a thousand. This kept many peasants away from their farms and denied the government a significant portion of its land tax revenue. To eliminate the influence of such private entrepreneurs, Emperor Wu nationalized the salt and iron industries in 117 BC and allowed many of the former industrialists to become officials administering the state monopolies. By Eastern Han times, the central government monopolies were repealed in favor of production by commandery and county administrations, as well as private businessmen.
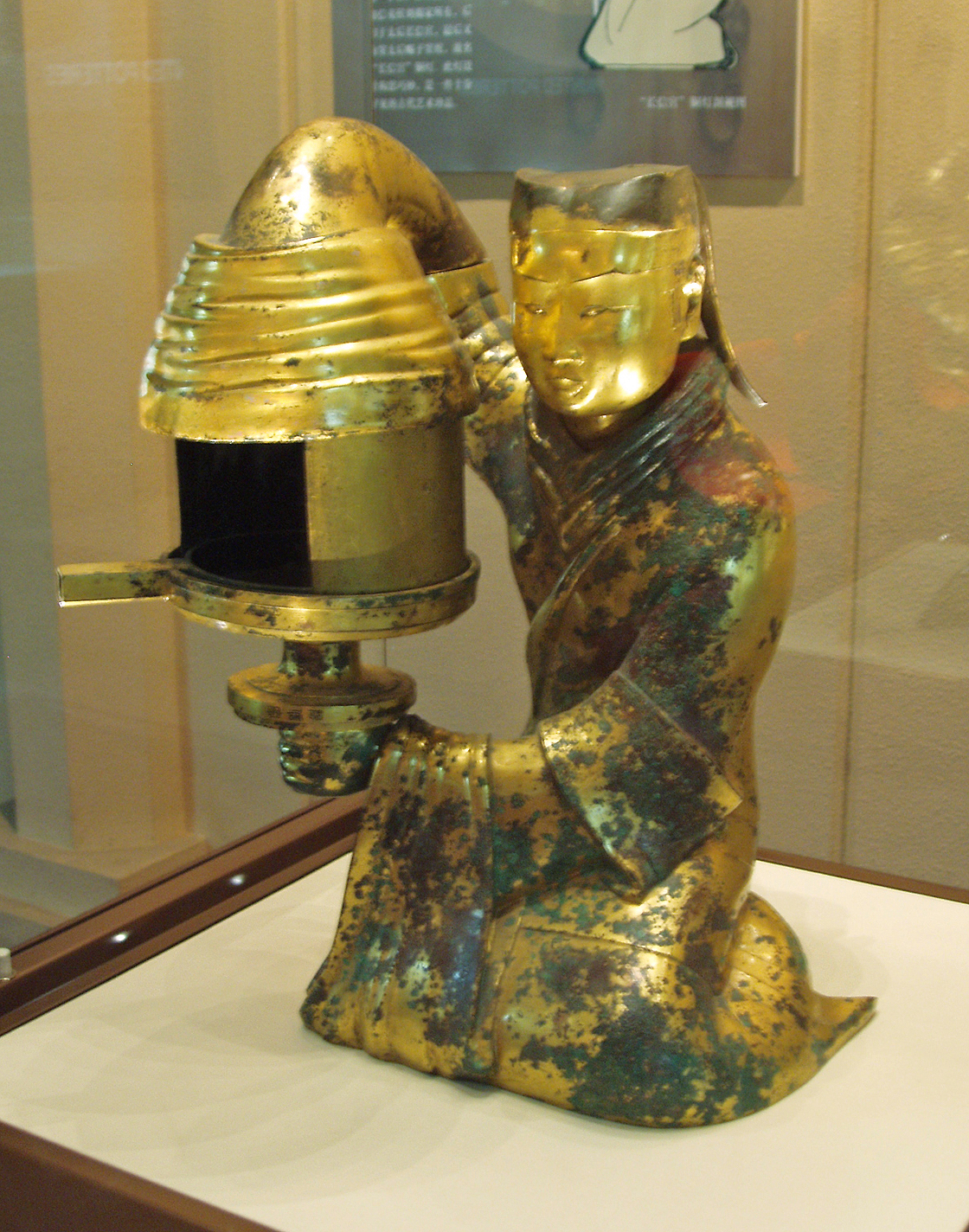 The Han dynasty was a unique period in the development of premodern Chinese science and technology, comparable to the level of scientific and technological growth during the Song dynasty (960–1279).
The Han dynasty was a unique period in the development of premodern Chinese science and technology, comparable to the level of scientific and technological growth during the Song dynasty (960–1279).
File:登封汉代少室阙.jpg, A pair of stone-carved Que (tower), ''que'' (闕) located at the temple of Mount Song in Dengfeng. (Eastern Han dynasty.)
File:幽州書佐秦君石闕 17.jpg, A pair of Han period stone-carved Que (tower), ''que'' (闕) located at Babaoshan, Beijing.
File:Gao Yi Que2.jpg, A stone-carved pillar-gate, or Que (tower), ''que'' (闕), 6 m (20 ft) in total height, located at the tomb of Gao Yi in Ya'an. (Eastern Han dynasty.)
File:Eastern Han tomb, Luoyang 2.jpg, An Eastern-Han Vault (architecture), vaulted tomb chamber at Luoyang made of small bricks
File:Winnowing machine and tilt hammer.JPG, A Han-dynasty pottery model of two men operating a Fengshanche, winnowing machine with a Crank (mechanism), crank handle and a Trip hammer, tilt hammer used to pound grain.
File:EastHanSeismograph.JPG, A modern replica of Zhang Heng's seismometer
File:Western Han Mawangdui Silk Map.JPG, An early Western Han dynasty silk map found in tomb 3 of Mawangdui, depicting the Kingdom of Changsha and Kingdom of Nanyue in southern China (note: the south direction is oriented at the top).
File:Eastern Han pottery boat.JPG, An Eastern Han dynasty pottery boat model with a steering rudder at the stern and anchor at the bow.
 Han-era medical physicians believed that the human body was subject to the same forces of nature that governed the greater universe, namely the cosmological cycles of yin and yang and the five phases. Each Zang-fu, organ of the body was associated with a particular phase. Illness was viewed as a sign that ''qi'' or "vital energy" channels leading to a certain organ had been disrupted. Thus, Han-era physicians prescribed medicine that was believed to counteract this imbalance.
For example, since the wood phase was believed to promote the fire phase, medicinal ingredients associated with the wood phase could be used to heal an organ associated with the fire phase. Besides dieting, Han physicians also prescribed moxibustion, acupuncture, and calisthenics as methods of maintaining one's health. When surgery was performed by the Chinese physician Hua Tuo (d. AD 208), he used anesthesia to numb his patients' pain and prescribed a rubbing ointment that allegedly sped the process of healing surgical wounds. Whereas the physician Zhang Zhongjing ( – ) is known to have written the ''Shanghan lun'' ("Dissertation on Typhoid Fever"), it is thought that both he and Hua Tuo collaborated in compiling the ''Shennong Ben Cao Jing'' medical text.
Han-era medical physicians believed that the human body was subject to the same forces of nature that governed the greater universe, namely the cosmological cycles of yin and yang and the five phases. Each Zang-fu, organ of the body was associated with a particular phase. Illness was viewed as a sign that ''qi'' or "vital energy" channels leading to a certain organ had been disrupted. Thus, Han-era physicians prescribed medicine that was believed to counteract this imbalance.
For example, since the wood phase was believed to promote the fire phase, medicinal ingredients associated with the wood phase could be used to heal an organ associated with the fire phase. Besides dieting, Han physicians also prescribed moxibustion, acupuncture, and calisthenics as methods of maintaining one's health. When surgery was performed by the Chinese physician Hua Tuo (d. AD 208), he used anesthesia to numb his patients' pain and prescribed a rubbing ointment that allegedly sped the process of healing surgical wounds. Whereas the physician Zhang Zhongjing ( – ) is known to have written the ''Shanghan lun'' ("Dissertation on Typhoid Fever"), it is thought that both he and Hua Tuo collaborated in compiling the ''Shennong Ben Cao Jing'' medical text.
Han dynasty by Minnesota State UniversityHan dynasty art with video commentary, Minneapolis Institute of ArtsEarly Imperial China: A Working Collection of Resources
"Han Culture," Hanyangling Museum WebsiteThe Han Synthesis
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Christopher Cullen, Carol Michaelson & Roel Sterckx (''In Our Time'', Oct. 14, 2004) {{Authority control Han dynasty, States and territories established in the 3rd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 3rd century 1st century BC in China, . 1st century in China, . 2nd century BC in China, . 2nd century in China, . 200s BC establishments 206 BC 220 disestablishments 3rd-century BC establishments in China 3rd-century disestablishments in China 3rd century BC in China, . Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history
Military
 At the beginning of the Han dynasty, every male commoner aged twenty-three was liable for
At the beginning of the Han dynasty, every male commoner aged twenty-three was liable for conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
into the military. The minimum age for the military draft was reduced to twenty after Emperor Zhao's ( BC) reign. Conscripted soldiers underwent one year of training and one year of service as non-professional soldiers. The year of training was served in one of three branches of the armed forces: infantry, cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
, or navy. Soldiers who completed their term of service still needed to train to maintain their skill because they were subject to annual military readiness inspections and could be called up for future service - until this practice was discontinued after 30 AD with the abolishment of much of the conscription system. The year of active service was served either on the frontier, in a king's court, or under the Minister of the Guards in the capital. A small professional (full time career) standing army was stationed near the capital.
During the Eastern Han, conscription could be avoided if one paid a commutable tax. The Eastern Han court favored the recruitment of a volunteer army. The volunteer army comprised the Southern Army (''Nanjun'' 南軍), while the standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or n ...
stationed in and near the capital was the Northern Army (''Beijun'' 北軍). Led by Colonels (''Xiaowei'' 校尉), the Northern Army consisted of five regiments, each composed of several thousand soldiers. When central authority collapsed after 189 AD, wealthy landowners, members of the aristocracy/nobility, and regional military-governors relied upon their retainers to act as their own personal troops. The latter were known as 部曲, a special social class in Chinese history.
During times of war, the volunteer army was increased, and a much larger militia was raised across the country to supplement the Northern Army. In these circumstances, a General (''Jiangjun'' 將軍) led a division, which was divided into regiments led by Colonels and sometimes Majors (''Sima'' 司馬). Regiments were divided into companies and led by Captains. Platoons were the smallest units of soldiers.
Economy
Currency
The Han dynasty inherited the ''ban liang
The Ban Liang ( Traditional Chinese: ; Pinyin: ''bàn liǎng'') was the first unified currency of the Chinese empire, first minted as early as 378 BCE and introduced by the first emperor Qin Shi Huang as China's first unified currency around ...
'' coin type from the Qin. In the beginning of the Han, Emperor Gaozu closed the government mint in favor of private minting of coins. This decision was reversed in 186 BC by his widow Grand Empress Dowager Lü Zhi (d. 180 BC), who abolished private minting. In 182 BC, Lü Zhi issued a bronze coin that was much lighter in weight than previous coins. This caused widespread inflation that was not reduced until 175 BC when Emperor Wen allowed private minters to manufacture coins that were precisely 2.6 g (0.09 oz) in weight.
In 144 BC Emperor Jing abolished private minting in favor of central-government and commandery-level minting; he also introduced a new coin. Emperor Wu introduced another in 120 BC, but a year later he abandoned the ''ban liangs'' entirely in favor of the '' wuzhu'' (五銖) coin, weighing 3.2 g (0.11 oz). The ''wuzhu'' became China's standard coin until the Tang dynasty (618–907 AD). Its use was interrupted briefly by several new currencies introduced during Wang Mang's regime until it was reinstated in 40 AD by Emperor Guangwu.
Since commandery-issued coins were often of inferior quality and lighter weight, the central government closed commandery mints and monopolized the issue of coinage in 113 BC. This central government issuance of coinage was overseen by the Superintendent of Waterways and Parks, this duty being transferred to the Minister of Finance during the Eastern Han.
Taxation and property
Aside from the landowner'sland tax
A land value tax (LVT) is a levy on the value of land without regard to buildings, personal property and other improvements. It is also known as a location value tax, a point valuation tax, a site valuation tax, split rate tax, or a site-value r ...
paid in a portion of their crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the c ...
, the poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
and property taxes were paid in coin cash. The annual poll tax rate for adult men and women was 120 coins and 20 coins for minors. Merchants were required to pay a higher rate of 240 coins. The poll tax stimulated a money economy that necessitated the minting of over 28,000,000,000 coins from 118 BC to 5 AD, an average of 220,000,000 coins a year.
The widespread circulation of coin cash allowed successful merchants to invest money in land, empowering the very social class the government attempted to suppress through heavy commercial and property taxes. Emperor Wu even enacted laws which banned registered merchants from owning land, yet powerful merchants were able to avoid registration and own large tracts of land.
The small landowner-cultivators formed the majority of the Han tax base; this revenue was threatened during the latter half of Eastern Han when many peasants fell into debt and were forced to work as farming tenants for wealthy landlords. The Han government enacted reforms in order to keep small landowner-cultivators out of debt and on their own farms. These reforms included reducing taxes, temporary remissions of taxes, granting loans, and providing landless peasants temporary lodging and work in agricultural colonies until they could recover from their debts.
In 168 BC, the land tax rate was reduced from one-fifteenth of a farming household's crop yield to one-thirtieth, and later to a one-hundredth of a crop yield for the last decades of the dynasty. The consequent loss of government revenue was compensated for by increasing property taxes.
The labor tax took the form of conscripted labor for one month per year, which was imposed upon male commoners aged fifteen to fifty-six. This could be avoided in Eastern Han with a commutable tax, since hired labor became more popular.
Private manufacture and government monopolies
 In the early Western Han, a wealthy salt or iron industrialist, whether a semi-autonomous king or wealthy merchant, could boast funds that rivaled the imperial treasury and amass a peasant workforce of over a thousand. This kept many peasants away from their farms and denied the government a significant portion of its land tax revenue. To eliminate the influence of such private entrepreneurs, Emperor Wu nationalized the salt and iron industries in 117 BC and allowed many of the former industrialists to become officials administering the state monopolies. By Eastern Han times, the central government monopolies were repealed in favor of production by commandery and county administrations, as well as private businessmen.
In the early Western Han, a wealthy salt or iron industrialist, whether a semi-autonomous king or wealthy merchant, could boast funds that rivaled the imperial treasury and amass a peasant workforce of over a thousand. This kept many peasants away from their farms and denied the government a significant portion of its land tax revenue. To eliminate the influence of such private entrepreneurs, Emperor Wu nationalized the salt and iron industries in 117 BC and allowed many of the former industrialists to become officials administering the state monopolies. By Eastern Han times, the central government monopolies were repealed in favor of production by commandery and county administrations, as well as private businessmen.
Liquor
Liquor (or a spirit) is an alcoholic drink produced by distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar, that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit drink, distilled beverage or hard ...
was another profitable private industry nationalized by the central government in 98 BC. However, this was repealed in 81 BC and a property tax rate of two coins for every 0.2 L (0.05 gallons) was levied for those who traded it privately. By 110 BC Emperor Wu also interfered with the profitable trade in grain when he eliminated speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, good (economics), goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline i ...
by selling government-stored grain at a lower price than that demanded by merchants. Apart from Emperor Ming's creation of a short-lived Office for Price Adjustment and Stabilization, which was abolished in 68 AD, central-government price control regulations were largely absent during the Eastern Han.
Science and technology
 The Han dynasty was a unique period in the development of premodern Chinese science and technology, comparable to the level of scientific and technological growth during the Song dynasty (960–1279).
The Han dynasty was a unique period in the development of premodern Chinese science and technology, comparable to the level of scientific and technological growth during the Song dynasty (960–1279).
Writing materials
In the 1st millennium BC, typical ancient Chinese writing materials were bronzewares, animal bones, andbamboo slip
Bamboo and wooden slips () were the main media for writing documents in China before the widespread introduction of paper during the first two centuries AD. (Silk was occasionally used, for example in the Chu Silk Manuscript, but was prohibit ...
s or wooden boards. By the beginning of the Han dynasty, the chief writing materials were clay tablets, silk cloth, hemp paper, and rolled scrolls made from bamboo strips sewn together with hempen string; these were passed through drilled holes and secured with clay stamps.
The oldest known Chinese piece of hempen paper dates to the 2nd century BC. The standard papermaking process was invented by Cai Lun
Cai Lun (; courtesy name: Jingzhong (); – 121 CE), formerly romanized as Ts'ai Lun, was a Chinese eunuch court official of the Eastern Han dynasty. He is traditionally regarded as the inventor of paper and the modern papermaking process ...
(AD 50–121) in 105. The oldest known surviving piece of paper with writing on it was found in the ruins of a Han watchtower that had been abandoned in AD 110, in Inner Mongolia.
Metallurgy and agriculture
Evidence suggests thatblast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
s, that convert raw iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
into pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silic ...
, which can be remelted in a cupola furnace to produce cast iron by means of a cold blast and hot blast, were operational in China by the late Spring and Autumn period (722–481 BC). The bloomery was nonexistent in ancient China; however, the Han-era Chinese produced wrought iron by injecting excess oxygen into a furnace and causing decarburization. Cast iron and pig iron could be converted into wrought iron and steel using a finery forge, fining process.
The Han dynasty Chinese used bronze and iron to make a range of weapons, culinary tools, carpenters' tools, and domestic wares. A significant product of these improved iron-smelting techniques was the manufacture of new agricultural tools. The three-legged iron seed drill, invented by the 2nd century BC, enabled farmers to carefully plant crops in rows instead of Sowing, casting seeds out by hand. The heavy moldboard iron plow, also invented during the Han dynasty, required only one man to control it with two oxen to pull it. It had three plowshares, a seed box for the drills, a tool which turned down the soil and could sow roughly 45,730 m2 (11.3 acres) of land in a single day.
To protect crops from wind and drought, the grain intendant Zhao Guo (趙過) created the alternating fields system (''daitianfa'' 代田法) during Emperor Wu's reign. This system switched the positions of Ridge and furrow, furrows and ridges between growing seasons. Once experiments with this system yielded successful results, the government officially sponsored it and encouraged peasants to use it. Han farmers also used the pit field system ( 凹田) for growing crops, which involved heavily fertilized pits that did not require plows or oxen and could be placed on sloping terrain. In the southern and small parts of central Han-era China, paddy fields were chiefly used to grow rice, while farmers along the Huai River used Transplanting, transplantation methods of rice production.
Structural and geotechnical engineering
Timber was the chief building material during the Han dynasty; it was used to build palace halls, multi-story residential towers and halls, and single-story houses. Because wood decays rapidly, the only remaining evidence of Han wooden architecture is a collection of scattered ceramic roof tiles. The oldest surviving wooden halls in China date to the Tang dynasty (AD 618–907). Architectural historian Robert L. Thorp points out the scarcity of Han-era archeological remains, and claims that often unreliable Han-era literary and artistic sources are used by historians for clues about lost Han architecture. Though Han wooden structures decayed, some Han-dynasty ruins made of brick, stone, and rammed earth remain intact. This includes stone pillar-gates, brick tomb chambers, rammed-earth Chinese city wall, city walls, rammed-earth and brick beacon towers, rammed-earth sections of the Great Wall, rammed-earth platforms where elevated halls once stood, and two rammed-earth castles inGansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
. The ruins of rammed-earth walls that once surrounded the capitals Chang'an and Luoyang still stand, along with their Sewage collection and disposal, drainage systems of brick arches, ditches, and ceramic water pipes. Que (tower), Monumental stone pillar-gates, twenty-nine of which survive from the Han period, formed entrances of walled enclosures at shrine and tomb sites. These pillars feature artistic imitations of wooden and ceramic building components such as roof tiles, eaves, and balustrades.
The courtyard house is the most common type of home portrayed in Han artwork. Ceramic architectural Architectural model, models of buildings, like houses and towers, were found in Han tombs, perhaps to provide lodging for the dead in the afterlife. These provide valuable clues about lost wooden architecture. The artistic designs found on ceramic roof tiles of tower models are in some cases exact matches to Han roof tiles found at archeological sites.
Over ten Han-era underground tombs have been found, many of them featuring archways, Vault (architecture), vaulted chambers, and domed roofs. Underground vaults and domes did not require buttress supports since they were held in place by earthen pits. The use of brick vaults and domes in aboveground Han structures is unknown.
From Han literary sources, it is known that wooden-trestle beam bridges, arch bridges, simple suspension bridges, and floating pontoon bridges existed in Han China. However, there are only two known references to arch bridges in Han literature, and only a single Han relief sculpture in Sichuan depicts an arch bridge.
Shaft mining, Underground mine shafts, some reaching depths over , were created for the extraction of metal ores. Borehole drilling and derricks were used to lift brine to iron pans where it was distilled into salt. The distillation furnaces were heated by natural gas funneled to the surface through Pipeline transport, bamboo pipelines. These boreholes perhaps reached a depth of 600 m (2000 ft).
Mechanical and hydraulic engineering
Han-era mechanical engineering comes largely from the choice observational writings of sometimes-disinterested Confucian scholars who generally considered scientific and engineering endeavors to be far beneath them. Professional artisan-engineers (''jiang'' 匠) did not leave behind detailed records of their work. Han scholars, who often had little or no expertise in mechanical engineering, sometimes provided insufficient information on the various technologies they described. Nevertheless, some Han literary sources provide crucial information. For example, in 15 BC the philosopher and poet Yang Xiong described the invention of the Belt (mechanical), belt drive for a quilling machine, which was of great importance to early textile manufacturing. The inventions of mechanical engineer and craftsman Ding Huan are mentioned in the ''Miscellaneous Notes on the Western Capital''. Around AD 180, Ding created a manually operated rotary fan used for air conditioning within palace buildings. Ding also used gimbals as pivotal supports for one of his incense burners and invented the world's first known zoetrope lamp. Modern archeology has led to the discovery of Han artwork portraying inventions which were otherwise absent in Han literary sources. As observed in Han miniature tomb models, but not in literary sources, the Crank (mechanism), crank handle was used to operate the Fan (mechanical), fans of Fengshanche, winnowing machines that separated grain from chaff. The odometer cart, invented during the Han period, measured journey lengths, using mechanical figures banging drums and gongs to indicate each distance traveled. This invention is depicted in Han artwork by the 2nd century, yet detailed written descriptions were not offered until the 3rd century. Modern archeologists have also unearthed specimens of devices used during the Han dynasty, for example a pair of sliding metal calipers used by craftsmen for making minute measurements. These calipers contain inscriptions of the exact day and year they were manufactured. These tools are not mentioned in any Han literary sources. The waterwheel appeared in Chinese records during the Han. As mentioned by Huan Tan about AD 20, they were used to turn gears that lifted iron trip hammers, and were used in pounding, threshing, and polishing grain. However, there is no sufficient evidence for the watermill in China until about the 5th century. The Nanyang Commandery Administrator, mechanical engineer, and :Metallurgists, metallurgist Du Shi (d. 38 AD) created a waterwheel-powered Reciprocating motion, reciprocator that worked the bellows for the smelting of iron. Waterwheels were also used to power chain pumps that lifted water to raised irrigation ditches. The chain pump was first mentioned in China by the philosopher Wang Chong in his 1st-century ''Lunheng, Balanced Discourse''. Thearmillary sphere
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of ...
, a three-dimensional representation of the movements in the celestial sphere, was invented in Han China by the 1st century BC. Using a water clock, waterwheel, and a series of gears, the Court Astronomer Zhang Heng (AD 78–139) was able to mechanically rotate his metal-ringed armillary sphere. To address the problem of slowed timekeeping in the pressure head of the inflow water clock, Zhang was the first in China to install an additional tank between the reservoir and inflow vessel.
Zhang also invented a device he termed an "earthquake weathervane" ( 候風地動儀), which the British biochemist, sinologist, and historian Joseph Needham described as "the ancestor of all seismographs". This device was able to detect the exact Cardinal direction, cardinal or ordinal direction of earthquakes from hundreds of kilometers away. It employed an inverted pendulum that, when disturbed by ground tremors, would trigger a set of gears that dropped a metal ball from one of eight dragon mouths (representing all eight directions) into a metal toad's mouth.
The account of this device in the ''Book of the Later Han'' describes how, on one occasion, one of the metal balls was triggered without any of the observers feeling a disturbance. Several days later, a messenger arrived bearing news that an earthquake had struck in Longxi Commandery (in modern Gansu Province), the direction the device had indicated, which forced the officials at court to admit the efficacy of Zhang's device.
Mathematics
Three Han mathematical treatises still exist. These are the ''Book on Numbers and Computation'', the ''Zhoubi Suanjing, Arithmetical Classic of the Gnomon and the Circular Paths of Heaven,'' and the ''Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art''. Han-era mathematical achievements include solving problems with Triangle#Types of triangle, right-angle triangles, square roots, cube roots, and Matrix (mathematics), matrix methods, finding more accurate Chronology of computation of π, approximations for pi, providing mathematical proof of the Pythagorean theorem, use of the Fraction (mathematics), decimal fraction, Gaussian elimination to solve System of linear equations, linear equations, and continued fractions to find the root of a function, roots of equations. One of the Han's greatest mathematical advancements was the world's first use ofnegative number
In mathematics, a negative number represents an opposite. In the real number system, a negative number is a number that is less than zero. Negative numbers are often used to represent the magnitude of a loss or deficiency. A debt that is owed m ...
s. Negative numbers first appeared in the ''Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' as black counting rods, where positive numbers were represented by red counting rods. Negative numbers were also used by the Greece, Greek mathematician Diophantus around AD 275, and in the 7th-century Bakhshali manuscript of Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
, South Asia, but were not widely accepted in Europe until the 16th century.
The Han applied mathematics to various diverse disciplines. In musical tuning, Jing Fang (78–37 BC) realized that 53 perfect fifths was approximate to 31 octaves while creating a musical scale of 60 tones, calculating the difference at 177147⁄176776 (the same value of 53 equal temperament discovered by the German mathematician Nicholas Mercator [1620–1687], i.e. 353/284).
Astronomy
Mathematics were essential in drafting the Chinese calendar, astronomical calendar, a lunisolar calendar that used the Sun and Moon as time-markers throughout the year. During the spring and autumn periods of the 5th century BC, the Chinese established the Sifen calendar (古四分历), which measured the tropical year at 365.25 days. This was replaced in 104 BC with the Taichu calendar (太初曆) that measured the tropical year at (~ 365.25016) days and the lunar month at days. However, Emperor Zhang later reinstated the Sifen calendar. Han Chinese astronomers made star catalogues and detailed records of comets that appeared in the night sky, including recording the 12 BC appearance of the comet now known as Halley's Comet. Han dynasty astronomers adopted a geocentric model of the universe, theorizing that it was celestial sphere, shaped like a sphere surrounding the earth in the center. They assumed that the Sun, Moon, and planets were spherical and not disc-shaped. They also thought that the illumination of the Moon and planets was caused by sunlight, that lunar eclipses occurred when the Earth obstructed sunlight falling onto the Moon, and that a solar eclipse occurred when the Moon obstructed sunlight from reaching the Earth. Although others disagreed with his model, Wang Chong accurately described the water cycle of the evaporation of water into clouds.Cartography, ships, and vehicles
Evidence found in Chinese literature, and archeological evidence, show that cartography existed in China before the Han. Some of the earliest Han maps discovered were ink-penned silk maps found amongst the Mawangdui Silk Texts in a 2nd-century-BC tomb. The generalMa Yuan Ma Yuan may refer to:
* Ma Yuan (Han dynasty) (馬援; 14 BC – 49 AD), general of the Han dynasty
* Ma Yuan (painter) (馬遠; 1160–1225), painter of the Song dynasty
* Ma Yuan (judge) (馬原), a former Vice President of the Supreme People's ...
created the world's first known raised-relief map from rice in the 1st century. This date could be revised if the tomb of Emperor Qin Shi Huang is excavated and the account in the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' concerning a model map of the empire is proven to be true.
Although the use of the Scale (map), graduated scale and grid reference for maps was not thoroughly described until the published work of Pei Xiu (AD 224–271), there is evidence that in the early 2nd century, cartographer Zhang Heng was the first to use scales and grids for maps.
Han dynasty Chinese sailed in a variety of ships different from those of previous eras, such as the Lou chuan, tower ship. The Junk (ship), ''junk'' design was developed and realized during the Han era. Junk ships featured a square-ended Bow (ship), bow and stern, a flat-bottomed Hull (watercraft), hull or Carvel (boat building), carvel-shaped hull with no keel or sternpost, and Bulkhead (partition), solid transverse bulkheads in the place of Boat building, structural ribs found in Western vessels. Moreover, Han ships were the first in the world to be steered using a rudder at the stern, in contrast to the simpler steering oar used for riverine transport, allowing them to sail on the high seas.
Although ox-carts and chariots were previously used in China, the wheelbarrow was first used in Han China in the 1st century BC. Han artwork of horse-drawn chariots shows that the Warring-States-Era heavy wooden yoke placed around a horse's chest was replaced by the softer ''breast strap''. Later, during the Northern Wei (386–534), the fully developed horse collar was invented.
Medicine
 Han-era medical physicians believed that the human body was subject to the same forces of nature that governed the greater universe, namely the cosmological cycles of yin and yang and the five phases. Each Zang-fu, organ of the body was associated with a particular phase. Illness was viewed as a sign that ''qi'' or "vital energy" channels leading to a certain organ had been disrupted. Thus, Han-era physicians prescribed medicine that was believed to counteract this imbalance.
For example, since the wood phase was believed to promote the fire phase, medicinal ingredients associated with the wood phase could be used to heal an organ associated with the fire phase. Besides dieting, Han physicians also prescribed moxibustion, acupuncture, and calisthenics as methods of maintaining one's health. When surgery was performed by the Chinese physician Hua Tuo (d. AD 208), he used anesthesia to numb his patients' pain and prescribed a rubbing ointment that allegedly sped the process of healing surgical wounds. Whereas the physician Zhang Zhongjing ( – ) is known to have written the ''Shanghan lun'' ("Dissertation on Typhoid Fever"), it is thought that both he and Hua Tuo collaborated in compiling the ''Shennong Ben Cao Jing'' medical text.
Han-era medical physicians believed that the human body was subject to the same forces of nature that governed the greater universe, namely the cosmological cycles of yin and yang and the five phases. Each Zang-fu, organ of the body was associated with a particular phase. Illness was viewed as a sign that ''qi'' or "vital energy" channels leading to a certain organ had been disrupted. Thus, Han-era physicians prescribed medicine that was believed to counteract this imbalance.
For example, since the wood phase was believed to promote the fire phase, medicinal ingredients associated with the wood phase could be used to heal an organ associated with the fire phase. Besides dieting, Han physicians also prescribed moxibustion, acupuncture, and calisthenics as methods of maintaining one's health. When surgery was performed by the Chinese physician Hua Tuo (d. AD 208), he used anesthesia to numb his patients' pain and prescribed a rubbing ointment that allegedly sped the process of healing surgical wounds. Whereas the physician Zhang Zhongjing ( – ) is known to have written the ''Shanghan lun'' ("Dissertation on Typhoid Fever"), it is thought that both he and Hua Tuo collaborated in compiling the ''Shennong Ben Cao Jing'' medical text.
See also
*Battle of Jushi *Campaign against Dong Zhuo *Comparative studies of the Roman and Han empires *Chinese emperors family tree (early)#Han Dynasty, Xin Dynasty and Shu Han, Han Emperors family tree *Shuanggudui *Ten AttendantsNotes
References
Citations
Sources cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (an abridgement of Joseph Needham's work) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
Han dynasty by Minnesota State University
"Han Culture," Hanyangling Museum Website
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Christopher Cullen, Carol Michaelson & Roel Sterckx (''In Our Time'', Oct. 14, 2004) {{Authority control Han dynasty, States and territories established in the 3rd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 3rd century 1st century BC in China, . 1st century in China, . 2nd century BC in China, . 2nd century in China, . 200s BC establishments 206 BC 220 disestablishments 3rd-century BC establishments in China 3rd-century disestablishments in China 3rd century BC in China, . Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history