Correlation Examples2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
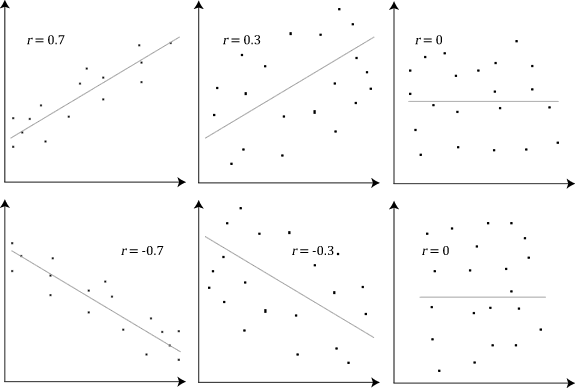 The most familiar measure of dependence between two quantities is the
The most familiar measure of dependence between two quantities is the
 Most correlation measures are sensitive to the manner in which and are sampled. Dependencies tend to be stronger if viewed over a wider range of values. Thus, if we consider the correlation coefficient between the heights of fathers and their sons over all adult males, and compare it to the same correlation coefficient calculated when the fathers are selected to be between 165 cm and 170 cm in height, the correlation will be weaker in the latter case. Several techniques have been developed that attempt to correct for range restriction in one or both variables, and are commonly used in meta-analysis; the most common are Thorndike's case II and case III equations.
Various correlation measures in use may be undefined for certain joint distributions of and . For example, the Pearson correlation coefficient is defined in terms of moments, and hence will be undefined if the moments are undefined. Measures of dependence based on quantiles are always defined. Sample-based statistics intended to estimate population measures of dependence may or may not have desirable statistical properties such as being unbiased, or asymptotically consistent, based on the spatial structure of the population from which the data were sampled.
Sensitivity to the data distribution can be used to an advantage. For example, scaled correlation is designed to use the sensitivity to the range in order to pick out correlations between fast components of time series. By reducing the range of values in a controlled manner, the correlations on long time scale are filtered out and only the correlations on short time scales are revealed.
Most correlation measures are sensitive to the manner in which and are sampled. Dependencies tend to be stronger if viewed over a wider range of values. Thus, if we consider the correlation coefficient between the heights of fathers and their sons over all adult males, and compare it to the same correlation coefficient calculated when the fathers are selected to be between 165 cm and 170 cm in height, the correlation will be weaker in the latter case. Several techniques have been developed that attempt to correct for range restriction in one or both variables, and are commonly used in meta-analysis; the most common are Thorndike's case II and case III equations.
Various correlation measures in use may be undefined for certain joint distributions of and . For example, the Pearson correlation coefficient is defined in terms of moments, and hence will be undefined if the moments are undefined. Measures of dependence based on quantiles are always defined. Sample-based statistics intended to estimate population measures of dependence may or may not have desirable statistical properties such as being unbiased, or asymptotically consistent, based on the spatial structure of the population from which the data were sampled.
Sensitivity to the data distribution can be used to an advantage. For example, scaled correlation is designed to use the sensitivity to the range in order to pick out correlations between fast components of time series. By reducing the range of values in a controlled manner, the correlations on long time scale are filtered out and only the correlations on short time scales are revealed.
 The Pearson correlation coefficient indicates the strength of a ''linear'' relationship between two variables, but its value generally does not completely characterize their relationship. In particular, if the conditional mean of given , denoted , is not linear in , the correlation coefficient will not fully determine the form of .
The adjacent image shows
The Pearson correlation coefficient indicates the strength of a ''linear'' relationship between two variables, but its value generally does not completely characterize their relationship. In particular, if the conditional mean of given , denoted , is not linear in , the correlation coefficient will not fully determine the form of .
The adjacent image shows
MathWorld page on the (cross-)correlation coefficient/s of a sample
Compute significance between two correlations
for the comparison of two correlation values. *
Proof that the Sample Bivariate Correlation has limits plus or minus 1
by Juha Puranen. * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150407112430/http://www.biostat.katerynakon.in.ua/en/association/correlation.html Correlation analysis. Biomedical Statistics* R-Psychologis
Correlation
visualization of correlation between two numeric variables {{DEFAULTSORT:Correlation And Dependence Covariance and correlation Dimensionless numbers
statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, indust ...
, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the po ...
s or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related.
Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve.
Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in general, the presence of a correlation is not sufficient to infer the presence of a causal relationship (i.e., correlation does not imply causation).
Formally, random variables are ''dependent'' if they do not satisfy a mathematical property of probabilistic independence. In informal parlance, ''correlation'' is synonymous with ''dependence''. However, when used in a technical sense, correlation refers to any of several specific types of mathematical operations between the tested variables and their respective expected values. Essentially, correlation is the measure of how two or more variables are related to one another. There are several correlation coefficients, often denoted or , measuring the degree of correlation. The most common of these is the '' Pearson correlation coefficient'', which is sensitive only to a linear relationship between two variables (which may be present even when one variable is a nonlinear function of the other). Other correlation coefficients – such as ''Spearman's rank correlation
In statistics, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient or Spearman's ''ρ'', named after Charles Spearman and often denoted by the Greek letter \rho (rho) or as r_s, is a nonparametric measure of rank correlation (statistical dependence between ...
'' – have been developed to be more robust than Pearson's, that is, more sensitive to nonlinear relationships. Mutual information can also be applied to measure dependence between two variables.
Pearson's product-moment coefficient
 The most familiar measure of dependence between two quantities is the
The most familiar measure of dependence between two quantities is the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, pronounced ) ― also known as Pearson's ''r'', the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), the bivariate correlation, or colloquially simply as the correlation coefficient ...
(PPMCC), or "Pearson's correlation coefficient", commonly called simply "the correlation coefficient". It is obtained by taking the ratio of the covariance of the two variables in question of our numerical dataset, normalized to the square root of their variances. Mathematically, one simply divides the covariance of the two variables by the product of their standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, whi ...
s. Karl Pearson
Karl Pearson (; born Carl Pearson; 27 March 1857 – 27 April 1936) was an English mathematician and biostatistician. He has been credited with establishing the discipline of mathematical statistics. He founded the world's first university st ...
developed the coefficient from a similar but slightly different idea by Francis Galton.
A Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient attempts to establish a line of best fit through a dataset of two variables by essentially laying out the expected values and the resulting Pearson's correlation coefficient indicates how far away the actual dataset is from the expected values. Depending on the sign of our Pearson's correlation coefficient, we can end up with either a negative or positive correlation if there is any sort of relationship between the variables of our data set.
The population correlation coefficient between two random variables
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the po ...
and with expected values and and standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, whi ...
s and is defined as:
where is the expected value operator, means covariance, and is a widely used alternative notation for the correlation coefficient. The Pearson correlation is defined only if both standard deviations are finite and positive. An alternative formula purely in terms of moments is:
Correlation and independence
It is a corollary of the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality that the absolute value of the Pearson correlation coefficient is not bigger than 1. Therefore, the value of a correlation coefficient ranges between −1 and +1. The correlation coefficient is +1 in the case of a perfect direct (increasing) linear relationship (correlation), −1 in the case of a perfect inverse (decreasing) linear relationship (anti-correlation), and some value in theopen interval
In mathematics, a (real) interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set. For example, the set of numbers satisfying is an interval which contains , , and all numbers in between. Other ...
in all other cases, indicating the degree of linear dependence
In the theory of vector spaces, a set of vectors is said to be if there is a nontrivial linear combination of the vectors that equals the zero vector. If no such linear combination exists, then the vectors are said to be . These concepts are ...
between the variables. As it approaches zero there is less of a relationship (closer to uncorrelated). The closer the coefficient is to either −1 or 1, the stronger the correlation between the variables.
If the variables are independent, Pearson's correlation coefficient is 0, but the converse is not true because the correlation coefficient detects only linear dependencies between two variables.
For example, suppose the random variable is symmetrically distributed about zero, and . Then is completely determined by , so that and are perfectly dependent, but their correlation is zero; they are uncorrelated. However, in the special case when and are jointly normal, uncorrelatedness is equivalent to independence.
Even though uncorrelated data does not necessarily imply independence, one can check if random variables are independent if their mutual information is 0.
Sample correlation coefficient
Given a series of measurements of the pair indexed by , the ''sample correlation coefficient'' can be used to estimate the population Pearson correlation between and . The sample correlation coefficient is defined as : where and are the sample means of and , and and are the corrected sample standard deviations of and . Equivalent expressions for are : where and are the ''uncorrected'' sample standard deviations of and . If and are results of measurements that contain measurement error, the realistic limits on the correlation coefficient are not −1 to +1 but a smaller range. For the case of a linear model with a single independent variable, the coefficient of determination (R squared) is the square of , Pearson's product-moment coefficient.Example
Consider thejoint probability distribution
Given two random variables that are defined on the same probability space, the joint probability distribution is the corresponding probability distribution on all possible pairs of outputs. The joint distribution can just as well be considered ...
of and given in the table below.
:
For this joint distribution, the marginal distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. It gives the probabilities of various values of the variables ...
s are:
:
:
This yields the following expectations and variances:
:
:
:
:
Therefore:
:
Rank correlation coefficients
Rank correlation coefficients, such as Spearman's rank correlation coefficient and Kendall's rank correlation coefficient (τ) measure the extent to which, as one variable increases, the other variable tends to increase, without requiring that increase to be represented by a linear relationship. If, as the one variable increases, the other ''decreases'', the rank correlation coefficients will be negative. It is common to regard these rank correlation coefficients as alternatives to Pearson's coefficient, used either to reduce the amount of calculation or to make the coefficient less sensitive to non-normality in distributions. However, this view has little mathematical basis, as rank correlation coefficients measure a different type of relationship than thePearson product-moment correlation coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, pronounced ) ― also known as Pearson's ''r'', the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), the bivariate correlation, or colloquially simply as the correlation coefficient ...
, and are best seen as measures of a different type of association, rather than as an alternative measure of the population correlation coefficient.Yule, G.U and Kendall, M.G. (1950), "An Introduction to the Theory of Statistics", 14th Edition (5th Impression 1968). Charles Griffin & Co. pp 258–270Kendall, M. G. (1955) "Rank Correlation Methods", Charles Griffin & Co.
To illustrate the nature of rank correlation, and its difference from linear correlation, consider the following four pairs of numbers :
:(0, 1), (10, 100), (101, 500), (102, 2000).
As we go from each pair to the next pair increases, and so does . This relationship is perfect, in the sense that an increase in is ''always'' accompanied by an increase in . This means that we have a perfect rank correlation, and both Spearman's and Kendall's correlation coefficients are 1, whereas in this example Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is 0.7544, indicating that the points are far from lying on a straight line. In the same way if always ''decreases'' when ''increases'', the rank correlation coefficients will be −1, while the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient may or may not be close to −1, depending on how close the points are to a straight line. Although in the extreme cases of perfect rank correlation the two coefficients are both equal (being both +1 or both −1), this is not generally the case, and so values of the two coefficients cannot meaningfully be compared. For example, for the three pairs (1, 1) (2, 3) (3, 2) Spearman's coefficient is 1/2, while Kendall's coefficient is 1/3.
Other measures of dependence among random variables
The information given by a correlation coefficient is not enough to define the dependence structure between random variables. The correlation coefficient completely defines the dependence structure only in very particular cases, for example when the distribution is a multivariate normal distribution. (See diagram above.) In the case of elliptical distributions it characterizes the (hyper-)ellipses of equal density; however, it does not completely characterize the dependence structure (for example, a multivariate t-distribution's degrees of freedom determine the level of tail dependence). Distance correlation was introduced to address the deficiency of Pearson's correlation that it can be zero for dependent random variables; zero distance correlation implies independence. The Randomized Dependence Coefficient is a computationally efficient, copula-based measure of dependence between multivariate random variables. RDC is invariant with respect to non-linear scalings of random variables, is capable of discovering a wide range of functional association patterns and takes value zero at independence. For twobinary variables
Binary data is data whose unit can take on only two possible states. These are often labelled as 0 and 1 in accordance with the binary numeral system and Boolean algebra.
Binary data occurs in many different technical and scientific fields, wher ...
, the odds ratio measures their dependence, and takes range non-negative numbers, possibly infinity: . Related statistics such as Yule's ''Y'' and Yule's ''Q'' normalize this to the correlation-like range . The odds ratio is generalized by the logistic model to model cases where the dependent variables are discrete and there may be one or more independent variables.
The correlation ratio, entropy-based mutual information, total correlation, dual total correlation and polychoric correlation are all also capable of detecting more general dependencies, as is consideration of the copula between them, while the coefficient of determination generalizes the correlation coefficient to multiple regression.
Sensitivity to the data distribution
The degree of dependence between variables and does not depend on the scale on which the variables are expressed. That is, if we are analyzing the relationship between and , most correlation measures are unaffected by transforming to and to , where ''a'', ''b'', ''c'', and ''d'' are constants (''b'' and ''d'' being positive). This is true of some correlationstatistic
A statistic (singular) or sample statistic is any quantity computed from values in a sample which is considered for a statistical purpose. Statistical purposes include estimating a population parameter, describing a sample, or evaluating a hypo ...
s as well as their population analogues. Some correlation statistics, such as the rank correlation coefficient, are also invariant to monotone transformations of the marginal distributions of and/or .
Correlation matrices
The correlation matrix of random variables is the matrix whose entry is : Thus the diagonal entries are all identicallyone
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
. If the measures of correlation used are product-moment coefficients, the correlation matrix is the same as the covariance matrix of the standardized random variables for . This applies both to the matrix of population correlations (in which case is the population standard deviation), and to the matrix of sample correlations (in which case denotes the sample standard deviation). Consequently, each is necessarily a positive-semidefinite matrix. Moreover, the correlation matrix is strictly positive definite if no variable can have all its values exactly generated as a linear function of the values of the others.
The correlation matrix is symmetric because the correlation between and is the same as the correlation between and .
A correlation matrix appears, for example, in one formula for the coefficient of multiple determination, a measure of goodness of fit in multiple regression.
In statistical modelling
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of sample data (and similar data from a larger population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, ...
, correlation matrices representing the relationships between variables are categorized into different correlation structures, which are distinguished by factors such as the number of parameters required to estimate them. For example, in an exchangeable correlation matrix, all pairs of variables are modeled as having the same correlation, so all non-diagonal elements of the matrix are equal to each other. On the other hand, an autoregressive matrix is often used when variables represent a time series, since correlations are likely to be greater when measurements are closer in time. Other examples include independent, unstructured, M-dependent, and Toeplitz.
In exploratory data analysis, the iconography of correlations consists in replacing a correlation matrix by a diagram where the “remarkable” correlations are represented by a solid line (positive correlation), or a dotted line (negative correlation).
Nearest valid correlation matrix
In some applications (e.g., building data models from only partially observed data) one wants to find the "nearest" correlation matrix to an "approximate" correlation matrix (e.g., a matrix which typically lacks semi-definite positiveness due to the way it has been computed). In 2002, Higham formalized the notion of nearness using the Frobenius norm and provided a method for computing the nearest correlation matrix using the Dykstra's projection algorithm, of which an implementation is available as an online Web API. This sparked interest in the subject, with new theoretical (e.g., computing the nearest correlation matrix with factor structure) and numerical (e.g. usage theNewton's method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valu ...
for computing the nearest correlation matrix) results obtained in the subsequent years.
Uncorrelatedness and independence of stochastic processes
Similarly for two stochastic processes and : If they are independent, then they are uncorrelated. The opposite of this statement might not be true. Even if two variables are uncorrelated, they might not be independent to each other.Common misconceptions
Correlation and causality
The conventional dictum that " correlation does not imply causation" means that correlation cannot be used by itself to infer a causal relationship between the variables. This dictum should not be taken to mean that correlations cannot indicate the potential existence of causal relations. However, the causes underlying the correlation, if any, may be indirect and unknown, and high correlations also overlap with identity relations ( tautologies), where no causal process exists. Consequently, a correlation between two variables is not a sufficient condition to establish a causal relationship (in either direction). A correlation between age and height in children is fairly causally transparent, but a correlation between mood and health in people is less so. Does improved mood lead to improved health, or does good health lead to good mood, or both? Or does some other factor underlie both? In other words, a correlation can be taken as evidence for a possible causal relationship, but cannot indicate what the causal relationship, if any, might be.Simple linear correlations
scatter plot
A scatter plot (also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram) is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. ...
s of Anscombe's quartet
Anscombe's quartet comprises four data sets that have nearly identical simple descriptive statistics, yet have very different distributions and appear very different when graphed. Each dataset consists of eleven (''x'',''y'') points. They were ...
, a set of four different pairs of variables created by Francis Anscombe. The four variables have the same mean (7.5), variance (4.12), correlation (0.816) and regression line (''y'' = 3 + 0.5''x''). However, as can be seen on the plots, the distribution of the variables is very different. The first one (top left) seems to be distributed normally, and corresponds to what one would expect when considering two variables correlated and following the assumption of normality. The second one (top right) is not distributed normally; while an obvious relationship between the two variables can be observed, it is not linear. In this case the Pearson correlation coefficient does not indicate that there is an exact functional relationship: only the extent to which that relationship can be approximated by a linear relationship. In the third case (bottom left), the linear relationship is perfect, except for one outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are ...
which exerts enough influence to lower the correlation coefficient from 1 to 0.816. Finally, the fourth example (bottom right) shows another example when one outlier is enough to produce a high correlation coefficient, even though the relationship between the two variables is not linear.
These examples indicate that the correlation coefficient, as a summary statistic, cannot replace visual examination of the data. The examples are sometimes said to demonstrate that the Pearson correlation assumes that the data follow a normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu i ...
, but this is only partially correct. The Pearson correlation can be accurately calculated for any distribution that has a finite covariance matrix, which includes most distributions encountered in practice. However, the Pearson correlation coefficient (taken together with the sample mean and variance) is only a sufficient statistic
In statistics, a statistic is ''sufficient'' with respect to a statistical model and its associated unknown parameter if "no other statistic that can be calculated from the same sample provides any additional information as to the value of the pa ...
if the data is drawn from a multivariate normal distribution. As a result, the Pearson correlation coefficient fully characterizes the relationship between variables if and only if the data are drawn from a multivariate normal distribution.
Bivariate normal distribution
If a pair of random variables follows a bivariate normal distribution, the conditional mean is a linear function of , and the conditional mean is a linear function of . The correlation coefficient between and , along with the marginal means and variances of and , determines this linear relationship: : where and are the expected values of and , respectively, and and are the standard deviations of and , respectively. The empirical correlation is an estimate of the correlation coefficient . A distribution estimate for is given bywhere is the Gaussian hypergeometric function and . This density is both a Bayesian posterior density and an exact optimal confidence distribution density.See also
* Autocorrelation * Canonical correlation * Coefficient of determination * Cointegration * Concordance correlation coefficient * Cophenetic correlation * Correlation function * Correlation gap * Covariance * Covariance and correlation * Cross-correlation * Ecological correlation *Fraction of variance unexplained
In statistics, the fraction of variance unexplained (FVU) in the context of a regression task is the fraction of variance of the regressand (dependent variable) ''Y'' which cannot be explained, i.e., which is not correctly predicted, by the ex ...
* Genetic correlation
* Goodman and Kruskal's lambda
* Iconography of correlations
* Illusory correlation
* Interclass correlation
* Intraclass correlation
* Lift (data mining)
* Mean dependence In probability theory, a random variable Y is said to be mean independent of random variable X if and only if its conditional mean E(Y , X = x) equals its (unconditional) mean E(Y) for all x such that the probability density/mass of X at x, f_X(x) ...
* Modifiable areal unit problem
* Multiple correlation
* Point-biserial correlation coefficient
* Quadrant count ratio
* Spurious correlation
In statistics, a spurious relationship or spurious correlation is a mathematical relationship in which two or more events or variables are associated but '' not'' causally related, due to either coincidence or the presence of a certain third, uns ...
* Statistical arbitrage
* Subindependence In probability theory and statistics, subindependence is a weak form of independence.
Two random variables ''X'' and ''Y'' are said to be subindependent if the characteristic function of their sum is equal to the product of their marginal character ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
MathWorld page on the (cross-)correlation coefficient/s of a sample
Compute significance between two correlations
for the comparison of two correlation values. *
Proof that the Sample Bivariate Correlation has limits plus or minus 1
by Juha Puranen. * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150407112430/http://www.biostat.katerynakon.in.ua/en/association/correlation.html Correlation analysis. Biomedical Statistics* R-Psychologis
Correlation
visualization of correlation between two numeric variables {{DEFAULTSORT:Correlation And Dependence Covariance and correlation Dimensionless numbers