|
Manzano Group
The Manzano Group is a group of geologic formations in central New Mexico. These have radiometric ages of 1601 to 1662 million years ( Ma), corresponding to the late Statherian period of the Paleoproterozoic. The name ''Manzano Group'' was previously applied to a group of sedimentary formations of Permian age in roughly the same geographical area. The original Manzano Group was historically important in the establishment of the paleontological time scale of the Permian period in western North America. However, the name was abandoned after 1920. Description The group consists of Statherian lithostratigraphic units exposed in the Los Pinos Mountains and nearby ranges of central New Mexico. These are mostly metarhyolite or quartzite units with some schist and amphibolite, and form a sequence in excess of thick. The group records deformation attributed to the Mazatzal orogeny, and the quartzites of the group may be the provenance of the lower conglomerates of the Marquena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (stratigraphy)
In geology, a group is a lithostratigraphic unit consisting of a series of related formations that have been classified together to form a group. Formations are the fundamental unit of stratigraphy. Groups may sometimes be combined into supergroups. Groups are useful for showing relationships between formations, and they are also useful for small-scale mapping or for studying the stratigraphy of large regions. Geologists exploring a new area have sometimes defined groups when they believe the strata within the groups can be divided into formations during subsequent investigations of the area. It is possible for only some of the strata making up a group to be divided into formations. An example of a group is the Glen Canyon Group, which includes (in ascending order) the Wingate Sandstone, the Moenave Formation, the Kayenta Formation, and the Navajo Sandstone. Each of the formations can be distinguished from its neighbor by its lithology, but all were deposited in the same vast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statherian
The Statherian Period (; grc, σταθερός, statherós, meaning "stable, firm") is the final geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The period was characterized on most continents by either new platforms or final cratonization of fold belts. Oxygen levels were 10% to 20% of current values. ''Rafatazmia'', controversially claimed to be present in Statherian beds in India, may be the oldest known confirmably eukaryotic fossil organism. By the beginning of the Statherian, the supercontinent Columbia had assembled. At roughly 1.7 billion years before present a series of natural nuclear fission reactors was operational in what is now Oklo Oklo is a region near the town of Franceville, in the Haut-Ogooué province of the Central African country of Gabon. Several natural nuclear fission reactors were discovered in the uranium mines in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquenas Formation
The Marquenas Formation is a geological formation that crops out in the Picuris Mountains of northern New Mexico. Detrital zircon geochronology gives it a maximum age of 1435 million years, corresponding to the Calymmian period. Description The Marquenas Formation was first believed to be over 80% quartzite, with the rest mostly metaconglomerate. The metaconglomerate lenses are found throughout the formation but particularly towards its top, and it was designated the Marquenas Quartzite. However, Bauer and Williams noted that the unit is about equally divided between quartzite and metaconglomerate, which led them to redesignate it as the Marquenas Formation. It can be divided into a lower, highly strained, poorly sorted boulder conglomerate; a middle quartzite member; and an upper, highly strained, pebble-to-cobble conglomerate. Cross stratification shows that the layering is overturned, and this supported the interpretation of the formation as part of the Vadito Group, likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conglomerate (geology)
Conglomerate () is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed of a substantial fraction of rounded to subangular gravel-size clasts. A conglomerate typically contains a matrix of finer-grained sediments, such as sand, silt, or clay, which fills the interstices between the clasts. The clasts and matrix are typically cemented by calcium carbonate, iron oxide, silica, or hardened clay. Conglomerates form by the consolidation and lithification of gravel. They can be found in sedimentary rock sequences of all ages but probably make up less than 1 percent by weight of all sedimentary rocks. In terms of origin and depositional mechanisms, they are closely related to sandstones and exhibit many of the same types of sedimentary structures, e.g., tabular and trough cross-bedding and graded bedding.Boggs, S. (2006) ''Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy.'', 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, New York. 662 pp. Friedman, G.M. (2003) ''Classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks.'' In G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provenance (geology)
Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the origin of sediments. The Earth is a dynamic planet, and all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface are sooner or later broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosional history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history. In the modern geological lexicon, "sediment provenance" specifically refers to the application of compositional analyses to determine the origin of sediments. This is often used in conjunction with the study of exhumation histories, interpretation of drainage networks and their evolution, and forward-modelling of paleo-earth systems. In combination, these help to characterise the "source to sink" journey of clastic sediments from hinterland to sedimentary bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
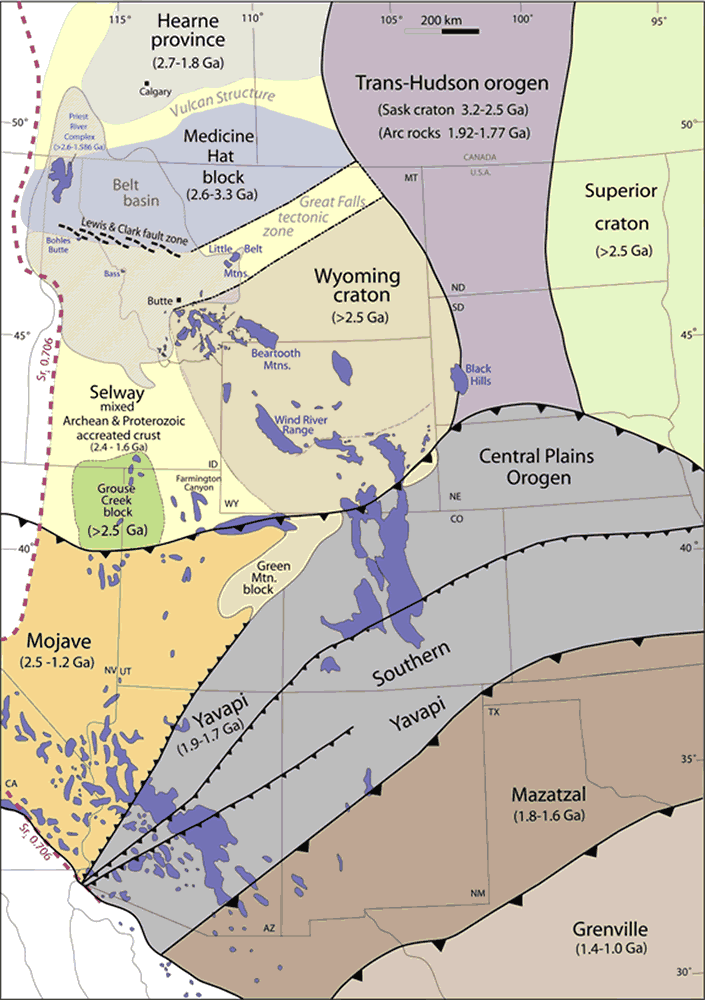
Mazatzal Orogeny
The Mazatzal orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1650 to 1600 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1700-1600 Mya age Mazatzal island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism. Description Age and isotope data show that southern North America is composed of a series of northeast-trending provinces representing island arc terranes accreted onto the 1800 Mya core of Laurentia. These are the Yavapai province (1800–1700 Mya), the Mazatzal province (1700–1650 Mya), the Granite-Rhyolite province (1500–1300 Mya), and the Llan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture (geology), texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as micas, talc, chlorite group, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz. Schist typically forms during regional metamorphism accompanying the process of mountain building (orogeny) and usually reflects a medium Metamorphism#Metamorphic grades, grade of metamorphism. Schist can form from many different kinds of rocks, including sedimentary rocks such as mudstones and igneous rocks such as tuffs. Schist metamorphosed from mudstone is particularly common and is often very rich in mica (a ''mica schist''). Where the type of the original rock (the protolith) is discernible, the schist is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metavolcanic Rock
Metavolcanic rock is volcanic rock that shows signs of having experienced metamorphism. In other words, the rock was originally produced by a volcano, either as lava or tephra. The rock was then subjected to high pressure, high temperature or both, for example by burial under younger rocks, causing the original volcanic rock to recrystallization (geology), recrystallize. Metavolcanic rocks are sometimes described informally as ''metavolcanics''. When it is possible to determine the original volcanic rock type from the properties of the metavolcanic rock (particularly if the degree of metamorphism is slight), the rock is more precisely named by appylying the prefix ''meta-'' to the original rock type. For example, a weakly metamorphosed basalt would be described as a ''metabasalt'', or a weakly metamorphosed tuff as a ''metatuff''. Metavolcanic rock is commonly found in greenstone belts. See also * References {{petrology-stub Metamorphic rocks Volcanic rocks Metamorphic pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Pinos Mountains
The Los Pinos Mountains are a small mountain range in the central part of New Mexico, US. They are the southernmost part of a mountain front, running north to south, that also includes the Sandia Mountains and the Manzano Mountains. The Los Pinos Mountains are separated from the Manzano Mountains by Abo Pass, which was cut by a small tributary to the Rio Grande. The mountains run slightly west of south for and widen to a maximum of about across before narrowing again. The southern end of the range is ill-defined, being marked by cuestas that merge into badlands to the south. The mountains are steep on their westward faces, where they rise over the Rio Grande Valley, but slope more gently to the east. There are five peaks over in elevation, of which the highest is Whiteface Mountain at . Most of the range falls within Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge. Geology The Los Pinos Mountains consist of a western ridge of Precambrian rock exposed by erosion. To the east and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithostratigraphic
Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geology, geological science associated with the study of stratum, strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology. In general, strata are primarily igneous or sedimentary relating to how the rock was formed. Sedimentary rock, Sedimentary layers are laid down by Deposition (sediment), deposition of sediment associated with weathering processes, decaying organic matter (biogenic) or through chemical precipitation. These layers are often distinguishable as having many fossils and are important for the study of biostratigraphy. Igneous layers occur as stacks of lava flows, layers of lava fragments (called tephra) both erupted onto the Earth's surface by volcanoes, and in layered intrusions formed deep underground. Igneous layers are generally devoid of fossils and represent Magmatism, magmatic or volcanic activity that occurred during the geologic history of an area. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontological
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (geology), epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from ancient language, Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, (Genitive, gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
