|
Battle Of Gaixia
The Battle of Gaixia was a last stand fought in December 203 BC during the Chu–Han Contention between the forces of Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han) and Xiang Yu. The battle concluded with victory for Liu Bang, who proclaimed himself Emperor of China and founded the Han Dynasty. This is the last major battle of the Chu-Han Contention, ending with the suicide of Xiang Yu and the undisputed rule of Liu Bang. Background In November 204 BC the Han General-in-Chief Han Xin defeated the Chu-Qi coalition in the Battle of Wei River, and in early 203 he completed the Han conquest of the State of Qi, an ally of Western Chu. For these reasons, the situation of Xiang Yu, the Hegemon-King of Western Chu, had become increasingly precarious. Since 205 he and Liu Bang, the King of Han, had worn each other down in a war of attrition in the Central Plain, and Xiang had effectively run out of options to wrest control of northern China from Han Xin. Therefore, Xiang Yu sent an envoy to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongyuan
Zhongyuan (), the Central Plain(s), also known as Zhongtu (, lit. 'central land') and Zhongzhou (, lit. 'central region'), commonly refers to the part of the North China Plain surrounding the lower and middle reaches of the Yellow River, centered on the region between Luoyang and Kaifeng. It has been perceived as the birthplace of the Chinese civilization. Historically, the Huaxia people viewed Zhongyuan as 'the center of the world'. Human activities in the Zhongyuan region can be traced back to the Palaeolithic period. In prehistoric times, Huaxia, a confederation of tribes that later developed into the Han ethnicity, lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The term 'Zhongguo' (Central State) was used to distinguish themselves from the Siyi tribes that were perceived as 'barbaric'. For a large part of Chinese history, Zhongyuan had been the political, economic, and cultural center of the Chinese civilization, as over 20 dynasties had located their capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (region)
Wu () refers to a region in China centered on Lake Tai in Jiangnan (the region south of the Yangtze River).非常2+1亲子游中国--迷失烟雨江浙 The Wu region was historically part of the ancient Yang Province in southeastern China. The name "Wu" came from the names of several historical kingdoms based in that area. History The first Wu state was established in the late Western Zhou dynasty. Once considered to be a vassal state of the Western Zhou dynasty, the Wu state emerged as a major power among the various states in China at the end of the Spring and Autumn period. The most influential one among the historical Wu kingdoms was the state of Eastern Wu, which existed during the Three Kingdoms period. In the Han dynasty, the Wu region was mainly under the jurisdiction of Wu Commandery, which was a commandery under the larger Yang Province. Wu Commandery was later converted to Wu Prefecture. In the Sui and Tang dynasties, the names changed several times between Wu a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guan Ying
Guan Ying (died 176 BC), posthumously known as Marquis Yi of Yingyin, was a Chinese military general and politician who served as a chancellor of the Western Han dynasty. Life Guan Ying was from Suiyang (), which is present-day Shangqiu, Henan. He served under Liu Bang, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty, and joined him in rebelling against the Qin dynasty. He also fought on Liu Bang's side during the Chu–Han Contention and assisted him in overcoming his rival, Xiang Yu. After Liu Bang became emperor and established the Han dynasty, Guan Ying served as General of Chariots and Cavalry (). He assisted Liu Bang in putting down Chen Xi's rebellion and killed Hou Chang (), one of Chen Xi's commanders, near Quni (; around west of present-day Baoding, Hebei) in 196BC. Following Liu Bang's death, Empress Lü and her clan seized power from the Liu family and controlled the Han government – this event is historically known as the Lü Clan Disturbance. When the prince Liu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae () was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman and Italian army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history. Having recovered from their losses at Trebia (218 BC) and Lake Trasimene (217 BC), the Romans decided to engage Hannibal at Cannae, with approximately 86,000 Roman and allied troops. They massed their heavy infantry in a deeper formation than usual, while Hannibal used the double envelopment tactic and surrounded his enemy, trapping the majority of the Roman army, who were then slaughtered. The loss of life on the Roman side meant it was one of the most lethal singl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannibal Barca
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago and Hasdrubal; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome". In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto, Spain), an ally of Rome, in Hispania, sparking the Second Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ying Bu
Ying Bu (died 195 BC) was a warlord and vassal king who lived in the early Han dynasty. He was a native of Lu County (六縣; present-day Lu'an, Anhui). In his early life under the Qin dynasty, Ying Bu was convicted and sentenced to ''qing'' (黥; a form of punishment which involved branding a criminal by tattooing his face), so he was also called Qing Bu (). He was then sent to Mount Li to perform hard labour by constructing Qin Shi Huang's mausoleum. He later escaped with some men and became the leader of a bandit gang. Ying Bu participated in the insurrection against the Qin dynasty after the Dazexiang Uprising broke out in 209 BC. After the uprising failed, he became part of a rebel force led by Xiang Liang. He assisted Xiang Liang's nephew and successor Xiang Yu in overthrowing the Qin dynasty. After the fall of Qin, he initially fought on Xiang Yu's side in the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), a power struggle for supremacy over China between Xiang Yu and Liu Bang (Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
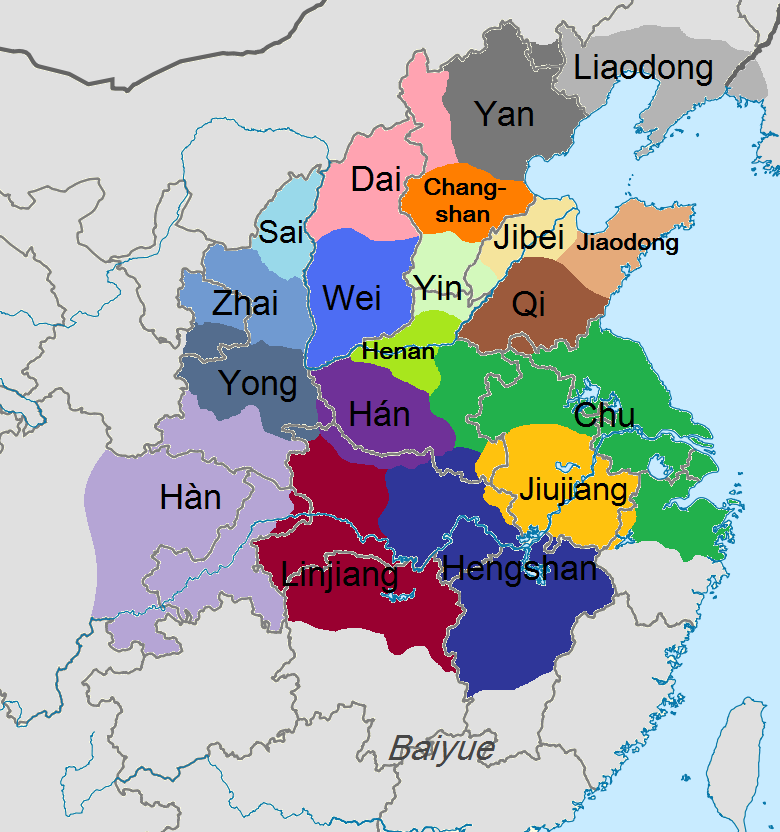
Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum known as the Chu-Han Contention. The details of the feudal division are as follows: The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived: almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention. Following many battles and changing alliances, Hàn defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Yan
Yan (; Old Chinese pronunciation: ''*'') was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Its capital was Ji (later known as Yanjing and now Beijing). During the Warring States period, the court was also moved to another capital at Xiadu at times. The history of Yan began in the Western Zhou in the early first millennium BC. After the authority of the Zhou king declined during the Spring and Autumn period in the 8th century BC, Yan survived and became one of the strongest states in China. During the Warring States period from the 5th to 3rd centuries BC, Yan was one of the last states to be conquered by the armies of Qin Shihuang: Yan fell in 222 BC, the year before the declaration of the Qin Empire. Yan experienced a brief period of independence after the collapse of the Qin dynasty in 207 BC, but it was eventually absorbed by the victorious Han. During its height, Yan stretched from the Yellow River (at the time, the river followed a more northerly course than at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained significant strength from the military reforms initiated during King Wuling's reign, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas now in modern Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi provinces. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei and Yan and various nomadic peoples, including the Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei Province. Zhao was home to administrative philosopher Shen Dao, sophist Gongsun Long and the Confucian Xun Kuang. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao clan within Jin had accumulated power for centuries, including annexing the Baidi state of Dai for themselves during the mid-5th centuryBC. At the end of the Spring and Autumn Period, Jin was divided up between three power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Kingdom
Liang (梁國) was a kingdom/principality in Han dynasty. Its territories was located within the modern Henan, Anhui and Shandong provinces. History Shortly before the establishment of the Han dynasty, the Qin-era Dang Commandery (碭郡) was granted to Peng Yue by Liu Bang as the Kingdom of Liang, named after the synonymous kingdom of the Warring States period. Six years later, Peng was executed on a fabricated treason charge, and the kingdom was granted to Liu Hui (劉恢), a son of Liu Bang. Dong Commandery was then added to Liang's territory. In the seventh year of Empress Dowager Lü's reign, Hui was moved to Zhao, where he committed suicide soon after. The kingdom was granted to Lü Chan (呂產), a nephew of the empress dowager. In this period, Liang was briefly renamed Lü. During the Lü Clan Disturbance, Lü Chan was killed, and the kingdom's two component commanderies was restored. Emperor Wen granted Liang to his fourth son Liu Yi (劉揖) in the second year of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Ping (Han Dynasty)
Chen Ping (陈平 d. 178 BC) was a Chinese politician who served as a chancellor in the early Western Han dynasty. He was an advisor to Liu Bang (Emperor Gao), the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. He played an important role in helping Liu Bang overcome his rival, Xiang Yu, in the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC). Early life Chen Ping was from Huyou Town (), Yangwu (陽武 present-day Lankao County, Henan). He was born in a peasant family, and his parents died when he was still young so he lived with his elder brother. His elder brother worked as a farmer on the 30 '' mu'' of land that their family owned while Chen Ping spent his time reading. As a child, Chen Ping had an ambition to serve his country. Chen Ping remained single until his 30s, when he met Zhang Fu (), a wealthy man. Zhang Fu had a granddaughter who married five times, but all her husbands died not long after they married her, so other men did not want to marry her. One day, Zhang Fu followed Chen Ping to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |