|
Glass Ionomer Cement
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calciumaluminofluorosilicate glass) and polyacrylic acid, an ionomer. Occasionally water is used instead of an acid, altering the properties of the material and its uses. This reaction produces a powdered cement of glass particles surrounded by matrix of fluoride elements and is known chemically as glass polyalkenoate. There are other forms of similar reactions which can take place, for example, when using an aqueous solution of acrylic/ itaconic copolymer with tartaric acid, this results in a glass-ionomer in liquid form. An aqueous solution of maleic acid polymer or maleic/acrylic copolymer with tartaric acid can also be used to form a glass-ionomer in liquid form. Tartaric acid plays a significant part in controlling the setting characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Ionomer
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. Despite bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth ( enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth ( enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antidep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Sealant
Dental sealants (also termed pit and fissure sealants, or simply fissure sealants) are a dental treatment intended to prevent tooth decay. Teeth have recesses on their biting surfaces; the back teeth have fissures (grooves) and some front teeth have cingulum pits. It is these pits and fissures that are most vulnerable to tooth decay because food and bacteria stick in them and because they are hard-to-clean areas. Dental sealants are materials placed in these pits and fissures to fill them in, creating a smooth surface which is easy to clean. Dental sealants are mainly used in children who are at higher risk of tooth decay, and are usually placed as soon as the adult molar teeth come through. Background Dental caries is an upset of the balance between loss and gain of minerals from a tooth surface. The loss of minerals from the teeth occurs from the bacteria within the mouth, fermenting foods and producing acids, whereas the tooth gains minerals from our saliva and fluoride that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the experiment. Generally, the temperature program for a DSC analysis is designed such that the sample holder temperature increases linearly as a function of time. The reference sample should have a well-defined heat capacity over the range of temperatures to be scanned. The technique was developed by E. S. Watson and M. J. O'Neill in 1962, and introduced commercially at the 1963 Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy. The first adiabatic differential scanning calorimeter that could be used in biochemistry was developed by P. L. Privalov and D. R. Monaselidze in 1964 at Institute of Physics in Tbilisi, Georgia. The term DSC was coined to descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
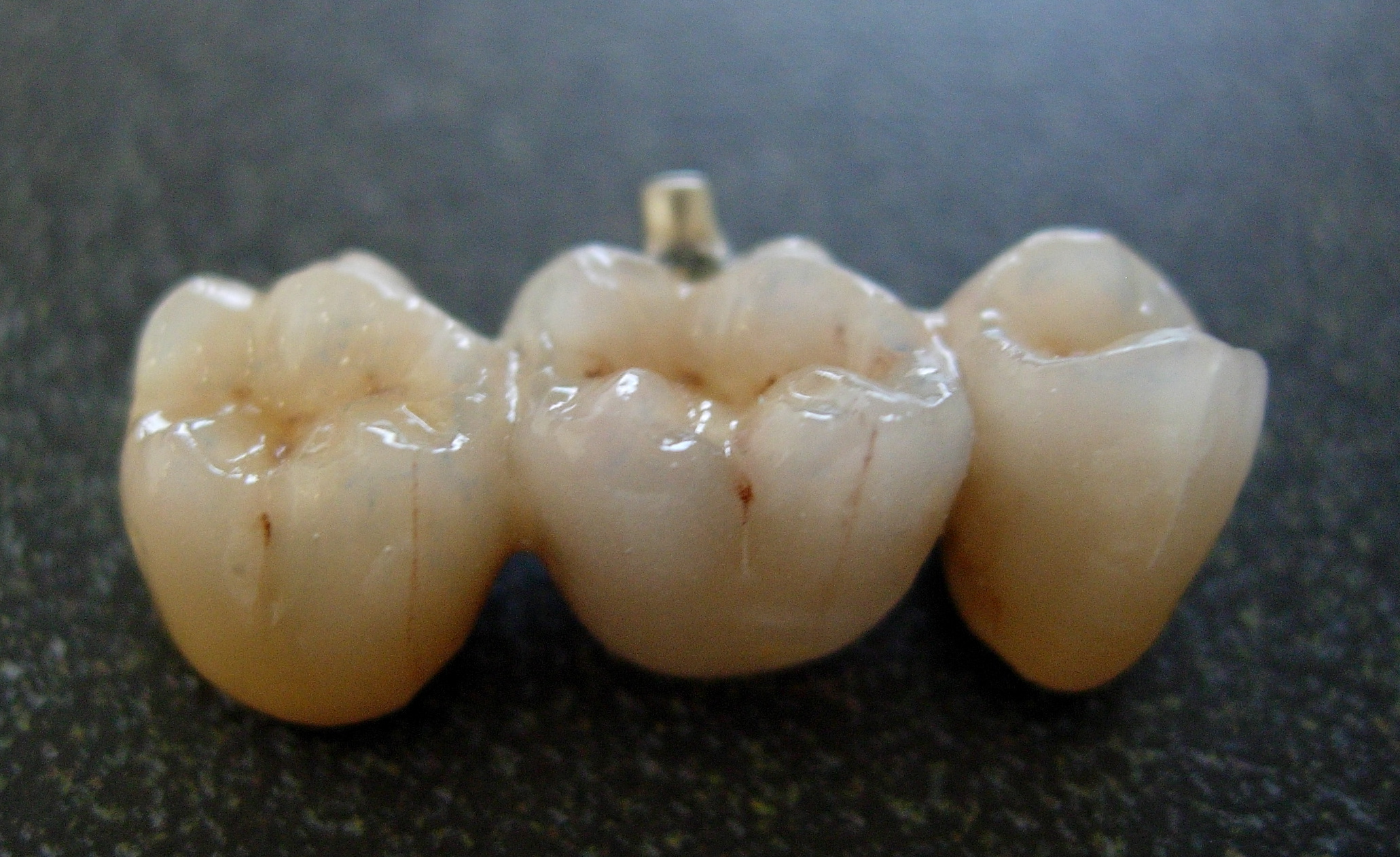
Bridge (dentistry)
A bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants. Definitions Fixed bridge: A dental prosthesis that is definitively attached to natural teeth and replaces missing teeth. Abutment: The tooth that supports and retains a dental prosthesis. Pontic: The artificial tooth that replaces a missing natural tooth. Retainer: The component attached to the abutment for retention of the prosthesis. Retainers can be major or minor. Unit: Pontics and abutment teeth are referred to as units. The total number of units in a bridge is equal to the number of pontics plus the number of abutment teeth. Saddle: The area on the alveolar ridge which is edentulous where at least one missing tooth is to be reinstated. Connector: Joins the pontic to the retainer or two retainers together. Connectors may be fixed or movable. Span: The length of the alveolar rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (dentistry)
In dentistry, a crown most commonly refers to a dental cap, a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large cavity threatens the health of a tooth. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using ''indirect methods''. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly. The most common method of crowning a tooth involves taking a dental impression of a tooth prepared by a dentist, then fabricating the crown outside of the mouth. The crown can then be inserted at a subsequent dental appointment. This ''indirect method'' of tooth restoration allows use of strong restorative material requiring time-consuming fabrication under intense heat, such as casting metal or firing porcelain, that would not be possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curing (chemistry)
Curing is a chemical process employed in polymer chemistry and process engineering that produces the toughening or hardening of a polymer material by cross-linking of polymer chains. Even if it is strongly associated with the production of thermosetting polymers, the term "curing" can be used for all the processes where a solid product is obtained from a liquid solution, such as with PVC plastisols. Curing process During the curing process, single monomers and oligomers, mixed with or without a curing agent, react to form a tridimensional polymeric network. In the very first part of the reaction branches of molecules with various architectures are formed, and their molecular weight increases in time with the extent of the reaction until the network size is equal to the size of the system. The system has lost its solubility and its viscosity tends to infinite. The remaining molecules start to coexist with the macroscopic network until they react with the network creating other c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks (repeat units). Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms, usually involving separate initiator molecules. Following its generation, the initiating free radical adds (nonradical) monomer units, thereby growing the polymer chain. Free-radical polymerization is a key synthesis route for obtaining a wide variety of different polymers and materials composites. The relatively non-specific nature of free-radical chemical interactions makes this one of the most versatile forms of polymerization available and allows facile reactions of polymeric free-radical chain ends and other chemicals or substrates. In 2001, 40 billion of the 110 billion pounds of polymers produced in the United States were produced by free-radical polymerization. Free-radical polymerization is a type of chain-growth polymeriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
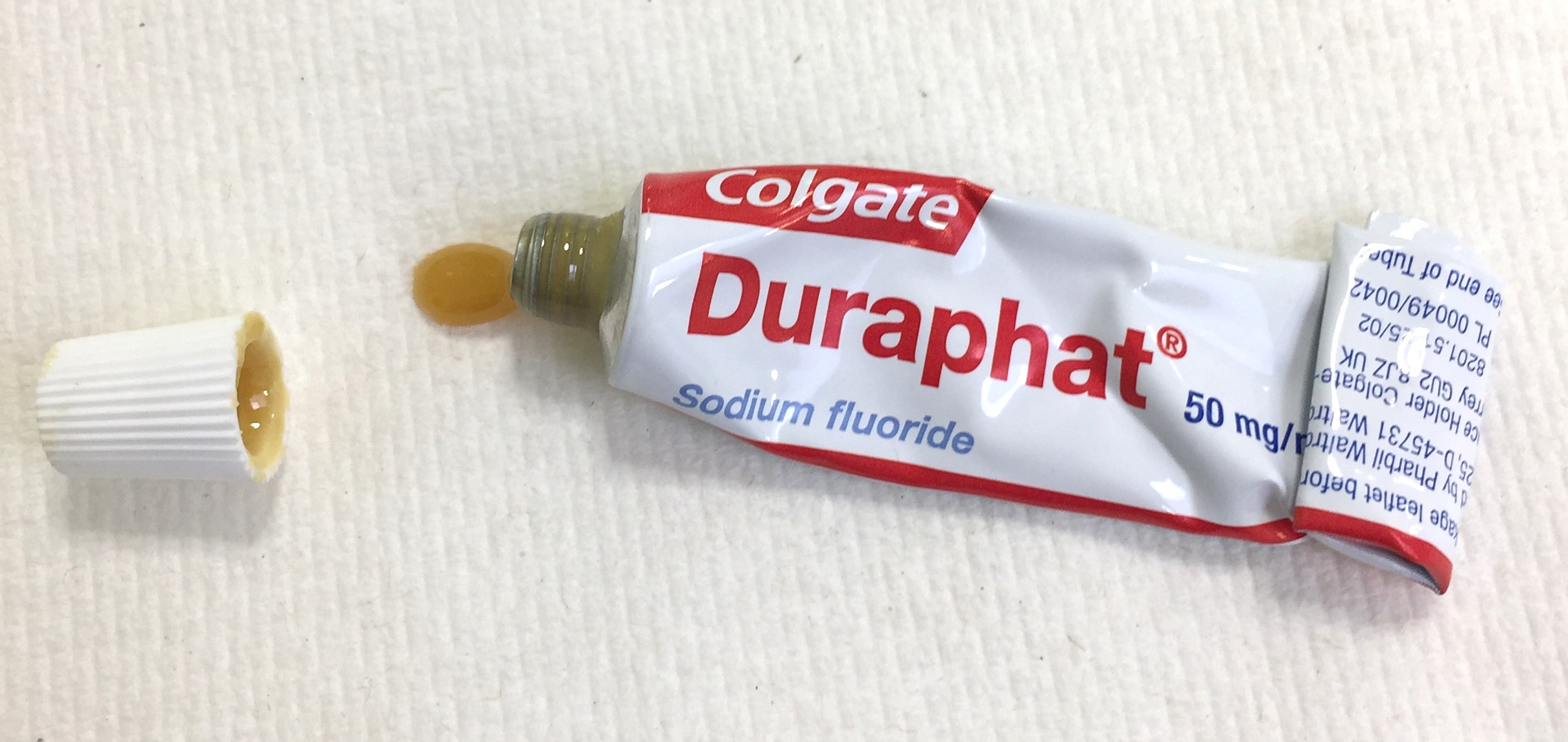
Fluoride Varnish
Fluoride varnish is a highly concentrated form of fluoride which is applied to the tooth's surface, by a dentist, dental hygienist or other health care professional, as a type of topical fluoride therapy. It is not a permanent varnish but due to its adherent nature it is able to stay in contact with the tooth surface for several hours. It may be applied to the Tooth enamel, enamel, dentine or cementum of the tooth and can be used to help prevent decay, remineralise the tooth surface and to treat dentine hypersensitivity. There are more than 30 fluoride-containing varnish products on the market today, and they have varying compositions and delivery systems. These compositional differences lead to widely variable pharmacokinetics, the effects of which remain largely untested clinically. Fluoride varnishes are relatively new in the United States, but they have been widely used in western Europe, Canada, South Africa and the Scandinavian countries since the 1980s as a dental caries pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remineralisation Of Teeth
Tooth remineralization is the natural repair process for non-cavitated tooth decay, tooth lesions, in which calcium, phosphate and sometimes fluoride ions are deposition (chemistry), deposited into crystal voids in demineralised Tooth_enamel, enamel. Remineralization can contribute towards restoring strength and function within tooth structure. Demineralization is the removal of minerals (mainly calcium) from any of the hard tissues: Tooth enamel, enamel, dentine, and cementum.Li X, Wang J, Joiner A, Chang J. The remineralization of enamel: a review of the literature. Journal of dentistry. 2014 Jun 30;42:S12-20. It begins at the surface, and may progress into either cavitation (tooth decay) or erosion (tooth wear). Tooth decay demineralization is caused by acids from bacteria in the dental plaque biofilm whilst tooth wear is caused by acids from non-bacterial sources. These can be extrinsic in source, such as carbonated drinks, or intrinsic acids, usually from stomach acid coming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demineralization (physiology)
Demineralization - it is the opposite process of mineralization, a process to reduce the content of mineral substances in tissue or organism, such as bone demineralization, of teeth. Demineralization can lead to serious diseases such as osteoporosis or tooth decay. Usually, treatment involves administration of appropriate dietary supplements A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extr ... to help restore the remineralization of human tissues and their physiological state. References {{Reflist Physiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |