|
Geology Of New Mexico
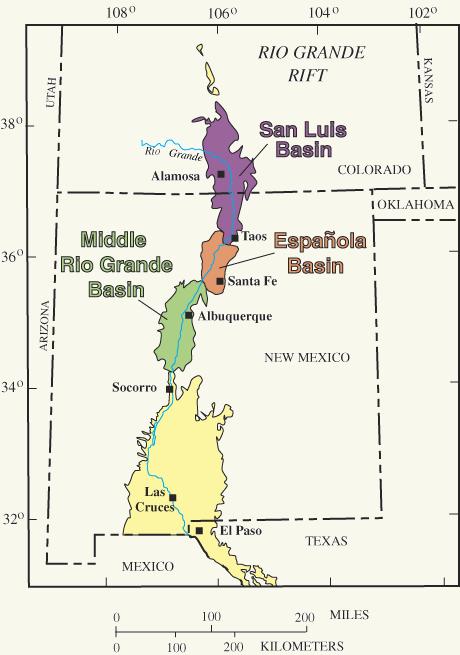
The geology of New Mexico includes bedrock exposures of four physiographic provinces, with ages ranging from almost 1800 million years ( Ma) to nearly the present day. Here the Great Plains, southern Rocky Mountains, Colorado Plateau, and Basin and Range Provinces meet, giving the state great geologic diversity. The geologic history of the state began with its assembly during the Yavapai and Mazatzal orogenies 1750 to 1650 million years ago ( Mya). This was followed by 200 million years of tectonic quiescence that ended in the Picuris orogeny. This event transformed the New Mexico crust into mature continental crust. Over a thousand million years of tectonic quiescence followed, ending with the rise of the Ancestral Rocky Mountains in Pennsylvanian time, 300 Mya. The Permian and most of the Mesozoic were another interval of relative tectonic quiescence, where gradual subsidence deposited formations that preserve an impressive stratigraphic record across the state. This ended wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico
) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Keres, Zuni , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = New Mexico Legislature , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = New Mexico Supreme Court , Senators = * * , Representative = * * * , postal_code = NM , TradAbbreviation = N.M., N.Mex. , area_rank = 5th , area_total_sq_mi = 121,591 , area_total_km2 = 314,915 , area_land_sq_mi = 121,298 , area_land_km2 = 314,161 , area_water_sq_mi = 292 , area_water_km2 = 757 , area_water_percent = 0.24 , population_as_of = 2020 , population_rank = 36th , 2010Pop = 2,117,522 , population_density_rank = 45th , 2000DensityUS = 17.2 , 2000Density = 6.62 , MedianHouseholdIncome = $51,945 , IncomeRank = 45th , AdmittanceOrder = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laramide Orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute. The Laramide orogeny occurred in a series of pulses, with quiescent phases intervening. The major feature that was created by this orogeny was deep-seated, thick-skinned deformation, with evidence of this orogeny found from Canada to northern Mexico, with the easternmost extent of the mountain-building represented by the Black Hills of South Dakota. The phenomenon is named for the Laramie Mountains of eastern Wyoming. The Laramide orogeny is sometimes confused with the Sevier orogeny, which partially overlapped in time and space. The orogeny is commonly attributed to events off the west coast of North America, where the Kula Plate, Kula and Farallon Plates were sliding under the North American plate. Most hypothes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series. There are three different types of eruptions: * Magmatic eruptions are the most well-observed type of eruption. They involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. * Phreatic eruptions are driven by the superheating of steam due to the close proximity of magma. This type exhibits no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock. * Phreatomagmatic eruptions are driven by the direct interaction of magma and water, as opposed to phreatic erup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into various short-lived radioactive elements and lead. Radon itself is the immediate decay product of radium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of only 3.8 days, making it one of the rarest elements. Since thorium and uranium are two of the most common radioactive elements on Earth, while also having three isotopes with half-lives on the order of several billion years, radon will be present on Earth long into the future despite its short half-life. The decay of radon produces many other short-lived nuclides, known as "radon daughters", ending at stable isotopes of lead. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in a moving medium, such as water, wind, or ice. Types of mass wasting include creep, solifluction, rockfalls, debris flows, and landslides, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place over timescales from seconds to hundreds of years. Mass wasting occurs on both terrestrial and submarine slopes, and has been observed on Earth, Mars, Venus, Jupiter's moons Io, and on many other bodies in the Solar System. Subsidence is sometimes regarded as a form of mass wasting. A distinction is then made between mass wasting by subsidence, which involves little horizontal movement, and mass wasting by slope movement. Rapid mass wasting events, such as landslides, can be deadly and destructive. More gradual mass wasting, such as soil cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. A ''sink'' or ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields. Flash floods may also occur after the collapse of a natural ice or debris dam, or a human structure such as a man-made dam, as occurred before the Johnstown Flood of 1889. Flash floods are distinguished from regular floods by having a timescale of fewer than six hours between rainfall and the onset of flooding. Flash floods are a significant hazard, causing more fatalities in the U.S. in an average year than lightning, tornadoes, or hurricanes. Flash floods can also deposit large quantities of sediments on floodplains and can be destructive of vegetation cover not adapted to frequent flood conditions. Causes Flash floods most often occur in dry areas that have recently received precipitation, but they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology. Related terms include aquitard, which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, and aquiclude (or ''aquifuge''), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer, the pressure of which could create a confined aquifer. The classification of aquifers is as follows: Saturated versus unsaturated; aquifers versus aquitards; confined versus unconfined; isotropic versus anisotropic; porous, karst, or fractured; transboundary aquifer. Challenges for using groundwater include: overdrafting (extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of the aquifer), groundwater-related subsidence of land, groundwater becoming sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jemez Mountains
The Jemez Mountains are a group of mountains in Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico, United States. Numerous Puebloan Indian tribes have lived in the Jemez Mountains region since before the Spanish arrived in New Mexico. The Pueblo Indians of this region are the Towa-speaking Jemez people for which this mountain range is named, the Keres-speaking Keresan Indians, and the Tewa-speaking Tewa Indians. Tsąmpiye'ip'įn is the Tewa language name for the Jemez Mountains. The highest point in the range is Chicoma Mountain (also spelled as Tschicoma or Tchicoma) at an elevation of . The town of Los Alamos and the Los Alamos National Laboratory adjoin the eastern side of the range while the town of Jemez Springs is to the west. Pajarito Mountain Ski Area is the only ski area in the Jemez. New Mexico State Highway 4 is the primary road that provides vehicular access to locations in the Jemez Mountains. Geology The Jemez Mountains lie to the north of the Alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


