Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the
most populous city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
and the
fourth-most populous city in the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between
historic
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark ( gd, Siorrachd Lannraig; sco, Lanrikshire), is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the central Lowlands of Scotland.
Lanarkshire is the most populous county in Scotl ...
and
Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32
council areas of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" ( gd, comhairlean), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Ga ...
, and is governed by
Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the
River Clyde in the country's
West Central Lowlands.
Glasgow has the largest
economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK.
Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the
Burrell Collection
The Burrell Collection is a museum in Glasgow, Scotland, managed by Glasgow Museums. It houses the art collection of Sir William Burrell and Constance, Lady Burrell. The museum reopened on 29 March 2022 with free entry, having been closed for ...
,
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, h ...
, the
Royal Conservatoire of Scotland
The Royal Conservatoire of Scotland ( gd, Conservatoire Rìoghail na h-Alba), formerly the Royal Scottish Academy of Music and Drama ( gd, Acadamaidh Rìoghail Ciùil is Dràma na h-Alba) is a conservatoire of dance, drama, music, production, and ...
, the
Royal Scottish National Orchestra
The Royal Scottish National Orchestra (RSNO) ( gd, Orcastra Nàiseanta Rìoghail na h-Alba) is a British orchestra, based in Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Throughout its history, the O ...
,
Scottish Ballet
Scottish Ballet is the national ballet company of Scotland and one of the five leading ballet companies of the United Kingdom, alongside the Royal Ballet, English National Ballet, Birmingham Royal Ballet and Northern Ballet. Founded in 1969, ...
and
Scottish Opera
Scottish Opera is the national opera company of Scotland, and one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Founded in 1962 and based in Glasgow, it is the largest performing arts organisation in Scotland.
History
Scottish ...
– enjoy international reputations. The city was the
European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
,
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
,
media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
,
music scene,
sports clubs
A sports club or sporting club, sometimes an athletics club or sports society or sports association, is a group of people formed for the purpose of playing sports.
Sports clubs range from organisations whose members play together, unpaid, and ...
and
transport connections. It is the fifth-most visited city in the United Kingdom. The city hosted the
2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) at its main events venue, the
SEC Centre
The SEC Centre (originally known as the Scottish Exhibition and Conference Centre until 2017) is Scotland's largest exhibition centre, locate ...
. Glasgow hosted the
2014 Commonwealth Games and the first
European Championships in 2018, and was one of the host cities for
UEFA Euro 2020
The 2020 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2020 (stylised as UEFA EURO 2020) or simply Euro 2020, was the 16th UEFA European Championship, the quadrennial international men's football championship of Europe ...
. The city is also well known in the sporting world for football, particularly the
Old Firm
The Old Firm is the collective name for the Scottish football clubs Celtic and Rangers, which are both based in Glasgow. The two clubs are by far the most successful and popular in Scotland, and the rivalry between them has become deeply em ...
rivalry between
Celtic and
Rangers.
Glasgow grew from a small rural settlement on the River Clyde to become the largest seaport in Scotland, and tenth largest by tonnage in Britain. Expanding from the
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
and
royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
, and the later establishment of the
University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
in the 15th century, it became a major centre of the
Scottish Enlightenment in the 18th century. From the 18th century onwards, the city also grew as one of Britain's main hubs of transatlantic trade with
North America and the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
. With the onset of the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, the population and economy of Glasgow and the surrounding region expanded rapidly to become one of the world's pre-eminent centres of chemicals, textiles and engineering; most notably in the
shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befo ...
and
marine engineering
Marine engineering is the engineering of boats, ships, submarines, and any other marine vessel. Here it is also taken to include the engineering of other ocean systems and structures – referred to in certain academic and professional circl ...
industry, which produced many innovative and famous vessels. Glasgow was the "Second City of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
" for much of the
Victorian and
Edwardian era
The Edwardian era or Edwardian period of British history spanned the reign of King Edward VII, 1901 to 1910 and is sometimes extended to the start of the First World War. The death of Queen Victoria in January 1901 marked the end of the Victor ...
s.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Glasgow's population grew rapidly, reaching a peak of 1,127,825 people in 1938. The population was greatly reduced following comprehensive
urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of blighte ...
projects in the 1960s which resulted in large-scale relocation of people to designated
new towns, such as
Cumbernauld
Cumbernauld (; gd, Comar nan Allt, meeting of the streams) is a large town in the historic county of Dunbartonshire and council area of North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It is the tenth most-populous locality in Scotland and the most populated t ...
,
Livingston,
East Kilbride
East Kilbride (; gd, Cille Bhrìghde an Ear ) is the largest town in South Lanarkshire in Scotland and the country's sixth-largest locality by population. It was also designated Scotland's first new town on 6 May 1947. The area lies on a rais ...
and peripheral suburbs, followed by successive boundary changes. Over 985,200 people live in the
Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
contiguous urban area, while the wider
Glasgow City Region is home to over 1,800,000 people, equating to around 33% of Scotland's population.
The city has one of the highest densities of any
locality
Locality may refer to:
* Locality (association), an association of community regeneration organizations in England
* Locality (linguistics)
* Locality (settlement)
* Suburbs and localities (Australia), in which a locality is a geographic subdivis ...
in Scotland at 4,023/km
2.
Etymology
The name Glasgow is
Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
in origin. The first element ''glas'', meaning "grey-green, grey-blue" both in
Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
,
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
and modern day
Welsh and the second ''*cöü'', "hollow" (c.f.
Welsh ''glas-cau''),
giving a meaning of "green-hollow". The green-hollow may refer to the ravine to the east of Glasgow Cathedral. It is often said that the name means "dear green place" or that "dear green place" is a translation from Gaelic ''Glas Caomh''. "The dear green place" remains an affectionate way of referring to the city. The modern Gaelic is ''Glaschu'' and derived from the same roots as the English.
The settlement probably had an earlier Cumbric name, Cathures; the modern name appears for the first time in the Gaelic period (1116), as ''Glasgu''. It is also recorded that the
King of Strathclyde
The list of the kings of Strathclyde concerns the kings of Alt Clut, later Strathclyde, a Brythonic kingdom in what is now western Scotland.
The kingdom was ruled from Dumbarton Rock, ''Alt Clut'', the Brythonic name of the rock, until around ...
,
Rhydderch Hael
Rhydderch Hael ( en, Rhydderch the Generous), Riderch I of Alt Clut, or Rhydderch of Strathclyde, ( ''fl.'' 580 – c. 614) was a ruler of Alt Clut, a Brittonic kingdom in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" of Britain. He was one of the most famous ...
, welcomed Saint Kentigern (also known as Saint Mungo), and procured his consecration as bishop about 540. For some thirteen years Kentigern laboured in the region, building his church at the
Molendinar Burn
The Molendinar Burn is a burn in Glasgow, Scotland. It was the site of the settlement, Mellingdenor, that grew to become the kernel of Glasgow, and where St Mungo founded his church in the 6th century. It was later used to power the growing town ...
where
Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
now stands, and making many converts. A large community developed around him and became known as ''Glasgu''.
History
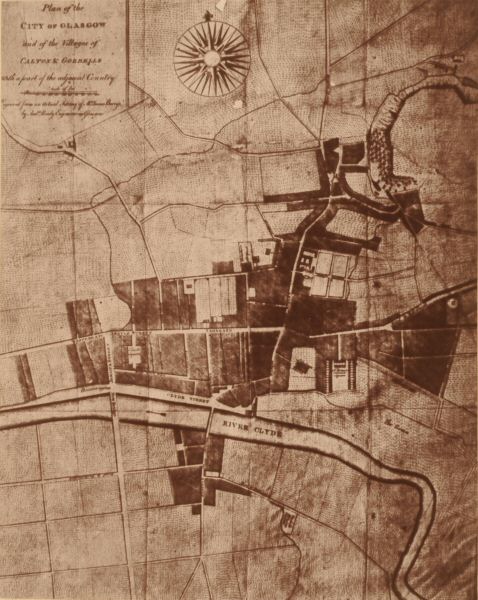
Origins and development
The area around Glasgow has hosted communities for millennia, with the
River Clyde providing a natural location for fishing. The
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
later built outposts in the area and, to protect Roman
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
from the
Brittonic speaking (
Celtic)
Caledonians, constructed the
Antonine Wall. Items from the wall, such as altars from
Roman forts
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
like
Balmuildy
Balmuildy is the site of a Roman fort on the Antonine Wall in Scotland. It is one of only two forts on the Antonine Wall to have been found with stone ramparts; the other is Castlecary. A digital reconstruction of the fort has been created.
L ...
, can be found at the
Hunterian Museum
The Hunterian is a complex of museums located in and operated by the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest museum in Scotland. It covers the Hunterian Museum, the Hunterian Art Gallery, the Mackintosh House, the Zoology M ...
today.
Glasgow itself was reputed to have been founded by the Christian
missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
Saint Mungo
Kentigern ( cy, Cyndeyrn Garthwys; la, Kentigernus), known as Mungo, was a missionary in the Brittonic Kingdom of Strathclyde in the late sixth century, and the founder and patron saint of the city of Glasgow.
Name
In Wales and England, this ...
in the 6th century. He established a church on the
Molendinar Burn
The Molendinar Burn is a burn in Glasgow, Scotland. It was the site of the settlement, Mellingdenor, that grew to become the kernel of Glasgow, and where St Mungo founded his church in the 6th century. It was later used to power the growing town ...
, where the present
Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
stands, and in the following years Glasgow became a religious centre.
Glasgow grew over the following centuries. The
Glasgow Fair reportedly began in 1190. The
first bridge over the River Clyde at Glasgow was recorded from around 1285, giving its name to the Briggait area of the city, forming the main north–south route over the river via
Glasgow Cross
Glasgow Cross is at the hub of the ancient royal burgh and now city of Glasgow, Scotland, close to its first crossing over the River Clyde. As a major junction in the city centre, its five streets run: north up the High Street to Glasgow Cathed ...
. The founding of the
University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
in 1451 and elevation of the
bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
to become the
Archdiocese of Glasgow
The Archdiocese of Glasgow was one of the thirteen (after 1633 fourteen) dioceses of the Scottish church. It was the second largest diocese in the Kingdom of Scotland, including Clydesdale, Teviotdale, parts of Tweeddale, Liddesdale, Annand ...
in 1492 increased the town's religious and educational status and landed wealth. Its early trade was in agriculture, brewing and fishing, with cured salmon and herring being exported to Europe and the Mediterranean.
[The City of Glasgow – The Third Statistical Account of Scotland, published 1958]
Following the European Protestant
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and with the encouragement of the
Convention of Royal Burghs, the 14 incorporated trade crafts federated as the Trades House in 1605 to match the power and influence in the town council of the earlier Merchants' Guilds who established their Merchants House in the same year.
Glasgow was subsequently raised to the status of
Royal Burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
in 1611. Glasgow's substantial fortunes came from international trade, manufacturing and invention, starting in the 17th century with sugar, followed by tobacco, and then cotton and linen, products of the
Atlantic triangular slave trade.
visited the city in the early 18th century and famously opined in his book ''
A tour thro' the whole island of Great Britain
''A Tour Thro' the Whole Island of Great Britain'' is an account of his travels by English author Daniel Defoe, first published in three volumes between 1724 and 1727. Other than ''Robinson Crusoe'', ''Tour'' was Defoe's most popular and financial ...
'', that Glasgow was "the cleanest and beautifullest, and best built city in Britain, London excepted". At that time the city's population was about 12,000, and the city was yet to undergo the massive expansionary changes to its economy and urban fabric, brought about by the
Scottish Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution.
Trading port
After the
Acts of Union in 1707, Scotland gained further access to the vast markets of the new British Empire, and Glasgow became prominent as a hub of international trade to and from the Americas, especially in sugar, tobacco, cotton, and manufactured goods. Starting in 1668, the city's
Tobacco Lords
The Tobacco Lords were a group of Scottish merchants and slave traders who in the 18th century made enormous fortunes by trading in tobacco. Many became so wealthy that they adopted the lifestyle of aristocrats, lavishing vast sums on great hous ...
created a deep water port at
Port Glasgow about down the
River Clyde, as the river from the city to that point was then too shallow for seagoing merchant ships. By the late 18th century more than half of the British tobacco trade was concentrated on the River Clyde, with over of tobacco being imported each year at its peak. At the time, Glasgow held a commercial importance as the city participated in the trade of sugar, tobacco and later cotton.
Industrialisation

The opening of the
Monkland Canal
The Monkland Canal was a canal designed to bring coal from the mining areas of Monklands to Glasgow in Scotland. In the course of a long and difficult construction process, it was opened progressively as short sections were completed, from 177 ...
and basin linking to the
Forth and Clyde Canal
The Forth and Clyde Canal is a canal opened in 1790, crossing central Scotland; it provided a route for the seagoing vessels of the day between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde at the narrowest part of the Scottish Lowlands. This allowe ...
at
Port Dundas in 1795, facilitated access to the extensive iron-ore and coal mines in
Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark ( gd, Siorrachd Lannraig; sco, Lanrikshire), is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the central Lowlands of Scotland.
Lanarkshire is the most populous county in Scotl ...
. After extensive
river engineering
River engineering is a discipline of civil engineering which studies human intervention in the course, characteristics, or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit. People have intervened in the natural course and be ...
projects to dredge and deepen the River Clyde as far as Glasgow, shipbuilding became a major industry on the upper stretches of the river, pioneered by industrialists such as
Robert Napier,
John Elder,
George Thomson,
Sir William Pearce and
Sir Alfred Yarrow
Sir Alfred Fernandez Yarrow, 1st Baronet, (13 January 1842 – 24 January 1932) was a British shipbuilder who started a shipbuilding dynasty, Yarrow Shipbuilders.
Origins
Yarrow was born of humble origins in East London, the son of Esther ( ...
. The River Clyde also became an important source of inspiration for artists, such as
John Atkinson Grimshaw
John Atkinson Grimshaw (6 September 1836 – 13 October 1893) was an English Victorian-era artist best known for his nocturnal scenes of urban landscapes.Alexander Robertson, ''Atkinson Grimshaw'', London, Phaidon Press, 1996 H. J. Dyos and ...
,
John Knox,
James Kay,
Sir Muirhead Bone,
Robert Eadie and
L.S. Lowry
Laurence Stephen Lowry ( ; 1 November 1887 – 23 February 1976) was an English artist. His drawings and paintings mainly depict Pendlebury, Lancashire (where he lived and worked for more than 40 years) as well as Salford and its vicinity ...
, willing to depict the new industrial era and the modern world, as did
Stanley Spencer downriver at
Port Glasgow.

Glasgow's population had surpassed that of Edinburgh by 1821. The development of civic institutions included the
City of Glasgow Police
The City of Glasgow Police or Glasgow City Police was the police of the City of Glasgow, Scotland. In the 17th century, Scottish cities used to hire watchmen to guard the streets at night, augmenting a force of unpaid citizen constables. On 3 ...
in 1800, one of the first municipal
police
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and th ...
forces in the world. Despite the crisis caused by the
City of Glasgow Bank's collapse in 1878, growth continued and by the end of the 19th century it was one of the cities known as the "Second City of the Empire" and was producing more than half Britain's tonnage of shipping and a quarter of all locomotives in the world. In addition to its pre-eminence in shipbuilding, engineering, industrial machinery, bridge building, chemicals, explosives, coal and oil industries it developed as a major centre in textiles, garment-making, carpet manufacturing, leather processing, furniture-making, pottery, food, drink and cigarette making; printing and publishing. Shipping, banking, insurance and professional services expanded at the same time.
Glasgow became one of the first cities in Europe to reach a population of one million. The city's new trades and sciences attracted new residents from across the
Lowlands
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of p ...
and the
Highlands of Scotland
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sco ...
, from
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
and other parts of Britain and from
Continental Europe.
During this period, the construction of many of the city's greatest architectural masterpieces and most ambitious civil engineering projects, such as the
Milngavie water treatment works
Milngavie water treatment works (commonly known as The Waterworks) is a Scottish Water-operated water treatment facility located in Milngavie, Scotland. It is primary source of the water for the city of Glasgow (and the Greater Glasgow area) in w ...
,
Glasgow Subway,
Glasgow Corporation Tramways
Glasgow Corporation Tramways were formerly one of the largest urban tramway systems in Europe. Over 1000 municipally-owned trams served the city of Glasgow, Scotland, with over 100 route miles (160 route kilometres) by 1922. The system closed i ...
,
City Chambers,
Mitchell Library
The Mitchell Library is a large public library and centre of the City Council public library system of Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The library, based in the Charing Cross district, was initially established in Ingram Street in 1877 following a ...
and
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, h ...
were being funded by its wealth. The city also held a series of
International Exhibitions at
Kelvingrove Park
Kelvingrove Park is a public park located on the River Kelvin in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland, containing the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum.
History
Kelvingrove Park was originally created as the West End Park in 1852, and ...
, in
1888
In Germany, 1888 is known as the Year of the Three Emperors. Currently, it is the year that, when written in Roman numerals, has the most digits (13). The next year that also has 13 digits is the year 2388. The record will be surpassed as late ...
,
1901
Events
January
* January 1 – The British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia federate as the Commonwealth of Australia; Edmund Barton becomes the first Prime Minist ...
and
1911
A notable ongoing event was the Comparison of the Amundsen and Scott Expeditions, race for the South Pole.
Events January
* January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory ...
, with Britain's last major International Exhibition, the
Empire Exhibition, being subsequently held in 1938 at
Bellahouston Park, which drew 13 million visitors.
The 20th century witnessed both decline and renewal in the city. After
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the city suffered from the impact of the
Post–World War I recession
The post–World War I recession was an economic recession that hit much of the world in the aftermath of World War I. In many nations, especially in North America, economic growth continued and even accelerated during World War I as nations mo ...
and from the later
Great Depression, this also led to a rise of radical socialism and the "
Red Clydeside
Red Clydeside was the era of political radicalism in Glasgow, Scotland, and areas around the city, on the banks of the River Clyde, such as Clydebank, Greenock, Dumbarton and Paisley, from the 1910s until the early 1930s. Red Clydeside is a ...
" movement. The city had recovered by the outbreak of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The city saw
aerial bombardment
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offic ...
by the
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
during the
Clydebank Blitz, during the war, then grew through the post-war boom that lasted through the 1950s. By the 1960s, growth of industry in countries like Japan and
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
, weakened the once pre-eminent position of many of the city's industries. As a result of this, Glasgow entered a lengthy period of relative economic decline and rapid de-industrialisation, leading to high unemployment, urban decay, population decline,
welfare dependency
Welfare dependency is the state in which a person or household is reliant on government welfare benefits for their income for a prolonged period of time, and without which they would not be able to meet the expenses of daily living. The United St ...
and poor health for the city's inhabitants. There were active attempts at regeneration of the city, when the Glasgow Corporation published its controversial ''
Bruce Report
The Bruce Report (or the Bruce Plan) is the name commonly given to the ''First Planning Report to the Highways and Planning Committee of the Corporation of the City of Glasgow''Robert Bruce (1945), ''First Planning report to the Highways and Pla ...
'', which set out a comprehensive series of initiatives aimed at turning round the decline of the city. The report led to a huge and radical programme of rebuilding and regeneration efforts that started in the mid-1950s and lasted into the late 1970s. This involved the mass demolition of the city's infamous slums and their replacement with large suburban housing estates and tower blocks.

The city invested heavily in roads infrastructure, with an extensive system of arterial roads and motorways that bisected the central area. There are also accusations that the
Scottish Office
The Scottish Office was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom from 1885 until 1999, exercising a wide range of government functions in relation to Scotland under the control of the Secretary of State for Scotland. Following the es ...
had deliberately attempted to undermine Glasgow's economic and political influence in post-war Scotland by diverting inward investment in new industries to other regions during the
Silicon Glen
Silicon Glen is a nickname for the high tech sector of Scotland, the name inspired by Silicon Valley in California. It is applied to the Central Belt triangle between Dundee, Inverclyde and Edinburgh, which includes Fife, Glasgow and Stirling ...
boom and creating the
new towns
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
of Cumbernauld, Glenrothes, Irvine, Livingston and
East Kilbride
East Kilbride (; gd, Cille Bhrìghde an Ear ) is the largest town in South Lanarkshire in Scotland and the country's sixth-largest locality by population. It was also designated Scotland's first new town on 6 May 1947. The area lies on a rais ...
, dispersed across the
Scottish Lowlands to halve the city's population base.
By the late 1980s, there had been a significant resurgence in Glasgow's economic fortunes. The "
Glasgow's miles better" campaign, launched in 1983, and opening of the
Burrell Collection
The Burrell Collection is a museum in Glasgow, Scotland, managed by Glasgow Museums. It houses the art collection of Sir William Burrell and Constance, Lady Burrell. The museum reopened on 29 March 2022 with free entry, having been closed for ...
in 1983 and
in 1985 facilitated Glasgow's new role as a European centre for business services and finance and promoted an increase in tourism and inward investment. The latter continues to be bolstered by the legacy of the city's
Glasgow Garden Festival
The Glasgow Garden Festival was the third of the five national garden festivals, and the only one to take place in Scotland.
It was held in Glasgow between 26 April and 26 September 1988. It was the first event of its type to be held in the cit ...
in 1988, its status as
European Capital of Culture in 1990, and concerted attempts to diversify the city's economy. However, it is the industrial heritage that serves as key tourism enabler. Wider economic revival has persisted and the ongoing
regeneration of inner-city areas, including the large-scale
Clyde Waterfront Regeneration
Clyde Waterfront is a 20 km stretch of the River Clyde, Scotland, running east–west from Glasgow Green in the heart of Glasgow, to Dumbarton on the Firth of Clyde. With over 200 projects on both sides of the Clyde, this is one of United K ...
, has led to more affluent people moving back to live in the centre of Glasgow, fuelling allegations of
gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ec ...
. In 2008, the city was listed by
Lonely Planet
Lonely Planet is a travel guide book publisher. Founded in Australia in 1973, the company has printed over 150 million books.
History Early years
Lonely Planet was founded by married couple Maureen and Tony Wheeler. In 1972, they embarke ...
as one of the world's top 10 tourist cities.
Despite Glasgow's economic renaissance, the
East End of the city remains the focus of social deprivation.
[ A Glasgow Economic Audit report published in 2007 stated that the gap between prosperous and deprived areas of the city is widening.][ while the ]Centre for Social Justice
The Centre for Social Justice (CSJ) is an independent centre-right think tank based in the United Kingdom, co-founded in 2004 by Iain Duncan Smith, Tim Montgomerie, Mark Florman and Philippa Stroud.
Political positions
The organisation's stated ...
reported 29.4% of the city's working-age residents to be "economically inactive".[ In 2008 the city was ranked at 43 for Personal Safety in the ]Mercer
Mercer may refer to:
Business
* Mercer (car), a defunct American automobile manufacturer (1909–1925)
* Mercer (consulting firm), a large human resources consulting firm headquartered in New York City
* Mercer (occupation), a merchant or trader, ...
index of top 50 safest cities in the world. The Mercer report was specifically looking at Quality of Living, yet by 2011 within Glasgow, certain areas were (still) "failing to meet the Scottish Air Quality Objective levels for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter (PM10)".
Sanitation
With the population growing, the first scheme to provide a public water supply was by the Glasgow Company in 1806. A second company was formed in 1812, and the two merged in 1838, but there was some dissatisfaction with the quality of the water supplied. The Gorbals Gravitation Water Company began supplying water to residents living to the south of the River Clyde in 1846, obtained from reservoirs, which gave 75,000 people a constant water supply, but others were not so fortunate, and some 4,000 died in an outbreak of cholera in 1848/1849.Loch Katrine
Loch Katrine (; or ) is a freshwater loch in the Trossachs area of the Scottish Highlands, east of Loch Lomond, within the historic county and registration county of Perthshire and the contemporary district of Stirling. The loch is about ...
and to convey clean water by gravity along a aqueduct to a holding reservoir at Milngavie, and then by pipes into the city. The project cost £980,000[ and was opened by ]Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
in 1859.
In the early 19th century an eighth of the people lived in single-room accommodation.
The engineer for the project was John Frederick Bateman
John Frederick La Trobe Bateman (30 May 1810 – 10 June 1889) was an English civil engineer whose work formed the basis of the modern United Kingdom water supply industry. For more than 50 years from 1835 he designed and constructed reser ...
, while James Morris Gale became the resident engineer for the city section of the project, and subsequently became Engineer in Chief for Glasgow Water Commissioners. He oversaw several improvements during his tenure, including a second aqueduct and further raising of water levels in Loch Katrine. Additional supplies were provided by Loch Arklet in 1902, by impounding the water and creating a tunnel to allow water to flow into Loch Katrine. A similar scheme to create a reservoir in Glen Finglas was authorised in 1903, but was deferred, and was not completed until 1965.[ Following the ]2002 Glasgow floods
The 2002 Glasgow Floods were a series of flash floods that occurred after thunderstorms in the Scottish Lowlands in the end of July and beginning of August 2002. The heaviest rainfall fell on the night of Tuesday, 30 July 2002.
The East End of Gl ...
, the waterborne parasite cryptosporidium was found in the reservoir at Milngavie, and so the new Milngavie water treatment works
Milngavie water treatment works (commonly known as The Waterworks) is a Scottish Water-operated water treatment facility located in Milngavie, Scotland. It is primary source of the water for the city of Glasgow (and the Greater Glasgow area) in w ...
was built. It was opened by Queen Elizabeth in 2007, and won the 2007 Utility Industry Achievement Award, having been completed ahead of its time schedule and for £10 million below its budgeted cost.
Good health requires both clean water and effective removal of sewage. The Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh an ...
rebuilt many of the sewers, as part of a deal to allow them to tunnel under the city, and sewage treatment works were opened at Dalmarnoch in 1894, Dalmuir in 1904 and Shieldhall in 1910. The works experimented to find better ways to treat sewage, and a number of experimental filters were constructed, until a full activated sludge plant was built between 1962 and 1968 at a cost of £4 million.Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive
The Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive 199191/271/EEC European Union directive concerning urban waste water "collection, treatment and discharge of urban waste water and the treatment and discharge of waste water from certain industrial sec ...
ended the practice. The sewerage infrastructure was improved significantly in 2017, with the completion of a tunnel long, which provides of storm water storage. It will reduce the risk of flooding and the likelihood that sewage will overflow into the Clyde during storms. Since 2002, clean water provision and sewerage have been the responsibility of Scottish Water
Scottish Water is a statutory corporation that provides water and sewerage services across Scotland. It is accountable to the public through the Scottish Government.
Operations
Scottish Water provides drinking water to 2.46 million household ...
.
Heraldry
The coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
of the City of Glasgow was granted to the royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
by the Lord Lyon on 25 October 1866. It incorporates a number of symbols and emblems associated with the life of Glasgow's patron saint, Mungo, which had been used on official seals prior to that date. The emblems represent miracles
A miracle is an event that is inexplicable by natural or scientific lawsOne dictionary define"Miracle"as: "A surprising and welcome event that is not explicable by natural or scientific laws and is therefore considered to be the work of a divin ...
supposed to have been performed by Mungo and are listed in the traditional rhyme:
::::''Here's the bird that never flew''
::::''Here's the tree that never grew''
::::''Here's the bell that never rang''
::::''Here's the fish that never swam''
St Mungo is also said to have preached a sermon containing the words ''Lord, Let Glasgow flourish by the preaching of the word and the praising of thy name''. This was abbreviated to "Let Glasgow Flourish" and adopted as the city's motto.
In 1450, John Stewart, the first Lord Provost of Glasgow, left an endowment so that a "St Mungo's Bell" could be made and tolled throughout the city so that the citizens would pray for his soul. A new bell was purchased by the magistrates in 1641 and that bell is still on display in the People's Palace Museum, near Glasgow Green
Glasgow Green is a park in the east end of Glasgow, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde. Established in the 15th century, it is the oldest park in the city. It connects to the south via the St Andrew's Suspension Bridge.
History
I ...
.
The supporters are two salmon bearing rings, and the crest is a half length figure of Saint Mungo. He wears a bishop's mitre and liturgical vestments and has his hand raised in "the act of benediction
A benediction ( Latin: ''bene'', well + ''dicere'', to speak) is a short invocation for divine help, blessing and guidance, usually at the end of worship service. It can also refer to a specific Christian religious service including the exposit ...
". The original 1866 grant placed the crest atop a helm, but this was removed in subsequent grants. The current version (1996) has a gold mural crown
A mural crown ( la, corona muralis) is a crown or headpiece representing city walls, towers, or fortresses. In classical antiquity, it was an emblem of tutelary deities who watched over a city, and among the Romans a military decoration. Later ...
between the shield and the crest. This form of coronet, resembling an embattled city wall, was allowed to the four area councils with city status.
The arms were re-matriculated by the City of Glasgow District Council
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
on 6 February 1975, and by the present area council on 25 March 1996. The only change made on each occasion was in the type of coronet over the arms.
Government and politics
Local government

 Although Glasgow
Although Glasgow Corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and ...
had been a pioneer in the municipal socialist movement from the late-nineteenth century, since the Representation of the People Act 1918, Glasgow increasingly supported left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
ideas and politics at a national level. The city council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
was controlled by the Labour Party for over thirty years, since the decline of the Progressives
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, techno ...
. Since 2007, when local government elections in Scotland began to use the single transferable vote
Single transferable vote (STV) is a multi-winner electoral system in which voters cast a single vote in the form of a ranked-choice ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternate ...
rather than the first-past-the-post system
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
, the dominance of the Labour Party within the city started to decline. As a result of the 2017 United Kingdom local elections
The 2017 United Kingdom local elections were held on Thursday 4 May 2017. Local elections were held across Great Britain, with elections to 35 English local authorities and all councils in Scotland and Wales.
Newly created combined authority ...
, the SNP was able to form a minority administration ending Labour's thirty-seven years of uninterrupted control.
In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
and the German Revolution of 1918–19, the city's frequent strikes and militant organisations caused serious alarm at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
, with one uprising in January 1919 prompting the Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
, David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for leading the United Kingdom during ...
, to deploy 10,000 soldiers and tanks on the city's streets. A huge demonstration in the city's George Square
George Square ( gd, Ceàrnag Sheòrais) is the principal civic square in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of six squares in the city centre, the others being Cathedral Square, St Andrew's Square, St Enoch Square, Royal Exchange S ...
on 31 January ended in violence after the Riot Act was read.
Industrial action at the shipyards gave rise to the "Red Clydeside
Red Clydeside was the era of political radicalism in Glasgow, Scotland, and areas around the city, on the banks of the River Clyde, such as Clydebank, Greenock, Dumbarton and Paisley, from the 1910s until the early 1930s. Red Clydeside is a ...
" epithet. During the 1930s, Glasgow was the main base of the Independent Labour Party
The Independent Labour Party (ILP) was a British political party of the left, established in 1893 at a conference in Bradford, after local and national dissatisfaction with the Liberals' apparent reluctance to endorse working-class candidates ...
. Towards the end of the twentieth century, it became a centre of the struggle against the poll tax; which was introduced in Scotland a whole year before the rest of the United Kingdom and also served as the main base of the Scottish Socialist Party
The Scottish Socialist Party (SSP; gd, Pàrtaidh Sòisealach na h-Alba; sco, Scots Socialist Pairtie) is a left-wing political party campaigning for the establishment of an independent socialist Scotland.
The party was founded in 1998. It c ...
, another left-wing political party in Scotland. The city has not had a Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
MP since the 1982 Hillhead by-election, when the SDP took the seat, which was in Glasgow's most affluent area. The fortunes of the Conservative Party continued to decline into the twenty-first century, winning only one of the 79 councillors on Glasgow City Council in 2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gat ...
, despite having been the controlling party (as the Progressives
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, techno ...
) from 1969 to 1972 when Sir Donald Liddle was the last non-Labour Lord Provost.
Glasgow is represented in both the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, and the Scottish Parliament in Holyrood, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
. At Westminster, it is represented by seven Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MPs), all elected at least once every five years to represent individual constituencies, using the first-past-the-post system of voting. In Holyrood, Glasgow is represented by sixteen Members of the Scottish Parliament
Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP; gd, Ball Pàrlamaid na h-Alba, BPA; sco, Memmer o the Scots Pairliament, MSP) is the title given to any one of the 129 individuals elected to serve in the Scottish Parliament.
Electoral system
The add ...
(MSPs), of whom nine are elected to represent individual constituencies once every four years using first-past-the-post, and seven are elected as additional regional members, by proportional representation. Since the 2016 Scottish Parliament election, Glasgow is represented at Holyrood by
9 Scottish National Party MSPs, 4 Labour MSPs, 2 Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
MSPs and 1 Scottish Green MSP. In the European Parliament, the city formed part of the Scotland constituency, which elected six Members of the European Parliament
A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament.
When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the ECSC) first met in 1952, its ...
(MEPs) prior to Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC ...
.
Central government
Since Glasgow is covered and operates under two separate central governments, the devolved Scottish Parliament and UK Government, they determine various matters that Glasgow City Council is not responsible for.
Scottish Parliament
The Glasgow electoral region of the Scottish Parliament covers the Glasgow City council area, a north-western part of South Lanarkshire and a small eastern portion of Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
. It elects nine of the parliament's 73 first past the post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast thei ...
constituency members and seven of the 56 additional members. Both kinds of member are known as Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs). The system of election is designed to produce a form of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
.
The first past the post seats were created in 1999 with the names and boundaries of then existing Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
(House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
) constituencies. In 2005, the number of Westminster Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MPs) representing Scotland was cut to 59, with new constituencies being formed, while the existing number of MSPs
Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP; gd, Ball Pàrlamaid na h-Alba, BPA; sco, Memmer o the Scots Pairliament, MSP) is the title given to any one of the 129 individuals elected to serve in the Scottish Parliament.
Electoral system
The ad ...
was retained at Holyrood. In the 2011 Scottish Parliament election
The 2011 Scottish Parliament election was held on Thursday, 5 May 2011 to elect 129 members to the Scottish Parliament.
The election delivered the first majority government since the opening of Holyrood, a remarkable feat as the Additional M ...
, the boundaries of the Glasgow region were redrawn.
Currently, the nine Scottish Parliament constituencies in the Glasgow electoral region are:
* Glasgow Anniesland
* Glasgow Cathcart
* Glasgow Kelvin
* Glasgow Maryhill and Springburn
Glasgow Maryhill and Springburn is a constituency of the Scottish Parliament ( Holyrood), being one of eight constituencies within the Glasgow City council area. It elects one Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) by the plurality (first p ...
* Glasgow Pollok
* Glasgow Provan
* Glasgow Shettleston
* Glasgow Southside
* Rutherglen
Rutherglen (, sco, Ruglen, gd, An Ruadh-Ghleann) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, immediately south-east of the city of Glasgow, from its centre and directly south of the River Clyde. Having existed as a Lanarkshire burgh in its own ...
At the 2021 Scottish Parliament election
The 2021 Scottish Parliament election took place on 6 May 2021, under the provisions of the Scotland Act 1998. All 129 Members of the Scottish Parliament were elected in the sixth election since the parliament was re-established in 1999. The e ...
, all nine of these constituencies were won by Scottish National Party (SNP) candidates. On the regional vote, the Glasgow electoral region is represented by four Labour MSPs, two Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
MSPs and one Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
MSP.
UK Parliament
Following reform of constituencies of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom (Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
) in 2005, which reduced the number of Scottish Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MPs), the current Westminster constituencies representing Glasgow are:
* Glasgow Central
* Glasgow East
* Glasgow North
* Glasgow North East
Glasgow North East is a burgh constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (at Westminster). It was first contested at the 2005 general election. The current Member of Parliament (MP) is Anne McLaughlin of the ...
* Glasgow North West
Glasgow North West is a constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (Westminster). It was first used at the 2005 general election.
Boundaries
The Glasgow City wards of Anniesland, Blairdardie, Drumry, Hayburn, ...
* Glasgow South
* Glasgow South West
Following the 2014 Scottish independence referendum, in which 53.49% of the electorate of Glasgow voted in favour of Scottish independence; the SNP won every seat in the city at the 2015 general election, including a record-breaking 39.3% swing from Labour to SNP in the Glasgow North East
Glasgow North East is a burgh constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (at Westminster). It was first contested at the 2005 general election. The current Member of Parliament (MP) is Anne McLaughlin of the ...
constituency.
At the 2017 snap general election, Glasgow was represented by 6 Scottish National Party MPs and 1 Labour MP; the Glasgow North East constituency which had a record 39.3% swing from Labour to SNP at the previous general election, was regained by Paul Sweeney
Paul John Sweeney FIES ( gd, Pòl Eòin Mac Suibhne; born 16 January 1989) is a Scottish politician. A member of the Scottish Labour and Co-operative Party, he currently serves as Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) for the Glasgow region ...
of the Labour Party, who narrowly defeated sitting SNP MP Anne McLaughlin
Anne McLaughlin (born 8 March 1966) is a Scottish National Party (SNP) politician serving as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Glasgow North East since 2019, and previously from 2015 to 2017.
She was previously a Member of the Scottish Parliame ...
by 242 votes.
Since the 2019 general election, Glasgow has been represented by 7 Scottish National Party MPs; the Glasgow North East constituency, was regained by Anne McLaughlin
Anne McLaughlin (born 8 March 1966) is a Scottish National Party (SNP) politician serving as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Glasgow North East since 2019, and previously from 2015 to 2017.
She was previously a Member of the Scottish Parliame ...
of the Scottish National Party, resulting in the same clean sweep like 4 years previously.
Referendums
In the Scottish independence referendum, Glasgow voted "Yes" by a margin of 53.5% to 46.5%.
In the Brexit referendum, results varied from constituency to constituency. Glasgow North recorded the biggest remain vote with 78% opting to stay in the EU whilst in Glasgow East this figure dropped to 56%. The city as a whole voted to remain in the EU, by 66.6% to 33.3%.
Voter turnout
Voter turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford Univ ...
has often been lower in Glasgow than in the rest of the United Kingdom. In the Referendum of 2014 turnout was 75%, the lowest in Scotland; in the Brexit referendum the city's voters, while joining the rest of Scotland in voting to remain part of the EU, again had a low turnout of 56.2%, although SNP MP Angus Robertson placed this in the historical context of traditional low turnout in Glasgow.
In the 2015 general election, the six Scottish constituencies with the lowest turnout were all in Glasgow; turnout further decreased in the 2017 election, when five of the city's seven seats reported a lowered turnout.
Geography
 Glasgow is located on the banks of the River Clyde, in West Central Scotland. Another important river is the
Glasgow is located on the banks of the River Clyde, in West Central Scotland. Another important river is the Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
, a tributary of the River Clyde, whose name was used in creating the title of Baron Kelvin the renowned physicist for whom the SI unit of temperature, Kelvin, is named.
On older maps Glasgow is shown within the area of the pre-1975 county of Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark ( gd, Siorrachd Lannraig; sco, Lanrikshire), is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the central Lowlands of Scotland.
Lanarkshire is the most populous county in Scotl ...
; from 1975 to 1996 it appears within Strathclyde Region; more recent maps generally show Glasgow as one of 32 Council Areas
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" ( gd, comhairlean), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Ga ...
in Scotland.
Location
Glasgow is located in the central belt of Scotland.
Climate
 Despite its northerly latitude, similar to that of
Despite its northerly latitude, similar to that of Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
, Glasgow's climate is classified as oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Cfb'').
Data is available online for 3 official weather stations in the Glasgow area: Paisley, Abbotsinch and Bishopton. All are located to the west of the city, in neighbouring Renfrewshire.
Owing to its westerly position and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, Glasgow is one of Scotland's milder areas. Winter temperatures are usually higher than in most places of equal latitude away from the UK, due to the warming influence of the Gulf Stream. However, this results in less distinct seasons as compared to continental Western Europe. At Paisley, the annual precipitation averages . Glasgow has been named as the rainiest city of the UK, having an average of 170 days of rain a year.
Winters are cool and overcast, with a January mean of , though lows sometimes fall below freezing. Since 2000 Glasgow has experienced few very cold, snowy and harsh winters where temperatures have fallen much below freezing. The most extreme instances have however seen temperatures around in the area. Snowfall accumulation is infrequent and short-lived. The spring months (March to May) are usually mild and often quite pleasant. Many of Glasgow's trees and plants begin to flower at this time of the year and parks and gardens are filled with spring colours.
During the summer months (June to August) the weather can vary considerably from day to day, ranging from relatively cool and wet to quite warm with the odd sunny day. Long dry spells of warm weather are generally quite scarce. Overcast and humid conditions without rain are frequent. Generally the weather pattern is quite unsettled and erratic during these months, with only occasional heatwaves. The warmest month is usually July, with average highs above . Summer days can occasionally reach up to 27 °C (81 °F), and very rarely exceed 30 °C (86 °F). Autumns are generally cool to mild with increasing precipitation. During early autumn there can be some settled periods of weather and it can feel pleasant with mild temperatures and some sunny days.
The official Met Office data series goes back to 1959 and shows that there only have been a few warm and no hot summers in Glasgow, in stark contrast to areas further south in Great Britain and eastwards in Europe. The warmest month on record in the data series is July 2006, with an average high of and low of .cold wave
A cold wave (known in some regions as a cold snap, cold spell or Arctic Snap) is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in tem ...
affecting the British Isles. Even then, the December high was above freezing at with the low of .
Demographics
 In the 1950s, the population of the City of Glasgow area peaked at 1,089,000. Glasgow was then one of the most densely populated cities in the world. After the 1960s, clearances of poverty-stricken inner city areas like the
In the 1950s, the population of the City of Glasgow area peaked at 1,089,000. Glasgow was then one of the most densely populated cities in the world. After the 1960s, clearances of poverty-stricken inner city areas like the Gorbals
The Gorbals is an area in the city of Glasgow, Scotland, on the south bank of the River Clyde. By the late 19th century, it had become densely populated; rural migrants and immigrants were attracted by the new industries and employment opportun ...
and relocation to "new towns
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
" such as East Kilbride
East Kilbride (; gd, Cille Bhrìghde an Ear ) is the largest town in South Lanarkshire in Scotland and the country's sixth-largest locality by population. It was also designated Scotland's first new town on 6 May 1947. The area lies on a rais ...
and Cumbernauld
Cumbernauld (; gd, Comar nan Allt, meeting of the streams) is a large town in the historic county of Dunbartonshire and council area of North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It is the tenth most-populous locality in Scotland and the most populated t ...
led to population decline. In addition, the boundaries of the city were changed twice during the late-twentieth century, making direct comparisons difficult.
The urban area continues to expand beyond the city council boundaries into surrounding suburban areas, encompassing around of all adjoining suburbs, if commuter town
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many ...
s and villages are included. There are two distinct definitions for the population of Glasgow: the Glasgow City Council Area which lost the districts of Rutherglen
Rutherglen (, sco, Ruglen, gd, An Ruadh-Ghleann) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, immediately south-east of the city of Glasgow, from its centre and directly south of the River Clyde. Having existed as a Lanarkshire burgh in its own ...
and Cambuslang to South Lanarkshire in 1996, and the Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
Urban Area which includes the conurbation around the city (however in the 2016 definitions the aforementioned Rutherglen and Cambuslang were included along with the likes of Paisley, Clydebank, Newton Mearns
Newton Mearns ( sco, The Mearns; gd, Baile Ùr na Maoirne ) is a suburban town and the largest settlement in East Renfrewshire, Scotland. It lies southwest of Glasgow City Centre on the main road to Ayrshire, above sea level. It has a popu ...
, Bearsden and Stepps but not others with no continuity of populated postcodes – although in some cases the gap is small – the excluded nearby settlements including Barrhead
Barrhead ( sco, Baurheid, gd, Ceann a' Bharra) is a town in East Renfrewshire, Scotland, southwest of Glasgow city centre on the edge of the Gleniffer Braes. At the 2011 census its population was 17,268.
History
Barrhead was formed when ...
, Erskine
Erskine (, sco, Erskin, gd, Arasgain) is a town in the council area of Renfrewshire, and historic county of the same name, situated in the West Central Lowlands of Scotland. It lies on the southern bank of the River Clyde, providing the l ...
and Kirkintilloch plus a large swathe of Lanarkshire which had been considered contiguous with Glasgow in previous definitions: the ' settlements' named Coatbridge & Airdrie, Hamilton and Motherwell & Wishaw, each containing a number of distinct smaller localities).Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, especially the north western counties of Donegal, Fermanagh
Historically, Fermanagh ( ga, Fir Manach), as opposed to the modern County Fermanagh, was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland, associated geographically with present-day County Fermanagh. ''Fir Manach'' originally referred to a distinct kin group of a ...
, Tyrone and Londonderry. In the 1881 UK Census, 83% of the population was born in Scotland, 13% in Ireland, 3% in England and 1% elsewhere. By 1911, the city was no longer gaining population by migration. The demographic percentages in the 1951 UK census were: born in Scotland 93%, Ireland 3%, England 3% and elsewhere 1%.Italian Scots
Italian Scots are people of Italian descent living in Scotland. These terms may refer to people who are born in Scotland and of Italian descent. It can also refer to people of mixed Scottish and Italian ancestry. A recent Italian voter census es ...
also settled in Glasgow, originating from provinces like Frosinone
Frosinone (, local dialect: ) is a town and ''comune'' in Lazio, central Italy, the administrative seat of the province of Frosinone. It is located about south-east of Rome close to the Rome-Naples A1 Motorway. The city is the main city of the ...
in Lazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
and Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one ...
in north-west Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
at this time, many originally working as " Hokey Pokey" men.
In the 1960s and 1970s, many Asians also settled in Glasgow, mainly in the Pollokshields
Pollokshields ( gd, Buthan Phollaig, Scots: ''Powkshiels'') is an area in the Southside of Glasgow, Scotland. Its modern boundaries are largely man-made, being formed by the M77 motorway to the west and northwest with the open land of Pollok ...
area. These number 30,000 Pakistanis, 15,000 Indians and 3,000 Bangladeshis
Bangladeshis ( bn, বাংলাদেশী ) are the citizens of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centered on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the eponymous bay.
Bangladeshi citizenship was formed in 1971, when the ...
as well as Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
people, many of whom settled in the Garnethill
Garnethill is a predominantly residential area of the city of Glasgow, Scotland with a number of important public buildings.
Geography
Located in the city centre, the area borders Cowcaddens to its north, Sauchiehall Street to its south, Cambr ...
area of the city. Since 2000, the UK government has pursued a policy of dispersal of asylum seekers to ease pressure on social housing in the London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
area. The city is also home to some 8,406 (1.42%) Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
.United Kingdom Census 2001
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.
The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for Nationa ...
the population decline has been reversed. The population was static for a time; but due to migration from other parts of Scotland as well as immigration from overseas, the population has begun to grow. The population of the city council area was 593,245 in 2011 and around 2,300,000 people live in the Glasgow travel to work area
A travel to work area or TTWA is a statistical tool used by UK Government agencies and local authorities, especially by the Department for Work and Pensions and Jobcentres, to indicate an area where the population would generally commute to a ...
.life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
of any UK city at 72.9 years. Much was made of this during the 2008 Glasgow East by-election
The 2008 Glasgow East by-election was a by-election for the UK Parliamentary constituency of Glasgow East which was held on 24 July 2008. The election was triggered when, on 30 June 2008, the sitting MP David Marshall stood down due to ill hea ...
. In 2008, a World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
report about health inequalities, revealing that male life expectancy varied from 54 years in Calton to 82 years in nearby Lenzie
Lenzie () is an affluent town by the Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway in the East Dunbartonshire council area of Scotland. It is about north-east of Glasgow city centre and south of Kirkintilloch. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 8,873. ...
, East Dunbartonshire
East Dunbartonshire ( sco, Aest Dunbartanshire; gd, Siorrachd Dhùn Bhreatainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It borders the north of Glasgow and contains many of the affluent areas to the north of the city, including Bea ...
.
Areas and suburbs

City centre
 The city centre is bounded by High Street up to
The city centre is bounded by High Street up to Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
at Castle Street, Glasgow Cross
Glasgow Cross is at the hub of the ancient royal burgh and now city of Glasgow, Scotland, close to its first crossing over the River Clyde. As a major junction in the city centre, its five streets run: north up the High Street to Glasgow Cathed ...
, Saltmarket including Glasgow Green
Glasgow Green is a park in the east end of Glasgow, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde. Established in the 15th century, it is the oldest park in the city. It connects to the south via the St Andrew's Suspension Bridge.
History
I ...
and St Andrew's Square to the east; Clyde Street and Broomielaw (along the River Clyde) to the south; and Charing Cross and Elmbank Street, beyond Blythswood Square to the west. The northern boundary (from east to west) follows Cathedral Street to North Hanover Street and George Square
George Square ( gd, Ceàrnag Sheòrais) is the principal civic square in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of six squares in the city centre, the others being Cathedral Square, St Andrew's Square, St Enoch Square, Royal Exchange S ...
.
Retail and theatre district
 The city centre is based on a grid system of streets on the north bank of the River Clyde. The heart of the city is
The city centre is based on a grid system of streets on the north bank of the River Clyde. The heart of the city is George Square
George Square ( gd, Ceàrnag Sheòrais) is the principal civic square in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of six squares in the city centre, the others being Cathedral Square, St Andrew's Square, St Enoch Square, Royal Exchange S ...
, site of many of Glasgow's public statues and the elaborate Victorian Glasgow City Chambers
The City Chambers or Municipal Buildings in Glasgow, Scotland, has functioned as the headquarters of Glasgow City Council since 1996, and of preceding forms of municipal government in the city since 1889. It is located on the eastern side of the ...
, headquarters of Glasgow City Council. To the south and west are the shopping precincts of Argyle Street, Sauchiehall Street
Sauchiehall Street () is one of the main shopping streets in the city centre of Glasgow, Scotland, along with Buchanan Street and Argyle Street.
Although commonly associated with the city centre, Sauchiehall Street is over in length. At its ...
and Buchanan Street
Buchanan Street is one of the main shopping thoroughfares in Glasgow, the largest city in Scotland. It forms the central stretch of Glasgow's famous shopping district with a generally more upmarket range of shops than the neighbouring streets: ...
, the last featuring more upmarket retailers and winner of the Academy of Urbanism "Great Street Award" 2008. The collection of shops around these streets accumulate to become known as "The Style Mile".
The main shopping areas include Buchanan Street, Buchanan Galleries, linking Buchanan Street and Sauchiehall Street, and the St. Enoch Centre linking Argyle Street and St Enoch Square), with the up-market Princes Square, which specifically features shops such as Ted Baker
Ted Baker is a British high-street clothing retail company known for suits, shirts, and dresses. It was founded in 1988 in Glasgow, Scotland. The company is owned by Authentic Brands Group, after its £211 million acquisition in October 2022. T ...
, Radley and Kurt Geiger. Buchanan Galleries and other city centre locales were chosen as locations for the 2013 film Under the Skin directed by Jonathan Glazer
Jonathan Glazer (born 26 March 1965) is an English film director and screenwriter. Born in London, Glazer began his career in theatre before transitioning into film. Over the course of a career spanning nearly three decades, Glazer's directing ...
. Although the Glasgow scenes were shot with hidden cameras, star Scarlett Johansson
Scarlett Ingrid Johansson (; born November 22, 1984) is an American actress. The world's highest-paid actress in 2018 and 2019, she has featured multiple times on the ''Forbes'' Celebrity 100 list. ''Time'' magazine named her one of the 100 ...
was spotted around town. The Italian Centre in Ingram Street also specialises in designer labels. Glasgow's retail portfolio forms the UK's second largest and most economically important retail sector after Central London.
The city centre is home to most of Glasgow's main cultural venues: the Glasgow Royal Concert Hall
Glasgow Royal Concert Hall is a concert and arts venue located in Glasgow, Scotland. It is owned by Glasgow City Council and operated by Glasgow Life, an agency of Glasgow City Council, which also runs Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket v ...
, Glasgow City Hall
Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket is a concert hall and former market located on Candleriggs, in the Merchant City, Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The City Halls are part of a market complex designed by John Carrick in 1882, but the grand ha ...
, Theatre Royal (performing home of Scottish Opera
Scottish Opera is the national opera company of Scotland, and one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Founded in 1962 and based in Glasgow, it is the largest performing arts organisation in Scotland.
History
Scottish ...
and Scottish Ballet
Scottish Ballet is the national ballet company of Scotland and one of the five leading ballet companies of the United Kingdom, alongside the Royal Ballet, English National Ballet, Birmingham Royal Ballet and Northern Ballet. Founded in 1969, ...
), the Pavilion Theatre, the King's Theatre, Glasgow Film Theatre
The Glasgow Film Theatre (GFT) is an independent cinema in the city centre of Glasgow. GFT is a registered charity. It occupies a purpose-built cinema building, first opened in 1939, and now protected as a category B listed building.
History ...
, Tron Theatre
The Tron Theatre is located in the corner of Trongate and Chisholm Street, in what was formerly the Tron Kirk which had started as the Collegiate Church of Our Lady and St. Anne in the Trongate area of Glasgow, Scotland. The Tron Steeple still ...
, Gallery of Modern Art (GoMA), Mitchell Library and Theatre, the Centre for Contemporary Arts
The Centre for Contemporary Arts (CCA) is an arts centre in Glasgow, Scotland. The year-round programme includes exhibitions, film, music, literature, festivals, spoken word, Gaelic and performances. The Centre commissions new work from artists ...
, McLellan Galleries and the Lighthouse Museum of Architecture. The world's tallest cinema, the eighteen-screen Cineworld
Cineworld Group plc is a British cinema operator headquartered in London, England. It is the world's second-largest cinema chain (after AMC Theatres), with 9,518 screens across 790 sites in 10 countries: Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Irela ...
, is situated on Renfrew Street.
The city centre is also home to four of Glasgow's higher education institutions: the University of Strathclyde
The University of Strathclyde ( gd, Oilthigh Shrath Chluaidh) is a public research university located in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded in 1796 as the Andersonian Institute, it is Glasgow's second-oldest university, having received its royal chart ...
, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland
The Royal Conservatoire of Scotland ( gd, Conservatoire Rìoghail na h-Alba), formerly the Royal Scottish Academy of Music and Drama ( gd, Acadamaidh Rìoghail Ciùil is Dràma na h-Alba) is a conservatoire of dance, drama, music, production, and ...
, Glasgow School of Art
The Glasgow School of Art (GSA; gd, Sgoil-ealain Ghlaschu) is a higher education art school based in Glasgow, Scotland, offering undergraduate degrees, post-graduate awards (both taught and research-led), and PhDs in architecture, fine art, an ...
and Glasgow Caledonian University
Glasgow Caledonian University ( gd, Oilthigh Chailleannach Ghlaschu, ), informally GCU, Caledonian or Caley, is a public university in Glasgow, Scotland. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of The Queen's College, Glasgow (founded in 1875) and G ...
, and to the largest college in Britain the City of Glasgow College in Cathedral Street.
Merchant City
 This is the commercial and part-residential district of the
This is the commercial and part-residential district of the Merchant City
The Merchant City, a new name introduced through urban renewal by the Scottish Development Agency and the city council in the 1980s is one part of the metropolitan central area of Glasgow. It commences at George Square and goes eastwards reachin ...
, a name coined by the historian Charles Oakley in the 1960s. This had started as a residential district of the wealthy city merchants involved in international trade and the textile industries in the 18th and early 19th centuries, with their warehouses nearby, including the Tobacco Lords
The Tobacco Lords were a group of Scottish merchants and slave traders who in the 18th century made enormous fortunes by trading in tobacco. Many became so wealthy that they adopted the lifestyle of aristocrats, lavishing vast sums on great hous ...
from whom many of the streets take their name. With its mercantile wealth, and continuing growth even before the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, the city expanded by creating the New Town around George Square
George Square ( gd, Ceàrnag Sheòrais) is the principal civic square in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of six squares in the city centre, the others being Cathedral Square, St Andrew's Square, St Enoch Square, Royal Exchange S ...
, soon followed by the New Town of Blythswood on Blythswood Hill
Blythswood Hill, crowned by the elegance of Blythswood Square, is the wealthiest part of central Glasgow, Scotland. It extends from the west edge of Buchanan Street to Gordon Street and Bothwell Street, Charing Cross, Sauchiehall Street ...
which includes Blythswood Square. The original medieval centre around Glasgow Cross and the High Street was left behind.
Glasgow Cross, situated at the junction of High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
, leading up to Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
, Gallowgate, Trongate
Trongate is one of the oldest streets in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. Trongate begins at Glasgow Cross, where the steeple of the old Glasgow Tolbooth is situated, being the original centre of medieval Glasgow, and goes westward changing its n ...
and Saltmarket was the original centre of the city, symbolised by its Mercat cross. Glasgow Cross encompasses the Tolbooth Steeple, all that remains of the original Glasgow Tolbooth
The Glasgow Tolbooth was a municipal structure at Glasgow Cross, Glasgow, Scotland. The main block, which was the meeting place of the Royal Burgh of Glasgow, was demolished in 1921 leaving only the steeple standing. The steeple is a Category A ...
, which was demolished in 1921. Moving northward up High Street towards Rottenrow
The Rottenrow is a street in the Townhead district of Glasgow, Scotland. One of the oldest streets in the city, it was heavily redeveloped in the 20th century and is now enveloped by the University of Strathclyde's John Anderson Campus.
Histor ...
and Townhead
Townhead ( gd, Ceann a' Bhaile, sco, Tounheid) is an area of the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated immediately north-east of Glasgow city centre and contains a residential sector (redeveloped from an older neighbourhood in the mid 20th ...
lies the 15th century Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
and the Provand's Lordship. Due to growing industrial pollution levels in the mid-to-late 19th century, the area fell out of favour with residents.
From the 1980s onwards, the Merchant City has been rejuvenated with luxury city centre flats and warehouse conversion
A loft is a building's upper storey or elevated area in a room directly under the roof (American usage), or just an attic: a storage space under the roof usually accessed by a ladder (primarily British usage). A loft apartment refers to large ...
s. This regeneration has supported an increasing number of cafés and restaurants. The area is also home to a number of high end boutique style shops and some of Glasgow's most upmarket stores.
The Merchant City is one centre of Glasgow's growing "cultural quarter", based on King Street, the Saltmarket and Trongate
Trongate is one of the oldest streets in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. Trongate begins at Glasgow Cross, where the steeple of the old Glasgow Tolbooth is situated, being the original centre of medieval Glasgow, and goes westward changing its n ...
, and at the heart of the annual Merchant City Festival
{{No footnotes, date=September 2011
The Merchant City Festival is a major cultural festival taking place in Glasgow's Merchant City area.
Attracting more than 55,000 people, the four-day Festival presents the cream of Scotland’s theatre, musi ...
. The area has supported a growth in art galleries, the origins of which can be found in the late 1980s when it attracted artist-led organisations that could afford the cheap rents required to operate in vacant manufacturing or retail spaces.[ and the recent development of Trongate 103, which houses galleries, workshops, artist studios and production spaces, is considered a major outcome of the continued partnership between both. The area also contains a number of theatres and concert venues, including the ]Tron Theatre
The Tron Theatre is located in the corner of Trongate and Chisholm Street, in what was formerly the Tron Kirk which had started as the Collegiate Church of Our Lady and St. Anne in the Trongate area of Glasgow, Scotland. The Tron Steeple still ...
, the Old Fruitmarket, the Trades Hall, St. Andrew's in the Square, Merchant Square, and the City Halls
Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket is a concert hall and former market located on Candleriggs, in the Merchant City, Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The City Halls are part of a market complex designed by John Carrick in 1882, but the grand ha ...
.
International Financial Services District
 To the western edge of the city centre, occupying the areas of
To the western edge of the city centre, occupying the areas of Blythswood Hill
Blythswood Hill, crowned by the elegance of Blythswood Square, is the wealthiest part of central Glasgow, Scotland. It extends from the west edge of Buchanan Street to Gordon Street and Bothwell Street, Charing Cross, Sauchiehall Street ...
and Anderston
Anderston ( sco, Anderstoun, gd, Baile Aindrea) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland. It is on the north bank of the River Clyde and forms the south western edge of the city centre. Established as a village of handloom weavers in the early 18th cent ...
, lies Glasgow's financial district, known officially as the International Financial Services District
The International Financial Services District (IFSD) (Scottish Gaelic: ''Sgìre Seirbheisean Ionmhais Eadar-nàiseanta'') is a public-private financial district in Glasgow, Scotland. Based at Scottish Enterprise, the £1 billion venture aims ...
(IFSD), although often irreverently nicknamed by the contemporary press as the "square kilometre" or "Wall Street on Clyde". Since the late 1980s the construction of many modern office blocks and high rise developments have paved the way for the IFSD to become one of the UK's largest financial quarters. With a reputation as an established financial services centre, coupled with comprehensive support services, Glasgow continues to attract and grow new business.
Of the 10 largest general insurance companies in the UK, 8 have a base or head office in Glasgow – including Direct Line
Direct Line is an insurance company based in Bromley, England. Founded in 1985, as the country's first direct car insurance company, it has since expanded to offer a range of general insurance products. Its policies are underwritten by the regul ...
, Esure
Esure Group plc (stylised as ''esure'') is an Internet and telephone based insurance company based in Reigate, Surrey, England. It also has offices in Manchester and Glasgow. The company was listed on the London Stock Exchange until it was acquir ...
, AXA and Norwich Union
Norwich Union was the name of insurance company Aviva's British arm before June 2009. It was originally established in 1797. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
On 29 April 2008, Aviva ...
. Key banking sector companies have also moved some of their services to commercial property in Glasgow – Resolution, JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered in New York City and incorporated in Delaware. As of 2022, JPMorgan Chase is the largest bank in the United States, the ...
, Barclays Wealth
Barclays Wealth Management serves affluent and high net worth clients through offices across the UK, offering personalised banking, credit, investment management and wealth planning services.
Reported client assets were £202.8 billion (as ...
, Tesco Personal Finance, Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is an American multinational investment management and financial services company headquartered at 1585 Broadway in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. With offices in more than 41 countries and more than 75,000 employees, the fir ...
, Lloyds Banking Group
Lloyds Banking Group is a British financial institution formed through the acquisition of HBOS by Lloyds TSB in 2009. It is one of the UK's largest financial services organisations, with 30 million customers and 65,000 employees. Lloyds Ban ...
, Clydesdale Bank
Clydesdale Bank ( gd, Banca Dhail Chluaidh) is a trading name used by Clydesdale Bank plc for its retail banking operations in Scotland.
In June 2018, it was announced that Clydesdale Bank's holding company CYBG would acquire Virgin Money for ...
, BNP Paribas, HSBC, Santander and the Royal Bank of Scotland. The Ministry of Defence have several departments and Clydeport, the Glasgow Stock Exchange
The Glasgow Stock Exchange is a prominent building and former financial institution in the centre of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
The exchange was founded in 1844. In 1973, it merged with the London Stock Exchange. the building is occupied b ...
, Student Loans Company
The Student Loans Company (SLC) is an executive non-departmental public body company in the United Kingdom that provides student loans. It is owned by the UK Government's Department for Education (85%), the Scottish Government (5%), the Welsh ...
, Scottish Executive Enterprise, Transport and Lifelong Learning Department, BT Group
BT Group plc ( trading as BT and formerly British Telecom) is a British multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered in London, England. It has operations in around 180 countries and is the largest provider of fixed-line, bro ...
, Scottish Friendly. Scottish Qualifications Authority and Scottish Enterprise
Scottish Enterprise is a non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government which encourages economic development, enterprise, innovation and investment in business. The body covers the eastern and central parts of Scotland whilst similar ...
also have their headquarters in the district. Royal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
also have one of their six worldwide Shared Business Centres located in the IFSD. Hilton have a corporate office based in the area.
West End
 Glasgow's West End grew firstly to and around Blythswood Square and
Glasgow's West End grew firstly to and around Blythswood Square and Garnethill
Garnethill is a predominantly residential area of the city of Glasgow, Scotland with a number of important public buildings.
Geography
Located in the city centre, the area borders Cowcaddens to its north, Sauchiehall Street to its south, Cambr ...
, extending then to Woodlands Hill and Great Western Road. It is a district of elegant townhouses and tenements with cafés, tea rooms, bars, boutiques, upmarket hotels, clubs and restaurants in the hinterland of Kelvingrove Park
Kelvingrove Park is a public park located on the River Kelvin in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland, containing the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum.
History
Kelvingrove Park was originally created as the West End Park in 1852, and ...
, the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
, Glasgow Botanic Gardens
Glasgow Botanic Gardens is a botanical garden located in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland. It features several glasshouses, the most notable of which is the Kibble Palace.
The Gardens has a wide variety of temperate and tropical flora, a ...
and the , focused especially on the area's main thoroughfares of Argyle Street (Finnieston
Finnieston is an area of Glasgow, Scotland, situated on the north bank of the River Clyde roughly between the city's West End and the city centre.
Finnieston is home to the SECC and SSE Hydro, where many musical concerts, sporting events a ...
), Great Western Road and Byres Road
Byres Road is a street in Hillhead, Glasgow, Scotland. It is the central artery of the city's West End.
Location and history
Byres Road is a mixed commercial, shopping and upmarket residential area consisting largely of traditional sandstone ...
. The area is popular with tourists and students.
The West End includes residential areas of Hillhead
Hillhead ( sco, Hullheid, gd, Ceann a' Chnuic) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland. Situated north of Kelvingrove Park and to the south of the River Kelvin, Hillhead is at the heart of Glasgow's fashionable West End, with Byres Road forming th ...
, Dowanhill, Kelvingrove, Kelvinside, Hyndland
Hyndland is a residential area in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
Description
Bordering Broomhill, Dowanhill, Kelvinside and Partickhill, it is an upper-middle-class neighbourhood populated mainly by professionals (many emp ...
, Broomhill, Scotstoun, Jordanhill
Jordanhill ( sco, Jordanhull, gd, Cnoc Iòrdain)
, Kelvindale
Kelvindale ( gd, Dail Chealbhainn) is a district in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland. Kelvindale shares the G12 postcode with the neighbouring residential districts of Kelvinside, Hillhead, Hyndland, Dowanhill, as well as Gartnave ...
, Anniesland
Anniesland ( gd, Fearann Anna) is a district in the West End of the Scottish city Glasgow. It is situated north of the River Clyde, and centres on the major road junction of the Great Western Road (A82) and Crow Road/Bearsden Road (A739), kno ...
and Partick
Partick ( sco, Pairtick, Scottish Gaelic: ''Partaig'') is an area of Glasgow on the north bank of the River Clyde, just across from Govan. To the west lies Whiteinch, to the east Yorkhill and Kelvingrove Park (across the River Kelvin), and ...
. The name is also increasingly being used to refer to any area to the west of Charing Cross. The West End is bisected by the River Kelvin
The River Kelvin (Scottish Gaelic: ''Abhainn Cheilbhinn'') is a tributary of the River Clyde in northern and northeastern Glasgow, Scotland. It rises on the moor south east of the village of Banton, east of Kilsyth. At almost long, it init ...
, which flows from the Campsie Fells
The Campsie Fells (also known as the Campsies; Scottish Gaelic: ''Monadh Chamaisidh'') are a range of hills in central Scotland, stretching east to west from Denny Muir to Dumgoyne in Stirlingshire and overlooking Strathkelvin to the south. Th ...
in the north and confluences with the River Clyde at Yorkhill Quay.
The spire of Sir George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started ...
's Glasgow University
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
main building (the second largest Gothic Revival building in Great Britain) is a major landmark, and can be seen from miles around, sitting atop Gilmorehill. The university itself is the fourth oldest in the English-speaking world
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest langua ...
. Much of the city's student population is based in the West End, adding to its cultural vibrancy.
The area is also home to the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, h ...
, Hunterian Museum and Art Gallery
The Hunterian is a complex of museums located in and operated by the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest museum in Scotland. It covers the Hunterian Museum, the Hunterian Art Gallery, the Mackintosh House, the Zoology M ...
, Kelvin Hall museums and research facilities, stores, and community sport. Adjacent to the Kelvin Hall was the Museum of Transport, which reopened in 2010 after moving to a new location on a former dockland site at Glasgow Harbour
Glasgow Harbour is an urban regeneration scheme at Partick in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
Construction
After many years of dereliction caused by the decline of shipbuilding and the migration of Glasgow's docks to the Firth o ...
where the River Kelvin flows into the Clyde. The new building is built to a design by Zaha Hadid
Dame Zaha Mohammad Hadid ( ar, زها حديد ''Zahā Ḥadīd''; 31 October 1950 – 31 March 2016) was an Iraqi-British architect, artist and designer, recognised as a major figure in architecture of the late 20th and early 21st centu ...
. The West End Festival
The West End Festival is an annual festival in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The West End Festival in Glasgow was started in 1996 by Michael Dale as a small local festival centred on Byres Road.
It has since become the biggest ...
, one of Glasgow's largest festivals, is held annually in June.
Glasgow is the home of the SECC, Great Britain's largest exhibition and conference centre. On 30 September 2013, a major expansion of the SECC facilities at the former Queen's Dock by Foster and Partners
Foster + Partners is a British architectural, engineering, and integrated design practice founded in 1967 as Foster Associates by Norman Foster. It is the largest architectural firm in the UK with over 1,500 employees in 13 studios worldwide ...
officially opened – the 13,000-seat Hydro
Hydro from Ancient Greek word ὕδωρ (húdōr), meaning ''water''.
Hydro may also refer to:
Energy technologies
* Water-derived power or energy:
** Hydropower, derived from water
** Hydroelectricity, in electrical form
* "Hydro", AC mains ...
arena. Adjacent to the SECC at Queen's Dock is the Clydeside distillery, a Scotch whisky distillery that opened in 2017 in the former dock pump house.
East End
 The East End extends from
The East End extends from Glasgow Cross
Glasgow Cross is at the hub of the ancient royal burgh and now city of Glasgow, Scotland, close to its first crossing over the River Clyde. As a major junction in the city centre, its five streets run: north up the High Street to Glasgow Cathed ...
in the City Centre to the boundary with North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South Lanarkshire. It is home to the Glasgow Barrowland market
The Barras is a major street and indoor weekend market in the East End of Glasgow, Scotland. The term "Barra" is Glaswegian dialect for "barrow" relating to the market's early years where traders sold their wares from handcarts. Barrowland is s ...
, popularly known as "The Barras", Barrowland Ballroom, Glasgow Green
Glasgow Green is a park in the east end of Glasgow, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde. Established in the 15th century, it is the oldest park in the city. It connects to the south via the St Andrew's Suspension Bridge.
History
I ...
, and Celtic Park
Celtic Park is the home stadium of Celtic Football Club, in the Parkhead area of Glasgow, Scotland. With a capacity of 60,832, it is the largest football stadium in Scotland, and the eighth-largest stadium in the United Kingdom. It is al ...
, home of Celtic FC
The Celtic Football Club, commonly known as Celtic (), is a Scottish professional football club based in Glasgow, which plays in the Scottish Premiership. The club was founded in 1887 with the purpose of alleviating poverty in the immigran ...
. Many of the original sandstone tenements remain in this district. The East End was once a major industrial centre, home to Sir William Arrol & Co., James Templeton & Co and William Beardmore and Company
William Beardmore and Company was a British engineering and shipbuilding conglomerate based in Glasgow and the surrounding Clydeside area. It was active from 1886 to the mid-1930s and at its peak employed about 40,000 people. It was founded and ...
. A notable local employer continues to be the Wellpark Brewery, home of Tennent's Lager.
The Glasgow Necropolis
The Glasgow Necropolis is a Victorian cemetery in Glasgow, Scotland. It is on a low but very prominent hill to the east of Glasgow Cathedral (St. Mungo's Cathedral). Fifty thousand individuals have been buried here. Typical for the period, only ...
Garden Cemetery was created by the Merchants House on a hill above the cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
in 1831. Routes curve through the landscape uphill to the statue of John Knox at the summit. There are two late 18th century tenements in Gallowgate. Dating from 1771 and 1780, both have been well restored. The construction of Charlotte Street was financed by David Dale
David Dale (6 January 1739–7 March 1806) was a leading Scottish industrialist, merchant and philanthropist during the Scottish Enlightenment period at the end of the 18th century. He was a successful entrepreneur in a number of areas, m ...
, whose former scale can be gauged by the one remaining house, now run by the National Trust for Scotland
The National Trust for Scotland for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, commonly known as the National Trust for Scotland ( gd, Urras Nàiseanta na h-Alba), is a Scottish conservation organisation. It is the largest membership organi ...
. Further along Charlotte Street there stands a modern Gillespie, Kidd & Coia
Gillespie, Kidd & Coia was a Scottish architectural firm famous for their application of modernism in churches and universities, as well as at St Peter's Seminary in Cardross. Though founded in 1927, they are best known for their work in the ...
building of some note. Once a school, it has been converted into offices. Surrounding these buildings are a series of innovative housing developments conceived as "Homes for the Future", part of a project during the city's year as UK City of Architecture and Design in 1999.
East of Glasgow Cross is St Andrew's in the Square, the oldest post-Reformation church in Scotland, built in 1739–1757 and displaying a Presbyterian grandeur befitting the church of the city's wealthy tobacco merchants. Also close by is the more modest Episcopalian St Andrew's-by-the-Green, the oldest Episcopal church in Scotland. The Episcopalian St Andrew's was also known as the "Whistlin' Kirk" due to it being the first church after the Reformation to own an organ.
 Overlooking Glasgow Green is the façade of Templeton On The Green, featuring vibrant
Overlooking Glasgow Green is the façade of Templeton On The Green, featuring vibrant polychromatic
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors.
Ancient Egypt
Colossal statu ...
brickwork intended to evoke the Doge's Palace in Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
.baronial
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knigh ...
mansion was built in 1848 by David Bryce
David Bryce FRSE FRIBA RSA (3 April 1803 – 7 May 1876) was a Scottish architect.
Life
Bryce was born at 5 South College Street in Edinburgh, the son of David Bryce (1763–1816) a grocer with a successful side interest in buildi ...
, which later housed the city's Children's Museum until the 1980s. Today, the mansion is a sheltered housing complex.
The new Scottish National Indoor Sports Arena, a modern replacement for the Kelvin Hall, is in Dalmarnock
Dalmarnock (, gd, Dail Mheàrnaig) is a district in the Scottish city of Glasgow. It is situated east of the city centre, directly north of the River Clyde opposite the town of Rutherglen. It is also bounded by the Glasgow neighbourhoods of P ...
. The area was the site of the Athletes' Village for the 2014 Commonwealth Games, located adjacent to the new indoor sports arena.
The ''East End Healthy Living Centre'' (EEHLC) was established in mid-2005 at Crownpoint Road with Lottery Funding and City grants to serve community needs in the area. Now called the ''Glasgow Club Crownpoint Sports Complex'', the centre provides service such as sports facilities, health advice, stress management, leisure and vocational classes. To the north of the East End lie the two large gasometers of Provan Gas Works
Provan Gas Works is an industrial gas holding plant in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. The plant lies between the Blackhill, Glasgow, Blackhill, Blochairn, Germiston, Glasgow, Germiston and Provanmill areas of the city, and was built by Glasgow Cor ...
, which stand overlooking Alexandra Park and a major interchange between the M8 and M80 motorways.
South Side
 Glasgow's South Side sprawls out south of the Clyde. The adjoining urban area includes some of Greater Glasgow's most affluent suburban towns, such as
Glasgow's South Side sprawls out south of the Clyde. The adjoining urban area includes some of Greater Glasgow's most affluent suburban towns, such as Newton Mearns
Newton Mearns ( sco, The Mearns; gd, Baile Ùr na Maoirne ) is a suburban town and the largest settlement in East Renfrewshire, Scotland. It lies southwest of Glasgow City Centre on the main road to Ayrshire, above sea level. It has a popu ...
, Clarkston, and Giffnock
Giffnock (; sco, Giffnock; gd, Giofnag, ) is a town and the administrative centre of East Renfrewshire in the Central Lowlands of Scotland.
It lies east of Barrhead, east-southeast of Paisley and northwest of East Kilbride, at the south ...
, all of which are in East Renfrewshire
East Renfrewshire ( sco, Aest Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù an Ear) is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. Until 1975, it formed part of the county of Renfrewshire for local government purposes along with the modern council areas ...
, as well as Thorntonhall
Thorntonhall ( sco, Thorntounhauch, gd, Dail Bhaile Dhealgaiche) is an affluent village in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, lying around to the south of Glasgow, and around west of East Kilbride. The village lies just east of the boundary of East ...
in South Lanarkshire. Newlands and Dumbreck are examples of high-value residential districts within the city boundaries. There are many areas containing a high concentration of sandstone tenements like Shawlands
Shawlands ( gd, Fearann na Doire) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland, located around south of the River Clyde. The area, considered the "Heart of the Southside", is known for its independent restaurants and cafés, art scene, public parks, period ...
, which is considered the "Heart of the Southside", with other examples being Battlefield
A battlefield, battleground, or field of battle is the location of a present or historic battle involving ground warfare. It is commonly understood to be limited to the point of contact between opposing forces, though battles may involve troops ...
, Govanhill
Govanhill ( gd, Cnoc a' Ghobhainn) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland, situated south of the River Clyde between Pollokshields, the Gorbals, Strathbungo, Crosshill, Glasgow, Crosshill, Polmadie and Queen's Park, Glasgow, Queen's Park. Shires of Sco ...
and Mount Florida
Mount Florida ( gd, Cnoc Florida) is an area in the south-east of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
Origins
The Glasgow district of Mount Florida originated on the "Lands of Mount Floridon", which were described in detail when offered for sale a ...
. The large suburb of Pollokshields
Pollokshields ( gd, Buthan Phollaig, Scots: ''Powkshiels'') is an area in the Southside of Glasgow, Scotland. Its modern boundaries are largely man-made, being formed by the M77 motorway to the west and northwest with the open land of Pollok ...
comprises both a quiet western part with undulating tree-lined boulevards lined with expensive villas, and a busier eastern part with a high-density grid of tenements and small shops. The south side also includes some post-war housing estates of various sizes such as Toryglen, Pollok
Pollok ( gd, Pollag, lit=a pool, sco, Powk) is a large housing estate on the south-western side of the city of Glasgow, Scotland. The estate was built either side of World War II to house families from the overcrowded inner city. Housing 30,0 ...
, Castlemilk
Castlemilk ( gd, Caisteal Mheilc) is a district of Glasgow, Scotland. It lies to the far south of the city centre, adjacent to the Croftfoot and Simshill residential areas within the city to the north-west, the town of Rutherglen - neighbourho ...
and Arden. The towns of Cambuslang and Rutherglen
Rutherglen (, sco, Ruglen, gd, An Ruadh-Ghleann) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, immediately south-east of the city of Glasgow, from its centre and directly south of the River Clyde. Having existed as a Lanarkshire burgh in its own ...
were included in the City of Glasgow district from 1975 to 1996, but are now in the South Lanarkshire council area.
Although predominantly residential, the area does have several notable public buildings including, Charles Rennie Mackintosh
Charles Rennie Mackintosh (7 June 1868 – 10 December 1928) was a Scottish architect, designer, water colourist and artist. His artistic approach had much in common with European Symbolism. His work, alongside that of his wife Margaret Macdo ...
's Scotland Street School Museum and House for an Art Lover; the Burrell Collection
The Burrell Collection is a museum in Glasgow, Scotland, managed by Glasgow Museums. It houses the art collection of Sir William Burrell and Constance, Lady Burrell. The museum reopened on 29 March 2022 with free entry, having been closed for ...
in Pollok Country Park
Pollok Country Park is a country park located between Shawlands, Crossmyloof, and Pollok in Glasgow, Scotland. In 2007, Pollok Country Park was named Britain's Best Park, and in 2008 it was named the Best Park in Europe, beating competition fr ...
; Alexander "Greek" Thomson
Alexander "Greek" Thomson (9 April 1817 – 22 March 1875) was an eminent Scottish architect and architectural theorist who was a pioneer in sustainable building. Although his work was published in the architectural press of his day, it was l ...
's Holmwood House
Holmwood House is the finest and most elaborate residential villa designed by the Scottish architect Alexander "Greek" Thomson. It is also rare in retaining much of its original interior decor, and being open to the public. A Category A listed ...
villa; the National Football Stadium Hampden Park in Mount Florida
Mount Florida ( gd, Cnoc Florida) is an area in the south-east of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
Origins
The Glasgow district of Mount Florida originated on the "Lands of Mount Floridon", which were described in detail when offered for sale a ...
(home of Queens Park FC) and Ibrox Stadium
Ibrox Stadium is a Soccer-specific stadium, football stadium on the south side of the River Clyde in the Ibrox, Glasgow, Ibrox area of Glasgow, Scotland. The home of Rangers F.C., Rangers Football Club, Ibrox is the third largest List of foot ...
(home of Rangers FC
Rangers Football Club is a Scottish professional football club based in the Govan district of Glasgow which plays in the Scottish Premiership. Although not its official name, it is often referred to as Glasgow Rangers outside Scotland. The fou ...
).
The former docklands site at Pacific Quay
Pacific Quay is an area south of the River Clyde in Glasgow, Scotland. It is located at the former Plantation Quay and Princes' Dock Basin. The Princes' Dock Basin was the largest on the River Clyde when it was opened by the Clyde Navigation T ...
on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite the SECC, is the site of the Glasgow Science Centre
Glasgow Science Centre is a visitor attraction located in the Clyde Waterfront Regeneration area on the south bank of the River Clyde in Glasgow, Scotland. Queen Elizabeth II opened Glasgow Science Centre on 5 July 2001. It is one of Scotland's ...
and the headquarters of BBC Scotland and STV Group
STV Group plc (formerly known as Scottish Television plc, Scottish Media Group plc and SMG plc) is a media company based in Glasgow, Scotland. Beginning as a television broadcaster in 1957, the company expanded into newspapers, advertising and r ...
(owner of STV), in a new purpose built digital media campus.
In addition, several new bridges spanning the River Clyde have been built, including the Clyde Arc
The Clyde Arc (known locally as the Squinty Bridge) is a road bridge spanning the River Clyde in Glasgow, Scotland, connecting Finnieston near the Clyde Auditorium and SEC with Pacific Quay and Glasgow Science Centre in Govan. Prominent feat ...
known by locals as the Squinty Bridge at Pacific Quay
Pacific Quay is an area south of the River Clyde in Glasgow, Scotland. It is located at the former Plantation Quay and Princes' Dock Basin. The Princes' Dock Basin was the largest on the River Clyde when it was opened by the Clyde Navigation T ...
and others at Tradeston
Tradeston () is a small district in the Scottish city of Glasgow adjacent to the city centre on the south bank of the River Clyde.
Geography
Tradeston is bounded by the River Clyde to the north, the Glasgow to Paisley railway line to the so ...
and Springfield Quay.
The South Side also includes many public parks, including Linn Park, Queen's Park, and Bellahouston Park and several golf clubs, including the championship course at Haggs Castle. The South Side is also home to the large Pollok Country Park
Pollok Country Park is a country park located between Shawlands, Crossmyloof, and Pollok in Glasgow, Scotland. In 2007, Pollok Country Park was named Britain's Best Park, and in 2008 it was named the Best Park in Europe, beating competition fr ...
, which was awarded the accolade of Europe's Best Park 2008. The southside also directly borders Rouken Glen Park in neighbouring Giffnock
Giffnock (; sco, Giffnock; gd, Giofnag, ) is a town and the administrative centre of East Renfrewshire in the Central Lowlands of Scotland.
It lies east of Barrhead, east-southeast of Paisley and northwest of East Kilbride, at the south ...
. Pollok Park is Glasgow's largest park and until the early 2000s was the only country park in the city's boundary. In the early 2000s the Dams to Darnley Country Park
Dams to Darnley Country Park is a 1350 acre country park in East Renfrewshire and Glasgow, in Scotland comprising the historic greenspace between the towns of Barrhead and Newton Mearns in East Renfrewshire, and the areas of Darnley, Parkhouse, Gl ...
was designated, although half of the park is in East Renfrewshire
East Renfrewshire ( sco, Aest Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù an Ear) is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. Until 1975, it formed part of the county of Renfrewshire for local government purposes along with the modern council areas ...
. As of 2021 the facilities at the still new park are quite lacking.
Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south ba ...
is a district and former burgh in the south-western part of the city. It is situated on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite Partick
Partick ( sco, Pairtick, Scottish Gaelic: ''Partaig'') is an area of Glasgow on the north bank of the River Clyde, just across from Govan. To the west lies Whiteinch, to the east Yorkhill and Kelvingrove Park (across the River Kelvin), and ...
. It was an administratively independent Police Burgh from 1864 until it was incorporated into the expanding city of Glasgow in 1912. Govan has a legacy as an engineering and shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befo ...
centre of international repute and is home to one of two BAE Systems Surface Ships shipyards on the River Clyde and the precision engineering
Precision engineering is a subdiscipline of electrical engineering, software engineering, electronics engineering, mechanical engineering, and optical engineering concerned with designing machines, fixtures, and other structures that have exce ...
firm, Thales Optronics
Thales Optronics is a optronics manufacturer and a division of the French defence corporation Thales Group. It is headquartered in Paris. The company has three main subsidiaries: Thales Optronique SA in France, Thales Optronics Limited in the Uni ...
. It is also home to the Queen Elizabeth University Hospital
The Queen Elizabeth University Hospital (QEUH) is a 1,677-bed acute hospital located in Govan, in the south-west of Glasgow, Scotland. The hospital is built on the site of the former Southern General Hospital and opened at the end of April 2015. ...
, one of the largest hospitals in the country, and the maintenance depot for the Glasgow Subway system. The wider Govan area includes the districts of Ibrox, Cessnock, Kinning Park
Kinning Park is a southern suburb of Glasgow, Scotland. It was formerly a separate police burgh between 1871 and 1905 before being absorbed by the city. In 1897, it had a population of 14,326.Govan Parish School Board, ''The Members' Year Book ...
and Kingston.
North Glasgow
 North Glasgow extends out from the north of the city centre towards the affluent suburbs of Bearsden,
North Glasgow extends out from the north of the city centre towards the affluent suburbs of Bearsden, Milngavie
Milngavie ( ; gd, Muileann-Ghaidh) is a town in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland and a suburb of Glasgow. It is on the Allander Water, at the northwestern edge of Greater Glasgow, and about from Glasgow city centre. It neighbours Bearsden. Mi ...
and Bishopbriggs
Bishopbriggs ( sco, The Briggs; gd, Achadh an Easbaig) is a town in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It lies on the northern fringe of Greater Glasgow, approximately from the city centre. Historically in Lanarkshire, the area was once part of ...
in East Dunbartonshire
East Dunbartonshire ( sco, Aest Dunbartanshire; gd, Siorrachd Dhùn Bhreatainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It borders the north of Glasgow and contains many of the affluent areas to the north of the city, including Bea ...
and Clydebank in West Dunbartonshire
West Dunbartonshire ( sco, Wast Dunbairtonshire; gd, Siorrachd Dhùn Breatann an Iar, ) is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland. The area lies to the west of the City of Glasgow and contains many of Glasgow's commuter to ...
. The area also contains some of the city's poorest residential areas.
This has led to large-scale redevelopment of much of the poorer housing stock in north Glasgow, and the wider regeneration of many areas, such as Ruchill
Ruchill () is a district in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It lies within the Canal Ward of north Glasgow in the Ruchill Community Council area between the Maryhill and Possilpark areas of the city. It has traditionally been characterised by ...
, which have been transformed; many run-down tenements have now been refurbished or replaced by modern housing estate
A housing estate (or sometimes housing complex or housing development) is a group of homes and other buildings built together as a single development. The exact form may vary from country to country.
Popular throughout the United States ...
s. Much of the housing stock in north Glasgow is rented social housing
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is usually owned by a government authority, either central or local. Although the common goal of public housing is to provide affordable housing, the details, terminology, d ...
, with a high proportion of high-rise tower blocks, managed by the North Glasgow Housing Association trading as NG Homes and Glasgow Housing Association
Wheatley Homes Glasgow (formerly Glasgow Housing Association or GHA) is the largest social landlord in Scotland with 40,000 homes across Glasgow. Wheatley Homes Glasgow is a not-for-profit company created in 2003 by the then Scottish Executive fo ...
.
Maryhill
Maryhill ( gd, Cnoc Màiri) is an area of the City of Glasgow in Scotland. Maryhill is a former burgh. Maryhill stretches over along Maryhill Road.
The far north west of the area is served by Maryhill railway station.
History
Hew Hill, ...
consists of well maintained traditional sandstone tenements. Although historically a working class area, its borders with the upmarket West End of the city mean that it is relatively wealthy compared to the rest of the north of the city, containing affluent areas such as Maryhill Park and North Kelvinside
North Kelvinside (also referred to as North Kelvin, gd, Cealbhainn a Tuath) is a residential district of the Scottish city of Glasgow.
It is usually regarded as a subdistrict of Maryhill, sharing its G20 postcode, as well as its House of Commo ...
. Maryhill is also the location of Firhill Stadium
Firhill Stadium is a football and former rugby union, rugby league and greyhound racing stadium located in the Maryhill area of Glasgow, Scotland which has been the home of Partick Thistle since 1909. The stadium is commonly referred to as simp ...
, home of Partick Thistle F.C.
Partick Thistle Football Club are a professional football club from Glasgow, Scotland. Despite their name, the club are based at Firhill Stadium in the Maryhill area of the city, and have not played in Partick since 1908. The club have been mem ...
since 1909. The junior
Junior or Juniors may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Junior'' (Junior Mance album), 1959
* ''Junior'' (Röyksopp album), 2009
* ''Junior'' (Kaki King album), 2010
* ''Junior'' (LaFontaines album), 2019
Films
* ''Junior'' (1994 ...
team, Maryhill F.C.
Maryhill Football Club are an association football team based in the Maryhill area of Glasgow, Scotland. The team is a member of the Scottish Junior Football Association, now playing in the West of Scotland Football League Second Division in t ...
are also located in this part of north Glasgow.
The Forth and Clyde Canal
The Forth and Clyde Canal is a canal opened in 1790, crossing central Scotland; it provided a route for the seagoing vessels of the day between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde at the narrowest part of the Scottish Lowlands. This allowe ...
passes through this part of the city, and at one stage formed a vital part of the local economy. It was for many years polluted and largely unused after the decline of heavy industry, but recent efforts to regenerate and re-open the canal to navigation have seen it rejuvenated, including art campuses at Port Dundas.
Sighthill was home to Scotland's largest asylum seeker
An asylum seeker is a person who leaves their country of residence, enters another country and applies for asylum (i.e., international protection) in that other country. An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and m ...
community but the area is now regenerated as part of the Youth Olympic Games bid.
A huge part of the economic life of Glasgow was once located in Springburn
Springburn ( gd, Allt an Fhuairainn) is an inner-city district in the north of the Scottish city of Glasgow, made up of generally working-class households.
Springburn developed from a rural hamlet at the beginning of the 19th century. Its ind ...
, where the Saracen Foundry, engineering works of firms like Charles Tennant
Charles Tennant (3 May 1768 – 1 October 1838) was a Scottish chemist and industrialist. He discovered bleaching powder and founded an industrial dynasty.
Biography
Charles Tennant was born at Laigh Corton, Alloway, Ayrshire, the sixth of thi ...
and locomotive workshops employed many Glaswegians. Indeed, Glasgow dominated this type of manufacturing, with 25% of all the world's locomotives being built in the area at one stage. It was home to the headquarters of the North British Locomotive Company. Today part of the Glasgow Works
Glasgow Works, formerly the St Rollox Works, is a railway rolling stock heavy maintenance and repair works established in the 1850s in the Glasgow district of Springburn by the Caledonian Railway Company, and known locally as 'the Caley'.
Ow ...
continues in use as a railway maintenance facility, all that is left of the industry in Springburn. It is proposed for closure in 2019.
Culture
 The city has many amenities for a wide range of cultural activities, from
The city has many amenities for a wide range of cultural activities, from curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns slidi ...
to opera and ballet and from football to art appreciation; it also has a large selection of museums that include those devoted to transport, religion, and modern art. Many of the city's cultural sites were celebrated in 1990 when Glasgow was designated European Capital of Culture.
The city's principal municipal library, the Mitchell Library
The Mitchell Library is a large public library and centre of the City Council public library system of Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The library, based in the Charing Cross district, was initially established in Ingram Street in 1877 following a ...
, has grown into one of the largest public reference libraries
A library is a collection of Document, materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or electronic media, digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a ...
in Europe, currently housing some 1.3 million books, an extensive collection of newspapers and thousands of photographs and map
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although ...
s.
Of academic libraries, Glasgow University Library started in the 15th century and is one of the oldest and largest libraries in Europe, with unique and distinctive collections of international status.
Most of Scotland's national arts organisations are based in Glasgow, including Scottish Opera
Scottish Opera is the national opera company of Scotland, and one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Founded in 1962 and based in Glasgow, it is the largest performing arts organisation in Scotland.
History
Scottish ...
, Scottish Ballet
Scottish Ballet is the national ballet company of Scotland and one of the five leading ballet companies of the United Kingdom, alongside the Royal Ballet, English National Ballet, Birmingham Royal Ballet and Northern Ballet. Founded in 1969, ...
, National Theatre of Scotland
The National Theatre of Scotland, established in 2006, is the national theatre company of Scotland. The company has no theatre building of its own; instead it tours work to theatres, village halls, schools and site-specific locations, both at h ...
, Royal Scottish National Orchestra
The Royal Scottish National Orchestra (RSNO) ( gd, Orcastra Nàiseanta Rìoghail na h-Alba) is a British orchestra, based in Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Throughout its history, the O ...
, BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra
The BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra (BBC SSO) is a Scottish broadcasting symphony orchestra based in Glasgow. One of five full-time orchestras maintained by the British Broadcasting Corporation ( BBC), it is the oldest full-time professional r ...
and Scottish Youth Theatre.
Glasgow has its own "Poet Laureate
A poet laureate (plural: poets laureate) is a poet officially appointed by a government or conferring institution, typically expected to compose poems for special events and occasions. Albertino Mussato of Padua and Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch ...
", a post created in 1999 for Edwin Morgan and occupied by Liz Lochhead
Liz Lochhead Hon FRSE (born 26 December 1947) is a Scottish poet, playwright, translator and broadcaster. Between 2011 and 2016 she was the Makar, or National Poet of Scotland, and served as Poet Laureate for Glasgow between 2005 and 2011.
E ...
from 2005 until 2011, when she stood down to take up the position of Scots Makar. Jim Carruth was appointed to the position of Poet Laureate for Glasgow in 2014 as part of the 2014 Commonwealth Games legacy.
In 2013, PETA declared Glasgow to be the most vegan-friendly city in the UK.
Recreation
Glasgow is home to a variety of theatres including the King's Theatre, the Theatre Royal and the Citizens Theatre
The Citizens Theatre, in what was the Royal Princess's Theatre, is the creation of James Bridie and is based in Glasgow, Scotland as a principal producing theatre. The theatre includes a 500-seat Main Auditorium, and has also included various ...
and is home to many museums and art galleries, the largest and most famous being the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, h ...
, the Hunterian Museum and Art Gallery
The Hunterian is a complex of museums located in and operated by the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest museum in Scotland. It covers the Hunterian Museum, the Hunterian Art Gallery, the Mackintosh House, the Zoology M ...
, the Gallery of Modern Art (GoMA) and the Burrell Collection
The Burrell Collection is a museum in Glasgow, Scotland, managed by Glasgow Museums. It houses the art collection of Sir William Burrell and Constance, Lady Burrell. The museum reopened on 29 March 2022 with free entry, having been closed for ...
. Most of the museums and galleries in Glasgow are publicly owned and free to enter.
The city has hosted many exhibitions over the years, including The Glasgow Garden Festival in 1988, being the UK City of Architecture 1999, European Capital of Culture 1990, National City of Sport 1995–1999 and European Capital of Sport 2003. Glasgow has also hosted the National Mòd no less than twelve times since 1895.[List of Mod's places]
for each year on Sabhal Mòr Ostaig
Sabhal Mòr Ostaig () (Great Barn of Ostaig) is a public higher education college situated in the Sleat peninsula in the south of the Isle of Skye, with an associate campus at Bowmore on the island of Islay, Ionad Chaluim Chille Ìle (the ...
website
In addition, unlike the older and larger Edinburgh Festival
__NOTOC__
This is a list of arts and cultural festivals regularly taking place in Edinburgh, Scotland.
The city has become known for its festivals since the establishment in 1947 of the Edinburgh International Festival and the Edinburgh Fe ...
(where all Edinburgh's main festivals occur in the last three weeks of August), Glasgow's festivals fill the calendar. Festivals include the Glasgow International Comedy Festival
Glasgow International Comedy Festival is a comedy festival in Glasgow, Scotland. The comedy festival started in 2002 and is held annually in March in venues across the city. The festival is supported financially by Glasgow City Council and sinc ...
, Glasgow International Festival of Visual Art, Glasgow International Jazz Festival
{{coord, 55.861, -4.259, display=title, region:GB_scale:20000
Glasgow International Jazz Festival is a jazz festival in Glasgow, Scotland.
Main Festival
The Glasgow International Jazz Festival is held annually in June in the Merchant City area ...
, Celtic Connections
The Celtic Connections festival started in 1994 in Glasgow, Scotland, and has since been held every January. Featuring over 300 concerts, ceilidhs, talks, free events, late night sessions and workshops, the festival focuses on the roots of tra ...
, Glasgow Fair, Glasgow Film Festival, West End Festival
The West End Festival is an annual festival in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland.
History
The West End Festival in Glasgow was started in 1996 by Michael Dale as a small local festival centred on Byres Road.
It has since become the biggest ...
, Merchant City Festival
{{No footnotes, date=September 2011
The Merchant City Festival is a major cultural festival taking place in Glasgow's Merchant City area.
Attracting more than 55,000 people, the four-day Festival presents the cream of Scotland’s theatre, musi ...
, Glasgay, and the World Pipe Band Championships
The World Pipe Band Championships is a pipe band competition held in Glasgow, Scotland. The World Pipe Band Championships as we currently know them have been staged since 1947 although the Grade 1 Pipe Band Competition winners at the annual Cowal ...
.
Music scene
 The city is home to numerous orchestras, ensembles and bands including those of
The city is home to numerous orchestras, ensembles and bands including those of Scottish Opera
Scottish Opera is the national opera company of Scotland, and one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Founded in 1962 and based in Glasgow, it is the largest performing arts organisation in Scotland.
History
Scottish ...
, Scottish Ballet
Scottish Ballet is the national ballet company of Scotland and one of the five leading ballet companies of the United Kingdom, alongside the Royal Ballet, English National Ballet, Birmingham Royal Ballet and Northern Ballet. Founded in 1969, ...
, Royal Scottish National Orchestra
The Royal Scottish National Orchestra (RSNO) ( gd, Orcastra Nàiseanta Rìoghail na h-Alba) is a British orchestra, based in Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of the five national performing arts companies of Scotland. Throughout its history, the O ...
, BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra
The BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra (BBC SSO) is a Scottish broadcasting symphony orchestra based in Glasgow. One of five full-time orchestras maintained by the British Broadcasting Corporation ( BBC), it is the oldest full-time professional r ...
and related to the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland
The Royal Conservatoire of Scotland ( gd, Conservatoire Rìoghail na h-Alba), formerly the Royal Scottish Academy of Music and Drama ( gd, Acadamaidh Rìoghail Ciùil is Dràma na h-Alba) is a conservatoire of dance, drama, music, production, and ...
, the National Youth Orchestra of Scotland
The National Youth Orchestras of Scotland (NYOS) caters for students aged between 8 and 25, through orchestras, jazz bands, training ensembles and outreach programmes.
In addition to organising residential training courses, rehearsals and nati ...
and the Universities and Colleges. Choirs of all type are well supported.
Glasgow has many live music venues, pubs, and clubs. Some of the city's more well-known venues include the Glasgow Royal Concert Hall
Glasgow Royal Concert Hall is a concert and arts venue located in Glasgow, Scotland. It is owned by Glasgow City Council and operated by Glasgow Life, an agency of Glasgow City Council, which also runs Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket v ...
, The OVO Hydro, the SECC, Glasgow Cathouse, The Art School, King Tut's Wah Wah Hut
King Tut's Wah Wah Hut, also known as King Tut's, is a live music venue and bar on St. Vincent Street, Glasgow, Scotland. It is owned and managed by Glasgow-based gig promoters DF Concerts.
The Glasgow live music venue takes its name from a ...
(where Oasis were spotted and signed by Glaswegian record mogul Alan McGee
Alan John McGee (born 29 September 1960) is a Scottish businessman and music industry executive. He has been a record label owner, musician, manager, and music blogger for ''The Guardian''. He co-founded the independent Creation Records label, r ...
), the Queen Margaret Union
The Queen Margaret Union (QMU) is one of two students' unions at the University of Glasgow, Scotland. Founded in 1890, it caters to the social and cultural needs of its members by providing a range of services including volunteering opportuni ...
(who have Kurt Cobain's footprint locked in a safe), the Barrowland, a ballroom converted into a live music venue as well as The Garage, which is the largest nightclub in Scotland. More recent mid-sized venues include ABC, destroyed in the art school fire of 15 June 2018, and the O2 Academy, which play host to a similar range of acts. There are also a large number of smaller venues and bars, which host many local and touring musicians, including Stereo, 13th Note and Nice N Sleazy. Most recent recipient of the SLTN Music Pub of the Year award was Bar Bloc, awarded in November 2011. In 2010, Glasgow was named the UK's fourth "most musical" city by PRS for Music
PRS for Music Limited (formerly The MCPS-PRS Alliance Limited) is a British music copyright collective, made up of two collection societies: the Mechanical-Copyright Protection Society (MCPS) and the Performing Right Society (PRS). It undertakes ...
.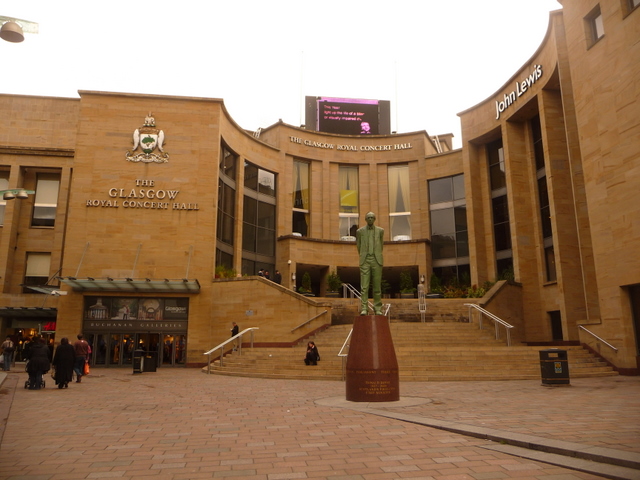 Since the 1980s, the success of bands such as
Since the 1980s, the success of bands such as The Blue Nile
The Blue Nile was a Scottish band which originated in Glasgow. The group's early music was built heavily on synthesizers and electronic instrumentation and percussion, although later works featured guitar more prominently. Following early cham ...
, Gun
A gun is a ranged weapon designed to use a shooting tube (gun barrel) to launch projectiles. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns/cannons, spray guns for painting or pressure washing, p ...
, Simple Minds, Del Amitri, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, Hipsway, Love & Money, Idlewild, Deacon Blue
Deacon Blue are a Scottish pop rock band formed in Glasgow during 1985. The line-up of the band consists of vocalists Ricky Ross and Lorraine McIntosh, keyboard player James Prime and drummer Dougie Vipond. The band released their debut albu ...
, Orange Juice
Orange juice is a liquid extract of the orange tree fruit, produced by squeezing or reaming oranges. It comes in several different varieties, including blood orange, navel oranges, valencia orange, clementine, and tangerine. As well as vari ...
, Lloyd Cole and the Commotions
Lloyd Cole and the Commotions were a British rock/pop band that formed in Glasgow, Scotland in 1982. Between 1984 and 1989, the band scored four Top 20 albums and five Top 40 singles in the UK; it also had success in several other countries in ...
, Teenage Fanclub, Belle and Sebastian, Camera Obscura
A camera obscura (; ) is a darkened room with a small hole or lens at one side through which an image is projected onto a wall or table opposite the hole.
''Camera obscura'' can also refer to analogous constructions such as a box or tent in w ...
, Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
Fr ...
, Mogwai
Mogwai () are a Scottish post-rock band, formed in 1995 in Glasgow. The band consists of Stuart Braithwaite (guitar, vocals), Barry Burns (guitar, piano, synthesizer, vocals), Dominic Aitchison (bass guitar), and Martin Bulloch (drums). Mog ...
, Travis, and Primal Scream has significantly boosted the profile of the Glasgow music scene, prompting ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
'' magazine to liken Glasgow to Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
during its 1960s Motown heyday. More recent successes include The Fratellis
The Fratellis are a Scottish rock band from Glasgow, formed in 2005. The band consists of three unrelated members, who perform under pseudonyms: lead vocalist and guitarist Jon Fratelli, bassist Barry Fratelli, and drummer Mince Fratelli. Thei ...
, Chvrches, Rustie, Vukovi
Vukovi (stylised as VUKOVI) is a Scottish rock band from Kilwinning, North Ayrshire, Scotland. The band released their self-titled debut album ''Vukovi'' on 10 Mar 2017. Their second album titled ''Fall Better'' was released on 24 January 2020. ...
, Glasvegas
Glasvegas are a Scottish indie rock band from Glasgow. The band consists of James Allan (vocals), Rab Allan (lead guitar) and Paul Donoghue (bass guitar), with Swedish drummer Jonna Löfgren joining the group in 2010 until her departure in 2020 ...
and Twin Atlantic
Twin Atlantic are a Scottish alternative rock band from Glasgow, Scotland. The group currently consists of Sam McTrusty (lead vocals, rhythm guitar), Ross McNae (bass) and Joe Lazarus (drums). Lead guitarist Barry McKenna departed from the b ...
. The city of Glasgow was appointed a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
City of Music on 20 August 2008 as part of the Creative Cities Network
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a project of UNESCO launched in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities which recognized creativity as a major factor in their urban development.[Slam
Slam, SLAM or SLAMS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional elements
* S.L.A.M. (Strategic Long-Range Artillery Machine), a fictional weapon in the ''G.I. Joe'' universe
* SLAMS (Space-Land-Air Missile Shield), a fictional anti-ball ...]
, and their record label Soma Quality Recordings
Soma Quality Recordings (or simply Soma Records) is an independent record label based in Glasgow, Scotland. It was co-founded in 1991 by the electronic music duo Slam, Dave Clarke and Glenn Gibbons. The label is known for releasing early works o ...
, with their Pressure club nights attracting DJs and clubbers from around the world, which was previously held at The Arches but following that venue's closure due to claims of unsafe level of drug use has moved to Sub Club.
The MOBO Awards
The MOBO Awards (Music of Black Origin, also known as the MOBOs) are an annual British music award presentation honouring achievements in " music of black origin", including hip hop, grime, UK Drill, R&B, soul, reggae, jazz, gospel, and ...
were held at the SECC on 30 September 2009, making Glasgow the first out-of-London city to host the event since its launch in 1995. On 9 November 2014, Glasgow hosted the 2014 MTV Europe Music Awards
The 2014 MTV EMAs (also known as the MTV Europe Music Awards) were held at The SSE Hydro, Glasgow, Scotland on 9 November 2014. This was the first time since 2003 when the awards were held in Scotland and the fifth time the United Kingdom has h ...
at The OVO Hydro, it was the second time Scotland hosted the show since 2003 in Edinburgh and overall the fifth time that the United Kingdom has hosted the show since 2011 in Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom ...
, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
. The event was hosted by Nicki Minaj
Onika Tanya Maraj-Petty (; born December 8, 1982), known professionally as Nicki Minaj ( ), is a Trinidadian-born rapper based in the United States. She is known for her musical versatility, animated Flow (rapping), flow in her rapping, alter e ...
and featured performances from Ariana Grande, Enrique Iglesias, Ed Sheeran
Edward Christopher Sheeran (; born 17 February 1991) is an English singer-songwriter. Born in Halifax, West Yorkshire and raised in Framlingham, Suffolk, he began writing songs around the age of eleven. In early 2011, Sheeran independently re ...
, U2 and Slash.
Media
 There have been hundreds of films made about Glasgow or in Glasgow.
Both BBC Scotland and STV have their headquarters in Glasgow. Television programs filmed in Glasgow include ''
There have been hundreds of films made about Glasgow or in Glasgow.
Both BBC Scotland and STV have their headquarters in Glasgow. Television programs filmed in Glasgow include ''Rab C. Nesbitt
''Rab C. Nesbitt'' is a Scottish comedy series which began in 1988. Produced by BBC Scotland, it stars Gregor Fisher as an alcoholic Glaswegian who seeks unemployment as a lifestyle choice. Rab C. Nesbitt was originally a recurring character ...
'', ''Taggart
''Taggart'' is a Scottish detective fiction television programme created by Glenn Chandler, who wrote many of the episodes, and made by STV Studios for the ITV network. It originally ran as the miniseries "Killer" from 6 until 20 Septembe ...
'', ''Tutti Frutti
Tutti frutti (from Italian ''tutti i frutti'', "all fruits"; also hyphenated tutti-frutti) is a colorful confectionery containing various chopped and usually candied fruits, or an artificial or natural flavouring simulating the combined flavou ...
'', ''High Times
''High Times'' is an American monthly magazine (and cannabis brand) that advocates the legalization of cannabis as well as other counterculture ideas. The magazine was founded in 1974 by Tom Forcade.Danko, Danny"Norml Founder Retires – Exha ...
'', ''River City
''River City'' is a Scottish television soap opera that was first broadcast on BBC One Scotland on 24 September 2002. ''River City'' follows the lives of the people who live and work in the fictional district of Shieldinch. In November 2017, a s ...
'', '' City Lights'', ''Chewin' the Fat
''Chewin' the Fat'' is a Scottish comedy sketch show, starring Ford Kiernan, Greg Hemphill and Karen Dunbar. Comedians Paul Riley and Mark Cox also appeared regularly on the show among other actors such as Gregor Fisher and Tom Urie.
''Ch ...
'', '' Still Game'', ''Limmy's Show
''Limmy's Show!'' is a Scottish surreal comedy sketch show broadcast on BBC Two Scotland, written, directed and based on the 2006 podcast Limmy's World of Glasgow by Brian "Limmy" Limond, who stars as himself and a variety of characters in a ...
'' and '' Lovesick''. Most recently the long-running series ''Question Time
A question time in a parliament occurs when members of the parliament ask questions of government ministers (including the prime minister), which they are obliged to answer. It usually occurs daily while parliament is sitting, though it can be ca ...
'' and the early evening quiz programme '' Eggheads'' moved its production base to the city. Most National Lottery game shows are also filmed in Glasgow. children's game show '' Copycats'' is filmed there, and the Irish/UK programme ''Mrs. Brown's Boys
''Mrs. Brown's Boys'' is an Irish television sitcom created by and starring Brendan O'Carroll and produced in the United Kingdom by BBC Scotland in partnership with BOC-PIX and Irish broadcaster RTÉ.
The series stars O'Carroll as Agnes ...
'' is filmed at BBC Scotland.
The Scottish press publishes various newspapers in the city such as '' The Evening Times '', '' The Herald'', ''The Sunday Herald
The ''Sunday Herald'' was a Scottish Sunday newspaper, published between 7 February 1999 and 2 September 2018. Originally a broadsheet, it was published in compact format from 20 November 2005. The paper was known for having combined a centre ...
'', the '' Sunday Mail'' and the '' Daily Record''. Scottish editions of Trinity Mirror and News International titles are printed in the city. STV Group
STV Group plc (formerly known as Scottish Television plc, Scottish Media Group plc and SMG plc) is a media company based in Glasgow, Scotland. Beginning as a television broadcaster in 1957, the company expanded into newspapers, advertising and r ...
is a Glasgow-based media conglomerate with interests in television, and publishing advertising. STV Group owns and operates both Scottish ITV franchises (Central Scotland and Grampian), both branded STV. Glasgow also had its own television channel, STV Glasgow, which launched in June 2014, which also shows some of Glasgow's own programs filmed at the STV headquarters in Glasgow. Shows included ''The Riverside Show'', ''Scottish Kitchen'', ''City Safari'', ''Football Show'' and ''Live at Five''. STV Glasgow merged with STV Edinburgh to form STV2 in April 2017 which eventually closed in June 2018.
Various radio stations are also located in Glasgow. BBC Radio Scotland
BBC Radio Scotland is a Scotland, Scottish radio station, radio network owned and operated by BBC Scotland, a division of the BBC. It broadcasts a wide variety of programmes. It replaced the Scottish BBC Radio 4 opt-out service of the same na ...
, the national radio broadcaster for Scotland, is located in the BBC's Glasgow headquarters alongside its Gaelic-language sister station, which is also based in Stornoway. Bauer Radio
Bauer Media Audio UK is a UK-based radio division of the Bauer Media Group.
History
In early 2008, German magazine publisher Bauer bought the radio division of British company Emap, which had been established as East Midland Allied Press in ...
owns the principal commercial radio stations in Glasgow: Clyde 1
Clyde 1 is an Independent Local Radio station based in Glasgow, Scotland, owned and operated by Bauer as part of the Hits Radio network. It broadcasts to Glasgow and West Central Scotland.
As of September 2022, the station has a weekly audi ...
and Clyde 2
Clyde 2 is an Independent Local Radio station based in Glasgow, Scotland, owned and operated by Bauer as part of the Greatest Hits Radio network. It broadcasts to Glasgow and West Central Scotland.
As of September 2022, the station has a wee ...
, which can reach over 2.3 million listeners. In 2004, STV Group plc (then known as SMG plc) sold its 27.8% stake in Scottish Radio Holdings
Scottish Radio Holdings (SRH) was a Scottish media company which owned 22 radio stations, and around 30 local newspapers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
History
SRH had its origins in the 1970s when Glasgow was awarded the third licence for ...
to the broadcasting group EMAP for £90.5 million. Other stations broadcasting from Glasgow include Smooth Scotland
Smooth Scotland is a Scottish independent local radio station owned and operated by Global as part of the Smooth network. The station replaced Saga 105.2 FM in 2007.
As well as being carried on FM in the Glasgow area, the station is also broad ...
, Heart Scotland, which are owned by Global
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
. Global Radio's Central Scotland radio station Capital Scotland
Capital Scotland (formerly known as Beat 106, XFM Scotland, and later Galaxy Scotland) is a regional radio station owned by Communicorp UK and operated by Global. It broadcasts to Scotland's Central Belt, an area surrounding the two citie ...
also broadcast from studios in Glasgow. Nation Radio Scotland, owned by Nation Broadcasting, also broadcasts from the city. The city has a strong community radio
Community radio is a radio service offering a third model of radio broadcasting in addition to commercial and public broadcasting. Community stations serve geographic communities and communities of interest. They broadcast content that is popula ...
sector, including Celtic Music Radio
Celtic Music Radio is a Community Radio station in Scotland, broadcasting to the Greater Glasgow on 95.0 FM, Edinburgh on DAB+ and also worldwide via the internet. Celtic Music Radio is a Scottish Charity, registration number SC041172.
The ...
, Subcity Radio, Radio Magnetic, Sunny Govan Radio, AWAZ FM and Insight Radio.
Religion
Glasgow is a city of significant religious diversity. The Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
are the two largest Christian denominations in the city. There are 147 congregations in the Church of Scotland's Presbytery of Glasgow
The Presbytery of Glasgow is one of the 46 Presbyteries of the Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped ...
(of which 104 are within the city boundaries, the other 43 being in adjacent areas). Within the city boundaries there are 65 parishes of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Glasgow
The Archdiocese of Glasgow ( la, Archidioecesis Glasguensis) is the metropolitan see of the Province of Glasgow in the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland. The episcopal seat of the developing diocese was established by Saint Kentigern in the 6t ...
and four parishes of the Diocese of Motherwell. The city has four Christian cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
s: Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbisho ...
, of the Church of Scotland; St Andrew's Cathedral, of the Roman Catholic Church; St Mary's Cathedral, of the Scottish Episcopal Church
The Scottish Episcopal Church ( gd, Eaglais Easbaigeach na h-Alba; sco, Scots Episcopal(ian) Kirk) is the ecclesiastical province of the Anglican Communion in Scotland.
A continuation of the Church of Scotland as intended by King James VI, and ...
, and St Luke's Cathedral, of the Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
. The Baptist Church and Salvation Army are well represented.
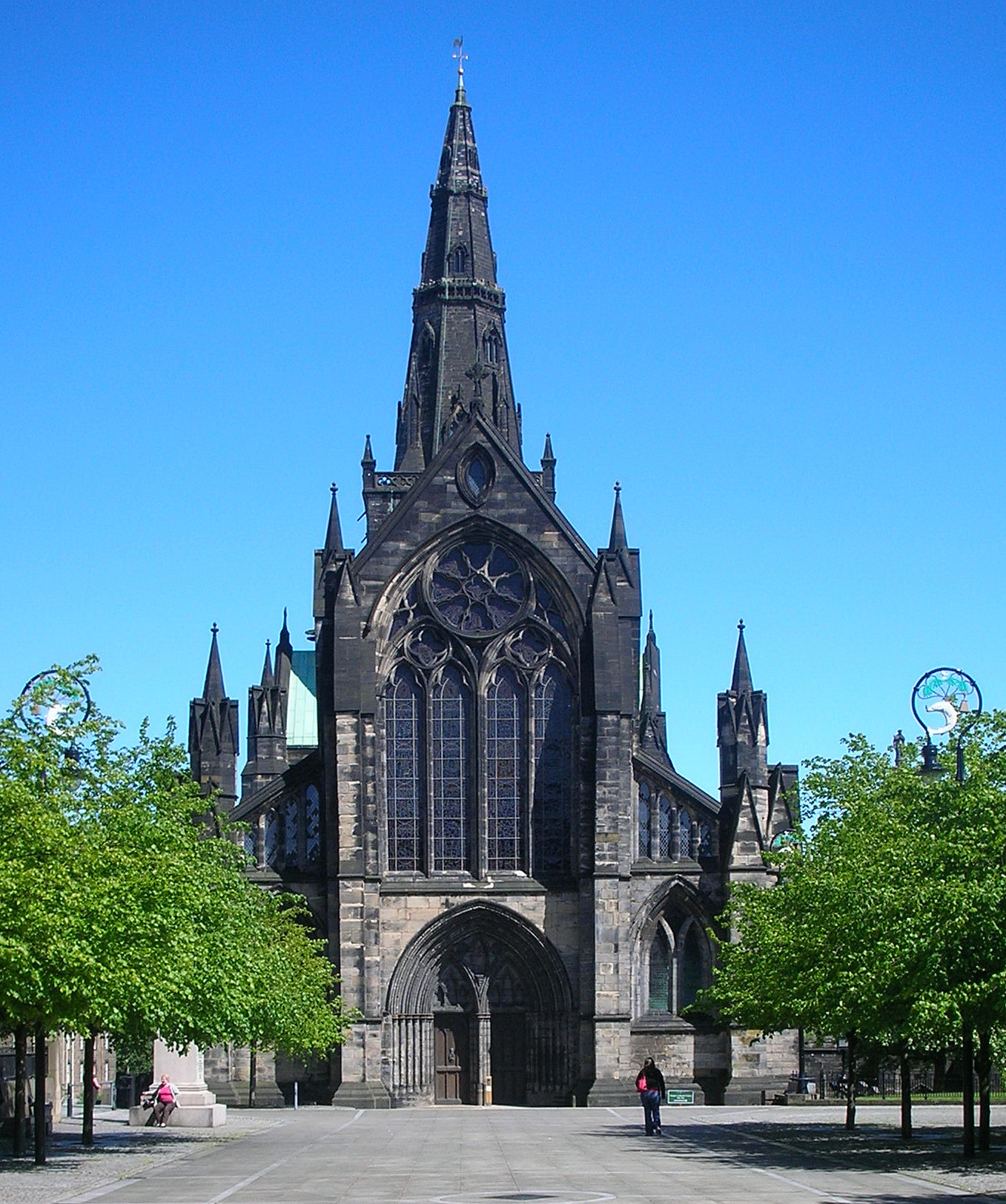 The Protestant churches are the largest in number, including Baptist, Episcopalian, Methodist and Presbyterian. 32% of the population follow the Protestant Church of Scotland whilst 29% following the Roman Catholic Church, according to the 2001 census (Christians overall form 65%). Much of the city's Roman Catholic population are those of Irish ancestry. The divisions between the two denominations and their respective communities play a major part in
The Protestant churches are the largest in number, including Baptist, Episcopalian, Methodist and Presbyterian. 32% of the population follow the Protestant Church of Scotland whilst 29% following the Roman Catholic Church, according to the 2001 census (Christians overall form 65%). Much of the city's Roman Catholic population are those of Irish ancestry. The divisions between the two denominations and their respective communities play a major part in sectarianism in Glasgow
Sectarianism in Glasgow takes the form of long-standing religious and political sectarian rivalry between Catholics and Protestants. It is particularly reinforced by the fierce rivalry between Celtic F.C. and Rangers F.C., the two largest Scott ...
, in a similar nature to that of Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, although not segregated territorially as in Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom ...
.
Biblical unitarians are represented by three Christadelphian
The Christadelphians () or Christadelphianism are a restorationist and millenarian Christian group who hold a view of biblical unitarianism. There are approximately 50,000 Christadelphians in around 120 countries. The movement developed in the ...
ecclesias, referred to geographically, as "South", "Central" and "Kelvin".
The Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
community is served by four Gurdwaras
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) ( Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all fai ...
. Two are situated in the West End (''Central Gurdwara Singh Sabha'' in Sandyford
Sandyford () is a suburb of Dublin, located in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland.
Sandyford Business District makes up much of the suburb and encompasses 4 business parks: Sandyford Business Park, Stillorgan Business Park, Central Park and S ...
and ''Guru Nanak Sikh Temple'' in Kelvinbridge
Kelvinbridge is the common name of the Great Western Bridge, a cast iron road and pedestrian bridge located in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland, built to carry the Great Western Road (A82) at a high level across the River Kelvin. ...
) and two in the Southside area of Pollokshields
Pollokshields ( gd, Buthan Phollaig, Scots: ''Powkshiels'') is an area in the Southside of Glasgow, Scotland. Its modern boundaries are largely man-made, being formed by the M77 motorway to the west and northwest with the open land of Pollok ...
(''Guru Granth Sahib Gurdwara'' and ''Sri Guru Tegh Bahadur Gurdwara''). In 2013, Scotland's first purpose-built Gurdwara opened in a massive opening ceremony. Built at a cost of £3.8M, it can hold 1,500 worshippers. Central Gurdwara is currently constructing a new building in the city. There are almost 10,000 Sikhs in Scotland and the majority live in Glasgow.
Glasgow Central Mosque
Glasgow Central Mosque is located on the south bank of the River Clyde in the Gorbals district of central Glasgow. The organization, 'Muslims in Britain' classify the Glasgow Central Mosque as, Deobandi.
The Mosque
The Mosque was designed b ...
in the Gorbals district is the largest mosque in Scotland and, along with twelve other mosques in the city, caters for the city's Muslim population, estimated to number 33,000.
Glasgow also has a Hindu mandir
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hind ...
.
Glasgow has seven synagogues, including the Romanesque-revival Garnethill Synagogue
Garnethill is a predominantly residential area of the city of Glasgow, Scotland with a number of important public buildings.
Geography
Located in the city centre, the area borders Cowcaddens to its north, Sauchiehall Street to its south, Camb ...
in the city centre. Glasgow currently has the seventh largest Jewish population in the United Kingdom after London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
, Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
, Gateshead
Gateshead () is a large town in northern England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank, opposite Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle to which it is joined by seven bridges. The town contains the Gateshead Millennium Bridge, Millennium Bridge, Sage ...
, Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
and Bournemouth
Bournemouth () is a coastal resort town in the Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole council area of Dorset, England. At the 2011 census, the town had a population of 183,491, making it the largest town in Dorset. It is situated on the Southern ...
but once had a Jewish population second only to London, estimated at 20,000 in the Gorbals alone.
In 1993, the St Mungo Museum of Religious Life and Art
The St Mungo Museum of Religious Life and Art is a museum of religion in Glasgow, Scotland. It has been described as the only public museum in the world devoted solely to this subject, although other notable museums of this kind are the State Mu ...
opened in Glasgow. It is believed to be the only public museum to examine all the world's major religious faiths.
Language
Glasgow is Scotland's main locus of Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
language use outside the Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands is an area of Scotland broadly covering the Scottish Highlands, plus Orkney, Shetland and Outer Hebrides (Western Isles).
The Highlands and Islands are sometimes defined as the area to which the Crofters' Act of 1886 ...
. In 2011, 5,878 residents of the city over age 3 spoke Gaelic, amounting to 1.0% of the population. Of Scotland's 25 largest cities and towns, only Inverness
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Histori ...
, the unofficial capital of the Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
, has a higher percentage of Gaelic speakers. In the Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
area there were 8,899 Gaelic-speakers, amounting to 0.8% of the population. Both the Gaelic language television station BBC Alba
BBC Alba is a Scottish Gaelic-language free-to-air public broadcast television channel jointly owned by the BBC and MG Alba. The channel was launched on 19 September 2008 and is on-air for up to seven hours a day with BBC Radio nan Gàidheal s ...
and the Gaelic language radio station BBC Radio nan Gàidheal
BBC Radio nan Gàidheal is a Scottish Gaelic language radio station owned and operated by BBC Scotland, a division of the BBC. The station was launched in 1985 and broadcasts Gaelic-language programming with the simulcast of BBC Radio Scotland.
...
have studios in Glasgow, their only locations outside the Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands is an area of Scotland broadly covering the Scottish Highlands, plus Orkney, Shetland and Outer Hebrides (Western Isles).
The Highlands and Islands are sometimes defined as the area to which the Crofters' Act of 1886 ...
.
Architecture
Very little of medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Glasgow remains; the two main landmarks from this period being the 15th-century Provand's Lordship and 13th-century St. Mungo's Cathedral, although the original medieval street plan (along with many of the street names) on the eastern side of the city centre has largely survived intact. Also in the 15th century began the building of Cathcart Castle
Cathcart Castle was a 15th-century castle, located in what is now Linn Park in the Cathcart area of southern Glasgow, Scotland. The castle was abandoned in the 18th century, and the remaining ruins were pulled down in 1980, leaving only founda ...
, completed c. 1450 with an impressive view over the landscape in all directions. It was at this castle Mary Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of Scot ...
supposedly spent the night before her defeat at the Battle of Langside
The Battle of Langside was fought on 13 May 1568 between forces loyal to Mary, Queen of Scots, and forces acting in the name of her infant son James VI. Mary’s short period of personal rule ended in 1567 in recrimination, intrigue, and disast ...
in May 1568. The castle was demolished in 1980 for safety reasons. The vast majority of the central city area as seen today dates from the 19th century. As a result, Glasgow has an impressive heritage of Victorian architecture
Victorian architecture is a series of architectural revival styles in the mid-to-late 19th century. ''Victorian'' refers to the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901), called the Victorian era, during which period the styles known as Victorian we ...
: the Glasgow City Chambers
The City Chambers or Municipal Buildings in Glasgow, Scotland, has functioned as the headquarters of Glasgow City Council since 1996, and of preceding forms of municipal government in the city since 1889. It is located on the eastern side of the ...
; the main building of the University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
, designed by Sir George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started ...
; and the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, h ...
, designed by Sir John W. Simpson, are notable examples.
The city is notable for architecture designed by the Glasgow School
The Glasgow School was a circle of influential artists and designers that began to coalesce in Glasgow, Scotland in the 1870s, and flourished from the 1890s to around 1910. Representative groups included The Four (also known as the Spook School ...
, the most notable exponent of that style being Charles Rennie Mackintosh
Charles Rennie Mackintosh (7 June 1868 – 10 December 1928) was a Scottish architect, designer, water colourist and artist. His artistic approach had much in common with European Symbolism. His work, alongside that of his wife Margaret Macdo ...
. Mackintosh was an architect and designer in the Arts and Crafts Movement and the main exponent of Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
in the United Kingdom, designing numerous noted Glasgow buildings such as the Glasgow School of Art
The Glasgow School of Art (GSA; gd, Sgoil-ealain Ghlaschu) is a higher education art school based in Glasgow, Scotland, offering undergraduate degrees, post-graduate awards (both taught and research-led), and PhDs in architecture, fine art, an ...
, Willow Tearooms
The Willow Tearooms are tearooms at 217 Sauchiehall Street, Glasgow, Scotland, designed by internationally renowned architect Charles Rennie Mackintosh, which opened for business in October 1903. They quickly gained enormous popularity, and ar ...
and the Scotland Street School Museum. A hidden gem of Glasgow, also designed by Mackintosh, is the Queen's Cross Church, the only church by the renowned artist to be built.
Another architect who has had an enduring impact on the city's appearance is Alexander Thomson
Alexander "Greek" Thomson (9 April 1817 – 22 March 1875) was an eminent Scottish architect and architectural theorist who was a pioneer in sustainable building. Although his work was published in the architectural press of his day, it was ...
, with notable examples including the Holmwood House
Holmwood House is the finest and most elaborate residential villa designed by the Scottish architect Alexander "Greek" Thomson. It is also rare in retaining much of its original interior decor, and being open to the public. A Category A listed ...
villa, and likewise Sir John James Burnet
Sir John James Burnet (31 May 1857 – 2 July 1938) was a Scotland, Scottish Edwardian architecture, Edwardian architect who was noted for a number of prominent buildings in Glasgow and London. He was the son of the architect John Burnet (arch ...
, awarded the R.I.B.A.'s Royal Gold Medal for his lifetime's service to architecture. The buildings reflect the wealth and self-confidence of the residents of the "Second City of the Empire". Glasgow generated immense wealth from trade and the industries that developed from the Industrial Revolution. The shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance a ...
s, marine engineering
Marine engineering is the engineering of boats, ships, submarines, and any other marine vessel. Here it is also taken to include the engineering of other ocean systems and structures – referred to in certain academic and professional circl ...
, steel making, and heavy industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); o ...
all contributed to the growth of the city.
Many of the city's most impressive buildings were built with red or blond sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
, but during the industrial era those colours disappeared under a pervasive black layer of soot and pollutants from the furnace
A furnace is a structure in which heat is produced with the help of combustion.
Furnace may also refer to:
Appliances Buildings
* Furnace (central heating): a furnace , or a heater or boiler , used to generate heat for buildings
* Boiler, used t ...
s, until the Clean Air Act was introduced in 1956. There are over 1,800 listed buildings in the city, of architectural and historical importance, and 23 Conservation Areas extending over . Such areas include the Central Area, Dennistoun, the West End, Pollokshields – the first major planned garden suburb in Britain – Newlands and the village of Carmunnock.
Modern buildings in Glasgow include the Glasgow Royal Concert Hall
Glasgow Royal Concert Hall is a concert and arts venue located in Glasgow, Scotland. It is owned by Glasgow City Council and operated by Glasgow Life, an agency of Glasgow City Council, which also runs Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket v ...
, and along the banks of the Clyde are the Glasgow Science Centre
Glasgow Science Centre is a visitor attraction located in the Clyde Waterfront Regeneration area on the south bank of the River Clyde in Glasgow, Scotland. Queen Elizabeth II opened Glasgow Science Centre on 5 July 2001. It is one of Scotland's ...
, The OVO Hydro and the , whose Clyde Auditorium
The SEC Armadillo (originally known as the Clyde Auditorium) is an auditorium located near the River Clyde, in Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of three venues on the Scottish Event Campus, which includes the SEC Centre and the OVO Hydro. was designed by Sir Norman Foster
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "Sieur" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as p ...
, and is colloquially known as the "Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along wi ...
". In 2006 Zaha Hadid
Dame Zaha Mohammad Hadid ( ar, زها حديد ''Zahā Ḥadīd''; 31 October 1950 – 31 March 2016) was an Iraqi-British architect, artist and designer, recognised as a major figure in architecture of the late 20th and early 21st centu ...
won a competition to design the new Museum of Transport. Hadid's museum opened on the waterfront in 2011 and has been renamed the Riverside Museum
The Riverside Museum (formerly known as the Glasgow Museum of Transport) is a museum in Glasgow, housed in a building at Pointhouse Quay in the Glasgow Harbour regeneration district of Glasgow, Scotland. The building opened in June 2011, winnin ...
to reflect the change in location and to celebrate Glasgow's rich industrial heritage stemming from the Clyde.
Glasgow's impressive historical and modern architectural traditions were celebrated in 1999 when the city was designated UK City of Architecture and Design, winning the accolade over Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
and Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
.
Economy

 Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland
Glasgow has the largest economy in ScotlandGreater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
area commute to the city every day. Once dominant export orientated manufacturing industries such as shipbuilding and other heavy engineering have been gradually replaced in importance by more diversified forms of economic activity, although major manufacturing firms continue to be headquartered in the city, such as Aggreko
Aggreko is a global supplier of mobile and modular power, temperature control equipment and energy services, headquartered in Glasgow, Scotland. The business was founded in 1962 and previously listed on the London Stock Exchange from 1997 to 20 ...
, Weir Group
The Weir Group plc is a Scottish multinational engineering company headquartered in Glasgow, Scotland. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
History
The company was established in 1871 as an e ...
, Clyde Blowers, Howden
Howden () is a market and minster town and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It lies in the Vale of York to the north of the M62, on the A614 road about south-east of York and north of Goole, which lies across the Ri ...
, Linn Products
Linn Products is an engineering company that manufactures hi-fi and audio equipment. Founded by Ivor Tiefenbrun in Glasgow, Scotland, in 1973, the company is best known as the manufacturer of the Linn Sondek LP12 turntable.
From 2007 Linn was ...
, Firebrand Games
Firebrand Games Limited is a British video game developer based in Glasgow, Scotland. The company was founded by chief executive officer Mark Greenshields in 2006 and has operated a second office in Merritt Island, Florida, since September 2007 ...
, William Grant & Sons
William Grant & Sons Ltd is an independent, family-owned Scottish company that distills Scotch whisky and other selected categories of spirits. It was established in 1887 by William Grant, and is run by Grant's descendants as of 2018. It is th ...
, Whyte and Mackay, The Edrington Group
Edrington (legally The Edrington Group Ltd.) is a privately owned international spirits company based in Glasgow, Scotland. It produces single malts The Macallan, Highland Park, The Glenrothes, Naked Malt and The Famous Grouse blended Sco ...
, British Polar Engines
British Polar Engines is a manufacturer of diesel engines based in Glasgow, Scotland. The company has over seventy years' experience in the manufacture and supply of spare parts for diesel engines. The engine and company take their name from the ...
and Albion Motors
Albion Motors was a Scottish automobile and commercial vehicle manufacturer.
Founded in 1899, Albion Motors was purchased by Leyland Motors in 1951. Vehicles continued to be manufactured under the Albion brand until 1972, after which they con ...
.
Glasgow was once one of the most significant cities in the UK for manufacturing, which generated a great deal of the city's wealth; the most prominent industry being shipbuilding based on the River Clyde. Among the historic vessels constructed there were the famed tea clipper ''Cutty Sark
''Cutty Sark'' is a British clipper ship. Built on the River Leven, Dumbarton, Scotland in 1869 for the Jock Willis Shipping Line, she was one of the last tea clippers to be built and one of the fastest, coming at the end of a long period of ...
'', the Royal Navy battlecruiser , and the transatlantic luxury liners Aquitania, , , and . Although Glasgow owed much of its economic growth to the shipbuilding industry, which still continues today in the form of Ferguson Marine
Ferguson Marine (Port Glasgow) Limited is a shipbuilding company whose yard, located in Port Glasgow on the Firth of Clyde in Scotland, was established in 1903. It is the last remaining shipbuilder on the lower Clyde and is currently the only ...
and BAE Systems Maritime - Naval Ships
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British Multinational corporation, multinational arms industry, arms, Information security, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the s ...
' two shipyards, the city has its roots in the tobacco trade and is noted to have "risen from its medieval slumber" from trade in tobacco, pioneered by figures such as John Glassford
John Glassford of Dougalston and Whitehill (1715 – 27 August 1783) was a Scotland, Scottish Tobacco Lords, Tobacco Lord, considered by his contemporaries to be the greatest of the era. He owned tobacco plantations in the American South, planta ...
. The city was also noted for its locomotive construction industryled by firms such as the North British Locomotive Companywhich grew during the 19th century before entering a decline in the 1960s.
 Whilst manufacturing has declined, Glasgow's economy has seen significant relative growth of
Whilst manufacturing has declined, Glasgow's economy has seen significant relative growth of tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
sector industries such as financial and business services (centred around the International Financial Services District
The International Financial Services District (IFSD) (Scottish Gaelic: ''Sgìre Seirbheisean Ionmhais Eadar-nàiseanta'') is a public-private financial district in Glasgow, Scotland. Based at Scottish Enterprise, the £1 billion venture aims ...
on the Broomielaw
Broomielaw is a major thoroughfare in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It runs adjacent to the River Clyde, on its north bank and forms the southern, waterside boundary of the city's International Financial Services District.
History
Named after ...
, once a stretch of riverside warehouses replaced by modern office blocks), communications, biosciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, ...
, creative industries, healthcare, higher education, retail and tourism. Glasgow is now the second most popular foreign tourist destination in Scotland (fifth in the UK) and offers Scotland's largest retail centre.
Between 1998 and 2001, the city's financial services sector grew at a rate of 30%, making considerable gains on Edinburgh, which has historically been the centre of the Scottish financial sector. Glasgow is now one of Europe's sixteen largest financial centres, with a growing number of Blue chip financial sector companies establishing significant operations or headquarters in the city.
The 1990s and first decade of the 21st century saw substantial growth in the number of call centre
A call centre ( Commonwealth spelling) or call center (American spelling; see spelling differences) is a managed capability that can be centralised or remote that is used for receiving or transmitting a large volume of enquiries by telephone. ...
s based in Glasgow. In 2007 roughly 20,000 people, a third of all call centre employees in Scotland, were employed by Glasgow call centres. This growth and its high use of recruitment agencies to hire graduates as temporary workers has led to accusations of exploitative practices such as long hours, poor pay and lack of job security by the TUC and other union bodies.
The city's main manufacturing industries include companies involved in; shipbuilding, engineering, construction, brewing and distilling, printing and publishing, chemicals and textiles as well as newer growth sectors such as optoelectronics
Optoelectronics (or optronics) is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that find, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, ''light'' often includes invisible forms of radiatio ...
, software development
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development invol ...
and biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
. Glasgow forms the western part of the Silicon Glen
Silicon Glen is a nickname for the high tech sector of Scotland, the name inspired by Silicon Valley in California. It is applied to the Central Belt triangle between Dundee, Inverclyde and Edinburgh, which includes Fife, Glasgow and Stirling ...
high tech sector of Scotland with consumer electronics companies such as RHA Technologies headquartered.
Transport
Public transport
 Glasgow has a large urban transport system, mostly managed by the
Glasgow has a large urban transport system, mostly managed by the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport
Strathclyde Partnership for Transport (SPT) is a regional transport partnership for the Strathclyde area of western Scotland. It is responsible for planning and coordinating regional transport, especially the public transport system in the are ...
(SPT).
 The city has many bus services; since
The city has many bus services; since bus deregulation
Bus deregulation in Great Britain was the abolition of Road Service Licensing outside of Greater London for bus services. This began in 1980 with the abolition of Road Service Licensing for long-distance bus services and was extended into local ...
almost all are provided by private operators, though SPT part-funds some services. The principal bus operators within the city are: First Glasgow
First Glasgow is the largest bus company serving the Greater Glasgow area in Scotland. It is a subsidiary of FirstGroup. The company operates within the area covered by the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport, a public body responsible for h ...
, McGill's Bus Services
McGill's Bus Services is a bus operator based in Greenock, Scotland.[Stagecoach West Scotland
Stagecoach West Scotland ( gd, Stagecoach an Iar na h-Alba) is an operating region of Stagecoach UK Bus, comprising Western Buses Ltd based in Ayr, Scotland.
Operations
Stagecoach West Scotland operates in west central and southwest Scotland ...]
and Glasgow Citybus
Glasgow Citybus is a bus company operating services across Glasgow and Dunbartonshire. It is a subsidiary of West Coast Motors.
History
Glasgow Citybus was formed in November 1999, by Russell Arden. The company was acquired by Campbeltown-based ...
. The main bus terminal in the city is Buchanan bus station
Buchanan bus station is the main bus terminus in Glasgow, Scotland.
The bus station is the terminus for journeys between the city and other towns and cities in Scotland, as well as long-distance services to other parts of the United Kingdom ...
.
Glasgow has the most extensive urban rail
Urban rail transit is an all-encompassing term for various types of local rail systems providing passenger service within and around urban or suburban areas. The set of urban rail systems can be roughly subdivided into the following categories ...
network in the UK outside London, with rail services travelling to a large part of the West of Scotland. Most lines were electrified under British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...
. All trains running within Scotland, including the local Glasgow trains, are operated by ScotRail
ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchise a ...
, which is owned by the Scottish Government. Central station
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the ...
and Queen Street station are the two main railway terminals. Glasgow Central is the terminus of the long West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
from London Euston
Euston railway station ( ; also known as London Euston) is a central London railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, managed by Network Rail. It is the southern terminus of the West Coast Main Line, the UK's busiest inter-city rail ...
, as well as TransPennine Express
TransPennine Express (TPE), legally First TransPennine Express Limited, is a British train operating company owned by FirstGroup that operates the TransPennine Express franchise. It runs regional and inter-city rail services between the major ci ...
services from Manchester and CrossCountry services from Birmingham, Bristol, Plymouth and various other destinations in England. Glasgow Central is also the terminus for suburban services on the south side of Glasgow, Ayrshire and Inverclyde, as well as being served by the cross city link from Dalmuir to Motherwell. Most other services within Scotland – the main line to Edinburgh, plus services to Aberdeen, Dundee, Inverness and the Western Highlands – operate from Queen Street station.
 The city's suburban network is currently divided by the River Clyde and the
The city's suburban network is currently divided by the River Clyde and the Crossrail Glasgow
Crossrail Glasgow (formerly known as Glasgow Crossrail) is a proposed railway development in Central Scotland to connect the stations Glasgow Central and Queen Street. It has been estimated at a cost of £200 million.
Since the 1970s, it has ...
initiative has been proposed to link them; it is currently awaiting funding from the Scottish Government. The city is linked to Edinburgh by four direct railway links. In addition to the suburban rail network, SPT operates the Glasgow Subway. The Subway is the United Kingdom's only completely underground metro
Metro, short for metropolitan, may refer to:
Geography
* Metro (city), a city in Indonesia
* A metropolitan area, the populated region including and surrounding an urban center
Public transport
* Rapid transit, a passenger railway in an urba ...
system and is generally recognised as the world's third oldest underground railway after the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent ceremonial counties of England, counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and He ...
and the Budapest Metro
The Budapest Metro ( hu, Budapesti metró) is the rapid transit system in the Hungarian capital Budapest. It is the world's oldest electrified underground railway system, and the second oldest underground railway system with multiple stations, ...
. Both railway and subway stations have a number of park and ride
A park and ride, also known as incentive parking or a commuter lot, is a parking lot with public transport connections that allows commuting, commuters and other people heading to city centres to leave their vehicles and transfer to a bus, Rail t ...
facilities.
As part of the wider regeneration along the banks of the River Clyde, a bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
system called Clyde Fastlink is operational between Glasgow City Centre to the Queen Elizabeth University Hospital.
Shipping
Global-ship-management is carried out by maritime and logistics firms in Glasgow, in client companies employing over 100,000 seafarers. This reflects maritime skills over many decades and the training and education of deck officers and marine engineers from around the world at the City of Glasgow College, Nautical Campus, from which graduate around one third of all such graduates in the United Kingdom.containerisation
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers and ISO containers). Containerization is also referred as "Container Stuffing" or "Container Loading", which is the pro ...
, most other facilities, such as Hunterston Terminal, are located in the deep waters of the Firth of Clyde#Shipping in the Firth, Firth of Clyde, which together handle some 7.5 million tonnes of cargo each year. Longer distant commercial sea shipping from Glasgow occurs regularly to many European destinations, including Mediterranean and Baltic ports via passage through the Sea of the Hebrides.
Leisure and tourist sailing is important, at marinas and towns of the Clyde, including the PS Waverley, PS ''Waverley'', the world's last operational seagoing paddle steamer, paddle-steamer.
Roads
 The main M8 motorway passes around the city centre and connects with the M77 motorway, M77, M74 motorway, M74, M73 motorway, M73 and M80 motorways, all of which pass within the city's boundaries. The A82 road, A82 connects Glasgow to Argyll and Bute, Argyll and the western
The main M8 motorway passes around the city centre and connects with the M77 motorway, M77, M74 motorway, M74, M73 motorway, M73 and M80 motorways, all of which pass within the city's boundaries. The A82 road, A82 connects Glasgow to Argyll and Bute, Argyll and the western Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
. The A74(M) and M74 motorways, M74 runs directly south towards Carlisle, Cumbria, Carlisle.
Other strategic roads in the city include the Glasgow East End Regeneration Route, East End Regeneration Route, which provides easier access to areas of the East End, linking the M8 to the extended M74.
Airports
There are three international airports within 45 minutes travel of the city centre, as well as a centrally located seaplane terminal. Two airports are dedicated to Glasgow, and Edinburgh International airport, situated on the west side of Edinburgh, is not far from Glasgow. These airports are Glasgow Airport (GLA) ( west of the city centre) in Renfrewshire, Glasgow Prestwick Airport (PIK) ( southwest) in Ayrshire, Edinburgh Airport (EDI), ( east) in Edinburgh and Glasgow Seaplane Terminal, by the Glasgow Science Centre on the River Clyde. There are also several smaller, domestic and private airports around the city. There is a heliport, Glasgow City Heliport, located at Stobcross Quay on the banks of the Clyde.
All of the international airports are easily accessible by public transport, with GLA and EDI directly linked by a bus routes from the main bus station and a direct rail connection to PIK from Glasgow Central Station. A series of proposals to provide a direct rail link to Glasgow International Airport have ended unsuccessfully, beginning with the Glasgow Airport Rail Link in 2009. As of 2019, local authorities have approved plans for a "Glasgow Metro", including a connection to the International Airport.
Housing
 Glasgow is known for its tenements; the red and blond
Glasgow is known for its tenements; the red and blond sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
buildings are some of the most recognisable features of the city. These were the most popular form of housing in 19th- and 20th-century Glasgow, and remain the most common form of dwelling in Glasgow today. Tenements are commonly bought by a wide range of social types and are favoured for their large rooms, high ceilings and original period features.Hyndland
Hyndland is a residential area in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland.
Description
Bordering Broomhill, Dowanhill, Kelvinside and Partickhill, it is an upper-middle-class neighbourhood populated mainly by professionals (many emp ...
area of Glasgow became the first tenement conservation area in the UK and includes some tenement houses with as many as six bedrooms.
Like many cities in the UK, Glasgow witnessed the construction of high-rise housing in tower blocks in the 1960s, along with large overspill estates on the periphery of the city, in areas like Pollok
Pollok ( gd, Pollag, lit=a pool, sco, Powk) is a large housing estate on the south-western side of the city of Glasgow, Scotland. The estate was built either side of World War II to house families from the overcrowded inner city. Housing 30,0 ...
, Nitshill, Castlemilk
Castlemilk ( gd, Caisteal Mheilc) is a district of Glasgow, Scotland. It lies to the far south of the city centre, adjacent to the Croftfoot and Simshill residential areas within the city to the north-west, the town of Rutherglen - neighbourho ...
, Easterhouse, Milton, Glasgow, Milton and Drumchapel. These were built to replace the decaying inner-city tenement buildings originally built for workers who migrated from the surrounding countryside, the Highlands, and the rest of the United Kingdom, particularly Ireland, to feed the local demand for labour. The massive demand at that time outstripped the pace of new building, and many originally fine tenements often became overcrowded and unsanitary. Many degenerated into infamous slums, such as the Gorbals.
 Efforts to improve this housing situation, most successfully with the City Improvement Trust in the late 19th century, cleared the slums of the old town areas such as the
Efforts to improve this housing situation, most successfully with the City Improvement Trust in the late 19th century, cleared the slums of the old town areas such as the Trongate
Trongate is one of the oldest streets in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. Trongate begins at Glasgow Cross, where the steeple of the old Glasgow Tolbooth is situated, being the original centre of medieval Glasgow, and goes westward changing its n ...
, High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
and Glasgow Cross
Glasgow Cross is at the hub of the ancient royal burgh and now city of Glasgow, Scotland, close to its first crossing over the River Clyde. As a major junction in the city centre, its five streets run: north up the High Street to Glasgow Cathed ...
.urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of blighte ...
initiatives, such as those motivated by the Bruce Report
The Bruce Report (or the Bruce Plan) is the name commonly given to the ''First Planning Report to the Highways and Planning Committee of the Corporation of the City of Glasgow''Robert Bruce (1945), ''First Planning report to the Highways and Pla ...
, entailed the comprehensive demolition of slum tenement areas, the development of New towns in the United Kingdom, new towns on the periphery of the city, and the construction of tower blocks.
The policy of tenement demolition is now considered to have been short-sighted, wasteful and largely unsuccessful.[ and the policy of demolition is considered to have destroyed many fine examples of a "universally admired architectural" style.]Glasgow Housing Association
Wheatley Homes Glasgow (formerly Glasgow Housing Association or GHA) is the largest social landlord in Scotland with 40,000 homes across Glasgow. Wheatley Homes Glasgow is a not-for-profit company created in 2003 by the then Scottish Executive fo ...
took ownership of the housing stock from the city council on 7 March 2003, and has begun a £96 million clearance and demolition programme to clear and demolish many of the high-rise flats.
Healthcare
 Medical care is mainly provided by NHS Scotland and is directly administered by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde.
Major hospitals, including those with Emergency department, Accident & Emergency provision, are: the Western Infirmary, Gartnavel General Hospital, Glasgow Royal Infirmary and the Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, Dental Hospital in the city Centre, Stobhill Hospital in the North and the Glasgow Victoria Infirmary, Victoria Infirmary and
Medical care is mainly provided by NHS Scotland and is directly administered by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde.
Major hospitals, including those with Emergency department, Accident & Emergency provision, are: the Western Infirmary, Gartnavel General Hospital, Glasgow Royal Infirmary and the Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, Dental Hospital in the city Centre, Stobhill Hospital in the North and the Glasgow Victoria Infirmary, Victoria Infirmary and Queen Elizabeth University Hospital
The Queen Elizabeth University Hospital (QEUH) is a 1,677-bed acute hospital located in Govan, in the south-west of Glasgow, Scotland. The hospital is built on the site of the former Southern General Hospital and opened at the end of April 2015. ...
in the South Side. Gartnavel Royal Hospital and The Priory are the two major psychiatric hospitals based in Glasgow.
The Queen Elizabeth University Hospital
The Queen Elizabeth University Hospital (QEUH) is a 1,677-bed acute hospital located in Govan, in the south-west of Glasgow, Scotland. The hospital is built on the site of the former Southern General Hospital and opened at the end of April 2015. ...
(QEUH) Campus is a 1,677-bed acute hospital located in Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south ba ...
in the south-west of Glasgow. The hospital is built on the site of the former Southern General Hospital and opened at the end of April 2015. The hospital comprises a newly built 1,109-bed adult hospital, a 256-bed children's hospital and two major A&E departments, one for adults and one for children in addition to buildings retained from the former hospital. The QEUH is the Regional Major Trauma Centre for the west of Scotland
Glasgow Street Aid
patrol the city centre offering welfare and medical assistance, as well as onward medical referrals to those requiring it. This allows for minor ailments and injuries to be attended to, generally without the attendance of an emergency ambulance. The charity also responds to major medical emergencies upon request, where life support can be administered whilst further assistance from the ambulance service can be sought.
Education
 Glasgow is a major centre of higher and academic research, with the following universities and colleges within of the city centre:
*
Glasgow is a major centre of higher and academic research, with the following universities and colleges within of the city centre:
* University of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
Flag
, latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis
, motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita
, ...
* University of Strathclyde
The University of Strathclyde ( gd, Oilthigh Shrath Chluaidh) is a public research university located in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded in 1796 as the Andersonian Institute, it is Glasgow's second-oldest university, having received its royal chart ...
* Glasgow Caledonian University
Glasgow Caledonian University ( gd, Oilthigh Chailleannach Ghlaschu, ), informally GCU, Caledonian or Caley, is a public university in Glasgow, Scotland. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of The Queen's College, Glasgow (founded in 1875) and G ...
* University of the West of Scotland
* Glasgow School of Art, The Glasgow School of Art
* Royal Conservatoire of Scotland
The Royal Conservatoire of Scotland ( gd, Conservatoire Rìoghail na h-Alba), formerly the Royal Scottish Academy of Music and Drama ( gd, Acadamaidh Rìoghail Ciùil is Dràma na h-Alba) is a conservatoire of dance, drama, music, production, and ...
* City of Glasgow CollegeShawlands
Shawlands ( gd, Fearann na Doire) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland, located around south of the River Clyde. The area, considered the "Heart of the Southside", is known for its independent restaurants and cafés, art scene, public parks, period ...
, Dennistoun and the West End of the city.
The City Council operates 29 secondary schools, 149 primary schools and three specialist schools – the Dance School of Scotland, Bellahouston Academy#Glasgow School of Sport, Glasgow School of Sport and the Glasgow Gaelic School (''Sgoil Ghàidhlig Ghlaschu''), the only secondary school in Scotland to teach exclusively in Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
. Outdoor Education facilities are provided by the city council at the Blairvadach Centre, near Helensburgh. Jordanhill School is operated directly by the Scottish Government. Glasgow also has a number of Independent schools, including The High School of Glasgow, founded in 1124 and the oldest school in Scotland; Hutchesons' Grammar School, founded in 1639 and one of the oldest school institutions in Britain; and others such as Craigholme School (closed 2020), Glasgow Academy, Kelvinside Academy and St. Aloysius' College, Glasgow, St. Aloysius' College. Glasgow is part of the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities.
Sport
Football
 The world's first international football match was held in 1872 at the West of Scotland Cricket Club's Hamilton Crescent ground in the
The world's first international football match was held in 1872 at the West of Scotland Cricket Club's Hamilton Crescent ground in the Partick
Partick ( sco, Pairtick, Scottish Gaelic: ''Partaig'') is an area of Glasgow on the north bank of the River Clyde, just across from Govan. To the west lies Whiteinch, to the east Yorkhill and Kelvingrove Park (across the River Kelvin), and ...
area of the city. The match, between Scotland national football team, Scotland and England national football team, England finished 0–0.
Glasgow was the first city (since joined by Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
in 1985, Madrid in 1986, 2014, 2016 and 2018, Milan in 1994 and London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
in 2019) to have had two football teams in European finals in the same season: in 1967, Celtic competed in the UEFA Champions League, European Cup final with rivals Rangers competing in the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup, Cup Winners' Cup final. Rangers were the first football club from the United Kingdom to reach a European final, doing so in 1961 European Cup Winners' Cup Final, 1961. They have also won more domestic top-tier league titles than any other football club in the world (currently 55). Celtic were the first non-Latin club to win the European Cup, under the management of Jock Stein in 1966–67 European Cup, 1967, before Manchester United F.C., Manchester United the following year. Celtic also went on to reach another European Cup Final in 1970 European Cup Final, 1970, losing to Feyenoord, and also the final of the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup in 2003 UEFA Cup Final, 2003, where they lost an enthralling match which finished 3–2 to Portuguese club FC Porto, Porto. Rangers also reached the final of the same competition in 2008 UEFA Cup Final, 2008, where they lost to FC Zenit Saint Petersburg, Zenit Saint Petersburg of Russia.
Hampden Park, which is Scotland's national football stadium, holds the European record for attendance at a football match: 149,547 saw Scotland beat England 3–1 in 1937, in the days before leading British stadia became All-seater stadium, all-seated. Hampden Park has hosted the final of the UEFA Champions League on three occasions, most recently in 2002 and hosted the UEFA Cup Final in 2007. Celtic Park
Celtic Park is the home stadium of Celtic Football Club, in the Parkhead area of Glasgow, Scotland. With a capacity of 60,832, it is the largest football stadium in Scotland, and the eighth-largest stadium in the United Kingdom. It is al ...
(60,411 seats) is located in the east end of Glasgow, and Ibrox Stadium
Ibrox Stadium is a Soccer-specific stadium, football stadium on the south side of the River Clyde in the Ibrox, Glasgow, Ibrox area of Glasgow, Scotland. The home of Rangers F.C., Rangers Football Club, Ibrox is the third largest List of foot ...
(50,817 seats) on the south side.
Glasgow has four professional football clubs, who all play in the SPFL: Celtic, Rangers, Partick Thistle F.C., Partick Thistle, and Queen's Park F.C., Queen's Park (after their move from amateur status in November 2019). Prior to this, Glasgow had two other professional teams: Clyde F.C., Clyde (now playing in Hamilton, South Lanarkshire, Hamilton) and Third Lanark A.C., Third Lanark (liquidated in 1967), plus four others active in the league in the 19th century: Thistle F.C., Thistle, Cowlairs F.C., Cowlairs, Northern F.C., Northern and Linthouse F.C., Linthouse. There are a number of West of Scotland Football League clubs within the city as well, such as Pollok F.C., Pollok, Maryhill F.C., Maryhill, Benburb F. C., Benburb, Ashfield F.C., Ashfield, Glasgow Perthshire F.C., Glasgow United F.C., Glasgow United (formerly Shettleston Juniors), and Petershill F.C., Petershill, plus numerous amateur teams.
The history of football in the city, as well as the status of the Old Firm
The Old Firm is the collective name for the Scottish football clubs Celtic and Rangers, which are both based in Glasgow. The two clubs are by far the most successful and popular in Scotland, and the rivalry between them has become deeply em ...
, attracts many visitors to football matches in the city throughout the season. The Scottish Football Association, the national governing body, and the Scottish Football Museum are based in Glasgow, as are the Scottish Professional Football League, Scottish Junior Football Association and Scottish Amateur Football Association. The Glasgow Cup was a once popular tournament, which was competed for by Rangers, Celtic, Clyde, Partick Thistle and Queen's Park. The competition is now played for by the youth sides of the five teams.
Glasgow is also home to six women's football teams. Currently, Glasgow City F.C., Glasgow City are the champions of the Scottish Women's Premier League. Other local teams include Glasgow Girls F.C., Glasgow Girls and the women's sections of the men's clubs: Celtic F.C. Women, Celtic and Rangers L.F.C., Rangers play in the top division.
Rugby union
Glasgow has a professional rugby union club, the Glasgow Warriors, which plays in the European Rugby Champions Cup and Pro14 alongside teams from Scotland, Ireland, Wales, Italy and South Africa. The Warriors current home is Scotstoun Stadium and has been since 2012, previously they played at Firhill Stadium
Firhill Stadium is a football and former rugby union, rugby league and greyhound racing stadium located in the Maryhill area of Glasgow, Scotland which has been the home of Partick Thistle since 1909. The stadium is commonly referred to as simp ...
. They have won the Melrose 7s in both 2014 and 2015 and were also crowned champions of the Pro12 at the end of the 2014/15 season after beating Irish side Munster in Belfast.
In the Scottish League, Glasgow Hawks RFC was formed in 1997 by the merger of two of Glasgow's oldest clubs: Glasgow Academicals RFC, Glasgow Academicals and Glasgow High Kelvinside (GHK). Despite the merger, the second division teams of Glasgow Academicals and Glasgow High Kelvinside re-entered the Scottish rugby league in 1998.
South of Glasgow, in East Renfrewshire, in the suburb of Giffnock, is based another of Glasgow area's most prominent clubs Glasgow Hutchesons Aloysians RFC (GHA). GHA was formed in 2002 with the merger of two of Glasgow's leading clubs at the time, Glasgow Southern RFC and Hutchesons Aloysians RFC.
Cartha Queens Park RFC, Cartha Queen's Park play at Dumbreck, within the city.
Glasgow was also home to one of the oldest rugby clubs in Scotland, West of Scotland F.C., which was formed in 1865, and was a founding member of the Scottish Rugby Union. The club was originally based in Partick at Hamilton Crescent but is now based outside the city, at Burnbrae, Milngavie in East Dunbartonshire.
Rugby league
The Easterhouse Panthers based in the East End of Glasgow are a rugby league team who play in the Rugby League Conference Scotland Division.
Ice hockey
From 1966 to 1986, the Glasgow Dynamos played at Crossmyloof Ice Rink. Since October 2010 a team called the Glasgow Clan based in the nearby Braehead Arena in Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
has played in the professional Elite Ice Hockey League alongside two other Scottish teams, the Fife Flyers and the Dundee Stars.
Swimming
The Arlington Baths Club was founded in 1870. It is situated in the Woodlands, Glasgow, Woodlands area of the city and is still in use today. It is believed the club's first Baths Master William Wilson (aquatics), William Wilson invented water polo at the club. The Arlington inspired other Swimming Clubs and the Western Baths, which opened in 1876, is also still in existence in nearby Hillhead
Hillhead ( sco, Hullheid, gd, Ceann a' Chnuic) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland. Situated north of Kelvingrove Park and to the south of the River Kelvin, Hillhead is at the heart of Glasgow's fashionable West End, with Byres Road forming th ...
.
Basketball
Glasgow hosts Scotland's only professional basketball team, the Caledonia Gladiators, who compete in the British Basketball League. Previously based in Renfrewshire's Braehead Arena and the 1,200-seat Kelvin Hall, the team has been based at the Emirates Arena since the 2012/13 season.
Other sports
 Major international sporting arenas include the Kelvin Hall and Scotstoun Sports Centre. In 2003 the National Academy for Badminton was completed in Scotstoun. In 2003, Glasgow was also given the title of European Capital of Sport.
Glasgow is also host to many cricket clubs including Clydesdale Cricket Club who have been title winners for the Scottish Cup many times. This club also acted as a neutral venue for a One Day International match between India national cricket team, India and Pakistan national cricket team, Pakistan in 2007, but due to bad weather it was called off.
Smaller sporting facilities include an abundance of outdoor playing fields, as well as golf clubs such as Haggs Castle and artificial ski slopes. Between 1998 and 2004, the Scottish Claymores American football team played some or all of their home games each season at Hampden Park and the venue also hosted World Bowl XI.
Glasgow Green and the
Major international sporting arenas include the Kelvin Hall and Scotstoun Sports Centre. In 2003 the National Academy for Badminton was completed in Scotstoun. In 2003, Glasgow was also given the title of European Capital of Sport.
Glasgow is also host to many cricket clubs including Clydesdale Cricket Club who have been title winners for the Scottish Cup many times. This club also acted as a neutral venue for a One Day International match between India national cricket team, India and Pakistan national cricket team, Pakistan in 2007, but due to bad weather it was called off.
Smaller sporting facilities include an abundance of outdoor playing fields, as well as golf clubs such as Haggs Castle and artificial ski slopes. Between 1998 and 2004, the Scottish Claymores American football team played some or all of their home games each season at Hampden Park and the venue also hosted World Bowl XI.
Glasgow Green and the Gorbals
The Gorbals is an area in the city of Glasgow, Scotland, on the south bank of the River Clyde. By the late 19th century, it had become densely populated; rural migrants and immigrants were attracted by the new industries and employment opportun ...
are home to a number of rowing (sport), rowing clubs, some with open membership the rest belonging to universities or schools. Historically, rowing races on the River Clyde here attracted huge crowds of spectators to watch regattas in the late 19th century and early 20th century; before football caught the public imagination. Two of Glasgow's rowing clubs separately claim that it was their members who were among the founders of Rangers Football Club.
Motorcycle speedway racing was first introduced to Glasgow in 1928 and is currently staged at Ashfield Stadium in the North of the city. The home club, Glasgow Tigers (speedway), Glasgow Tigers, compete in the SGB Championship, the second tier of motorcycle speedway in Britain.
Glasgow is also one of five places in Scotland that hosts the final of the Scottish Cup of Shinty, better known as the Camanachd Cup. This is usually held at Old Anniesland. Once home to numerous Shinty clubs, there is now only one senior club in Glasgow, Glasgow Mid-Argyll.
Glasgow Glasgow bid for the 2018 Summer Youth Olympics, bid to host the 2018 Summer Youth Olympics but lost to Buenos Aires in the 4 July 2013 vote.
Glasgow was the host of the 2018 European Sports Championships along with Berlin (hosts of the 2018 European Athletics Championships).
2014 Commonwealth Games
On 9 November 2007, Glasgow was selected to be the host city of the 2014 Commonwealth Games. The games were held at a number of existing and newly constructed sporting venues across the city, including a refurbished Hampden Park, Kelvingrove Park
Kelvingrove Park is a public park located on the River Kelvin in the West End of the city of Glasgow, Scotland, containing the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum.
History
Kelvingrove Park was originally created as the West End Park in 1852, and ...
, Kelvin Hall, and the OVO Hydro at the SECC. The opening ceremony was held at Celtic Park. 2014 was the third time the Games have been held in Scotland.
Major incidents and tragedies
 * 5 April 1902 – 1902 Ibrox disaster – 25 spectators died and more than 500 were injured when a new wooden stand at the Ibrox Park (1887–99), Ibrox Park stadium collapsed during an England–Scotland football rivalry, England–Scotland match.
* 1960s/1970s – Many perished at three major blazes: the Cheapside Street whisky bond fire in Cheapside Street,
* 5 April 1902 – 1902 Ibrox disaster – 25 spectators died and more than 500 were injured when a new wooden stand at the Ibrox Park (1887–99), Ibrox Park stadium collapsed during an England–Scotland football rivalry, England–Scotland match.
* 1960s/1970s – Many perished at three major blazes: the Cheapside Street whisky bond fire in Cheapside Street, Anderston
Anderston ( sco, Anderstoun, gd, Baile Aindrea) is an area of Glasgow, Scotland. It is on the north bank of the River Clyde and forms the south western edge of the city centre. Established as a village of handloom weavers in the early 18th cent ...
(1960, 19 killed); the James Watt Street fire (1968, 22 killed); and the Kilbirnie Street fire (1972, seven killed).
* 2 January 1971 – 1971 Ibrox disaster – 66 people were killed in a crush, as supporters attempted to vacate the stadium.
* 11 May 2004 – Stockline Plastics factory explosion – The ICL Plastics factory (commonly referred to as Stockline Plastics factory), in the Woodside district of Glasgow, exploded. Nine people were killed, including two company directors, and 33 injured – 15 seriously. The four-storey building was largely destroyed.
* 30 June 2007 – 2007 Glasgow International Airport attack – Two jihadist terroristsBilal Abdullah and Kafeel AhmedVehicle-ramming attack, deliberately drove a Jeep Cherokee Sport utility vehicle, SUV loaded with propane cylinders into the glass doors of a crowded terminal at Glasgow International Airport in an attempted suicide attack. A Hostile vehicle mitigation, concrete security pillar blocked the car from entering the terminal. The two perpetrators were both apprehended; Ahmed died of burn wounds sustained in the attack, while Abdullah was convicted in Woolwich Crown Court of conspiracy to murder through terrorism and was sentenced to at least 32 years' imprisonment.[UK bomb plot doctor jailed for 32 years]
, CNN (17 December 2008). The perpetrators were also linked to a 2007 London car bombs, failed car bombing in London the previous day. Ahmed's brother Sabeel Ahmed pleaded guilty to failing to disclose information about an act of terrorism and was deported.[
* 29 November 2013 – 2013 Glasgow helicopter crash – A Eurocopter EC135-T2+ police helicopter (operated by Bond Air Services for Police Scotland) crashed on top of The Clutha Vaults Bar in Glasgow City Centre, killing all aboard the helicopter (the pilot and two crew members) and seven people in the pub. The cause of the crash was fuel starvation due to pilot error.]
Namesake area on Mars
There is an area on Planet Mars which NASA has named Glasgow, after Scotland's largest city. The Curiosity (rover), Mars rover Curiosity, which landed on the planet in August 2012, has drilled at the site.
Twin towns and sister cities
Glasgow is Sister city, twinned with various cities.
* Nuremberg, Germany (since 1985)
* Rostov-on-Don, Russia (since 1986)
* Dalian, China (since 1997)
* Havana, Cuba (since 2002)
* Turin, Italy (since 2003)
Partnerships
The city is also in a partnership with:
* Oulu, Finland
Notable people
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
*
* Butt, John, and George Gordon, eds. ''Strathclyde: Changing Horizons'' (1985)
*
* Cowan, J. "From Glasgow's Treasure Chest" (1951)
*
*
* Cunnison, J. and JBS Gilfillan, ''The City of Glasgow'', The Third Statistical Account of Scotland (1958)
* Daiches, David. ''Glasgow'' (1982), scholarly history
* Doak, A M and Young, A M. "Glasgow at a Glance" (1983)
* Gibb, Andrew. ''Glasgow: The Making of a City'' (1983)
* Gomme, A H and Walker, D. "Architecture of Glasgow" (1987)
* Horsey, M. "Tenements & Towers: Glasgow Working-Class Housing 1890–1990" (1990)
* Hume, John. "Industrial Archaeology of Glasgow" (1974)
*
* Maver, Irene. ''Glasgow'' (2000)
* Malcolm, Sandra. "Old Glasgow and The Clyde: From the Archives of T. and R. Annan" (2005)
* McKean, Charles. "Central Glasgow: An Illustrated Architectural Guide" (1993)
* Oakley, Charles. ''The Second City'' (1975)
* Small, G P. "Greater Glasgow: An Illustrated Architectural Guide" (2008)
* Urquhart, Gordon R. "Along Great Western Road: An Illustrated History of Glasgow's West End" (2000)
* Williamson, Elizabeth et al. ''Glasgow'' (The Buildings of Scotland) (1999)
* Worsdall, Frank. "The Tenement: A Way of Life" (1979)
* Worsdall, Frank. "The City That Disappeared: Glasgow's Demolished Architecture" (1981)
* Worsdall, Frank. "The Victorian City: Selection of Glasgow's Architecture" (1988)
External links
*
Glasgow districts map and other Glasgow maps
*
Glasgow City Council
TheGlasgowStory
National Library of Scotland: Scottish Screen Archive (archive films relating to Glasgow)
{{Authority control
Glasgow,
Articles containing video clips
6th-century establishments in Scotland
Council areas of Scotland
Cities in Scotland
Lieutenancy areas of Scotland
Populated places established in the 6th century
Port cities and towns in Scotland
Populated places in Glasgow
Types of monuments and memorials

 The opening of the
The opening of the  Glasgow's population had surpassed that of Edinburgh by 1821. The development of civic institutions included the
Glasgow's population had surpassed that of Edinburgh by 1821. The development of civic institutions included the  The city invested heavily in roads infrastructure, with an extensive system of arterial roads and motorways that bisected the central area. There are also accusations that the
The city invested heavily in roads infrastructure, with an extensive system of arterial roads and motorways that bisected the central area. There are also accusations that the 
 Although Glasgow
Although Glasgow  Glasgow is located on the banks of the River Clyde, in West Central Scotland. Another important river is the
Glasgow is located on the banks of the River Clyde, in West Central Scotland. Another important river is the  Despite its northerly latitude, similar to that of
Despite its northerly latitude, similar to that of  In the 1950s, the population of the City of Glasgow area peaked at 1,089,000. Glasgow was then one of the most densely populated cities in the world. After the 1960s, clearances of poverty-stricken inner city areas like the
In the 1950s, the population of the City of Glasgow area peaked at 1,089,000. Glasgow was then one of the most densely populated cities in the world. After the 1960s, clearances of poverty-stricken inner city areas like the 
 The city centre is bounded by High Street up to
The city centre is bounded by High Street up to  The city centre is based on a grid system of streets on the north bank of the River Clyde. The heart of the city is
The city centre is based on a grid system of streets on the north bank of the River Clyde. The heart of the city is  This is the commercial and part-residential district of the
This is the commercial and part-residential district of the  To the western edge of the city centre, occupying the areas of
To the western edge of the city centre, occupying the areas of  Overlooking Glasgow Green is the façade of Templeton On The Green, featuring vibrant
Overlooking Glasgow Green is the façade of Templeton On The Green, featuring vibrant  Glasgow's South Side sprawls out south of the Clyde. The adjoining urban area includes some of Greater Glasgow's most affluent suburban towns, such as
Glasgow's South Side sprawls out south of the Clyde. The adjoining urban area includes some of Greater Glasgow's most affluent suburban towns, such as  North Glasgow extends out from the north of the city centre towards the affluent suburbs of Bearsden,
North Glasgow extends out from the north of the city centre towards the affluent suburbs of Bearsden,  The city has many amenities for a wide range of cultural activities, from
The city has many amenities for a wide range of cultural activities, from  The city is home to numerous orchestras, ensembles and bands including those of
The city is home to numerous orchestras, ensembles and bands including those of  Since the 1980s, the success of bands such as
Since the 1980s, the success of bands such as  The Protestant churches are the largest in number, including Baptist, Episcopalian, Methodist and Presbyterian. 32% of the population follow the Protestant Church of Scotland whilst 29% following the Roman Catholic Church, according to the 2001 census (Christians overall form 65%). Much of the city's Roman Catholic population are those of Irish ancestry. The divisions between the two denominations and their respective communities play a major part in
The Protestant churches are the largest in number, including Baptist, Episcopalian, Methodist and Presbyterian. 32% of the population follow the Protestant Church of Scotland whilst 29% following the Roman Catholic Church, according to the 2001 census (Christians overall form 65%). Much of the city's Roman Catholic population are those of Irish ancestry. The divisions between the two denominations and their respective communities play a major part in 
 Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and is at the hub of the metropolitan area of West Central Scotland. The city itself sustains more than 410,000 jobs in over 12,000 companies. Over 153,000 jobs were created in the city between 2000 and 2005 – a growth rate of 32%. Glasgow's annual economic growth rate of 4.4% is now second only to that of London. In 2005, over 17,000 new jobs were created, and 2006 saw private-sector investment in the city reaching £4.2 billion, an increase of 22% in a single year. 55% of the residents in the
Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and is at the hub of the metropolitan area of West Central Scotland. The city itself sustains more than 410,000 jobs in over 12,000 companies. Over 153,000 jobs were created in the city between 2000 and 2005 – a growth rate of 32%. Glasgow's annual economic growth rate of 4.4% is now second only to that of London. In 2005, over 17,000 new jobs were created, and 2006 saw private-sector investment in the city reaching £4.2 billion, an increase of 22% in a single year. 55% of the residents in the  Whilst manufacturing has declined, Glasgow's economy has seen significant relative growth of
Whilst manufacturing has declined, Glasgow's economy has seen significant relative growth of  The city has many bus services; since
The city has many bus services; since  The city's suburban network is currently divided by the River Clyde and the
The city's suburban network is currently divided by the River Clyde and the  The main M8 motorway passes around the city centre and connects with the M77 motorway, M77, M74 motorway, M74, M73 motorway, M73 and M80 motorways, all of which pass within the city's boundaries. The A82 road, A82 connects Glasgow to Argyll and Bute, Argyll and the western
The main M8 motorway passes around the city centre and connects with the M77 motorway, M77, M74 motorway, M74, M73 motorway, M73 and M80 motorways, all of which pass within the city's boundaries. The A82 road, A82 connects Glasgow to Argyll and Bute, Argyll and the western  Glasgow is known for its tenements; the red and blond
Glasgow is known for its tenements; the red and blond  Efforts to improve this housing situation, most successfully with the City Improvement Trust in the late 19th century, cleared the slums of the old town areas such as the
Efforts to improve this housing situation, most successfully with the City Improvement Trust in the late 19th century, cleared the slums of the old town areas such as the  Medical care is mainly provided by NHS Scotland and is directly administered by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde.
Major hospitals, including those with Emergency department, Accident & Emergency provision, are: the Western Infirmary, Gartnavel General Hospital, Glasgow Royal Infirmary and the Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, Dental Hospital in the city Centre, Stobhill Hospital in the North and the Glasgow Victoria Infirmary, Victoria Infirmary and
Medical care is mainly provided by NHS Scotland and is directly administered by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde.
Major hospitals, including those with Emergency department, Accident & Emergency provision, are: the Western Infirmary, Gartnavel General Hospital, Glasgow Royal Infirmary and the Glasgow Dental Hospital and School, Dental Hospital in the city Centre, Stobhill Hospital in the North and the Glasgow Victoria Infirmary, Victoria Infirmary and  Glasgow is a major centre of higher and academic research, with the following universities and colleges within of the city centre:
*
Glasgow is a major centre of higher and academic research, with the following universities and colleges within of the city centre:
*  The world's first international football match was held in 1872 at the West of Scotland Cricket Club's Hamilton Crescent ground in the
The world's first international football match was held in 1872 at the West of Scotland Cricket Club's Hamilton Crescent ground in the  Major international sporting arenas include the Kelvin Hall and Scotstoun Sports Centre. In 2003 the National Academy for Badminton was completed in Scotstoun. In 2003, Glasgow was also given the title of European Capital of Sport.
Glasgow is also host to many cricket clubs including Clydesdale Cricket Club who have been title winners for the Scottish Cup many times. This club also acted as a neutral venue for a One Day International match between India national cricket team, India and Pakistan national cricket team, Pakistan in 2007, but due to bad weather it was called off.
Smaller sporting facilities include an abundance of outdoor playing fields, as well as golf clubs such as Haggs Castle and artificial ski slopes. Between 1998 and 2004, the Scottish Claymores American football team played some or all of their home games each season at Hampden Park and the venue also hosted World Bowl XI.
Glasgow Green and the
Major international sporting arenas include the Kelvin Hall and Scotstoun Sports Centre. In 2003 the National Academy for Badminton was completed in Scotstoun. In 2003, Glasgow was also given the title of European Capital of Sport.
Glasgow is also host to many cricket clubs including Clydesdale Cricket Club who have been title winners for the Scottish Cup many times. This club also acted as a neutral venue for a One Day International match between India national cricket team, India and Pakistan national cricket team, Pakistan in 2007, but due to bad weather it was called off.
Smaller sporting facilities include an abundance of outdoor playing fields, as well as golf clubs such as Haggs Castle and artificial ski slopes. Between 1998 and 2004, the Scottish Claymores American football team played some or all of their home games each season at Hampden Park and the venue also hosted World Bowl XI.
Glasgow Green and the  * 5 April 1902 – 1902 Ibrox disaster – 25 spectators died and more than 500 were injured when a new wooden stand at the Ibrox Park (1887–99), Ibrox Park stadium collapsed during an England–Scotland football rivalry, England–Scotland match.
* 1960s/1970s – Many perished at three major blazes: the Cheapside Street whisky bond fire in Cheapside Street,
* 5 April 1902 – 1902 Ibrox disaster – 25 spectators died and more than 500 were injured when a new wooden stand at the Ibrox Park (1887–99), Ibrox Park stadium collapsed during an England–Scotland football rivalry, England–Scotland match.
* 1960s/1970s – Many perished at three major blazes: the Cheapside Street whisky bond fire in Cheapside Street,