dental material on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dental products are specially fabricated
 It is usually supplied as 2 pastes, a glycol salicylate and another paste containing Zinc Oxide with Calcium Hydroxide. On mixing a chelate compounds are formed. Light activated versions are also available which contains polymersation activators, hydroexyethyl methacrylate, dimethacrylate which when light activated will result in a light activated polymerization reaction of a modified methacrylate monomer.
Polycarboxylate cement
Polycarboxylate cement have decent compressive strength to resists amalgam condensation and are acidic but less acidic than phosphate cements due to it having a higher molecular weight and polyacrylic acid being a weaker acid than phosphoric acid. They also form a strong bond with dentine and enamel allowing it to form a coronal seal. In addition it is an electrical and thermal insulator while also releasing fluoride rendering it bacteriostatic, furthermore it being radio-opaque makes it an excellent lining material.
Care has to be taken in handling such material as it has a strong bond with stainless steel instruments once it sets.
Commonly used as luting agents or as cavity base materials, however they tend to be rubbery during its setting reaction and adhere to stainless steel instruments thus most operators would prefer not to use them in deep cavities.
It is usually supplied as a power containing Zinc Oxide and a liquid containing aqueous Polyacrylic acid. The reaction consists of an acid base reaction with Zinc oxide reacting with the acid groups in polyacid to form a reaction product of unreacted zinc oxide cores bound by a salt matrix with polyacrylic acid chains cross linking with zinc ions.
Glass ionomer
It has the strongest compressive and tensile strength out of all the linings, thus it can withstand amalgam condensation in high stress bearing areas such as class II cavities. GI is used as a lining material as it is very compatible with most restorative materials, insulates thermally and electrically and adheres to enamel and dentine. Lining GI contains glass of smaller particle sizes in comparison to its adhesive restorative mix to allow formation of a thinner film. Some variations are also radiopaque which makes it good for X ray cavity detection. In addition, GI is bacteriostatic due to its fluoride release from un-reacted glass cores.
GIs are usually used as a lining material for composite resins or as luting agents for orthodontic bands.
The reaction is an acid-base reaction between calcium-aluminum-silicate glass powder and polyacrylic acid. They come in a powder and liquid which are mixed on a pad or in capsules which are for single usage. The resin-modified GIs contain a photo-initiator usually camphorquinone and an amide, and are light cured with a LED light curing unit. Setting takes place by a combination of acid-base reaction and chemically activated polymerization.
Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol has the lowest compressive and tensile strength in relative to the rest of the liners thus this lining should be limited to small or non stress bearing areas such as Class V cavities. This cavity lining is often used with a high strength base to provide strength, rigidity and thermal insulation. Zinc oxide eugenol can be used as linings in deep cavities without causing harm to the pulp, due to its obtundant effect on the pulp as well as its bactericidal properties due to Zinc. However eugenol may have an effect on resin based filling materials as it interferes with the polymerization and occasionally causes discoloration, thus caution should be taken when using both in tandem. It is also radio-opaque allowing fillings to be visible by X-rays.
Zinc oxide eugenol is usually used as a temporary filling/luting agent due to its low compressive strength and thus easily removed or as a lining for amalgam as it is incompatible with composites resins.
It is supplied as a two paste system. Equal length of 2 pastes are dispensed into a paper pad and mixed.
It is usually supplied as 2 pastes, a glycol salicylate and another paste containing Zinc Oxide with Calcium Hydroxide. On mixing a chelate compounds are formed. Light activated versions are also available which contains polymersation activators, hydroexyethyl methacrylate, dimethacrylate which when light activated will result in a light activated polymerization reaction of a modified methacrylate monomer.
Polycarboxylate cement
Polycarboxylate cement have decent compressive strength to resists amalgam condensation and are acidic but less acidic than phosphate cements due to it having a higher molecular weight and polyacrylic acid being a weaker acid than phosphoric acid. They also form a strong bond with dentine and enamel allowing it to form a coronal seal. In addition it is an electrical and thermal insulator while also releasing fluoride rendering it bacteriostatic, furthermore it being radio-opaque makes it an excellent lining material.
Care has to be taken in handling such material as it has a strong bond with stainless steel instruments once it sets.
Commonly used as luting agents or as cavity base materials, however they tend to be rubbery during its setting reaction and adhere to stainless steel instruments thus most operators would prefer not to use them in deep cavities.
It is usually supplied as a power containing Zinc Oxide and a liquid containing aqueous Polyacrylic acid. The reaction consists of an acid base reaction with Zinc oxide reacting with the acid groups in polyacid to form a reaction product of unreacted zinc oxide cores bound by a salt matrix with polyacrylic acid chains cross linking with zinc ions.
Glass ionomer
It has the strongest compressive and tensile strength out of all the linings, thus it can withstand amalgam condensation in high stress bearing areas such as class II cavities. GI is used as a lining material as it is very compatible with most restorative materials, insulates thermally and electrically and adheres to enamel and dentine. Lining GI contains glass of smaller particle sizes in comparison to its adhesive restorative mix to allow formation of a thinner film. Some variations are also radiopaque which makes it good for X ray cavity detection. In addition, GI is bacteriostatic due to its fluoride release from un-reacted glass cores.
GIs are usually used as a lining material for composite resins or as luting agents for orthodontic bands.
The reaction is an acid-base reaction between calcium-aluminum-silicate glass powder and polyacrylic acid. They come in a powder and liquid which are mixed on a pad or in capsules which are for single usage. The resin-modified GIs contain a photo-initiator usually camphorquinone and an amide, and are light cured with a LED light curing unit. Setting takes place by a combination of acid-base reaction and chemically activated polymerization.
Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol has the lowest compressive and tensile strength in relative to the rest of the liners thus this lining should be limited to small or non stress bearing areas such as Class V cavities. This cavity lining is often used with a high strength base to provide strength, rigidity and thermal insulation. Zinc oxide eugenol can be used as linings in deep cavities without causing harm to the pulp, due to its obtundant effect on the pulp as well as its bactericidal properties due to Zinc. However eugenol may have an effect on resin based filling materials as it interferes with the polymerization and occasionally causes discoloration, thus caution should be taken when using both in tandem. It is also radio-opaque allowing fillings to be visible by X-rays.
Zinc oxide eugenol is usually used as a temporary filling/luting agent due to its low compressive strength and thus easily removed or as a lining for amalgam as it is incompatible with composites resins.
It is supplied as a two paste system. Equal length of 2 pastes are dispensed into a paper pad and mixed.
 Dental restorative materials are used to replace
Dental restorative materials are used to replace  Biocompatibility refers to how well the material coexists with the biological equilibrium of the tooth and body systems. Since fillings are in close contact with mucosa, tooth, and pulp, biocompatibility is very important. Common problems with some of the current dental materials include chemical leakage from the material, pulpal irritation and less commonly allergy. Some of the byproducts of the chemical reactions during different stages of material hardening need to be considered.
*Radiopacity in dental materials is an important property that allows for distinguishing restorations from teeth and surrounding structures, assessing the absorption of materials into bone structure, and detecting cement dissolution or other failures that could cause harm to the patient. Cements, composites, endodontic sealers, bone grafts, and acrylic resins all benefit from the addition of radiopaque materials. Examples of these materials include
Biocompatibility refers to how well the material coexists with the biological equilibrium of the tooth and body systems. Since fillings are in close contact with mucosa, tooth, and pulp, biocompatibility is very important. Common problems with some of the current dental materials include chemical leakage from the material, pulpal irritation and less commonly allergy. Some of the byproducts of the chemical reactions during different stages of material hardening need to be considered.
*Radiopacity in dental materials is an important property that allows for distinguishing restorations from teeth and surrounding structures, assessing the absorption of materials into bone structure, and detecting cement dissolution or other failures that could cause harm to the patient. Cements, composites, endodontic sealers, bone grafts, and acrylic resins all benefit from the addition of radiopaque materials. Examples of these materials include
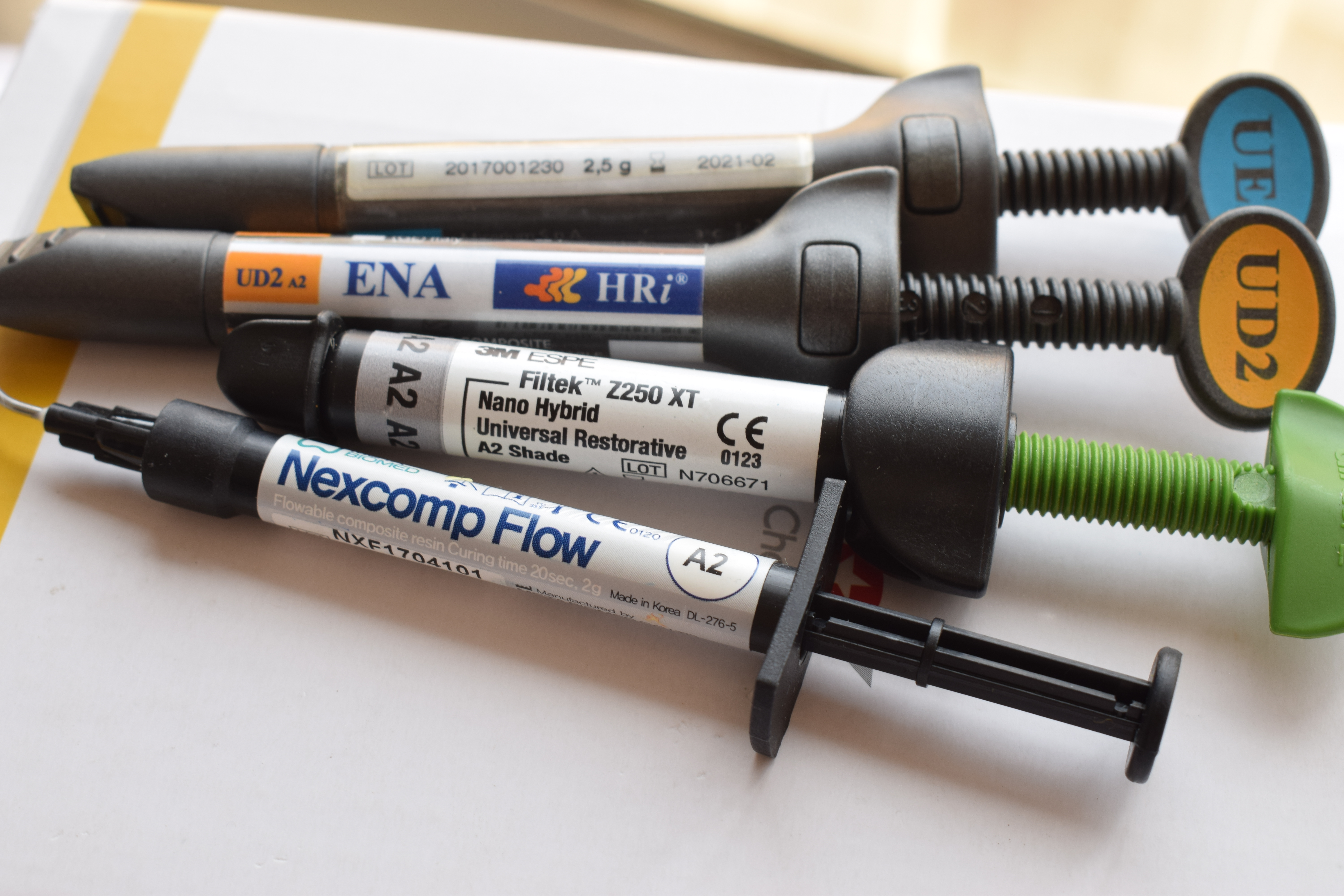 ''Composite resin'' fillings (also called white fillings) are a mixture of
''Composite resin'' fillings (also called white fillings) are a mixture of
 Indirect restorations are ones where the tooth or teeth to receive the restoration are first prepared, then a
Indirect restorations are ones where the tooth or teeth to receive the restoration are first prepared, then a
material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geologi ...
s, designed for use in dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions o ...
. There are many different types of dental products, and their characteristics vary according to their intended purpose.
Temporary dressings
A temporary dressing is a dental filling which is not intended to last in the long term. They are interim materials which may have therapeutic properties. A common use of temporary dressing occurs if root canal therapy is carried out over more than one appointment. In between each visit, the pulp canal system must be protected from contamination from the oral cavity, and a temporary filling is placed in the access cavity. Examples include: *Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) is a material created by the combination of zinc oxide and eugenol contained in oil of cloves. An acid-base reaction takes place with the formation of zinc eugenolate chelate. The reaction is catalysed by water and is acc ...
—bactericidal, cheap and easy to remove. Eugenol
Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil ...
is derived from oil of cloves, and has an obtundant effect on the tooth and decreases toothache
Toothache, also known as dental pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the te ...
. It is suitable temporary material providing there are no biting forces on it. It is also contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
if the final restorative material is composite because eugenol adversely effects the bond/polymerization process, also, when applied directly on the pulp tissue, it can produce chronic inflammation and result in pulp necrosis. Examples brands: Kalzinol, Sedanol.
Cements
Dental cements are used most often to bond indirect restorations such as crowns to the natural tooth surface. Examples include: *Zinc Oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white powder that is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, food supplements, rubbers, plastics, ceramics, glass, cemen ...
cement—self setting and harden when in contact with saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
. Example brands: Cavit, Coltosol.
*Zinc Phosphate
Zinc phosphate is an inorganic compound with the formula Zn3( PO4)2. This white powder is widely used as a corrosion resistant coating on metal surfaces either as part of an electroplating process or applied as a primer pigment (see also red lead ...
cement
*Zinc Polycarboxylate
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic ta ...
cement—Adheres to enamel and dentin. Example brands: PolyF.
*Glass Ionomer cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calc ...
*Resin-based cement
*Copper-based cement
Impression materials
Dental impressions are negative imprints of teeth and oral soft tissues from which a positive representation can be cast. They are used inprosthodontics
Prosthodontics, also known as dental prosthetics or prosthetic dentistry, is the area of dentistry that focuses on dental prostheses. It is one of 12 dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association (ADA), Royal College of Surge ...
(to make dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, and are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or ...
), orthodontics
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial ...
, restorative dentistry
Restorative dentistry is the study, diagnosis and integrated management of diseases of the teeth and their supporting structures and the rehabilitation of the dentition to functional and aesthetic requirements of the individual. Restorative dentis ...
, dental implantology and oral and maxillofacial surgery.
* Rigidity- Inelastic (rigid) impression materials are used with patients with shallow undercuts.
* Elasticity- Elastic impression materials are used in patients with deep undercuts as it must be flexible enough to reach the end-point of the undercut.
These two properties are essential because patients have varying soft-tissue undercuts (shallow or deep undercuts). In order to obtain an accurate impression, a suitable property of impression material must be used. Impression materials are designed to be liquid or semi-solid when first mixed, then set hard in a few minutes, leaving imprints of oral structures.
Common dental impression materials include:
* sodium alginate
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. With metals such as sodium and calcium, its salts are known as alginates. Its colou ...
* polyether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
* silicones
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cookin ...
Historically these products were used as impression materials:
* plaster of Paris
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
* zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) is a material created by the combination of zinc oxide and eugenol contained in oil of cloves. An acid-base reaction takes place with the formation of zinc eugenolate chelate. The reaction is catalysed by water and is acc ...
* agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is ...
Lining materials
Dental lining materials are used during restorations of large cavities, and are placed between the remaining tooth structure and the restoration material. The purpose of this is to protect thedentinal tubules
Bone canaliculi are microscopic canals between the lacunae of ossified bone. The radiating processes of the osteocytes (called filopodia) project into these canals. These cytoplasmic processes are joined together by gap junctions. Osteocytes do ...
and the sensitive pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
, forming a barrier-like structure. After drilling the caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
out of the tooth, the dentist applies a thin layer (approximately 1/2mm) to the base of the tooth, followed by light curing. Another layer might be applied if the cavity is very large and deep.
There are many functions to dental lining materials, some of which are listed below:
* Lining materials protect the weak tooth from post-operative hypersensitivity, reducing patient discomfort and allowing the tooth to heal at a faster rate after the procedure.
* Some dental restorative materials such as acrylic monomers in resin-based materials and phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
in silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is al ...
materials may pose toxic and irritable effects to the pulp. Lining materials protect the tooth from the aforementioned irritants.
* Lining materials serve as an insulating layer to the tooth pulp from sudden changes in temperature when the patient takes hot or cold food, protecting it from potential pain resulting from thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
.
* Additionally, lining materials are electrically insulating, preventing corrosion by galvanic cell
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction reactions. A common apparatus ...
in the event where two dissimilar metals (e.g.: gold or amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital
...
) are placed next to each other.
Type
Calcium Hydroxide Calcium Hydroxide has a relatively low compressive strength and a viscous consistency making them difficult to apply to cavities in thick sections, a common technique used to overcome this issue would be to apply a thin sub-lining of a calcium hydroxide lining and then building up with zinc phosphate prior to amalgam condensation. Generates a relatively high pH environment around area surrounding the cement due to calcium hydroxide leaking out thus making it bactericidal. It also has a unique effect of initiating calcification and stimulating the formation of secondary dentine due to an irritation effect of the pulp tissues by the cement. It is also radio-opaque and acts as a good thermal and electrical insulation. However, due to its low compressive strength it is unable to withstand amalgam packing thus a strong cement base material should be placed above it to counter this. Calcium silicate-based liners have become alternatives to calcium hydroxide and a preferred material among practitioners for its bioactive and sealing properties; the material triggers a biological response and results in formation of bonding with the tissue. Commonly used as pulp capping agents and lining materials for silicate and resin-based filling materials. It is usually supplied as 2 pastes, a glycol salicylate and another paste containing Zinc Oxide with Calcium Hydroxide. On mixing a chelate compounds are formed. Light activated versions are also available which contains polymersation activators, hydroexyethyl methacrylate, dimethacrylate which when light activated will result in a light activated polymerization reaction of a modified methacrylate monomer.
Polycarboxylate cement
Polycarboxylate cement have decent compressive strength to resists amalgam condensation and are acidic but less acidic than phosphate cements due to it having a higher molecular weight and polyacrylic acid being a weaker acid than phosphoric acid. They also form a strong bond with dentine and enamel allowing it to form a coronal seal. In addition it is an electrical and thermal insulator while also releasing fluoride rendering it bacteriostatic, furthermore it being radio-opaque makes it an excellent lining material.
Care has to be taken in handling such material as it has a strong bond with stainless steel instruments once it sets.
Commonly used as luting agents or as cavity base materials, however they tend to be rubbery during its setting reaction and adhere to stainless steel instruments thus most operators would prefer not to use them in deep cavities.
It is usually supplied as a power containing Zinc Oxide and a liquid containing aqueous Polyacrylic acid. The reaction consists of an acid base reaction with Zinc oxide reacting with the acid groups in polyacid to form a reaction product of unreacted zinc oxide cores bound by a salt matrix with polyacrylic acid chains cross linking with zinc ions.
Glass ionomer
It has the strongest compressive and tensile strength out of all the linings, thus it can withstand amalgam condensation in high stress bearing areas such as class II cavities. GI is used as a lining material as it is very compatible with most restorative materials, insulates thermally and electrically and adheres to enamel and dentine. Lining GI contains glass of smaller particle sizes in comparison to its adhesive restorative mix to allow formation of a thinner film. Some variations are also radiopaque which makes it good for X ray cavity detection. In addition, GI is bacteriostatic due to its fluoride release from un-reacted glass cores.
GIs are usually used as a lining material for composite resins or as luting agents for orthodontic bands.
The reaction is an acid-base reaction between calcium-aluminum-silicate glass powder and polyacrylic acid. They come in a powder and liquid which are mixed on a pad or in capsules which are for single usage. The resin-modified GIs contain a photo-initiator usually camphorquinone and an amide, and are light cured with a LED light curing unit. Setting takes place by a combination of acid-base reaction and chemically activated polymerization.
Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol has the lowest compressive and tensile strength in relative to the rest of the liners thus this lining should be limited to small or non stress bearing areas such as Class V cavities. This cavity lining is often used with a high strength base to provide strength, rigidity and thermal insulation. Zinc oxide eugenol can be used as linings in deep cavities without causing harm to the pulp, due to its obtundant effect on the pulp as well as its bactericidal properties due to Zinc. However eugenol may have an effect on resin based filling materials as it interferes with the polymerization and occasionally causes discoloration, thus caution should be taken when using both in tandem. It is also radio-opaque allowing fillings to be visible by X-rays.
Zinc oxide eugenol is usually used as a temporary filling/luting agent due to its low compressive strength and thus easily removed or as a lining for amalgam as it is incompatible with composites resins.
It is supplied as a two paste system. Equal length of 2 pastes are dispensed into a paper pad and mixed.
It is usually supplied as 2 pastes, a glycol salicylate and another paste containing Zinc Oxide with Calcium Hydroxide. On mixing a chelate compounds are formed. Light activated versions are also available which contains polymersation activators, hydroexyethyl methacrylate, dimethacrylate which when light activated will result in a light activated polymerization reaction of a modified methacrylate monomer.
Polycarboxylate cement
Polycarboxylate cement have decent compressive strength to resists amalgam condensation and are acidic but less acidic than phosphate cements due to it having a higher molecular weight and polyacrylic acid being a weaker acid than phosphoric acid. They also form a strong bond with dentine and enamel allowing it to form a coronal seal. In addition it is an electrical and thermal insulator while also releasing fluoride rendering it bacteriostatic, furthermore it being radio-opaque makes it an excellent lining material.
Care has to be taken in handling such material as it has a strong bond with stainless steel instruments once it sets.
Commonly used as luting agents or as cavity base materials, however they tend to be rubbery during its setting reaction and adhere to stainless steel instruments thus most operators would prefer not to use them in deep cavities.
It is usually supplied as a power containing Zinc Oxide and a liquid containing aqueous Polyacrylic acid. The reaction consists of an acid base reaction with Zinc oxide reacting with the acid groups in polyacid to form a reaction product of unreacted zinc oxide cores bound by a salt matrix with polyacrylic acid chains cross linking with zinc ions.
Glass ionomer
It has the strongest compressive and tensile strength out of all the linings, thus it can withstand amalgam condensation in high stress bearing areas such as class II cavities. GI is used as a lining material as it is very compatible with most restorative materials, insulates thermally and electrically and adheres to enamel and dentine. Lining GI contains glass of smaller particle sizes in comparison to its adhesive restorative mix to allow formation of a thinner film. Some variations are also radiopaque which makes it good for X ray cavity detection. In addition, GI is bacteriostatic due to its fluoride release from un-reacted glass cores.
GIs are usually used as a lining material for composite resins or as luting agents for orthodontic bands.
The reaction is an acid-base reaction between calcium-aluminum-silicate glass powder and polyacrylic acid. They come in a powder and liquid which are mixed on a pad or in capsules which are for single usage. The resin-modified GIs contain a photo-initiator usually camphorquinone and an amide, and are light cured with a LED light curing unit. Setting takes place by a combination of acid-base reaction and chemically activated polymerization.
Zinc oxide eugenol
Zinc oxide eugenol has the lowest compressive and tensile strength in relative to the rest of the liners thus this lining should be limited to small or non stress bearing areas such as Class V cavities. This cavity lining is often used with a high strength base to provide strength, rigidity and thermal insulation. Zinc oxide eugenol can be used as linings in deep cavities without causing harm to the pulp, due to its obtundant effect on the pulp as well as its bactericidal properties due to Zinc. However eugenol may have an effect on resin based filling materials as it interferes with the polymerization and occasionally causes discoloration, thus caution should be taken when using both in tandem. It is also radio-opaque allowing fillings to be visible by X-rays.
Zinc oxide eugenol is usually used as a temporary filling/luting agent due to its low compressive strength and thus easily removed or as a lining for amalgam as it is incompatible with composites resins.
It is supplied as a two paste system. Equal length of 2 pastes are dispensed into a paper pad and mixed.
Restorative materials
 Dental restorative materials are used to replace
Dental restorative materials are used to replace tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
structure loss, usually due to dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
(dental cavities), but also tooth wear
Tooth wear refers to loss of tooth substance by means other than dental caries. Tooth wear is a very common condition that occurs in approximately 97% of the population. This is a normal physiological process occurring throughout life; but with in ...
and dental trauma. On other occasions, such materials may be used for cosmetic
Cosmetic may refer to:
*Cosmetics, or make-up, substances to enhance the beauty of the human body, apart from simple cleaning
*Cosmetic, an adjective describing beauty, aesthetics, or appearance, especially concerning the human body
*Cosmetic, a t ...
purposes to alter the appearance of an individual's teeth.
There are many challenges for the physical properties of the ideal dental restorative material. The goal of research and development in restorative materials is to develop the ideal restorative material. The ideal restorative material would be identical to natural tooth structure in strength, adherence, and appearance. The properties of an ideal filling material can be divided into four categories: physical properties, biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is related to the behavior of biomaterials in various contexts. The term refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific situation. The ambiguity of the term reflects the ongoing de ...
, aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed thr ...
and application.
* Requisite physical properties include low thermal conductivity and expansion, resistance to different categories of forces and wear such as attrition and abrasion, and resistance to chemical erosion. There must also be good bonding strength to the tooth. Everyday masticatory forces and conditions must be withstood without material fatigue.
* Biocompatibility refers to how well the material coexists with the biological equilibrium of the tooth and body systems. Since fillings are in close contact with mucosa, tooth, and pulp, biocompatibility is very important. Common problems with some of the current dental materials include chemical leakage from the material, pulpal irritation and less commonly allergy. Some of the byproducts of the chemical reactions during different stages of material hardening need to be considered.
*Radiopacity in dental materials is an important property that allows for distinguishing restorations from teeth and surrounding structures, assessing the absorption of materials into bone structure, and detecting cement dissolution or other failures that could cause harm to the patient. Cements, composites, endodontic sealers, bone grafts, and acrylic resins all benefit from the addition of radiopaque materials. Examples of these materials include
Biocompatibility refers to how well the material coexists with the biological equilibrium of the tooth and body systems. Since fillings are in close contact with mucosa, tooth, and pulp, biocompatibility is very important. Common problems with some of the current dental materials include chemical leakage from the material, pulpal irritation and less commonly allergy. Some of the byproducts of the chemical reactions during different stages of material hardening need to be considered.
*Radiopacity in dental materials is an important property that allows for distinguishing restorations from teeth and surrounding structures, assessing the absorption of materials into bone structure, and detecting cement dissolution or other failures that could cause harm to the patient. Cements, composites, endodontic sealers, bone grafts, and acrylic resins all benefit from the addition of radiopaque materials. Examples of these materials include zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white powder that is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, food supplements, rubbers, plastics, ceramics, glass, cemen ...
, zirconium dioxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabi ...
, titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insolubl ...
, barium sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium an ...
, and ytterbium(III) fluoride
Ytterbium(III) fluoride () is an inorganic chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chem ...
.
* Ideally, filling materials should match the surrounding tooth structure in shade, translucency, and texture.
* Dental operators require materials that are easy to manipulate and shape, where the chemistry of any reactions that need to occur are predictable or controllable.
Direct restorative materials
Direct restorations are ones which are placed directly into a cavity on a tooth, and shaped to fit. The chemistry of the setting reaction for direct restorative materials is designed to be more biologically compatible. Heat and byproducts generated cannot damage the tooth or patient, since the reaction needs to take place while in contact with the tooth during restoration. This ultimately limits the strength of the materials, since harder materials need moreenergy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
to manipulate.
The type of filling (restorative) material used has a minor effect on how long they last. The majority of clinical studies indicate the annual failure rates (AFRs) are between 1% and 3% with tooth colored fillings on back teeth. Note that root canaled (endodontically) treated teeth have AFR's between 2% and 12%. The main reasons for failure are cavities that occur around the filling and fracture of the real tooth. These are related to personal cavity risk and factors like grinding teeth (bruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the gene ...
).
Amalgam
Amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital
...
is a metallic filling material composed from a mixture of mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
(from 43% to 54%) and powdered alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
made mostly of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, commonly called the amalgam alloy. Amalgam does not adhere to tooth structure without the aid of cements or use of techniques which lock in the filling, using the same principles as a dovetail joint
A dovetail joint or simply dovetail is a joinery technique most commonly used in woodworking joinery (carpentry), including furniture, cabinets, log buildings, and traditional timber framing. Noted for its resistance to being pulled apart (ten ...
.
Amalgam is still used extensively in many parts of the world because of its cost effectiveness, superior strength and longevity. However, the metallic colour is not aesthetically pleasing and tooth coloured alternatives are continually emerging with increasingly comparable properties. Due to the known toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
of the element mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, there is some controversy about the use of amalgams. The Swedish government banned the use of mercury amalgam in June 2009.
Research has shown that, while amalgam use is controversial and may increase mercury levels in the human body, these levels are below safety threshold levels established by the WHO and the EPA. However, there are certain subpopulations who, due to inherited genetic variabilities, exhibit sensitivity to mercury levels lower than these threshold levels. These particular individuals may experience adverse effects caused by amalgam restoration. These include neural defects, mainly caused by impaired neurotransmitter processing.
Composite resin
 ''Composite resin'' fillings (also called white fillings) are a mixture of
''Composite resin'' fillings (also called white fillings) are a mixture of nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 1 ...
or powdered glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
and plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
resin, and can be made to resemble the appearance of the natural tooth. Although cosmetically superior to amalgam fillings, composite resin fillings are usually more expensive. Bis-GMA
Bis-GMA (bisphenol A-glycidyl methacrylate) is a resin commonly used in dental composite, dental sealants. and dental cement. It is the diester derived from methacrylic acid and the bisphenol A diglycidyl ether. Bearing two polymerizable groups, ...
based resins contain Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial s ...
, a known endocrine disrupter chemical, and may contribute to the development of breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a re ...
. However, it has been demonstrated that the extremely low levels of bis-GMA released by composite restorations do not cause a significant increase in markers of renal injury, when compared to amalgam restorations. That is, there is no added risk of renal or endocrine injury in choosing composite restorations over amalgams. PEX
PEX is cross-linked polyethylene, a form of polyethylene with cross-links.
PEX or Pex may also refer to: Science and technology
*Peer exchange, a method to gather peers for BitTorrent
* PHIGS Extension to X, in programming
* Pex (software), a un ...
-based materials do not contain Bisphenol A and are the least cytotoxic material available.
Most modern composite resins are light-cured photopolymers, meaning that they harden with light exposure. They can then be polished to achieve maximum aesthetic results. Composite resins experience a very small amount of shrinkage upon curing, causing the material to pull away from the walls of the cavity preparation. This makes the tooth slightly more vulnerable to microleakage and recurrent decay
Decay may refer to:
Science and technology
* Bit decay, in computing
* Software decay, in computing
* Distance decay, in geography
* Decay time (fall time), in electronics
Biology
* Decomposition of organic matter
* Tooth decay (dental caries ...
. Microleakage can be minimized or eliminated by utilizing proper handling techniques and appropriate material selection.
In some circumstances, less tooth structure can be removed compared to preparation for other dental materials such as amalgam and many of the indirect methods of restoration. This is because composite resins bind to enamel (and dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by ena ...
too, although not as well) via a micromechanical bond. As conservation of tooth structure is a key ingredient in tooth preservation, many dentists prefer placing materials like composite instead of amalgam fillings whenever possible.
Generally, composite fillings are used to fill a carious lesion involving highly visible areas (such as the central incisors or any other teeth that can be seen when smiling) or when conservation of tooth structure is a top priority.
The bond of composite resin to tooth, is especially affected by moisture contamination and cleanliness of the prepared surface. Other materials can be selected when restoring teeth where moisture control techniques are not effective.
Glass ionomer cement
The concept of using "smart" materials in dentistry has attracted a lot of attention in recent years. Conventional glass-ionomer (GI) cements have a large number of applications in dentistry. They are biocompatible with the dental pulp to some extent. Clinically, this material was initially used as a biomaterial to replace the lost osseous tissues in the human body. These fillings are a mixture ofglass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
and an organic acid. Although they are tooth-colored, glass ionomers vary in translucency. Although glass ionomers can be used to achieve an aesthetic result, their aesthetic potential does not measure up to that provided by composite resins.
The cavity preparation of a glass ionomer filling is the same as a composite resin. However, one of the advantages of GI compared to other restorative materials is that they can be placed in cavities without any need for bonding agents (4).
Conventional glass ionomers are chemically set via an acid-base reaction. Upon mixing of the material components, there is no light cure needed to harden the material once placed in the cavity preparation. After the initial set, glass ionomers still need time to fully set and harden.
Advantages:
# Glass ionomer can be placed in cavities without any need for bonding agents .
# They are not subject to shrinkage and microleakage, as the bonding mechanism is an acid-base reaction and not a polymerization reaction.(GICs do not undergo great dimensional changes in a moist environment in response to heat or cold and it appears heating results only in water movement within the structure of the material. These exhibit shrinkage in a dry environment at temperature higher than 50C, which is similar to the behavior of dentin.
# Glass ionomers contain and release fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typ ...
, which is important to preventing carious lesions. Furthermore, as glass ionomers release their fluoride, they can be "recharged" by the use of fluoride-containing toothpaste. Hence, they can be used as a treatment modality
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
for patients who are at high risk for caries. Newer formulations of glass ionomers that contain light-cured resins can achieve a greater aesthetic result, but do not release fluoride as well as conventional glass ionomers.
Disadvantages:
The most important disadvantage is lack of adequate strength and toughness. In an attempt to improve the mechanical properties of the conventional GI, resin-modified ionomers have been marketed.
GICs are usually weak after setting and are not stable in water; however, they become stronger with the progression of reactions and become more resistant to moisture.
New generations: The aim is tissue regeneration and use of biomaterial in the form of a powder or solution is to induce local tissue repair. These bioactive materials release chemical agents in the form of dissolved ions or growth factors such as bone morphogenic protein, which stimulates activate cells.
Glass ionomers are about as expensive as composite resin. The fillings do not wear as well as composite resin fillings. Still, they are generally considered good materials to use for root caries and for sealants.
Resin modified glass-ionomer cement (RMGIC)
A combination of glass-ionomer and composite resin, these fillings are a mixture ofglass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
, an organic acid, and resin monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
s that harden when light cured (light-activated polymerization besides the acid-base reaction of convetional glass-ionomer). The cost is similar to composite resin. It holds up better than glass ionomer, but not as well as composite resin, and is not recommended for biting surfaces of adult teeth, or when control of moisture cannot be achieved.
Generally, resin modified glass-ionomer cements can achieve a better aesthetic result than conventional glass ionomers, but not as good as pure composites.
Compomers
Another combination of composite resin and glass ionomer technology, with focus lying towards the composite resin end of the spectrum. Compomers are essentially made up of filler, dimethacrylate monomer, difunctional resin, photo-activator and initiator, and hydrophilic monomers. The primary reason of the addition of filler is to decrease the proportion of resin and increase the mechanical strength besides improving the material's appearance. Although compomers have better mechanical and aesthetic properties than RMGIC, they have few disadvantages which limit their applications. * Compomers have weaker wear properties. * Compomers are not adhesive, therefore they require bonding materials. Compomers themselves cannot adhere to the tooth tissue due to the presence of resin which can make it shrink on polymerisation. As a result, any bonding attempted will be disrupted at this stage. * Compomers release fluoride at low level, so they cannot act as a fluoride reservoir. * Compomers have high staining susceptibility. Uptake of oral fluid causes them to show staining soon after placement. Due to its relatively weaker mechanical properties, Compomers are unfit for stress-bearing restorations but can be used in the deciduous dentition where lower loads are anticipated.Cermets
Dental cermets, also known as silver cermets, were created to improve thewear resistance
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology.
Wear in m ...
and hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard ...
of glass ionomer cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calc ...
s (mentioned above) through the addition of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
. While the incorporation of silver achieved this, cermets have poorer aesthetics, appearing metallic rather than white. Cermets also have a similar compressive strength
In mechanics, compressive strength or compression strength is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (as opposed to tensile strength which withstands loads tending to elongate). In other words, compre ...
, flexural strength
Flexural strength, also known as modulus of rupture, or bend strength, or transverse rupture strength is a material property, defined as the stress in a material just before it yields in a flexure test. The transverse bending test is most freque ...
, and solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
as glass ionomer cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calc ...
s, some of the main limiting factor
A limiting factor is a variable of a system that causes a noticeable change in output or another measure of a type of system. The limiting factor is in a pyramid shape of organisms going up from the producers to consumers and so on. A factor not l ...
s for both materials. Clinical studies have shown cermets perform poorly. All these disadvantages led to the decline in the use of this restorative material.
Below is a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of dental cermets.
Advantages:
* Radio-opaque
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
- this helps with identification of secondary caries when future radiographs
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnos ...
are taken as there will be a greater contrast between the cermet and tooth tissue on the radiographic image
* Adheres directly to tooth tissue
* Higher wear resistance
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology.
Wear in m ...
than glass ionomer cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calc ...
s (GICs)
* Greater hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard ...
than GICs
Disadvantages:
* Low compressive strength
In mechanics, compressive strength or compression strength is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (as opposed to tensile strength which withstands loads tending to elongate). In other words, compre ...
* Low flexural strength
Flexural strength, also known as modulus of rupture, or bend strength, or transverse rupture strength is a material property, defined as the stress in a material just before it yields in a flexure test. The transverse bending test is most freque ...
* Soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
* Poor aesthetics
* Poorer fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typ ...
release than GICs
* Poor clinical performance
Indirect restorative materials
 Indirect restorations are ones where the tooth or teeth to receive the restoration are first prepared, then a
Indirect restorations are ones where the tooth or teeth to receive the restoration are first prepared, then a dental impression
A dental impression is a negative imprint of hard (teeth) and soft tissues in the mouth from which a positive reproduction (cast or model) can be formed. It is made by placing an appropriate material in a stock or custom dental impression tray w ...
is taken and sent to a dental technician
A dental technologist (dental laboratory technician) is a member of the dental team who, upon prescription from a dental clinician, constructs custom-made restorative and dental appliances.
There are four major disciplines within dental technol ...
who fabricates the restoration according to the dentist's prescription.
Porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainl ...
fillings are hard, but can cause wear on opposing teeth. They are brittle and are not always recommended for molar fillings. They are hard and rigid thus able to resist abrasion forces, are brittle due to surface irregularities, porosities, tendency to undergo static fatigue, and is good aesthetically as it mimics appearance of natural teeth due to various levels of shades. Porcelain materials can be strengthened by soaking fired material in molten salt to allow exchange of sodium and potassium ions on the surface as this successfully create compressive stresses on the outer layer, by controlling cooling after firing, and by the use of pure alumina inserts, a core of alumina or alumina powder, as they act as crack stoppers and are highly compatible to porcelain.
Tooth colored dental composite
Dental composite resins (better referred to as "resin-based composites" or simply "filled resins") are dental cements made of synthetic resins. Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, of good tooth-like appea ...
materials are either used as direct filling or as construction material of an indirect inlay. It is usually cured by light.
Nano-ceramic particles embedded in a resin matrix, are less brittle and therefore less likely to crack, or chip, than all-ceramic indirect fillings; they absorb the shock of chewing more like natural teeth, and more like resin or gold fillings, than do ceramic fillings; and at the same time more resistant to wear than all-resin indirect fillings. These are available in blocks for use with CAD-CAM systems.
Gold fillings have excellent durability, wear well, and do not cause excessive wear to the opposing teeth, but they do conduct heat and cold, which can be irritating. There are two categories of gold fillings, cast gold fillings (gold inlays and onlays) made with 14 or 18 kt gold, and gold foil made with pure 24 kt gold that is burnished layer by layer. For years, they have been considered the benchmark of restorative dental materials. Recent advances in dental porcelains and consumer focus on aesthetic results have caused demand for gold fillings to drop in favor of advanced composites and porcelain veneers and crowns. Gold fillings are sometimes quite expensive; yet, they do last a very long time—which can mean gold restorations are less costly and painful in the long run. It is not uncommon for a gold crown to last 30 years.
Other historical fillings
Lead fillings were used in the 18th century, but became unpopular in the 19th century because of their softness. This was beforelead poisoning
Lead poisoning, also known as plumbism and saturnism, is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, inferti ...
was understood.
According to American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
-era dental handbooks from the mid-19th century, since the early 19th century metallic fillings had been used, made of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platinu ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
, or amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital
...
. A pellet was rolled slightly larger than the cavity, condensed into place with instruments, then shaped and polished in the patient's mouth. The filling was usually left "high", with final condensation—"tamping down"—occurring while the patient chewed food. Gold foil was the most popular and preferred filling material during the Civil War. Tin and amalgam were also popular due to lower cost, but were held in lower regard.
One survey of dental practices in the mid-19th century catalogued dental fillings found in the remains of seven Confederate soldiers from the U.S. Civil War; they were made of:
*Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
foil
Foil may refer to:
Materials
* Foil (metal), a quite thin sheet of metal, usually manufactured with a rolling mill machine
* Metal leaf, a very thin sheet of decorative metal
* Aluminium foil, a type of wrapping for food
* Tin foil, metal foil ...
: Preferred because of its durability and safety.
*Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platinu ...
: Was rarely used because it was too hard, inflexible and difficult to form into foil.
*Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
: A material which failed because of its lack of malleability but has been added to some amalgams.
*Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
: Believed to have been a very popular filling material during the Civil War. Tin foil was recommended when a cheaper material than gold was requested by the patient, however tin wore down rapidly and even if it could be replaced cheaply and quickly, there was a concern, specifically from Harris
Harris may refer to:
Places Canada
* Harris, Ontario
* Northland Pyrite Mine (also known as Harris Mine)
* Harris, Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Harris No. 316, Saskatchewan
Scotland
* Harris, Outer Hebrides (sometimes called the Isle of ...
, that it would oxidise
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
in the mouth and thus cause a recurrence of caries. Due to the blackening, tin was only recommended for posterior teeth.
*Thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high me ...
: Radioactivity was unknown at that time, and the dentist probably thought he was working with tin.
*Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
and tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
mixture, probably coming from shotgun pellets. Lead was rarely used in the 19th century, it is soft and quickly worn down by mastication, and had known harmful health effects.
Acrylic polymers
Acrylics are used in the fabrication ofdentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, and are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or ...
, artificial teeth, impression trays, maxillofacial / orthodontic appliances
Orthodontic technology is a specialty of dental technology that is concerned with the design and fabrication of dental appliances for the treatment of malocclusions, which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, ...
and temporary (provisional) restorations, however they can not be used as tooth filling materials because they can lead to pulpitis
Pulpitis is inflammation of dental pulp tissue. The pulp contains the blood vessels, the nerves, and connective tissue inside a tooth and provides the tooth’s blood and nutrients. Pulpitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection which itself is ...
and periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
as they may generate heat and acids during (setting) curing, and in addition they shrink.
Failure of dental restorations
Fillings have a finite lifespan; composites appear to have a higher failure rate than amalgam over five to seven years. How well people keep their teeth clean and avoid cavities is probably a more important factor than the material chosen for the restoration.Evaluation and regulation of dental materials
The Nordic Institute of Dental Materials (NIOM) evaluates dental materials in theNordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; literal translation, lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmar ...
. This research and testing institution are accredited to perform several test procedures for dental products. In Europe, dental materials are classified as medical devices according to the Medical Devices Directive
The Medical Device Directive (Council Directive 93/42/EEC of 14 June 1993 concerning medical devices, OJ No L 169/1 of 1993-07-12) is intended to harmonise the laws relating to medical devices within the European Union. The MD Directive is a ' ...
. In USA, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
is the regulatory body for dental products.
References
*''User Guide of Dental Impression Material: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-keGMbCHC2A'' *''Dental Materials Fact Sheet'', Dental Board of California, May 2004 {{DEFAULTSORT:Dental Restorative Materials Dental materials Restorative dentistry