Geology Of New Zealand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The geology of New Zealand is noted for its
The geology of New Zealand is noted for its
 New Zealand's basement rocks range in age from mid-
New Zealand's basement rocks range in age from mid-

 An
An
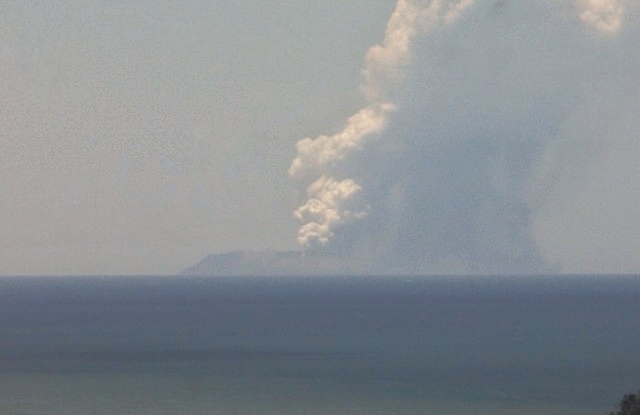 Volcanism is recorded in New Zealand throughout its whole geological history. Most volcanism in New Zealand, both modern and ancient, has been caused by the subduction of one tectonic plate under another; this causes melting in the
Volcanism is recorded in New Zealand throughout its whole geological history. Most volcanism in New Zealand, both modern and ancient, has been caused by the subduction of one tectonic plate under another; this causes melting in the
 Intra-plate basaltic volcanic eruptions also occurred in the North Island, near the Bay of Islands in Northland, in the Late Miocene (10 Mya), and again more recently (0.5 Mya). The South Auckland volcanic field was active in
Intra-plate basaltic volcanic eruptions also occurred in the North Island, near the Bay of Islands in Northland, in the Late Miocene (10 Mya), and again more recently (0.5 Mya). The South Auckland volcanic field was active in
 The Tongariro Volcanic Centre developed over the last 275,000 years and contains the active andesitic volcanic cones of Ruapehu, Tongariro, and Ngauruhoe (really a side cone of Tongariro). Ruapehu erupts about once a decade, and while the eruptions cause havoc for skiers, plane flights and hydroelectric dams, the eruptions are relatively minor. However, the sudden collapse of the crater wall caused major problems when it generated a lahar in 1953, that destroyed a rail bridge, and caused 151 deaths at Tangiwai. The last significant eruption was 1995–96. Ngauruhoe last erupted 1973–75. Taranaki is a perfectly formed andesitic strato-volcano, that last erupted in 1755.
Lake Taupō, the largest lake in the North Island, is a volcanic caldera, responsible for rhyolitic eruptions about once every 1,000 years. The largest eruption in the last 65,000 years was the cataclysmic
The Tongariro Volcanic Centre developed over the last 275,000 years and contains the active andesitic volcanic cones of Ruapehu, Tongariro, and Ngauruhoe (really a side cone of Tongariro). Ruapehu erupts about once a decade, and while the eruptions cause havoc for skiers, plane flights and hydroelectric dams, the eruptions are relatively minor. However, the sudden collapse of the crater wall caused major problems when it generated a lahar in 1953, that destroyed a rail bridge, and caused 151 deaths at Tangiwai. The last significant eruption was 1995–96. Ngauruhoe last erupted 1973–75. Taranaki is a perfectly formed andesitic strato-volcano, that last erupted in 1755.
Lake Taupō, the largest lake in the North Island, is a volcanic caldera, responsible for rhyolitic eruptions about once every 1,000 years. The largest eruption in the last 65,000 years was the cataclysmic
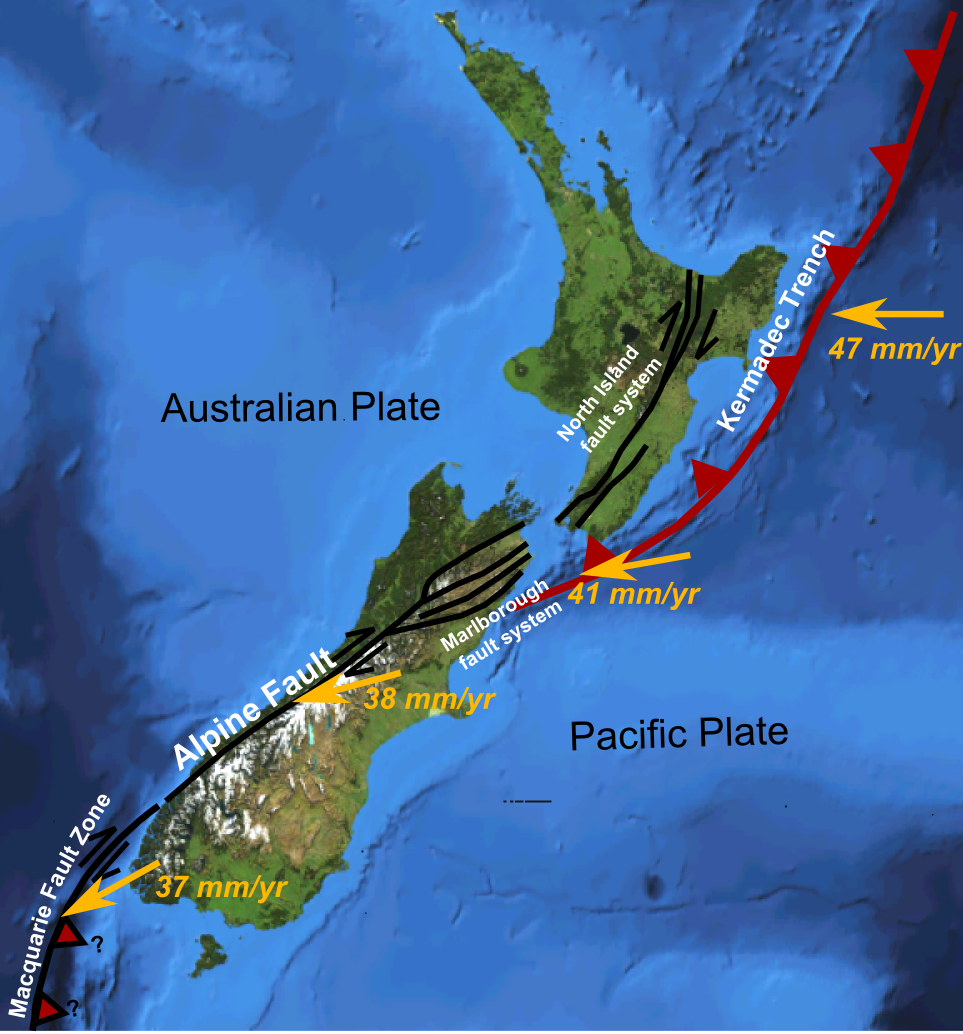 New Zealand is currently astride the convergent boundary between the Pacific and Australian Plates. Over time, the relative motion of the plates has altered and the current configuration is geologically recent. Currently the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Australian Plate from around
New Zealand is currently astride the convergent boundary between the Pacific and Australian Plates. Over time, the relative motion of the plates has altered and the current configuration is geologically recent. Currently the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Australian Plate from around
 Since Zealandia separated from Gondwana (80 mya) in the Cretaceous the climate has typically been far warmer than today. However, since the
Since Zealandia separated from Gondwana (80 mya) in the Cretaceous the climate has typically been far warmer than today. However, since the
 New Zealand suffers from many natural hazards, including earthquakes and tsunamis, volcanic and hydrothermal eruptions and
New Zealand suffers from many natural hazards, including earthquakes and tsunamis, volcanic and hydrothermal eruptions and
Geonet
– Current New Zealand Earthquake and Volcanic Activity. The universities of
An Overview of New Zealand Geology
*''Hot Stuff to Cold Stone'' – Aitken, Jefley; GNS Science, 1997. . *''Rocked and Ruptured'' – Aitken, Jefley; Reed Books, in association with GNS Science, 1999. . *''The Rise and Fall of the Southern Alps'' – Coates, Glenn; Canterbury University Press, 2002. . *''Plate Tectonics for Curious Kiwis'' – Aitken, Jefley; GNS Science, 1996. . *''Lava and Strata: A guide to the volcanoes and rock formations of Auckland'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil & Kermode, Les; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 2000. . *''Vanishing volcanoes : a guide to the landforms and rock formations of Coromandel Peninsula'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 1992. . *''Reading the rocks : a guide to geological features of the Wairarapa Coast'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil & Kermode, Les; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 1989.
from GNS Science
Geological Society of New ZealandNew Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics
A simple geological map of New Zealand
from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand {{Oceania topic, Geology of
volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
activity, earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s and geothermal areas because of its position on the boundary of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and I ...
s. New Zealand is part of Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as ( Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L ...
, a microcontinent nearly half the size of Australia that broke away from the Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
n supercontinent about 83 million years ago. New Zealand's early separation from other landmasses and subsequent evolution have created a unique fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
record and modern ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
.
New Zealand's geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
can be simplified into three phases. First the basement rocks of New Zealand formed. These rocks were once part of the super-continent of Gondwana, along with South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
and Australia. The rocks that now form the, mostly submerged, continent of Zealandia were then nestled between Eastern Australia and Western Antarctica. Secondly New Zealand drifted away from Gondwana and many sedimentary basins formed, which later became the sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
s covering the geological basement. The final phase is represented by the uplift of the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Souther ...
and the eruptions of the Taupō Volcanic Zone
The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand that has been active for the past two million years and is still highly active.
Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward thro ...
.
Basement rocks (Cambrian-Cretaceous)
 New Zealand's basement rocks range in age from mid-
New Zealand's basement rocks range in age from mid-Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
in north-west Nelson to Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
near Kaikoura. These rocks were formed in a marine environment before New Zealand separated from Gondwana. They are divided into the "Western Province", consisting mainly of greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke ( German ''grauwacke'', signifying a grey, earthy rock) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or li ...
, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
and gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures a ...
, and an "Eastern Province", consisting mainly of greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke ( German ''grauwacke'', signifying a grey, earthy rock) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or li ...
and schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes ...
. The provinces are further divided into terranes – large slices of crust with different geological histories that have been brought together by tectonic activity ( subduction and strike-slip faulting) to form New Zealand.
The Western Province is older than the Eastern Province and outcrops along the west coast of the South Island from Nelson to Fiordland. The Western Province is divided into the Buller and Takaka terranes which formed in mid-Cambrian to Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w ...
time (510–400 Ma). This includes New Zealand's oldest rocks, trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
containing greywacke, which are found in the Cobb Valley in north-west Nelson.
Large sections of the Western Province have been intruded by plutonic rocks or metamorphosed to gneiss. These plutonic basement rocks are subdivided into the Hohonu, Karamea, Median and Paparoa batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, su ...
s. These rocks form the foundations beneath offshore Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dis ...
, and much of the West Coast, Buller, north-west Nelson, Fiordland and Stewart Island / Rakiura. Most of these plutonic rocks were formed in Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w ...
- Carboniferous time (380–335 Ma) and Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
time (155–100 Ma). The Median Batholith represents a long-lived batholith dividing the Western and Eastern Provinces. Before Zealandia's separation from Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
it stretched from Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
, through what is now New Zealand, into West Antarctica. It marks the site of a former subduction zone on the edge of Gondwana.
The Eastern Province underlies more of New Zealand than the Western Province, including the greywacke and schist of the Southern Alps and all of the basement rocks of the North Island. The Eastern Province contains seven main terranes, the Drumduan, Brook Street, Murihiku, Dun Mountain-Maitai, Caples, Torlesse Composite (Rakaia, Aspiring and Pahau terranes) and Waipapa Composite (Morrinsville and Hunua Terranes). They are mostly composed of greywacke together with argillite
:''"Argillite" may also refer to Argillite, Kentucky.''
Argillite () is a fine-grained sedimentary rock composed predominantly of indurated clay particles. Argillaceous rocks are basically lithified muds and oozes. They contain variable amo ...
, except for the Brook Street and Dun Mountain-Maitai Terranes which have significant igneous components (see Dun Mountain Ophiolite Belt). New Zealand's greywacke is mostly from the Caples, Torlesse Composite (Rakaia and Pahau) and Waipapa Composite (Morrinsville and Hunua) terranes formed in Carboniferous-Cretaceous time (330–120 Ma). Much of these rocks were deposited as submarine fan
Abyssal fans, also known as deep-sea fans, underwater deltas, and submarine fans, are underwater geological structures associated with large-scale sediment deposition and formed by turbidity currents. They can be thought of as an underwater ve ...
s. They have different origins, as shown by different chemical compositions and different fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
. In general, the sedimentary basement terranes become younger from West to East across the country, as the newer terranes were scraped off the subducting paleo-Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and I ...
, and accreted to the boundary of Gondwana over hundreds of millions of years.
Many rocks in the Eastern Province have been metamorphosed into the Haast Schist, due to exposure to high pressures and temperatures. Rocks grade continuously from greywacke (e.g., in Canterbury) to high-grade schist (e.g., around the Caples-Torlesse boundary in Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government reg ...
and Marlborough, and Torlesse
Torlesse is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Arthur David Torlesse (1902–1995), Royal Navy officer
* Charles Torlesse (1825–1866), New Zealand surveyor
* Elizabeth Torlesse Elizabeth Henrietta Torlesse (1835 – 22 Sep ...
rocks just to the East of the Alpine Fault). The Alpine Fault that corresponds to the line of the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Souther ...
has separated the basement rocks that used to be adjacent by about 480 km.
Separation from Gondwana (Cretaceous-Eocene)
The Australia-New Zealand continental fragment of Gondwana split from the rest of Gondwana in the late Cretaceous time (95–90 Ma). Then around 83 Ma, Zealandia started to separate from Australia forming theTasman Sea
The Tasman Sea ( Māori: ''Te Tai-o-Rēhua'', ) is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer ...
, initially separating from the south. By 75 Ma, Zealandia was essentially separate from Australia and Antarctica, although only shallow seas might have separated Zealandia and Australia in the north. Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s continued to live in New Zealand after it separated from Gondwana, as shown by sauropod footprints from 70 million years ago in Nelson. this meant that dinosaurs had about 20 million years to evolve unique New Zealand species. During the Cretaceous extension large normal faults Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* Normal (2003 film), ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* Normal (2007 film), ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keit ...
formed throughout New Zealand, the Hawks Crag Breccia formed next to scarps and it has become New Zealand's best uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly ...
mineral deposit
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April ...
.
Currently, New Zealand has no native snakes or land mammals (other than bats). Neither marsupials
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
nor placental mammals evolved and reached Australia in time to be on New Zealand when it drifted away 85 million years ago. The evolution and dispersal of snakes is less certain, but there is no hard evidence of them being in Australia before the opening of the Tasman Sea. The multituberculates, another type of mammal which is now extinct, may have been in time to cross the land bridge to New Zealand.
The landmasses continued to separate until early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
times (53 Ma). The Tasman Sea, and part of Zealandia then locked together with Australia to form the Australian Plate (40 Ma), and a new plate boundary was created between the Australian Plate and Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and I ...
. Zealandia ended up at a pivot point between the Pacific and Australian Plates, with spreading in the south, and convergence in the north, where the Pacific Plate was subducted beneath the Australian Plate. A precursor to the Kermadec Arc was created. The convergent part of the plate boundary propagated through Zealandia from the north, eventually forming a proto-Alpine Fault in Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
times (23 Ma). The various ridges and basins north of New Zealand relate to previous positions of the plate boundary.
Sedimentary basins and allochthons (Cretaceous-Recent)

Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is di ...
and deposition has led to much of Zealandia now being covered in sedimentary rocks that formed in swamps and marine sedimentary basins. Much of New Zealand was low lying around Mid Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
-Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but ...
times (40–23 Ma). Swamps became widespread, forming coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
. The land subsided further, and marine organisms produced limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
deposits. Limestone of Oligocene-Early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
age formed in many areas, including the King Country, known for the Waitomo Glowworm Cave
The Waitomo Glowworm Caves attraction is a cave at Waitomo on the North Island of New Zealand. It is known for its population of ''Arachnocampa luminosa,'' a glowworm species found exclusively in New Zealand. This cave is part of the waitomo s ...
. In the South Island, limestone is present in Buller, Nelson, and the West Coast, including the Pancake Rocks at Punakaiki in Oligocene-Early Miocene times (34–15 Ma). It is debated whether all of New Zealand was submerged at this time or if small islands remained as "arks" preserving fauna and flora.
 An
An allochthon
upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a window. A klippe is a solitary outcrop of the nappe in the middle of autochthonous material.
An allochthon, or an alloc ...
is land that formed elsewhere and slid on top of other land (in other words, the material of an enormous landslide). Much of the land of Northland Northland may refer to:
Corporations
* Northland Organic Foods Corporation, headquartered in Saint Paul, Minnesota
* Northland Resources, a mining business
* Northland Communications, an American cable television, telephone and internet service ...
and East Cape were created in this manner. Around 25–22 Ma, Northland and East Cape were adjacent, with East Cape near Whangarei. Northland-East Cape was an undersea basin. Much of the land that now forms Northland-East Cape was higher land to the Northeast (composed of rocks formed 90–25 Ma). The Pacific-Australian plate boundary was further to the Northeast, with the Pacific Plate subducting under the Australian Plate. Layers of rocks were peeled off the higher land, from the top down, and slid Southwest under the influence of gravity, to be stacked the right way up, but in reverse order. Most of the material to slide were sedimentary rocks, however, the last rocks to be slid across were slabs of oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafi ...
( ophiolites), mainly basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
. Widespread volcanic activity also occurred (23–15 Ma), and is intermixed with the foreign rocks. Sedimentary basins formed on the allochthons while they were moving. East Cape was later separated from Northland and moved further south and east to its present position.
Volcanic activity
 Volcanism is recorded in New Zealand throughout its whole geological history. Most volcanism in New Zealand, both modern and ancient, has been caused by the subduction of one tectonic plate under another; this causes melting in the
Volcanism is recorded in New Zealand throughout its whole geological history. Most volcanism in New Zealand, both modern and ancient, has been caused by the subduction of one tectonic plate under another; this causes melting in the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
, the layer of the earth below the crust. This produces a volcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate,
with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...
, composed of mainly basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
, andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
and rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained ( aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The min ...
. Basaltic eruptions tend to be fairly placid, producing scoria cones and lava flows, such as the volcanic cones in the Auckland volcanic field, although Mount Tarawera's violent 1886 eruption was an exception. Andesitic eruptions tend to form steep stratovolcanoes, including mountains such as Ruapehu, Tongariro and Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dis ...
, islands such as Little Barrier, Whakaari / White and Raoul Island
Raoul Island (''Sunday Island'') is the largest and northernmost of the main Kermadec Islands, south south-west of 'Ata Island of Tonga and north north-east of New Zealand's North Island. It has been the source of vigorous volcanic activity ...
s, or submarine seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise a ...
s like Monowai Seamount. Rhyolitic eruptions with large amounts of water tend to cause violent eruptions, producing calderas
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
, such as Lake Taupō and Lake Rotorua. New Zealand also has many volcanoes which are not clearly related to plate subduction including the extinct Dunedin Volcano and Banks Peninsula, and the dormant Auckland Volcanic Field.
Extinct volcanoes
The South Island has no currently active volcanoes. However, in the lateCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
(100–65 Ma), there was widespread volcanic activity in Marlborough, West Coast, Canterbury and Otago; and in Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
times (40 Ma), there was volcanic activity in Oamaru. The most well known Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
volcanic centres are the intra-plate Dunedin Volcano and Banks Peninsulas. The Dunedin Volcano which later eroded to form Otago Peninsula near Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. Th ...
was built up by a series of mainly basaltic intra-plate volcanic eruptions in Miocene times (16–10 Ma). Banks Peninsula near Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon Rive ...
was built from two mainly basaltic intra-plate volcanoes in Miocene times (12–6 Ma and 9.5–7.5 Ma), corresponding to the Lyttelton / Whakaraupo and Akaroa
Akaroa is a small town on Banks Peninsula in the Canterbury Region of the South Island of New Zealand, situated within a harbour of the same name. The name Akaroa is Kāi Tahu Māori for "Long Harbour", which would be spelled in standa ...
Harbours. Southland's Solander Islands / Hautere were active around 1 to 2 million years ago. There are also minor volcanic from a similar time period throughout Canterbury, Otago and also on the Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) ( Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about t ...
.
 Intra-plate basaltic volcanic eruptions also occurred in the North Island, near the Bay of Islands in Northland, in the Late Miocene (10 Mya), and again more recently (0.5 Mya). The South Auckland volcanic field was active in
Intra-plate basaltic volcanic eruptions also occurred in the North Island, near the Bay of Islands in Northland, in the Late Miocene (10 Mya), and again more recently (0.5 Mya). The South Auckland volcanic field was active in Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed ...
times (1.5–0.5 Ma). The Auckland volcanic field started erupting around 250,000 years ago. It includes around 50 distinct eruptions, with most of the prominent cones formed in the last 30,000 years, and the most recent eruption, which formed Rangitoto Island, around 600 years ago. The field is currently dormant and further eruptions are expected. Over time the volcanic field has slowly been drifting northwards.
Volcanism in the North Island has been dominated by a series of volcanic arcs which have evolved into the still active Taupō Volcanic Zone
The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand that has been active for the past two million years and is still highly active.
Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward thro ...
. Over time, volcanic activity has moved south and east, as the plate boundary moved eastward. This started in Miocene times (23 Ma) when a volcanic arc became active to the west of Northland, and gradually moved South down to New Plymouth
New Plymouth ( mi, Ngāmotu) is the major city of the Taranaki region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after the English city of Plymouth, Devon from where the first English settlers to New Plymouth migrated. Th ...
, where Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dis ...
is still active. It produced mainly andesitic strato-volcanoes. The Northland volcanoes include the volcanoes that produced the Waipoua Plateau (site of the Waipoua Forest) and the Kaipara Volcano. The Waitakere Volcano (22–16 Ma) has mainly been eroded, but conglomerate
Conglomerate or conglomeration may refer to:
* Conglomerate (company)
* Conglomerate (geology)
* Conglomerate (mathematics)
In popular culture:
* The Conglomerate (American group), a production crew and musical group founded by Busta Rhymes
** Co ...
from the volcano forms the Waitākere Ranges, and produced most of the material that makes up the Waitemata sandstones and mudstones. Lahars produced the coarser Parnell Grit. Notable visible volcanoes in the Waikato include Karioi and Pirongia
Pirongia is a small town in the Waipa District of the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is 12 kilometres to the west of Te Awamutu, on the banks of the Waipā River, close to the foot of the 962 metre Mount Pirongia, which lies in ...
(2.5 Ma). The volcanoes off the West coast of the North Island, together with Taranaki and the Tongariro Volcanic Centre, are responsible for the black iron sand on many of the beaches between Taranaki and Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
.
Shortly after (18 Ma), a volcanic arc developed further east to create the Coromandel Ranges and undersea Colville Ridge. The initial activity was andesitic but later became rhyolitic (12 Ma). In the Kauaeranga Valley, volcanic plugs remain, as does a lava lake that now forms the top of Table Mountain. Active geothermal systems, similar to those that now exist near Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompa ...
, were present around 6 Ma, and produced the gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
deposits that were later mined
Mined may refer to:
* Mined (text editor), a terminal-based text editor
* Mining, the extraction of valuable geological materials from the Earth
See also
* Mind (disambiguation)
* Mine (disambiguation)
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer ...
in the Coromandel gold rush. Later (5–2 Ma), volcanic activity moved further south to form the Kaimai Range.
Active volcanoes and geothermal areas
After this, activity shifted further East to the Taupō Volcanic Zone, which runs from the Tongariro Volcanic Centre ( Ruapehu and Tongariro), through Taupō,Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompa ...
, and out to sea to form the Kermadec Ridge. Activity was initiated around 2 Ma, and continues to this day. The Tongariro Volcanic Centre is composed of andesitic volcanoes, while the areas around Taupō and Rotorua are largely rhyolitic with minor basalt. Early eruptions between Taupō and Rotorua around 1.25 Ma, and 1 Ma, were large enough to produce an ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surro ...
sheet that reached Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
, Napier Napier may refer to:
People
* Napier (surname), including a list of people with that name
* Napier baronets, five baronetcies and lists of the title holders
Given name
* Napier Shaw (1854–1945), British meteorologist
* Napier Waller (1893–19 ...
, and Gisborne. This includes vast pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
deposits generated from eruptions in the Taupō Volcanic Zone occur throughout the central North Island, Bay of Plenty, Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, t ...
, King Country and Manawatū-Whanganui regions. Every so often, there are swarms of earthquakes within an area of the Taupō Volcanic Zone, which last for years. These earthquake swarms indicate that some movement of magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
is occurring below the surface. While they have not resulted in an eruption in recent times, there is always the potential for a new volcano to be created, or a dormant volcano to come to life.
 The Tongariro Volcanic Centre developed over the last 275,000 years and contains the active andesitic volcanic cones of Ruapehu, Tongariro, and Ngauruhoe (really a side cone of Tongariro). Ruapehu erupts about once a decade, and while the eruptions cause havoc for skiers, plane flights and hydroelectric dams, the eruptions are relatively minor. However, the sudden collapse of the crater wall caused major problems when it generated a lahar in 1953, that destroyed a rail bridge, and caused 151 deaths at Tangiwai. The last significant eruption was 1995–96. Ngauruhoe last erupted 1973–75. Taranaki is a perfectly formed andesitic strato-volcano, that last erupted in 1755.
Lake Taupō, the largest lake in the North Island, is a volcanic caldera, responsible for rhyolitic eruptions about once every 1,000 years. The largest eruption in the last 65,000 years was the cataclysmic
The Tongariro Volcanic Centre developed over the last 275,000 years and contains the active andesitic volcanic cones of Ruapehu, Tongariro, and Ngauruhoe (really a side cone of Tongariro). Ruapehu erupts about once a decade, and while the eruptions cause havoc for skiers, plane flights and hydroelectric dams, the eruptions are relatively minor. However, the sudden collapse of the crater wall caused major problems when it generated a lahar in 1953, that destroyed a rail bridge, and caused 151 deaths at Tangiwai. The last significant eruption was 1995–96. Ngauruhoe last erupted 1973–75. Taranaki is a perfectly formed andesitic strato-volcano, that last erupted in 1755.
Lake Taupō, the largest lake in the North Island, is a volcanic caldera, responsible for rhyolitic eruptions about once every 1,000 years. The largest eruption in the last 65,000 years was the cataclysmic Oruanui Eruption
The Oruanui eruption of New Zealand's Taupō Volcano (also known as the Kawakawa eruption or Kawakawa/Oruanui event) was the world's most recent supereruption.}
Eruption
With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, it is one of the largest eruptio ...
26,500 years ago, producing 530 cubic kilometres of magma. The most recent eruption, around 233 AD was also a major event, the biggest eruption worldwide in the last 5,000 years. The eruption caused a pyroclastic flow that devastated the land from Waiouru to Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompa ...
in 10 minutes.
The Ōkataina Volcanic Centre, to the East of Rotorua, is also responsible for major cataclysmic rhyolitic eruptions. The last eruption, of Tarawera and Lake Rotomahana in 1886, was a relatively minor eruption, which was thought to have destroyed the famous Pink and White Terraces
The Pink and White Terraces ( and ), were natural wonders of New Zealand. They were reportedly the largest silica sinter deposits on earth. Until recently, they were lost and thought destroyed in the 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera, while new hy ...
, and covered much of the surrounding countryside in ash, killing over 100 people. In 2017 researchers rediscovered the locations of the Pink and White Terraces using a forgotten survey from 1859. Many lakes around Rotorua are calderas
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
from rhyolitic eruptions. For example, Lake Rotorua erupted around 13,500 years ago.
A line of undersea volcanoes extends out along the Kermadec Ridge. Whakaari / White Island
Whakaari / White Island (, mi, Te Puia Whakaari, lit. "the dramatic volcano"), also known as White Island or Whakaari, is an active andesite stratovolcano situated from the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, in the Bay of Plen ...
, in the Bay of Plenty, represents the southern end of this chain and is a very active andesitic volcano, erupting with great frequency. It has the potential to cause a tsunami in the Bay of Plenty, as does the dormant Mayor Island / Tūhua volcano.
The Taupō Volcanic Zone is known for its geothermal activity. For example, Rotorua and the surrounding area have many areas with geysers
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only ...
, silica terraces, fumaroles, mud-pools, hot springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by c ...
, etc. Notable geothermal areas include Whakarewarewa, Tikitere, Waimangu
Waimangu is a place in Rotorua, New Zealand that got affected by the 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera. It is known for Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley. Waimangu is a thirty minutes drive from Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty reg ...
, Waiotapu, Craters of the Moon Craters of the Moon may refer to:
* Lunar craters, craters on the Earth's Moon
* Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve, a volcanic preserve in Idaho
* Craters of the Moon (geothermal site)
Craters of the Moon Thermal Area (or ''Kara ...
and Orakei Korako. Geothermal energy is used to generate electricity at Wairakei, near Taupō. Hot pools abound throughout New Zealand. Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pre ...
is used to generate electricity in the Taupō Volcanic Zone.
Modern tectonic setting and earthquakes
 New Zealand is currently astride the convergent boundary between the Pacific and Australian Plates. Over time, the relative motion of the plates has altered and the current configuration is geologically recent. Currently the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Australian Plate from around
New Zealand is currently astride the convergent boundary between the Pacific and Australian Plates. Over time, the relative motion of the plates has altered and the current configuration is geologically recent. Currently the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Australian Plate from around Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
in the north, through the Tonga Trench, Kermadec Trench, and Hikurangi Trough
The Hikurangi Trench, also called the Hikurangi Trough, is an oceanic trench in the bed of the Pacific Ocean off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, lying between the southern end of the Cook Strait and the Chatham Rise. It is the ...
to the east of the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
of New Zealand, down to Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
. Through most of the South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasma ...
, the plates slide past each other ( Alpine Fault), with slight obduction
Obduction is a geological process whereby denser oceanic crust (and even upper mantle) is scraped off a descending ocean plate at a convergent plate boundary and thrust on top of an adjacent plate. When oceanic and continental plates converge, ...
of the Pacific Plate over the Australian Plate, forming Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Souther ...
. From Fiordland south, the Australian Plate subducts under the Pacific Plate forming the Puysegur Trench. This configuration has led to volcanism and extension in the North Island forming the Taupō Volcanic Zone and uplift in the South Island forming the Southern Alps.
The Pacific Plate is colliding with the Australian Plate at a rate of about 40 mm/yr. The East coast of the North Island is being compressed and lifted by this collision, producing the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
and Marlborough Fault Systems. The East Coast of the North Island is also rotating clockwise, relative to Northland, Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
and Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dis ...
, stretching the Bay of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty ( mi, Te Moana-a-Toi) is a region of New Zealand, situated around a bight of the same name in the northern coast of the North Island. The bight stretches 260 km from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaw ...
, and producing the Hauraki Rift (Hauraki Plains and Hauraki Gulf) and Taupō Volcanic Zone. The East Coast of the South Island is sliding obliquely towards the Alpine Fault, relative to Westland, causing the Southern Alps to rise about 10 mm/yr (although they are also worn down at a similar rate). The Hauraki Plains, Hamilton, Bay of Plenty, Marlborough Sounds, and Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon Rive ...
are sinking. The Marlborough Sounds are known for their sunken mountain ranges. As Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by m ...
rises, and Marlborough sinks, Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
is being shifted further south.
Great stress is built up in the earth's crust due to the constant movement of the tectonic plates. This stress is released by earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s, which can occur on the plate boundary or on any of thousands of smaller faults throughout New Zealand. Because the Pacific Plate is subducting under the eastern side of the North Island, there are frequent deep earthquakes east of a line from the Bay of Plenty to Nelson (the approximate edge of the subducted plate), with the earthquakes being deeper to the west, and shallower to the east. Because the Australian Plate is subducting under the Pacific Plate in Fiordland, there are frequent deep earthquakes near Fiordland, with the earthquakes being deeper to the east and shallower near the west.
Shallow earthquakes are more widespread, occurring almost everywhere throughout New Zealand (especially the Bay of Plenty, East Cape to Marlborough, and Alpine Fault). However, Northland, Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, t ...
, and Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government reg ...
are relatively stable. Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
had been without a major earthquake in recorded history until the 7.1 Canterbury earthquake on 4 September 2010. The volcanic activity in the central North island also creates many shallow earthquakes.
Paleoclimate of New Zealand
Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describ ...
(2.9 mya) Zealandia has experienced climate either cooler or only slightly warmer than today.
In the Cretaceous, New Zealand was positioned at 80 degrees south at the boundary between Antarctica and Australia. But it was covered in trees as the climate of 90 million years ago was much warmer and wetter than today. During the warm Eocene Period vast swamps covered New Zealand which became coal seams in Southland and Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, t ...
. In the Miocene there are paleontological records of warm lakes in Central Otago with palm trees and small land mammals.
Over the past 30,000 years three major climate events are recorded in New Zealand, the last glacial maximum's coldest period from 28 to 18,000 years ago, a transitional period from 18 to 11,000 years ago and the Holocene Inter Glacial which has been occurring for the past 11,000 years. Throughout the last glacial maximum, global sea levels were about lower than present levels. When this happened the North Island, South Island, and Stewart Island
Stewart Island ( mi, Rakiura, ' glowing skies', officially Stewart Island / Rakiura) is New Zealand's third-largest island, located south of the South Island, across the Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land ar ...
were joined. Temperatures dropped by about 4–5 °C. Much of the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Souther ...
and Fiordland were glaciated, but the rest of New Zealand was largely ice-free. The land to the North of Hamilton was forested, but much of the rest of New Zealand was covered in grass or shrubs, due to the cold and dry climate. This lack of vegetation cover lead to greater wind erosion and the deposition of loess (windblown dust).
The study of New Zealand's paleoclimate has settled some of the debate regarding links between the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
(LIA) in the Northern Hemisphere and the climate in New Zealand at the same time. The key facts to emerge are that New Zealand did experience a noticeable cooler climate, but at a slightly later date than in the Northern Hemisphere.
Geological hazards
 New Zealand suffers from many natural hazards, including earthquakes and tsunamis, volcanic and hydrothermal eruptions and
New Zealand suffers from many natural hazards, including earthquakes and tsunamis, volcanic and hydrothermal eruptions and landslides
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, ...
.
The largest earthquake in New Zealand was an M8.2 event in the Wairarapa
The Wairarapa (; ), a geographical region of New Zealand, lies in the south-eastern corner of the North Island, east of metropolitan Wellington and south-west of the Hawke's Bay Region. It is lightly populated, having several rural service t ...
, in 1855, and the most deaths (261) occurred in a M7.8 earthquake in Hawkes Bay in 1931. Widespread property damage was caused by the 2010 Canterbury earthquake, which measured 7.1; The M6.3 aftershock of 22 February 2011 ( 2011 Canterbury earthquake) resulted in 185 fatalities. Most recently, the M7.8 Kaikōura earthquake struck just after midnight on November 14, 2016, killing two people in the remote Kaikoura area northeast of Christchurch. Numerous aftershocks of M5.0 or greater are spread over a large area between Wellington and Culverden.
New Zealand is at risk from tsunamis that are generated from both local and international faults. The eastern coast of New Zealand is most at risk as the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
is more tectonically active than the Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea ( Māori: ''Te Tai-o-Rēhua'', ) is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer ...
. Locally the faults along the North Island's east coast provide the greatest risk. Minor tsunamis have occurred in New Zealand from earthquakes in Chile, Alaska and Japan.
There are many potentially dangerous volcanoes in the Taupō Volcanic Zone. The most severe volcanic eruption since the arrival of Europeans is the Tarawera eruption in 1886. A lahar from Mount Ruapehu destroyed a bridge and derailed a train in December 1953, killing 151 people. Even a minor eruption at Ruapehu could cause the loss of electricity for Auckland, due to ash on the power lines, and in the Waikato River (stopping the generation of hydroelectric power).
Many parts of New Zealand are susceptible to landslides, particularly due to deforestation and the high earthquake risk. Much of the North Island is steep, and composed of soft mudstone known as papa, that easily generates landslides.
Geological resources
New Zealand main geological resources are coal, gold, oil, and natural gas.Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
has been mined in Northland, the Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, t ...
, Taranaki, Nelson and Westland, Canterbury, Otago, and Southland. The West Coast contains some of New Zealand's best bituminous coal
Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the coal seam, ...
. The largest coal deposits occur in Southland. Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
has been mined in the Coromandel and Kaimai Ranges (especially the Martha Mine at Waihi), Westland, Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and trib ...
, and Eastern Otago (especially Macraes Mine), and on the west coast of the South Island. The only area in New Zealand with significant known oil and gas deposits is the Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dis ...
area, but many other offshore areas have the potential for deposits. Iron sand is also plentiful on the west coast from Taranaki to Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
. Jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
( Pounamu in Māori) from South Island ophiolites continues to be extracted, mostly from alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
, and worked for sale. Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidat ...
reservoirs are extracted throughout the country, but are particularly valuable in the dryer eastern regions of both the North and South Islands.
History of New Zealand geology
The detailed study of New Zealand's geology began with Julius von Haast and Ferdinand von Hochstetter who created numerous regional geological maps of the country during resource exploration in the mid-late 1800s. In 1865James Hector
Sir James Hector (16 March 1834 – 6 November 1907) was a Scottish-New Zealand geologist, naturalist, and surgeon who accompanied the Palliser Expedition as a surgeon and geologist. He went on to have a lengthy career as a government employe ...
was appointed to found the Geological Survey of New Zealand. Patrick Marshall
Patrick Marshall (1869 – November 1950) was a geologist who lived in New Zealand. Benson W. N. (1951). "Patrick Marshall". ''Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New Zealand'' 79''152–155
Early life
Marshall was born on 22 ...
coined the terms '' andesite line'' and ''ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surro ...
'' in the early 1900s while working in the Taupō Volcanic Zone. Harold Wellman
Harold William Wellman (25 March 1909 – 28 April 1999) was an English-born New Zealand geologist known for his work on plate tectonics. He is notable for his discovery of South Island's Alpine Fault. Wellman became a Fellow of the Royal Society ...
discovered the Alpine Fault and its 480 km offset in 1941. Even though Wellman proved that large blocks of land could move considerable distances, the New Zealand geological survey was largely a late adopter of plate tectonics.
Charles Cotton
Charles Cotton (28 April 1630 – 16 February 1687) was an English poet and writer, best known for translating the work of Michel de Montaigne from the French, for his contributions to '' The Compleat Angler'', and for the influential '' The C ...
became an international authority on geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
using New Zealand active tectonics and variable climate to create universally applicably rules. His major works becoming standard text books in New Zealand and overseas. Charles Fleming established the Wanganui Basin as a classic site for studying past sea levels and climates. In 1975 the palaeontologist Joan Wiffen discovered the first dinosaur fossils in New Zealand.
The Geological Survey of New Zealand now known as GNS Science has done extensive mapping through New Zealand at 1:250,000 and 1:50:000 scales. The most modern map series are the "QMAPs" at 1:250,000. New Zealand's geological research is published by GNS Science, in the New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, and internationally. A Map showing the distribution of earthquakes in New Zealand can be obtained from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Current earthquake and volcanic activity can be obtained from the GeoNet website.– Current New Zealand Earthquake and Volcanic Activity. The universities of
Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
, Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
, Massey, Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government reg ...
, Victoria and Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, t ...
are activity engaged in geological research in New Zealand, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ...
, the wider South Pacific and elsewhere.
See also
* Alpine Fault * Geography of New Zealand * Hikurangi Trench * Indo-Australian Plate * Kaikōura Canyon * List of dinosaurs of New Zealand * List of earthquakes in New Zealand *List of rock formations in New Zealand
This is a list of rock formations in New Zealand based on their aesthetic and cultural importance. New Zealand's geomorphology is formed through an interaction between uplift, erosion and the underlying rock type. Most of the notable examples l ...
* Marlborough Fault System
* Natural history of New Zealand
*New Zealand geologic time scale
While also using the international geologic time scale, many nations–especially those with isolated and therefore non-standard prehistories–use their own systems of dividing geologic time into epochs and faunal stages. In New Zealand, these epo ...
* North Island Fault System
*Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and I ...
* Stratigraphy of New Zealand
* Zealandia (continent)
Regional geology
* Geology of the Northland Region *Geology of the Auckland Region
The Auckland Region of New Zealand is built on a basement of greywacke rocks that form many of the islands in the Hauraki Gulf, the Hunua Ranges, and land south of Port Waikato. The Waitākere Ranges in the west are the remains of a large ande ...
** Auckland volcanic field
*Geology of the Waikato-King Country Region The Waikato and King Country regions of New Zealand are built upon a basement of greywacke rocks, which form many of the hills. Much of the land to the west of the Waikato River and in the King Country to the south has been covered by limestone and ...
*Taupō Volcanic Zone
The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand that has been active for the past two million years and is still highly active.
Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward thro ...
**Whakaari / White Island
Whakaari / White Island (, mi, Te Puia Whakaari, lit. "the dramatic volcano"), also known as White Island or Whakaari, is an active andesite stratovolcano situated from the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, in the Bay of Plen ...
** Rotorua Caldera
** Mount Tarawera
** Taupō Volcano
** Mount Tongariro
** Mount Ngauruhoe
**Mount Ruapehu
Mount Ruapehu (; ) is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is northeast of Ohakune and southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupō, within the Tong ...
*Geology of the Raukumara Region The Raukumara Region of New Zealand corresponds to the East Cape of the North Island, and associated mountain ranges.
To the east of the North Island is the Hikurangi Trough, a collision zone between the Pacific Plate and the Australian Plate. The ...
* Geology of Taranaki
** Mount Taranaki
* Geology of the Wellington Region
*Geology of the Tasman District
The Tasman Region, and the small adjoining Nelson Region, form one of the more geologically interesting regions of New Zealand. It contains the oldest rocks of anywhere on New Zealand's main islands. It contains all the main terranes that make u ...
*Geology of Canterbury, New Zealand
Canterbury in New Zealand is the portion of the South Island to the east of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana, from the Waiau Uwha River in the north, to the Waitaki River in the south (this is smaller than the area administered by Env ...
*Geology of the West Coast Region
The geology of the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island is divided in two by the Alpine Fault, which runs through the Region in a North-East direction. To the West of the fault Paleozoic basement rocks are interluded by plutones and both ar ...
References
Further reading
*Graham, Ian J. et al.;''A continent on the move : New Zealand geoscience into the 21st century'' – The Geological Society of New Zealand in association with GNS Science, 2008. *Campbell, Hamish; Hutching, Gerard; ''In Search of Ancient New Zealand'', Penguin Books in association with GNS Science, 2007, *Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New ZealanAn Overview of New Zealand Geology
*''Hot Stuff to Cold Stone'' – Aitken, Jefley; GNS Science, 1997. . *''Rocked and Ruptured'' – Aitken, Jefley; Reed Books, in association with GNS Science, 1999. . *''The Rise and Fall of the Southern Alps'' – Coates, Glenn; Canterbury University Press, 2002. . *''Plate Tectonics for Curious Kiwis'' – Aitken, Jefley; GNS Science, 1996. . *''Lava and Strata: A guide to the volcanoes and rock formations of Auckland'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil & Kermode, Les; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 2000. . *''Vanishing volcanoes : a guide to the landforms and rock formations of Coromandel Peninsula'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 1992. . *''Reading the rocks : a guide to geological features of the Wairarapa Coast'' – Homer, Lloyd; Moore, Phil & Kermode, Les; Landscape Publications and the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, 1989.
External links
from GNS Science
Geological Society of New Zealand
A simple geological map of New Zealand
from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand {{Oceania topic, Geology of