Cultural Depictions Of Elephants on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In Islamic tradition, the year 570 is when the Prophet
In Islamic tradition, the year 570 is when the Prophet
 Indian
Indian
 Asian cultures admire the high intelligence and good memory of Asian elephants. As such, they symbolize wisdom and royal power. They are used as a representative of various political parties such as
Asian cultures admire the high intelligence and good memory of Asian elephants. As such, they symbolize wisdom and royal power. They are used as a representative of various political parties such as  The elephant also lends its name to some landmarks in Asia.
The elephant also lends its name to some landmarks in Asia.
 In 1229, the so-called Cremona elephant was presented by Sultan of Egypt Al-Kamil to the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, and the elephant was used by the Emperor in parades. The elephant is mentioned in the visit of Frederick's brother-in-law Richard of Cornwall to Cremona in 1241, in the Chronica Maiora of Matthew Paris. The presence of the animal is also recorded in 1237 in the Cremona city annals.
In 1229, the so-called Cremona elephant was presented by Sultan of Egypt Al-Kamil to the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, and the elephant was used by the Emperor in parades. The elephant is mentioned in the visit of Frederick's brother-in-law Richard of Cornwall to Cremona in 1241, in the Chronica Maiora of Matthew Paris. The presence of the animal is also recorded in 1237 in the Cremona city annals.
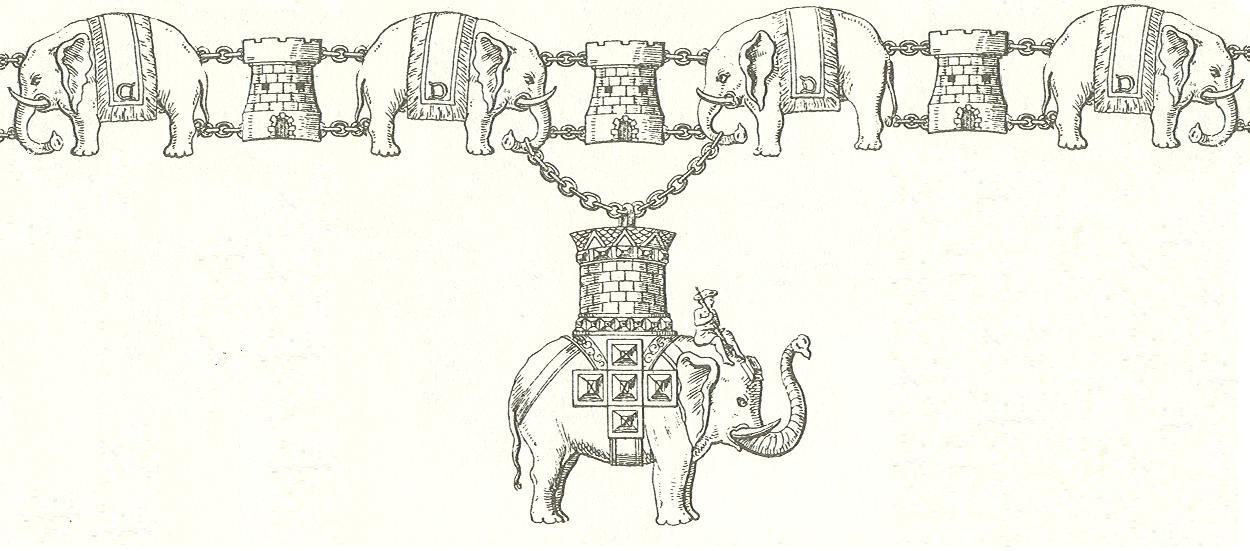 In 1478, the Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) was founded by King Christian I. This very select religious organization is the highest order of Denmark, and uses the elephant as a symbol of docility, sobriety and piety; instituted in its current form in 1693 by King Christian V.
In the early 1800s
In 1478, the Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) was founded by King Christian I. This very select religious organization is the highest order of Denmark, and uses the elephant as a symbol of docility, sobriety and piety; instituted in its current form in 1693 by King Christian V.
In the early 1800s  In 1870, the killing and eating of the elephants
In 1870, the killing and eating of the elephants  In Central London, England, an area known as the "
In Central London, England, an area known as the "
 The elephant as the symbol for the Republican Party of the United States originated in an 1874 political cartoon of an Asian elephant by
The elephant as the symbol for the Republican Party of the United States originated in an 1874 political cartoon of an Asian elephant by
 The elephant is viewed in both positive and negative lights in similar fashion as humans in various forms of literature. In fact,
The elephant is viewed in both positive and negative lights in similar fashion as humans in various forms of literature. In fact,
Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s have been depicted in mythology, symbolism and popular culture. They are both revered in religion and respected for their prowess in war. They also have negative connotations such as being a symbol for an unnecessary burden. Ever since the Stone Age, when elephants were represented by ancient petroglyphs
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
and cave art, they have been portrayed in various forms of art, including pictures, sculptures, music, film, and even architecture.

Religion, mythology and philosophy
TheAsian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus ''Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the no ...
appears in various religious traditions
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, tra ...
and mythologies. They are treated positively and are sometimes revered as deities, often symbolising strength and wisdom. Similarly, the African elephant is seen as the wise chief who impartially settles disputes among the forest creatures in African fables, and the Ashanti tradition
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or ...
holds that they are human chiefs from the past.
The Earth is supported and guarded by mythical World Elephant
The Ashtadiggajas () is a group of eight legendary elephants that appear in Hindu cosmology, serving as the guardians of the eight zones of the universe. There are also eight female elephants that stand beside the Ashtadiggajas, referred to as the ...
s at the compass points of the cardinal directions
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
, according to the Hindu cosmology
Hindu cosmology is the description of the universe and its states of matter, cycles within time, physical structure, and effects on living entities according to Hindu texts. Hindu cosmology is also intertwined with the idea of a creator who all ...
of ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
. The classical Sanskrit literature also attributes earthquakes to the shaking of their bodies when they tire. Wisdom is represented by the elephant in the form of the deity Ganesh
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu ...
a, one of the most popular gods in the Hindu religion
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
's pantheon
Pantheon may refer to:
* Pantheon (religion), a set of gods belonging to a particular religion or tradition, and a temple or sacred building
Arts and entertainment Comics
*Pantheon (Marvel Comics), a fictional organization
* ''Pantheon'' (Lone S ...
. The deity is very distinctive in having a human form with the head of an elephant which was put on after the human head was either was cut off or burned, depending on the version of the story from various Hindu sources. Lord Ganesha's birthday (rebirth) is celebrated as the Hindu festival known as Ganesha Chaturthi
Ganesh Chaturthi (ISO: ), also known as Vinayak Chaturthi (), or Ganeshotsav () is a Hindu festival commemorating the birth of the Hindu god Ganesha. The festival is marked with the installation of Ganesha's clay idols privately in homes and p ...
. In Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had ...
, their adaptation of Ganesha is known as Kangiten
Kangiten or Kankiten ( ja, 歓喜天, "god of bliss"; Sanskrit (IAST): ), also known as Binayaka (毘那夜迦; Skt. ), Ganabachi (誐那鉢底, alternatively Ganahachi or Ganahattei; Skt. ), or more commonly, Shōten or Shōden (聖天, lit. " ...
("Deva of Bliss"), often represented as an elephant-headed male and female pair shown in a standing embrace to represent unity of opposites
The unity of opposites is the central category of dialectics, said to be related to the notion of non-duality in a deep sense.
.
In Hindu iconography
Over the millennia of its development, Hinduism has adopted several iconography, iconic symbols, forming part of Hindu iconography, that are imbued with spiritual meaning based on either the Hindu scriptures, scriptures or cultural traditions ...
, many ''deva
Deva may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Deva'' (1989 film), a 1989 Kannada film
* ''Deva'' (1995 film), a 1995 Tamil film
* ''Deva'' (2002 film), a 2002 Bengali film
* Deva (2007 Telugu film)
* ''Deva'' (2017 film), a 2017 Marathi film
* Deva ...
s'' are associated with a mount or vehicle known as a ''vāhana
''Vahana'' ( sa, वाहन, or animal vehicle, literally "that which carries, that which pulls") denotes the being, typically an animal or mythical, a particular Hindu God is said to use as a vehicle. In this capacity, the vahana is often ...
''. In addition to providing a means of transport, they symbolically represent a divine attribute. The elephant ''vāhana'' represents wisdom, divine knowledge and royal power; it is associated with Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism. She is the goddess of wealth, fortune, power, beauty, fertility and prosperity, and associated with ''Maya'' ("Illusion"). Alo ...
, Brihaspati
Brihaspati ( sa, बृहस्पति, ), also known as Guru, is a Hindu deity. In the ancient Vedic scriptures of Hinduism, Brihaspati is a deity associated with fire, and the word also refers to a rishi (sage) who counsels the devas (god ...
, Shachi
Indrani (Sanskrit: इन्द्राणी, IAST: ''Indrāṇī, lit.'' Indra's queen), also known as Shachi (Sanskrit: शची, IAST: ''Śacī''), is the queen of the devas in Hinduism. Described as tantalisingly beautiful, proud and ...
and Indra.
Indra was said to ride on a flying white elephant
A white elephant is a possession that its owner cannot dispose of, and whose cost, particularly that of maintenance, is out of proportion to its usefulness. In modern usage, it is a metaphor used to describe an object, construction project, sch ...
named Airavata
Indra (alias Sakra) and Shachi riding the five-headed Divine Elephant Airavata, Folio from a Jain text, Panch Kalyanaka">Shachi.html" ;"title="Indra (alias Sakra) and Shachi">Indra (alias Sakra) and Shachi riding the five-headed Divine Elepha ...
, who was made the King of all elephants by Lord Indra. A white elephant is rare and given special significance. It is often considered sacred and symbolises royalty in Thailand and Burma, where it is also considered a symbol of good luck. In Buddhist iconography, the elephant is associated with Queen Māyā of Sakya, the mother of Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lu ...
. She had a vivid dream foretelling her pregnancy in which a white elephant featured prominently. To the royal sages, the white elephant signifies royal majesty and authority; they interpreted the dream as meaning that her child was destined for greatness as a universal monarch or a ''buddha''.
Elephants remain an integral part of religion in South Asia and some are even featured in various religious practices. Temple elephants are specially trained captive elephants that are lavishly caparison
A caparison is a cloth covering laid over a horse or other animal for protection and decoration. In modern times, they are used mainly in parades and for historical reenactments. A similar term is horse-trapper. The word is derived from the Lat ...
ed and used in various temple activities. Among the most famous of the temple elephants is Guruvayur Keshavan
Gajarajan Guruvayur Keshavan (1912—2 December 1976) is perhaps the most famous and celebrated temple elephant in Kerala, India. Keshavan was donated to the Guruvayur temple by the royal family of Nilambur on 4 January 1922 .
Standing over ...
of Kerala, India
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South C ...
. They are also used in festivals in Sri Lanka such as the Esala Perahera
The Kandy Esala Perahera (the Sri Dalada Perahara procession of Kandy) also known as The Festival of the Tooth is a festival held in July and August in Kandy, Sri Lanka. This historical procession is held annually to pay homage to the Sacred To ...
.
In the version of the Chinese zodiac
The Chinese zodiac is a traditional classification scheme based on the lunar calendar that assigns an animal and its reputed attributes to each year in a repeating twelve-year cycle. Originating from China, the zodiac and its variations remain ...
used in Northern Thailand
Northern Thailand, or more specifically Lanna, is geographically characterised by several mountain ranges, which continue from the Shan Hills in bordering Myanmar to Laos, and the river valleys which cut through them. Though like most of Thailan ...
, the last year in the 12-year cycle – called "Year of the Pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
" in China – is known instead as "Year of the Elephant", reflecting the importance of elephants in Thai culture.
 In Islamic tradition, the year 570 is when the Prophet
In Islamic tradition, the year 570 is when the Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
was born and is known as the Year of the Elephant
The ʿām al-fīl ( ar, عام الفيل, Year of the Elephant) is the name in Islamic history for the year approximately equating to 570–571 CE. According to Islamic resources, it was in this year that Muhammad was born.Hajjah Adil, Amina, ...
. In that year, Abraha
Abraha ( Ge’ez: አብርሃ) (also spelled Abreha, died after CE 570;Stuart Munro-Hay (2003) "Abraha" in Siegbert Uhlig (ed.) ''Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: A-C''. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. r. 525–at least 553S. C. Munro-Hay (1991) ''Aksum ...
, ruler of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
tried to conquer Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and demolish the Kaaba, reportedly in retaliation for the previous Meccan defilement of Al–Qalis Church in Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
, a cathedral Abraha had constructed.Hajjah Adil, Amina, "''Prophet Muhammad''", ISCA, 1 Jun 2002, However, his plan was foiled when his white elephant named Mahmud refused to cross the boundary of Mecca. The elephant, who led Abraha's forty thousand men, could not be persuaded with reason or even with violence, which was regarded as a crucial omen by Abraha's soldiers. This is generally related in the five verses of the chapter titled ' The Elephant' — en, The Elephant) in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
.
In the Judeo-Christian tradition, medieval artists depicted the mutual killing of both Eleazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elʽazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, from cr ...
the Maccabee
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees ( he, מַכַּבִּים, or , ; la, Machabaei or ; grc, Μακκαβαῖοι, ), were a group of Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. ...
and a war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
carrying an important Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
general as described in the apocrypha
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
l book of 1 Maccabees
The First Book of Maccabees, also known as First Maccabees (written in shorthand as 1 Maccabees or 1 Macc.), is a book written in Hebrew by an anonymousRappaport, U., ''47. 1 Maccabees'' in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001)The Oxford Bible Comme ...
. The early illustrators knew little of the elephant and their portrayals are highly inaccurate.
The unfamiliarity with the exotic beast has also made elephants a subject of widely different interpretations thus giving rise to mythological creatures. The story of the blind men and an elephant was written to show how reality may be viewed from differing perspectives. The source of this parable is unknown, but it appears to have originated in India. It has been attributed to Buddhists, Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Jainists, and Sufis
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
, and was also used by Discordians. The scattered skulls of prehistoric dwarf elephant
Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example ...
s, on the islands of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
may have formed the basis of belief in existence of cyclopes
In Greek mythology and later Roman mythology, the Cyclopes ( ; el, Κύκλωπες, ''Kýklōpes'', "Circle-eyes" or "Round-eyes"; singular Cyclops ; , ''Kýklōps'') are giant one-eyed creatures. Three groups of Cyclopes can be distinguish ...
, the one-eyed giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
*Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'gi ...
featured in Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Iliad'', th ...
(c. 800~600 BC). As early as the 1370s, scholars had noted that the skulls feature a large nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the human nose, nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. ...
at the front that could be mistaken for a singular eye socket; and the skulls, twice the size of a human's, looked as if they could belong to giant humanoids. It is also suggested that the Behemoth described in the Book of Job may be the elephant due to its grazing habits and preference to rivers.
In art
From Stone Age rock-art to Modern age street-art, the elephant has remained a popular subject for artists.Prehistoric
Prehistoric North Africa
The prehistory of North Africa spans the period of earliest human presence in the region to gradual onset of historicity in the Maghreb (Berber:Tamazgha) during classical antiquity. Early anatomically modern humans are known to have been presen ...
ns depicted the elephant in Paleolithic age
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος '' lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
rock art. For example, the Libyan Tadrart Acacus
The Acacus Mountains or Tadrart Akakus ( ar, تدرارت أكاكوس / ALA-LC: ''Tadrārt Akākūs'') form a mountain range in the desert of the Ghat District in western Libya, part of the Sahara. They are situated east of the city of Ghat, Li ...
, a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, features a rock carving of an elephant from the last phase of the Pleistocene epoch
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
(12,000–8000 BC) rendered with remarkable realism. There are many other prehistoric examples, including Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
rock art of south Oran (Algeria)
The rock art of south Oran, are prehistoric engravings dating from the Neolithic period, which are found in the south of Oran Province, Algeria, in the Saharan Atlas Mountains, in the regions (from west to east) of Figuig, Ain Sefra, El-Bayadh, ...
, and a white elephant rock painting in 'Phillip's Cave' by the San in the Erongo
Erongo is one of the 14 regions of Namibia. The capital is Swakopmund. It is named after Mount Erongo, a well-known landmark in Namibia and in this area. Erongo contains the municipalities of Walvis Bay, Swakopmund, Henties Bay and Omaruru, as w ...
region of Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
. From the Bovidian period (3550–3070 BCE), elephant images by the San bushmen in the South African Cederberg Wilderness Area suggest to researchers that they had "a symbolic association with elephants" and "had a deep understanding of the communication, behaviour and social structure of elephant family units" and "possibly developed a symbiotic relationship with elephants that goes back thousands of years."
Ancient
 Indian
Indian rock relief
A rock relief or rock-cut relief is a relief sculpture carved on solid or "living rock" such as a cliff, rather than a detached piece of stone. They are a category of rock art, and sometimes found as part of, or in conjunction with, ...
s include a number of depictions of elephants, notably the ''Descent of the Ganges
''Descent of the Ganges'', known locally as ''Arjuna's Penance'', is a monument at Mamallapuram, on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal, in the Chengalpattu district of the state of Tamil Nadu, India. Measuring , it is a giant open-air roc ...
'' at Mahabalipuram
Mamallapuram, also known as Mahabalipuram, is a town in Chengalpattu district in the southeastern Indian state of Tamil Nadu, best known for the UNESCO World Heritage Site of 7th- and 8th-century Hindu Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram. It is o ...
, a large 7th-century Hindu scene with many figures that uses the form of the rock to shape the image. At Unakoti
Unkoti Hill is a sculptural emblem and ancient Shaivite place that hosts approx ''ninety-nine lakh ninety-nine thousand nine hundred and ninety-nine'' rock carvings figures and images of gods and goddesses. It is a place of worship with huge ...
, Tripura
Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ...
there is an 11th-century group of reliefs related to Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
, including several elephants.
Indian painting
Indian painting has a very long tradition and history in Indian art, though because of the climatic conditions very few early examples survive.Blurton, 193 The earliest Indian paintings were the rock paintings of prehistoric times, such as the ...
includes many elephants, especially ones ridden for battle and royal transport in Mughal miniature
Mughal painting is a style of painting on paper confined to miniatures either as book illustrations or as single works to be kept in albums ( muraqqa), from the territory of the Mughal Empire in South Asia. It emerged from Persian miniature pai ...
s.
Modern
Elephants are often featured in modern artistic works, including those by artists such asNorman Rockwell
Norman Percevel Rockwell (February 3, 1894 – November 8, 1978) was an American painter and illustrator. His works have a broad popular appeal in the United States for their reflection of Culture of the United States, the country's culture. Roc ...
, Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol (; born Andrew Warhola Jr.; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American visual artist, film director, and producer who was a leading figure in the Art movement, visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore th ...
and Banksy
Banksy is a pseudonymous England-based street artist, political activist and film director whose real name and identity remain unconfirmed and the subject of speculation. Active since the 1990s, his satirical street art and subversive epigram ...
. The stork-legged elephant, found in many of Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (; ; ; 11 May 190423 January 1989) was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarre images in ...
's works, is one of the surrealist
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to ...
's best known icons, and adorn the walls of the Dalí Museum in Spain. Dali used an elephant motif in various works such as ''Dream Caused by the Flight of a Bee Around a Pomegranate a Second Before Awakening
''Dream Caused by the Flight of a Bee Around a Pomegranate a Second Before Awakening'' is a surrealist painting by Salvador Dalí. A shorter alternate title for the painting is ''Dream Caused by the Flight of a Bee''. It was painted in 1944, and t ...
'', ''The Elephants
''The Elephants'' ( es, Los Elefantes) is a 1948 painting by the Spanish surrealist artist Salvador Dalí.
Background
The elephant is a recurring theme in the works of Dalí, first appearing in his 1944 work '' Dream Caused by the Flight of a Be ...
'' and in '' The Temptation of Saint Anthony''. The Elephant and Obelisk
''Elephant and Obelisk'' is a statue of an elephant carrying an obelisk, designed by the Italian artist Gian Lorenzo Bernini. It was unveiled in 1667 in the Piazza della Minerva in Rome, adjacent to the church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, where ...
motif also found its way to various works by this artist. Rembrandt did a series of sketches of the famous 17th century elephant, Hansken
__NOTOC__
Hansken (1630 – Florence, 9 November 1655) was a female elephant that became famous in early 17th-century Europe. She toured many countries, demonstrating circus tricks, and influenced many artists including Stefano della Bella, ...
, and featured her as a symbol of chastity in his 1638 etching ''Adam and Eve''.
Politics and secular society
The elephant is also depicted by various political groups and in secular society.In Asia
 Asian cultures admire the high intelligence and good memory of Asian elephants. As such, they symbolize wisdom and royal power. They are used as a representative of various political parties such as
Asian cultures admire the high intelligence and good memory of Asian elephants. As such, they symbolize wisdom and royal power. They are used as a representative of various political parties such as United National Party
The United National Party, often abbreviated as UNP ( si, එක්සත් ජාතික පක්ෂය, translit=Eksath Jāthika Pakshaya, ta, ஐக்கிய தேசியக் கட்சி, translit=Aikkiya Tēciyak Kaṭci), ...
of Sri Lanka and Bahujan Samaj Party of India. The Elephants of Kerala are an integral part of the daily life in Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, South India. These Indian elephant
The Indian elephant (''Elephas maximus indicus'') is one of four extant recognised subspecies of the Asian elephant and native to mainland Asia.
Since 1986, the Asian elephant has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List as the wild pop ...
s are loved, revered, groomed and given a prestigious place in the state's culture. There they are often referred to as the 'sons of the '' sahya''.' The elephant is the state animal of Kerala and is featured on the emblem of the Government of Kerala
Government of Kerala is the Subnational administrative division, subnational government of the Indian state of Kerala. The government is led by a chief minister, who selects all the other ministers. The chief minister and their most senior mini ...
, and previously on the coat of arms of Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
. The elephant is also on the flag of the Kingdom of Laos with three elephants visible, supporting an umbrella (another symbol of royal power) until it became a republic in 1975. Other Southeast Asian realms have also displayed one or more white elephants.
 The elephant also lends its name to some landmarks in Asia.
The elephant also lends its name to some landmarks in Asia. Elephanta Island
Elephanta Island (also called Gharapuri (literally "the city of caves") or Pory Island) is one of a number of islands in Mumbai Harbour, east of Mumbai, India.
Tourist attractions and accessibility
This island is a popular tourist destinati ...
(also called "Gharapuri Island") in Mumbai Harbour
Mumbai Harbour (also English; Bombay Harbour or Front Bay, Marathi''Mumba'ī bandar''), is a natural deep-water harbour in the southern portion of the Ulhas River estuary. The narrower, northern part of the estuary is called Thana Creek. The ...
was given this name by 17th century Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
explorers who saw a monolithic basalt sculpture of an elephant near the entrance to what became known as the Elephanta Caves
The Elephanta Caves are a collection of cave temples predominantly dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva. They are on Elephanta Island, or ''Gharapuri'' (literally "the city of caves"), in Mumbai Harbour, east of Mumbai in the Indian state of Mahā ...
. The Portuguese attempted to take it home with them but ended up dropping it into the sea because their chains were not strong enough. Later, the British moved this elephant to the Victoria and Albert Museum (now Dr. Bhau Daji Lad Museum
Dr. Bhau Daji Lad Museum is the oldest museum in Mumbai. Situated in the vicinity of Byculla Zoo, Byculla East, it was originally established in 1855 as a treasure house of the decorative and industrial arts, and was later renamed in honour of ...
) in Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
.
In Europe
Aside from being a curiosity for Europeans, the elephant also became a symbol of military might from the experience of fighting foreign powers that fieldedwar elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
s throughout history.
In 326 BC after Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's victory over King Porus
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only men ...
of India, the captured war elephants became a symbol of imperial power
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
, being used as an emblem of the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
Diadoch
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wa ...
empire.
In about the year 800 AD, an elephant called Abul-Abbas
Abul-Abbas ( – 810) was an Asian elephant brought back to the Carolingian emperor Charlemagne by his diplomat Isaac the Jew. The gift was from the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid and symbolizes the beginning of Abbasid–Carolingian relati ...
was brought from Baghdad to Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
's residence in Aachen as a symbol of the beginning of the Abbasid–Carolingian alliance.
 In 1229, the so-called Cremona elephant was presented by Sultan of Egypt Al-Kamil to the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, and the elephant was used by the Emperor in parades. The elephant is mentioned in the visit of Frederick's brother-in-law Richard of Cornwall to Cremona in 1241, in the Chronica Maiora of Matthew Paris. The presence of the animal is also recorded in 1237 in the Cremona city annals.
In 1229, the so-called Cremona elephant was presented by Sultan of Egypt Al-Kamil to the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, and the elephant was used by the Emperor in parades. The elephant is mentioned in the visit of Frederick's brother-in-law Richard of Cornwall to Cremona in 1241, in the Chronica Maiora of Matthew Paris. The presence of the animal is also recorded in 1237 in the Cremona city annals.
 In 1478, the Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) was founded by King Christian I. This very select religious organization is the highest order of Denmark, and uses the elephant as a symbol of docility, sobriety and piety; instituted in its current form in 1693 by King Christian V.
In the early 1800s
In 1478, the Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) was founded by King Christian I. This very select religious organization is the highest order of Denmark, and uses the elephant as a symbol of docility, sobriety and piety; instituted in its current form in 1693 by King Christian V.
In the early 1800s Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
wanted a monument to his own imperial power, and he decreed that a colossal bronze elephant fountain be cast from guns captured at his victorious 1807 Battle of Friedland
The Battle of Friedland (14 June 1807) was a major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars between the armies of the French Empire commanded by Napoleon I and the armies of the Russian Empire led by Count von Bennigsen. Napoleon and the French obtai ...
. This was intended for the site where the Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stor ...
once stood.
 In 1870, the killing and eating of the elephants
In 1870, the killing and eating of the elephants Castor and Pollux
Castor; grc, Κάστωρ, Kástōr, beaver. and Pollux. (or Polydeukes). are twin half-brothers in Greek and Roman mythology, known together as the Dioscuri.; grc, Διόσκουροι, Dióskouroi, sons of Zeus, links=no, from ''Dîos'' ('Z ...
from the Botanical gardens
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
during the Siege of Paris received considerable attention at the time. This became emblematic of the hardships and degradation caused by siege and war, especially since the two elephants were previously very popular with the Parisian public.
The city of Catania, Sicily has an immemorial connection with the elephant. The local sorcerer Heliodorus
Heliodorus is a Greek name meaning "Gift of the Sun". Several persons named Heliodorus are known to us from ancient times, the best known of which are:
*Heliodorus (minister) a minister of Seleucus IV Philopator c. 175 BC
* Heliodorus of Athen ...
, was credited with either riding a magic elephant or transforming himself into this animal. Under medieval Arab rule Catania was known as ''Medinat-ul-Fil'' or ''Balad-ul-Fil'' (City/State of the Elephant). The symbol of the city is the ''Fontana dell'Elefante'' (Fountain of the Elephant) assembled in its present form in 1736 by Giovanni Battista Vaccarini
Giovanni Battista Vaccarini (3 February 1702 – 11 March 1768) was a Sicilian architect, notable for his work in the Sicilian Baroque style in his homeland during the period of massive rebuilding following the earthquake of 1693. Many of his pri ...
.
 In Central London, England, an area known as the "
In Central London, England, an area known as the "Elephant and Castle
The Elephant and Castle is an area around a major road junction in London, England, in the London Borough of Southwark. The name also informally refers to much of Walworth and Newington, due to the proximity of the London Underground stati ...
" (or "The Elephant") is centered on a major road intersection and a station of the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
. The "Castle" in the location's name refers to a medieval European perception of a howdah
A howdah, or houdah (Hindi: हौदा ''haudā''), derived from the Arabic (hawdaj), which means "bed carried by a camel", also known as ''hathi howdah'' (''hāthī haudā'', हाथी हौदा), is a carriage which is positioned on ...
. The heraldic
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known bran ...
elephant and castle has also been associated with the city of Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
, England since medieval times, where it denotes religious symbolism and with the town of Dumbarton, Scotland
Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990.
Dumbarton was the ca ...
. More recently in Britain, Welephant, a red elephant cartoon character with a fireman's helmet, was originally used as a mascot by fire brigades in the United Kingdom to promote fire safety for children and has become the mascot for the Children's Burn Trust.
In America
 The elephant as the symbol for the Republican Party of the United States originated in an 1874 political cartoon of an Asian elephant by
The elephant as the symbol for the Republican Party of the United States originated in an 1874 political cartoon of an Asian elephant by Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast (; ; September 26, 1840December 7, 1902) was a German-born American caricaturist and editorial cartoonist often considered to be the "Father of the American Cartoon".
He was a critic of Democratic Representative "Boss" Tweed and ...
in ''Harper's Weekly
''Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization'' was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, ...
''. This cartoon, titled "Third Term Panic", is a parody of Aesop's fable
Aesop's Fables, or the Aesopica, is a collection of fables credited to Aesop, a slave and storyteller believed to have lived in ancient Greece between 620 and 564 BCE. Of diverse origins, the stories associated with his name have descended to ...
, "The Ass in the Lion's Skin
The Ass in the Lion's Skin is one of Aesop's Fables, of which there are two distinct versions. There are also several Eastern variants, and the story's interpretation varies accordingly.
Fables
Of the two Greek versions of this story, the one ca ...
". It depicts an elephant (labelled ''The Republican Vote'') running toward a ''chasm of chaos''; frightening a jackass in a lion's skin (labelled ''Caesarism
Caesarism is an authoritarian or autocratic political philosophy inspired by Julius Caesar. It has been used in various ways by both proponents and opponents as a pejorative.
Historical use of the term
The first documented use of the word is ...
'') which scatters animals representing various interests. Although Nast used the elephant seven more times to represent the "Republican Vote", he did not use it to represent the ''Republican Party'' until March 1884 in "The Sacred Elephant".
In Africa
Many African cultures revere the African Elephant as a symbol of strength and power. It is also praised for its size, longevity, stamina, mental faculties, cooperative spirit, and loyalty. South Africa, uses elephant tusks in theircoat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
to represent wisdom, strength, moderation and eternity. The elephant is symbolically important to the nation of Ivory Coast (''Côte d'Ivoire''); the Coat of arms of Ivory Coast features an elephant head escutcheon as its focal point.
In the western African Kingdom of Dahomey (now part of Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the nort ...
) the elephant was associated with the 19th century rulers of the Fon people, Guezo and his son Glele
Glele, or Badohou (died December 29, 1889), was the tenth King of Dahomey, ruling from 1858 until his suicide in 1889.
Life
Badohou, who took the throne name Glele, is considered (if Adandozan is not counted) to be the tenth King of the Aja king ...
. The animal is believed to evoke strength, royal legacy, and enduring memory as related by the proverbs: "''There where the elephant passes in the forest, one knows''" and "''The animal steps on the ground, but the elephant steps down with strength''." Their flag depicted an elephant wearing a royal crown.
Popular culture
The elephant has entered into popular culture through various idiomatic expressions and adages. The phrase "Elephants never forget" refers to the belief that elephants have excellent memories. The variation "Women and elephants never forget an injury" originates from the 1904 book ''Reginald on Besetting Sins'' by British writerSaki
Hector Hugh Munro (18 December 1870 – 14 November 1916), better known by the pen name Saki and also frequently as H. H. Munro, was a British writer whose witty, mischievous and sometimes macabre stories satirize Edwardian society and cultu ...
.
This adage seems to have a basis in fact, as reported in ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
'':
::Remarkable recall power, researchers believe, is a big part of how elephants survive. Matriarch elephants, in particular, hold a store of social knowledge that their families can scarcely do without, according to research conducted on elephants at Amboseli National Park
Amboseli National Park, formerly Maasai Amboseli Game Reserve, is a national park in Kajiado South Constituency in Kajiado County, Kenya. The park is in size at the core of an ecosystem that spreads across the Kenya-Tanzania border. The local ...
in Kenya.
" Seeing the Elephant" is a 19th-century Americanism denoting a world-weary experience; often used by soldiers, pioneers and adventurers to qualify new and exciting adventures such as the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
and the California Gold Rush. A "white elephant
A white elephant is a possession that its owner cannot dispose of, and whose cost, particularly that of maintenance, is out of proportion to its usefulness. In modern usage, it is a metaphor used to describe an object, construction project, sch ...
" has become a term referring to an expensive burden, particularly when much has been invested with false expectations. The term 'white elephant sale' was sometimes used in Australia as a synonym for jumble sale
A jumble sale (UK), bring and buy sale (Australia) or rummage sale (U.S and Canada) is an event at which second hand goods are sold, usually by an institution such as a local Boys' Brigade Company, Scout group, Girlguiding group or church, ...
. In the U.S., a White elephant gift exchange
A white elephant gift exchange, Yankee swap or Dirty Santa
is a party game where amusing and impractical gifts are exchanged during festivities. The goal of a white elephant gift exchange is to entertain party-goers rather than to gain a gen ...
is a popular winter holiday party activity. The idiom Elephant in the room
The expression “the elephant in the room” (or "the elephant in the living room") is a metaphorical idiom in English for an important or enormous topic, question, or controversial issue that is obvious or that everyone knows about but no one ...
tells of an obvious truth that no one wants to discuss, alluding to the animal's size compared to a small space. "Seeing pink elephants
"Seeing pink elephants" is a euphemism for hallucinations caused by delirium tremens or alcoholic hallucinosis, especially the former. The term dates back to at least the early 20th century, emerging from earlier idioms about seeing snakes and o ...
" refers to a drunken hallucination and is the basis for the Pink Elephants on Parade sequence in the 1941 Disney animated feature
This list of theatrical animated feature films consists of animated films produced or released by The Walt Disney Studios, the film division of The Walt Disney Company.This list does not include films or specials streamed on Disney+ as Disne ...
, ''Dumbo
''Dumbo'' is a 1941 American animated fantasy film produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by RKO Radio Pictures. The fourth Disney animated feature film, it is based upon the storyline written by Helen Aberson and Harold Pearl, ...
''. "Jumbo" has entered the English language as a synonym for "large". Jumbo
Jumbo (about December 25, 1860 – September 15, 1885), also known as Jumbo the Elephant and Jumbo the Circus Elephant, was a 19th-century male African bush elephant born in Sudan. Jumbo was exported to Jardin des Plantes, a zoo in Paris, and t ...
originally was the name of a huge elephant acquired by circus showman P. T. Barnum
Phineas Taylor Barnum (; July 5, 1810 – April 7, 1891) was an American showman, businessman, and politician, remembered for promoting celebrated hoaxes and founding the Barnum & Bailey Circus (1871–2017) with James Anthony Bailey. He was ...
from the London Zoo in 1882. The name itself may have come from a West African native word for "elephant".
Literature
 The elephant is viewed in both positive and negative lights in similar fashion as humans in various forms of literature. In fact,
The elephant is viewed in both positive and negative lights in similar fashion as humans in various forms of literature. In fact, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
praised the beast in his ''Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. ...
'' as one that is closest to a human in sensibilities. The elephant's different connotations clash in Ivo Andrić
Ivo Andrić ( sr-Cyrl, Иво Андрић, ; born Ivan Andrić; 9 October 1892 – 13 March 1975) was a Yugoslav novelist, poet and short story writer who won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1961. His writings dealt mainly with life in ...
's novella ''The Vizier's Elephant''. Here the citizens of Travnik
Travnik is a town and a municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the administrative center of Central Bosnia Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is situated in central Bosnia and Herzegovina, west of Sarajevo. As of 2 ...
despise the young elephant who symbolises the cruelty of the unseen Vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was ...
. However, the elephant itself is young and innocent despite unknowingly causing havoc due to youthful play. In the Tarzan
Tarzan (John Clayton II, Viscount Greystoke) is a fictional character, an archetypal feral child raised in the African jungle by the Mangani great apes; he later experiences civilization, only to reject it and return to the wild as a heroic adv ...
novels of Edgar Rice Burroughs, ''Tantor
''Tantor'' is a generic name for elephants in ''Mangani'', the fictional language of the great apes in the Tarzan novels of Edgar Rice Burroughs. In Burroughs's works a number of elephants appear under the name of ''Tantor'', most notably one pa ...
'' is the generic term for "elephant" in the fictional simian ''Mangani
''Mangani'' is the name of a fictional species of great apes in the Tarzan novels of Edgar Rice Burroughs, and of the invented language used by these apes. In the invented language, ''Mangani'' (meaning "great-ape") is the apes' word for their own ...
'' language, but is associated with a particular elephant who eventually becomes Tarzan's faithful companion. Other elephant characters that are shown in a positive light include Jean de Brunhoff
Jean de Brunhoff (; 9 December 1899 – 16 October 1937) was a French writer and illustrator remembered best for creating the Babar series of children's books concerning a fictional elephant, the first of which was published in 1931.
Early life
D ...
's Babar
Babar ( ur, ), also variously spelled as Baber, Babur, and Babor is a male given name of Pashto, and Persian origin, and a popular male given name in Pakistan. It is generally taken in reference to the Persian ''babr'' (Persian: ببر), meaning ...
and Dr. Seuss
Theodor Seuss Geisel (;"Seuss"
'' Horton Horton may refer to: Places Antarctica * Horton Glacier, Adelaide Island, Antarctica * Horton Ledge, Queen Elizabeth Land, Antarctica Australia * Horton, Queensland, a town and locality in the Bundaberg Region * Horton River (Australia), ...
. Jules Verne featured a steam-powered mechanical elephant in his 1880 novel '''' Horton Horton may refer to: Places Antarctica * Horton Glacier, Adelaide Island, Antarctica * Horton Ledge, Queen Elizabeth Land, Antarctica Australia * Horton, Queensland, a town and locality in the Bundaberg Region * Horton River (Australia), ...
The Steam House
''The Steam House'' (french: La maison à vapeur) is an 1880 Jules Verne novel recounting the travels of a group of British colonists in the Raj in a wheeled house pulled by a steam-powered mechanical elephant. Verne uses the mechanical house ...
''. In addition, the animal is depicted in its military use through the oliphaunts of J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien (, ; 3 January 1892 – 2 September 1973) was an English writer and philologist. He was the author of the high fantasy works ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''.
From 1925 to 1945, Tolkien was the Rawlins ...
's ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's b ...
'' trilogy and the alien invaders of Larry Niven
Laurence van Cott Niven (; born April 30, 1938) is an American science fiction writer. His best-known works are '' Ringworld'' (1970), which received Hugo, Locus, Ditmar, and Nebula awards, and, with Jerry Pournelle, '' The Mote in God's E ...
and Jerry Pournelle
Jerry Eugene Pournelle (; August 7, 1933 – September 8, 2017) was an American scientist in the area of operations research and human factors research, a science fiction writer, essayist, journalist, and one of the first bloggers. In the 1960s ...
's 1985 science fiction novel, ''Footfall
''Footfall'' is a 1985 science fiction novel by American writers Larry Niven and Jerry Pournelle. The book depicts the arrival of members of an alien species called the Fithp that have traveled to the Solar System from Alpha Centauri in a large ...
''.
Notable short stories featuring elephants include Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's "All the Mowgli Stories
''All the Mowgli Stories'' is a collection of short stories by Rudyard Kipling. As the title suggests, the book is a chronological compilation of the stories about Mowgli from ''The Jungle Book'' and ''The Second Jungle Book'', together with " I ...
", "Toomai of the Elephants
Toomai of the Elephants is a short story by Rudyard Kipling about a young elephant-handler. It was first published in the December 1893 issue of ''St. Nicholas (magazine), St. Nicholas'' magazine and reprinted in the collection of Kipling short ...
" and "The Elephant's Child
''Just So Stories for Little Children'' is a 1902 collection of origin stories by the British author Rudyard Kipling. Considered a classic of children's literature, the book is among Kipling's best known works.
Kipling began working on the ...
"; as well as Mark Twain's " The Stolen White Elephant". George Orwell wrote an allegorical
As a literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a hidden meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory t ...
essay
An essay is, generally, a piece of writing that gives the author's own argument, but the definition is vague, overlapping with those of a letter, a paper, an article, a pamphlet, and a short story. Essays have been sub-classified as formal a ...
, "Shooting an Elephant
"Shooting an Elephant" is an essay by British writer George Orwell, first published in the literary magazine '' New Writing'' in late 1936 and broadcast by the BBC Home Service on 12 October 1948.
The essay describes the experience of the Englis ...
"; and in "Hills Like White Elephants
"Hills Like White Elephants" is a short story by Ernest Hemingway. It was first published in August 1927, in the literary magazine ''transition'', then later in the 1927 short story collection '' Men Without Women''. Later the story was adapted f ...
", Ernest Hemingway
Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and journalist. His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th-century f ...
used the allegorical white elephant, alluding to a pregnancy as an unwanted gift.
The animal is also seen in historical novels. ''The Elephant's Journey
''The Elephant's Journey'' ( pt, A Viagem do Elefante) is a novel by Nobel Prize-winning author José Saramago. It was first published in 2008 with an English translation in 2010.
Plot
In 1551, King João III of Portugal gave Archduke Maxim ...
'' (Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
: ''A Viagem do Elefante'', 2008) is a novel by Nobel laureate José Saramago
José de Sousa Saramago, GColSE ComSE GColCa (; 16 November 1922 – 18 June 2010), was a Portuguese writer and recipient of the 1998 Nobel Prize in Literature for his "parables sustained by imagination, compassion and irony ith which hec ...
. This is a fictional account based on an historical 16th century journey from Lisbon to Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
by an elephant named Solomon. '' An Elephant for Aristotle'' is a 1958 historical novel by L. Sprague de Camp
Lyon Sprague de Camp (; November 27, 1907 – November 6, 2000) was an American writer of science fiction, fantasy and non-fiction. In a career spanning 60 years, he wrote over 100 books, including novels and works of non-fiction, including biog ...
. It concerns the adventures of a Thessalian
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thess ...
cavalry commander who has been tasked by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
to bring an elephant captured from King Porus
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only men ...
of India, to Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
as a present for Alexander's old tutor, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
.
Elephants can also represent the hugeness and wildness of the imagination, as in Ursula Dubosarsky
Ursula Dubosarsky (born ''Ursula Coleman''; 1961 in Sydney) is an Australian writer of fiction and non-fiction for children and young adults, whose work is characterised by a child's vision and comic voice of both clarity and ambiguity. She ha ...
's 2012 children's book, ''Too Many Elephants in This House'', which also plays with the notion of the elephant in the room
The expression “the elephant in the room” (or "the elephant in the living room") is a metaphorical idiom in English for an important or enormous topic, question, or controversial issue that is obvious or that everyone knows about but no one ...
. An imaginary elephant can (perhaps) become real, as with the elusive Heffalump
A Heffalump is a type of elephant-like character in the Winnie the Pooh stories by A. A. Milne. Heffalumps are mentioned, and only appear, in Pooh and Piglet's dreams in ''Winnie-the-Pooh'' (1926), and seen again in ''The House at Pooh Corner'' ...
. Although never specified as an elephant in A. A. Milne
Alan Alexander Milne (; 18 January 1882 – 31 January 1956) was an English writer best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh, as well as for children's poetry. Milne was primarily a playwright before the huge success of Winni ...
's Winnie the Pooh
Winnie-the-Pooh, also called Pooh Bear and Pooh, is a fictional Anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic teddy bear created by English author A. A. Milne and English illustrator E. H. Shepard.
The first collection of stories about the character w ...
stories, a heffalump physically resembles an elephant; and E. H. Shepard's illustration shows an Indian elephant. "''Heffalump''" has since been defined as "a child's term for an elephant."
Sports
The elephant is used as a mascot or logo for various sports groups. Circus showmanP. T. Barnum
Phineas Taylor Barnum (; July 5, 1810 – April 7, 1891) was an American showman, businessman, and politician, remembered for promoting celebrated hoaxes and founding the Barnum & Bailey Circus (1871–2017) with James Anthony Bailey. He was ...
donated the stuffed hide of Jumbo
Jumbo (about December 25, 1860 – September 15, 1885), also known as Jumbo the Elephant and Jumbo the Circus Elephant, was a 19th-century male African bush elephant born in Sudan. Jumbo was exported to Jardin des Plantes, a zoo in Paris, and t ...
the elephant to Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
in 1885, where Jumbo soon became the mascot for their sports teams. However, all that remains of Jumbo are some ashes stored in a peanut butter jar and a piece of his tail following a fire in 1975. "Jumbo's spirit lives on" in the peanut butter jar which is ceremoniously passed on to successive athletic directors.
The mascot for the Oakland Athletics baseball team is based on the figurative white elephant. The story of picking the mascot began when New York Giants' manager John McGraw
John Joseph McGraw (April 7, 1873 – February 25, 1934) was an American Major League Baseball (MLB) player and manager who was for almost thirty years manager of the New York Giants. He was also the third baseman of the pennant-winning 1890 ...
told reporters that Philadelphia manufacturer Benjamin Shibe, who owned the controlling interest in the new team, had a "white elephant on his hands"; manager Connie Mack
Cornelius McGillicuddy (December 22, 1862 – February 8, 1956), better known as Connie Mack, was an American professional baseball catcher, manager, and team owner. The longest-serving manager in Major League Baseball history, he holds untoucha ...
defiantly adopted the white elephant as the team mascot. The A's are sometimes, but infrequently, referred to as the 'Elephants' or 'White Elephants'. Their mascot is nicknamed Stomper.
University of Alabama
The University of Alabama (informally known as Alabama, UA, or Bama) is a public research university in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. Established in 1820 and opened to students in 1831, the University of Alabama is the oldest and largest of the publi ...
's Crimson Tide mascot has been an elephant since 1930 after a sportswriter wrote of a fan yelling "Hold your horses, the elephants are coming!" as the football team rumbled onto the field. Their elephant-costumed " Big Al" officially debuted at the 1979 Sugar Bowl
The 1979 Sugar Bowl was the 45th edition of the college football bowl game, played at the Louisiana Superdome in New Orleans, Louisiana, on Monday, January 1. Part of the 1978–79 bowl game season, it matched the top-ranked Penn State Nitt ...
.
Catania, Italy
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
uses the elephant to represent their football team, referencing the animal that has represented their city since ancient times.
The crest of Kerala Blasters FC
Kerala Blasters Football Club (), commonly referred to as The Blasters, is an Indian professional football club based in Kochi, Kerala, that competes in the Indian Super League, the top tier of football in India. The club was established ...
, an Indian association football club is designed around an elephant holding football. Elephants are the state animal of Kerala and have a main role in their culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
. They are considered as symbol of unity, power, and pride. The crest of the club symbolises the heritage, culture, spirit, and passion of Kerala, and its love for football.
Music
The elephant is also represented in music such asHenry Mancini
Henry Mancini ( ; born Enrico Nicola Mancini, ; April 16, 1924 – June 14, 1994) was an American composer, conductor, arranger, pianist and flautist. Often cited as one of the greatest composers in the history of film, he won four Academy Award ...
's hit song "Baby Elephant Walk
"Baby Elephant Walk" is a song composed in 1961 by Henry Mancini for the 1962 film ''Hatari!'' Lyrics by Hal David were not used in the film version. The instrumental earned Mancini a Grammy Award for Best Instrumental Arrangement in .
Backgrou ...
", which has been described as "musical shorthand for kookiness of any stripe". The American band the White Stripes
The White Stripes were an American rock duo from Detroit formed in 1997. The group consisted of Jack White (songwriter, vocals, guitar, piano, and mandolin) and Meg White (drums and vocals). After releasing several singles and three albums wit ...
' fourth album was entitled ''Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
''in honour of the animal's brute strength and closeness to its relatives. The hit single "Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
" by British recording artist Alexandra Burke is based on the expression "elephant in the room
The expression “the elephant in the room” (or "the elephant in the living room") is a metaphorical idiom in English for an important or enormous topic, question, or controversial issue that is obvious or that everyone knows about but no one ...
". "Nellie the Elephant
"Nellie the Elephant" is a children's song written in 1956 by Ralph Butler and Peter Hart about a fictional anthropomorphic elephant of that name.
Original version
The original version, released on Parlophone R 4219 in October 1956, was recorde ...
" is a children's song first released in 1956 and since covered by many artists including the punk-rock band Toy Dolls; For her album, ''Leave Your Sleep
''Leave Your Sleep'' is the fifth studio album by American singer-songwriter Natalie Merchant. Produced by Merchant and Andres Levin, the double concept album is "a project about childhood" and is a collection of music adapted from 19th and 20th ...
'', Natalie Merchant set to music "The Blind Men and the Elephant" poem by John Godfrey Saxe, which is based on the parable.
Film and television
The elephant is also featured in film and on television. Thailand has produced various movies about the animal, from the 1940 historical drama film '' King of the White Elephant'' to the 2005 martial-arts action film, ''Tom-Yum-Goong
''Tom-Yum-Goong'' ( Thai: ต้มยำกุ้ง, ) is a 2005 Thai martial arts action film starring Tony Jaa. The film was directed by Prachya Pinkaew, who also directed Jaa's prior breakout film ''Ong-Bak''. As with ''Ong-Bak'', the fights ...
''. In the West, the elephant was popularised by ''Dumbo
''Dumbo'' is a 1941 American animated fantasy film produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by RKO Radio Pictures. The fourth Disney animated feature film, it is based upon the storyline written by Helen Aberson and Harold Pearl, ...
'', the elephant who learns to fly in the 1941 Disney animated feature
This list of theatrical animated feature films consists of animated films produced or released by The Walt Disney Studios, the film division of The Walt Disney Company.This list does not include films or specials streamed on Disney+ as Disne ...
of the same name. Kipling's "Toomai of the Elephants
Toomai of the Elephants is a short story by Rudyard Kipling about a young elephant-handler. It was first published in the December 1893 issue of ''St. Nicholas (magazine), St. Nicholas'' magazine and reprinted in the collection of Kipling short ...
" was adapted as the 1937 British adventure film '' Elephant Boy''. In popular modern films, Tai the elephant-actress has portrayed Bo Tat in ''Operation Dumbo Drop
''Operation Dumbo Drop'' is a 1995 American action comedy-drama war film directed by Simon Wincer. The storyline was conceived from a screenplay written by Gene Quintano and Jim Kouf based on a true story by United States Army major Jim Morris. ...
'' (1995), Vera in '' Larger than Life'' (1996), and Rosie in ''Water for Elephants
''Water for Elephants'' is the third novel by the Canadian–American author Sara Gruen. The book was published in 2006 by Algonquin Books of Chapel Hill. The historical fiction novel is a 20th century circus drama. Gruen wrote the book as pa ...
'' (2011). Elephants have also been featured in the modern live action Disney movies '' Whispers: An Elephant's Tale'' (2000), and the '' 2019 remake'' of Dumbo.
''Horton Hears a Who!
''Horton Hears a Who!'' is a children's book written and illustrated by Theodor Seuss Geisel under the pen name Dr. Seuss. It was published in 1954 by Random House. This book tells the story of Horton the Elephant and his adventures saving Whovi ...
'' was a 2008 American computer animated
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes ( still images) and dynamic images ( moving images), while computer animation re ...
adventure
An adventure is an exciting experience or undertaking that is typically bold, sometimes risky. Adventures may be activities with danger such as traveling, exploring, skydiving, mountain climbing, scuba diving, river rafting, or other extreme ...
comedy film
A comedy film is a category of film which emphasizes humor. These films are designed to make the audience laugh through amusement. Films in this style traditionally have a happy ending (black comedy being an exception). Comedy is one of the ol ...
based on the 1954 book of the same name by Dr. Seuss
Theodor Seuss Geisel (;"Seuss"
'' Blue Sky Studios and distributed by

"The Elephant in Medieval Legend and Art"
''Journal of the Royal Archaeological Institute''. (Vol. 76) London, 1919 * * * Pichayapat Naisupa
"The Emblematic Elephant: Elephants, the Dutch East India Company, and Eurasian Diplomacy in the Seventeenth Century"
Master Thesis, Colonial and Global History, Leiden University, 2020. * * *
'' Blue Sky Studios and distributed by
20th Century Fox
20th Century Studios, Inc. (previously known as 20th Century Fox) is an American film production company headquartered at the Fox Studio Lot in the Century City area of Los Angeles. As of 2019, it serves as a film production arm of Walt Dis ...
.
In the Malayalam film industry, there are several films, depicting elephants like - '' Guruvayur Kesavan'' (1977),''Gajakesariyogam
''Gajakesariyogam'' () is a 1990 Indian Malayalam-language film directed by P. G. Viswambharan and starring Innocent, K. P. A. C. Lalitha, and Mukesh. The film is about the struggles Nair faces after purchasing an elephant named Sreevidya from a ...
'' (1990), and ''Aanachandam
''Aanachandam'' is a 2006 Indian Malayalam language film directed by Jayaraj and starring Jayaram, Remya Nambeesan, Sai Kumar, Innocent, Cochin Haneefa, Salim Kumar anf Jagathy Sreekumar. It was released in 2006. This film was a commercial su ...
'' (2006).
On television, ''Nellie the Elephant
"Nellie the Elephant" is a children's song written in 1956 by Ralph Butler and Peter Hart about a fictional anthropomorphic elephant of that name.
Original version
The original version, released on Parlophone R 4219 in October 1956, was recorde ...
'' is a 1990 UK cartoon series inspired by the 1956 song of the same name, featuring Scottish singer Lulu
Lulu may refer to:
Companies
* LuLu, an early automobile manufacturer
* Lulu.com, an online e-books and print self-publishing platform, distributor, and retailer
* Lulu Hypermarket, a retail chain in Asia
* Lululemon Athletica or simply Lulu, ...
voicing Nelly. Britt Allcroft
Britt Allcroft (born Hilary Mary Allcroft, 14 December 1943) is a British writer, producer, director and voice actress. She is the creator of the children's television series ''Thomas the Tank Engine & Friends'' (later re-titled ''Thomas & Friend ...
adapted "Mumfie" the elephant from Katherine Tozer's series of children's books, originally in a '70s televised puppet show
Puppetry is a form of theatre or performance that involves the manipulation of puppets – inanimate objects, often resembling some type of human or animal figure, that are animated or manipulated by a human called a puppeteer. Such a performan ...
and then in the '90s animated ''Magic Adventures of Mumfie
''Magic Adventures of Mumfie'' is a British animated children's television series and movie, inspired by the works of Katharine Tozer (1907-1943) with an original music score containing more than 22 songs. The series was created by Britt Allcrof ...
'' series.
The 2016 action-comedy film ''The Brothers Grimsby
''Grimsby'' (released in the United States and Canada as ''The Brothers Grimsby'') is a 2016 spy action comedy film directed by Louis Leterrier and written by Sacha Baron Cohen, Phil Johnston, and Peter Baynham. The film stars Baron Cohen, Mark ...
'' gained notoriety for its crude and graphic elephant scene.
Games
The elephant can also be found in games. Inshatranj
Shatranj ( ar, شطرنج; fa, شترنج; from Middle Persian ''chatrang'' ) is an old form of chess, as played in the Sasanian Empire. Its origins are in the Indian game of chaturaṅga. Modern chess gradually developed from this game, as i ...
, the medieval game from which chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
developed, the piece corresponding to the modern bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
was known as ''Pil'' or ''Alfil'' ("Elephant"; from Persian and Arabic, respectively). In the Indian chaturanga game the piece is also called "Elephant" (''Gaja''). The same is true in Chinese chess
''Xiangqi'' (; ), also called Chinese chess or elephant chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is the most popular board game in China. ''Xiangqi'' is in the same family of games as ''shogi'', ''janggi'', Western chess, ''chatu ...
, which has an elephant piece ("Xiàng", 象) that serves as a defensive piece, being the only one that may not cross the river dividing the game board. In the Japanese shogi version, the piece was known as the "''Drunken'' Elephant"; however, it was dropped by order of the Emperor Go-Nara
was the 105th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. He reigned from June 9, 1526 until his death in 1557, during the Sengoku period. His personal name was Tomohito (知仁).
Genealogy
He was the second son of Emper ...
and no longer appears in the version played in contemporary Japan. Even with modern Chess, the word for the bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
is still ''Alfil'' in Spanish, ''Alfiere'' in Italian, ''Feel'' in Persian, and "Elephant" (Слон) in Russian. All of these games originally simulated a kind of battlefield, thus this piece represented a war elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
. In the present-day canonical Staunton chess set, the piece's deep groove, which originally represented the elephant's tusks, is now regarded as representing a bishop's mitre
The mitre (Commonwealth English) (; Greek: μίτρα, "headband" or "turban") or miter (American English; see spelling differences), is a type of headgear now known as the traditional, ceremonial headdress of bishops and certain abbots in ...
.
Architecture
In the 18th-century, French architectCharles Ribart
Charles François Ribart de Chamoust (''fl.'' 1776–1783 ) was an 18th-century French architect.
Architectural career
In 1758, Ribart planned an addition to the Champs-Élysées in Paris, to be constructed where the Arc de Triomphe now stands. I ...
planned to build a three-level elephant building at the Paris site where the Arc de Triomphe was eventually built. Nothing became of this, but in the early 19th-century, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
conceived of an even larger elephant structure, the Elephant of the Bastille
The Elephant of the Bastille was a monument in Paris which existed between 1813 and 1846. Originally conceived in 1808 by Napoléon I, the colossal statue was intended to be created out of bronze and placed in the Place de la Bastille, but only ...
. Although the ambitious project was never completed with its intended bronze elephant, a full-sized plaster and wood-frame model stood in its place. After Napoleon's defeat, this structure eventually became a neglected eyesore, and a setting in Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
's 1862 novel, ''Les Misérables
''Les Misérables'' ( , ) is a French historical novel by Victor Hugo, first published in 1862, that is considered one of the greatest novels of the 19th century.
In the English-speaking world, the novel is usually referred to by its origin ...
''.
Three multi-story elephant shaped buildings were built in America by James V. Lafferty James Vincent de Paul Lafferty, Jr. (1856–1898) was an Irish-American inventor, most famous for his construction of Lucy the Elephant, the Elephantine Colossus and The Light of Asia (also known as "Old Dumbo"). Born to Irish parents in Philadelph ...
in the 1880s. The largest, seven-story, thirty-one room Elephantine Colossus
The Elephantine Colossus (also known as the Colossal Elephant or the Elephant Colossus, or by its function as the Elephant Hotel) was a tourist attraction located on Coney Island in Brooklyn, New York City. It was built in the shape of an elepha ...
served as a hotel, concert hall, and attraction on Coney Island before it burned down in 1896. The six-story Lucy the Elephant
Lucy the Elephant is a six-story elephant-shaped example of novelty architecture, constructed of wood and tin sheeting in 1881 by James V. Lafferty in Margate City, New Jersey, approximately five miles (8 km) south of Atlantic City. Origin ...
is the only remaining of the three, and survives as a tourist attraction near Atlantic City. These giant elephant structures, however, are dwarfed by the 32-story Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estimated populati ...
Elephant Tower in Thailand. This iconic elephant-inspired building reflects the influence of the elephant in Thai culture.
Gallery

See also
* Aung Pinle Hsinbyushin, Lord of the White Elephant of Aung Pinle, a Great Nat of Burma. * Bholu (mascot), iconic mascot for Indian Railways *Elephants in ancient China
The existence of elephants in ancient China is attested both by archaeological evidence and by depictions in Chinese artwork. Long thought to belong to an extinct subspecies of the Asian elephant named ''Elephas maximus rubridens'', they lived in C ...
* Elephants in Kerala culture
* Elephants in Thailand
The elephant has been a contributor to Thai society and its icon for many centuries. The elephant has had a considerable impact on Thai culture. The Thai elephant ( th, ช้างไทย, ''chang Thai'') is the official national animal of Thai ...
* Elephant riddle
* Elephant test
The duck test is a form of abductive reasoning, usually expressed as "If it looks like a duck, swims like a duck, and quacks like a duck, then it probably is a duck."
The test implies that a person can identify an unknown subject by observing t ...
* Elephant clock
The elephant clock was a model of water clock invented by the medieval Islamic engineer Ismail al-Jazari (1136–1206). Its design was detailed in his book, ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices.''
Representation of multicultur ...
* Elephant Parade, sculpture exhibit
* Execution by elephant
Execution by elephant was a method of capital punishment in South and Southeast Asia, particularly in India, where Asian elephants were used to crush, dismember or torture captives in public executions. The animals were trained to kill victims ...
* Elephants and mice sub-section of Fear of mice
Fear of mice and rats is one of the most common specific phobias. It is sometimes referred to as musophobia (from Greek ''μῦς'' "mouse") or murophobia (a coinage from the taxonomic adjective "murine" for the family Muridae that encompasses m ...
article
* ''Faithful Elephants , is a story written by Yukio Tsuchiya and originally published in Japan in 1951, was published and marketed as a true story of the elephants in Tokyo's Ueno Zoo during World War II.
According to the picture book, the Japanese Army had requested t ...
'', story of the elephants in Tokyo's Ueno Zoo during World War II
* Gaja
Gaja () is a Sanskrit word for elephant. It is one of the significant animals finding references in Hindu scriptures, as well as Buddhist and Jain texts.
Symbolism
In general, a gaja personifies a number of positive attributes, including abund ...
, elephants in ancient Hindu mythology
* Hastin
Hastin (हस्तिन्) is a term for elephant used in Vedic texts. Other terms for elephant include Ibha (इभ) and Vārana (वारण).
The elephant in the Rigveda
In Rig Veda 1.84.17 and 4.4.1. and probably other instances the Rig ...
, elephants in Vedic texts.
* ''Jumbo'', 1935 musical and 1962 Film
* Temple elephant
Temple elephants are a type of Captive elephants, captive elephant. Many major temples own elephants; others hire or are donated elephants during the festive seasons. Temple elephants are usually wild animals, poached from the forests of North E ...
* The Sultan's Elephant
The Sultan's Elephant was a show created by the Royal de Luxe theatre company, involving a huge moving mechanical elephant, a giant marionette of a girl and other associated public art installations. In French it was called ''La visite du sultan ...
, traveling show featuring a huge mechanical elephant
* War elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elepha ...
* List of fictional elephants
This list of fictional pachyderms is a subsidiary to the List of fictional ungulates. Characters from various fictional works are organized by medium.
Outside strict biological classification, the term " pachyderm" is commonly used to describe ...
* List of historical elephants
*Abul-Abbas, Charlemagne's elephant
* Arjuna, lead elephant of the Mysore Dasara procession and carries the idol of the deity Chamundeshwari on the Golden Howdah
*Balarama, preceded Arjuna (see above); Golden Howdah-carrier between 1999 and 2011
...
* National Elephant Day (Thailand) On 26 May 1998, the government of Thailand, Thai government declared the 13th of March to annually be the Thai National Elephant Day or Chang Thai Day (Thai: วันช้างไทย). The observance was suggested by the Asian Elephant Foundat ...
* : Metaphors referring to elephants
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * —the evolution of the Elephant Riddle that entered U.S. folklore in California in 1963 * Druce, George C"The Elephant in Medieval Legend and Art"
''Journal of the Royal Archaeological Institute''. (Vol. 76) London, 1919 * * * Pichayapat Naisupa
"The Emblematic Elephant: Elephants, the Dutch East India Company, and Eurasian Diplomacy in the Seventeenth Century"
Master Thesis, Colonial and Global History, Leiden University, 2020. * * *
External links
* — Elephant-World.com * * — Depictions from illuminated manuscripts {{Mammals in culture Elephants in art Elephants in literature Elephants in Indian culture Elephants Cultural depictions of animals