|
Hikurangi Trench
The Hikurangi Trench, also called the Hikurangi Trough, is an oceanic trench in the bed of the Pacific Ocean off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, lying between the southern end of the Cook Strait and the Chatham Rise. It is the southward continuation of the much deeper Kermadec Trench. It lies in the Hikurangi Margin subduction zone, which is the southern extension of the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone. The Hikurangi Margin is the subduction zone where the thick oceanic Hikurangi Plateau is subducting beneath continental crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. By contrast, the Kermadec and Tonga trenches represent the parts of the subduction zone where oceanic crust of the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath oceanic crust of the Indo-Australian Plate. Although shallower than the trenches north of it, the Hikurangi Trench reaches depths of 3,000 metres as close as 80 kilometres from shore. Its maximum depth is about .Keith B. Lewis, Jean-Yves Collott and Serge E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
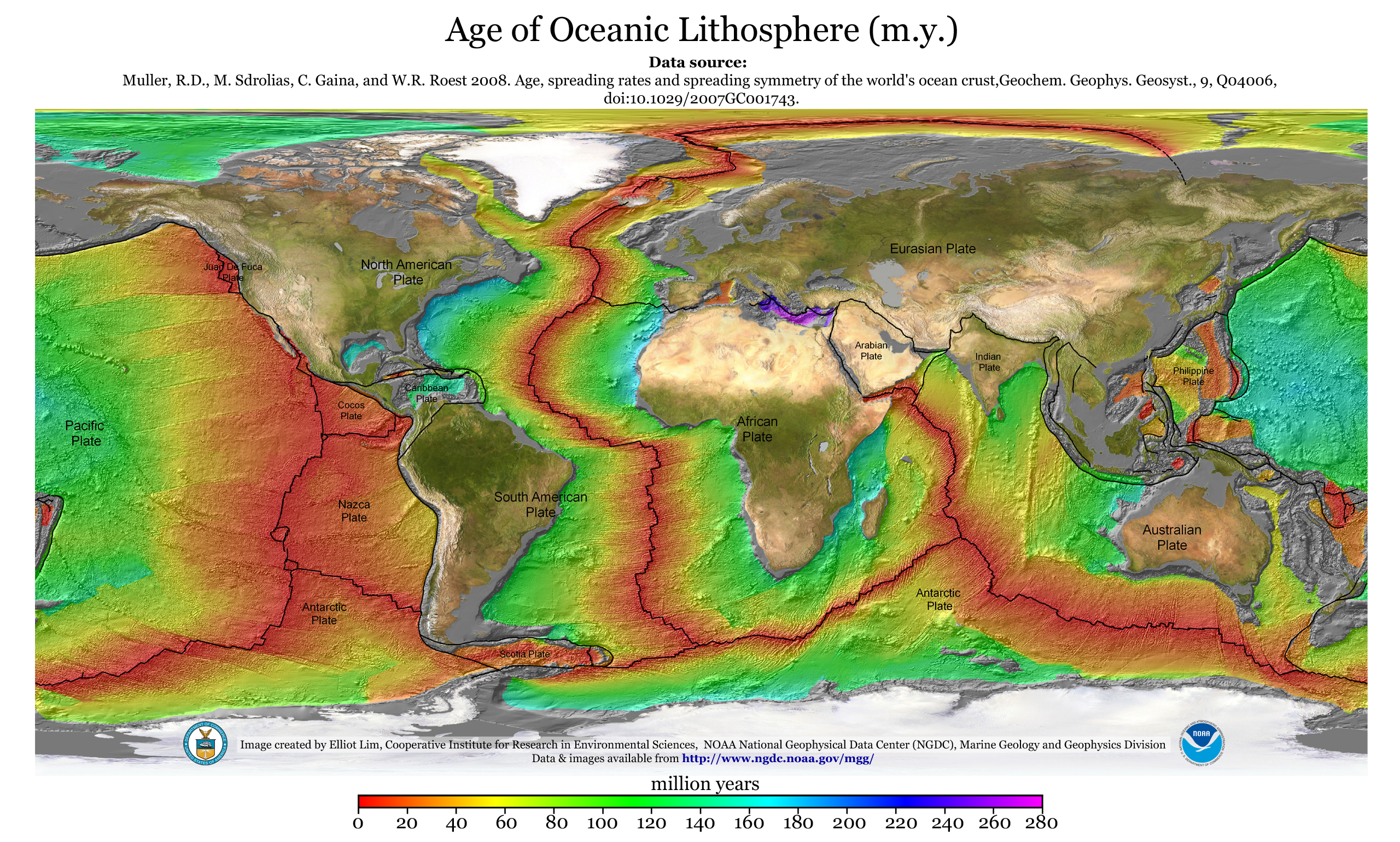
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived from earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of The New Zealand Seabed
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
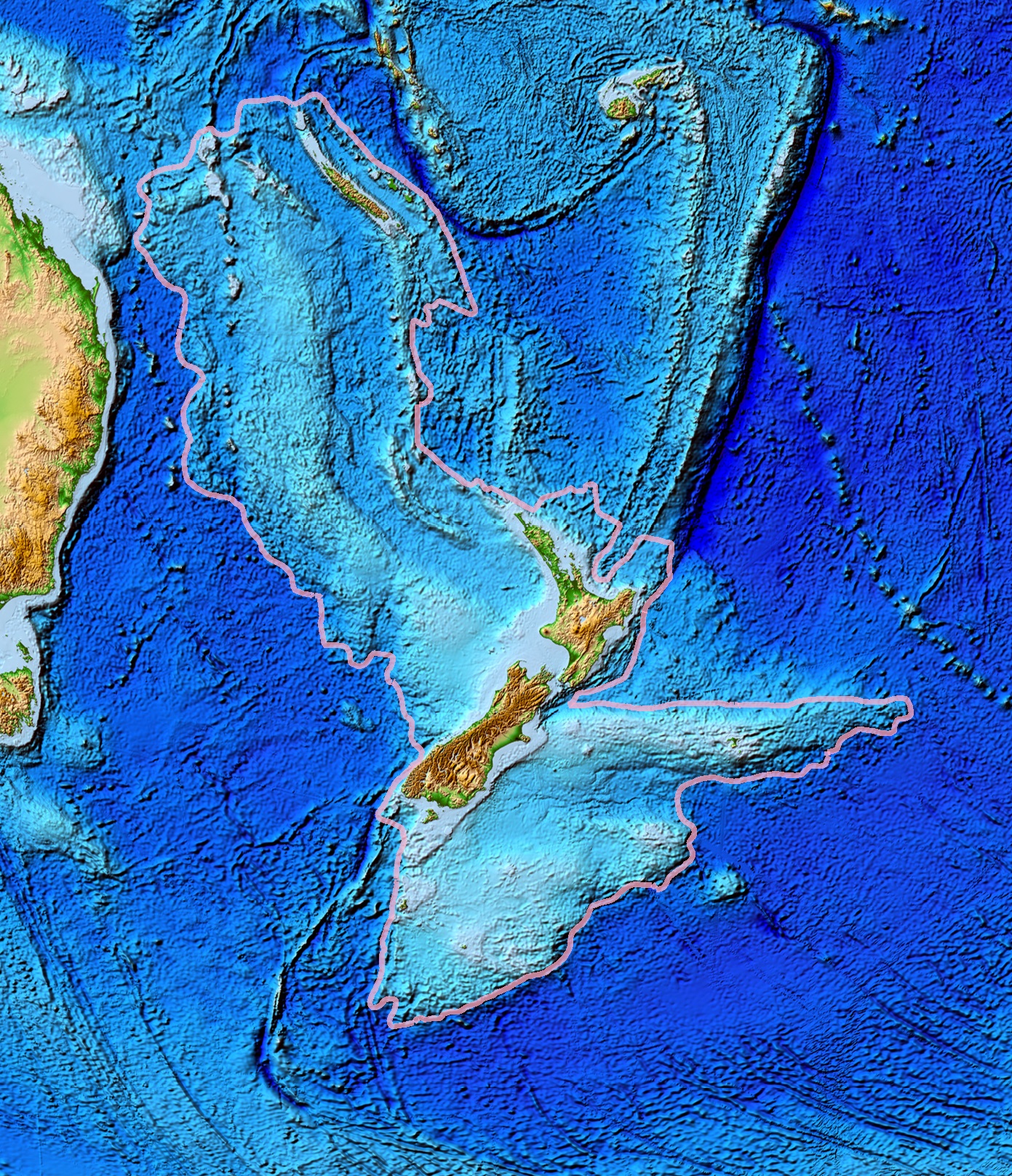
Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., 2004, Evolving force balance during incipient subduction: Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, v. 5, Q07001, https://doi.org/10.01029/02003GC000681 It has been described variously as a submerged continent, a continental fragment (or microcontinent), and a continent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995, and satellite imagery shows it to be almost the size of Australia. A 2021 study suggests Zealandia is 1 billion years old, about twice as old as geologists previously thought. By approximately 23 million years ago the landmass may have been completely submerged. Today, most of the landmass (94%) remains submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean. New Zealand is the largest part of Zealandia that is above sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaikōura Canyon
The Kaikōura Canyon is a geologically active submarine canyon located southwest of the Kaikōura Peninsula off the northeastern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is long, and is generally U-shaped. The canyon descends into deep water and merges into an ocean channel system that can be traced for hundreds of kilometres across the deep ocean floor. At the head of the Kaikōura Canyon, the depth of water is around , but it drops rapidly to and continues down to around deep where it meets the Hikurangi Channel. Sperm whales can be seen close to the coast south of Goose Bay, because the deep water of the Kaikōura Canyon is only off the shoreline in this area. Studies of the Kaikōura Canyon have found that it is a highly productive ecosystem with 10 to 100 times the density of marine life found in other deep sea habitats. Prior to the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake, studies had indicated the likelihood of a submarine landslide in the canyon, potentially producing a ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of New Zealand
The geology of New Zealand is noted for its volcanic activity, earthquakes and geothermal areas because of its position on the boundary of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plates. New Zealand is part of Zealandia, a microcontinent nearly half the size of Australia that broke away from the Gondwanan supercontinent about 83 million years ago. New Zealand's early separation from other landmasses and subsequent evolution have created a unique fossil record and modern ecology. New Zealand's geology can be simplified into three phases. First the basement rocks of New Zealand formed. These rocks were once part of the super-continent of Gondwana, along with South America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Antarctica and Australia. The rocks that now form the, mostly submerged, continent of Zealandia were then nestled between Eastern Australia and Western Antarctica. Secondly New Zealand drifted away from Gondwana and many sedimentary basins formed, which later became the sedimentary rocks cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally very unlikely that a deforming body will experience "pure" shortening or "pure" strike-slip. The relative amounts of shortening and strike-slip can be expressed in the convergence angle alpha which ranges from zero (ideal strike-slip) to 90 degrees (ideal convergence). During shortening, unless material is lost, transpression produces vertical thickening in the crust. Transpression that occurs on a regional scale along plate boundaries is characterized by oblique convergence. More locally, transpression occurs within restraining bends in strike-slip fault zones. Transpressional structures Transpressional shear zones are characterized by an association of structures that suggest zone-normal shortening and zone-parallel shearing. Commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
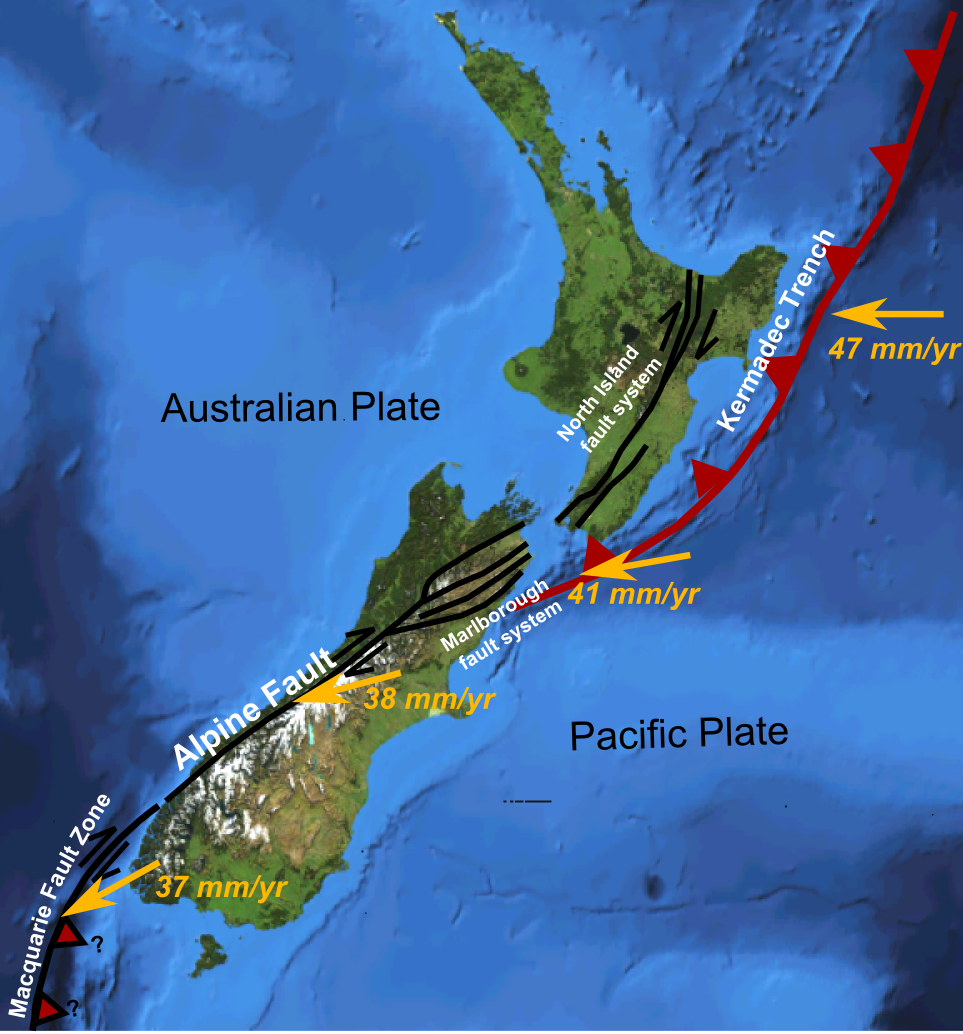
Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fault over the last 12 million years in a series of earthquakes. However, most of the motion on the fault is strike-slip (side to side), with the Tasman district and West Coast moving North and Canterbury and Otago moving South. The average slip rates in the fault's central region are about 38 mm a year, very fast by global standards. The last major earthquake on the Alpine Fault was in c. 1717 AD, and the probability of another one occurring within the next 50 years is estimated at about 75 percent. Geographic extent and plate motion ThPacific Plate and Indo-Australian Plate boundaryforms the Macquarie Fault Zone in the Puysegur Trench off the southwestern corner of the South Island and comes onshore as the Alpine Fault just nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marlborough Fault System
The Marlborough Fault System is a set of four large dextral strike-slip faults and other related structures in the northern part of South Island, New Zealand, which transfer displacement between the mainly transform plate boundary of the Alpine fault and the mainly destructive boundary of the Kermadec Trench, and together form the boundary between the Australian and Pacific Plates. Geometry The Marlborough Fault System consists of four main dominantly strike-slip fault strands, which together carry almost all of the displacement associated with the plate boundary. Other smaller faults form as splays of these main faults or accommodate deformation of the crust between them, such as the Newton and Hura Faults at the western end of the Hope Fault and the Jordan Thrust that formed the Seaward Kaikoura Range. The dextral strike-slip across this zone has also involved clockwise rotation of the intervening fault blocks of about 20° since the early Pliocene. Development The Marlbor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whales
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and porpoises. Dolphins and porpoises may be considered whales from a formal, cladistic perspective. Whales, dolphins and porpoises belong to the order Cetartiodactyla, which consists of even-toed ungulates. Their closest non-cetacean living relatives are the hippopotamuses, from which they and other cetaceans diverged about 54 million years ago. The two parvorders of whales, baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti), are thought to have had their last common ancestor around 34 million years ago. Mysticetes include four extant (living) families: Balaenopteridae (the rorquals), Balaenidae (right whales), Cetotheriidae (the pygmy right whale), and Eschrichtiidae (the grey whale). Odontocetes include the Monodontidae (belugas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marlborough Region
Marlborough District or the Marlborough Region (, or ''Tauihu''), commonly known simply as Marlborough, is one of the 16 regions of New Zealand, located on the northeast of the South Island. Marlborough is a unitary authority, both a district and a region. Marlborough District Council is based at Blenheim, the largest town. The unitary region has a population of . Marlborough is known for its dry climate, the Marlborough Sounds, and Sauvignon blanc wine. It takes its name from the earlier Marlborough Province, which was named after General The 1st Duke of Marlborough, an English general and statesman. Geography Marlborough's geography can be roughly divided into four sections. The south and west sections are mountainous, particularly the southern section, which rises to the peaks of the Kaikōura Ranges. These two mountainous regions are the final northern vestiges of the ranges that make up the Southern Alps, although that name is rarely applied to mountains this far no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |