|
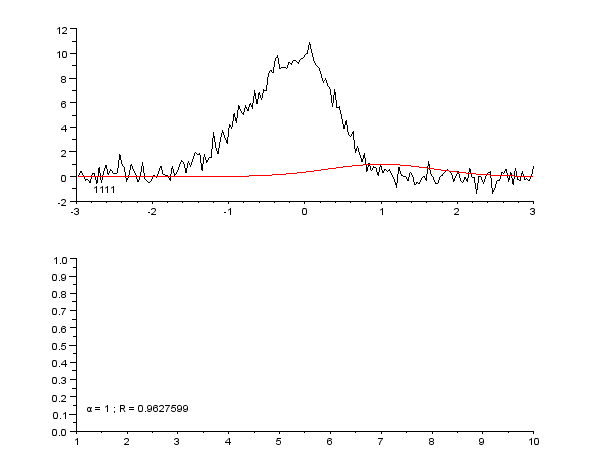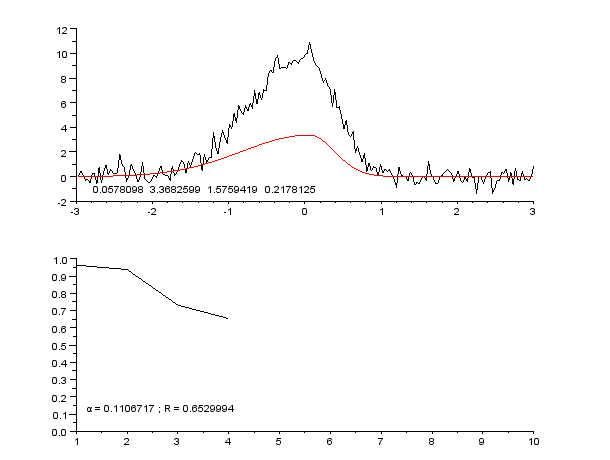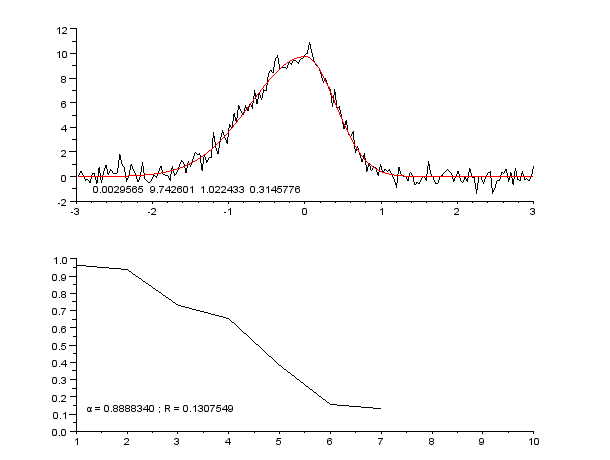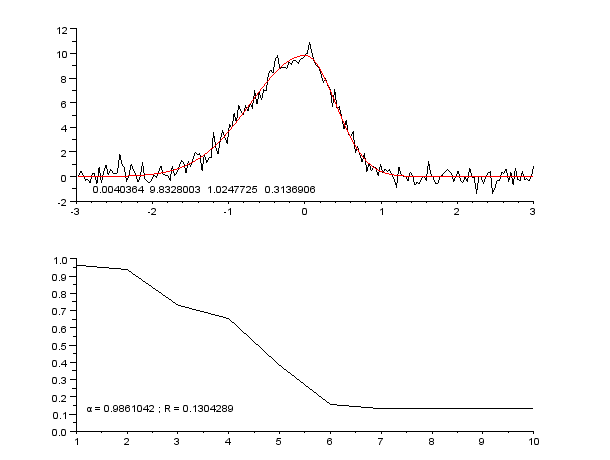
Scatter Plot
A scatter plot, also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram, is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis. History According to Michael Friendly and Daniel Denis, the defining characteristic distinguishing scatter plots from line charts is the representation of specific observations of bivariate data where one variable is plotted on the horizontal axis and the other on the vertical axis. The two variables are often abstracted from a physical representation like the spread of bullets on a target or a geographic or celestial projection. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fitted to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rug Plot
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of Pile (textile), pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fiber, synthetic fibres such as polypropylene, nylon, and polyester have often been used, as these fibres are less expensive than wool. The pile usually consists of twisted Tufting, tufts that are typically heat-treated to maintain their structure. The term ''carpet'' is often used in a similar context to the term rug, but rugs are mostly considered to be smaller than a room and not attached to the floor. Carpets are used for a variety of purposes. These include insulating a person's feet from a cold tile or concrete floor, making a room more comfortable as a place to sit on the floor (e.g., when playing with children or as a prayer rug), reducing sound from walking (particularly in apartment buildings), and adding decoration or colour to a room. Carpets can be made in any colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data And Information Visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data (''exploratory visualization''). When intended for the general public (mass communication) to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner (''presentational'' or ''explanatory visualization''), it is typically called information gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriz De Gráficos De Dispersão
Matriz may refer to the following subjects: Places in Portugal * Matriz (Borba), a civil parish in the municipality of Borba * Matriz (Horta), a civil parish in the municipality of Horta, island of Faial (Azores) * Matriz (Ribeira Grande), a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande, island of São Miguel (Azores) *Matriz, the former name of São Sebastião (Ponta Delgada), a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada, island of São Miguel (Azores) Other uses * ''Matriz'' (album), by Brazilian singer-songwriter Pitty {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
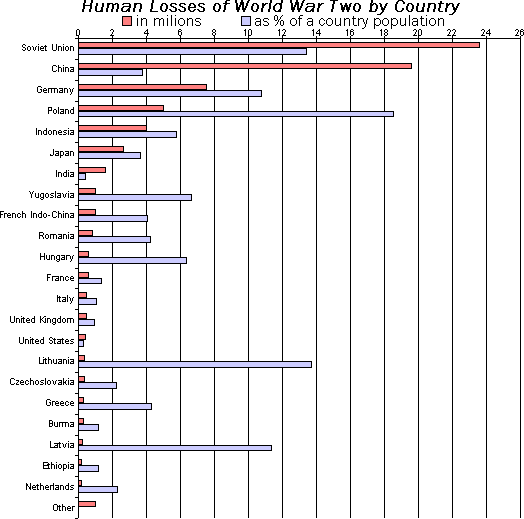
Bar Chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical variable, categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart and has been identified as the prototype of charts. A bar graph shows comparisons among discrete variable, discrete categorical variable, categories. One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a measured value. Some bar graphs present bars clustered or stacked in groups of more than one, showing the values of more than one measured variable. History Many sources consider William Playfair (1759-1824) to have invented the bar chart and the ''Exports and Imports of Scotland to and from different parts for one Year from Christmas 1780 to Christmas 1781'' graph from his ''The Commercial and Political Atlas'' to be the first bar chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluctuation Diagram , price fluctuation
{{disambiguation ...
Fluctuation may refer to: Physics and mathematics * Statistical fluctuations, in statistics, statistical mechanics, and thermodynamics ** Thermal fluctuations, statistical fluctuations in a thermodynamic variable * Quantum fluctuation, arising from the uncertainty principle ** Primordial fluctuations, density variations in the early universe ** Universal conductance fluctuations, a quantum physics phenomenon encountered in electrical transport experiments in mesoscopic species Finance and economics * Economic conjuncture, a critical combination of events in economics * Volatility (finance) In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
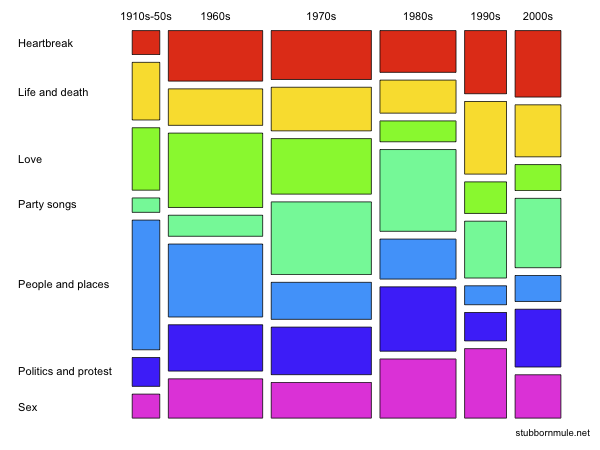
Mosaic Plot
A mosaic plot, Marimekko chart, Mekko chart, or sometimes percent stacked bar plot, is a graphical visualization of data from two or more qualitative variables. It is the multidimensional extension of spineplots, which graphically display the same information for only one variable. It gives an overview of the data and makes it possible to recognize relationships between different variables. For example, independence is shown when the boxes across categories all have the same areas. Mosaic plots were introduced by Hartigan and Kleiner in 1981 and expanded on by Friendly in 1994. Mosaic plots are also called Marimekko or Mekko charts because they resemble some Marimekko prints. However, in statistical applications, mosaic plots can be colored and shaded according to deviations from independence, whereas Marimekko charts are colored according to the category levels, as in the image. As with bar charts and spineplots, the area of the tiles, also known as the bin size, is proportional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. It is similar to a scatter plot except that the measurement points are ordered (typically by their x-axis value) and joined with straight line segments. A line chart is often used to visualize a trend in data over intervals of time – a time series – thus the line is often drawn chronologically. In these cases they are known as run charts. History Some of the earliest known line charts are generally credited to Francis Hauksbee, Nicolaus Samuel Cruquius, Johann Heinrich Lambert and the Scottish engineer William Playfair. Line charts often display time as a variable on the x-axis. Playfair was one of the first to visualize data this way. In 1786, he plotted ten years of money spent by the Royal Navy. He supplemented the chart with a det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble Chart
A bubble chart is a type of chart that displays three dimensions of data. Each entity with its triplet (''v''1, ''v''2, ''v''3) of associated data is plotted as a disk that expresses two of the ''vi'' values through the disk's ''xy'' location and the third through its size. Bubble charts can facilitate the understanding of social, economical, medical, and other scientific relationships. Bubble charts can be considered a variation of the scatter plot, in which the data points are replaced with bubbles. As the documentation for Microsoft Office explains, "You can use a bubble chart instead of a scatter chart if your data has three data series that each contain a set of values. The sizes of the bubbles are determined by the values in the third data series.". Choosing bubble sizes correctly Using bubbles to represent scalar (one-dimensional) values can be misleading. The human visual system most naturally experiences a disk's size in terms of its diameter, rather than area. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milwaukee, Wisconsin
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States and the fifth-most populous city in the Midwest with a population of 577,222 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the county seat of Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Milwaukee County. The Milwaukee metropolitan area is the Metropolitan statistical area, 40th-most populous metropolitan area in the U.S. with 1.57 million residents. Founded in the early 19th century and incorporated in 1846, Milwaukee grew rapidly due to its location as a port city. History of Milwaukee, Its history was heavily influenced by German immigrants and it continues to be a Germans in Milwaukee, center for German-American culture, specifically known for Beer in Milwaukee, its brewing industry. The city developed as an industrial powerhouse during the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Quality
The American Society for Quality (ASQ), formerly the American Society for Quality Control (ASQC), is a society of quality professionals, with more than 30,000 members, in more than 140 countries. History ASQC was established on 16 February 1946 by 253 members in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, with George D. Edwards as its first president. The organization was first created as a way for quality experts and manufacturers to sustain quality-improvement techniques used during World War II. In 1948, ASQC's Code of Ethics established standards for members to conduct their activities and business. Business writer Armand V. Feigenbaum served as president of the society in 1961–63. In 1997, the members of the organization voted to change its name from "American Society for Quality Control" to "American Society for Quality". Quality ASQ provides its members with certification, training, publications, conferences, and other services. ASQ is a founding partner of the American Customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |