Geology Of New Mexico on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The geology of
 New Mexico is entirely landbound, with just 0.2% of the state covered with water, and most of the state has an arid to semiarid climate. Much of the state is mountainous, except for the easternmost
New Mexico is entirely landbound, with just 0.2% of the state covered with water, and most of the state has an arid to semiarid climate. Much of the state is mountainous, except for the easternmost

 The crust underlying the state formed between 1.7 and 1.8 billion years ago as
The crust underlying the state formed between 1.7 and 1.8 billion years ago as

 New Mexico at the start of the Paleozoic was dominated by the
New Mexico at the start of the Paleozoic was dominated by the
 The Mesozoic began with the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The
The Mesozoic began with the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The
 The Laramide Orogeny changed the topography of New Mexico into one of high uplifts and deep basins. The basins began to fill with sediments during the
The Laramide Orogeny changed the topography of New Mexico into one of high uplifts and deep basins. The basins began to fill with sediments during the
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
includes bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
exposures of four physiographic provinces
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific charact ...
, with ages ranging from almost 1800 million years ( Ma) to nearly the present day. Here the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
, southern Rocky Mountains
The Southern Rocky Mountains are a major subregion of the Rocky Mountains of North America located in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Wyoming, the central and western portions of Colorado, the northern portion of New Mexico, and ex ...
, Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of ...
, and Basin and Range
Basin and range topography is characterized by alternating parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is a result of crustal extension due to mantle upwelling, gravitational collapse, crustal thickening, or relaxation of confining stresses. The e ...
Provinces meet, giving the state great geologic diversity.
The geologic history of the state began with its assembly during the Yavapai
The Yavapai are a Native American tribe in Arizona. Historically, the Yavapai – literally “people of the sun” (from ''Enyaava'' “sun” + ''Paay'' “people”) – were divided into four geographical bands who identified as separate, i ...
and Mazatzal orogenies
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted t ...
1750 to 1650 million years ago (Mya
Mya may refer to:
Brands and product names
* Mya (program), an intelligent personal assistant created by Motorola
* Mya (TV channel), an Italian Television channel
* Midwest Young Artists, a comprehensive youth music program
Codes
* Burmese ...
). This was followed by 200 million years of tectonic quiescence that ended in the Picuris orogeny
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and int ...
. This event transformed the New Mexico crust into mature continental crust. Over a thousand million years of tectonic quiescence followed, ending with the rise of the Ancestral Rocky Mountains
The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through cen ...
in Pennsylvanian time, 300 Mya. The Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
and most of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
were another interval of relative tectonic quiescence, where gradual subsidence deposited formations that preserve an impressive stratigraphic record across the state. This ended with the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
, beginning around 70 Mya, which elevated most of the mountain ranges of modern New Mexico and was accompanied by violent volcanic activity. The opening of the Rio Grande rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihua ...
commenced around 30 Mya, and was followed by late Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
volcanism along the Jemez Lineament
The Jemez Lineament is a chain of late Cenozoic volcanic fields, long, reaching from the Springerville and White Mountains volcanic fields in East-Central Arizona to the Raton-Clayton volcanic field in Northeastern New Mexico.
The lineament ...
, particularly in the Jemez volcanic field
The Jemez Mountains are a group of mountains in Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico, United States.
Numerous Puebloan Indian tribes have lived in the Jemez Mountains region since before the Spanish arrived in New Mexico. T ...
.
Most of New Mexico has a semiarid to arid climate, and ground water in aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
is an important geologic resource for farmers and municipal areas. In 2019, oil and gas production yielded $3.1 billion in oil and gas taxes and revenues for the state. Mining has historically also been important.
Geologic hazards are infrequent in New Mexico, but potential dangers include erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
or flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
ing in arroyos; arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
or other contamination of ground water or soil; sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s or other subsidence; earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s; mass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
(such as landslides); mine hazards; oil field hazards; radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
accumulation in homes; or volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
s.
Physiography

 New Mexico is entirely landbound, with just 0.2% of the state covered with water, and most of the state has an arid to semiarid climate. Much of the state is mountainous, except for the easternmost
New Mexico is entirely landbound, with just 0.2% of the state covered with water, and most of the state has an arid to semiarid climate. Much of the state is mountainous, except for the easternmost Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
region. The state thus has extensive bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
exposures, which are assigned to four physiographic provinces
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific charact ...
. These are the Great Plains, which makes up the eastern third of the state; the southern Rocky Mountains
The Southern Rocky Mountains are a major subregion of the Rocky Mountains of North America located in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Wyoming, the central and western portions of Colorado, the northern portion of New Mexico, and ex ...
in the north-central part of the state; the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of ...
in the northwestern part of the state; and Basin and Range
Basin and range topography is characterized by alternating parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is a result of crustal extension due to mantle upwelling, gravitational collapse, crustal thickening, or relaxation of confining stresses. The e ...
Provinces in the southwestern part of the state. The presence of these four physiographic provinces gives the state great geological diversity.
Rocks exposed in the southern Rocky Mountains are as old as nearly 1800 million years ( Ma), while some volcanic flows in the state are geologically very young.
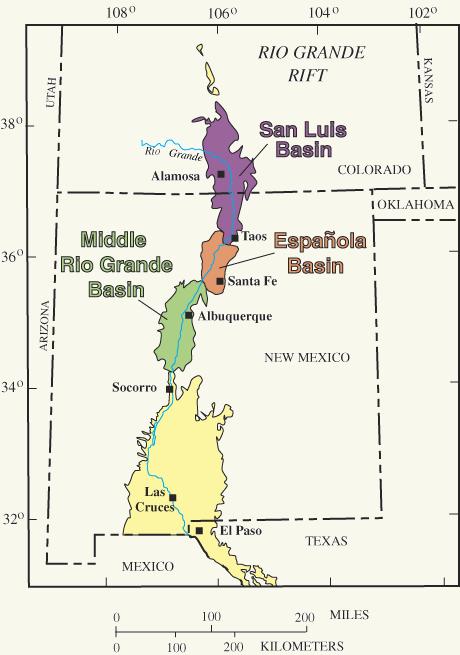
An important geologic feature of New Mexico is the Rio Grande Rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihua ...
. This extends from central Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
to northern Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
*Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mun ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, passing from north to south through the center of the state, cutting across the southern Rocky Mountains and the Basin and Range provinces, and roughly coinciding with the valley of the Rio Grande River
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
. The rift marks where the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of ...
in the west has pulled away from the interior of the North American craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
on the east. It has been the focus of significant scientific research on continental rift processes.
Stratigraphy, tectonics, and geologic history
Proterozoic

island arcs
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
. This is recorded in the rocks of the Moppin Complex
The Moppin Complex is a Precambrian geologic complex found in the Tusas Mountains of northern New Mexico. It has not been directly dated, but is thought to be Statherian based on a minimum age of 1.755 Gya from radiometric dating of magmatic ...
, the Gold Hill complex, and the Pecos greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies.
The name comes from the green ...
in northern New Mexico. These are described as juvenile crust, because their Nd model ages are close to the crystallization ages determined from U-Pb dating. This indicates that the material making up the island arcs was extracted from the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate rock between the crust and the outer core. It has a mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg and thus makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly sol ...
only shortly before the island arcs formed.
These rocks are mostly amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky ...
s thought to be formed by metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chem ...
of tholeiitic
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma i ...
basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
.
The island arcs were carried into a subduction zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
along the margin of Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although ...
, the ancient core of North America, around 1700 million years ago, an event called the Yavapai orogeny
The Yavapai orogeny was an orogenic (mountain-building) event in what is now the Southwestern United States that occurred between 1710 and 1680 million years ago ( Mya), in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Recorded in the rocks of N ...
. The arcs accreted to the continental margin, forming a band of new continental crust stretching from Arizona to Newfoundland and from the Wyoming-Colorado border to central New Mexico. These events are recorded in the rocks of the Vadito Group
The Vadito Group is a group of geologic formations that crops out in most of the Precambrian-cored uplifts of northern New Mexico. Detrital zircon geochronology and radiometric dating give a consistent age of 1700 Mya for the group, correspondi ...
and Hondo Group
The Hondo Group is a group of geologic formations that crops out in most of the Precambrian-cored uplifts of northern New Mexico. Detrital zircon geochronology gives a maximum age for the lower Hondo Group of 1765 to 1704 million years ( Mya), c ...
. A second set of slightly younger island arcs accreted to the continented shortly after, around 1650 to 1600 Mya, during the Mazatzal orogeny. The Mazatzal beds now underlie most of southern New Mexico and the Mazatzal orogeny is recorded in the Manzano Group of the Manzano and Los Pinos mountains.
Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
rocks crop out across approximately five percent of New Mexico and underlie the entire state. The rocks now exposed at the surface were uplifted during the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
, the early Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
as well as block faulting and tilting in the more recent geologic past. For the most part, these rocks are exposed along the Rio Grande rift in the center of New Mexico, except in the Zuni Mountains Zuni may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Zuni people, an indigenous people of the United States
* Zuni language, their language
Places
* Zuni, Virginia, an unincorporated town in Virginia in the United States
* Zuni Pueblo, New Mexico, a ce ...
and Big Burro Mountains
The Big Burro Mountains are a moderate length long, mountain range located in central Grant County, New Mexico. The range's northwest-southeast 'ridgeline' is located 15 mi southwest of Silver City.
The southeast end of the range has the Co ...
. The total relief of Precambrian rocks is 11 kilometers.
The rocks are 70 percent plutons
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
and 30 percent supracrustal formed between 1.765 and 1.4 billion years ago in the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
, based on uranium-lead dating. All of the rocks more than 1.65 billion years old show evidence of metamorphism ranging between greenschist
Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically and 2–10 kilobars (). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite ...
and amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky ...
grade on the sequence of metamorphic facies
A metamorphic facies is a set of mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks formed under similar pressures and temperatures.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak The assemblage is typical of what is formed in conditions corresponding ...
. An area in the Cimarron Range in the vicinity of Taos reached granulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated w ...
facies. Geologists debate the extent of different terranes—sections of continental crust—that joined. Metavolcanic rocks in the Tusas Mountains may be among the oldest, which are intruded by 1.65 billion year old trondhjemite
Trondhjemite is a leucocratic (light-colored) intrusive igneous rock. It is a variety of tonalite in which the plagioclase is mostly in the form of oligoclase. Trondhjemites that occur in the oceanic crust or in ophiolites are usually called pla ...
, but display more than one metamorphic fabric.
Precambrian rocks formed volcanogenic polymettalic sulfides, rich in gold, silver and tungsten, kyanite
Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally ...
, copper veins and pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic com ...
with beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form mi ...
, lithium, niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
, tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
and mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is ...
.
The region was tectonically quiescent until around 1400 Mya, when the poorly understood Picuris orogeny
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and int ...
deformed and metamorphosed much of the crust of New Mexico. This event is recorded in the rock of the Trampas Group and in extensive batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
s intruded into the crust throughout the western United States, such as the Sandia Crest
Sandia Crest, also known locally as Sandia Peak or simply as the Crest, is a mountain ridge that, at , is the highpoint of the Sandia–Manzano Mountains, and is located in the Sandia Mountains of Bernalillo County, New Mexico, United States. ...
batholith. Following the Picuris orogeny, northern New Mexico was again tectonically quiet, while southern New Mexico experience some deformation associated with the Grenville orogeny
The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, ...
. This is recorded in the Allamoore and Tumbledown Formations (about 1250 Mya) and the De Baca Group and Los Animas Formation (about 1200 Mya). Thereafter the region experienced steady erosion, which in some cases brought rock near the surface that had been buried as deep as . This beveled much of New Mexico almost completely flat, forming a peneplain
390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny.
In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage ...
.
Paleozoic (541-251 million years ago)

 New Mexico at the start of the Paleozoic was dominated by the
New Mexico at the start of the Paleozoic was dominated by the Transcontinental Arch The Transcontinental Arch refers to the islands of North America which extended from New Mexico to Minnesota and the Great Lakes region. These islands were present during the Sauk sequence, the earliest cratonic sequence. As a result of the Sauk ...
, an elevated region from Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
to northern New Mexico. Small quantities of alkaline magma were intruded in the early Cambrian along north–south faults, which may indicate incipient rifting of the New Mexico aulacogen. Later in the Cambrian, the sea began to advance northeast across New Mexico, beginning in the boot heel of the state (Sauk sequence
The Sauk sequence was the earliest of the six cratonic sequences that have occurred during the Phanerozoic in North America. It was followed by the Tippecanoe, Kaskaskia, Absaroka, Zuñi, and Tejas sequences.
The sequence dates from the late ...
) and sedimentary beds were deposited during the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
through Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
, beginning with the Cambrian Bliss Formation. The sea did not submerge the Transcontinental Arch until Mississippian time.
By the late Paleozoic, in the Pennsylvanian and Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
, the rise of the Ancestral Rocky Mountains
The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through cen ...
broke the ancient peneplain into basins separated by uplifts. Fossiliferous marine limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
such as the Madera Group
The Madera Group is a group of geologic formations in northern New Mexico. Its fossil assemblage dates the formation to the middle to late Pennsylvanian period.
Description
The group consists primarily of marine limestones, and it is exposed in ...
was deposited in the basin shelves, while areas receiving debris eroded off the highlands formed clastic sedimentary formations such as Flechado Formation or Sangre de Cristo Formation
The Sangre de Cristo Formation is a geologic formation in Colorado and New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the late Pennsylvanian to early Permian.
Description
The formation is divided into an informal lower member and an upper Crest ...
. Towards the end of the Pennsylvanian, fluctuations in sea level caused by global glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
produced cyclic formations like the Bursum Formation
The Bursum Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico.red bed
Red beds (or redbeds) are sedimentary rocks, typically consisting of sandstone, siltstone, and shale, that are predominantly red in color due to the presence of ferric oxides. Frequently, these red-colored sedimentary strata locally contain th ...
formations such as the Abo Formation
The Abo Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico. It contains fossils characteristic of the Cisuralian epoch of the Permian period.
Description
The Abo Formation consists of fluvial redbed mudstones and sandstones, including river channel ...
or the Cutler Group
The Cutler Formation or Cutler Group is a rock unit that is exposed across the U.S. states of Arizona, northwest New Mexico, southeast Utah and southwest Colorado. It was laid down in the Early Permian during the Wolfcampian epoch.
Descri ...
. The Cutler Group contain important fossil quarries that shed light on the early evolution of tetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids ...
. Continental sedimentation began in the north and prograded to the south.
At the same time, a deep basin, the Delaware Basin
The Delaware Basin is a geologic depositional and structural basin in West Texas and southern New Mexico, famous for holding large oil fields and for a fossilized reef exposed at the surface. Guadalupe Mountains National Park and Carlsbad Cavern ...
, formed in southeastern New Mexico and Texas, surrounded by the massive Capitan
Capitan and Kapitan are equivalents of the English Captain in other European languages.
Capitan, Capitano, and Kapitan may also refer to:
Places in the United States
* Capitan, Louisiana, an unincorporated community
*Capitan, New Mexico, a villag ...
barrier reef. A brief rise in sea level deposited the limestone of the San Andres Formation across much of New Mexico, making this the most extensive Paleozoic formation exposed in the state. The subsequent retreat of the sea resulted in deposition of large deposits of gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
, potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
and salt of the Castile and Salado Formation
The Salado Formation is a geologic formation in west Texas and southeastern New Mexico. It was deposited in the Ochoan Stage of the Permian period.
Description
The formation consists of up to of halite with significant anhydrite, red beds, and p ...
s in the Delaware Basin.
Mesozoic (251-66 million years ago)
 The Mesozoic began with the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The
The Mesozoic began with the Permian-Triassic extinction event. The Sevier
Sevier ( ) is an unincorporated community in southwestern Sevier County, Utah, United States. It lies in the valley of the Sevier River along U.S. Route 89 southwest of the city of Richfield, the county seat of Sevier County. Its elevation is ...
and Nevadan
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, t ...
orogenies pushed up mountains to the west of New Mexico that produced a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
, giving New Mexico an exquisitely hot and dry climate through much of the early Mesozoic.
The lower Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a un ...
is recorded nowhere in the rock beds of New Mexico, but the middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and ...
is recorded in beds of the Moenkopi and Anton Chico Formation
The Anton Chico Formation is a geologic Formation (geology), formation exposed in New Mexico that was deposited in the Anisian Age (geology), Age of the middle Triassic Period (geology), Period.
Description
The formation consists mostly of very ...
s. The Moenkopi represents deposition in a coastal plain by rivers running to the west. This pattern continued into the late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch ...
, when the climate become somewhat cooler and wetter, and a substantial river system developed through New Mexico that deposited the Chinle Group
The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geological formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. In Ne ...
. The Rock Point Formation
The Rock Point Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. It preserves fossils dating back to the late Triassic.
Description
The formation is up to 70 m thick and is mostly reddish-brown and grayish-red massive siltstone ...
of the Chinle Group preserved large numbers of fossils of ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period from t ...
'', one of the earliest known genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
of dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
.
The Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
was again a time of arid climate. A great dune sea, or erg
The erg is a unit of energy equal to 10−7joules (100 nJ). It originated in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It has the symbol ''erg''. The erg is not an SI unit. Its name is derived from (), a Greek word meaning 'work' o ...
, spread across northern New Mexico and deposited the sandstone of the Entrada Formation
The Entrada Sandstone is a formation in the San Rafael Group found in the U.S. states of Wyoming, Colorado, northwest New Mexico, northeast Arizona, and southeast Utah. Part of the Colorado Plateau, this formation was deposited during the Jurass ...
. This was followed by flooding of northern New Mexico by an arm of the Sundance Sea
The Sundance Sea was an epeiric sea that existed in North America during the mid-to-late Jurassic Period of the Mesozoic Era. It was an arm of what is now the Arctic Ocean, and extended through what is now western Canada into the central western ...
, leading to deposition of the limestone and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
beds of the Todilto Formation. The Jurassic ended with the deposition of the Summerville and Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Late Jurassic, Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandsto ...
s, the latter deposited in a vast foreland basin
A foreland basin is a structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt. Foreland basins form because the immense mass created by crustal thickening associated with the evolution of a mountain belt causes the lithospher ...
east of the coastal mountains thrown up by the Sevier orogeny.
The increasing weight of the Sonoma mountains to the west drove subsidence of its foreland basin, which included most of New Mexico. During the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
, the region was submerged by the Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea, ...
, which deposited shore formations such as the Dakota Formation
The Dakota is a sedimentary geologic unit name of formation and group rank in Midwestern North America. The Dakota units are generally composed of sandstones, mudstones, clays, and shales deposited in the Mid-Cretaceous opening of the Western Int ...
and marine formations such as the Mancos Formation. Advances and retreats of the coastline are recorded in formations such as the Mesaverde Group
The Mesaverde Group is a Late Cretaceous stratigraphic group found in areas of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming, in the Western United States.
History
The Mesaverde Formation was first described by W.H.Holmes in 1877 during the Hayden ...
.
Towards the end of the Cretaceous, shallow subduction of the Farallon plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate. It formed one of the three main plates of Panthalassa, alongside the Phoenix Plate and Izanagi Plate, which were connected by a triple junction. The Farallon Plate began subducting under the west c ...
drove the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
, which uplifted the Rocky Mountains and lasted into the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
.
Cenozoic (66 million years ago-present)
 The Laramide Orogeny changed the topography of New Mexico into one of high uplifts and deep basins. The basins began to fill with sediments during the
The Laramide Orogeny changed the topography of New Mexico into one of high uplifts and deep basins. The basins began to fill with sediments during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
, recorded in formations such as the San Jose Formation
The San Jose Formation is an Early Eocene (Wasatchian in the NALMA classification) geologic formation in the San Juan Basin of New Mexico and Colorado.Galisteo Formation
The Galisteo Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico. It contains fossils characteristic of the Bartonian stage of the Eocene epoch, Duchesnean in the NALMA classification.Baca Formation
The Baca Formation is a geologic formation in southern New Mexico and Arizona. It preserves fossils dating back to the Eocene period.
Description
The formation consists of coarse conglomerate, red and white sandstone, and red clay. Its total ...
.
As the Farallon plate disintegrated and sank into the mantle, hot asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between ~ below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not ...
rock rose to take its place. This helped trigger the Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up
The Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up, was a dramatic period of volcanic eruptions in mid-Cenozoic time, approximately 25–40 million years ago, centered in the western United States. These eruptions are seen today as deposits of ignimbrite, the ...
, which deposited significant ash falls across much of New Mexico. The vast Mogollon-Datil volcanic field
The Mogollon-Datil volcanic field is a large () silicic volcanic field in western New Mexico (Mogollon Mountains-Datil, New Mexico). It is a part of an extensive Eocene to Oligocene volcanic event which includes the San Juan volcanic field in sou ...
was active during this time, as were the smaller Latir volcanic field
The Latir volcanic field is a large volcanic field near Questa, New Mexico, that was active during the late Oligocene to early Miocene, 28 to 22 million years ago ( Ma). It includes the Questa caldera, in whose deeply eroded interior is located ...
and the Ortiz porphyry belt
The rise of hot asthenosphere below New Mexico reversed the compression of the crust and put it into tension, resulting in the opening of the Rio Grande rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihua ...
, beginning about 30 Mya, and the development of Basin and Range geology across the southern part of the state. The development of the Rio Grande rift is recorded in the rocks of the Santa Fe Group.
The Jemez volcanic field
The Jemez Mountains are a group of mountains in Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico, United States.
Numerous Puebloan Indian tribes have lived in the Jemez Mountains region since before the Spanish arrived in New Mexico. T ...
began to develop around 15 Mya, and volcanic activity subsequently spread southwest and northeast along the Jemez Lineament
The Jemez Lineament is a chain of late Cenozoic volcanic fields, long, reaching from the Springerville and White Mountains volcanic fields in East-Central Arizona to the Raton-Clayton volcanic field in Northeastern New Mexico.
The lineament ...
. The Valles Caldera
Valles Caldera (or Jemez Caldera) is a wide volcanic caldera in the Jemez Mountains of northern New Mexico. Hot springs, streams, fumaroles, natural gas seeps and volcanic domes dot the caldera floor landscape. The highest point in the caldera i ...
(or Jemez Caldera) formed in the Jemez Mountains 1.25 Mya ago in the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
, exploding and then collapsing into its magma chamber and emplacing the Bandelier Tuff
The Bandelier Tuff is a geologic formation exposed in and around the Jemez Mountains of northern New Mexico. It has a radiometric age of 1.85 to 1.25 million years, corresponding to the Pleistocene epoch. The tuff was erupted in a series of at ...
. Small mountain glaciers formed in the Brazos and Sangre de Cristo Mountains.
Natural resource geology
Under Spanish rule turquoise and lead were mined near Cerillos and copper was found at Santa Rita in the southwest in 1798.Artisanal mining
An artisanal miner or small-scale miner (ASM) is a subsistence miner who is not officially employed by a mining company, but works independently, mining minerals using their own resources, usually by hand.
Small-scale mining includes enterprises ...
for placer gold took place after an 1821 discovery in the Ortiz Mountains
The Ortiz Mountains are a mountain range in northern New Mexico, United States, in Santa Fe County, northeast of the Sandia Mountains and due north of the San Pedro Mountains. The Ortiz include Placer Peak, the highest peak in the range at 8,858 ...
south of Santa Fe. New deposits, along with the reopened Spanish mine in Silver City prompted a boom in copper mining in the late 19th century. Placer gold mining expanded into the Sangre de Cristo Mountains and along the Rio Grande, while lead mining got underway in Las Cruces. Coal was discovered near gold and copper mines and potentially recoverable gold deposits grew more numerous as prospectors traced placer gold back to the veins where it originated.
In 1863, silver was found in Magdalena, west of Socorro, followed by a large find in Grant County. Silver City, White Oaks, Ute Creek, Cerrillos, Elizabethtown, Twining, Chloride, Hondo Canyon, Red River Canyon and Socorro were soon discovered to also have silver. Rising costs and depleted ore bodies have led to widespread abandonment and ghost towns throughout the state, which remain comparatively well-preserved in the dry climate.
Mining is still a cornerstone of the New Mexico economy, although it has largely shifted to open-pit extraction. Coal is mined in the northwest and copper, silver, gold, manganese, zinc and lead are extracted near Silver City. Molybdenum is an important resource in the Sangre de Cristo mountains, including the Questa Mine. Uranium is still mined close to Grants, although production has dropped after a high point between the 1950s and the 1970s. Gypsum, limestone, potash and salt are mined out of Pennsylvanian and Permian rocks in the east. Mining accounted for 3,763 jobs by 2018.
The San Juan Basin
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah a ...
in the northwest has active oil and gas production, along with the small extent of the Permian Basin
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
in the southeast. Oil and gas production in the state totalled 1,820,963,878 MCF of natural gas and 331,460,749 barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
of oil in 2019, yielding $3.1 billion in oil and gas taxes and revenues for the state. Mining has historically been important, but accounted for just 3,763 jobs by 2018.
Because of New Mexico's typically semiarid climate, ground water in aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
is an important geologic resource for farmers and municipal areas. The groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
potential of the Santa Fe Group was recognized by Kirk Bryan in 1938, and the Alamosa subbasin of the San Luis Valley
The San Luis Valley is a region in south-central Colorado with a small portion overlapping into New Mexico. The valley is approximately long and wide, extending from the Continental Divide on the northwest rim into New Mexico on the south. It co ...
, the central part of the Albuquerque Basin
The Albuquerque Basin (or Middle Rio Grande Basin) is a structural basin and ecoregion within the Rio Grande rift in central New Mexico. It contains the city of Albuquerque.
Geologically, the Albuquerque Basin is a half-graben that slopes down to ...
, and the southern Mesilla basin from Las Cruces to El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
are now among the most productive groundwater reservoirs in the western United States.
Geologic hazards
Geologic hazards are infrequent in New Mexico, but potential dangers includeerosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
or flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
ing in arroyos; arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
or other contamination of ground water or soil; sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s or other subsidence; earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s; mass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
(such as landslides); mine hazards; oil field hazards; radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through ...
accumulation in homes; or volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
s.
Flooding is one of the more common geologic hazards in New Mexico. Historically significant flooding events included extensive river flooding accompanied by local flash floods in September 1941; river flooding across the northeastern High Plains region between June 14–17, 1965; severe flooding resulting from rainfall onto heavy snow accumulations in southwestern and south central New Mexico on December 18–19, 1978; flooding after heavy rainfall from the remnants of Hurricane Doly between July 26–28, 2008; and widespread flooding from an unusually wet monsoon season in the summer of 2006. The state is occasionally impacted by remnants of East Pacific tropical storms
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dependi ...
that carry considerable moisture, and such storm remnants contributed to both the 1941 and the 2008 floods.
Earthquake hazards are moderate in New Mexico compared with California or the Wasatch Front
The Wasatch Front is a metropolitan region in the north-central part of the U.S. state of Utah. It consists of a chain of contiguous cities and towns stretched along the Wasatch Range from approximately Provo in the south to Logan in the north ...
in Utah. One estimate puts the probability of a large earthquake in the southern Rio Grande Rift in the next century at 5%. However, faults are concentrated along the Rio Grande Rift, with its urban centers, and while only 20 faults in the state are considered active, the consequences of an earthquake could be serious. The large number of faults increases the likelihood of an earthquake even though rupture of any one fault is infrequent. The largest earthquakes in historic times were two magnitude 5.8 earthquakes in 1906 near Socorro, likely associated with the Socorro magma body, a shallow horizontal magma intrusion in the crust.
References
{{Geology of the United States by political divisionNew Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...