Flamenco (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flamenco () is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, the term is used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the
 In the 1970s, there were airs of social and political change in Spain, and Spanish society was already quite influenced by various musical styles from the rest of Europe and the United States. There were also numerous singers who had grown up listening to Antonio Mairena, Pepe Marchena and Manolo Caracol. The combination of both factors led to a revolutionary period called flamenco fusion.
The singer
In the 1970s, there were airs of social and political change in Spain, and Spanish society was already quite influenced by various musical styles from the rest of Europe and the United States. There were also numerous singers who had grown up listening to Antonio Mairena, Pepe Marchena and Manolo Caracol. The combination of both factors led to a revolutionary period called flamenco fusion.
The singer
La Emi
is a professional Flamenco dancer and native to New Mexico who performs as well as teaches Flamenco in Santa Fe. She continues studying her art by traveling to Spain to work intensively with Carmela Greco and La Popi, as well as José Galván, Juana Amaya, Yolanda Heredia, Ivan Vargas Heredia, Torombo and Rocio Alcaide Ruiz.
 '' Palos'' (formerly known as ''cantes'') are flamenco styles, classified by criteria such as rhythmic pattern, mode, chord progression,
'' Palos'' (formerly known as ''cantes'') are flamenco styles, classified by criteria such as rhythmic pattern, mode, chord progression,
The alegrías are thought to derive from the Aragonese jota, which took root in Cadiz during the Peninsular war and the establishment of the Cortes de Cadiz. That is why its classic lyrics contain so many references to the Virgen del Pilar, the Ebro River and Navarra.
Enrique Butrón is considered to have formalized the current flamenco style of alegrías and Ignacio Espeleta who introduced the characteristic "tiriti, tran, tran...". Some of the best known interpreters of alegrías are Enrique el Mellizo, Chato de la Isla, Pinini, Pericón de Cádiz, Aurelio Sellés, La Perla de Cádiz, Chano Lobato and El Folli.
One of the structurally strictest forms of flamenco, a traditional dance in alegrías must contain each of the following sections: a salida (entrance), paseo (walkaround), silencio (similar to an adagio in ballet), castellana (upbeat section
zapateado
(Literally "a tap of the foot") and bulerías. This structure though, is not followed when alegrías are sung as a standalone song (with no dancing). In that case, the stanzas are combined freely, sometimes together with other types of cantiñas. Alegrías has a rhythm consisting of 12 beats. It is similar to Soleares. Its beat emphasis is as follows: 1 2 '' 4 5 '' 7 '' 9 0'' 11 2''. Alegrías originated in Cádiz. Alegrías belongs to the group of ''palos'' called Cantiñas and it is usually played in a lively rhythm (120–170 beats per minute). The livelier speeds are chosen for dancing, while quieter rhythms are preferred for the song alone.
Bulerías a fast flamenco rhythm made up of a 12 beat cycle with emphasis in two general forms as follows: 2'' 1 2 '' 4 5 '' 7 '' 9 0'' 11 or 2'' 1 2 '' 4 5 6 '' '' 9 0'' 11. It originated among the Calé Romani people of Jerez during the 19th century, originally as a fast, upbeat ending to '' soleares'' or '' alegrias''. It is among the most popular and dramatic of the flamenco forms and often ends any flamenco gathering, often accompanied by vigorous dancing and tapping.
 A typical chord sequence, usually called the "
A typical chord sequence, usually called the "
 "Flamenco puro" otherwise known as "flamenco por derecho" is considered the form of performance flamenco closest to its gitano influences. In this style, the dance is often performed solo, and is based on signals and calls of structural improvisation rather than choreographed. In the improvisational style, castanets are not often used.
"Classical flamenco" is the style most frequently performed by Spanish flamenco dance companies. It is danced largely in a proud and upright style. For women, the back is often held in a marked back bend. Unlike the more gitano influenced styles, there is little movement of the hips, the body is tightly held, and the arms are long, like a ballet dancer. In fact, many of the dancers in these companies are trained in Ballet Clásico Español more than in the improvisational language of flamenco. Flamenco has both influenced and been influenced by Ballet Clásico Español, as evidenced by the fusion of the two ballets created by 'La Argentinita' in the early part of the 20th century and later, by Joaquín Cortés, eventually by the entire
"Flamenco puro" otherwise known as "flamenco por derecho" is considered the form of performance flamenco closest to its gitano influences. In this style, the dance is often performed solo, and is based on signals and calls of structural improvisation rather than choreographed. In the improvisational style, castanets are not often used.
"Classical flamenco" is the style most frequently performed by Spanish flamenco dance companies. It is danced largely in a proud and upright style. For women, the back is often held in a marked back bend. Unlike the more gitano influenced styles, there is little movement of the hips, the body is tightly held, and the arms are long, like a ballet dancer. In fact, many of the dancers in these companies are trained in Ballet Clásico Español more than in the improvisational language of flamenco. Flamenco has both influenced and been influenced by Ballet Clásico Español, as evidenced by the fusion of the two ballets created by 'La Argentinita' in the early part of the 20th century and later, by Joaquín Cortés, eventually by the entire  The flamenco most foreigners are familiar with is a style that was developed as a spectacle for tourists. To add variety, group dances are included and even solos are more likely to be choreographed. The frilly, voluminous spotted dresses are derived from a style of dress worn for the Sevillanas at the annual Feria in Seville.
In traditional flamenco, only the very young or older dancers are considered to have the emotional innocence or maturity to adequately convey the '' duende'' (soul) of the genre . Therefore, unlike other dance forms, where dancers turn professional through techniques early on to take advantage of youth and strength, many flamenco dancers do not hit their peak until their thirties and will continue to perform into their fifties and beyond. One artist that is considered a young master is Juan Manuel Fernandez Montoya, otherwise known as "Farruquito". At age 12, Farruquito was considered a pioneer and for "Flamenco Puro", or "Flamenco por Derecho", because of his emotional depth.
The flamenco most foreigners are familiar with is a style that was developed as a spectacle for tourists. To add variety, group dances are included and even solos are more likely to be choreographed. The frilly, voluminous spotted dresses are derived from a style of dress worn for the Sevillanas at the annual Feria in Seville.
In traditional flamenco, only the very young or older dancers are considered to have the emotional innocence or maturity to adequately convey the '' duende'' (soul) of the genre . Therefore, unlike other dance forms, where dancers turn professional through techniques early on to take advantage of youth and strength, many flamenco dancers do not hit their peak until their thirties and will continue to perform into their fifties and beyond. One artist that is considered a young master is Juan Manuel Fernandez Montoya, otherwise known as "Farruquito". At age 12, Farruquito was considered a pioneer and for "Flamenco Puro", or "Flamenco por Derecho", because of his emotional depth.
File:Castelucho.jpg,
;Scenes of flamenco performance in Seville.
Flamenco en el Palacio Andaluz, Sevilla, España, 2015-12-06, DD 07.JPG
Flamenco en el Palacio Andaluz, Sevilla, España, 2015-12-06, DD 11.JPG
Flamenco en el Palacio Andaluz, Sevilla, España, 2015-12-06, DD 20.JPG
Flamenco en el Palacio Andaluz, Sevilla, España, 2015-12-06, DD 23.JPG
 Flamenco guitar studies in official educational centers began in Spain in 1988 at the hands of the great concert performer and teacher from Granada
Flamenco guitar studies in official educational centers began in Spain in 1988 at the hands of the great concert performer and teacher from Granada
Superior Conservatory de Música Rafael Orozco
from Córdoba. There are specialized flamenco conservatories throughout the country, although mainly in the Andalusia region, such as the aforementioned Córdoba Conservatory, th
Murcia Superior Music Conservatory
or the
''Rito y geografía del cante''. Serie documental de los años 70 del siglo XX sobre los orígenes, estilos y pervivencia del cante flamenco
con
Nuestro flamenco
': programa de
Agencia Andaluza para el Desarrollo del Flamenco
Flamenco Viejo
Flamenco Olímpico
Reportaje Documental
''Flamenco de la A a la Z''
breve enciclopedia del flamenco que incluye diccionario en e
sitio
de Radiolé. * GRANDE, Félix: ''Memoria del flamenco'', con prólogo de
Texto
en ''
Flamenco en Sevilla
* Lafuente Alcántara, Emilio (1825–1868): ''Cancionero popular. Colección escogida de seguidillas y coplas'', 1865. ** Vol. II
''Coplas''
texto en Google Books. *
Sobre Emilio Lafuente Alcántara
, hermano de
sitio
Biblioteca Virtual de Arabistas y Africanistas Españoles.
* Universo Lorca
El Concurso del Cante Jondo de 1922. Web dedicada a la vida y obra de Federico García Lorca y su vinculación con Granada.
(Diputación de Granada) * Los Palos del Flamenco
Los Palos del Flamenco. Artículos sobre el origen y evolución del arte flamenco.
(Flamencos Online)
Flamenco show in Seville
Flamenco, Spanish music Andalusian music Romani dances Spanish dances Spanish folk music European folk dances Articles containing video clips Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity Romani culture Romani music
Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage.
The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' (The Moroccan Letters) by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of dances, and ''toques'', perfection, newspapers, graphic documents in paintings and engravings. ... in continuous evolution together with rhythm, the poetic stanzas, and the ambiance."
On 16 November 2010, UNESCO declared flamenco one of the Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity
The Proclamation of Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity was made by the Director-General of UNESCO starting in 2001 to raise awareness of intangible cultural heritage and encourage local communities to protect them and t ...
.
Etymology
Historically, the term ''Flamenco'' was used to identify the Romani people ( Gitanos) of Spain. The English traveller George Borrow who travelled through Spain during the 1830s stated that the Gitanos were also called Flemish (in Spanish, 'flamenco') due to German and Fleming being erroneously considered synonymous. According to flamencologist Cristina Cruces-Roldán, a year prior to Borrow's account, there already existed a Gitano party in Madrid that was clearly identified as Flamenco. This equivalency between Gitano and Flamenco is also noted byManuel Fernández y González
Manuel may refer to:
People
* Manuel (name)
* Manuel (Fawlty Towers), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers''
* Charlie Manuel
Charles Fuqua Manuel Jr. (born January 4, 1944), is an American former professional baseball playe ...
, Demófilo
Antonio Machado Álvarez, better known by his pseudonym Demófilo (Santiago de Compostela, 1848 – Seville, 4 February 1893), was a writer, anthropologist, and Spanish folklorist. He was the son of the noted Spanish folklorist, Cipriana Álvar ...
, and the scholar Iriving Brown who stated in 1938 that "Flamenco is simply another term for Gitano, with special connotations."
The origins of the term lie in the sociological prejudice towards the Roma who were seen as ruffians and cocky troublemakers by the Spaniards and were thus associated with the 18th century German colonists of the Sierra Morena who formed groups of urban Bohemians that lived outside the law and were seen as idle and lazy. Other less successful hypotheses include those of Felipe Pedrell
Felip Pedrell Sabaté (Spanish: Felipe) (19 February 1841 – 19 August 1922) was a Catalan composer, guitarist and musicologist.
Life
Pedrell was born in Tortosa (Catalonia), and sang as a boy soprano at Tortosa Cathedral from age 9, where he ...
and Carlos Alemendros who state that while the term Flamenco is Spanish for Flemish, it is actually synonymous with ''Cantador'' (professional singer) in reference to the group of Flemish singers brought by Spanish King Carlos I in 1516. Another hypothesis that is not widely accepted is the Arabist
An Arabist is someone, often but not always from outside the Arab world, who specialises in the study of the Arabic language and culture (usually including Arabic literature).
Origins
Arabists began in medieval Muslim Spain, which lay on the ...
theory of Blas Infante, which presents in his book ''Orígenes de lo flamenco (Origins of flamenco)'''','' Flamenco as a phonetic deformation of Arabic ''fellah-mengu'' (runaway laborer) or was derived from the Arabic terms ''Felah-Mengus,'' which together mean "wandering peasant".
The first use of the term Flamenco to refer to the music genre appears in a 1847 newspaper article of ''El Espectador'' where it was referred to as a "Gitano genre." In the early years of Flamenco, the term was versatile and was used to refer to a variety of concepts in the Gitano-Andalusian world. For example, in the 1860s-70s this versatility was exemplified through its use to refer to a musical style and a certain aesthetic, manners, and way of life that were perceived to be Gitano. At that time, Flamenco was not a strict genre but a way of performing music in a Gitano-Andalusian style.
History
Cultural Origins
There are hypotheses that point to the influence on flamenco of types of dance from the Indian subcontinent; the place of origin of the Romani people. The Indo-Pakistani scales of Flamenco were introduced to Andalusia by the Romani migrations from Northern India. These Roma migrants also brought bells, and an extensive repertoire of songs and dances. Upon arrival to Andalusia in the 15th century, they were exposed to the rich Arab-Andalusian music culture, itself a hybrid of Spanish music tradition going back to the 8th century with the establishment of Al-Andalus, which brought in traditions and music from theArabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, Northern Africa and Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), ...
features. Some of the instruments associated with Flamenco and Spanish folklore in different regions today, are the wooden castanets and tambourines, both believed to originate during the Al Andalus period. This centuries-long period of cultural intermingling, formed the roots of Flamenco song and dance genres.
Birth of Flamenco
It is believed that the flamenco genre emerged at the end of the 18th century in cities and agrarian towns of Baja Andalusia, highlighting Jerez de la Frontera as the first written vestige of this art, although there is practically no data related to those dates and the manifestations of this time are more typical of thebolero
Bolero is a genre of song which originated in eastern Cuba in the late 19th century as part of the trova tradition. Unrelated to the older Spanish dance of the same name, bolero is characterized by sophisticated lyrics dealing with love. It has ...
school than of flamenco. It appeared as a modern art form from the convergence of the urban subaltern groups, Gitano communities, and journeyman of Andalusia that formed the marginalized Flamenco artistic working class who established Flamenco as a singular art form, marked from the beginning by the Gitano brand. Andalusia was the origin and cradle of the early Flamenco cantaores and of the three or four dozen Gitano families who created and cultivated Flamenco.
The casticismo
During the end of the 18th and beginning of the 19th century, a number of factors led to rise in Spain of a phenomenon known as "Costumbrismo Andaluz" or "Andalusian Mannerism". In 1783 Carlos III promulgated a pragmatics that regulated the social situation of the . This was a momentous event in the history of Spanish gitanos who, after centuries of marginalization and persecution, saw their legal situation improve substantially. After the Spanish War of Independence (1808–1812), a feeling of racial pride developed in the Spanish conscience, in opposition to the "gallified" "Afrancesados" - Spaniards who were influenced by French culture and the idea of the enlightenment. In this context, gitanos were seen as an ideal embodiment ofSpanish culture
The culture of ''Spain'' is based on a variety of historical influences, primarily based on the culture of ancient Rome, Spain being a prominent part of the Greco-Roman world for centuries, the very name of Spain comes from the name that the Rom ...
and the emergence of the bullfighting
Bullfighting is a physical contest that involves a bullfighter attempting to subdue, immobilize, or kill a bull, usually according to a set of rules, guidelines, or cultural expectations.
There are several variations, including some forms wh ...
schools of Ronda and Seville, the rise of the Bandidos and Vaqueros led to a taste for Andalusian romantic culture which triumphed in the Madrid court.
At this time there is evidence of disagreements due to the introduction of innovations in art.
Los cafés cantantes
In 1881Silverio Franconetti
Silverio Franconetti y Aguilar, also known simply as Silverio (June 10, 1831 – May 30, 1889) was a singer and the leading figure of the period in flamenco history known as The Golden Age, which was marked by the creation and definition of ...
opened the first flamenco singer café in Seville. In Silverio's café the cantaores were in a very competitive environment, which allowed the emergence of the professional cantaor and served as a crucible where flamenco art was configured. Locals learned the cantes, while reinterpreting the Andalusian folk songs in their own style, expanding the repertoire. Likewise, the taste of the public contributed to configure the flamenco genre, unifying its technique and its theme.
The antiflamenquismo of " La generación del 98"
''Flamenquismo'', defined by the Royal Spanish Academy as a "fondness for flamenco art and customs", is a conceptual catch-all where flamenco singing and a fondness for bullfighting, among other traditional Spanish elements, fit. These customs were strongly attacked by the generation of 98, all of its members being "anti-flamenco", with the exception of the Machado brothers, Manuel and Antonio. Being Sevillians and sons of the folklorist Demófilo Machado, the brothers had a more complex view of the matter. The greatest standard bearer of anti-flamenquism was the Madrid writer Eugenio Noel, who, in his youth, had been a militant ''casticista''. Noel attributed to flamenco and bullfighting the origin of the ills of Spain which he saw as manifestations of the country'sOriental
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of ''Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the ...
character which hindered economic and social development. These considerations caused an insurmountable rift to be established for decades between flamenco and most "intellectuals" of the time.
The flamenca opera
Between 1920 and 1955, flamenco shows began to be held in bullrings and theaters, under the name "flamenco opera". This denomination was an economic strategy of the promoters, since opera only paid 3% while variety shows paid 10%. At this time, flamenco shows spread throughout Spain and the main cities of the world. The great social and commercial success achieved by flamenco at this time eliminated some of the oldest and most sober styles from the stage, in favor of lighter airs, such as cantiñas, loscantes de ida y vuelta Cantes de ida y vuelta () is a Spanish expression literally meaning roundtrip songs. It refers to a group of flamenco musical forms or palos with diverse musical features, which "travelled back" from Latin America (mainly Cuba) as styles that, havi ...
and fandangos, of which many personal versions were created. The purist critics attacked this lightness of the cantes, as well as the use of falsete and the gaitero style.
In the line of purism, the poet Federico García Lorca and the composer Manuel de Falla had the idea of concurso de cante jondo en Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the fo ...
en 1922. Both artists conceived of flamenco as folklore, not as a scenic artistic genre; for this reason, they were concerned, since they believed that the massive triumph of flamenco would end its purest and deepest roots. To remedy this, they organized a cante jondo contest in which only amateurs could participate and in which festive cantes (such as cantiñas) were excluded, which Falla and Lorca did not consider jondos, but flamencos. The jury was chaired by Antonio Chacón, who at that time was the leading figure in cante. The winners were "El Tenazas", a retired professional cantaor from Morón de la Frontera, and Manuel Ortega, an eight-year-old boy from Seville who would go down in flamenco history as Manolo Caracol. The contest turned out to be a failure due to the scant echo it had and because Lorca and Falla did not know how to understand the professional character that flamenco already had at that time, striving in vain to seek a purity that never existed in an art that was characterized by mixture and the personal innovation of its creators. Apart from this failure, with the Generation of '27, whose most eminent members were Andalusians and therefore knew the genre first-hand, the recognition of flamenco by intellectuals began.
At that time, there were already flamenco recordings related to Christmas, which can be divided into two groups: the traditional flamenco carol and flamenco songs that adapt their lyrics to the Christmas theme. These cantes have been maintained to this day, the Zambomba Jerezana being spatially representative, declared an Asset of Intangible Cultural Interest by the Junta de Andalucía in December 2015.
During the Spanish Civil War, a large number of singers were exiled or died defending the Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
and the humiliations to which they were being subjected by the National Party: Bando Nacional
Bando ( my, ဗန်တို, ) is a defensive unarmed martial art from Myanmar. Bando is sometimes mistakenly used as a generic word for all Burmese martial arts, but it is only one martial art; Burmese fighting systems collectively are refe ...
: Corruco de Algeciras, Chaconcito, El Carbonerillo
EL, El or el may refer to:
Religion
* El (deity), a Semitic word for "God"
People
* EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer
* El DeBarge, music artist
* El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ...
, El Chato De Las Ventas
EL, El or el may refer to:
Religion
* El (deity), a Semitic word for "God"
People
* EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer
* El DeBarge, music artist
* El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ...
, Vallejito, Rita la Cantaora
Rita Giménez García, most commonly known as ''Rita la Cantaora'' (1859 in Jerez de la Frontera, Cádiz – 1937 in Zorita del Maestrazgo, Castellón), was one of the most famous Spanish singers of flamenco in her time due to her performances ...
, Angelillo
Ángel Sampedro Montero (12 January 1908 in Vallecas, Madrid- 24 November 1973 in Buenos Aires, Argentina), better known as Angelillo, was a Spanish singer of popular songs in his time. He has been described as a "popular idol of the flamenco cop ...
, Guerrita are some of them. In the postwar period and the first years of the Franco regime
Francoist Spain ( es, España franquista), or the Francoist dictatorship (), was the period of Spanish history between 1939 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death in 1975, Spai ...
, the world of flamenco was viewed with suspicion, as the authorities were not clear that this genre contributed to the national conscience. However, the regime soon ended up adopting flamenco as one of the quintessential Spanish cultural manifestations. The singers who have survived the war go from stars to almost outcasts, singing for the young men in the private rooms of the brothels in the center of Seville where they have to adapt to the whims of aristocrats, soldiers and businessmen who have become rich.
In short, the period of the flamenco opera was a time open to creativity and that definitely made up most of the flamenco repertoire. It was the Golden Age of this genre, with figures such as Antonio Chacón, Manuel Vallejo , Manuel Torre
Manuel Soto Loreto, known as Manuel Torre or Manuel Torres (1878 – 1933), was a Romani (Kalo) flamenco singer.
Beginning
Torre was born in Jerez de la Frontera, Spain, in the neighbourhood of San Miguel, which together with the neighbou ...
, La Niña de los Peines
Pastora Pavón Cruz, known as La Niña de los Peines (10 February 1890 – 26 November 1969), is considered the most important woman flamenco singer of the 20th century. She was a sister of singers Arturo Pavón and Tomás Pavón, also an importa ...
, Pepe Marchena and Manolo Caracol.
Flamencología
Starting in the 1950s, abundant anthropological and musicological studies on flamenco began to be published. In 1954 Hispavox published the first Antología del Cante Flamenco, a sound recording that was a great shock to its time, dominated by orchestrated cante and, consequently, mystified. In 1955, the Argentine intellectual Anselmo González Climent published an essay called "Flamencología", whose title he baptized the "set of knowledge, techniques, etc., on flamenco singing and dancing." This book dignified the study of flamenco by applying the academic methodology of musicology to it and served as the basis for subsequent studies on this genre. As a result, in 1956 the National Contest of Cante Jondo de Córdoba was organized and in 1958 the first flamencology chair was founded in Jerez de la Frontera, the oldest academic institution dedicated to the study, research, conservation, promotion and defense of the flamenco art. Likewise, in 1963 the Cordovan poet Ricardo Molina and the Sevillian cantaor Antonio Mairena published Alalimón Mundo y Formas del Cante flamenco, which has become a must-have reference work. For a long time the Mairenistas postulates were considered practically unquestionable, until they found an answer in other authors who elaborated the "Andalusian thesis", which defended that flamenco was a genuinely Andalusian product, since it had been developed entirely in this region and because its styles basic ones derived from the folklore of Andalusia. They also maintained that the Andalusian Gitanos had contributed decisively to their formation, highlighting the exceptional nature of flamenco among gypsy music and dances from other parts of Spain and Europe. The unification of the Gitanos and Andalusian thesis has ended up being the most accepted today. In short, between the 1950s and 1970s, flamenco went from being a mere show to also becoming an object of study.Flamenco protest during the Franco regime
Flamenco became one of the symbols of Spanish national identity during theFranco regime
Francoist Spain ( es, España franquista), or the Francoist dictatorship (), was the period of Spanish history between 1939 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death in 1975, Spai ...
, since the regime knew how to appropriate a folklore traditionally associated with Andalusia to promote national unity and attract tourism, constituting what was called national-flamenquismo. Hence, flamenco had long been seen as a reactionary or retrograde element. In the mid-60s and until the transition, cantaores who opposed the regime began to appear with the use of protest lyrics. These include: José Menese and lyricist Francisco Moreno Galván, Enrique Morente, Manuel Gerena, El Lebrijano, El Cabrero, Lole y Manuel, el Piki or Luis Marín, among many others.
In contrast to this conservatism with which it was associated during the Franco regime, flamenco suffered the influence of the wave of activism that also shook the university against the repression of the regime when university students came into contact with this art in the recitals that were held, for example, at the Colegio Mayor de San Juan Evangelista: "flamenco amateurs and professionals got involved with performances of a manifestly political nature. It was a kind of flamenco protest charged with protest, which meant censorship and repression for the flamenco activists ".
As the political transition progressed, the demands were deflated as flamenco inserted itself within the flows of globalized art. At the same time, this art was institutionalized until it reached the point that the Junta de Andalucía was attributed in 2007 "exclusive competence in matters of knowledge, conservation, research, training, promotion and dissemination".
Flamenco fusion
 In the 1970s, there were airs of social and political change in Spain, and Spanish society was already quite influenced by various musical styles from the rest of Europe and the United States. There were also numerous singers who had grown up listening to Antonio Mairena, Pepe Marchena and Manolo Caracol. The combination of both factors led to a revolutionary period called flamenco fusion.
The singer
In the 1970s, there were airs of social and political change in Spain, and Spanish society was already quite influenced by various musical styles from the rest of Europe and the United States. There were also numerous singers who had grown up listening to Antonio Mairena, Pepe Marchena and Manolo Caracol. The combination of both factors led to a revolutionary period called flamenco fusion.
The singer Rocío Jurado
María del Rocío Mohedano Jurado (, 18 September 1944 – 1 June 2006), better known as Rocío Jurado, was a Spanish singer and actress. She was born in Chipiona (Cádiz) and nicknamed "La más grande" ("The Greatest").
In 2000 in New York Cit ...
internationalized flamenco at the beginning of the 70s, replacing the bata de cola with evening dresses. Her facet in the "Fandangos de Huelva" and in the Alegrías was recognized internationally for her perfect voice tessitura in these genres. She used to be accompanied in her concerts by guitarists Enrique de Melchor and Tomatito, not only at the national level but in countries like Colombia, Venezuela and Puerto Rico.
The musical representative José Antonio Pulpón was a decisive character in that fusion, as he urged the cantaor Agujetas to collaborate with the Sevillian Andalusian rock group " Pata Negra", the most revolutionary couple since Antonio Chacón and Ramón Montoya, initiating a new path for flamenco. It also fostered the artistic union between the virtuoso guitarist from Algeciras Paco de Lucía and the long-standing singer from the island Camarón de la Isla, who gave a creative impulse to flamenco that would mean its definitive break with Mairena's conservatism. When both artists undertook their solo careers, Camarón became a mythical cantaor for his art and personality, with a legion of followers, while Paco de Lucía reconfigured the entire musical world of flamenco, opening up to new influences, such as Brazilian music, Arabic and jazz and introducing new musical instruments such as the Peruvian cajon, the transverse flute, etc.
Other leading performers in this process of formal flamenco renewal were Juan Peña El Lebrijano, who married flamenco with Andalusian music, and Enrique Morente, who throughout his long artistic career has oscillated between the purism of his first recordings and the crossbreeding with rock, or Remedios Amaya from Triana, cultivator of a unique style of tangos
Tangos may refer to:
* "Tangos" (song), a song popularized in Spain
* Tangos (district), a district or barangay in Navotas, Philippines
* ''Tangos'' (album), a 1973 album by Buenos Aires 8
* ''Tangos'' (Rubén Blades album), a 2014 album by Ru ...
from Extremadura, and a wedge of purity in her cante make her part of this select group of established artists. Other singers with their own style include Cancanilla de Marbella. In 2011 this style became known in India thanks to María del Mar Fernández
María del Mar Fernández (born 1 October 1978 in Cádiz) is a Spanish flamenco singer best known for her rendering of the song " Señorita" from the 2011 Hindi film ''Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara''.
Career
María began her career as a singer at th ...
, who acts in the video clip of the film You Live Once, entitled Señorita. The film was seen by more than 73 million viewers.
New flamenco
In the 1980s a new generation of flamenco artists emerged who had been influenced by the mythical cantaor Camarón, Paco de Lucía, Morente, etc. These artists were interested in popular urban music, which in those years was renewing the Spanish music scene, it was the time of the Movida madrileña. Among them are " Pata Negra", who fused flamenco with blues and rock, Ketama, of pop and Cuban inspiration and Ray Heredia, creator of his own musical universe where flamenco occupies a central place. Also the recording company Nuevos Medios released many musicians under the label nuevo flamenco and this denomination has grouped musicians very different from each other like Rosario Flores, daughter of Lola Flores, or the renowned singerMalú
María Lucía Sánchez Benítez, known as Malú, is a Spanish singer.
She is the niece of the composer and guitarist Paco de Lucía, and is known for songs such as "Aprendiz", "Como Una Flor", "Toda", "Diles", "Si Estoy Loca" and "No Voy a Cambia ...
, niece of Paco de Lucía and daughter of Pepe de Lucía, who despite sympathizing with flamenco and keeping it in her discography has continued with her personal style. However, the fact that many of the interpreters of this new music are also renowned cantaores, in the case of José Mercé, El Cigala, and others, has led to labeling everything they perform as flamenco, although the genre of their songs differs quite a bit from the classic flamenco. This has generated very different feelings, both for and against.
Other contemporary artists of that moment were O'Funkillo and Ojos de Brujo, Arcángel, Miguel Poveda, Mayte Martín, Marina Heredia, Estrella Morente or Manuel Lombo, etc.
But the discussion between the difference of flamenco and new flamenco in Spain has just gained strength during since 2019 due to the success of new flamenco attracting the taste of the youngest Spanish fans but also in the international musical scene emphasizing the problem of how should we call this new musical genre mixed with flamenco.
One of these artist who has reinvented flamenco is Rosalía, an indisputable name on the international music scene. "Pienso en tu mirá", "Di mi nombre" or the song that catapulted her to fame, "Malamente", are a combination of styles that includes a flamenco/south Spain traditional musical base. Rosalía has broken the limits of this musical genre by embracing other urban rhythms, but has also created a lot of controversy about which genre is she using. The Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
artist has been awarded several Latin GrammyAwards and MTV Video Music Awards
The MTV Video Music Awards (commonly abbreviated as the VMAs) is an award show presented by the cable channel MTV to honour the best in the music video medium. Originally conceived as an alternative to the Grammy Awards (in the video category) ...
, which also, at just 30 years old, garners more than 40 million monthly listeners on Spotify.
But it is not the only successful case, the Granada-born Dellafuente, C. Tangana
Antón Álvarez Alfaro (born July 16, 1990), known professionally as C. Tangana, is a Spanish rapper and songwriter. He began his musical career while in high school, rapping under the pseudonym Crema and releasing a seven-track EP titled ''É ...
, MAKA Maka or MAKA may refer to:
* Maká, a Native American people in Paraguay
** Maká language, spoken by the Maká
* Maka (satrapy), a province of the Achaemenid Empire
* Maka, Biffeche, capital of the kingdom of Biffeche in pre-colonial Senegal
* M ...
, RVFV, Demarco Flamenco, Maria Àrnal and Marcel Bagés, El Niño de Elche, Sílvia Pérez Cruz; Califato 3/4, Juanito Makandé, Soledad Morente, María José Llergo o Fuel Fandango
Top 100 España is a record chart published weekly by Productores de Música de España, PROMUSICAE (Productores de Música de España), a non-profit organization composed of Spanish and multinational Record label, record companies. This associati ...
are only a few of the new spanish musical scene that includes flamenco in their music.
It seems that the Spanish music scene is experiencing a change in its music and new rhythms are re-emerging together with new artists who are experimenting to cover a wider audience that wants to maintain the closeness that flamenco has transmitted for decades.
Flamenco Culture Overseas
The state of New Mexico, located in the southwest of the United States maintains a strong identity with Flamenco culture. The University of New Mexico located in Albuquerque offers a graduate degree program in Flamenco. Flamenco performances are widespread in the Albuquerque and Santa Fe communities, with the National institute of Flamenco sponsoring an annual festival, as well as a variety of professional flamenco performances offered at various locales. Emmy Grimm, known by her stage namLa Emi
is a professional Flamenco dancer and native to New Mexico who performs as well as teaches Flamenco in Santa Fe. She continues studying her art by traveling to Spain to work intensively with Carmela Greco and La Popi, as well as José Galván, Juana Amaya, Yolanda Heredia, Ivan Vargas Heredia, Torombo and Rocio Alcaide Ruiz.
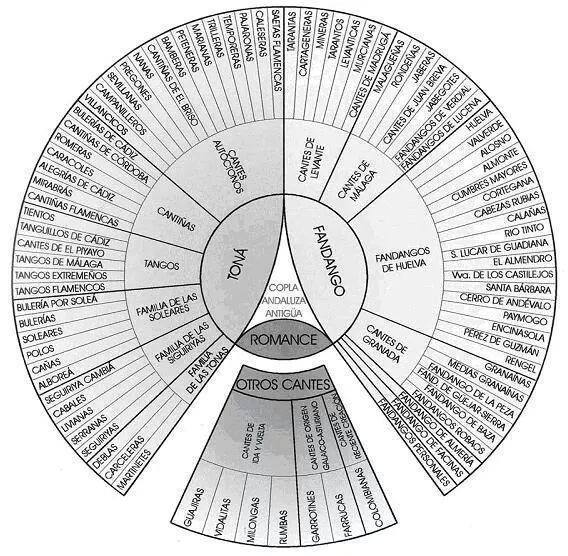
Main ''Palos''
 '' Palos'' (formerly known as ''cantes'') are flamenco styles, classified by criteria such as rhythmic pattern, mode, chord progression,
'' Palos'' (formerly known as ''cantes'') are flamenco styles, classified by criteria such as rhythmic pattern, mode, chord progression, stanza
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian language, Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or Indentation (typesetting), indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme scheme, rhyme and ...
ic form and geographic origin. There are over 50 different ''palos'', some are sung unaccompanied while others have guitar or other accompaniment. Some forms are danced while others are not. Some are reserved for men and others for women while some may be performed by either, though these traditional distinctions are breaking down: the ''Farruca'', for example, once a male dance, is now commonly performed by women too.
There are many ways to categorize ''Palos'' but they traditionally fall into three classes: the most serious is known as '' cante jondo'' (or '' cante grande''), while lighter, frivolous forms are called '' Cante Chico''. Forms that do not fit either category are classed as '' Cante Intermedio'' . These are the best known ''palos'' (; ):
zapateado
(Literally "a tap of the foot") and bulerías. This structure though, is not followed when alegrías are sung as a standalone song (with no dancing). In that case, the stanzas are combined freely, sometimes together with other types of cantiñas. Alegrías has a rhythm consisting of 12 beats. It is similar to Soleares. Its beat emphasis is as follows: 1 2 '' 4 5 '' 7 '' 9 0'' 11 2''. Alegrías originated in Cádiz. Alegrías belongs to the group of ''palos'' called Cantiñas and it is usually played in a lively rhythm (120–170 beats per minute). The livelier speeds are chosen for dancing, while quieter rhythms are preferred for the song alone.
Saeta
SAETA Air Ecuador (legally ''Sociedad Anónima Ecuatoriana de Transportes Aéreos S.A.'') was a privately held airline of Ecuador, which was founded in 1966. During its heyday in the 1990s, it flew to numerous destinations in North and South Ame ...
Tangos
Tangos may refer to:
* "Tangos" (song), a song popularized in Spain
* Tangos (district), a district or barangay in Navotas, Philippines
* ''Tangos'' (album), a 1973 album by Buenos Aires 8
* ''Tangos'' (Rubén Blades album), a 2014 album by Ru ...
Tanguillos
Tarantos
Music
Structure
A typical flamenco recital with voice and guitar accompaniment comprises a series of pieces (not exactly "songs") in different palos. Each song is a set of verses (called ''copla'', ''tercio'', or ''letras''), punctuated by guitar interludes ('' falsetas''). The guitarist also provides a short introduction setting the tonality, ''compás'' (see below) and tempo of the cante . In some palos, these falsetas are played with a specific structure too; for example, the typical sevillanas is played in an AAB pattern, where A and B are the same falseta with only a slight difference in the ending .Harmony
Flamenco uses theflamenco mode
In music theory, the flamenco mode (also Major-Phrygian) is a harmonized mode or scale abstracted from its use in flamenco music. In other words, it is the collection of pitches in ascending order accompanied by chords representing the pitches ...
(which can also be described as the modern Phrygian mode (''modo frigio''), or a harmonic version of that scale with a major 3rd degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathemati ...
), in addition to the major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
and minor
Minor may refer to:
* Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities.
** A person who has not reached the age of majority
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Music theory
*Minor chord
** Barb ...
scales commonly used in modern Western music. The Phrygian mode occurs in ''palos'' such as soleá, most bulerías, siguiriya
''Siguiriyas'' (; also ''seguiriyas'',
''siguerillas'', ''siguirillas'', ''seguidilla gitana'', etc.) are a form of flamenco music in the cante jondo category. This deep, expressive style is among the most important in flamenco. Unlike other pal ...
s, tangos
Tangos may refer to:
* "Tangos" (song), a song popularized in Spain
* Tangos (district), a district or barangay in Navotas, Philippines
* ''Tangos'' (album), a 1973 album by Buenos Aires 8
* ''Tangos'' (Rubén Blades album), a 2014 album by Ru ...
and tientos.
Andalusian cadence
The Andalusian cadence (diatonic phrygian tetrachord) is a term adopted from flamenco music for a chord progression comprising four chords descending stepwise – a iv–III–II–I progression with respect to the Phrygian mode or i–VII–VI� ...
" may be viewed as in a modified Phrygian: in E the sequence is Am–G–F–E . According to Manolo Sanlúcar
Manolo Sanlúcar (born Manuel Muñoz Alcón, 24 November 1943 – 27 August 2022) was a Spanish flamenco composer and guitarist. He was considered one of the most important Spanish composers of recent times, and together with Paco de Lucía, T ...
E is here the tonic, F has the harmonic function of dominant while Am and G assume the functions of subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
and mediant In music, the mediant (''Latin'': to be in the middle) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note i ...
respectively .
Guitarists tend to use only two basic inversions or "chord shapes" for the tonic chord (music)
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes (also called "pitches") that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords (in whic ...
, the open 1st inversion E and the open 3rd inversion A, though they often transpose these by using a capo. Modern guitarists such as Ramón Montoya, have introduced other positions: Montoya himself started to use other chords for the tonic in the modern Dorian sections of several ''palos''; F for ''tarantas
''Tarantas'' and ''Taranto'' are two related styles ('' palos'') of Flamenco music, that originated in the ''Andalusian'' province of Almería. Each is characterized by a shared modality (F-sharp Phrygian) and harmonic progression (Bm–A7– ...
'', B for '' granaínas'' and A for the ''minera''. Montoya also created a new ''palo'' as a solo for guitar, the '' rondeña'' in C with '' scordatura''. Later guitarists have further extended the repertoire of tonalities, chord positions and ''scordatura''.
There are also ''palos'' in major mode; most cantiñas and alegrías, guajiras, some '' bulerías'' and '' tonás'', and the ''cabales'' (a major type of '' siguiriyas''). The minor mode is restricted to the '' Farruca'', the ''milongas'' (among ''cantes de ida y vuelta Cantes de ida y vuelta () is a Spanish expression literally meaning roundtrip songs. It refers to a group of flamenco musical forms or palos with diverse musical features, which "travelled back" from Latin America (mainly Cuba) as styles that, havi ...
''), and some styles of ''tangos, bulerías'', etc. In general traditional palos in major and minor mode are limited harmonically to two-chord (tonic–dominant) or three-chord (tonic–subdominant–dominant) progressions . However modern guitarists have introduced chord substitution, transition chords, and even modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informatio ...
.
'' Fandangos'' and derivative ''palos'' such as '' malagueñas'', ''tarantas'' and '' cartageneras are bimodal'': guitar introductions are in Phrygian mode while the singing develops in major mode, modulating to Phrygian at the end of the stanza .
Melody
Dionisio Preciado, quoted by Sabas de , established the following characteristics for the melodies of flamenco singing: # Microtonality: presence of intervals smaller than the semitone. # Portamento: frequently, the change from one note to another is done in a smooth transition, rather than using discrete intervals. #Short tessitura or range: Most traditional flamenco songs are limited to a range of a sixth (four tones and a half). The impression of vocal effort is the result of using different timbres, and variety is accomplished by the use of microtones. #Use of enharmonic scale. While inequal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, wh ...
scales, enharmonic
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written n ...
s are notes with identical pitch but different spellings (e.g. A♭ and G♯); in flamenco, as in unequal temperament scales, there is a microtonal intervalic difference between enharmonic notes.
#Insistence on a note and its contiguous chromatic notes (also frequent in the guitar), producing a sense of urgency.
#Baroque ornamentation, with an expressive, rather than merely aesthetic function.
#Apparent lack of regular rhythm, especially in the siguiriyas: the melodic rhythm of the sung line is different from the metric rhythm of the accompaniment.
#Most styles express sad and bitter feelings.
#Melodic improvisation
Improvisation is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of impr ...
: flamenco singing is not, strictly speaking, improvised, but based on a relatively small number of traditional songs, singers add variations on the spur of the moment.
Musicologist Hipólito Rossy adds the following characteristics :
*Flamenco melodies are characterized by a descending tendency, as opposed to, for example, a typical opera aria, they usually go from the higher pitches to the lower ones, and from forte to piano, as was usual in ancient Greek scales.
*In many styles, such as soleá or siguiriya
''Siguiriyas'' (; also ''seguiriyas'',
''siguerillas'', ''siguirillas'', ''seguidilla gitana'', etc.) are a form of flamenco music in the cante jondo category. This deep, expressive style is among the most important in flamenco. Unlike other pal ...
, the melody tends to proceed in contiguous degrees of the scale. Skips of a third or a fourth are rarer. However, in fandangos and fandango-derived styles, fourths and sixths can often be found, especially at the beginning of each line of verse. According to Rossy, this is proof of the more recent creation of this type of songs, influenced by Castilian jota.
Compás or time signature
Compás is the Spanish word for metre or time signature (in classicalmusic theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
). It also refers to the rhythmic cycle, or layout, of a ''palo''.
The compás is fundamental to flamenco. Compás is most often translated as rhythm but it demands far more precise interpretation than any other Western style of music. If there is no guitarist available, the compás is rendered through hand clapping (''palmas'') or by hitting a table with the knuckles. The guitarist uses techniques like strumming (''rasgueado'') or tapping the soundboard (''golpe''). Changes of chords emphasize the most important downbeats.
Flamenco uses three basic counts or measures: Binary, Ternary and a form of a twelve-beat cycle that is unique to flamenco. There are also free-form styles including, among others, the tonás, saetas, malagueñas, tarantos, and some types of fandangos:
*Rhythms in or . These metres are used in forms like tangos
Tangos may refer to:
* "Tangos" (song), a song popularized in Spain
* Tangos (district), a district or barangay in Navotas, Philippines
* ''Tangos'' (album), a 1973 album by Buenos Aires 8
* ''Tangos'' (Rubén Blades album), a 2014 album by Ru ...
, tientos, gypsy rumba, zambra
''Zambra'' (), (from Andalusi Arabic ''zamra'', originally from classical Arabic ''zamr'') is a style of flamenco dance, typical of the Roma of the provinces of Granada and Almería (Andalusia, Spain).
It is believed that the zambra is a continua ...
and tanguillos.
*Rhythms in . These are typical of fandangos and sevillanas, suggesting their origin as non-Roma styles, since the and measures are not common in ethnic Roma music.
*12-beat rhythms usually rendered in amalgams of + and sometimes . The 12-beat cycle is the most common in flamenco, differentiated by the accentuation of the beats in different palos. The accents do not correspond to the classic concept of the downbeat. The alternating of groups of 2 and 3 beats is also common in Spanish folk dances of the 16th century such as the ''zarabanda'', ''jácara'' and ''canarios''.
There are three types of 12-beat rhythms, which vary in their layouts, or use of accentuations: soleá, seguiriya and bulería:
# peteneras and guajiras: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12. Both palos start with the strong accent on 12. Hence the meter is 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11.
#The seguiriya, liviana, serrana, toná liviana, cabales: 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12. It could also be counted like starting a bulerías scheme from 8 (see below).
# soleá, within the cantiñas group of palos which includes the alegrías, cantiñas, mirabras, romera, caracoles and soleá por bulería (also " bulería por soleá"): 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12. For practical reasons, when transferring flamenco guitar music to sheet music, this rhythm is written as a regular .
The Bulerías is the emblematic palo of flamenco: today its 12-beat cycle is most often played with accents on the 3rd, 6th, 8th, 10th and 12th beats. The accompanying ''palmas'' are played in groups of 6 beats, giving rise to a multitude of counter-rhythms and percussive voices within the 12 beat compás. In certain regions like, Jerez, Spain, the rhythm stays in a simpler six-count rhythm, only including the twelve count in a musical resolve. This is like starting the counting at 9 so it goes this way: 9 10 11 12 1 2 - again, bold means the emphasis when clapping. In real life it is counted from 1 like: 1 2 3 4 5 6 and so on.
Forms of flamenco expression
Toque (guitar)
The posture and technique of flamenco guitarists, called "tocaores", differs from that used by the players of classical guitar. While the classical guitarist supports the guitar on his left leg in an inclined way, the flamenco guitarist usually crosses his legs and supports it on the one that is higher, placing the neck in an almost horizontal position with respect to the ground. Modern guitarists usually use classical guitars, although there is a specific instrument for this genre called flamenco guitar. This is less heavy, and its body is narrower than that of the classical guitar, so its sound is lower and does not overshadow the cantaor. It is usually made ofcypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word ''cypress'' is derived from Old French ''cipres'', which was imported from Latin ''cypressus'', the ...
wood, with the handle of cedar and the top of fir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
. The cypress gives it a brilliant sound very suitable for the characteristics of flamenco. Formerly, the palo santo from Rio or India was also used, being the first of higher quality, but currently it is in disuse due to its scarcity. The palo santo gave guitars an amplitude of sound especially suitable for solo playing. At present, the most widely used headstock
A headstock or peghead is part of a guitar or similar stringed instruments such as a lute, mandolin, banjo, ukulele and others of the lute lineage. The main function of a headstock is to house the pegs or mechanism that holds the strings at the ...
is the metal one, since the wooden one poses tuning problems.
The main guitar makers were Antonio de Torres
Antonio de Torres Jurado (13 June 1817 – 19 November 1892) was a Spanish guitarist and luthier, and "the most important Spanish guitar maker of the 19th century."
It is with his designs that the first recognisably modern classical guitars are ...
Jurado ( Almería, 1817–1892) considered the father of the guitar, , the Great Ramírez (Madrid, 1864 -1920), and his disciples Santos Hernández (Madrid, 1873–1943), who built several guitars for the maestro Sabicas
Sabicas (proper name: Agustín Castellón Campos) (16 March 1912 – 14 April 1990) was a Spanish flamenco guitarist of Romani origin.
Biography
Sabicas was born in Pamplona, Spain, and began playing guitar at the age of five and made his perfor ...
, Domingo Esteso and . Also noteworthy are the Conde Brothers, Faustino (1913–1988), Mariano (1916–1989) and Julio (1918–1996), nephews of Domingo Esteso, whose children and heirs continue the saga.
The guitarists use the technique of alzapúa, picado, the strum and the tremolo
In music, ''tremolo'' (), or ''tremolando'' (), is a trembling effect. There are two types of tremolo.
The first is a rapid reiteration:
* Of a single Musical note, note, particularly used on String instrument#Bowing, bowed string instrument ...
, among others. One of the first touches that is considered flamenco, such as the "rondeña", was the first composition recorded for solo guitar, by Julián Arcas
Julián Arcas (25 October 1832 – 16 February 1882) was a Spanish classical guitarist and composer, who influenced Francisco Tárrega and Antonio de Torres. He was "one of the most important figures in Spanish music in the 19th century".
Biograp ...
( María, Almería, 1832 – Antequera
Antequera () is a city and municipality in the Comarca de Antequera, province of Málaga, part of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia. It is known as "the heart of Andalusia" (''el corazón de Andalucía'') because of its central locat ...
, Málaga, 1882) in Barcelona in 1860. The strum can be performed with 5, 4 or 3 fingers, the latter invented by Sabicas
Sabicas (proper name: Agustín Castellón Campos) (16 March 1912 – 14 April 1990) was a Spanish flamenco guitarist of Romani origin.
Biography
Sabicas was born in Pamplona, Spain, and began playing guitar at the age of five and made his perfor ...
. The use of the thumb is also characteristic of flamenco playing. Guitarists rest their thumb on the guitar's soundboard and their index and middle fingers on the string above the one they are playing, thus achieving greater power and sound than the classical guitarist. The middle finger is also placed on the pickguard of the guitar for more precision and strength when plucking the string. Likewise, the use of the pickguard as an element of percussion gives great strength to flamenco guitar playing. The melodic or flourishing phrase that is inserted between the chord sequences intended to accompany the couplet is called "falseta".
The accompaniment and solo playing of flamenco guitarists is based on both the modal harmonic system and the tonal system, although the most frequent is a combination of both. Some flamenco songs are performed "a palo seco" (a cappella
''A cappella'' (, also , ; ) music is a performance by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment, or a piece intended to be performed in this way. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Ren ...
), without guitar accompaniment.
Cante (song)
According to the Royal Spanish Academy, "cante" is called the "action or effect of singing any Andalusian singing", defining "flamenco singing" as "agitated Andalusian singing" and cante jondo as "the most genuine song. Andalusian, of deep feeling ". The interpreter of flamenco singing is called ''cantaor'' instead of singer, with the loss of the intervocalic characteristic of the Andalusian dialect. The most important award in flamenco singing is probably the , which has been awarded five times to: , , Antonio Mairena, Camarón de la Isla and Fosforito.Baile (dance)
''El baile flamenco'' is known for its emotional intensity, proud carriage, expressive use of the arms and rhythmic stamping of the feet, unlike tap dance or Irish dance which use different techniques. As with any dance form, many different styles of flamenco have developed. In the 20th century, flamenco danced informally at gitano (Roma) celebrations in Spain was considered the most "authentic" form of flamenco. There was less virtuoso technique in gitano flamenco, but the music and steps are fundamentally the same. The arms are noticeably different from classical flamenco, curving around the head and body rather than extending, often with a bent elbow. "Flamenco puro" otherwise known as "flamenco por derecho" is considered the form of performance flamenco closest to its gitano influences. In this style, the dance is often performed solo, and is based on signals and calls of structural improvisation rather than choreographed. In the improvisational style, castanets are not often used.
"Classical flamenco" is the style most frequently performed by Spanish flamenco dance companies. It is danced largely in a proud and upright style. For women, the back is often held in a marked back bend. Unlike the more gitano influenced styles, there is little movement of the hips, the body is tightly held, and the arms are long, like a ballet dancer. In fact, many of the dancers in these companies are trained in Ballet Clásico Español more than in the improvisational language of flamenco. Flamenco has both influenced and been influenced by Ballet Clásico Español, as evidenced by the fusion of the two ballets created by 'La Argentinita' in the early part of the 20th century and later, by Joaquín Cortés, eventually by the entire
"Flamenco puro" otherwise known as "flamenco por derecho" is considered the form of performance flamenco closest to its gitano influences. In this style, the dance is often performed solo, and is based on signals and calls of structural improvisation rather than choreographed. In the improvisational style, castanets are not often used.
"Classical flamenco" is the style most frequently performed by Spanish flamenco dance companies. It is danced largely in a proud and upright style. For women, the back is often held in a marked back bend. Unlike the more gitano influenced styles, there is little movement of the hips, the body is tightly held, and the arms are long, like a ballet dancer. In fact, many of the dancers in these companies are trained in Ballet Clásico Español more than in the improvisational language of flamenco. Flamenco has both influenced and been influenced by Ballet Clásico Español, as evidenced by the fusion of the two ballets created by 'La Argentinita' in the early part of the 20th century and later, by Joaquín Cortés, eventually by the entire Ballet Nacional de España
Ballet Nacional de España (English: ''National Ballet of Spain''; BNE) is a dance company founded in 1978. It is part of the National Institute of Performing Arts and Music (Spanish: ''Instituto Nacional de las Artes Escénicas y de la Música''; ...
et al.
In the 1950s Jose Greco
Jose is the English language, English transliteration of the Hebrew language, Hebrew and Aramaic language, Aramaic name ''Yose'', which is etymologically linked to ''Yosef'' or Joseph. The name was popular during the Mishnaic and Talmudic periods ...
was one of the most famous male flamenco dancers, performing on stage worldwide and on television including the Ed Sullivan Show, and reviving the art almost singlehandedly. Greco's company left a handful of prominent pioneers, most notably: Maria Benitez and Vicente Romero of New Mexico. Today, there are many centers of flamenco art. Albuquerque, New Mexico is considered the "Center of the Nation" for flamenco art. Much of this is due to Maria Benitez's 37 years of sold-out summer seasons. Albuquerque boasts three distinct prominent centers: National Institute of Flamenco, Casa Flamenca and Flamenco Works. Each center dedicates time to daily training, cultural diffusion and world-class performance equaled only to world-class performances one would find in the heart of Southern Spain, Andalucía.
Modern flamenco is a highly technical dance style requiring years of study. The emphasis for both male and female performers is on lightning-fast footwork performed with absolute precision. In addition, the dancer may have to dance while using props such as castanets, canes, shawls and fans.
" Flamenco nuevo" is a recent marketing phenomenon in flamenco. Marketed as a "newer version" of flamenco, its roots came from world-music promoters trying to sell albums of artists who created music that "sounded like" or had Spanish-style influences. Though some of this music was played in similar pitches, scales and was well-received, it has little to nothing to do with the art of flamenco guitar, dance, cante Jondo or the improvisational language. "Nuevo flamenco" consists largely of compositions and repertoire, while traditional flamenco music and dance is a language composed of stanzas, actuated by oral formulaic calls and signals.
 The flamenco most foreigners are familiar with is a style that was developed as a spectacle for tourists. To add variety, group dances are included and even solos are more likely to be choreographed. The frilly, voluminous spotted dresses are derived from a style of dress worn for the Sevillanas at the annual Feria in Seville.
In traditional flamenco, only the very young or older dancers are considered to have the emotional innocence or maturity to adequately convey the '' duende'' (soul) of the genre . Therefore, unlike other dance forms, where dancers turn professional through techniques early on to take advantage of youth and strength, many flamenco dancers do not hit their peak until their thirties and will continue to perform into their fifties and beyond. One artist that is considered a young master is Juan Manuel Fernandez Montoya, otherwise known as "Farruquito". At age 12, Farruquito was considered a pioneer and for "Flamenco Puro", or "Flamenco por Derecho", because of his emotional depth.
The flamenco most foreigners are familiar with is a style that was developed as a spectacle for tourists. To add variety, group dances are included and even solos are more likely to be choreographed. The frilly, voluminous spotted dresses are derived from a style of dress worn for the Sevillanas at the annual Feria in Seville.
In traditional flamenco, only the very young or older dancers are considered to have the emotional innocence or maturity to adequately convey the '' duende'' (soul) of the genre . Therefore, unlike other dance forms, where dancers turn professional through techniques early on to take advantage of youth and strength, many flamenco dancers do not hit their peak until their thirties and will continue to perform into their fifties and beyond. One artist that is considered a young master is Juan Manuel Fernandez Montoya, otherwise known as "Farruquito". At age 12, Farruquito was considered a pioneer and for "Flamenco Puro", or "Flamenco por Derecho", because of his emotional depth.
Claudio Castelucho
Claudio Castelucho y Diana (5 July 1870 in Barcelona – 31 October 1927 in Paris) was a Spanish sculptor, painter and art teacher from Catalonia who lived in France.
Biography
His father, , was a stage designer. Claudio received his firs ...
, flamenco
File:Theatre Flamenco Work Sample.webm, Theatre flamenco work sample
File:Baile andaluz 1893 José Villegas Cordero.jpg, José Villegas Cordero, Baile Andaluz
File:Sargent John Singer Spanish Dancer.jpg, John Singer Sargent
John Singer Sargent (; January 12, 1856 – April 14, 1925) was an American expatriate artist, considered the "leading portrait painter of his generation" for his evocations of Edwardian-era luxury. He created roughly 900 oil paintings and more ...
, ''Spanish Dancer''
Regulated teaching of flamenco in educational centers
In Spain, regulated flamenco studies are officially taught in various music conservatories, dance conservatories and music schools in various autonomous communities.Conservatories of music
 Flamenco guitar studies in official educational centers began in Spain in 1988 at the hands of the great concert performer and teacher from Granada
Flamenco guitar studies in official educational centers began in Spain in 1988 at the hands of the great concert performer and teacher from Granada Manuel Cano Tamayo
Manuel may refer to:
People
* Manuel (name)
* Manuel (Fawlty Towers), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers''
* Charlie Manuel, manager of the Philadelphia Phillies
* Manuel I Komnenos, emperor of the Byzantine Empire
* Manu ...
, who obtained a position as emeritus professor at thSuperior Conservatory de Música Rafael Orozco
from Córdoba. There are specialized flamenco conservatories throughout the country, although mainly in the Andalusia region, such as the aforementioned Córdoba Conservatory, th
Murcia Superior Music Conservatory
or the
Superior Music School of Catalonia
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
, among others. Outside of Spain, a unique case is the Rotterdam Conservatory
Codarts University for the Arts ( nl, Codarts hogeschool voor de kunsten) is a Dutch vocational university in Rotterdam that teaches music, dance and circus. It was established in its present location in 2000.
History
Codarts can trace its orig ...
, in the Netherlands, which offers regulated flamenco guitar studies under the direction of maestro Paco Peña since 1985, a few years before they existed in Spain.
University
In 2018 the first university master's degree in flamenco research and analysis begins, after the previous attempts of the "Doctorate Program of Approach to Flamenco", taught by several universities such as Huelva, Seville, Cádiz and Córdoba, among others.History
The fandango, which in the 17th century was the most widespread song and dance throughout Spain, eventually ended up generating local and regional variants, especially in the province of Huelva. In Alta Andalucía and bordering areas, the fandangos were accompanied with the bandola, an instrument with which they accompanied themselves following a regular beat that allowed dancing and from whose name the style derives " abandoned ". Thus arose the fandangos of Lucena, thedrones of Puente Genil
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
, the primitive malagueñas, the rondeñas, the jaberas, the jabegotes, the verdiales, the chacarrá, the granaína, the taranto and the taranta. Due to the expansion of the Sevillanas in Baja Andalusia, the fandango gradually lost its role as a support for the dance, which allowed the singer to shine and freedom, generating a multitude of fandangos of personal creation in the 20th century. Likewise, thousands of Andalusian peasants, especially from the Eastern Andalusian provinces, emigrated to the mining sites Murcian, where the tarantos and taranta s evolved. The Tarante de Linares Linares may refer to:
People
*Fernando de Alencastre, 1st Duke of Linares (1641–1717), Spanish nobleman and military officer; viceroy of New Spain from 1711 to 1716
*Andreu Linares (born 1975), Spanish futsal player
* Art Linares, American polit ...
, evolved into the mining of the Union, the Cartagena and the Levantica. At the time of the cafés cantantes, some of these cantes were separated from the dance and acquired a free beat, which allowed the performers to show off. The great promoter of this process was Antonio Chacón, who developed precious versions of malagueñas, granainas and cantes mineros.
The stylization of romance and cord sheets
Cord or CORD may refer to:
People
* Alex Cord (1933–2021), American actor and writer
* Chris Cord (born 1940), American racing driver
* Errett Lobban Cord (1894–1974) American industrialist
* Ronnie Cord (1943–1986), Brazilian singer
* Co ...
gave rise to corrido
The corrido () is a popular narrative metrical tale and poetry that forms a ballad. The songs are often about oppression, history, daily life for criminals, the vaquero lifestyle, and other socially relevant topics. Corridos were widely popular ...
. The extraction of the romances from quatrains or three significant verses gave rise to the primitive tonás, the caña and the polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ...
, which share meter and melody, but differing in their execution. The guitar accompaniment gave them a beat that made them danceable. It is believed that their origin was in Ronda, a city in Alta Andalucía
Alta or ALTA may refer to:
Acronyms
* Alt-A, short for Alternative A-paper, is a type of U.S. mortgage
* American Land Title Association, a national trade association representing the land title industry
* American Literary Translators Associatio ...
close to Baja Andalucía
Baja or Bája may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions In the Americas
* Baja California Peninsula, in northwestern Mexico
* Baja California state in the northern part of the above peninsula
* Baja California Sur state in the southern part of t ...
and closely related to it, and that from there they reached the Sevillian suburb of Triana, with a great tradition of corridos, where they became the soleá. From the festive performance of corridos and soleares, the jaleos arose in Triana, who traveled to Extremadura and in Jerez and Utrera led to the bulería, from where they spread throughout Baja Andalucía, generating local variations.
Lexicon
Ole
Adolfo Salazar states that the expressive voice ''ole'', with which Andalusian ''cantaores'' and ''bailaores'' are encouraged, can come from the Hebrew verb ''oleh'' which means "to throw upwards", showing that the dervish girovaghi of Tunisia, Maghreb, also dance around to the sound of repeated "ole" or "joleh". The use of the word "arza", which is theAndalusian dialect
The Andalusian dialects of Spanish ( es, andaluz, , ) are spoken in Andalusia, Ceuta, Melilla, and Gibraltar. They include perhaps the most distinct of the southern variants of peninsular Spanish, differing in many respects from northern varietie ...
form, of pronouncing the voice imperative "rise", with the characteristic Andalusian equalization of / l / and / r / implosives. The indiscriminate use of the voices "arza" and "ole" is frequent when it comes to ''jalear'', but the most evidence of the origin of this word can be from the caló: ''Olá'', which means "come". Likewise, in Andalusia it is known as jaleo al ojeo de hunt, that is, the act of glancing, which is "driving away the game with voices, shots, blows or noise, so that they 'get up.
Duende
According to the RAE dictionary (1956!) The "duende" in Andalusia is a "mysterious and ineffable charm", a charisma that the Gitanos call duende. Federico García Lorca, in his lecture ''Teoría y juego del duende'' confirms this ineffability of the duende by defining it with the following words from Goethe: "Mysterious power that everyone feels and that no philosopher explains". In the flamenco imaginary, the duende goes beyond technique and inspiration, in Lorca's words "To search for the duende there is no map or exercise". When a flamenco artist experiences the arrival of this mysterious charm, the expressions "have duende" or sing, play or dance "with duende" are used. Along with those previously mentioned, there are many other words and expressions characteristic of the flamenco genre, such as "tablao flamenco", "flamenco spree", "third", "aflamencar", and "flamenco".See also
References
Sources
* * * Álvarez Caballero, Ángel: ''El cante flamenco'', Alianza Editorial, Madrid, Second edition, 1998. (First edition: 1994) * Álvarez Caballero, Ángel: ''La Discografía ideal del cante flamenco'', Planeta, Barcelona, 1995. * * * * Arredondo Pérez, Herminia, and Francisco J. García Gallardo: "Música flamenca. Nuevos artistas, antiguas tradiciones" In ''Andalucía en la música. Expresión de comunidad, construcción de identidad'', edited by Francisco J. García y Herminia Arredondo. Sevilla: Centro de Estudios Andaluces, 2014, pp. 225–242. * Banzi, Julia Lynn (PhD): "Flamenco Guitar Innovation and the Circumscription of Tradition" 2007, 382 pages; AAT 328581, DAI-A 68/10, University of California, Santa Barbara. * Caba Landa, Pedro, and Carlos Caba Landa. ''Andalucía, su comunismo y su cante jondo''. First edition, Editorial Atlántico 1933. Third edition, Editorial Renacimiento 2008. * * Coelho, Víctor Anand (Editor): "Flamenco Guitar: History, Style, and Context", in '' The Cambridge Companion to the Guitar'', Cambridge University Press, 2003, pp. 13–32. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Mairena, Antonio, and Ricardo Molina. ''Mundo y formas del cante flamenco'', Librería Al-Ándalus, third edition, 1979 (First Edition: Revista de Occidente, 1963) * * * *. * Martín Salazar, Jorge: ''Los cantes flamencos'', Diputación Provincial de Granada, Granada, 1991 * * * Ortiz Nuevo, José Luis: ''Alegato contra la pureza'', Libros PM, Barcelona, 1996. * * * * * *''Rito y geografía del cante''. Serie documental de los años 70 del siglo XX sobre los orígenes, estilos y pervivencia del cante flamenco
con
José María Velázquez
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ).
In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacul ...
-Gaztelu.
* Nuestro flamenco
': programa de
Radio Clásica
Radio Clásica is a Spanish free-to-air radio station owned and operated by Radio Nacional de España (RNE), the radio division of state-owned public broadcaster Radiotelevisión Española (RTVE). It is the corporation's second radio station, and ...
, con José María Velázquez-Gaztelu.
Agencia Andaluza para el Desarrollo del Flamenco
Flamenco Viejo
Flamenco Olímpico
Reportaje Documental
''Flamenco de la A a la Z''
breve enciclopedia del flamenco que incluye diccionario en e
sitio
de Radiolé. * GRANDE, Félix: ''Memoria del flamenco'', con prólogo de
José Manuel Caballero Bonald
José Manuel Caballero Bonald (November 11, 1926 – May 9, 2021) was a Spanish novelist, lecturer and poet.
Early life
Caballero was born in Calle Caballeros, Jerez de la Frontera, Spain. His father was Plácido Caballero, a Cuban whose mother ...
. Galaxia Gutenberg/ Círculo de Lectores, Barcelona, 1991.
*Texto
en ''
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
''.
Flamenco en Sevilla
* Lafuente Alcántara, Emilio (1825–1868): ''Cancionero popular. Colección escogida de seguidillas y coplas'', 1865. ** Vol. II
''Coplas''
texto en Google Books. *
Sobre Emilio Lafuente Alcántara
, hermano de
Miguel Lafuente Alcántara
-->
Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to:
Places
* Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands
*São Miguel (disamb ...
, en esitio
Biblioteca Virtual de Arabistas y Africanistas Españoles.
* Universo Lorca
El Concurso del Cante Jondo de 1922. Web dedicada a la vida y obra de Federico García Lorca y su vinculación con Granada.
(Diputación de Granada) * Los Palos del Flamenco
Los Palos del Flamenco. Artículos sobre el origen y evolución del arte flamenco.
(Flamencos Online)
Notes
External links
{{Authority controlFlamenco show in Seville
Flamenco, Spanish music Andalusian music Romani dances Spanish dances Spanish folk music European folk dances Articles containing video clips Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity Romani culture Romani music