East Lothian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
East Lothian (; sco, East Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Ear) is one of the 32
 Haddingtonshire was heavily involved in several medieval and early modern conflicts and several fortified castles and buildings such as
Haddingtonshire was heavily involved in several medieval and early modern conflicts and several fortified castles and buildings such as
 Haddingtonshire County Council was created in 1890 under the
Haddingtonshire County Council was created in 1890 under the
File:Physicalmapjoined.jpg, Orographical Map of East Lothian
File:WhiteadderReservoir01.jpg, The Whiteadder Reservoir
File:BassRockNB.JPG, Bass Rock in the Firth of Forth
File:Traprain Law from the north.JPG,
 East Lothian is served by seven railway stations:
East Lothian is served by seven railway stations:

 *
*
 In 1894, John Martine published ''Reminiscences and Notices of Ten Parishes of the County of Haddington''.
*
In 1894, John Martine published ''Reminiscences and Notices of Ten Parishes of the County of Haddington''.
*
 There are a range of schools in the county, including six
There are a range of schools in the county, including six
 In November 2017, a county flag competition was launched in East Lothian to register an official flag of East Lothian. Anyone willing to enter this competition was allowed to enter, which resulted in 623 entries to the competition. The end of the entry submission time was the 28th of February 2018. Four final flag designs will be placed in a vote to the residents of East Lothian. In December 2018 the winning design was announced, designed by Archie Martin, a local man from Musselburgh and residing in Gifford who had worked for the council for 23 years. Martin died in July 2018. The flag features a saltire representing East Lothian as the birthplace of Scotland's flag. A gold cross signifies the wealth of East Lothian's farmlands and reputation as the granary of Scotland with a lion in the centre representing the Haddington lion along with blue stripes to represent the rivers Esk and Tyne.
In November 2017, a county flag competition was launched in East Lothian to register an official flag of East Lothian. Anyone willing to enter this competition was allowed to enter, which resulted in 623 entries to the competition. The end of the entry submission time was the 28th of February 2018. Four final flag designs will be placed in a vote to the residents of East Lothian. In December 2018 the winning design was announced, designed by Archie Martin, a local man from Musselburgh and residing in Gifford who had worked for the council for 23 years. Martin died in July 2018. The flag features a saltire representing East Lothian as the birthplace of Scotland's flag. A gold cross signifies the wealth of East Lothian's farmlands and reputation as the granary of Scotland with a lion in the centre representing the Haddington lion along with blue stripes to represent the rivers Esk and Tyne.
East Lothian Council
''official government website'' * {{Authority control Counties of Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Council areas of Scotland Counties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922)
council areas of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" ( gd, comhairlean), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Ga ...
, as well as a historic county, registration county
A registration county was, in Great Britain and Ireland, a statistical unit used for the registration of births, deaths and marriages and for the output of census information. In Scotland registration counties are used for land registration purpose ...
and lieutenancy area
Lieutenancy areas are the separate areas of the United Kingdom appointed a lord-lieutenant – a representative of the British monarch. In many cases they have similar demarcation and naming to, but are not necessarily coterminate with, the coun ...
. The county was called Haddingtonshire until 1921.
In 1975, the historic county was incorporated for local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
purposes into Lothian Region
Lothian (; sco, Lowden, Loudan, -en, -o(u)n; gd, Lodainn ) is a region of the Scottish Lowlands, lying between the southern shore of the Firth of Forth and the Lammermuir Hills and the Moorfoot Hills. The principal settlement is the Sc ...
as East Lothian District, with some slight alterations of its boundaries. The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994
The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 (c. 39) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the current local government structure of 32 unitary authorities covering the whole of Scotland.
It abolished the two-tie ...
later created East Lothian as one of 32 modern council areas. East Lothian lies south of the Firth of Forth in the eastern central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands, sometimes called the Midland Valley or Central Valley, is a geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland. It consists of a rift valley between the Highland Boundary Fault to the north and ...
of Scotland. It borders Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
to the west, Midlothian to the south-west and the Scottish Borders to the south. Its administrative centre and former county town is Haddington while the largest town is Musselburgh.
Haddingtonshire has ancient origins and is named in a charter of 1139 as ''Hadintunschira'' and in another of 1141 as ''Hadintunshire''. Three of the county's towns were designated as royal burghs
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
: Haddington, Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
, and North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
.
As with the rest of Lothian, it formed part of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
and later the Kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
. Popular legend suggests that it was at a battle between the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from e ...
and Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
in the East Lothian village of Athelstaneford
Athelstaneford () is a village in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies almost 6 kilometres (3.5 mi) north-east of the market town of Haddington and about 28 kilometres (17 mi) east of Edinburgh.
Battle of Athelstaneford
According to popul ...
in 823 that the flag of Scotland
The flag of Scotland ( gd, bratach na h-Alba; sco, Banner o Scotland, also known as St Andrew's Cross or the Saltire) is the national flag of Scotland, which consists of a white saltire defacing a blue field. The Saltire, rather than the ...
was conceived. From the 10th century, Lothian transferred from the Kingdom of England to the authority of the monarchs of Scotland. It was a cross-point in battles between England and Scotland and later the site of a significant Jacobite victory against Government forces in the Battle of Prestonpans
The Battle of Prestonpans, also known as the Battle of Gladsmuir, was fought on 21 September 1745, near Prestonpans, in East Lothian, the first significant engagement of the Jacobite rising of 1745.
Jacobite forces, led by the Stuart exile C ...
. In the 19th century, the county is mentioned in the Gazetteer for Scotland as chiefly agricultural, with farming, fishing and coal-mining forming significant parts of the local economy.
History
Early history
Following the end of the Roman occupation of Britain, Lothian was populated by Brythonic-speakingAncient Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
and formed part of the kingdom of the Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
, within the Hen Ogledd
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population sp ...
or Old North. In the 7th century, all of the Gododdin's territory fell to the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, with Lothian becoming part of the kingdom of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
.
Bernicia united into the Kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
which itself became part of the early Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
. Lothian came under the control of the Scottish monarchy in the 10th century.
The earliest reference to the shire of Haddington, or Haddingtonshire, occurred in the 12th century, in two charters issued by King David. The shire covered the eastern part of Lothian.
Medieval and early modern period
 Haddingtonshire was heavily involved in several medieval and early modern conflicts and several fortified castles and buildings such as
Haddingtonshire was heavily involved in several medieval and early modern conflicts and several fortified castles and buildings such as Dunbar Castle
Dunbar Castle was one of the strongest fortresses in Scotland, situated in a prominent position overlooking the harbour of the town of Dunbar, in East Lothian. Several fortifications were built successively on the site, near the English-Scotti ...
, Tantallon Castle and Dirleton Castle
Dirleton Castle is a medieval fortress in the village of Dirleton, East Lothian, Scotland. It lies around west of North Berwick, and around east of Edinburgh. The oldest parts of the castle date to the 13th century, and it was abandoned by th ...
date from this period.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Palace of Haddington
The Palace of Haddington was a 12th13th-century royal palace in Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland. The palace stood in King Street (now Court Street), on the site of the present East Lothian Council buildings. Remains of the vaulting of the pala ...
was one of the seats of the Kings of Scotland
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have grown ...
. King William the Lion
William the Lion, sometimes styled William I and also known by the nickname Garbh, "the Rough"''Uilleam Garbh''; e.g. Annals of Ulster, s.a. 1214.6; Annals of Loch Cé, s.a. 1213.10. ( 1142 – 4 December 1214), reigned as King of Scots from 11 ...
of Scotland used the palace from time to time and it was the birthplace of Alexander II in 1198. The palace and town were burned and pillaged in 1216, by an English army under the command of King John of England
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the t ...
. In 1296, the Battle of Dunbar was a decisive victory for the forces of Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vas ...
against the forces of John Balliol
John Balliol ( – late 1314), known derisively as ''Toom Tabard'' (meaning "empty coat" – coat of arms), was King of Scots from 1292 to 1296. Little is known of his early life. After the death of Margaret, Maid of Norway, Scotland entered an ...
, the Scottish king who was Edward's vassal.
Haddingtonshire was also the site of conflict during the war of the Rough Wooing
The Rough Wooing (December 1543 – March 1551), also known as the Eight Years' War, was part of the Anglo-Scottish Wars of the 16th century. Following its break with the Roman Catholic Church, England attacked Scotland, partly to break the ...
, with many houses and villages burnt by the English in May 1544 after the sacking of Edinburgh, the Scottish defeat at the battle of Pinkie
The Battle of Pinkie, also known as the Battle of Pinkie Cleugh ( , ), took place on 10 September 1547 on the banks of the River Esk near Musselburgh, Scotland. The last pitched battle between Scotland and England before the Union of the Crow ...
, Dunbar Castle
Dunbar Castle was one of the strongest fortresses in Scotland, situated in a prominent position overlooking the harbour of the town of Dunbar, in East Lothian. Several fortifications were built successively on the site, near the English-Scotti ...
burnt in 1548, and the siege of Haddington
The sieges of Haddington were a series of sieges staged at the Royal Burgh of Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland, as part of the War of the Rough Wooing, one of the last Anglo-Scottish Wars. Following Regent Arran's defeat at the battle of P ...
. Haddingtonshire lairds supported the English cause, including John Cockburn of Ormiston
John Cockburn, (d. 1583) laird of Ormiston, East Lothian, Scotland, was an early supporter of the Scottish Reformation. He was the eldest son of William Cockburn of Ormiston and Janet Somerville. John was usually called "Ormiston." During his lif ...
, Alexander Crichton of Brunstane, and Regent Arran
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state ''pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy, ...
demolished their houses.
During the War of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 B ...
, another Battle of Dunbar took place in 1650 between Scottish Covenanter forces and the Parliamentary forces under Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
. The Parliamentary forces were victorious and able to march on to take Edinburgh.
Following the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
of the monarchy, Glorious Revolution and Acts of Union, Jacobite forces conflicted with Government forces, with the main conflict taking place as part of the 1715 Rising
The Jacobite rising of 1715 ( gd, Bliadhna Sheumais ;
or 'the Fifteen') was the attempt by James Edward Stuart (the Old Pretender) to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland for the exiled Stuarts.
At Braemar, Aberdeenshire, lo ...
and 1745 Rising. Under the command of Sir John Cope, the British Army met with the Jacobites under Charles Edward Stuart at the Battle of Prestonpans
The Battle of Prestonpans, also known as the Battle of Gladsmuir, was fought on 21 September 1745, near Prestonpans, in East Lothian, the first significant engagement of the Jacobite rising of 1745.
Jacobite forces, led by the Stuart exile C ...
in the west of the county in September 1745, with the Jacobite side gaining a significant victory before being defeated at the Battle of Culloden in April 1746.
Modern history
 Haddingtonshire County Council was created in 1890 under the
Haddingtonshire County Council was created in 1890 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889
The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c. 50) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which was passed on 26 August 1889. The main effect of the act was to establish elected county councils in Scotland. In this it foll ...
, which established elected county councils across Scotland, taking over most of the functions of the Commissioners of Supply
Commissioners of Supply were local administrative bodies in Scotland from 1667 to 1930. Originally established in each sheriffdom to collect tax, they later took on much of the responsibility for the local government of the counties of Scotland. ...
, which had been the main administrative body of the shire since 1667. The county council was based at County Buildings in Court Street, Haddington, which had been built in 1833 and also served as the county's sheriff court.
In April 1921 the county council voted to request a change of the county's name from Haddingtonshire to "East Lothian". The government agreed and brought the change into effect as part of the East Lothian County Buildings Order Confirmation Act 1921, which received royal assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
on 8 November 1921. The act also transferred ownership of the County Buildings to the county council.
In 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, Scotland's county councils were dissolved and a new system of regional and district councils was created. East Lothian District
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
was created within the wider Lothian region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
. The district comprised the historic county of East Lothian plus the burgh of Musselburgh and the parish of Inveresk
Inveresk (Gaelic: ''Inbhir Easg'') is a village in East Lothian, Scotland situated to the south of Musselburgh. It has been designated a conservation area since 1969. It is situated on slightly elevated ground on the north bank of a loop o ...
(which included Wallyford
Wallyford is a village near Musselburgh and approximately east of Edinburgh in East Lothian, Scotland.
History
The village was initially populated by coal miners and later grew as an overspill/commuter town for workers in Musselburgh and Edi ...
and Whitecraig
Whitecraig is a village in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies between Musselburgh and Dalkeith, to the east of the city of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotla ...
) from the county of Midlothian.
When further reforms in 1996 moved Scotland to a system of 32 unitary local authorities, the modern council area of East Lothian was created.
Geography
East Lothian is predominantly rural. It has of coastline where the towns of Musselburgh,Prestonpans
Prestonpans ( gd, Baile an t-Sagairt, Scots language, Scots: ''The Pans'') is a small mining town, situated approximately eight miles east of Edinburgh, Scotland, in the Council area of East Lothian. The population as of is. It is near the si ...
, Cockenzie and Port Seton
Cockenzie and Port Seton ( sco, Cockennie ; gd, Cùil Choinnich, meaning "cove of Kenneth") is a unified town in East Lothian, Scotland. It is on the coast of the Firth of Forth, four miles east of Musselburgh. The burgh of Cockenzie was crea ...
, Gullane
Gullane ( or ) is a town on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth in East Lothian on the east coast of Scotland. There has been a church in the village since the ninth century. The ruins of the Old Church of St. Andrew built in the twel ...
, North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
and Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
lie along the coast of the Firth of Forth. The coast has several headlands and bays, most notably Gosford Bay
Gosford is the city and administrative centre of the Central Coast Council local government area in the heart of the Central Coast region, about north of Sydney and about south of Newcastle. The city centre is situated at the northern extre ...
, Aberlady Bay
Aberlady Bay in East Lothian, Scotland lies between Aberlady and Gullane.
In 1952, Aberlady Bay became the UK's first Local Nature Reserve (LNR) and is served by the East Lothian Council Rangers.
The Scottish Ornithologists' Club has Watersto ...
, Gullane Point, Sandy Hirst, Tyne Mouth, Belhaven Bay, Barns Ness, Chapel Point and Torness Point. There are several small islands off the coast north of North Berwick, the largest of these being Fidra
Fidra (archaically Fidrey or Fetheray) is a currently uninhabited island in the Firth of Forth, northwest of North Berwick, on the east coast of Scotland. The island is an RSPB Scotland nature reserve.
Geography
Like the other islands near N ...
, Lamb
Lamb or The Lamb may refer to:
* A young sheep
* Lamb and mutton, the meat of sheep
Arts and media Film, television, and theatre
* ''The Lamb'' (1915 film), a silent film starring Douglas Fairbanks Sr. in his screen debut
* ''The Lamb'' (1918 ...
, Craigleith
Craigleith ( gd, Creag Lìte) is a small island in the Firth of Forth off North Berwick in East Lothian, Scotland. Its name comes from the Scottish Gaelic ''Creag Lìte'' meaning "rock of Leith". It is at its highest point.
Geography and geo ...
and Bass Rock
The Bass Rock, or simply the Bass (), ( gd, Creag nam Bathais or gd, Am Bas) is an island in the outer part of the Firth of Forth in the east of Scotland. Approximately offshore, and north-east of North Berwick, it is a steep-sided volca ...
.
Only two towns are landlocked, Tranent
Tranent is a town in East Lothian (formerly Haddingtonshire), in the south-east of Scotland. The town lies 6 miles from the boundary of Edinburgh, and 9.1 miles from the city centre. It lies beside the A1 road, the A1 runs through the paris ...
and Haddington. To the south are the Lammermuir Hills along the boundary with Berwickshire; it is here that Meikle Says Law
The Lammermuirs are a range of hills in southern Scotland, forming a natural boundary between East Lothian and the Borders. The name "Lammermuir" comes from the Old English ''lambra mōr'', meaning "moorland of the lambs".
Geology
The Lamme ...
, the highest point in the county at , can be found. The River Tyne flows through Haddington and several of East Lothian's villages, reaching the Firth of Forth near Belhaven. The River Esk flows through Inveresk and Musselburgh where it empties at the north of the town into the Firth of Forth. Major bodies of water include Pressmennan Lake
Pressmennan Lake is a lake in East Lothian in Scotland.
It is an artificial reservoir constructed in 1819 by a Mr Nesbit who dammed the streams flowing into the gully, it was said to be well stocked with carp, perch and trout. It lies in a gully ...
, the Whiteadder Reservoir, Hopes Reservoir, Stobshiel Reservoir and Lammerloch Reservoir.
Traprain Law
Traprain Law is a hill east of Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland, It is the site of a hill fort or possibly ''oppidum'', which covered at its maximum extent about . It is the site of the Traprain Law Treasure, the largest Roman silver hoard ...
File:Geomapjoined.jpg, Geological Map of East Lothian
Transport
Road
The A1 road travels through East Lothian where it meets the Scottish Borders southbound and Edinburgh northbound. The A1 throughout East Lothian is dual carriageway and major junctions include Dunbar, Haddington, Tranent, Prestonpans and Musselburgh. Starting inLeith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by ''Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
, the A199 road also travels through East Lothian beginning at Musselburgh and passing through Wallyford, Tranent, Macmerry
Macmerry is a village located on the old A1 (now renumbered the A199) just east of Tranent.
The village has a primary school with a roll of around 100.
There is an industrial estate to the east of the town. Originally this area was part of t ...
and Haddington before joining the A1 in West Barns.
Some non-primary routes in East Lothian are the A198, A1087, A6093 and A6137 roads.
Public transport
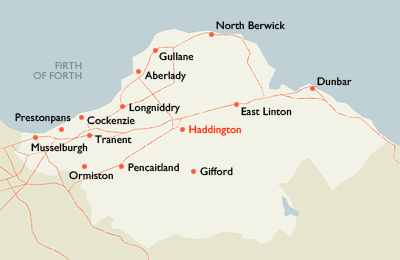
 East Lothian is served by seven railway stations:
East Lothian is served by seven railway stations: Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
and Musselburgh on the East Coast Main Line; and North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
, Drem
Drem (Scottish Gaelic: ''Druim'') is a small village in East Lothian, Scotland.
It is approximately 20 miles east of Edinburgh and is close to Haddington (to the south), North Berwick (northeast), Dirleton (north) and Gullane (north west).
It ...
, Longniddry
Longniddry ( sco, Langniddry, gd, Nuadh-Treabh Fada)
...
, ...
Prestonpans
Prestonpans ( gd, Baile an t-Sagairt, Scots language, Scots: ''The Pans'') is a small mining town, situated approximately eight miles east of Edinburgh, Scotland, in the Council area of East Lothian. The population as of is. It is near the si ...
and Wallyford
Wallyford is a village near Musselburgh and approximately east of Edinburgh in East Lothian, Scotland.
History
The village was initially populated by coal miners and later grew as an overspill/commuter town for workers in Musselburgh and Edi ...
on the North Berwick Line
The North Berwick Branch is a short railway branch line built by the North British Railway to connect North Berwick, in East Lothian, Scotland to the East Coast Main Line (at Drem). It was built as a tactical means of excluding competitors from ...
. Rail service operators which travel through and stop at stations in the area include: ScotRail on both lines; and CrossCountry and London North Eastern Railway on the East Coast Main Line.
Bus operators in East Lothian are: Lothian Buses
Lothian Buses is a major bus operator based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is the largest municipal bus company in the United Kingdom: the City of Edinburgh Council (through Transport for Edinburgh) owns 91%, Midlothian Council 5%, East Lothi ...
and its subsidiary East Coast Buses, Eve Coaches of Dunbar, Prentice of Haddington and Borders Buses
Borders Buses operates both local and regional bus services in the City of Edinburgh, East Lothian, Midlothian and Scottish Borders, Scotland, as well as Cumbria and Northumberland, England. It is a subsidiary of West Coast Motors.
History
T ...
. East Coast Buses is the main bus service provider connecting the towns and villages of East Lothian to Edinburgh. The company has depots in North Berwick and Musselburgh.
Demography
The population of East Lothian as of 2019 is 105,790. This is an increase of over 6,000 since 2011 and this is projected to reach over 120,000 by the 2030s. The fastest growing district in East Lothian is the Tranent, Wallyford and Macmerry ward which is expected to see its population of just over 20,000 increase to just under 30,000 by 2026.Ethnicity
Population by major ethnic group in East Lothian according to the 2011 Scottish census is as follows:Politics
In the 2014 Scottish independence referendum, a majority of voters in the East Lothian council area opted for Scotland to remain a part of the United Kingdom - with 61.72% casting their ballots for the Union and 38.28% voting for independence.Parliament of the United Kingdom
East Lothian is a constituency in theHouse of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, electing one Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
. It is one of only 4 UK Parliamentary Constituencies in Scotland which matches the boundaries of its Local Authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
area. The other examples being Inverclyde
Inverclyde ( sco, Inerclyde, gd, Inbhir Chluaidh, , "mouth of the Clyde") is one of 32 council areas used for local government in Scotland. Together with the East Renfrewshire and Renfrewshire council areas, Inverclyde forms part of the hist ...
, Moray, and Na h-Eileanan an Iar, East Lothian is one of the few UK Parliamentary Constituencies which fully covers the boundaries of its Council area.
The current MP for East Lothian is Kenny MacAskill
Kenneth Wright MacAskill (born 28 April 1958) is a Scottish politician who has been Member of Parliament (MP) for East Lothian since 2019. He previously served as Cabinet Secretary for Justice from 2007 to 2014 and was a Member of the Scottish ...
of the Alba Party, who has represented the constituency since the 2019 general election when he was elected for the SNP.
Former UK Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern pr ...
Arthur Balfour
Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour, (, ; 25 July 184819 March 1930), also known as Lord Balfour, was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905. As foreign secretary in the ...
was born on 25 July 1848 at Whittingehame House
Whittingehame is a parish with a small village in East Lothian, Scotland, about halfway between Haddington and Dunbar, and near East Linton. The area is on the slopes of the Lammermuir Hills. Whittingehame Tower dates from the 15th century a ...
in what is now the East Lothian constituency.

Scottish Parliament
Most of East Lothian is in the East Lothian Scottish Parliament constituency and South Scotland region with the exception of Musselburgh which is in Midlothian North and Musselburgh and the Lothians region.Local government
East Lothian Council
East Lothian Council is one of the 32 local government councils in Scotland covering the East Lothian area. Since the last boundary changes in 2017, 22 councillors have been elected from 6 wards.
History
East Lothian District Council had been ...
is based in the historic county town of Haddington, with the council meeting at the Haddington Town House
Haddington Town House is a municipal structure in Court Street, Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland. The structure, which is the meeting place of East Lothian Council, is a Category A listed building.
History
The first municipal building in the ...
and offices at nearby at John Muir House. The unitary local authority contains six wards, electing 22 councillors.
Places of interest
*Aberlady Bay
Aberlady Bay in East Lothian, Scotland lies between Aberlady and Gullane.
In 1952, Aberlady Bay became the UK's first Local Nature Reserve (LNR) and is served by the East Lothian Council Rangers.
The Scottish Ornithologists' Club has Watersto ...
* Bass Rock
The Bass Rock, or simply the Bass (), ( gd, Creag nam Bathais or gd, Am Bas) is an island in the outer part of the Firth of Forth in the east of Scotland. Approximately offshore, and north-east of North Berwick, it is a steep-sided volca ...
* Dirleton Castle
Dirleton Castle is a medieval fortress in the village of Dirleton, East Lothian, Scotland. It lies around west of North Berwick, and around east of Edinburgh. The oldest parts of the castle date to the 13th century, and it was abandoned by th ...
* Dunglass Collegiate Church
* Fa'side Castle
Fa'side Castle (Faside Estate) has previously been known as Fawside, Falside, Ffauside, Fauxside, or Fawsyde and is a 15th-century keep located in East Lothian in Scotland. The castle is approximately southwest of Tranent, and southeast of M ...
* Fenton Barns Retail & Leisure Village
* Hailes Castle
Hailes Castle is a mainly 14th century castle about a mile and a half south-west of East Linton, East Lothian, Scotland. This castle, which has a fine riverside setting, belonged to the Hepburn family during the most important centuries of it ...
* Hopetoun Monument
* Lennoxlove
Lennoxlove House is a historic house set in woodlands half a mile south of Haddington in East Lothian, Scotland. The house comprises a 15th-century tower, originally known as Lethington Castle, and has been extended several times, principally i ...
historic house
A historic house generally meets several criteria before being listed by an official body as "historic." Generally the building is at least a certain age, depending on the rules for the individual list. A second factor is that the building be in ...
* Longniddry Bents
The area is popular, mostly in the summer months, with local families, holidaymakers, picnickers, horseriders, ramblers, metal detectors, dogwalkers and the occasional kite buggy. The shallow bay is a popular watersports location for windsurfers, ...
* Muirfield Golf Links
* Museum of Flight
The Museum of Flight is a private non-profit air and space museum in the Seattle metropolitan area. It is located at the southern end of King County International Airport (Boeing Field) in the city of Tukwila, immediately south of Seattle. ...
, East Fortune
East Fortune is a village in East Lothian, Scotland, located 2 miles (3 km) north west of East Linton. The area is known for its airfield which was constructed in 1915 to help protect Britain from attack by German Zeppelin airships during t ...
* North Berwick Harbour
The Harbour at North Berwick in East Lothian, Scotland, was originally a ferry port for pilgrims travelling to St Andrews in Fife. Today the water is home to leisure craft, a famous tourist launch and the remains of the fishing fleet that once dom ...
* North Berwick Law
North Berwick Law, sometimes abbreviated to Berwick Law, is a conical hill which rises conspicuously from the surrounding landscape (this is the definition of the Lowland Scots word "law"). It overlooks the East Lothian town of North Berwick, ...
* Preston Mill
Preston Mill is a watermill on the River Tyne at the eastern edge of East Linton on the B1407 Preston Road, in East Lothian, Scotland, UK. It is situated close to Prestonkirk Parish Church, the Smeaton Hepburn Estate, Smeaton Lake, and Ph ...
* Prestongrange Industrial Heritage Museum
Prestongrange Museum is an industrial heritage museum at Prestongrange between Musselburgh and Prestonpans on the B1348 on the East Lothian coast, Scotland. Founded as the original site of the National Mining Museum, its operation reverted t ...
* Scottish Seabird Centre, North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
* Seacliff Beach
* Seton Collegiate Church
Seton Collegiate Church, known locally as Seton Chapel, is a collegiate church south of Port Seton, East Lothian, Scotland. It is adjacent to Seton House. The church is designated as a scheduled monument.
Description
The church consists of t ...
* Tantallon Castle
* Chesters Hill Fort
Chesters Hill Fort is an Iron Age hill fort in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies south of Drem, east of Ballencrieff Castle, north of Haddington, and west of Athelstaneford. The name "Chesters" comes from Latin ''castra'', a fortified place. ...
* Torness Nuclear Power Station
Torness nuclear power station is a nuclear power station located approximately east of Edinburgh at Torness Point near Dunbar in East Lothian, Scotland. It was the last of the United Kingdom's second generation nuclear power plants to be commi ...
* Traprain Law
Traprain Law is a hill east of Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland, It is the site of a hill fort or possibly ''oppidum'', which covered at its maximum extent about . It is the site of the Traprain Law Treasure, the largest Roman silver hoard ...
* Yellowcraigs
Yellowcraig, also known as Broad Sands Beach, is a coastal area of forest, beach and grassland in East Lothian, south-east Scotland. Yellowcraig is partly within the Firth of Forth Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI). It is bordered to ...
, a beach and conservation area
Towns and villages
 *
* Aberlady
Aberlady ( sco, Aiberleddy, Gaelic: ''Obar Lobhaite'') is a coastal village in the Scottish council area of East Lothian. The village had an estimated population of in .
Etymology
The name ''Aberlady'' has Brittonic origins. The first part of ...
* Athelstaneford
Athelstaneford () is a village in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies almost 6 kilometres (3.5 mi) north-east of the market town of Haddington and about 28 kilometres (17 mi) east of Edinburgh.
Battle of Athelstaneford
According to popul ...
* Auldhame
Auldhame and Scoughall are hamlets in East Lothian, Scotland. They are close to the town of North Berwick and the village of Whitekirk, and are approximately east of Edinburgh.
Saint Baldred's legacy
It is said that the 8th-century Christ ...
* Ballencrieff
* Bara
* Belhaven
* Biel
, french: Biennois(e)
, neighboring_municipalities= Brügg, Ipsach, Leubringen/Magglingen (''Evilard/Macolin''), Nidau, Orpund, Orvin, Pieterlen, Port, Safnern, Tüscherz-Alfermée, Vauffelin
, twintowns = Iserlohn (Germany) ...
* Bilsdean
Bilsdean is a village between Thorntonloch and Cockburnspath on the East Lothian coast of Scotland.
See also
*List of places in East Lothian
''Map of places in East Lothian compiled from this list''
The List of places in East Lothian is a ...
* Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th ...
* Broxburn
Broxburn ( gd, Srath Bhroc, IPA: �s̪ɾaˈvɾɔʰk is a town in West Lothian, Scotland, on the A89 road, from the West End of Edinburgh, from Edinburgh Airport and to the north of Livingston.
Etymology
The name Broxburn is a corruption of ...
* Canty Bay
Canty Bay is a small inlet and coastal hamlet on the northern coast of East Lothian, Scotland. It is east of North Berwick and is opposite the Bass Rock and Tantallon Castle. Other settlements nearby include Auldhame, Scoughall, Seacliff, and t ...
* Cockenzie
Cockenzie and Port Seton ( sco, Cockennie ; gd, Cùil Choinnich, meaning "cove of Kenneth") is a unified town in East Lothian, Scotland. It is on the coast of the Firth of Forth, four miles east of Musselburgh. The burgh of Cockenzie was created ...
* Dirleton
Dirleton is a village and civil parish in East Lothian, Scotland approximately east of Edinburgh on the A198. It contains . Dirleton lies between North Berwick (east), Gullane (west), Fenton Barns (south) and the Yellowcraigs nature reserve ...
* Drem
Drem (Scottish Gaelic: ''Druim'') is a small village in East Lothian, Scotland.
It is approximately 20 miles east of Edinburgh and is close to Haddington (to the south), North Berwick (northeast), Dirleton (north) and Gullane (north west).
It ...
* Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
* Dunglass
Dunglass is a hamlet in East Lothian, Scotland, lying east of the Lammermuir Hills on the North Sea coast, within the parish of Oldhamstocks. It has a 15th-century collegiate church, now in the care of Historic Scotland. Dunglass is the birthpla ...
* East Fortune
East Fortune is a village in East Lothian, Scotland, located 2 miles (3 km) north west of East Linton. The area is known for its airfield which was constructed in 1915 to help protect Britain from attack by German Zeppelin airships during t ...
* East Linton
East Linton is a village and former police burgh in East Lothian, Scotland, situated on the River Tyne and A199 road (former A1 road) five miles east of Haddington, with an estimated population of in .
During the 19th century the population ...
* East Saltoun
* Elphinstone
* Fenton Barns
* Fisherrow
Fisherrow is a harbour and former fishing village at Musselburgh, East Lothian, Scotland, to the east of Portobello and Joppa, and west of the River Esk.
History
There has been fishing at Fisherrow and Musselburgh since Roman times, and the p ...
(''historically within Midlothian'')
* Garvald
* Gifford
* Gladsmuir
Gladsmuir is a village and parish in East Lothian, Scotland, situated on the A199 and near Tranent and Prestonpans.
Description
Gladsmuir's principal "claim to fame" relates to its role as the site of the Battle of Prestonpans (1745). Some sour ...
* Glenkinchie
* Gullane
Gullane ( or ) is a town on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth in East Lothian on the east coast of Scotland. There has been a church in the village since the ninth century. The ruins of the Old Church of St. Andrew built in the twel ...
* Haddington
* Humbie
Humbie is a hamlet and rural parish in East Lothian, Scotland lying in south-east of the county, approximately south-west of Haddington and south-east of Edinburgh. Humbie as it is known today was formed as the result of the union between Keit ...
* Innerwick
Innerwick ( gd, Inbhir Mhuice) is a coastal civil parish and small village, which lies in the east of East Lothian, from Dunbar and approximately from Edinburgh.
Name
The name Innerwick is of Anglo-saxon origin and means inland farm or dwel ...
* Inveresk
Inveresk (Gaelic: ''Inbhir Easg'') is a village in East Lothian, Scotland situated to the south of Musselburgh. It has been designated a conservation area since 1969. It is situated on slightly elevated ground on the north bank of a loop o ...
(''historically within Midlothian'')
* Kingston
* Longniddry
Longniddry ( sco, Langniddry, gd, Nuadh-Treabh Fada)
...
* ...
Luffness
Luffness is a hamlet in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies between the towns of Gullane and Aberlady and is approximately 20 miles east of Edinburgh.
History
Most of the houses in Luffness are traditional farm cottages; among its notable buildings ...
* Macmerry
Macmerry is a village located on the old A1 (now renumbered the A199) just east of Tranent.
The village has a primary school with a roll of around 100.
There is an industrial estate to the east of the town. Originally this area was part of t ...
* Markle
* Monktonhall (''historically within Midlothian'')
* Musselburgh (''historically within Midlothian'')
* North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
* Oldhamstocks
Oldhamstocks or Aldhamstocks ("old dwelling place") is a civil parish and small village in the east of East Lothian, Scotland, adjacent to the Scottish Borders and overlooking the North Sea . It is located south-east of Dunbar and has a popul ...
* Ormiston
Ormiston is a village in East Lothian, Scotland, near Tranent, Humbie, Pencaitland and Cranston, located on the north bank of the River Tyne at an elevation of about .
The village was the first planned village in Scotland, founded in 1735 ...
* Peaston
Peaston is a small settlement on the B6371 road in the parish of Ormiston in East Lothian, Scotland, about south-east of Edinburgh, south-west of Haddington, east of Ormiston and east of Pencaitland
Pencaitland is a village in East L ...
* Pencaitland
* Phantassie
Phantassie is an agricultural hamlet near East Linton, East Lothian, Scotland. It is close to the River Tyne, Preston Mill, and Prestonkirk Parish Church.
The Phantassie Farm and Workshop, presently owned by Hamilton Farmers, is the birthpla ...
* Port Seton
Cockenzie and Port Seton ( sco, Cockennie ; gd, Cùil Choinnich, meaning "cove of Kenneth") is a unified town in East Lothian, Scotland. It is on the coast of the Firth of Forth, four miles east of Musselburgh. The burgh of Cockenzie was crea ...
* Preston
* Prestonpans
Prestonpans ( gd, Baile an t-Sagairt, Scots language, Scots: ''The Pans'') is a small mining town, situated approximately eight miles east of Edinburgh, Scotland, in the Council area of East Lothian. The population as of is. It is near the si ...
* Samuelston
Samuelston ( Scots: ''Sammelstoun'') is a small town just outside of Haddington, East Lothian. It has a population of 957.
George Ker, laird of Samuelston, supervised building work at the church of Ladykirk for James IV. His daughter Nichola Ke ...
* Scoughall
Auldhame and Scoughall are hamlets in East Lothian, Scotland. They are close to the town of North Berwick and the village of Whitekirk, and are approximately east of Edinburgh.
Saint Baldred's legacy
It is said that the 8th-century Christ ...
* Spittal
* Spott
* Stenton
Stenton ( sco, Staneton) is a parish and village in East Lothian, Scotland. It is bounded on the north by parts of the parishes of Prestonkirk and Dunbar, on the east by Spott and on the west by Whittingehame. The name is said to be of Saxon de ...
* Tranent
Tranent is a town in East Lothian (formerly Haddingtonshire), in the south-east of Scotland. The town lies 6 miles from the boundary of Edinburgh, and 9.1 miles from the city centre. It lies beside the A1 road, the A1 runs through the paris ...
* Tyninghame
Tyninghame is a small settlement in East Lothian, Scotland, about two miles north-east of East Linton. Together with the nearby settlement of Whitekirk, it gives its name to the parish of Whitekirk and Tyninghame.
Tyninghame
Tyninghame is ...
* Wallyford
Wallyford is a village near Musselburgh and approximately east of Edinburgh in East Lothian, Scotland.
History
The village was initially populated by coal miners and later grew as an overspill/commuter town for workers in Musselburgh and Edi ...
(''historically within Midlothian'')
* West Barns
* West Saltoun
* Whitecraig
Whitecraig is a village in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies between Musselburgh and Dalkeith, to the east of the city of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotla ...
(''historically within Midlothian'')
* Whitekirk and Tyninghame
Whitekirk and Tyninghame is a civil parish in East Lothian, Scotland, which takes its name from the two small settlements of Whitekirk and Tyninghame. The two separate ancient parishes were joined in 1761.
See also
* List of listed buildings i ...
* Whittingehame
Whittingehame is a parish with a small village in East Lothian, Scotland, about halfway between Haddington and Dunbar, and near East Linton. The area is on the slopes of the Lammermuir Hills. Whittingehame Tower dates from the 15th century an ...
Civil parishes
 In 1894, John Martine published ''Reminiscences and Notices of Ten Parishes of the County of Haddington''.
*
In 1894, John Martine published ''Reminiscences and Notices of Ten Parishes of the County of Haddington''.
* Aberlady
Aberlady ( sco, Aiberleddy, Gaelic: ''Obar Lobhaite'') is a coastal village in the Scottish council area of East Lothian. The village had an estimated population of in .
Etymology
The name ''Aberlady'' has Brittonic origins. The first part of ...
* Athelstaneford
Athelstaneford () is a village in East Lothian, Scotland. It lies almost 6 kilometres (3.5 mi) north-east of the market town of Haddington and about 28 kilometres (17 mi) east of Edinburgh.
Battle of Athelstaneford
According to popul ...
* Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th ...
* Dirleton
Dirleton is a village and civil parish in East Lothian, Scotland approximately east of Edinburgh on the A198. It contains . Dirleton lies between North Berwick (east), Gullane (west), Fenton Barns (south) and the Yellowcraigs nature reserve ...
* Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
* Garvald
* Gladsmuir
Gladsmuir is a village and parish in East Lothian, Scotland, situated on the A199 and near Tranent and Prestonpans.
Description
Gladsmuir's principal "claim to fame" relates to its role as the site of the Battle of Prestonpans (1745). Some sour ...
* Haddington
* Humbie
Humbie is a hamlet and rural parish in East Lothian, Scotland lying in south-east of the county, approximately south-west of Haddington and south-east of Edinburgh. Humbie as it is known today was formed as the result of the union between Keit ...
* Innerwick
Innerwick ( gd, Inbhir Mhuice) is a coastal civil parish and small village, which lies in the east of East Lothian, from Dunbar and approximately from Edinburgh.
Name
The name Innerwick is of Anglo-saxon origin and means inland farm or dwel ...
* Morham
Morham, East Lothian, sometimes spelt Moram, Morum, or Morhame in old records, is the smallest (agricultural) parish in Scotland, sandwiched between five other parishes: Haddington, Garvald, Yester, Whittingehame, and Prestonkirk, in the undula ...
* North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable ...
* Oldhamstocks
Oldhamstocks or Aldhamstocks ("old dwelling place") is a civil parish and small village in the east of East Lothian, Scotland, adjacent to the Scottish Borders and overlooking the North Sea . It is located south-east of Dunbar and has a popul ...
* Ormiston
Ormiston is a village in East Lothian, Scotland, near Tranent, Humbie, Pencaitland and Cranston, located on the north bank of the River Tyne at an elevation of about .
The village was the first planned village in Scotland, founded in 1735 ...
* Pencaitland
* Prestonkirk
East Linton is a village and former police burgh in East Lothian, Scotland, situated on the River Tyne and A199 road (former A1 road) five miles east of Haddington, with an estimated population of in .
During the 19th century the populatio ...
* Prestonpans
Prestonpans ( gd, Baile an t-Sagairt, Scots language, Scots: ''The Pans'') is a small mining town, situated approximately eight miles east of Edinburgh, Scotland, in the Council area of East Lothian. The population as of is. It is near the si ...
* Saltoun
East Saltoun and West Saltoun are separate villages in East Lothian, Scotland, about 5 miles (8 kilometres) south-west of Haddington and 20 miles (32 kilometres) east of Edinburgh.
Geography
The villages of East Saltoun and West Saltoun, toge ...
* Spott
* Stenton
Stenton ( sco, Staneton) is a parish and village in East Lothian, Scotland. It is bounded on the north by parts of the parishes of Prestonkirk and Dunbar, on the east by Spott and on the west by Whittingehame. The name is said to be of Saxon de ...
* Tranent
Tranent is a town in East Lothian (formerly Haddingtonshire), in the south-east of Scotland. The town lies 6 miles from the boundary of Edinburgh, and 9.1 miles from the city centre. It lies beside the A1 road, the A1 runs through the paris ...
* Whittingehame
Whittingehame is a parish with a small village in East Lothian, Scotland, about halfway between Haddington and Dunbar, and near East Linton. The area is on the slopes of the Lammermuir Hills. Whittingehame Tower dates from the 15th century an ...
* Whitekirk and Tyninghame
Whitekirk and Tyninghame is a civil parish in East Lothian, Scotland, which takes its name from the two small settlements of Whitekirk and Tyninghame. The two separate ancient parishes were joined in 1761.
See also
* List of listed buildings i ...
* Yester
Education
 There are a range of schools in the county, including six
There are a range of schools in the county, including six state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
secondaries: Dunbar Grammar School, Knox Academy
Knox Academy is a co-educational state secondary school located in Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland. Originally founded in 1379 as a medieval grammar school, it is one of the oldest schools in the world.
History
The modern school can be trac ...
(formerly the Grammar School) in Haddington, Musselburgh Grammar School, North Berwick High School
North Berwick High School is a non-denominational state secondary school in North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the F ...
, Preston Lodge High School
Preston Lodge High School is a six-year non-denominational school located in Prestonpans, Scotland. It serves students from Prestonpans, Port Seton, Longniddry and the surrounding areas.
Primary Schools
A student goes to Preston Lodge High S ...
in Prestonpans and Ross High School in Tranent
Tranent is a town in East Lothian (formerly Haddingtonshire), in the south-east of Scotland. The town lies 6 miles from the boundary of Edinburgh, and 9.1 miles from the city centre. It lies beside the A1 road, the A1 runs through the paris ...
.
There are two independent schools in the county. Loretto School
Loretto School, founded in 1827, is an independent boarding and day school for boys and girls aged 0 to 18. The campus occupies in Musselburgh, East Lothian, Scotland.
History
The school was founded by the Reverend Thomas Langhorne in 1827. ...
is a day and boarding school in Musselburgh founded in 1827 and Belhaven Hill School
Belhaven Hill School is an independent, co-educational preparatory school for boarding and day pupils aged 5 to 13 in Dunbar, East Lothian, Scotland.
The current headmaster is Olly Langton.
Notable former pupils
* Hugh Buchanan (artist), S ...
, established in 1923 is a smaller preparatory school in Dunbar also providing boarding.
In 2007, Queen Margaret University
Queen Margaret University is a university, founded in 1875 and located in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is named after the Scottish Queen Saint Margaret.
History
The university was founded in 1875, as ''The Edinburgh School of Cookery and Domestic ...
began its move to a new, purpose-built campus in Musselburgh within East Lothian, providing it with its first university.
Culture and community
Symbols
Local media
East Lothian is served by two local paid-for weekly newspapers, the ''East Lothian Courier'' and the ''East Lothian News''. The ''East Lothian Courier'' (often locally "The Courier") began as the Haddingtonshire Courier in 1859, before changing its name in 1971. It was owned by D&J Croal, based in Haddington, until its purchase by the Dunfermline Press Group in 2004. The ''East Lothian News'' was first published in 1971, as part of Scottish County Press Group, with editorial offices in Dalkeith and printing at Bonnyrigg (both in Midlothian). The Scottish County Press Group was acquired by Regional Independent Media in 2000, which was in turn bought by Johnston Press in 2002. There are two local community radio stations in East Lothian, broadcasting on FM and online. East Coast FM, based in Haddington, has been broadcasting since 2009.Radio Saltire
Radio Saltire is a community radio station broadcasting primarily to East Lothian, Scotland on 106.7 & 107.2 FM and online.
The station is a charity registered in Scotland (SC044336).
The station is run by volunteers from across East Lothian a ...
, formerly East Lothian FM, is now based in Tranent.
Notable people (by date of death)
*Gospatric II, Earl of Lothian
Gospatric II (died 1138) was Earl of Lothian or Earl of Dunbar in the early 12th century.
He was the son of Gospatric I, sometime Earl of Northumbria (d. after 1073). In the earliest sources, occurring at dates between 1120 and 1134 he is not s ...
, d.1138
* Gospatric III, Earl of Lothian
Gospatric III or Cospatric III (died 1166) was a twelfth-century Anglo-Celtic noble, who was Earl of Lothian and later the Earl of Dunbar, and feudal Lord of Beanley.
He was the son of Gospatric II, Earl of Lothian (later called Earl of Dunbar ...
, d.1166
* Waltheof, Earl of Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
, d.1182
* Alexander II, King of Scots, 1198–1249
* Black Agnes, 4th Countess of Moray, c.1312-1369
* Abbot Walter Bower, ca.1385–1449, canon regular of Inchcolm Abbey
Inchcolm Abbey is a medieval abbey located on the island of Inchcolm in the Firth of Forth in Scotland. The Abbey, which is located at the centre of the island, was founded in the 12th century during the episcopate of Gregoir, Bishop of Dunkeld ...
, chronicler, born about at Haddington
* Sawney Bean
Alexander "Sawney" Bean was said to be the head of a 45-member clan in Scotland in the 16th century that murdered and cannibalized over 1,000 people in 25 years. According to legend, Bean and his clan members were eventually caught by a search ...
, cannibal
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, bo ...
and outlaw, 15th to 16th century
* William Dunbar
William Dunbar (born 1459 or 1460 – died by 1530) was a Scottish makar, or court poet, active in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries. He was closely associated with the court of King James IV and produced a large body of work i ...
, medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems ( oral or wri ...
, 1460–1520
* John Mair John Mair may refer to:
*John Major (philosopher)
John Major (or Mair; also known in Latin as ''Joannes Majoris'' and ''Haddingtonus Scotus''; 1467–1550) was a Scottish philosopher, theologian, and historian who was much admired in his day ...
or Major, philosopher, 1467–1550
* John Knox, leading Protestant reformer in Scotland and founder of Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
, c.1510-1572
* John Cockburn of Ormiston
John Cockburn, (d. 1583) laird of Ormiston, East Lothian, Scotland, was an early supporter of the Scottish Reformation. He was the eldest son of William Cockburn of Ormiston and Janet Somerville. John was usually called "Ormiston." During his lif ...
, (d.1583) early supporter of the Scottish Reformation
* Ninian Cockburn
Ninian Cockburn (died 6 May 1579) was a Scottish soldier and officer of the Garde Écossaise, a company which guarded the French king. He had an ambiguous role in political relations between Scotland, France and England during the war of the Rough ...
(d.1579), soldier, an officer of the Garde Écossaise
The Scottish Guards () was a bodyguard unit founded in 1418 by the Valois Charles VII of France, to be personal bodyguards to the French monarchy. They were assimilated into the '' Maison du Roi'' and later formed the first company of the '' Gar ...
, political intriguer
* Andrew Fletcher of Saltoun
Andrew Fletcher of Saltoun (1655 – September 1716) was a Scottish writer and politician, remembered as an advocate for the non-incorporation of Scotland, and an opponent of the 1707 Act of Union between Scotland and England. Fletcher became ...
(1655–1716), writer, politician, soldier and patriot
* Adam Cockburn, Laird of Ormiston, Lord Ormiston (1656–1735), administrator, politician and judge
* John Cockburn, agricultural improver, 1695–1758
* Andrew Meikle
Andrew Meikle (5 May 1719 – 27 November 1811) was a Scottish mechanical engineer credited with inventing the threshing machine, a device used to remove the outer husks from grains of wheat. He also had a hand in assisting Firbeck in the inve ...
, inventor of the Threshing machine
A threshing machine or a thresher is a piece of farm equipment that threshes grain, that is, it removes the seeds from the stalks and husks. It does so by beating the plant to make the seeds fall out.
Before such machines were developed, thre ...
, 1719–1811
* John Brown of Haddington
John Brown of Haddington (1722 – 19 June 1787), was a Scottish minister and author. He was born at Carpow, in Perthshire. He was almost entirely self-educated, having acquired a knowledge of ancient languages while employed as a shepher ...
, 1722–1787
* Rev. Dr. John Witherspoon
John Witherspoon (February 5, 1723 – November 15, 1794) was a Scottish-American Presbyterian minister, educator, farmer, slaveholder, and a Founding Father of the United States. Witherspoon embraced the concepts of Scottish common sense real ...
, a signatory to the United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ( ...
, 1723–1794
* George Brodie (1786?-1867), historian
* Robert Cadell
Robert Cadell (16 December 1788 – 20 January 1849) was a bookseller and publisher closely associated with Sir Walter Scott.
Life
He was born at Cockenzie, East Lothian, Scotland, the fifth son of John Cadell, a Laird of Cockenzie, and Marie ...
(1788–1849), bookseller and publisher, closely associated with Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy' ...
* Robert Moffat 1795–1883, Congregationalist missionary to Africa, and father in law of David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, and pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, an explorer in Africa, and one of the most popular British heroes of t ...
* Jane Welsh Carlyle
Jane Baillie Carlyle ( Welsh; 14 July 1801 – 21 April 1866) was a Scottish writer and the wife of Thomas Carlyle.
She did not publish any work in her lifetime, but she was widely seen as an extraordinary letter writer. Virginia Woolf ca ...
, 1801–1866, letter-writer, and wife of Thomas Carlyle
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature and philosophy.
Born in Ecclefechan, Dum ...
, 1801–1866
* Sir William Fergusson, 1st Baronet
Sir William Fergusson, 1st Baronet FRCS FRS FRSE (20 March 180810 February 1877) was a Scottish surgeon.
Biography
William Fergusson son of James Fergusson of Lochmaben, Dumfriesshire, was born at Prestonpans, East Lothian on 20 March 180 ...
, surgeon, 1808–1877
* Samuel Smiles, author of Self-Help, 1812–1904
* Mary Balfour Herbert
Mary Balfour Herbert (1817–1893) was a British artist. She was born Mary Balfour in 1817, the daughter of James Balfour MP and Lady Eleanor Maitland; they were grandparents of Arthur Balfour 1st Earl Balfour. She grew up in Whittingehame H ...
, watercolour painter, 1817–1893
* Samuel Morison Brown, chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe t ...
, poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems ( oral or wri ...
and essayist
An essay is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a letter, a paper, an article, a pamphlet, and a short story. Essays have been sub-classified as formal ...
, 1817–1856
* John Muir
John Muir ( ; April 21, 1838December 24, 1914), also known as "John of the Mountains" and "Father of the National Parks", was an influential Scottish-American naturalist, author, environmental philosopher, botanist, zoologist, glaciologist ...
, father of the US National Parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
, 1838–1914
* Eleanor Mildred Sidgwick
Eleanor Mildred Sidgwick (née Balfour; 11 March 1845 – 10 February 1936), known as Nora to her family and friends, was a physics researcher assisting Lord Rayleigh, an activist for the higher education of women, Principal of Newnham College o ...
, Principal of Newnham College
Newnham College is a women's constituent college of the University of Cambridge.
The college was founded in 1871 by a group organising Lectures for Ladies, members of which included philosopher Henry Sidgwick and suffragist campaigner Millice ...
, 1845–1936
* James Porteous
James Porteous (1848–1922) was the Scottish-American inventor of the Fresno scraper.
James Porteous was born in Haddington, East Lothian, Scotland. His father, William Porteous, had been a wheelwright and blacksmith who built and repair ...
, inventor of the Fresno Scraper, 1848–1922
* Peter Hume Brown
Peter Hume Brown, FBA (17 December 1849 – 1 December 1918) was a Scottish historian and professor who played an important part in establishing Scottish history as a significant academic discipline. As well as teaching and writing, he spent 16 ...
, historian, 1849–1918
* Arthur Balfour
Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour, (, ; 25 July 184819 March 1930), also known as Lord Balfour, was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905. As foreign secretary in the ...
(1848-1930), Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
, 1902–1905
* Eleanor Mildred Sidgwick
Eleanor Mildred Sidgwick (née Balfour; 11 March 1845 – 10 February 1936), known as Nora to her family and friends, was a physics researcher assisting Lord Rayleigh, an activist for the higher education of women, Principal of Newnham College o ...
(1845-1936), mathematician and co-founder of Newham College, University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
* William George Nicholson Geddes
William George Nicholson Geddes CBE DSc FRSE FEng (29 July 1913 – 10 November 1993) was a Scottish civil engineer.
Life
George Geddes was born in Oldhamstocks, East Lothian the son of Ina Nicholson and her husband, William Brydon Geddes ...
1913–1993, civil engineer
* Maureen Mollie Hunter McIlwraith, commonly known as Mollie Hunter 1922–2012, Scottish writer
* Peter Kerr b.1940, best-selling author of travel books and fiction
* John Bellany
John Bellany (18 June 1942 – 28 August 2013) was a Scottish people, Scottish painter.
Early life
Bellany was born in Port Seton. His father and grandfather were fishermen in Port Seton and Eyemouth near Edinburgh.
During the early 1960 ...
, painter, 1942-2013
* Rhona Cameron
Rhona Cameron (born 27 September 1965) is a Scottish comedian, writer and TV presenter. She rose to prominence via the stand-up comedy circuit, and was a regular on British television in the 1990s.
Television career
In 1992, she won ''So You ...
, comedian and activist, b.1965
A number of sports personalities also have links with East Lothian:
* Willie Anderson, golfer, four times U.S. Open Golf Champion, 1901, 1903–05
* Ian Black, professional footballer
* Callum Booth, professional footballer
* Billy Brown, football coach
* Kenny Miller
Kenneth Miller (born 23 December 1979) is a Scottish professional football coach and former player. Miller, who played as a striker, is one of only five post-war players to have played for both Rangers and Celtic.
Miller began his career at ...
, professional footballer
* Colin Nish
Colin John Nish (born 7 March 1981) is a Scottish former football player, coach and manager. Nish played for Dunfermline Athletic, Alloa Athletic, Clyde, Kilmarnock, Hibernian, Hartlepool United, Dundee, Dumbarton and Cowdenbeath. Whilst pla ...
, professional footballer
* Jim Calder rugby union player
* Gary Anderson, Darts player
* Andrew Driver
Andrew David Driver (born 20 November 1987) is a former professional footballer who played as a midfielder. He has represented Scotland at schoolboy level and England, where he was born, for the under-21 side.
Club career Hearts
Driver was bor ...
, professional footballer
* Danny Handling
Daniel Handling (born 6 February 1994) is a Scottish footballer who plays for Scottish League One side Edinburgh City. Handling has previously played for Hibernian and Dumbarton as well as Berwick Rangers and Raith Rovers on loan.
Early lif ...
, professional footballer
* Jason Holt, Professional footballer
* David Huish
David Huish (born 23 April 1944) is a Scottish professional golfer, perhaps best known for being the halfway leader of The Open Championship in 1975.
Personal life
Huish (pronounced "hush") was born in North Berwick, Scotland. He married his se ...
, professional golfer
* Allan Jacobsen, rugby union player
* Jim Jefferies, football manager
* John McGlynn
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
, football manager
* Catriona Matthew, golfer
* Mathew Dawson
Mathew Dawson (1820–1898) was a British racehorse trainer. In a career which lasted from 1840 until his death in 1898 he trained the winners of twenty-eight British Classic Races, a figure surpassed by only two other men. He was significan ...
, racehorse trainer
* Euan Burton
Euan Michael Burton MBE (born 31 March 1979) is a Scottish judoka (a Judo practitioner).
Biography
Burton was born in Ascot, Berkshire but lives in Edinburgh, he was educated at Pencaitland Primary School, Ross High School and the Univer ...
, judoka and 2012 Olympics contender
* Finlay Calder
Finlay Calder OBE (born 20 August 1957) is a Scotland international former rugby union player.
Rugby Union career
Amateur career
Born in Haddington, East Lothian and educated at Stewart's Melville College,
Calder played at open side fla ...
, rugby union player
* Ross Muir, professional snooker player
* Scott Murray, rugby union player
* Garry O'Connor
Garry Lawrence John O'Connor (born 7 May 1983) is a Scottish former professional footballer. He played for Hibernian, Peterhead, Lokomotiv Moscow, Barnsley, Tom Tomsk, Birmingham City, Greenock Morton and represented Scotland.
O'Connor beg ...
, professional footballer
* Willie Ormond
William Esplin Ormond (23 February 1927 – 4 May 1984) was a Scottish football player and manager. As a player, Ormond was well known as one of Hibernian's Famous Five forward line, winning three league championships in the late 1940s an ...
, footballer and manager
* Jock Taylor, World Champion motorcycle sidecar
A sidecar is a one-wheeled device attached to the side of a motorcycle, scooter, or bicycle, making the whole a three-wheeled vehicle. A motorcycle with a sidecar is sometimes called a ''combination'', an ''outfit'', a ''rig'' or a ''hack''.
...
racer
* Ben Sayers
Bernard "Ben" Sayers (23 June 1856 – 9 March 1924) was a Scottish professional golfer, who later became a distinguished golf teacher, golf course designer and manufacturer of golf clubs and equipment. Sayers had a reputation for making good q ...
, professional golfer & club maker
* John White, footballer
* Willie Wood (bowler)
William Walker Wood MBE (born 26 April 1938 in Haddington, East Lothian) is a former Scottish professional bowls player, who has mainly competed in the outdoor or lawn form of the game. He is regarded as one of the leading bowlers of his gener ...
, professional bowler
* Dean Brett, footballer
* Josh Taylor Josh or Joshua Taylor may refer to:
* Josh Taylor (actor) (born 1943), American comedy and dramatic television actor
* Josh Taylor (baseball) (born 1993), American professional baseball pitcher
* Josh Taylor (boxer) (born 1991), Scottish professi ...
, boxer
Freedom of the County
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the County of East Lothian.Individuals
*John Bellany
John Bellany (18 June 1942 – 28 August 2013) was a Scottish people, Scottish painter.
Early life
Bellany was born in Port Seton. His father and grandfather were fishermen in Port Seton and Eyemouth near Edinburgh.
During the early 1960 ...
: 2004.
* Catriona Matthew : 2009.
Military Units
* 1st Battalion TheRoyal Scots Borderers
The Royal Scots Borderers, 1st Battalion, the Royal Regiment of Scotland (1 SCOTS) was an infantry battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland. The battalion formed on 1 August 2006 when its antecedent regiments - the Royal Scots and the King's O ...
: 2012.
* E Squadron The Scottish and North Irish Yeomanry
The Scottish and North Irish Yeomanry (SNIY) is a reserve Light Cavalry Regiment, formed in 2014, created out of the restructuring of the British Army's Territorial Army. It is operationally paired with The Royal Scots Dragoon Guards, (SCOTS D ...
: 6 July 2019.
References
Bibliography
Church and parish histories: Presbytery of Haddington
* The Lamp of Lothian ; or, The History of Haddington. James Miller (new edition, 1900). * Reminiscences of the Royal Burgh of Haddington. John Martine (1883). * Reminiscences of the County of Haddington. John Martine (1890). * Reminiscences of the County of Haddington. Second Series, ed. E. J. Wilson (1895). * The History of Morham. David Louden (1889). * North Berwick and its Vicinity. George Ferrier (1875). * The Bass Rock, its Civil and Ecclesiastical History. Thomas M'Crie, D.D. (1847). * Emeralds chased in Gold. Rev. John Dickson (1899). * Prestonpans and Vicinity. P. M'Neill (1902). * Tranent and its Surroundings. P. M'Neill (1884). * East Lothian Studies. Louden and Whitfield (1891). * East Lothian. Charles E. Green (1907). * Sketches of East Lothian. D. Croal (1873).Presbytery of Dunbar
* Coldingham: Parish and Priory otices of Cockburnspath, etc. A. Thomson (1908). * The History of Dunbar. James Miller (1859). * An Old Kirk Chronicle. Peter Hately Waddell, D.D. (1893). * The Churches of St Baldred. Rev. A. I. Ritchie (1880). * Saint Mary's, Whitekirk. Rev. E. B. Rankin (1914). * History of Berwickshire Naturalists' Club or Cockburnspath, Oldhamstocks, etc.External links
*East Lothian Council
''official government website'' * {{Authority control Counties of Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Council areas of Scotland Counties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922)