|
Palo (flamenco)
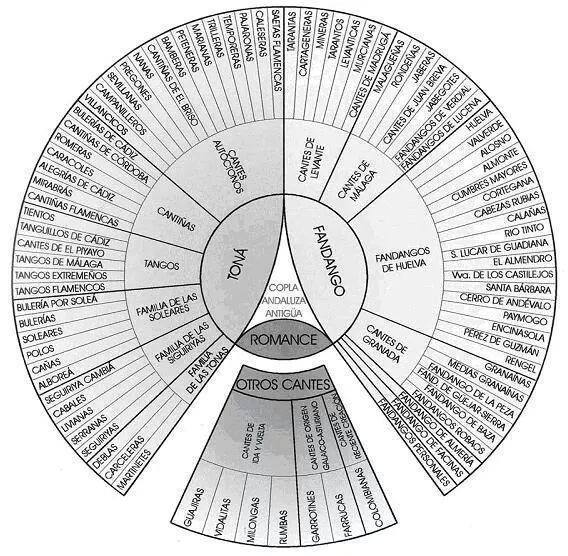
A ''palo'' () or cante is the name given in flamenco for the different traditional musical forms. The word ''palo'', in Spanish, has several meanings, the main one being "stick", "pole" "rod" or "Tree", but in this case it has the sense of " suit of cards" i.e. category or classification. Identifying palos Each ''palo'' is identified by a variety of musical features such as its rhythmic pattern, its mode, its characteristic motifs, the type of stanza used for the lyrics, and its origin. The concept of ''palo'' is not straightforward or rigorous. It is a popular, sometimes inconsistent way of classifying songs according to similar characteristics. For example, to determine that a song belongs to the ''palo'' called Bulerías, only the rhythm is taken into consideration, no matter its mode or stanza. Fandangos, on the other hand, include a variety of forms in or , but later it developed "free" forms (that is, with no determined rhythm). Most ''palos'' include dozens of tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palos Flamencos
Palos may refer to: __NOTOC__ Arts and entertainment *Two drums, the ''palos major'' and ''palos menor'', used in the music of the Dominican Republic *Palo (flamenco), a flamenco musical forms * ''Palos'' (TV series), a 2008 Philippine TV series Military *Battle of Cape Palos (1815), battle of the Second Barbary War * Battle of Cape Palos (1938), battle of the Spanish Civil War Places *Palos de la Frontera, a municipality in Spain, from where Columbus sailed in 1492 *Palos Verdes, a place in Los Angeles, California, U.S. *Cape Palos, cape on the Mediterranean coast of Spain *Palos, Illinois (other), several communities within Palos Township *Paloș (other), several places in Romania * Palos Site, Native American archaeological site in Illinois People *Enrique Palos Enrique Eduardo Palos Reyes (born 31 May 1986) is a former Mexican professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. Club career Tigres Palos has spent most of his career as 2nd/3rd goalkeeper u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarantas (flamenco Palo)
''Tarantas'' and ''Taranto'' are two related styles ('' palos'') of Flamenco music, that originated in the ''Andalusian'' province of Almería. Each is characterized by a shared modality (F-sharp Phrygian) and harmonic progression (Bm–A7–G–F-sharp), but differ significantly with respect to rhythm and meter. ''Tarantas'' is a cante libre (or toque libre, if played as a solo), meaning that it lacks both a regular rhythmic pattern ( ''compás'', in flamenco terminology) and a regular rhythmic unit (or beat). It can be sung or played, but not danced. ''Taranto'', conversely, has a regular 2/4-meter, and is danceable. When played on, or accompanied by, the guitar The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected stri ..., both ''palos'' have a unique and characteristic sound that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polo (flamencu Palo)
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ball through the opposing team's goal. Each team has four mounted riders, and the game usually lasts one to two hours, divided into periods called ''chukkas'' or "''chukkers''". Polo has been called "the sport of kings", and has become a spectator sport for equestrians and high society, often supported by sponsorship. The progenitor of the game and its variants existed from the to the as equestrian games played by nomadic Iranian and Turkic peoples. In Persia, where the sport evolved and developed, it was at first a training game for cavalry units, usually the royal guard or other elite troops. A notable example is Saladin, who was known for being a skilled polo player which contributed to his cavalry training. It is now popular around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caña (flamenco)
Caña may refer to: * Sugarcane or other canes * a general term for rum, or any hard liquor from sugar * Caña (Chilean slang), a hangover * Caña blanca, a white rum from a sugar and molasses mixture, without dark molasses or caramel, without oak ageing * a nickname for Orujo, hard liquor from grape pressings (pomace) * La Caña, a district of Los Ríos, Distrito Nacional, Dominican Republic * Potrero de Caña, a corregimiento in Tolé District, Chiriquí Province, Panama * Caña (flamenco), a musical form similar to the polo * Kelvin Caña (born 1987), Venezuelan épée fencer * Another name for the Baston, a martial arts weapon See also * Flor de Caña (other) * Cana (other) CANA or Cana may refer to: Cana Cana may refer to: Places Biblical *Kanah, town and brook mentioned in the Book of Joshua of the Hebrew Bible (see Wadi Qana) *Cana, village mentioned in the Gospel of John as "Cana of Galilee", site of the Marriag ... * * Cañita (other) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christof Jung
Christof is a masculine given name. It is a German variant of Christopher. Notable people with the name include: *Christof Babatz (born 1974), German former professional footballer *Christof Duffner (born 1971), German former ski jumper *Christof Ebert (born 1964), German computer scientist and entrepreneur *Christof Heyns, South African academic *Christof Innerhofer (born 1984), Italian alpine ski racer *Christof Koch (born 1956), American neuroscientist *Christof Lauer (born 1953), German saxophonist *Christof Lindenmayer (born 1977), American former soccer player *Christof Marselis, (1670s – 1731), Polish-Dutch architect *Christof Mauch, German historian *Christof Migone, Swiss-born experimental sound artist and writer *Christof Perick (born Christof Prick, 1946), German conductor *Christof Plümacher or Christof Pluemacher (born 1963), German photographer *Christof Putzel, American journalist *Christof Schwaller (born 1966), Swiss curler *Christof Unterberger (born 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tientos
''Tiento'' (, pt, Tento ) is a musical genre originating in Spain in the mid-15th century. It is formally analogous to the fantasia (fantasy), found in England, Germany, and the Low Countries, and also the ricercare, first found in Italy. By the end of the 16th century the tiento was exclusively a keyboard form, especially of organ music. It continued to be the predominant form in the Spanish organ tradition through the time of Cabanilles, and developed many variants. Additionally, many 20th-century composers have written works entitled "''tiento''". Name The word derives from the Spanish verb ''tentar'' (meaning either to touch, to tempt or to attempt), and was originally applied to music for various instruments. In the early eighteenth century, some composers also used the term ''obra'', originally a more general term meaning "work", to refer to this genre. Formal aspects The tiento is formally extraordinarily diverse, more a set of guidelines than a rigid structural m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compás
Flamenco (), in its strictest sense, is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, it is a portmanteau term used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fandango Libre
Fandango is a lively partner dance originating from Portugal and Spain, usually in triple meter, traditionally accompanied by guitars, castanets, or hand-clapping. Fandango can both be sung and danced. Sung fandango is usually bipartite: it has an instrumental introduction followed by "variaciones". Sung fandango usually follows the structure of "cante" that consist of four or five octosyllabic verses (coplas) or musical phrases (tercios). Occasionally, the first copla is repeated. The meter of fandango is similar to that of the bolero and seguidilla. It was originally notated in time, of slow tempo, mostly in the minor, with a trio in the major; sometimes, however, the whole was in a major key. Later it took the 3-4 tempo, and the characteristic Spanish rhythm. Origins The earliest fandango melody is found in the anonymous "Libro de diferentes cifras de guitarra" from 1705, and the earliest description of the dance itself is found in a 1712 letter by Martín Martí, a Spanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulerías
''Bulería'' (; interchangeable with the plural, ''bulerías'') is a fast flamenco rhythm made up of a 12 beat cycle with emphasis in two general forms as follows: This may be thought of as a measure of followed by a measure of (known as hemiola). For dancers, it is commonly viewed with a compas or bar of 6 counts as opposed to 12. An interesting counting method has been used by Pepe Romero, in his book ''Classical Guitar Style and Technique'', which is 2 measures of time followed by 3 measures of time. This puts the emphasis on the last beat of each measure: When performed, the ''bulería'' always starts on beat twelve of the ''compas'', so the accented beat is heard first. It is normally played at 195-240 beats per minute, most commonly in an A- phrygian mode (por medio) with a sharpened third to make A major the root chord. A typical ''rasgueado'' pattern involves only the A and B chords, were golpes are used to accent the chords as follows: '' — — ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tango (flamenco)
In flamenco a ''tango'' () is one of the flamenco palos closely related in form and feeling to the rumba flamenca. It is often performed as a finale to a flamenco tiento. Its compás and llamada are the same as that of the farruca and share the farruca's lively nature. However, the tango is normally performed in the A Phrygian mode. In some English sources the flamenco tango is written with an -s; "the tangos is..." The flamenco tango is distinct from the flamenco rumba primarily through the guitar playing. In Rumba the guitar flows more freely, whereas in Tangos the accents on beats 2, 3 & 4 are marked clearly with heavy strumming. Tangos is only vaguely related to Argentine tango, and objectively they only share ''compás binario'' or double stroke rhythm. The fact that Argentine tango is one of the first couple dances in America has led historians to believe that both could be based in a minuet-style European dance, therefore sharing a common ancestor, while those who compare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siguiriyas
''Siguiriyas'' (; also ''seguiriyas'', ''siguerillas'', ''siguirillas'', ''seguidilla gitana'', etc.) are a form of flamenco music in the cante jondo category. This deep, expressive style is among the most important in flamenco. Unlike other palos of flamenco, siguiriyas stands out for being purely Romani (Calé) in origin. Siguiriyas are normally played in the key of A Phrygian with each measure (the compás) consisting of 12 counts with emphasis on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, 8th and 11th beats as shown here: : : '' 2 '' 4 '' 6 7 '' 9 10 1'' 12 This rhythm can be contrasted with the rhythmic pattern of the soleares, which also has 12 beats, but the accents fall differently. Taking the unusual accenting into account, it can technically be seen as a measure of 3/4 (counted in eighth notes) starting on "2", then a measure of 6/8 followed by the "1 and" of the 3/4. Every note is evenly spaced apart. For example: : : '' and '' and '' 2 3 '' 5 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |